Apologia Biology 3rd edition Final Exam Vocab
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Taxonomy
The science dealing with the description, identification, naming, and classifying of organisms.
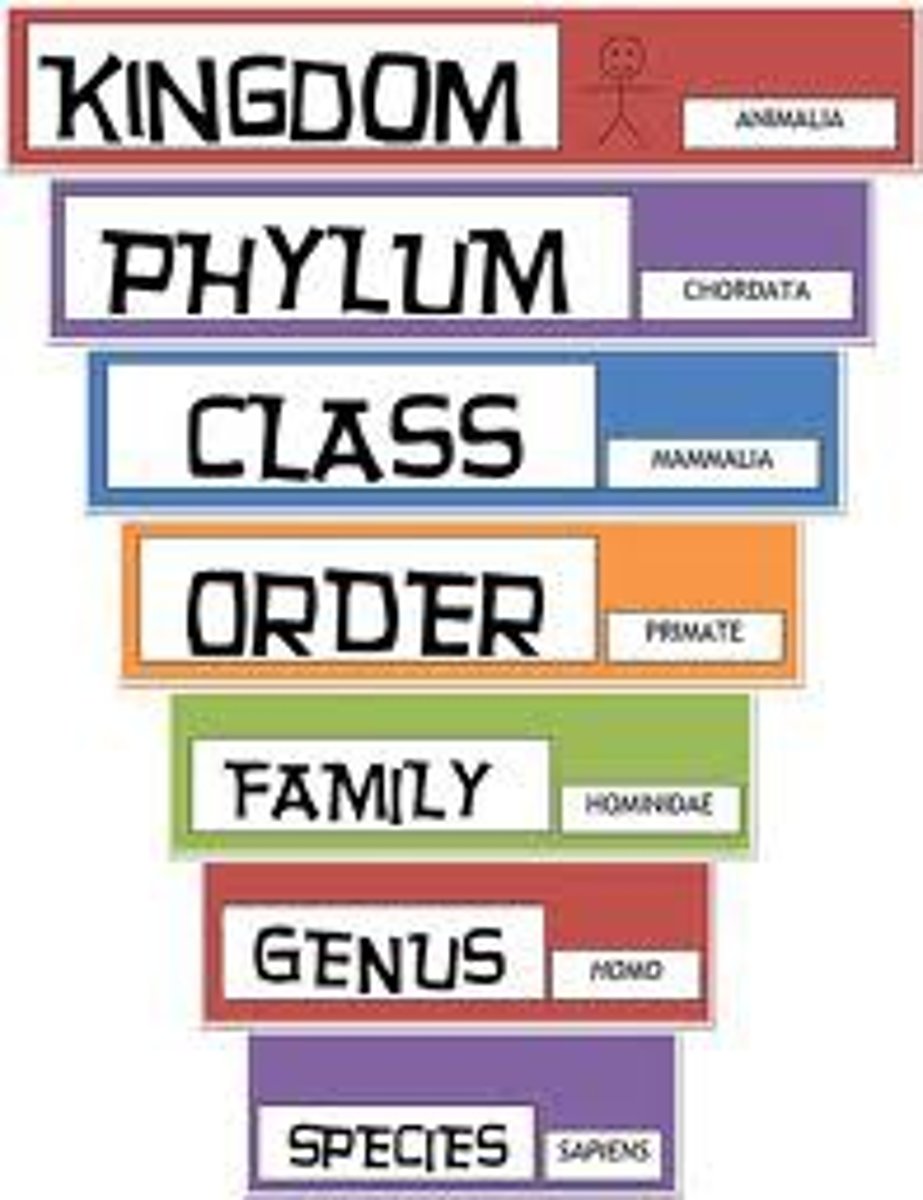
Binomial nomenclature
Naming an organism with its genus and species name

antibiotic
Chemical secreted by a living organism that kills or reduces the reproduction rate of other organisms.
Pathogen
Saprophyte
An organism that causes disease.
