chapter 1, 2, & 3 of ultrasound physics
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
edelman, chat gpt, and YouTube
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
ultrasound refers to sound waves with frequences greater than _
20,000 Hz, beyond the range of human hearing.
audible sound typycally ranges between _ and _ Hertz
20 - 20,000
Medical ultrasound typically uses frequencies between
2 MHz and 15,000 MHz
infrasound is lower than
20 Hz
differences between directly related (directly proportional), related (proportional), and inversely related (inversely proportional)
Directly related variables increase together
related variables are associated or affiliated, but the relationship isn’t specified
Inversely related variables move in opposite directions.
What is a reciprocal relationship
Two numbers whose product is equal to one. A special form of an inverse relationship, where one variable increases while the other decreases.
for a numerical answer to a question to be comprehensive, it requires a
unit of measurement.
increase by the factor means to _ by that number, and decrease by the factor means to _ by that number
multiply, divide
a number followed b y a percent is
unitless and represents a ratio of the number to 100.
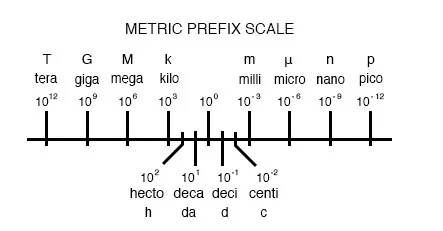
metric system power of ten chart
sound is a _, _ wave that travels through a medium by particle vibration
mechanical, longitudinal
sound requires a _ to propagate
medium, it cannot travel through a vacuum
The difference between longitudinal and mechanical properties in sound waves
Longitudinal waves refer to sound waves where particle vibration occurs in the same direction as wave propagation, while mechanical properties involve the physical characteristics of the medium through which the sound travels.
sound travels as a series of _ and _
compressions and rarefactions
what are acoustic variables
Acoustic variables are physical quantities that describe the state of a sound wave.
What are the 3 acoustic variables
Pressure (Pascals, Pa), density (kg/m³), and distance (particle motion, mm, cm)
what are acoustic parameters
Acoustic parameters are characteristics that define the properties of sound waves, including frequency, wavelength, amplitude, and speed.
Difference between acoustic variables and acoustic parameters
Acoustic variables describe the state of a sound wave, while acoustic parameters define the features of those sound waves.
Period | µs | Time for one cycle |
Frequency | MHz | Cycles per second |
Amplitude | dB | Strength of the wave |
Power | Watts | Rate of energy transfer |
Intensity | W/cm² | Power per area |
Wavelength | mm | Distance of one cycle |
Propagation Speed | m/s | Speed through a medium |
in ultrasonography, sound pulses created by a transducer travel through biological tissue, or
media
all waves carry _ from one location to another
energy
Many different forms of waves exist, including
heat, sound, magnetic, and light.
sound is a _ wave
mechanical
sound _ travel through a vacuum, it travels through a
cannot, medium
sound travels in a _ line
straight
sound waves are _ waves
longitudinal
acoustic propagation properties
The effects of the medium upon the sound wave, such as speed, frequency, and wavelength. media affects sound
biological effects
The effects of the sound wave upon the biological tissue through which it passes. Sound affects media
Pressure is the concentration of force in an _, units are _
area, pascals
density is the concentration of mass in a _, units are _
volume, kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³)
Distance is the measure of _, units are _
particle motion, cm, feet, mile
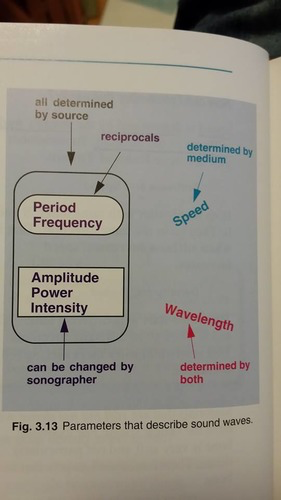
What are the seven acoustic parameters
period, frequency, amplitude, power, intensity, wavelength, and propagation speed.
difference between transverse waves and longitudinal waves
Transverse waves move perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer, while longitudinal waves move parallel. Examples include waves on a string for transverse and sound waves for longitudinal.
