Intro to Psychology final
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
What is psychology
The science that studies behavior and mental processes
what is 1 field of psychology and describe it
clinical psychologists help patients with mental disorders adjust to the demands of life
who came up with “know thyself” and the concept of introspection
Socrates
What does introspection mean?
deliberately looking into ones own cognitive to examine your thoughts and emotions
name 1 pioneer of psychology, what did he find, and what does that foundation mean?
John B Watson founded behaviorism which is the study of behavior and studies the relationship between stimuli and response
Name 1 method of observation and describe 1 advantage and disadvantage of it
The laboratory method is a method of observation with an advantage of being in a controlled setting and a disadvantage of not being able to get the same results you would if you were in a natural setting
Evolutionary Perspective
theory that focuses on the evolution of behavior and mental processes
Socialculture perspective
The influence of ethnicity, gender, culture, and socioeconomic status on hbehavior and mental processes
Cognitive Perspective
Emphasizes the role of the thought process in determining behavior
Learning Perspective
Emphasizes the effects of learning on behavior
Biopsychosocial perspective
mental process influenced by biological, psychological, and social factors
What is ethics in psychology?
To have a purpose and reason for doing an experiment or study while still knowing and acknowledging the life and dignity of another human or animal
Explain the Placebo effect and how it’s used in psychology
using a substance to test the effectiveness of another substance. It can be used in psychology to study how the things you hear about a substance can affect the results of said substance
Explain confidentiality and when it is appropriate to break it
Confidentiality is where a psychologist or counselor cannot tell anyone the things their patient is confiding with them unless that patient is harming themselves, others, or is being harmed by another
Explain why it is important to do animal research and what we have learned because of animal research
Some animals have similar anatomy, reactions and thought processes that humans have and from animal testing we have learned a lot about human behavior, stimuli , and responses such as B.F skinners experiments or reinforcements with rats
Psychosexual development
The process where libidinal energy is expressed through different erogenous zones during different stages of development
Id
Present at birth, represents psychological drives and is fully unconscious
Phallic stage
3rd stage, characterized by a shift of libido to phallic region
Ego
Characterized by self awareness, planning, and delay of gratification
Personality
the reasonably stable patterns of emotions, motives, and behavior that distinguish one person from another
Superego
A moral guardian and sets forth high standards for behavior
Oedipus Complex
a conflict where the boy wishes to posses his mother and views the father as a rival
Latency
repression of sexual impulse
Anal stage
2nd stage, where gratification is attained through anal activity
Psychodynamic theory
The importance of the unconscious mind and conflicts as forces that determine behavior
Oral stage
1st stage, gratification Is hypothesized to be obtained primarily through oral activities
Electra Complex
A conflict where the girl longs for her father and resents her mother
Genital Stage
Preferred expression of libido through intercourse with an adult of the other gender
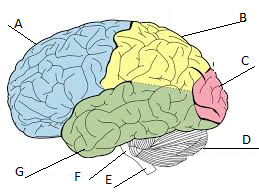
Frontal lobe
A
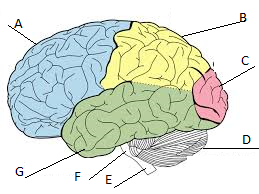
Parietal lobe
Label B
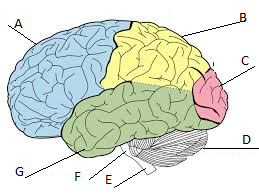
Occipital lobe
Label C
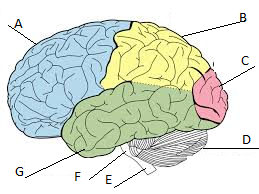
Cerebellum
Label D
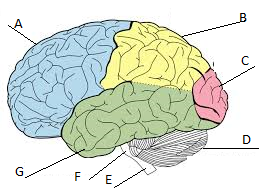
Temporal lobe
Label G
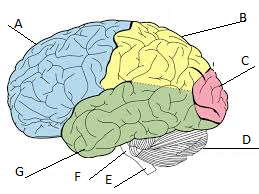
Cerebrum
A, B, C, and D
What sections is the brain divided into?
