MCB244 Tissues
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
Tissue
group of similar cells and extracellular material/matrix (ECM), generally sharing a common function
Autopsy
examination of organs of a dead body to determine the cause of death or study the changes caused by disease
What are the 4 types of tissues
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
What are the functions of epithelial tissue
physical protection (dehydration, abrasion, destruction)
selective permeability (allows passage of some substances while preventing passage of others)
Secretions: some cells are specialized to secrete
sensation: supply info to NS
What are the classifications of epithelial cells by cell layers
simple, straified, and pseudostratified
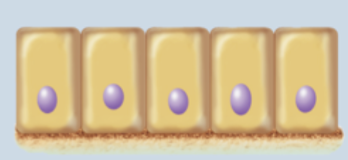
Simple Epithelium
one cell later thick; all cells contact basement membrane
filtration, absorption, or secretion is primary function
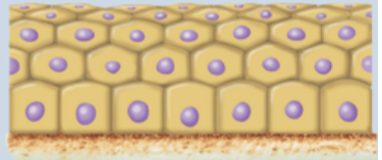
Stratified Epithelium
2 or more layers of epithelial cells
only basal layer in contact with basement membrane
in areas subjected to mechanical stress
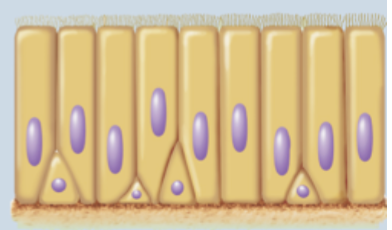
Pseudostratified Epithelium
appears layered
all cells contact basement membrane, but may not reach apical surface
What are the classifications of epithelial tissue by cell shape
Squamous, cuboidal, and columnar
Squamous Cells
flat, wide, irregular in shape
nucleus flat

Cuboidal Cell
about as tall as they are wide
nucleus spherical and in center of cell

Columnar Cells
slender and taller than they are wide
nucleus oval; oriented lengthwise in basal region

Transitional Cells
can change shape, depending on the stretch of the epithelium
simple squamous epithelium
single layer of flat cells with a spherical/oval nucleus
Function: thinnest barrier that allows rapid diffusion and filtration; secretion in serous membrane
found in lining of lung air sacs (alveoli), lining of blood and lymph vessel (endothelium), serous membranes of body cavities (mesothelium)
Alveoli
lung air sacs
endothelium
blood and lymph vessel walls
mesothelium
serous membrane of body cavities
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
single layer of uniformly shaped cells; about as tall as they are wide
centrally located spherical nucleus
Function: absorption and secretion; forms secretory tissue of most glands and small ducts
Where are simple cuboidal epithelium tissue found
lining of kidney tubules, thyroid gland follicles, surface of ovaries, secretory regions and ducts of most exocrine glands
Simple Columnar Epithelium
single later of cells
taller than they are wide
oval nucleus, lengthwise in basal region
ideal for secretory and absorptive functions
2 forms : non-ciliated, ciliated
Non-ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium
single layer of non-ciliated cells taller than they are wide
oval nuclei oriented lengthwise in basal region
apical surface may contain microvilli/brush border
may contain unicellular glands called goblet cells that secrete glycoprotein mucin
functions: absorption and secretion
Where are non-ciliated simple columnar epithelium
lining of most of digestive tract from stomach to anal canal
Ciliated simple columnar epithelium
single layer of ciliated cells taller than they are wide
oval nuclei oriented lengthwise in basal region; cilia projecting from apical surface move mucus along
Goblet cells interspersed
functions: secretion of mucin and mucus movement; oocyte movement through uterine tube
Where are ciliated simple columnar epithelium found
lining of bronchioles in the lung and uterine tubes
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
appears in multiple cell layers but not really stratified
all cells in direct contact with basement membrane
nuclei scattered at different distances
not all cells reach apical surface
2 forms
ciliated
nonciliated
Ciliated Psuedostratified Columnar Epithelium
single layer of cells; varying heights
all cells connect to basement membrane but not all cells reach apical surface
cells have cilia (on apical surface) and goblet cells
Functions: protection, secretion of mucin, movement of mucus along the epithelial surface by cilia
Where are ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium found
large passageways of respiratory system (nasal cavity, parts of pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi)
Non-cilliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
single layer of cells with varying heights
all cells connect to basement membrane but not all cells reach apical surface
cells lack cilia and goblet cells
Function: protection
where are non-ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium found?
