Week 5 - Respiratory System (Nasal Cavity, Pharynx, and Larynx)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
conducting zone
region of the respiratory system that includes the organs and structures that provide passageways for air and are not directly involved in gas exchange
respiratory zone
region of the respiratory system that includes the organs and structures that are directly involved in gas exchange
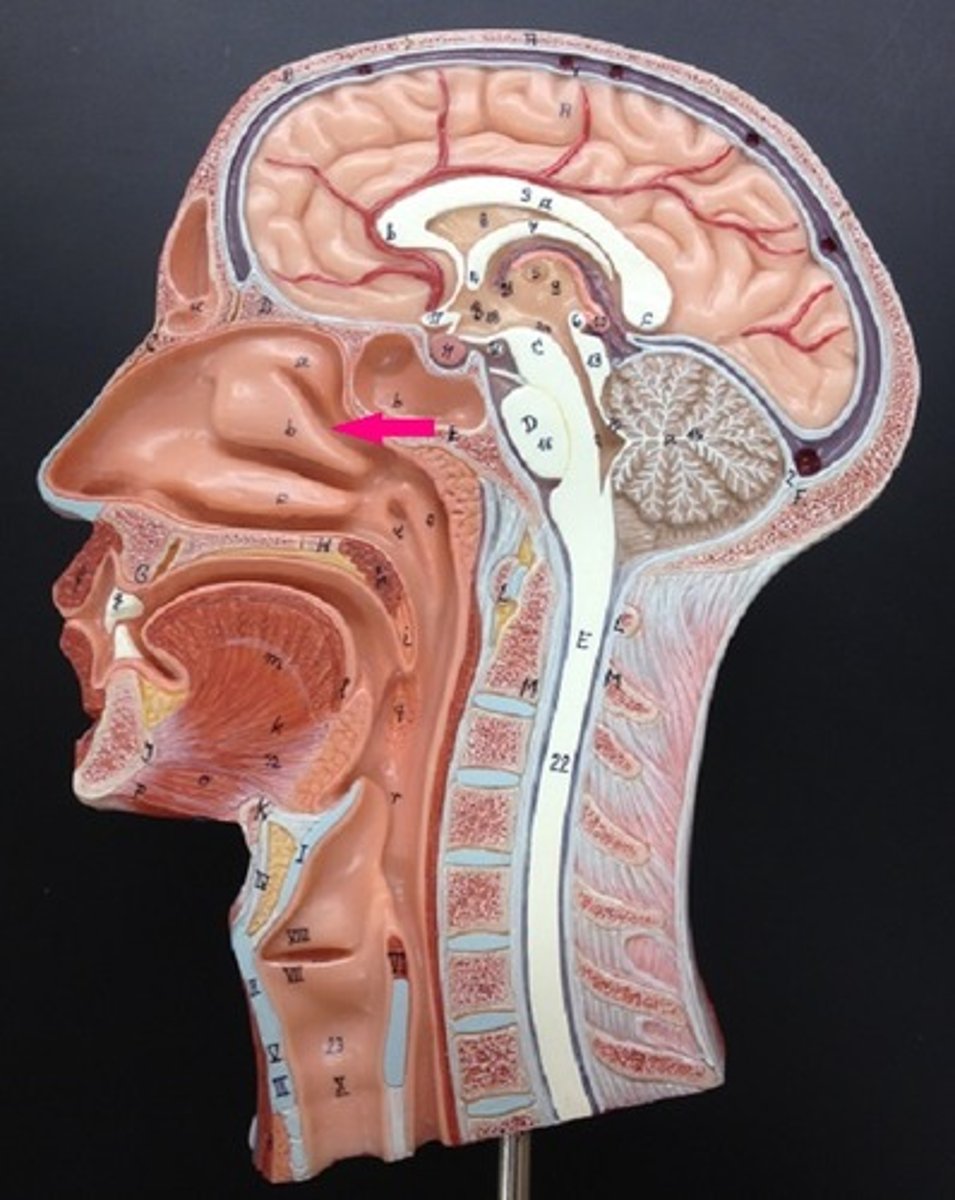
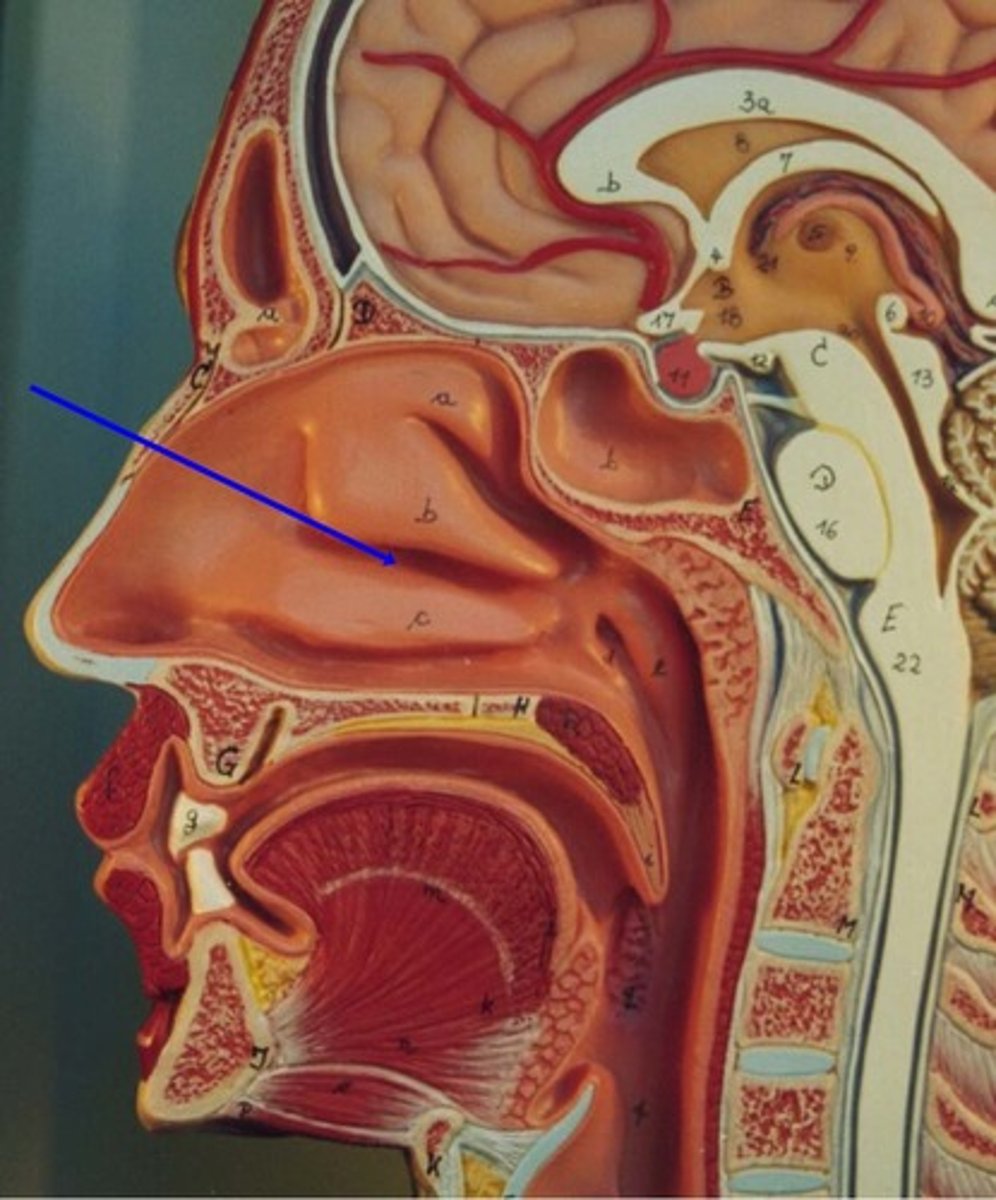
external nose
region of the nose that is easily visible to others
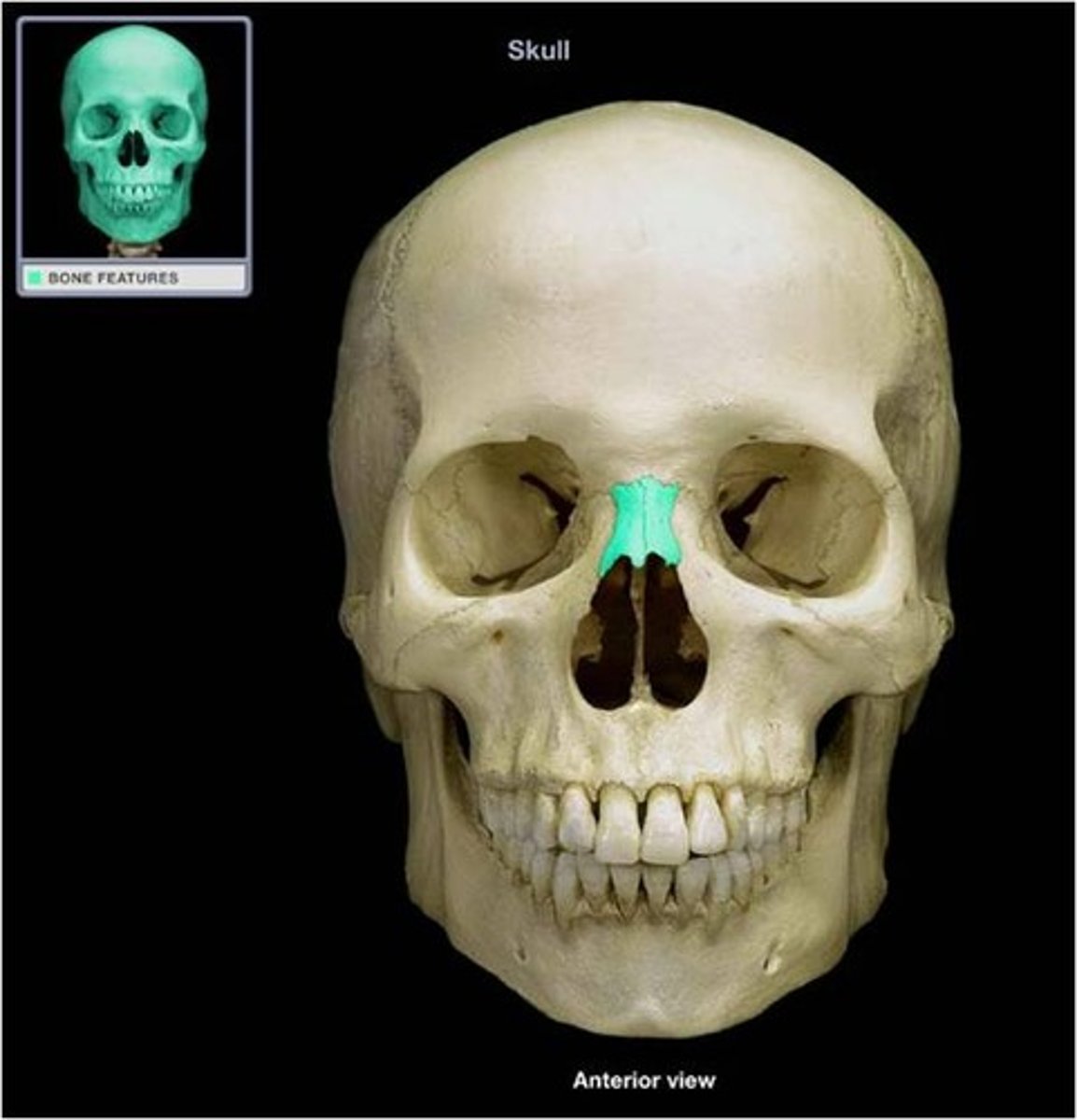