the hindbrain, the midbrain, and the forebrain
What is one way we can study the brain and explain how it would be conducted
lesions by cutting or destroying parts of the brain
Occipital lobe
primary visual area; helps us to see
Temporal lobe
Hearing and auditory; helps us to hear
Parietal lobe
sensory; helps us feel sensations like warmth, cold, touch, and pain
Frontal lobe
problem solving; helps to make plans and decisions
what reflex is triggered by your body’s automatic response to a trigger without input from your brain
Spinal reflex
Medulla
involved in regulation of heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and circulation
Cerebellum
essential to balance and coordination
pons
involved in regulation of movement, sleep, and arousal and respiration
cerebrum
center of thinking and language, prefrontal area contains “executive center” of brain
thalamus
relay station for sensory information
pituitary gland
secretes hormones that regulate many body functions, including secretion of hormones from other glands; sometimes referred to as the “master gland”
corpus callosum
thick bundle of axons that serves as a bridge between the two cerebral hemispheres
Hypothalamus
secretes hormones that stimulate secretion of hormones by the pituitary gland; involved in basic drives such as hunger, sex, and aggression
Reticular function
involved in regulation of sleep and walking; stimulation of reticular formation increases arousal
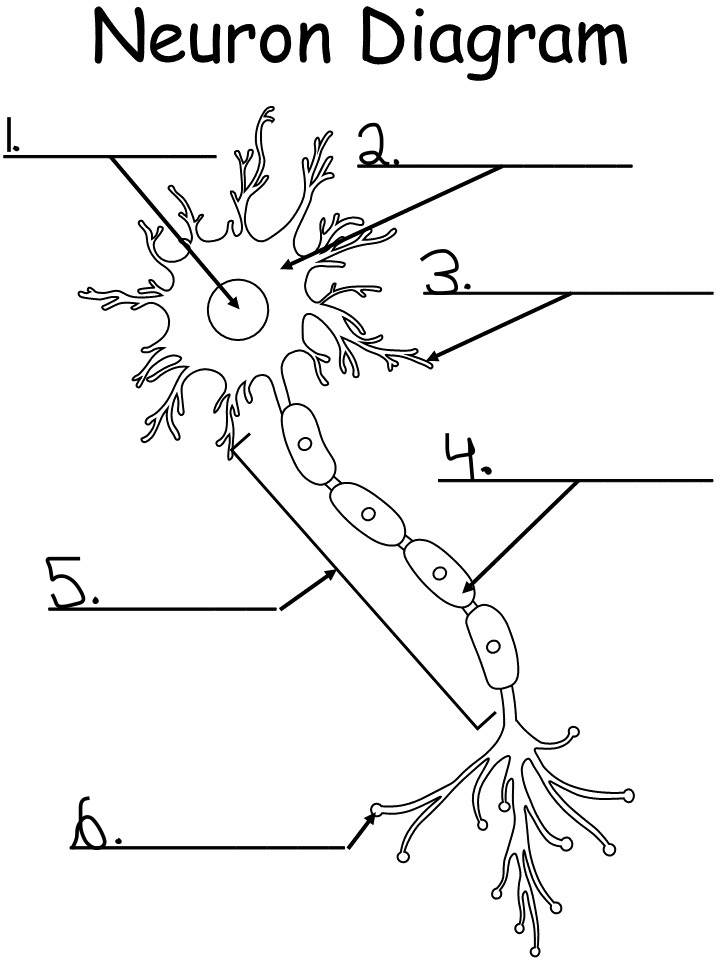
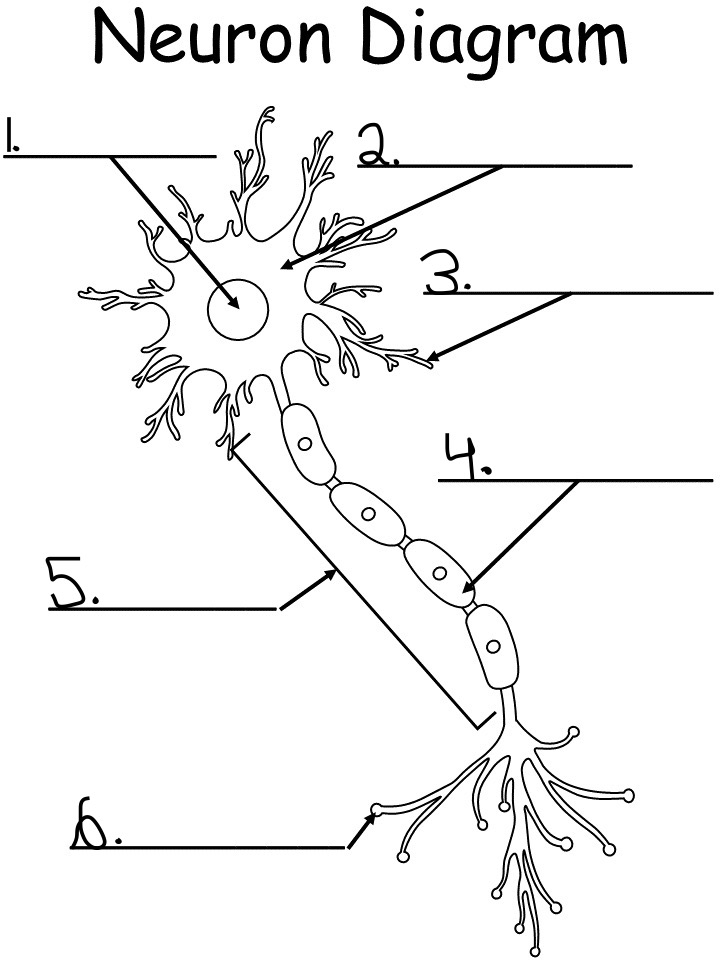
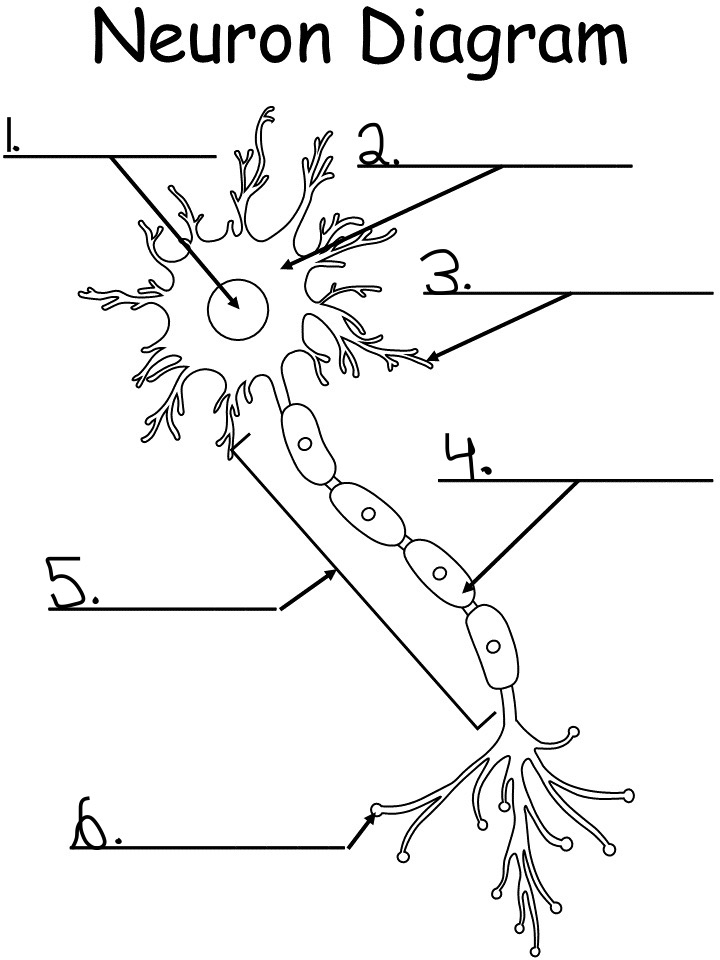
nucleus: controls activity of the cell, contains chromosomes, the DNA
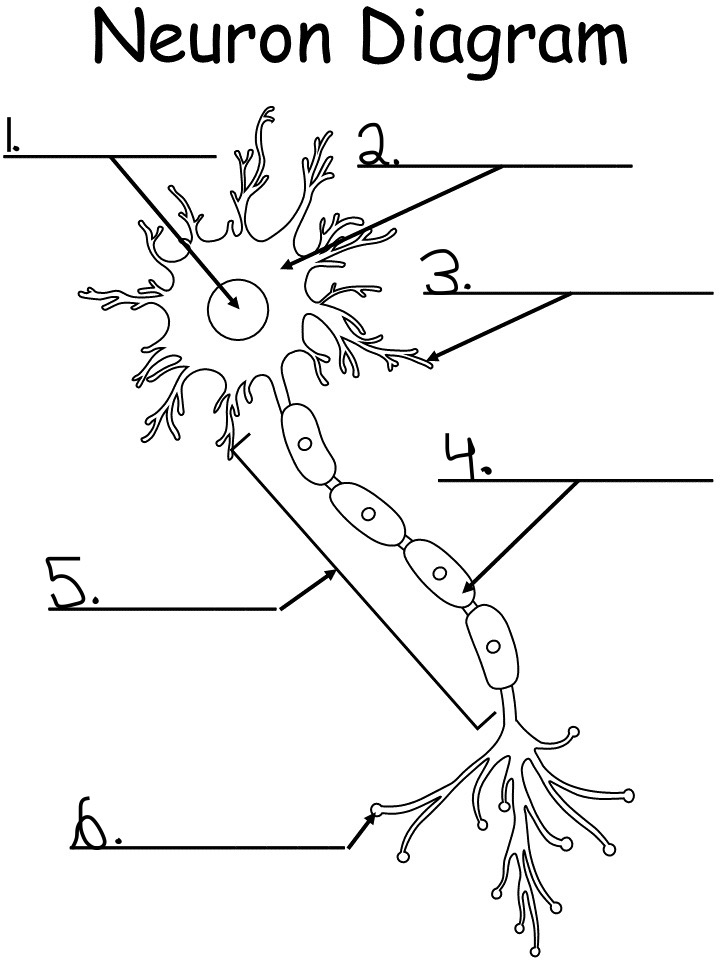
2.
soma (cell body): produced energy needed for activity of the cell
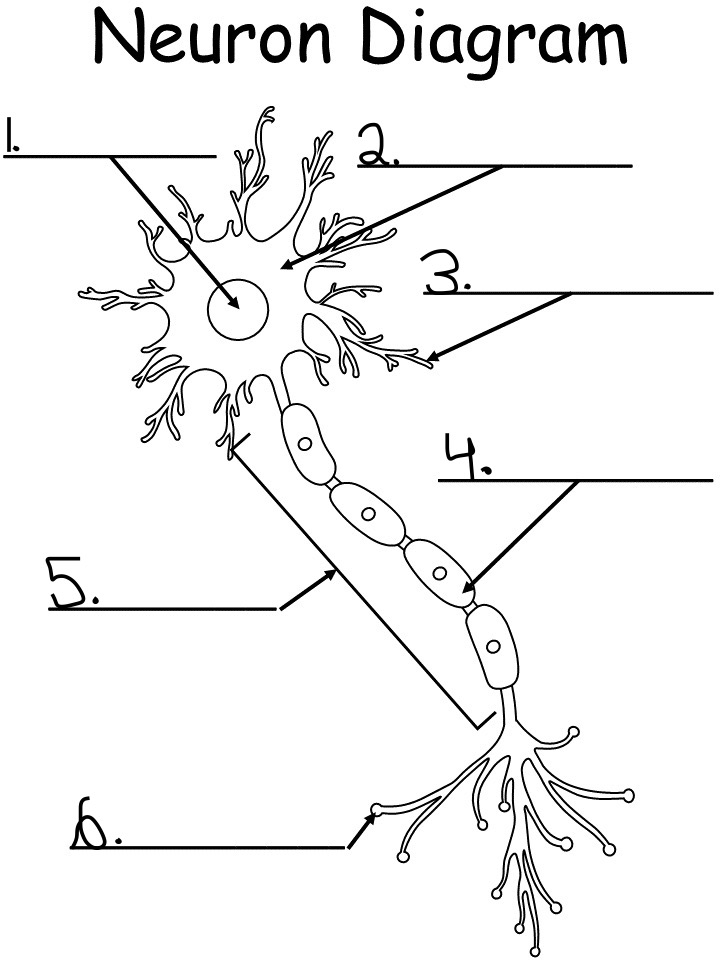
dendrites: branch like extensions of a neuron that receives the impulse and conducts them towards cell body
4.