rare- found mainly in male urethre and epididymis
Stratified squamous epithelium
multiple cell layers; only the deepest layer is in direct contact with basement membrane
basal layers with cuboidal shape
apical cells with squamous shape
function: protects against abrasion and friction
stem cells in basal layer continuously divide and replace lost cells at surface
2 forms: keratinized and non-keratinized
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
multiple cell layers
basal cells: cuboidal or polyhedral and alive
apical (superficial cells): squamous and are dead; lack nuclei and organelles but are filled with keratin
function: protection of underlying tissue from abrasion
Where are keratinized stratified squamous epithelium found
epidermis of the skin
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
multiple cell layers
basal cells: cuboidal or polyhedral; apical (superficial cells)- squamous
all cells are alive
kept moist with secretions (saliva, mucus)
cells have organelles and microscopically visible nuclei, but lack keratin
Function: protection of underlying tissue from abrasion
Where are non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium found
lining of oral cavity, part of pharynx, esophagus, vagina, anus
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
2 or more layers of cells
superficial cuboidal in shape- as tall as they are wide
functions: protection and secretion
forms walls of ducts in most exocrine glands
Where are stratified cuboidal epithelium found
ducts of most exocrine glands and ovarian follicles
Stratified columnar epithelium
rare
two or more layers of cells
columnar cells at apical surface
functions: protection and secretion
Where are stratified columnar epithelium found
large ducts of salivary glands, conjunctiva of the eye, parts of male urethra
Transitional epithelium
in relaxed state, basal cells look cuboidal or polyhedral; apical cells large and rounged
in stretched state, apical cells flattened
some cells are binucleated
function: allows for stretching as bladder fills
Where is transitional epithelium found
limited to urinary tract (bladder, ureters, and parts of urethra)
Glands
individual cells or multicellular organs composed of epithelial tissue
Endocrine glands
lack ducts; secrete hormones into blood
exocrine glands
invaginated epithelium in connective tissue
connected with epithelial surface by duct (an epithelium-lined tube for gland secretion)
What are some examples of exocrine glands
sweat glands, mammary glands, salivary glands
Unicellular Exocrine Glands
do not contain a duct
located close to epithelium surface
most common type: goblet cell
Multicellular Exocrine Gland
numerous cells
Acini: cell clusters the produce secretions
ducts transport secretions to epithelial surface
surrounded by a fibrous capsule, extensions of which may form septa, partitioning a gland into lobes
What are the classifications of glands
simple, compound, tubular, acinar, tubuloacinar
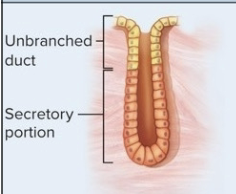
Simple glands
single, unbranched duct
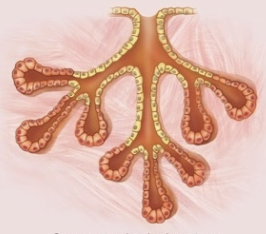
compound gland
branched ducts
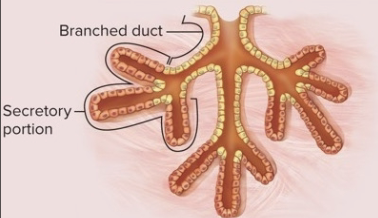
tubular glands
secretory portion and duct same diameter
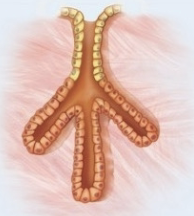
Acinar glands
secretory portion forms expanded sa
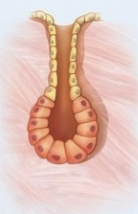
tubuloacinar gland
both tubules and acini
Merocrine gland
packaged secretions into vesicles, released by exocytosis
ex: lacrimal and salivary glands
Apocrine Glands
apical membrane pinches off an becomes secretion
ex: mammary and ceruminous glands
Holocrine glands
ruptured cell becomes secretion
ex: sebaceous (oil) glands
Connective tissue
most diverse, abundant, and widely distributed of the tissue tupes
What are the components of connective tissue
cells, protein fibers, and ground substance
What is the function of connective tissues
physical protection, support and structural framework, binding of structures, storage, transport, and immune protection
What are the 2 classes of connective tissue cells
wandering cells and resident cells
Wandering cells
continuously move through CT
components of immune system
repair damaged extracellular matrix
type of leukocytes (white blood cell)
protect body from harmful agents
Resident cells
stationary, house in CT, support, maintain, repair extracellular matrix
ex: fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, etc.