nasal bone
bone of the skull that lies under the root and bridge of the nose and is connected to the frontal and maxillary bones
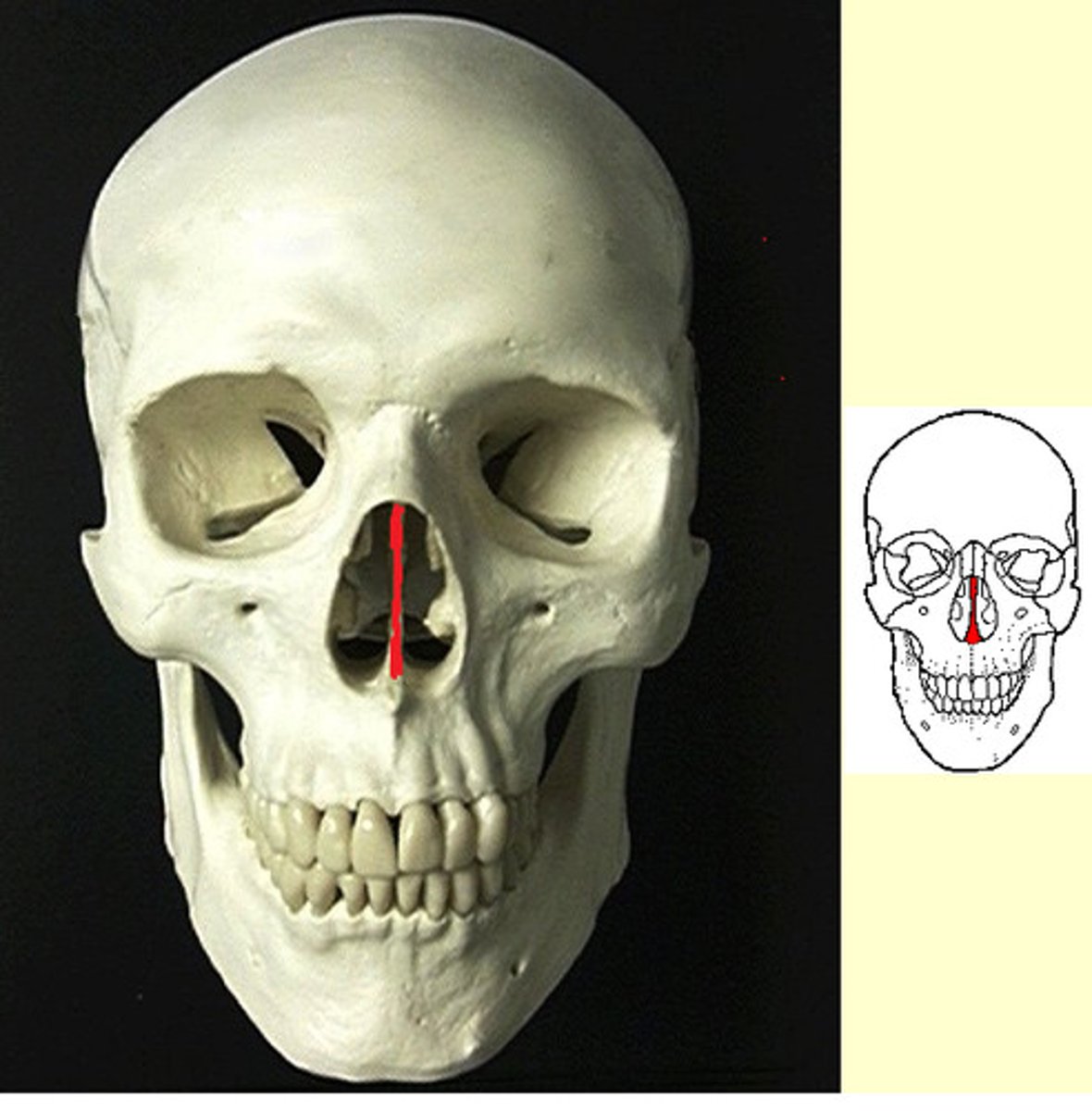
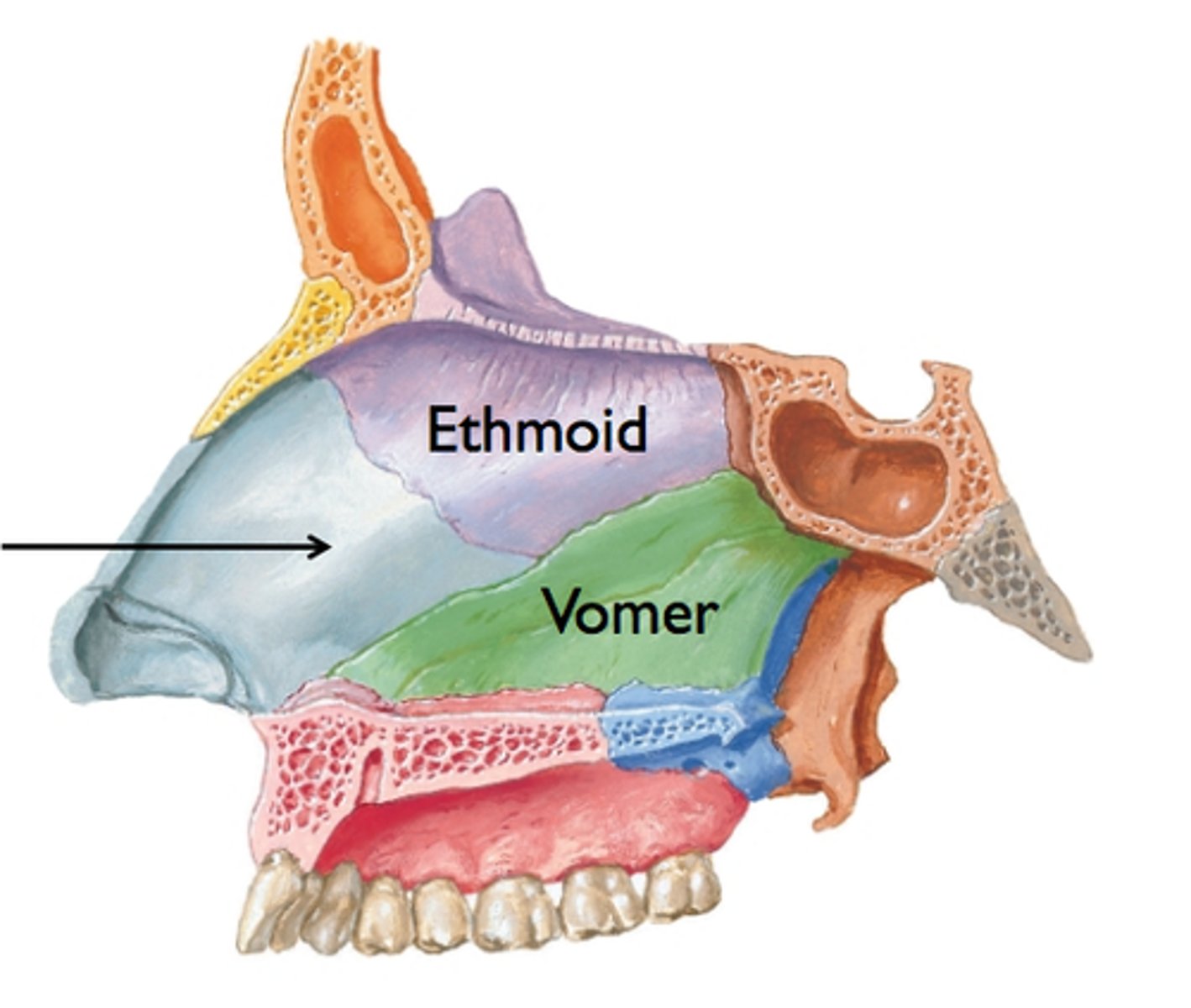
nasal septum
wall composed of bone and cartilage that separates the left and right nasal cavities
osseous nasal septum
the posterior bony nasal septum, consisting of ethmoid and vomer bone
septal cartilage
flat cartilage structure that forms the anterior portion of the nasal septum
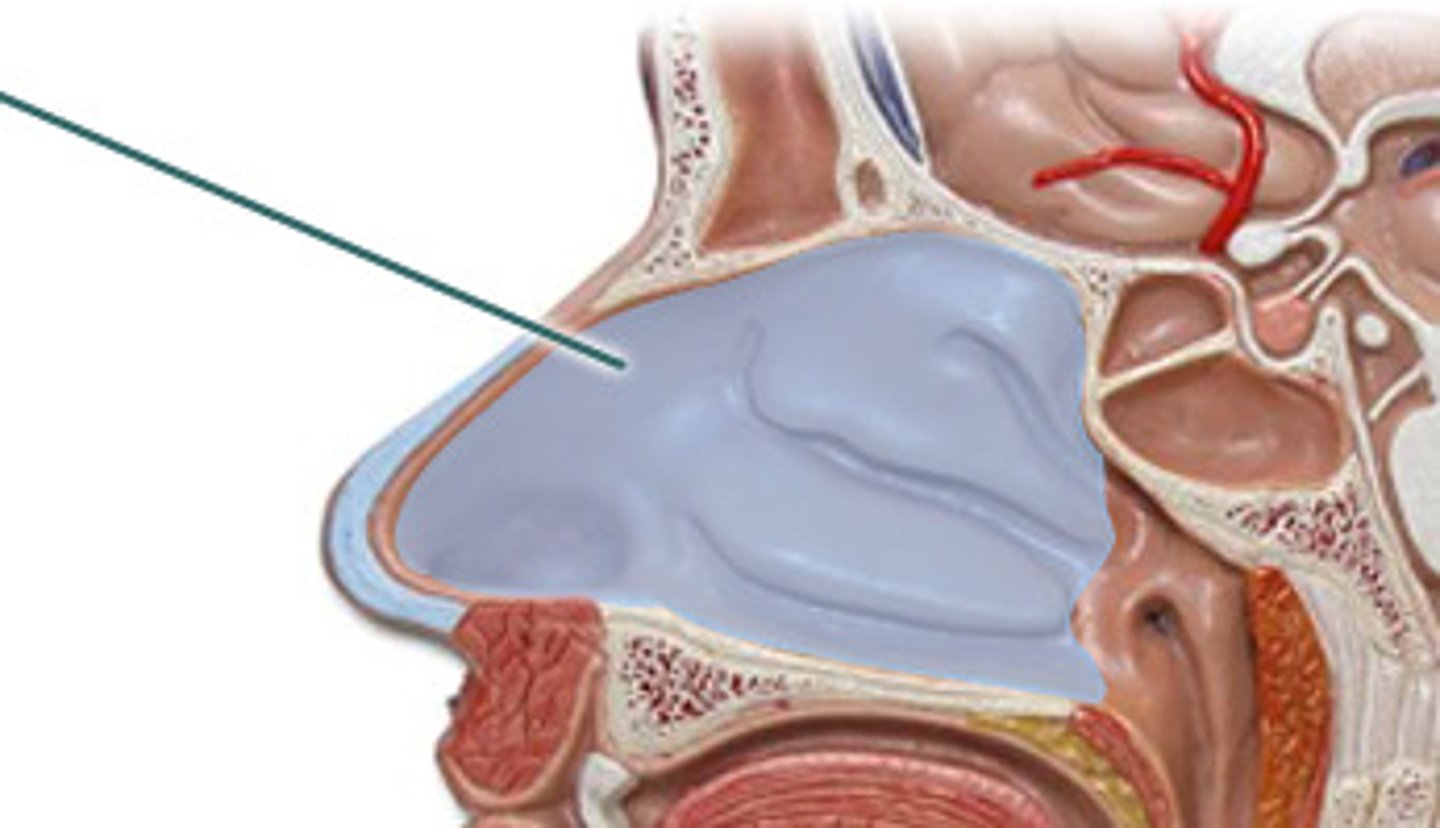
nasal cavity
hollow space behind the nose