myelin sheath: a white fatty substance that insulates axons and enables rapid transmission of neural impulses
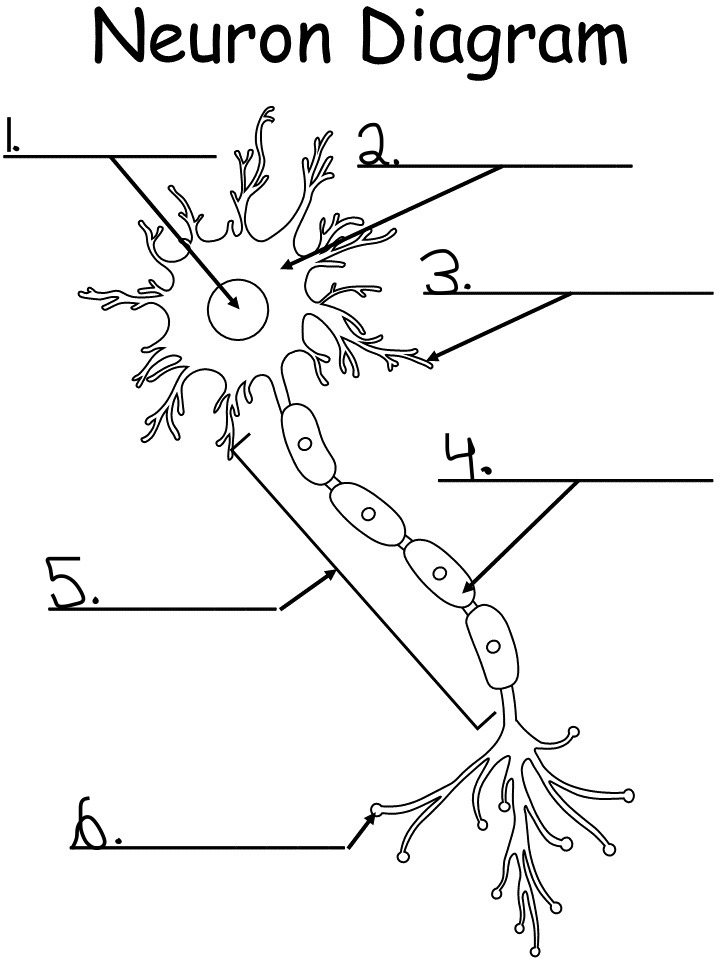
axon: long tubelike structure attached to a neuron that transmits impulse away from the neuron cell body
6.