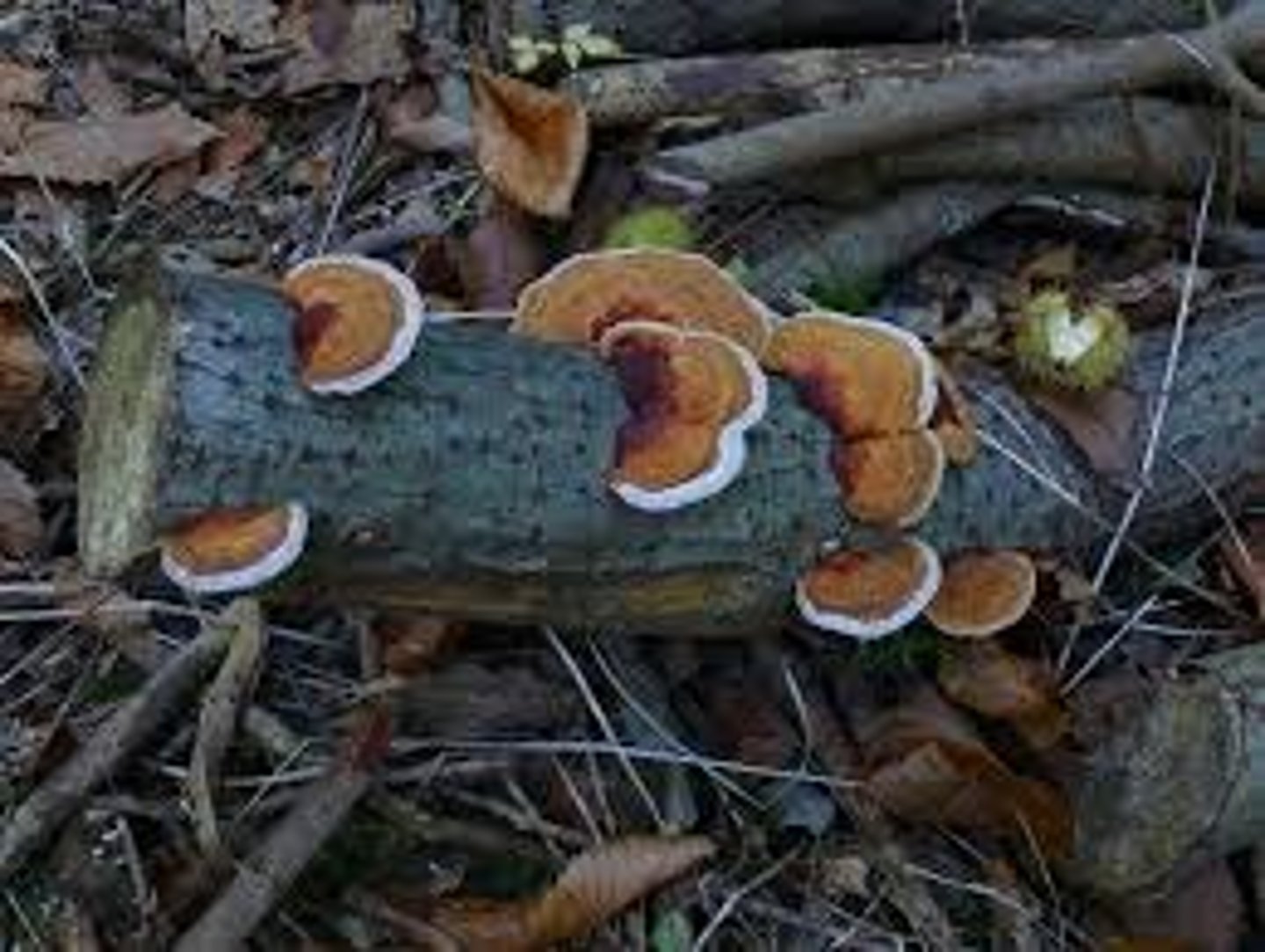

Endospore
A thick internal wall (made of several hard layers), produced by the bacterium, that encloses its DNA and other essential parts.