nasal conchae
superior, middle, inferior bony projections to increase the surface area of the nasal cavity and create the turbulence of inhaled air
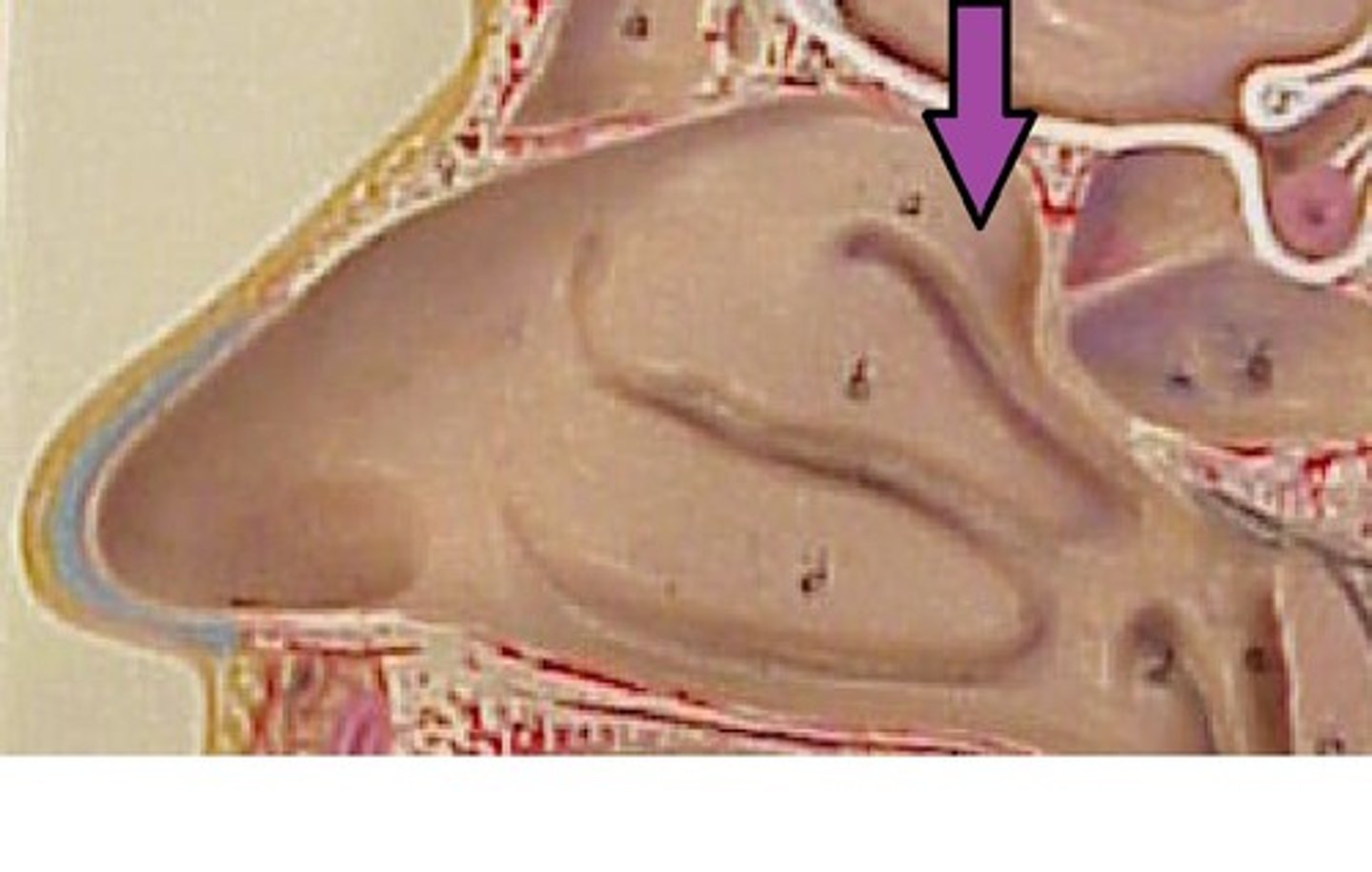
superior nasal conchae
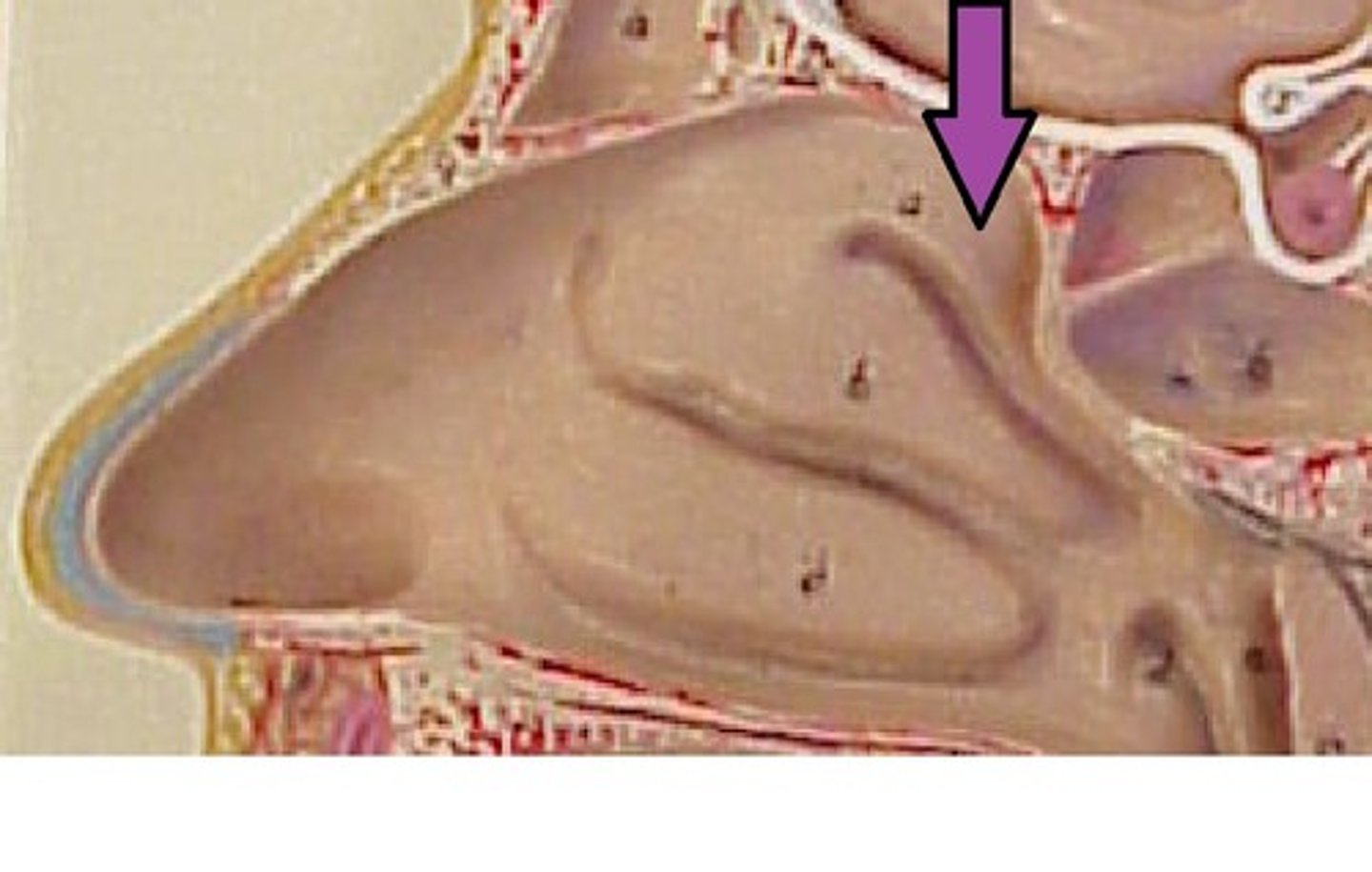
middle nasal conchae
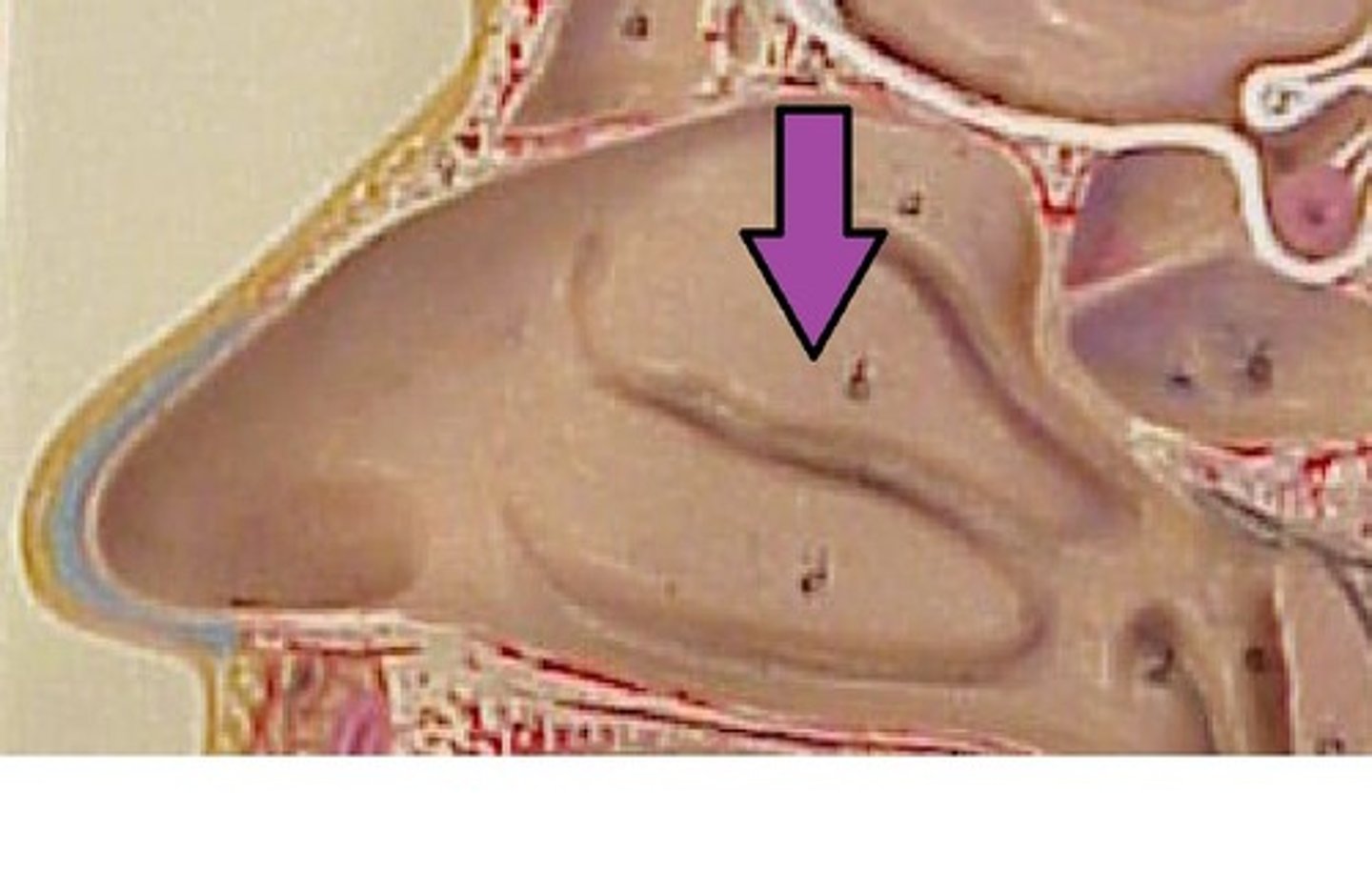
inferior nasal conchae
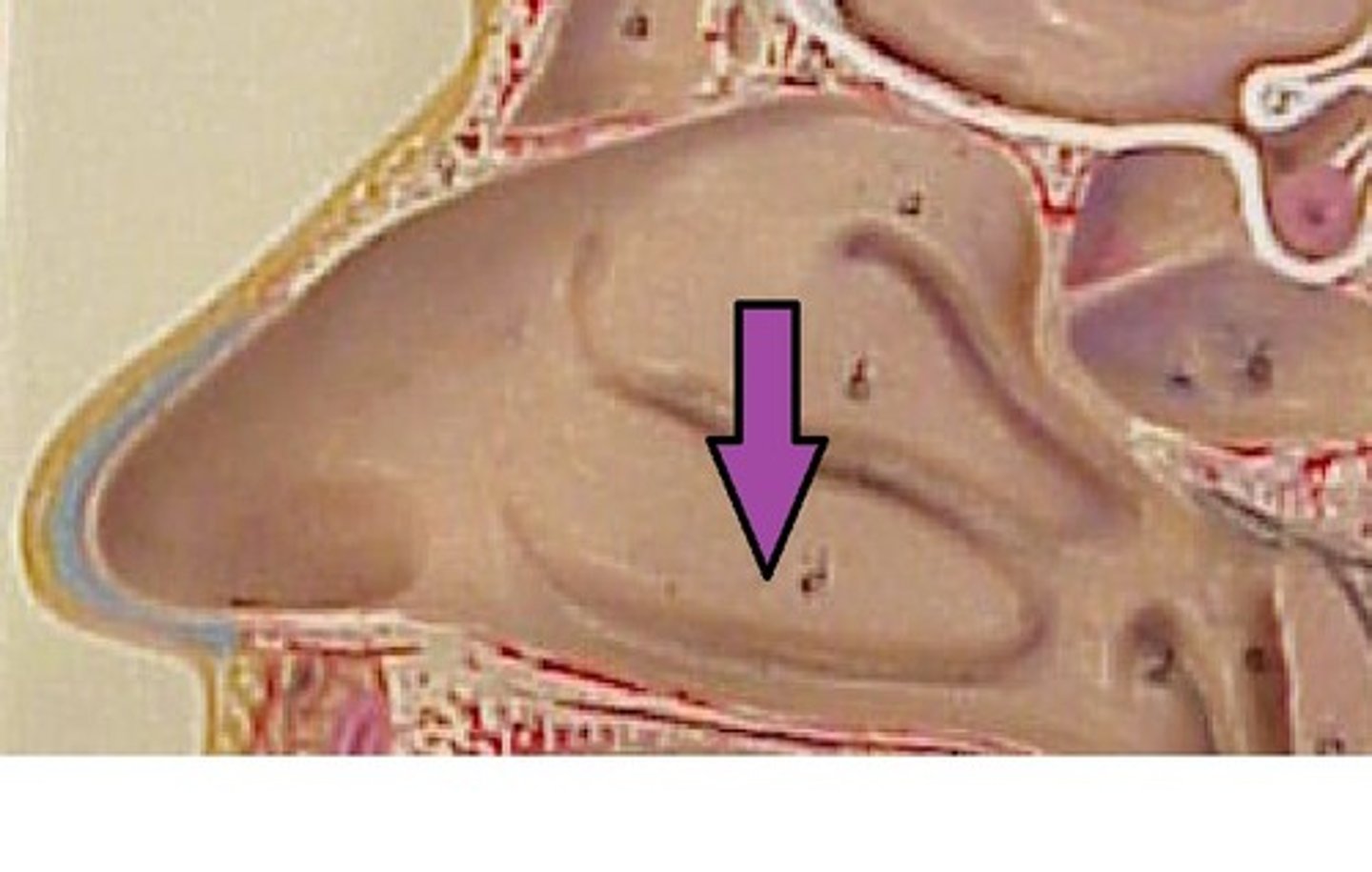
nasal meatus
one of three recesses (superior, middle, and inferior) in the nasal cavity attached to the conchae that increase the surface area of the nasal cavity
superior nasal meatuses
middle nasal meatuses