axon terminal: small fibers branding out from axon
nervous system
central nervous system & peripheral nervous system
central nervous system
spinal cord & brain
peripheral nervous system
somatic & automatic → sympathetic & parasympathetic system
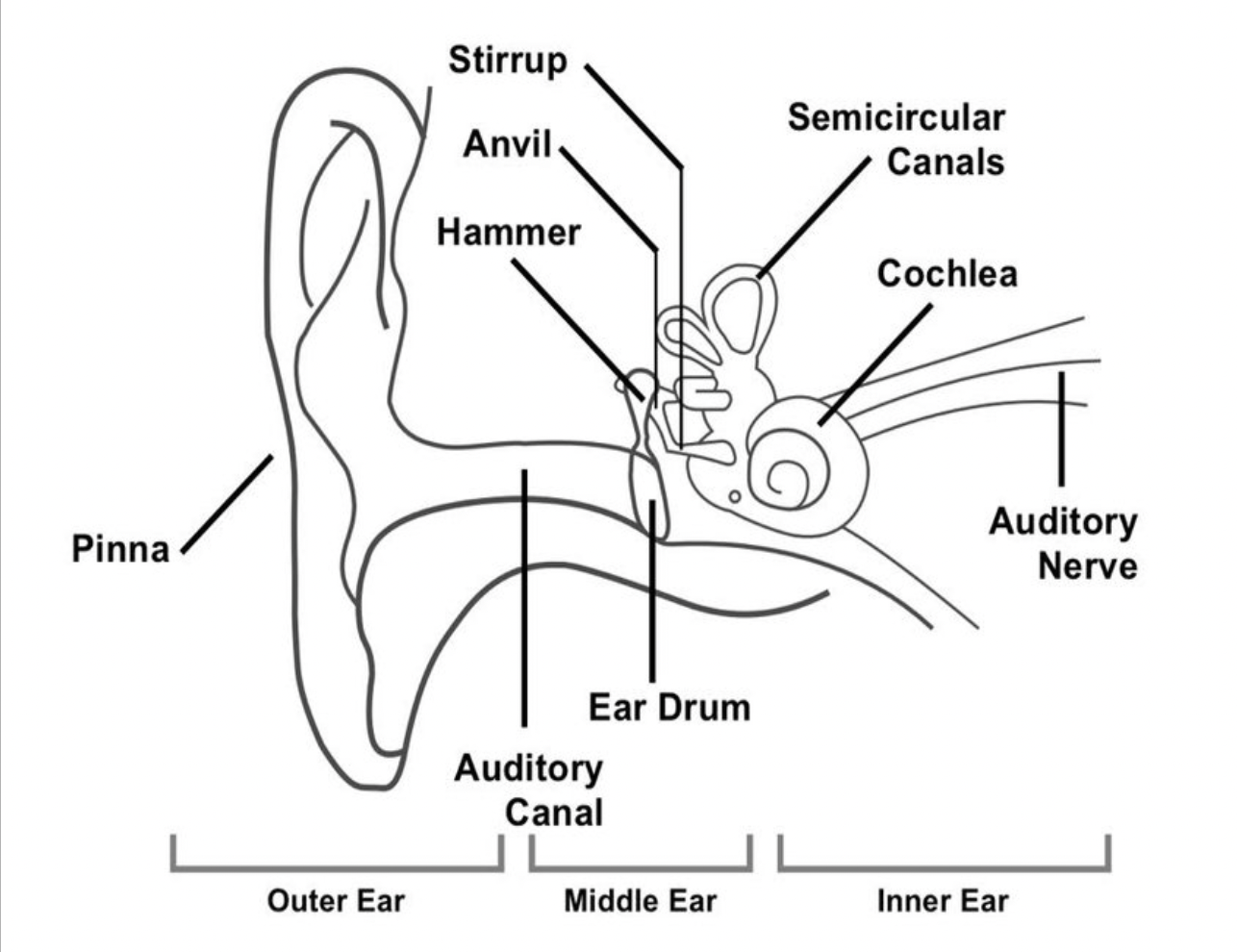
ear diagram
the opening center of the eye that adjusts to the amount of light entering is called?
pupil
the part of the retina that contains no photoreceptors is called?
blind spot
What are the names of the small bones in the middle ear?
hammer, anvil, stirrup
the illusion of movement is produced by showing the rapid progression of images or objects that are not moving
stribascopic motion
this is the nerve that transmits information about odors from receptor neurons to the brain
olfactory nerve
the weakest amount of stimulation that can be sense is called?
absolute threshold
the method of distinguishing sensory stimuli that takes into account not only the strength of the stimuli but also such elements as setting and ones physical state, mood, and attitude is called?
