CH: 9 Nervous System: Basic Structure and Function
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
What is the NS composed of
MOSTLY nervous tissue
blood vessels
CT
two cell types of nervous tissue
neurons
neuroglial cells
neurons
specialized to react to physical + chemical changes in surroundings
can engage in AP
dendrites
cellular processes that receive input
branches to provide receptive surfaces to which processes from other neurons can communicate
Neurons can have MANY dendrites but only ONE axon
dendritic spines
tiny spines on surface of dendrites
axons
long cellular processes that carry impulses away from neuron
vary in sizes
axon hillock
initial portion of axon
closest to cell body
axon terminals
end of axon
has synaptic end bulbs
made up of multiple telodendria
collaterals
branches of axons (extra)
axonal transport
process an axon uses to convey biochemicals that are produced in cell body
schwann cells
produce myelin
has neurilemma
only PNS
neurilemma
portion of schwann cell
outside myelin sheath
myelin
lipid-rich substance
produces myelin sheath
myelin sheath
coats axon
speeds up transactions
insulates
Myelinated axons have
unmyelinated axons dont have
what is white matter made of?
myelinated axons
what is gray matter made of?
unmyelinated axons
dendrites
cell bodies of neurons
node of ranvier
narrow gap between myelin sheaths
impulses
bioelectrical signals produced by neurons
nerve definition
bundle of axons
synapse
small space between neuron and the cells it communicates with
AKA synaptic cleft OR neuromuscular junction in muscle cells
synaptic knob
specialized ending of an axon
swollen
vesicles filled with neurotransmitters
neurotransmitters
biological messengers produced by neurons`
central nervous system
CNS
contains brain and spinal cord
skull
Cerebral spinal fluid
meninges (D.A.P)
vertebrae
signals are integrated —> decisions are made and acted upon by motor functions
Peripheral nervous system
PNS
contains cranial and spinal nerves
nerves connected to brain: 12 pairs
spinal nerves have 31 paits
receives info from outside CNS
has motor neurons
located in the autonomic nervous system
sympathetic NS
enteric NS
digestive system organs
parasympathetic NS
signals are integrated
decisions are made and acted upon by means of motor function
skeletal motor
has sensory neurons
dorsal root ganglia
cranial nerve ganglia
three functions of NS
sensory
integrative
motor
sensory receptors
located at the ends of peripheral neurons
provide sensory function of nervous system
receptors
gather information
tells NS the intensity of pain
convert info into nerve impulses
transmitted over the peripheral nerves to the central nervous system
motor functions
use neurons to carry impulses from CNS to effectors
effectors
start the action
muscles and glands (motor neurons)
motor divisions
somatic and autonomic
somatic NS
motor division
involved in conscious activities
skeletal
autonomic NS
motor division
involved in unconscious activities
cardiac and smooth muscles and glands
divisions of autonomic NS
sympathetic division
parasympathetic division
enteric NS
brain
receives + processes sensory information
initiates responses
stores memories + generates thoughts + emotions
spinal cord
conduct signals to and from the brain
controls reflex
sympathetic division
fight or flight
parasympathetic division
rest of digest
SLUDD
Salivation: saliva
Lacrimation: tears
Urination: pee
Digestion
Defecation: p00p
3 (4) structural types of neurons
multipolar
bipolar
unipolar
(pseudo-unipolar)
neuron’s cell body
SOMA
contains:
granular cytoplasm
mitochondria
lysosomes
Golgi apparatus
large nucleus
neurofibrils
fine threads that extend into axon
Nissl bodies
chromatophilic substance
located on cell bodies
membranous sacs that contain rough Er
named after Franz Nissl
what cells divide?
mature neurons usually DO NOT divide
neural stems DO divide
how many axons and dendrites do neurons usually have?