inferior nasal meatuses
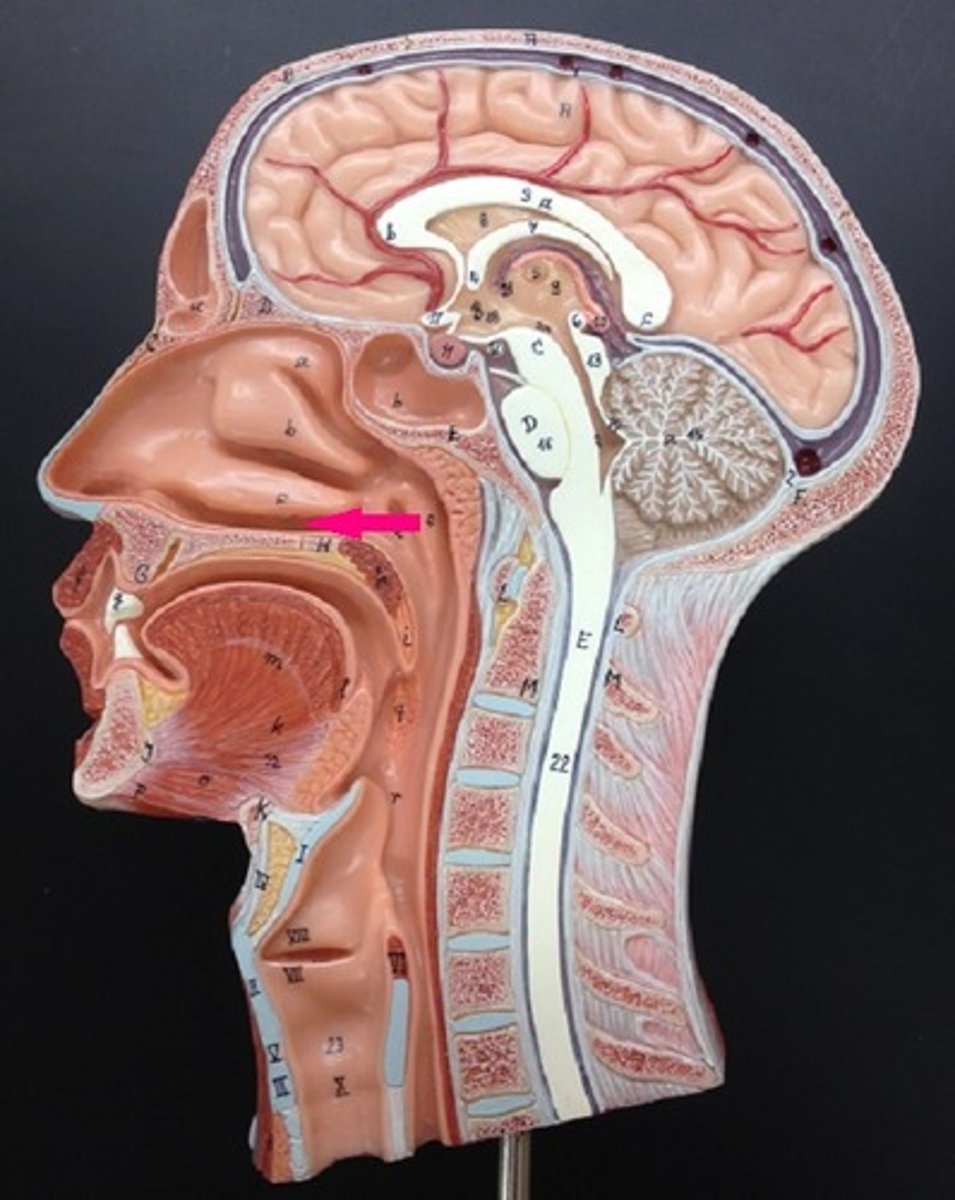
paranasal sinuses
one of the cavities within the skull that is connected to the conchae that serve to warm and humidify incoming air, produce mucus, and lighten the weight of the skull; consists of frontal, maxillary, sphenoidal, and ethmoidal sinuses
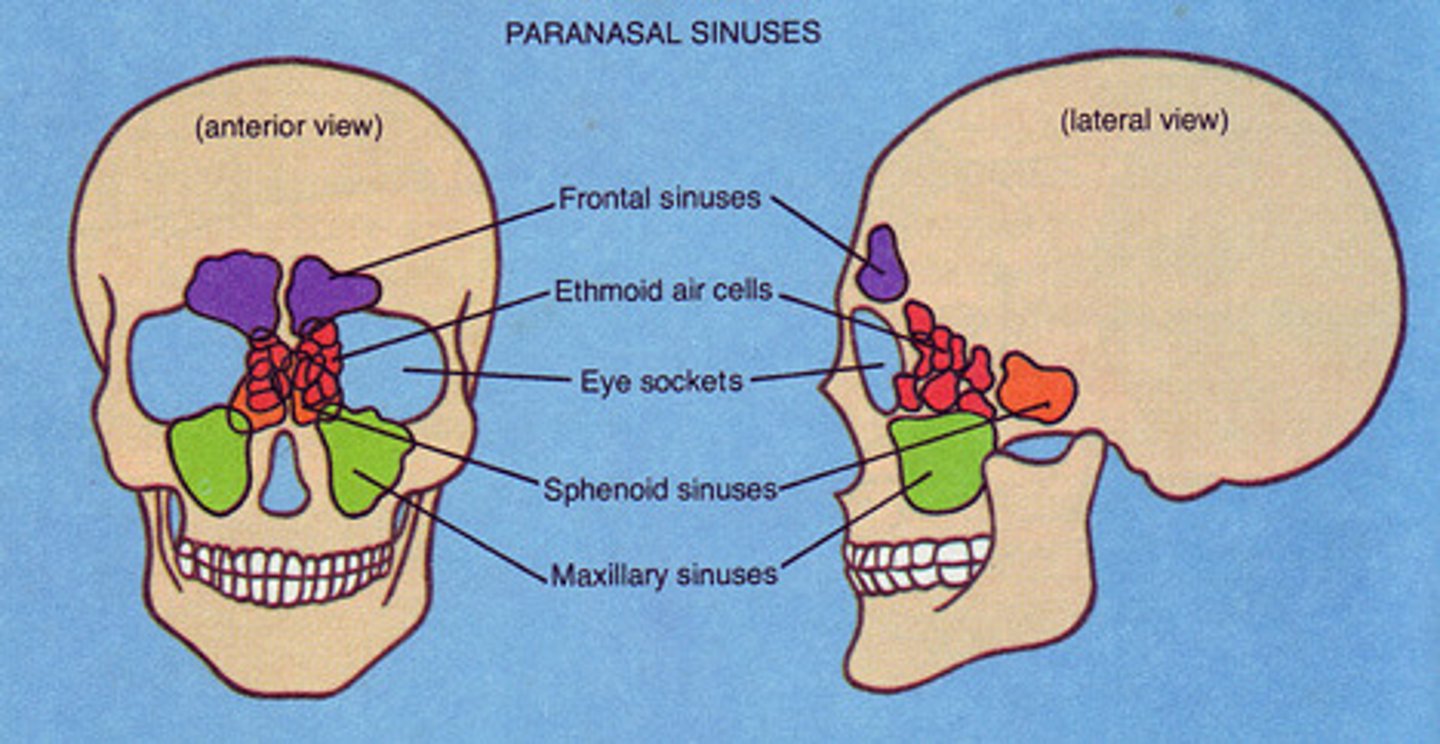
frontal sinuses
located in the frontal bone just above the eyebrows
sphenoid sinuses
located in the sphenoid bone, close to the optic nerves; an infection here can damage vision
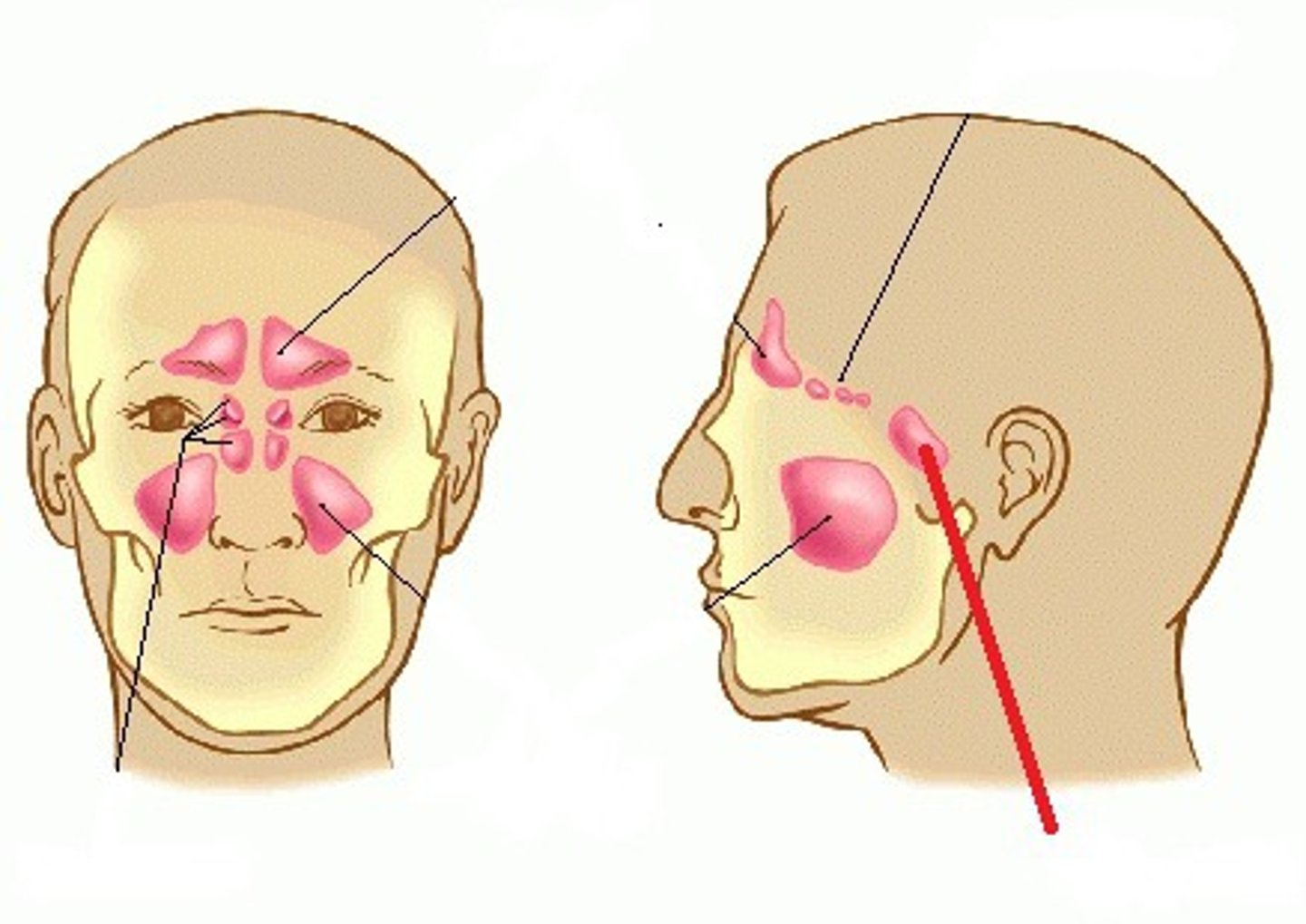