what is considered an in-phase wave
An in-phase wave is when two or more waves have the same frequency and their peaks and troughs align, resulting in constructive interference and increased amplitude.
what is considered an out-of-phase wave
An out-of-phase wave occurs when two or more waves have a frequency but their peaks and troughs do not align, resulting in destructive interference and decreased amplitude.
what is interference in sound waves
Interference in sound waves refers to the phenomenon that occurs when two or more sound waves overlap and combine, resulting in either an increase (constructive interference) or decrease (destructive interference) in sound intensity, depending on their phase relationship.
constructive interference vs destructive interference
Constructive interference occurs when waves align in phase, leading to an increase in amplitude, while destructive interference happens when waves are out of phase, causing a reduction in amplitude.
out-of-phase waves of equal amplitude may
cancel each other out
the source of a sound wave is the ultrasound system and
transducer
tissue is also called the
medium
period is the _ it takes a wave to vibrate in a _
time , single cycle
period is deteremined by the _ only, not the
sound source, medium
is period adjustable
no
frequency is the _ of particular events that occur in a specific duration of
number, time
in diagnostic ultrasound, the frequency of a wave is described as the number of _ that occurs in _ second
cycles, one
frequency of a sound wave is determined by the _ only
sound source
is frequency adjustable
no
period and frequency are _ related to each other
inversely
as frequency increases, period
decreases
period and frequency also have a _ relationship
reciprocal
period x frequency =
1
what are the 3 bigness parameters
Amplitude, Power, Intensity
amplitude is the bigness of the wave, it is the difference between the _ value and _value of an acoustic variable
maximum?minimum, average or undisturbed
Amplitude is usually expressed in
decibels
amplitude can have units of
any acoustic variable
amplitude is determined only by the
sound source
is amplitude adjustible
yes
amplitude is measured by the _ value to the _ value
middle (undisturbed), maximum
peak-to-peak amplitude
is the difference between the maximum and minimum values of the waveform.
power is the rate of _ transfer or the rate at which work is performed
energy
power has units of
watts
power is deteremined only by the _, power _ as sound propagates through the body
sound source, decreases
is power adjustable
yes
what is the relationship between amplitude and power
Power is proportional to the square of the amplitude; as amplitude increases, power increases dramatically.
formula between power and amplitude relationship
Power = Amplitude²
intensity is the concentration of _ in a _
energy, sound beam
the units of intensity are
watts per square meter (W/m²)
intensity is determined by the
sound source
is intensity adjustable
yes
intensity formula
power (w)/ area (cm²)
intesity is _ to power
proportional
intensity is proportional to the wave’s amplitude _
squared
squared always follows the word
amplitude
wavelength is the _ or _ of one complete cycle
distance or length
wavelength is deteremined by both
the source and the medium
is wavelegnth adjustable
no
wavelength is the only parameter that is determined by both
the source of the ultrasound and the medium through which it travels.
both _ and _ describe a single cycle in a sound wave
wavelegnth and period
what is the relationship between wavelength and frequency
Wavelength and frequency are inversely related; as the frequency of a sound wave increases, its wavelength decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is described by the equation: speed = frequency x wavelength.