ALWAYS one axon
can vary in amount of dendrites but can have more than one
bipolar neuron
two processes
dendrite
axon
found in eyes, ears, nose (PNS)
unipolar neuron
one process
axon
peripheral process is associated dendrites near a peripheral body part and central process enters brain or spinal cord
located in ganglia
cluster of neuron cells in the PNS
multipolar neuron
multiple dendrites + ONE axon
located in brain and spinal cord
CNS
three classes of functional differences
sensory
motor
interneurons
sensory neuron
carry nerve impulses from peripheral body parts into the brain or spinal cord
PNS
have specialized sensory receptors at the distal ends of dendrite
usually unipolar but some are bipolar
interneurons
located in brain and spinal cord
multipolar
form links between other neurons
motor neurons
carry nerve impulses from the brain and spinal cord to effectors
control skeletal muscles, glands, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle
found in CNS
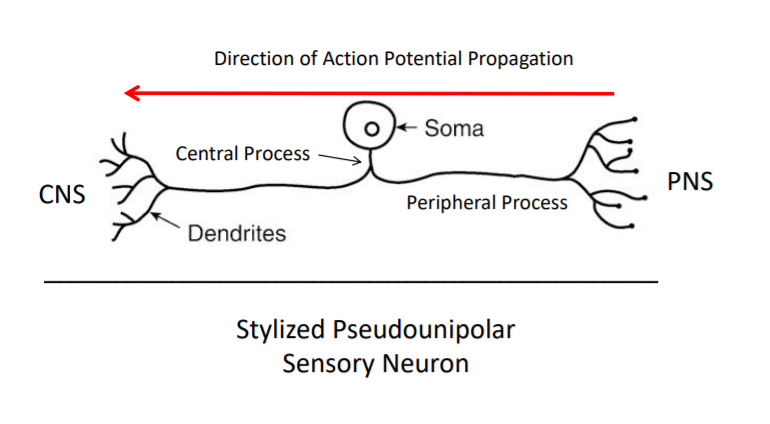
pseudounipolar neurons
can be classified as just unipolar
PNS
one short axon that splits into two processes
central process
The branch that extends from the cell body (soma) towards the CNS, carrying sensory signals from the peripheral process into the spinal cord/brain
peripheral process
The branch extending from the cell body out to the body's periphery (skin, muscles, organs) to detect sensory stimuli like touch, pain, and temperature
anaxonic neuron
Axon cannot be distinguished from many dendrites
CNS in the brain and in special sense organs
neuroglial
binds and supports NS
6 types
smaller than neurons
mitotic (will replicate)
tumors result in division
four types of neuroglial cells of CNS
astrocytes
oligodendrocytes
microglial cells
ependymal cells
astrocytes
star shaped
found between neurons and blood vessels
most numerous
helps neurotransmitters + monitors potassium levels
provide support and hold structures together
aid metabolism of glucose for brain energy
respond to injury of brain tissue to form special scar tissue
plays role in the BBB
blood-brain barrier
astrocytes
blood vessels designed to prevent things from entering the brain
restricts movement of substances between blood and CNS
oligodendrocytes
rows along myelinated axons
form myelin in brain and spinal cord
does not form neurilemma like schwann cells
microglia
smallest neuroglia
removes dead neurons + neuroglia
secretes stuff to kill bacteria
function to support neurons
ependymal cells
form inner lining of central canal of spinal cord and ventricles of brain (spaces)
helps produce CSF + move it through ventricles
neuroglia found in PNS
schwann cells
satellite cells
satellite cells
PNS
support clusters of neuron cell bodies (ganglia)
protection and repair
what happens when neuron is damaged
cell body: neuron suicide
axon: slowly regenerates
presynaptic neuron
neuron that brings impulse to synapse
postsynaptic neuron
neuron that stimulated by presynaptic neuron
synaptic transmission
process by which impulse in presynaptic neuron signals post synaptic neuron
polarization
unequal distribution of positive and negative ions on either side of membrane
when cell membrane is polarized, inside is negative and outside is positive
intracellular positive ion
potassium (K+)
positive ion located inside the cell
extracellular cation
Sodium (Na+)
positive ion located outside the cell
what is used to transport Na+ and K+ through sodium-potassium pumps
ATP
volts
electrical differences between two points
potential difference because it represents stored electrical energy that can be used to do work
millivolts
the units used to measure potential difference across a cell membrane
-70
neurons are __________ because they respond to changes in surroundings
excitable
hyperpolarized
membrane potential becomes more negative than resting potential
depolarization
membrane is less negative than resting potential
threshold potential
sufficient depolarization that triggers action potential
trigger zone
the initial segment of axon
contains many voltage-gated sodium channels
repolarization
membrane is polar again or returned to original resting state
which parts of the neuron are capable of action potential
axons
not soma or dendrites
all-or-nothing response
if neuron responds at all to a nerve impulse, it responds completely
refractory period
stimulus will NOT trigger another impulse bc the axon needs to repolarize
limits how many action potentials may be generated
absolute refractory period
Axon’s membrane cannot be stimulated
First part of the refractory period
relative refractory period
stronger stimulus can trigger impulse
saltatory conduction
nerve impulse that occurs only at nodes of ranvier
nerve fiber classification
classified according to diameter, degree of myelination, speed of conduction
group A
group B
group C
group A fibers
fastest
large diameter
myelinated sheath
somatic sensory and motor fibers
group B fibers
intermediate diameter
lightly myelinated ANS fibers
heart and glands
group C fibers
slowest
smallest diameter
unmyelinated ANS fiber
no sheath
where do released neurotransmitters diffuse to
across synaptic cleft and react with molecules that form receptors in or on postsynaptic neuron membrane
synaptic potentials
local potentials created by changes in chemically gated ion channels
synaptic potentials
can depolarize or hyperpolarize the receiving cell membrane
excitatory postsynaptic potential
type of change where cell membrane is depolarized
causes Na+ channels to open (leaves)
EX: glutamate
inhibitory postsynaptic potential
cell membrane is hyperpolarized
causes Cl- channels to- open (leaves)
acetylcholine
stimulates skeletal muscle contractions
thinking + comprehension
monoamines
epinephrine
norepinephrine
dopamine
serotonin
unmodified amino acids
glycine
glutamic acid
aspartic acid
GABA
peptides
synthesized in R.E.R
ex: substance P, enkephalins
reuptake
neurotransmitters are transported back into synaptic knobs of presynaptic neurons
glutamte
memory
GABA
eating
sleeping
aggression
dopamine
movement
attention
pleasure + reward