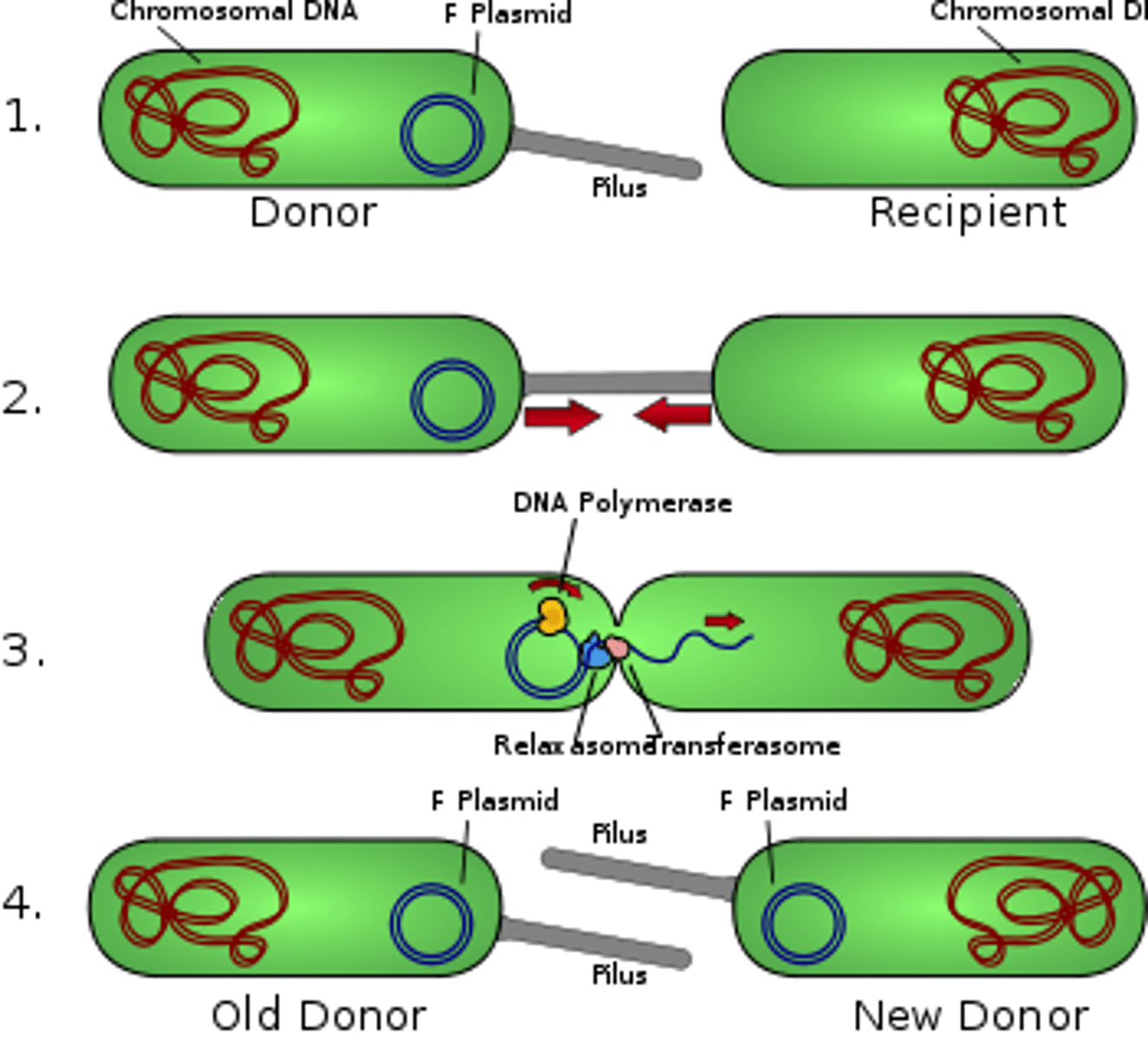
Conjugation
A temporary union of two organisms for the purpose of DNA transfer.
Transformation
The transfer of a DNA segment from a nonfunctional donor cell to that of a functional recipient cell.
Transduction
The process in which infection by a virus results in DNA being transferred from one bacterium to another.
Virus
A non-cellular infectious agent that has two characteristics: (1) It has genetic material (DNA or RNA) inside a protective protein coat. (2) It cannot reproduce on its own; it must infect a living cell.

