CP1 - Passive Solute Transport
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What are the two main rules for passive solute transport?
You do not spend energy
You go only where they move you / only in certain directions
What is Homeostasis?
Process of the maintenance of the composition of the extracellular fluid
What type of process is homeostasis?
What does this mean?
Dynamic process; means continuous adjustments are being made to maintain the variables in a range required for life
What is the main role of these body systems:
Cardiovascular?
Renal / Urinary?
Digestive?
Nervous and Endocrine?
Cardiovascular: distribution of nutrients (through blood)
Renal / Urinary: removal of organic waste and controls salts and water levels
Digestive: removal of unabsorbed matter
Nervous and Endocrine: regulate the other body systems
Which three methods / processes do we use to achieve homeostasis?
Negative feedback
Positive feedback
Feedforward
How does negative feedback maintain homeostasis?
What is an easy way to remember it?
What are some examples of this type of system?
Opposes deviations of a system from its desired level, returning it to the normal values
A increases B, then B decreases A
Examples include temp, blood pressure, O2, CO2, and ion balance
What are the various components of a Negative feedback system?
Controlled Variable — variable that is regulated by the system
Sensor (in the Afferent / Sensory pathway) — detects the change(s) in the CV
Integrator — compares the Set Point to the CV
Set Point — desired value of the variable controlled by the system
Effector (in the Efferent / Motor Pathway) — sends the CV back to normal via some change
How does positive feedback maintain homeostasis?
What is an easy way to remember it?
What are some examples of this type of system?
Reinforces movement further away from the set point
A increases B, then B increases A
Examples include depolarization phase of an AP, labor, and shock
What is feedforward?
What is the main example given of this process?
Response in anticipation of a change in a variable
Example is the secretion of fluids and digestive enzymes in the GI tract when smelling and / or seeing the food
How many total liters of water are contained within the body?
What percent of the body weight does this water make up?
42 total liters, for a 70 kg individual
This is about 60% of body weight
How much of the total body water is composed of intracellular fluid?
Extracellular fluid?
Where are both contained?
Intracellular — contained within cells, makes up 25 of the 42 L
Extracellular — located outside cells, makes up 17 of the 42 L
What two things make up the Extracellular fluid in cells?
Where are they located?
How much of the extracellular fluid do each of these contain?
Interstitial Fluid — located between cells in body tissues, makes up 14 of the 17 L
Blood Plasma — located in the blood, makes up 3 of the 17 L
What two kinds of fluid are included in the Blood?
How much of the blood do each of them make up?
How much blood is contained in the body?
Intracellular (inside cells) — 2.5 of the total 5.5 L
Extracellular (plasma) — 3 of the total 5.5 L
5.5 L total blood volume
What creates and maintains the difference in the conc. of solutes between the intracellular and extracellular fluids?
Membranes
What are membranes?
Bilayer of lipids (6-10 nm thick) with proteins imbedded in the bilayer
What are the two major types of membrane lipids?
What are they composed of?
Phospholipids — composed of a Glycerol backbone, a polar Phosphate group (hydrophilic head), and two Fatty Acid chains (hydrophobic tails)
Cholesterol — steroid ring structure
What is the main function of Cholesterol?
Associates with the phospholipids to reduce the fluidity of the membrane and stiffening it
Where are the hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails of the lipid bilayer oriented towards?
Hydrophilic heads — create hydrogen bonds with other polar molecules and face the surface of the membrane
Hydrophobic tails — oriented away from water molecules forming the inner core of the bilayer
What are the main types of proteins and regions contained in the membrane?
Nonpolar regions — keep proteins attached to the membrane, associated with phospholipids, and make up the inner membrane area
Polar regions — interacts with water to form the bilayer
Peripheral proteins — only inside or outside the membrane; associate with other proteins via hydrogen bonds
Integral proteins — peripheral or transmembrane proteins that are permanently attached to the membrane
Transmembrane proteins — penetrate through onto both sides of the membrane
What are some of the main functions of membranes?
Regulate passage of substances into and out of the cell to form a selective barrier
Detect chemical messengers arriving at cell surface through receptors and initiate responses
Recognition of “self” for immune function
Links cells to the extracellular matrix to form tissues
Link adjacent cells together by membrane junctions and regulates solute transport and cell-to-cell communication
What are membrane junctions?
What are the main two types?
What are their main functions?
Membrane junctions are specialized structures between cells
Tight Junctions — structures that encircle cells and join adjacent cells
Form barrier between cells and control (or prevent) the movement of solutes between cells
Characterized by “leakiness” (whether or not they pass or do not pass water), which varies among tissues
Gap Junctions — channels that allow small molecules and ions to pass between cells (connects through the membranes)
Important for the synchronized contraction of smooth and cardiac muscle cells
Allows for rapid spread of electrical signals
What are the two types of passage conducted by Tight Junctions?
Transcellular — through the cells themselves
Paracellular — between the cells
What are the two main characteristics of passive solute transport across membranes?
does NOT require external energy
solutes travel DOWN their concentration gradients
What is the concept of Brownian Motion?
solutes in solutions are constantly moving
it does not stop (motion), only net movement (high to low) across the membrane does
Which direction does movement go during simple diffusion?