Signal detection theory
what are the 4 basic taste qualities we have on our tongue?
sweet, sour, salty, and bitter
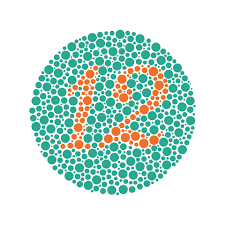
the image below was used for what?
color blind testing
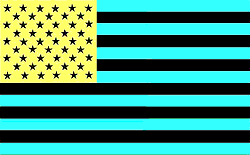
the image was used to give an example of what?
After images
what are the two photoreceptors called?
cones & rods

what is this perception called
ground figure: perception of figures against a backround
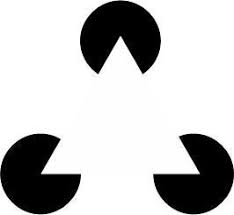
what is this perception called
closure: tendency to perceive a complete figure even when there are gaps in what your senses tell you
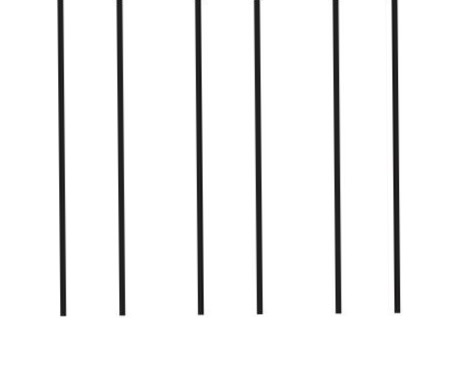
what is this perception called
proximity: tendency to group together visual and auditory events that are near to each other
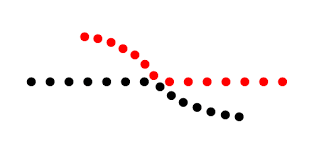
what is this perception called
continuity: tendency to group stimuli into a continuous pattern
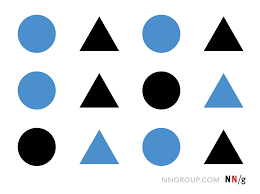
what is this perception called
similarity: tendency to group together element that seem alike
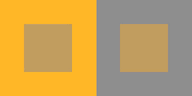
what is this consistency
color: tendency to perceive objects as keeping their color even though different lighting might change the appearance
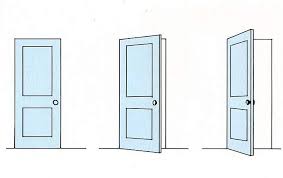
what is this consistency
shape: tendency to see an object keeping its form despite changes in orientation

what is this consistency
brightness: tendency to perceive an object as being equally bright even when the intensitity of the light around it changes

what is this consistency
size: tendency to perceive an object as being one size no matter how far away the object is
Attitude
an enduring mental representation of a person, place, or thing that typically evokes an emotional response and related behavior
Social psychology
Studies the nature and causes of behavior and mental processes in social situations
Cognitive dissonance theory
the view that we are motivated to make our cognitions or beliefs consistent with each other and with our behavior
prejudice
attitude toward a group that leads people to evaluate members of that group negatively
discrimination
hostile behavior directed against groups toward whom one is prejudiced
stereotyping
erroneous assumptions that all members of a group share the same traits or characteristics
attraction
an attitude of liking or disliking (negative attraction)
triangular model of love
love involved combination of three components: intimacy, passion, and committment
intimacy
partners share their innermost feelings
passion
strong romantic snd sexual feelings
commitment
decision to maintain a relationship
consummate love
combines passion. intimacy, and comittment
romantic love
intense positive emotion that involved sexual attraction, feelings of caring, and the belief that one is in love
Social Perception
studies the ways in which we form and modify impressions of others
primacy effect
the tendency to evaluate others in terms of first impressions
recency effect
the tendency to evaluate others in terms of the most recent impressions
attribution
a belief concerning why people behave in a certain way
dispositional attributions
an assumption that a persons behavior is determined by internal causes such as personal traits