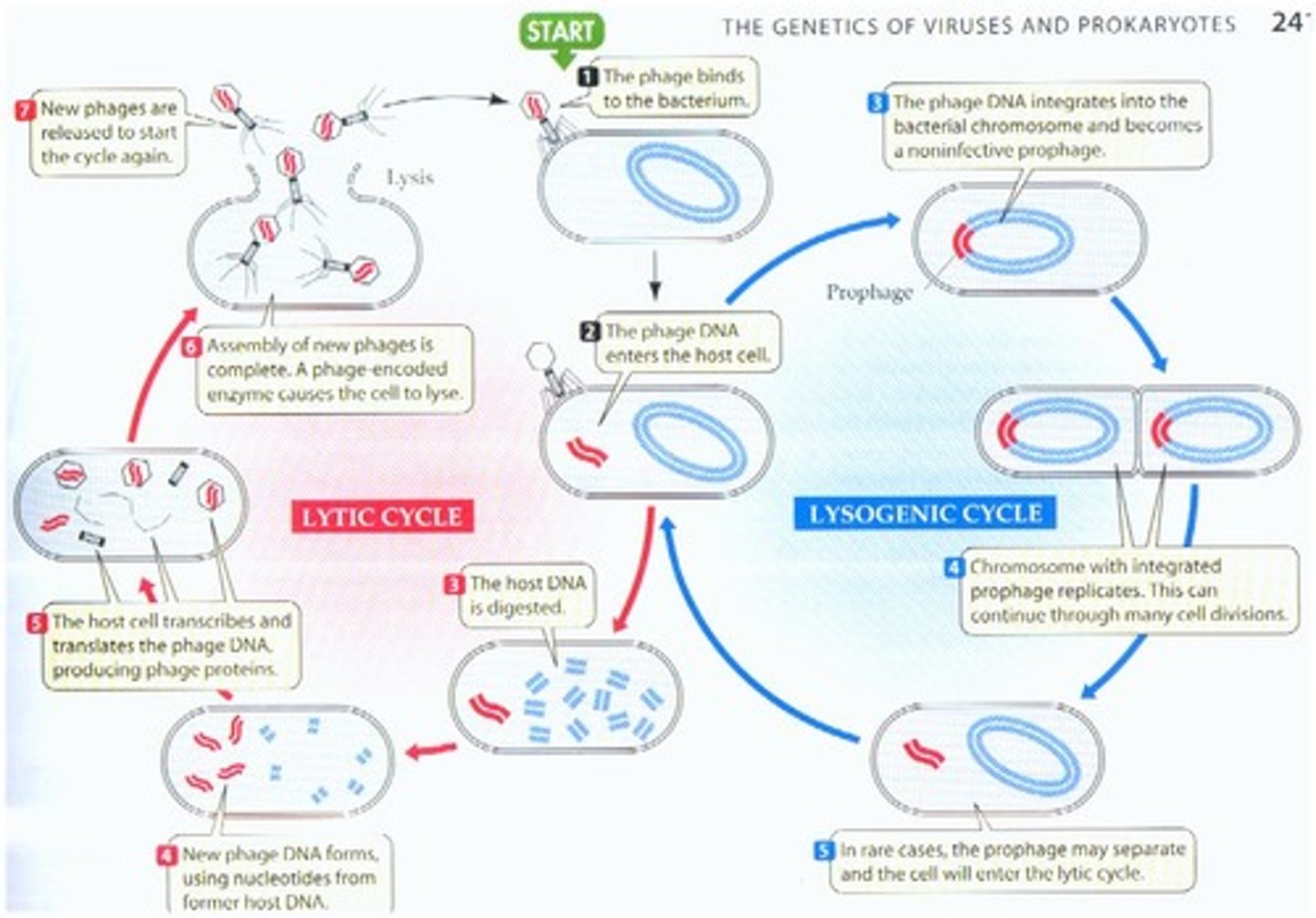
Lytic Cycle
A virus enters a cell, hijacks the host cell's DNA replication system, makes copies of itself, and causes the cell to burst, releasing more viruses.
Lysogenic cycle
A virus enters a cell, embeds its DNA into the DNA of the hose cell, and is replicated along with the host cell's DNA.
Vaccine
A weakened or inactive version of a pathogen that stimulates the body's production of antibodies that aid in destroying the pathogen.