shorter wavelengths are created by _ frequency sounds
high
propagation speed is the rate at which a sound wave travels through the
medium
speed of sound in the body ranges between
500 m/s to 4000 m/s depending on the tissue
speed is determined only by the
medium
is speed adjustable
no
what is the speed of sound in soft tissue
Approximately 1540 m/s or 1.54 mm/us
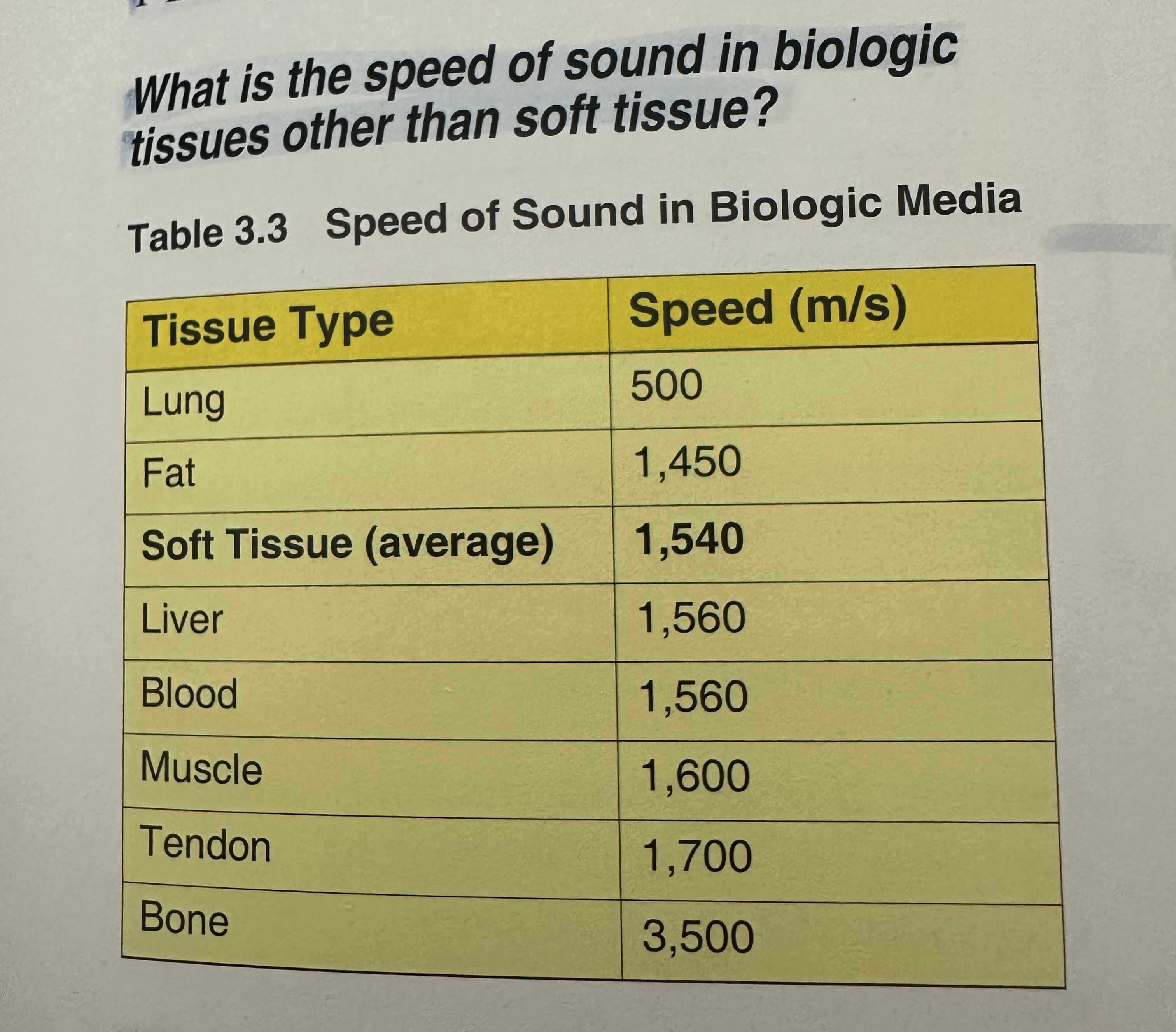
speed of sound in air, water, and metals
approximately 330 m/s in air, 1480 m/s in water, and about 2,000 to 7,000 m/s in metals.
speed formula
speed = frequency × wavelength.
two characteristics of a medium affect the speed of sound
stiffness and density
stiffness describes the ability of an object to resist
compression when a force is applied.
density describes the relative _ of a material
weight
stiffness and speed are _ related
directly
Bulk modulus is the same as
stiffness
what is the opposite of stiffness
compressibility and elasticity
density and speed are _ related
inversely
sound travels faster in media with _ density
low
if two media are equally stiff, the _ medium will have a lower speed
denser
speed is determined by the _ and _
stiffness and speed
Stiffness increase, speed _
increases