ethmoid sinuses
located in the ethmoid bones, separated from the orbital cavity by only a thin layer of bone
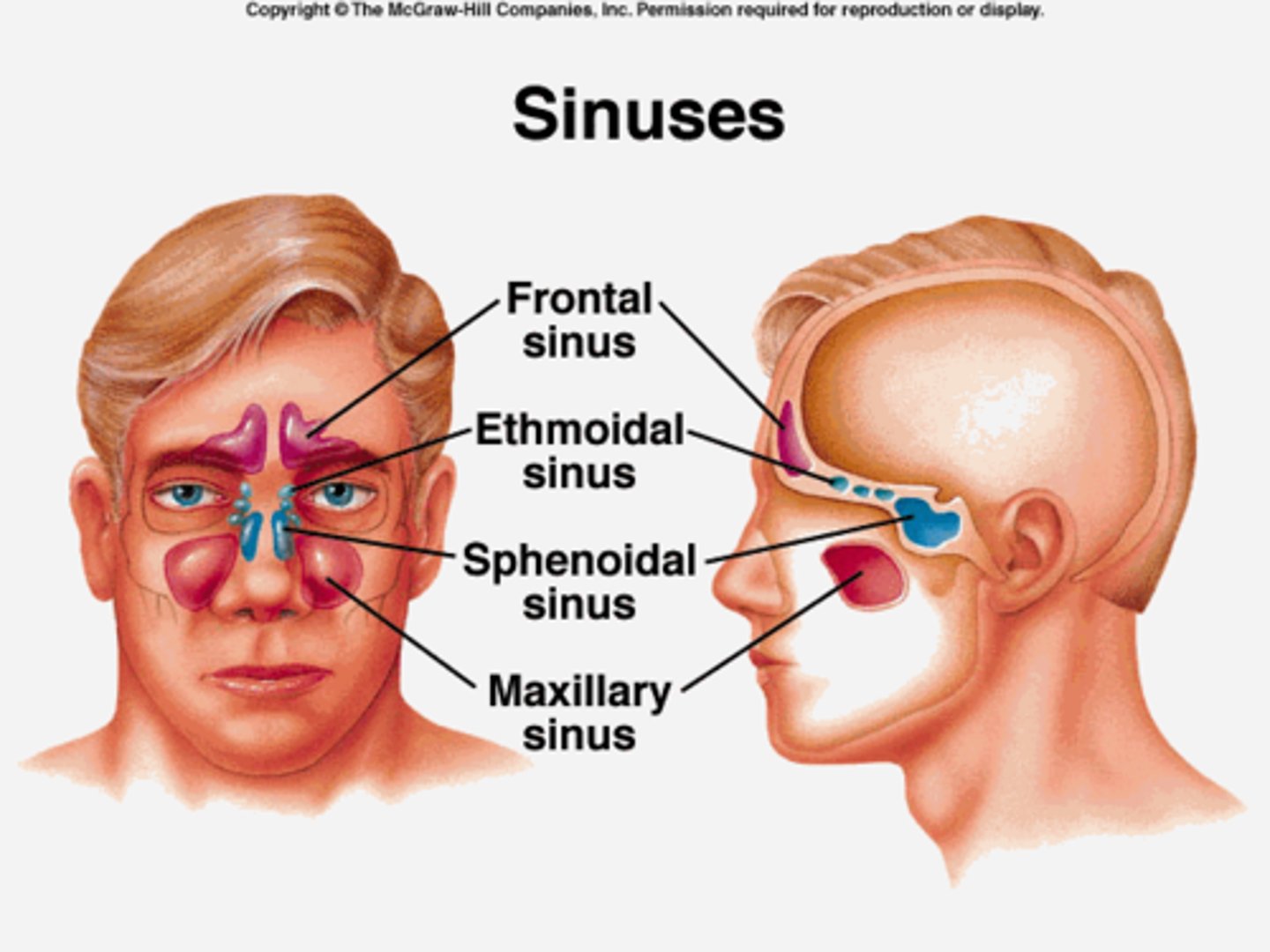
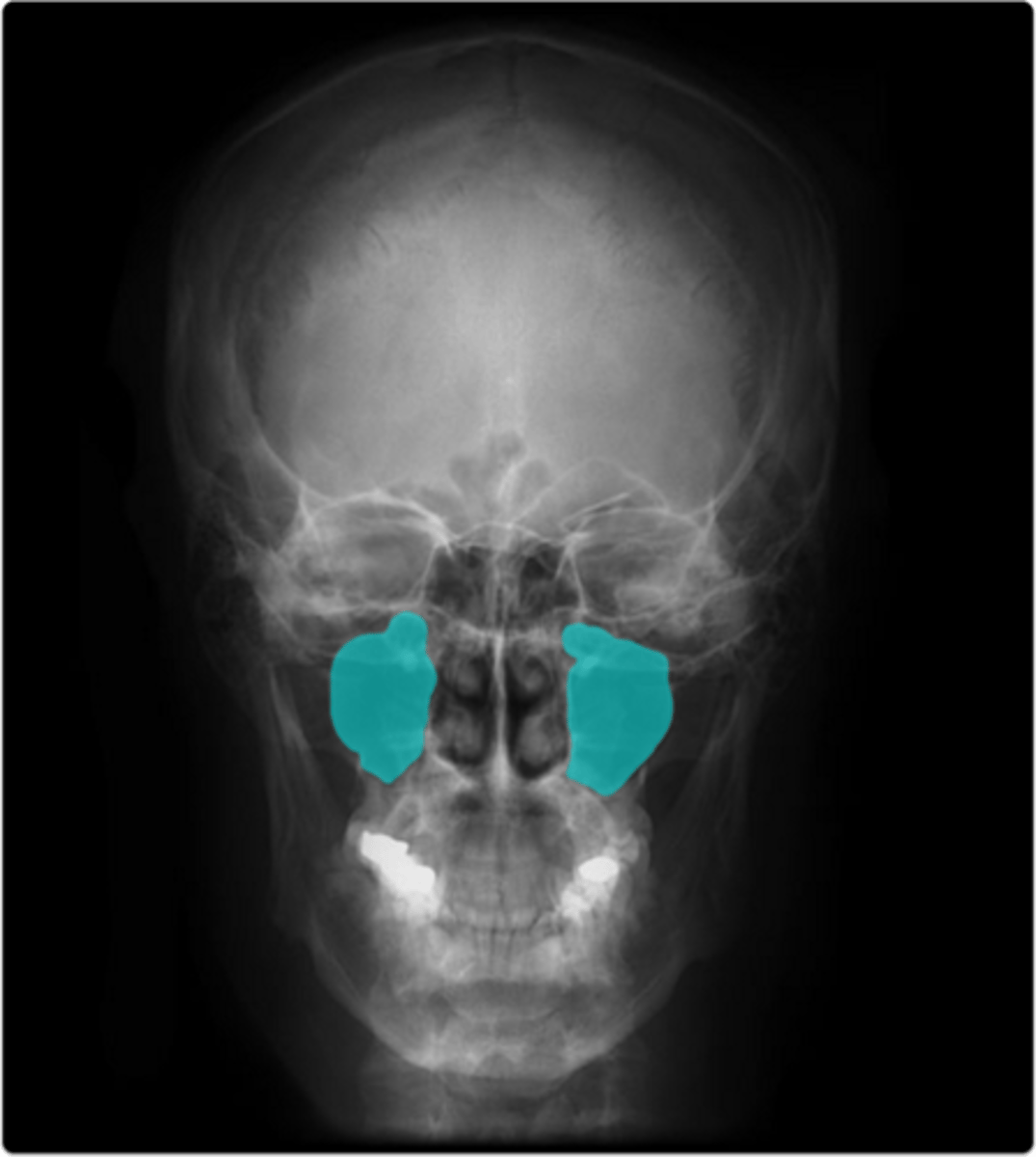
maxillary sinuses
located in the maxillary bones; an infection here can cause pain in the posterior maxillary teeth
pharynx
region of the conducting zone that forms a tube of skeletal muscle lined with respiratory epithelium; located between the nasal conchae and the esophagus and trachea
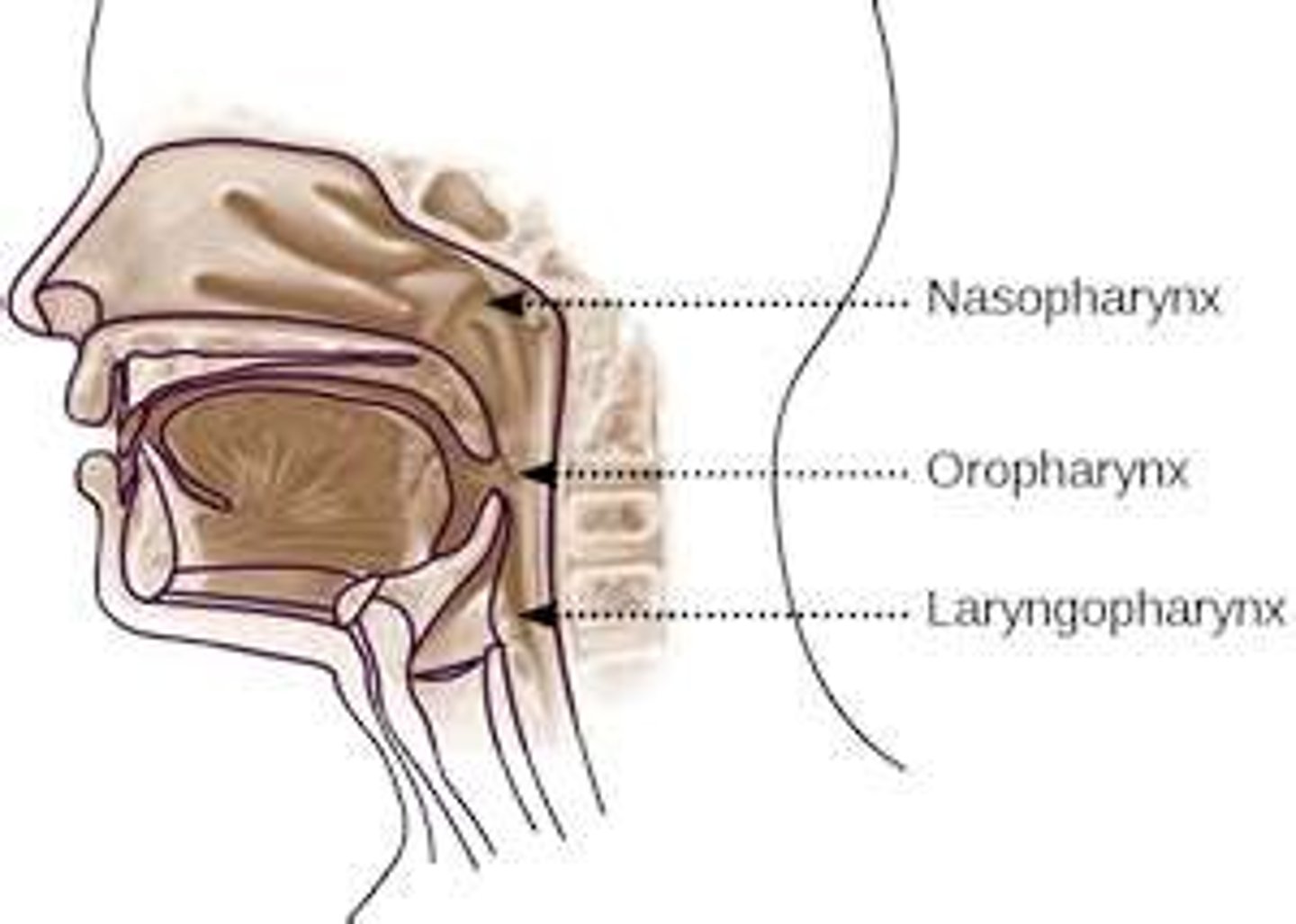
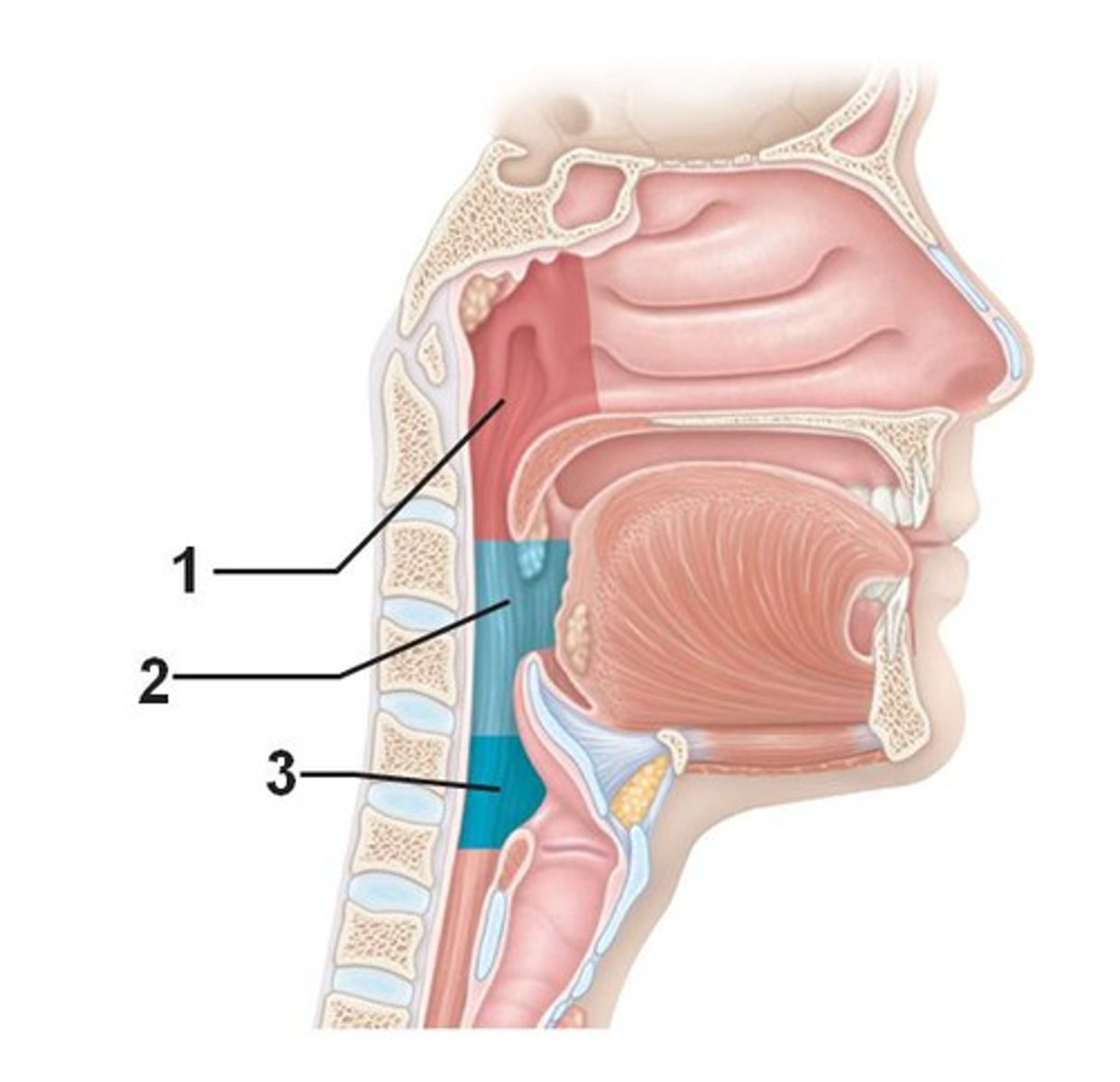
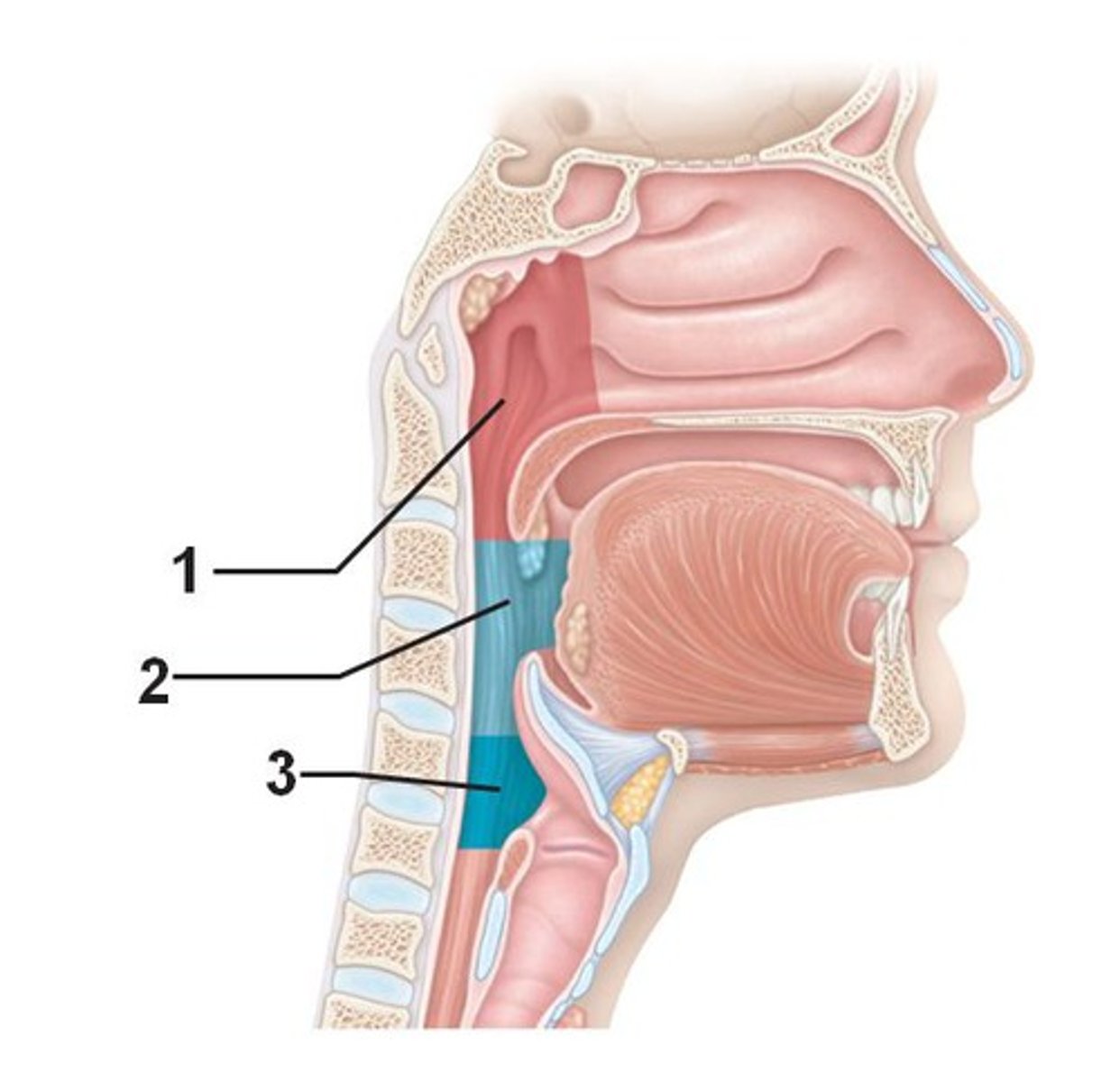