From high to low concentration, down the concentration gradient
What equation is used to determine the rate of diffusion across membranes?
J = PA(C0 - Ci)
where:
J = net flux (or Rate of Diffusion)
A = surface area of membrane
C0 - Ci = concentration difference across membrane
P = permeability coefficient (the ability of the solute to pass through the lipid bilayer)
What is the relationship between hydrophilicity and permeability coefficients?
Diffusion rate?
Hydrophobic Solutes — HIGH permeability coefficients (high P), diffuse RAPIDLY
Hydrophilic Solutes — LOW permeability coefficients (low P), diffuse SLOWLY
What two groups of molecules do not diffuse across the lipid bilayer?
Large polar (those with uneven distribution of charge) molecules and large charged (have either a + or - charge) molecules
Does water diffuse across the lipid bilayer?
How fast?
Why?
Yes, but not easily
Diffuses slowly (takes ~1 min to travel the 6-10 nm bilayer)
Polar molecule, but is also very small (allows it to sneak between lipoproteins)
How fast are action potentials?
APs can pass 3.7 miles per 1 min
Do ions diffuse across the lipid bilayer?
No, they are charged
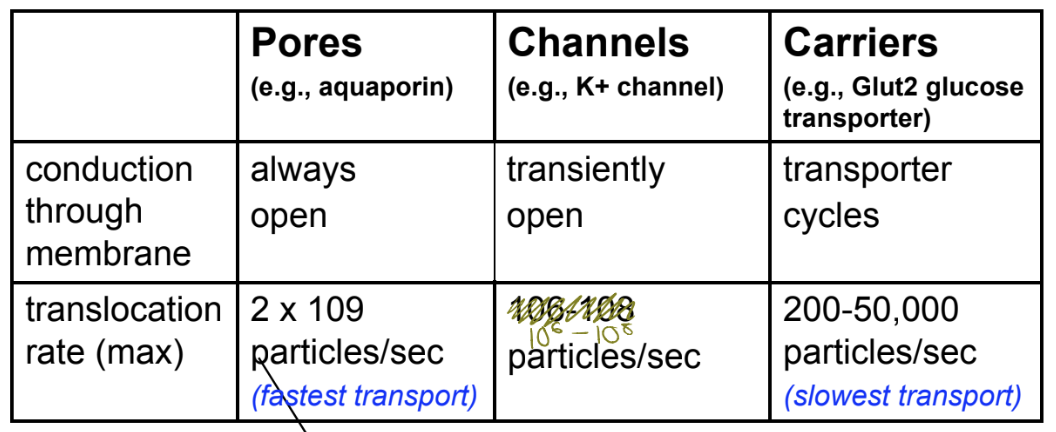
What are pores?
What direction of passage do they allow for?
Is this up or down the concentration gradient?
Transmembrane proteins located in membranes that provide a passage for solutes across the membranes and are ALWAYS open
Allow for passage in BOTH directions, but it is always DOWN the solute’s concentration gradient
What is an example of passage via pores?
passage of water through Aquaporins
What are ion channels?
What direction of passage do they allow for?
Is this up or down the concentration gradient?
Transmembrane proteins that allow passage of ions across the membrane (including Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Cl-) that are normally closed (with exceptions)
Allow for bidirectional passage and unidirectional passage in some, but ions will ALWAYS flow DOWN their electrochemical gradient
What are the three types of ion channels?
Ligand-gated channels — channel acts as a channel and receptor at the same time
Voltage-gated channels — channel opens based on change in electrical membrane potential
Mechanically-gated channels (via mechano-receptors) — channel physically opens
What two factors determine a channels selectivity for ions?
Do all channels have the same level of selectivity?
Size of ion
Charge of ion
Not all channels are as selective as others; some are more selective
What are carrier proteins?
What direction of passage do they allow for?
Is this up or down the concentration gradient?
Transmembrane proteins that allow for passage of molecules (ex. glucose, urea, etc.)
Allows for transport DOWN the molecules’ concentration gradient, in BOTH directions
How do carrier proteins transport molecules?
COME BACK AND FILL OUT
Include conformational change and cycles
What are the main characteristics of Carrier Proteins?
Specificity — carrier requires a specific structure and charge of solutes
Competition — molecules of similar structure will compete for the same transporter (ex. glucose, galactose, and fructose)
Saturation — transport will plateau when all of the transporters are occupied
Does simple diffusion saturate when you increase the concentration of solutes?
No, only diffusion via carriers does
What is ‘facilitated diffusion’ most often used to describe?
What is it more generally used for?
Most often: used to describe passive transport of molecules via carriers
Most generally: used for passive transport of any solutes via transport proteins
What is transported and in which direction is something transported during facilitated diffusion?
Via aquaporins — water, down the conc. gradient
Via ion channels — ions, down the electrochemical gradient
For this course, what do we consider Facilitated Diffusion?
What is another name used for it?
PASSIVE transport of molecules via carrier proteins
Also known as “mediated transport”
Give a summary of the three types of passive transport we talked about in this lesson.
Transporters that work in cycles are slow and can saturate (including primary and secondary active transporters)