Fibroblast
flat cells with tapered ends
most abundant resident cells in CT proper
produce fibers and ground substances of ECM
Adipocytes
appear in small clusters in some types of CT proper
adipose connective tissue: dominant area of large clusters
Mesenchymal cells
embryonic stem cell
divides to replace damaged cells
one replaces mesenchymal cell, other becomes committed cell
Fixed macrophages
relatively large, irregular-shaped cells
derived from monocytes (type of leukocyte)
dispersed throughout matrix
phagocytize (engulf) damaged cells or pathogens
released chemicals to stimulate immune system/attract wandering cells
What are the types of protein fibers in connective tissue
collagen, reticular, and elastic
Collagen Fibers
unbranched, “cable-like” long fibers (white glistening appearance)
numerous in tendons and ligaments
Reticular fibers
similar to collagen fibers but thinner
abundant in stroma of some organs
Elastic fibers
contain protein elastin (thinner than collagen), usually coated with the glycoprotein fibrillin
stretch and recoil easily
found in skin, walls of arteries
Ground substance
molecular material produced by CT (connective tissue) cells
residence for CT cells and protein fibers
can have viscous, semisolid, or solid consistency
absorbs compression forces, protects delicate cells from injury
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
large molecule in ground substance (chondroitin sulfate, heparin, hyaluronic acid); charge attracts cations, water follows
Proteoglycans
formed with GAG linked to a protein; form thick colloids
Glycoproteins
proteins with carbohydrates attached; bond CT cells and fibers to ground substance
Mesenchyma
source of connective tissue cells
adult CT often has mesenchymal stem cells
Mucous connective tissue
found in umbilical cord only
Loose Connective Tissue
fewer cells and protein fibers than dense CT
protein fibers are sparse and irregularly arranged
abundant ground substance
body’s “packing material”, supports structure
Types: areolar, adipose, and reticular
Areolar CT
loose organization of collagen and elastic fibers
highly vascularized (many blood vessels)
predominant cells are fibroblasts within abundant and viscous ground substance
Function of Areolar CT
protection of tissues and organs; binding skin and some epithelia to deeper tissue; providing space for blood vessels and nerves
Where are areolar ct found?
the papillary layer of dermis, subcutaneous layer, and surrounding organs, nerve and muscle cells, and blood vessels
Adipose CT
commonly referred to as fat
composed closely packed adipocytes; nucleus pushed to the edge of the cell by large fat droplet
2 types: white and brown
adipose gain/loss due to adipocytes enlarging or shrinking
White adipose CT
stores energy, acts as insulator, cushions
Brown Adipose CT
found in newborns, generates heat, lost as we age
Function of adipose CT
energy storage; insulation/cushioning and protection
Where is adipose tissue found
subcutaneous layer; covers some organs
Reticular CT
meshwork of reticular fibers, fibroblasts, leukocytes within a viscous ground substance
Function of Reticular CT
providing structural framework for many lymphatic organs
Where are reticular CT found
spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, and red bone marrow
Dense Connective Tissue
mostly protein fibers
less ground substance than loose CT
3 types: regular, irregular, and elastic
Dense Regular CT
fibroblasts squeezed between densly packed, parallel collagen fibers
stress typically applied in a single direction
few blood vessels; limited ground substance
takes long to heat
Function of Dense Regular CT
attach muscle to bone or bone to bone; resists pressure applied in one direction
Where are dense regular CT found
tendons (attach muscle to bone) and ligaments (attach bone to bone)
Dense Irregular CT
fibroblasts between densely packed, randomly arranged clumps of collagen fibers
extensive blood vessels; more ground substance than in dense regular CT
Function of Irregular CT
provides support and resistance to stress in multiple directions; durability
Where is dense irregular CT found
reticular layer of dermis, periosteum of bone, perichondrium of cartiliage, capsules around internal organs; epimysuim of muscle
Elastic CT
limited fibroblasts between branching and densely packed elastic fibers
Elastic CT Function
allows stretching and recoil
Where is elastic CT found
walls of large arteries, trachea, vocal cords
What are the 2 types of supporting connective tissue
Cartilage and bone
Cartilage
firm, semisolid extracellular matrix
collage and elastic protein fibers
Chondrocytes": mature cells
more flexible than bone
strong and resilient
occupe small spaces called lacunae
3 types: Hyaline Cartilage, Fibrocartilage, and Elastic Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
most common cartilage
irregularly arranged chondrocytes in lacunae, surrounded by ground substance (perichondrium)