nasopharynx
portion of the pharynx flanked by the conchae and oropharynx that serves as an airway and it's the openings to the paired auditory tubes(1)
hard palate
anterior portion, supported by bone
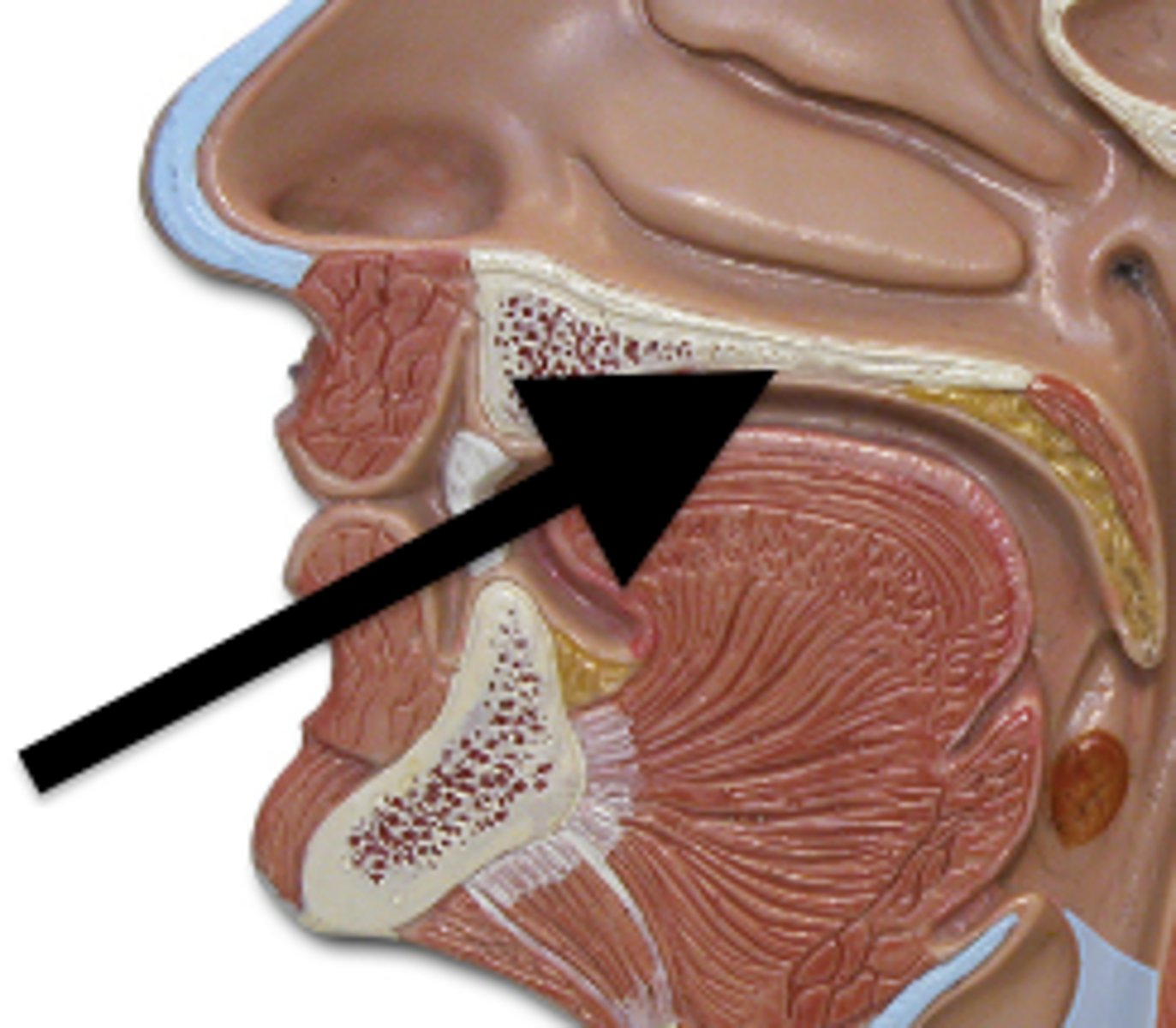
soft palate
posterior portion, not supported by bone
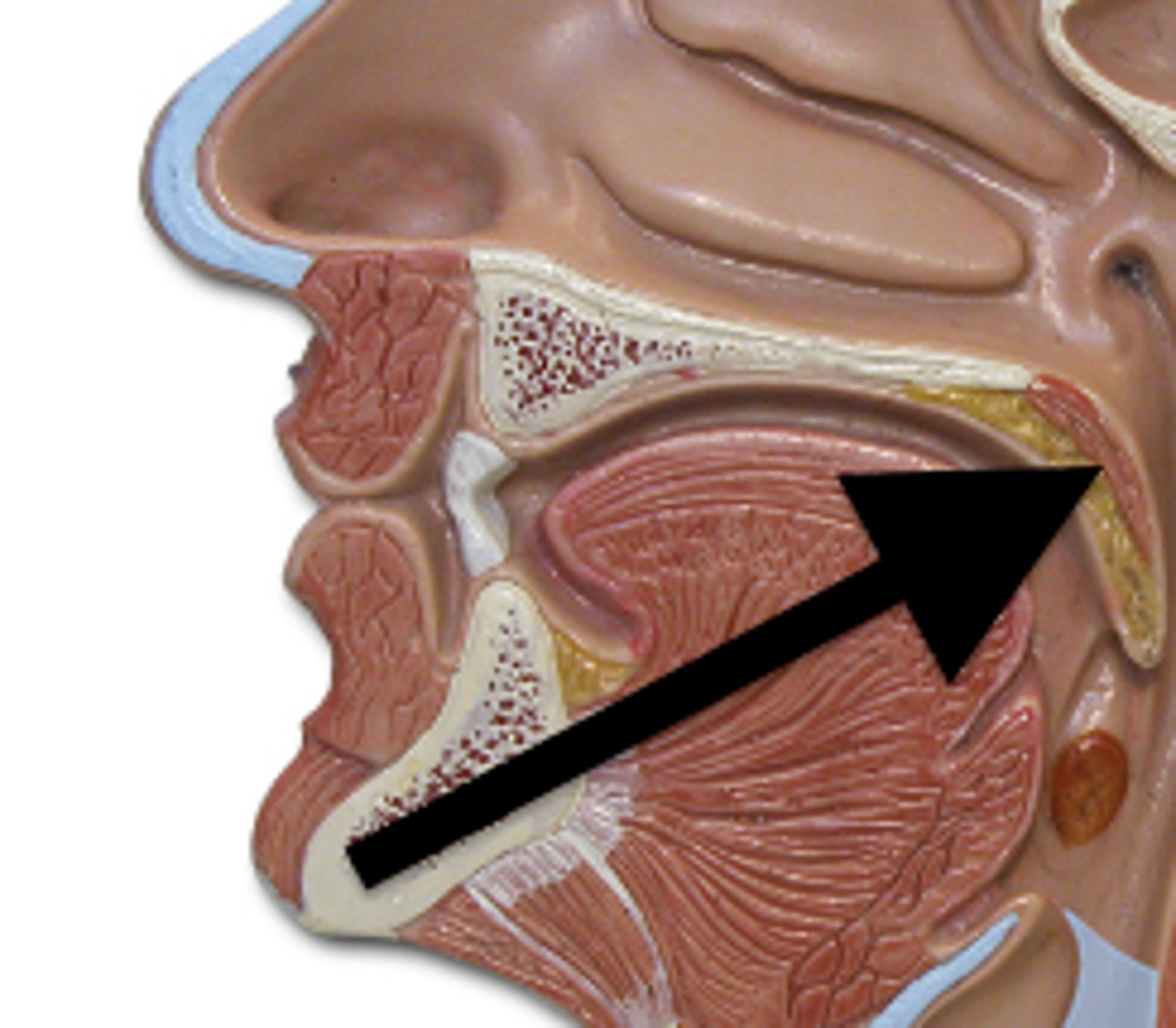
uvula
soft tissue hanging from the middle of the soft palate
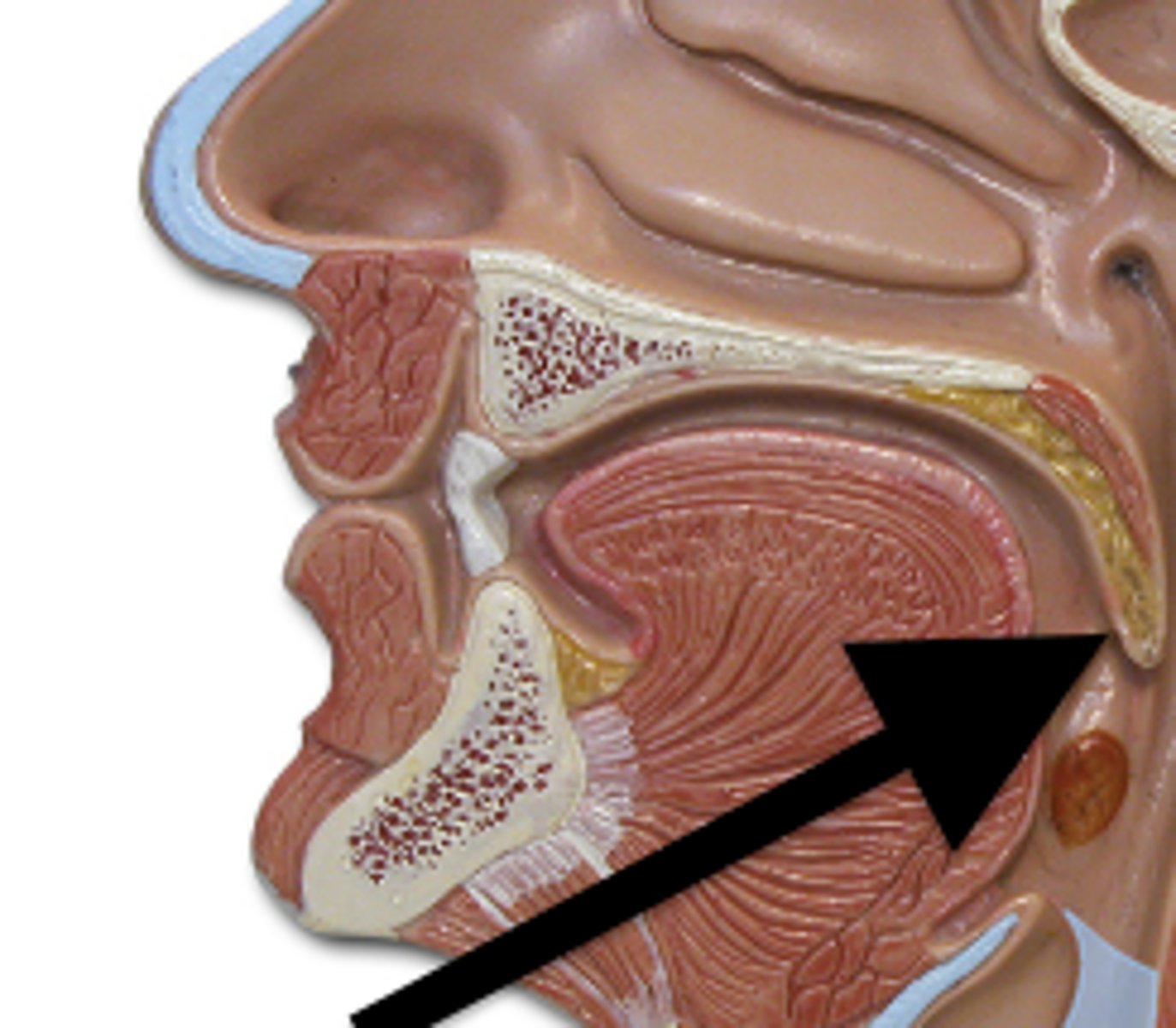
oropharynx
portion of the pharynx flanked by the nasopharynx, oral cavity, and laryngopharynx that is a passageway for both air and food (2)
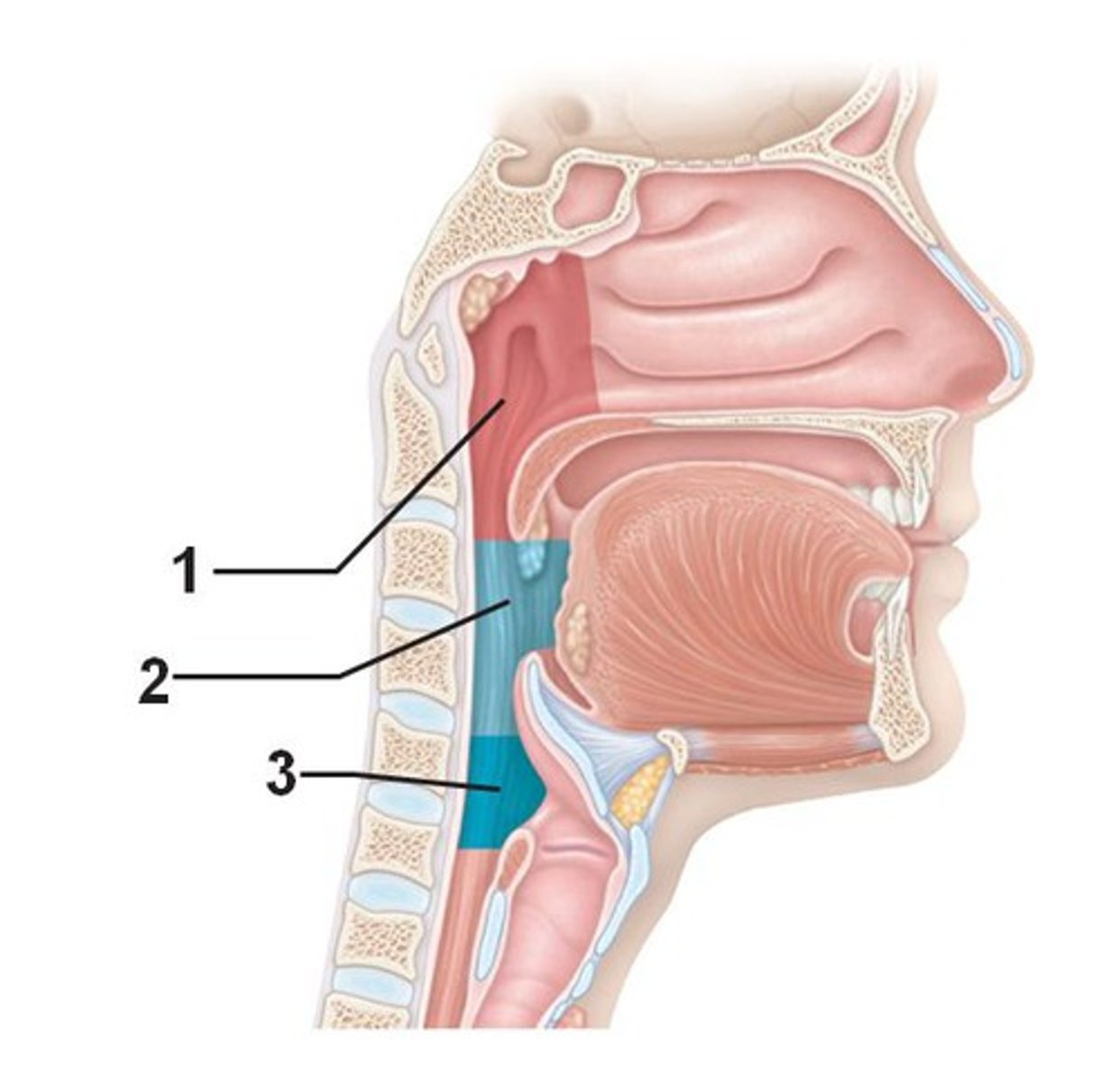
laryngopharynx
portion of the pharynx bordered by the oropharynx superiorly and esophagus and trachea inferiorly; serves as a route for both air and food (3)
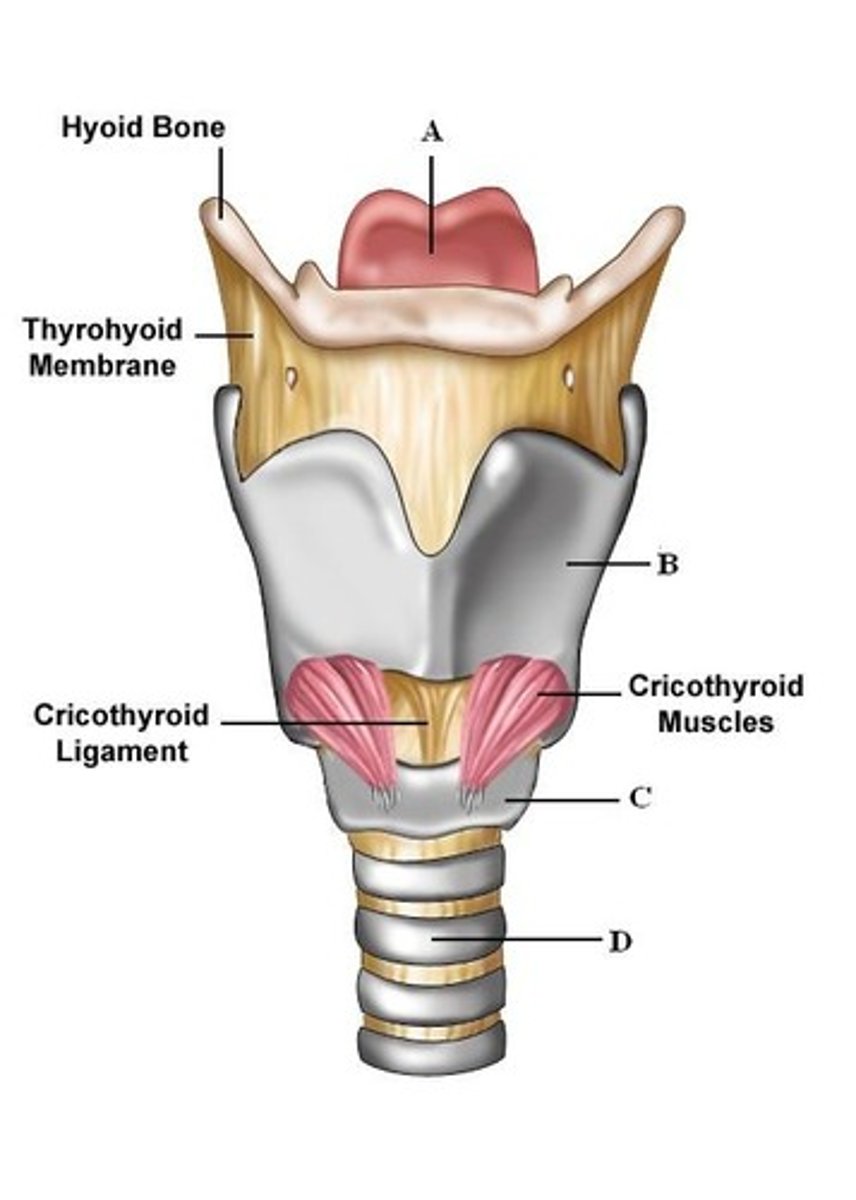
larynx
cartilaginous structure that produces the voice, prevents food and beverages from entering the trachea, and regulates the volume of air that enters and leaves the lungs
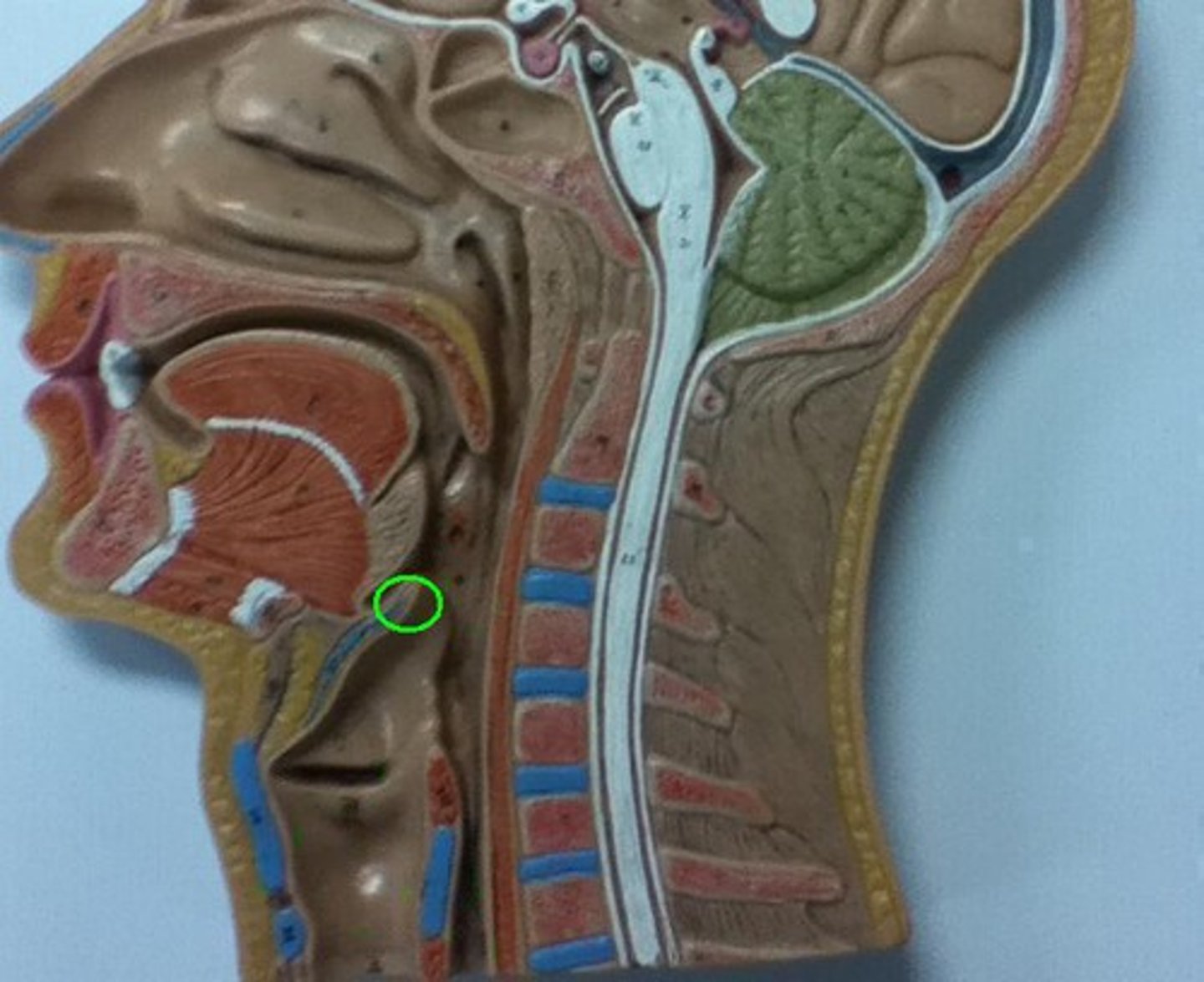
Epiglottis
a flap of cartilage at the root of the tongue, which is depressed during swallowing to cover the opening of the windpipe.
thyroid cartilage
largest piece of cartilage that makes up the larynx and consists of two lamina
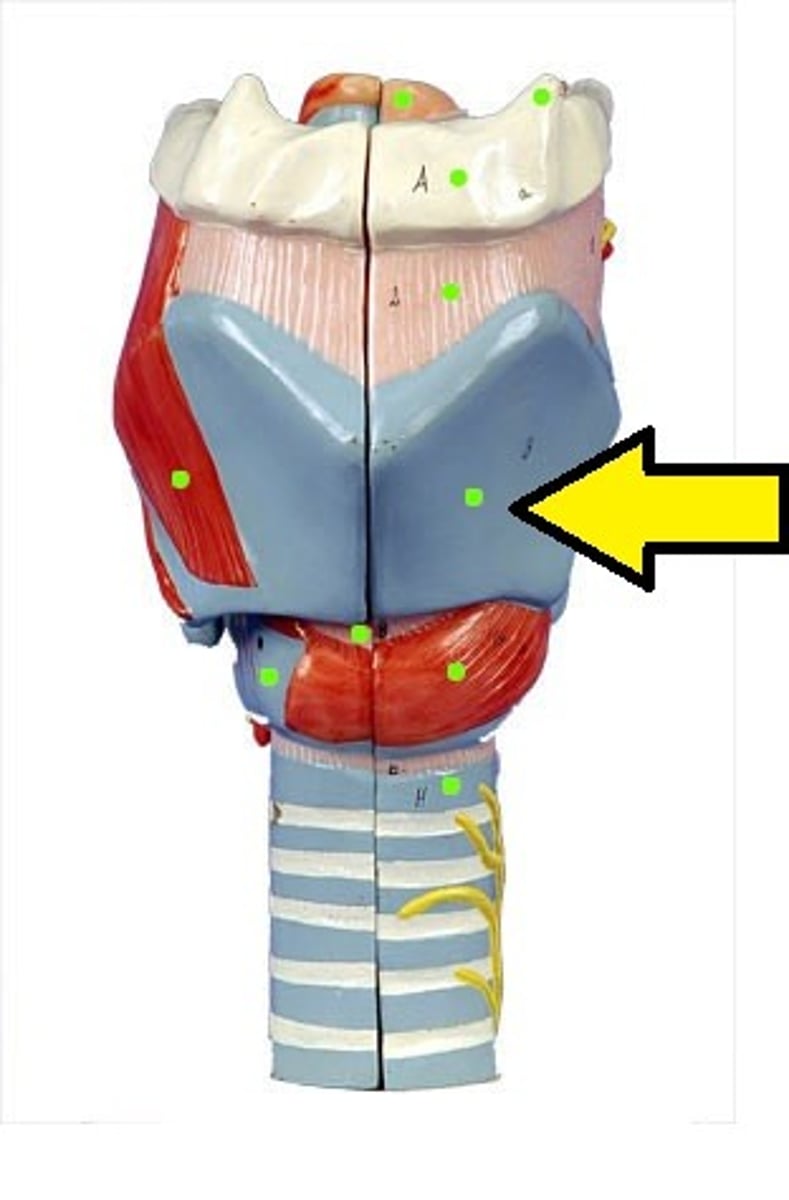
laryngeal prominence
Adam's apple (thyroid cartilage)
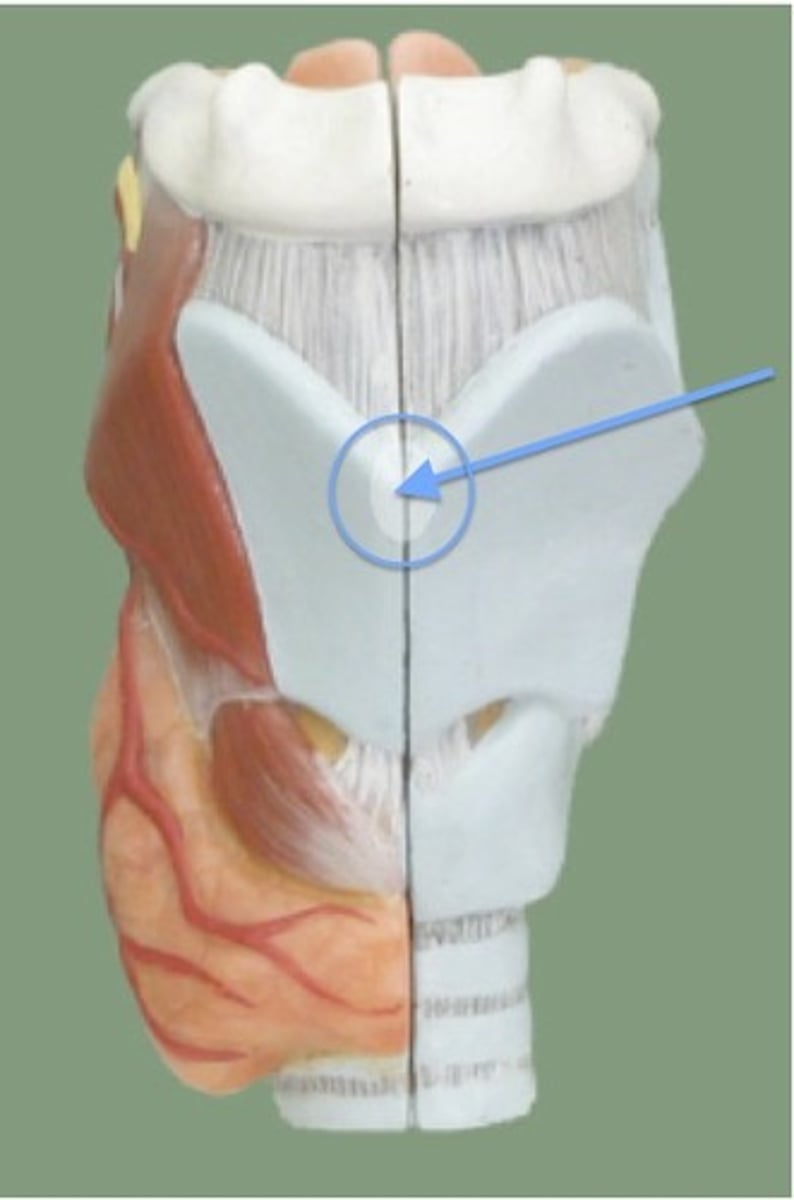
cricoid cartilage
portion of the larynx composed of a ring of cartilage with a wide posterior region and a thinner anterior region; attached to the oesophagus
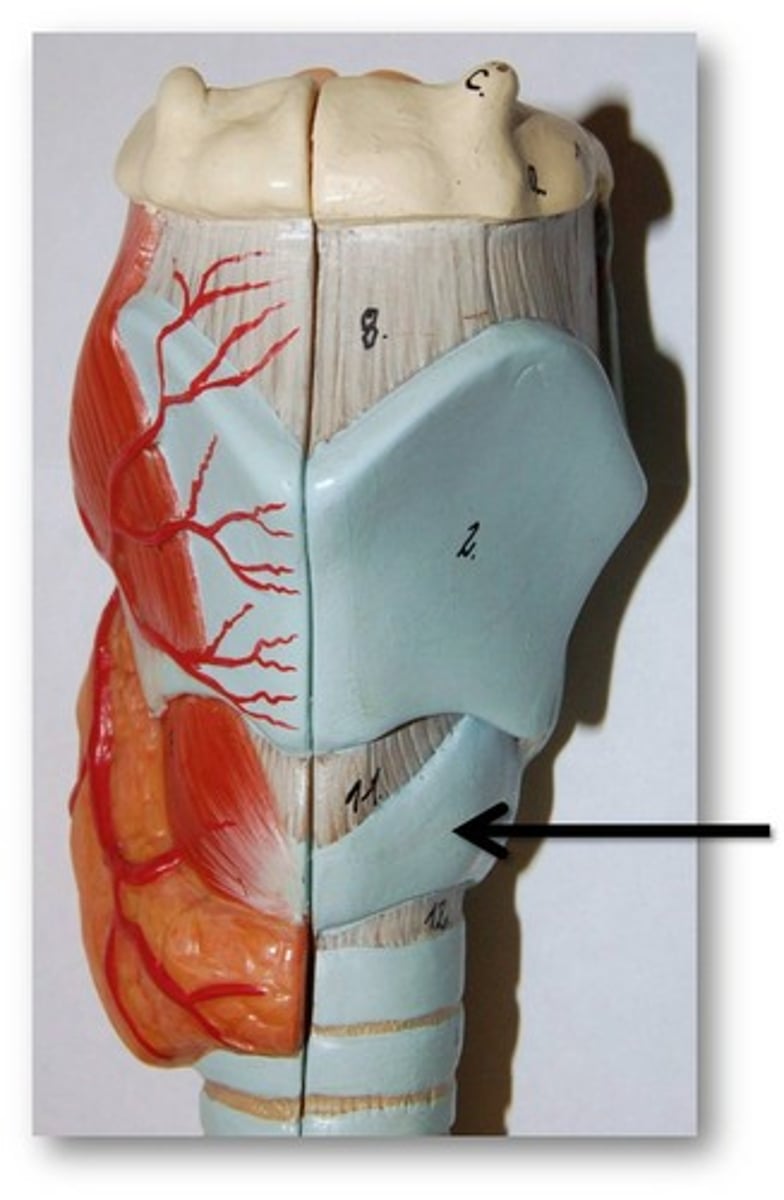
epiglottic cartilage
spoon-shaped supportive plate in epiglottis; most superior one
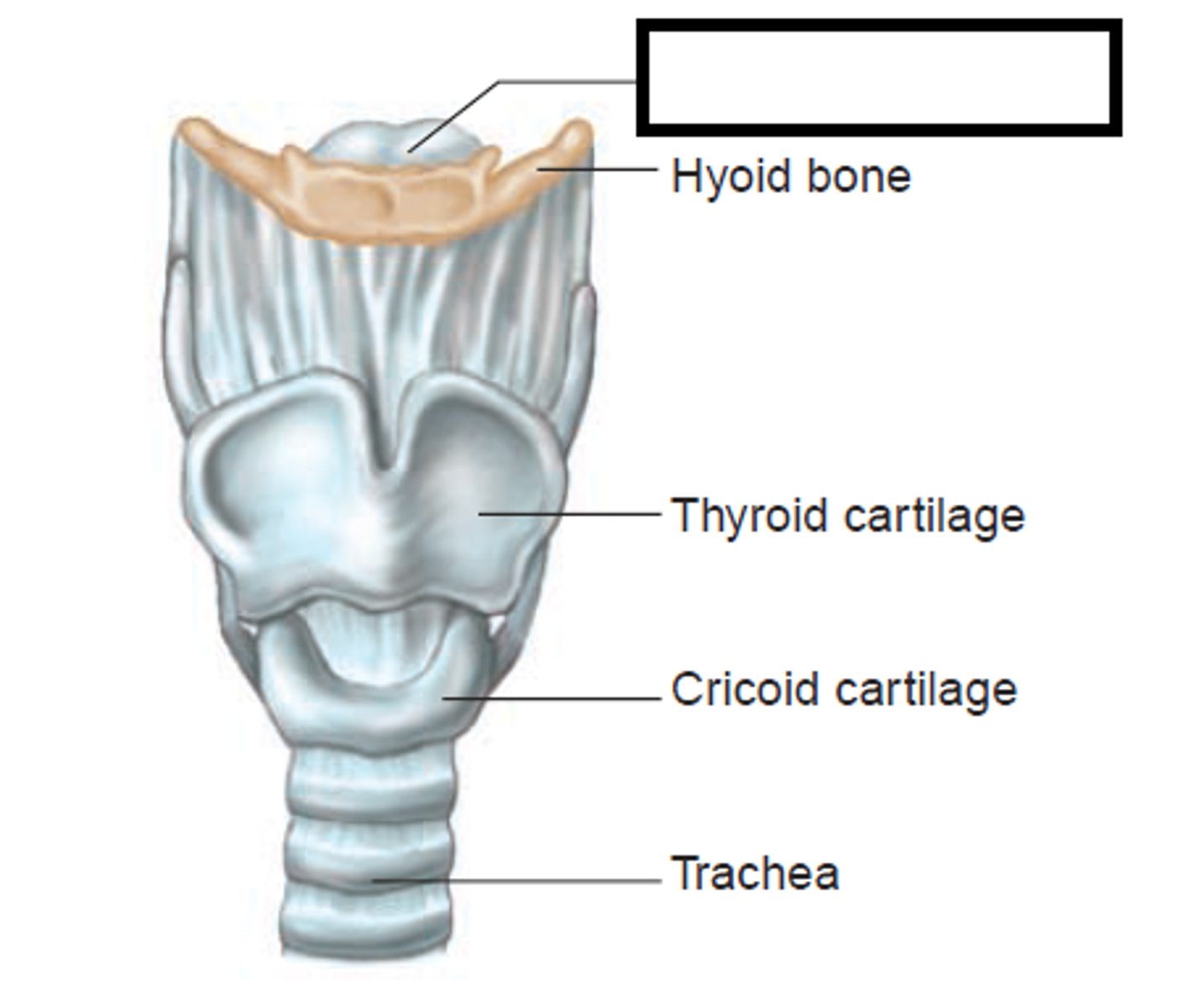
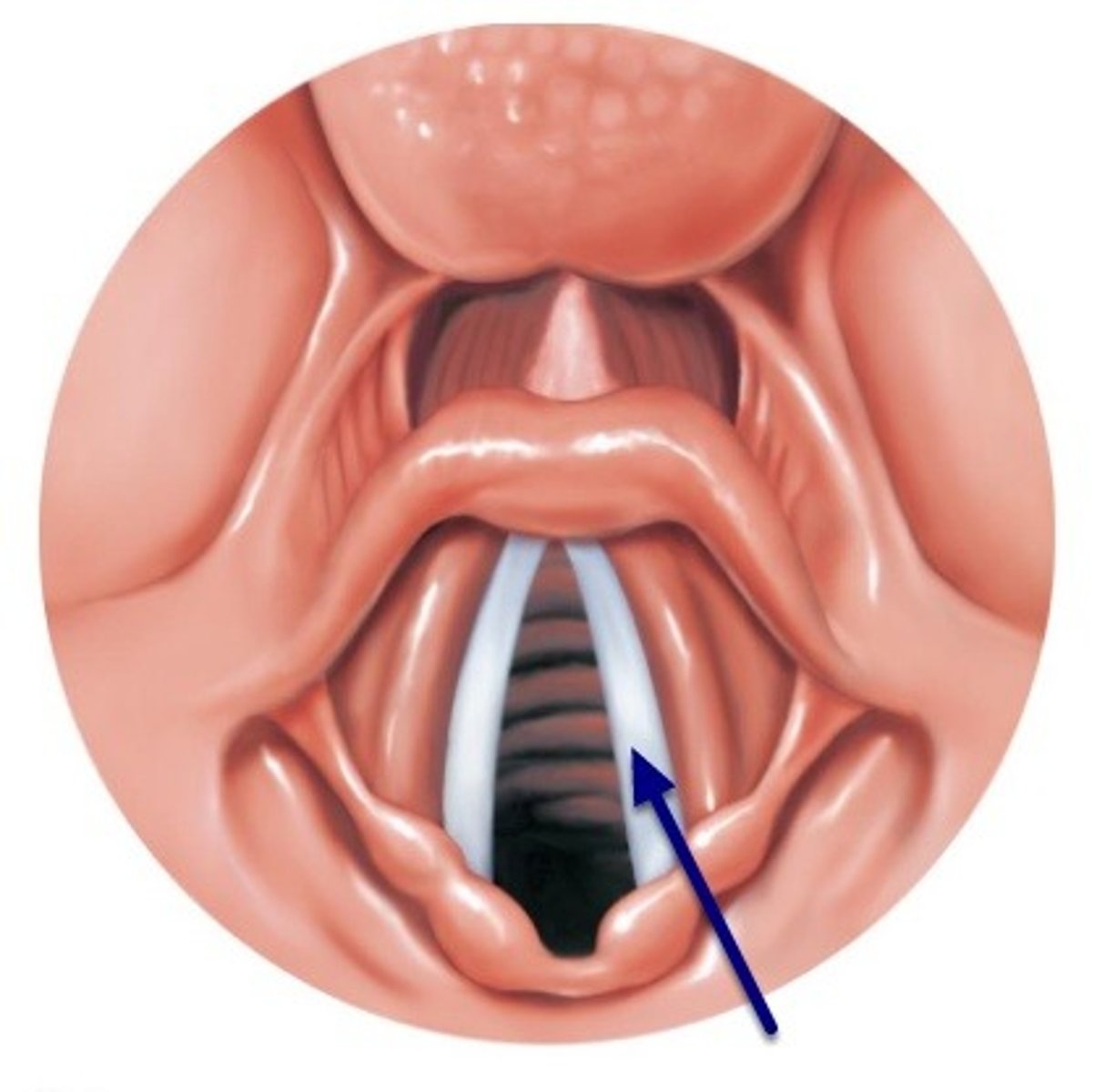
true vocal cord
one of the pair of folded, white membranes that have a free inner edge that oscillates as air passes through to produce sound