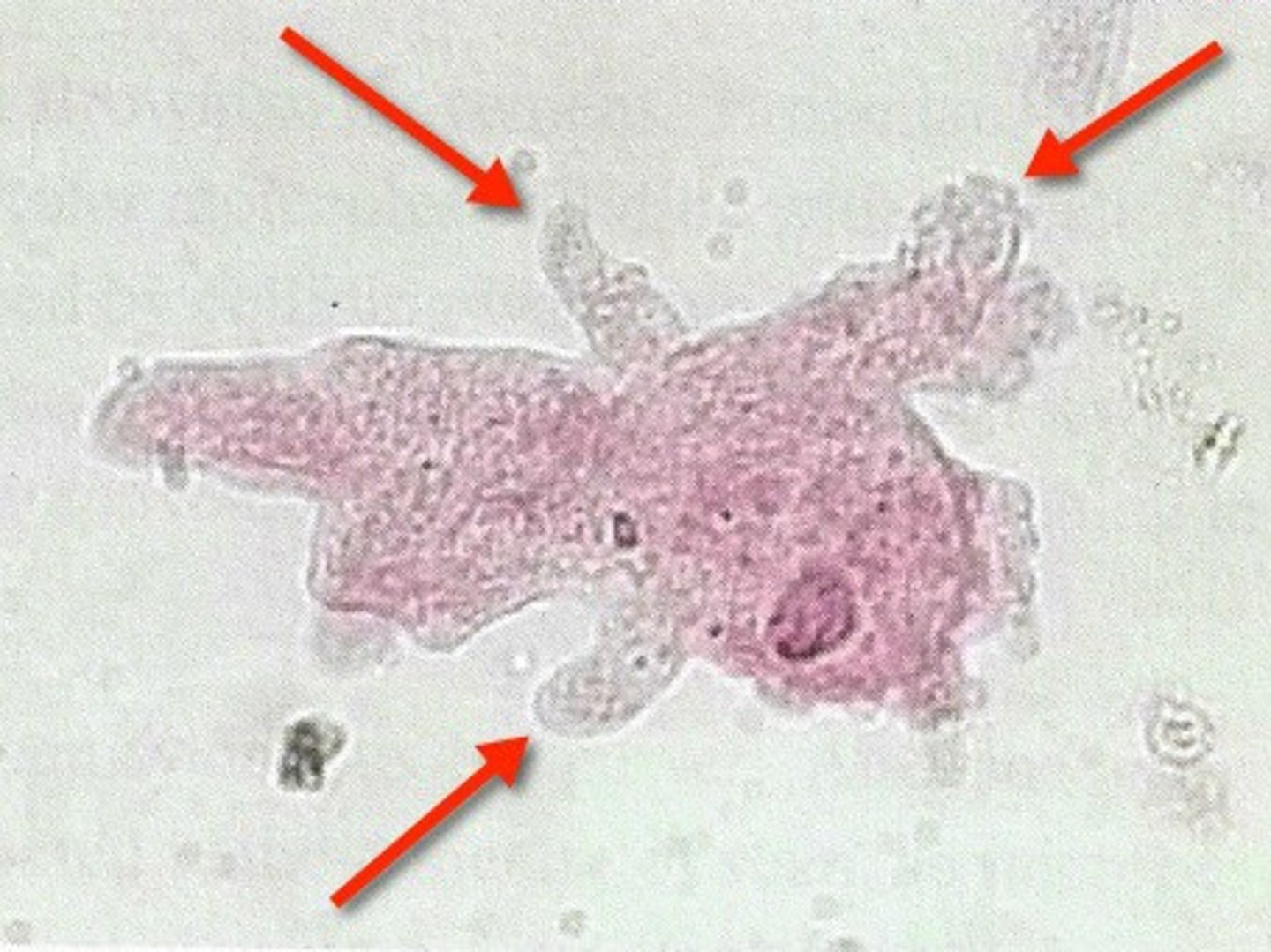
Pseudopod
A temporary, footlike extension of a cell, used for locomotion or engulfing food.
Spore
A reproductive cell with a hard, protective coating.

Plankton
Tiny organisms that float in the water.

Zooplankton
Tiny floating organisms that are either small animals or protozoans.

Phytoplankton
Tiny floating photosynthetic organisms, primarily algae.
Pellicle
A firm, flexible coating outside the plasma membrane.
Eyespot
A light-sensitive region in certain protists.
Holdfast
A special structure used by an organism to anchor itself.
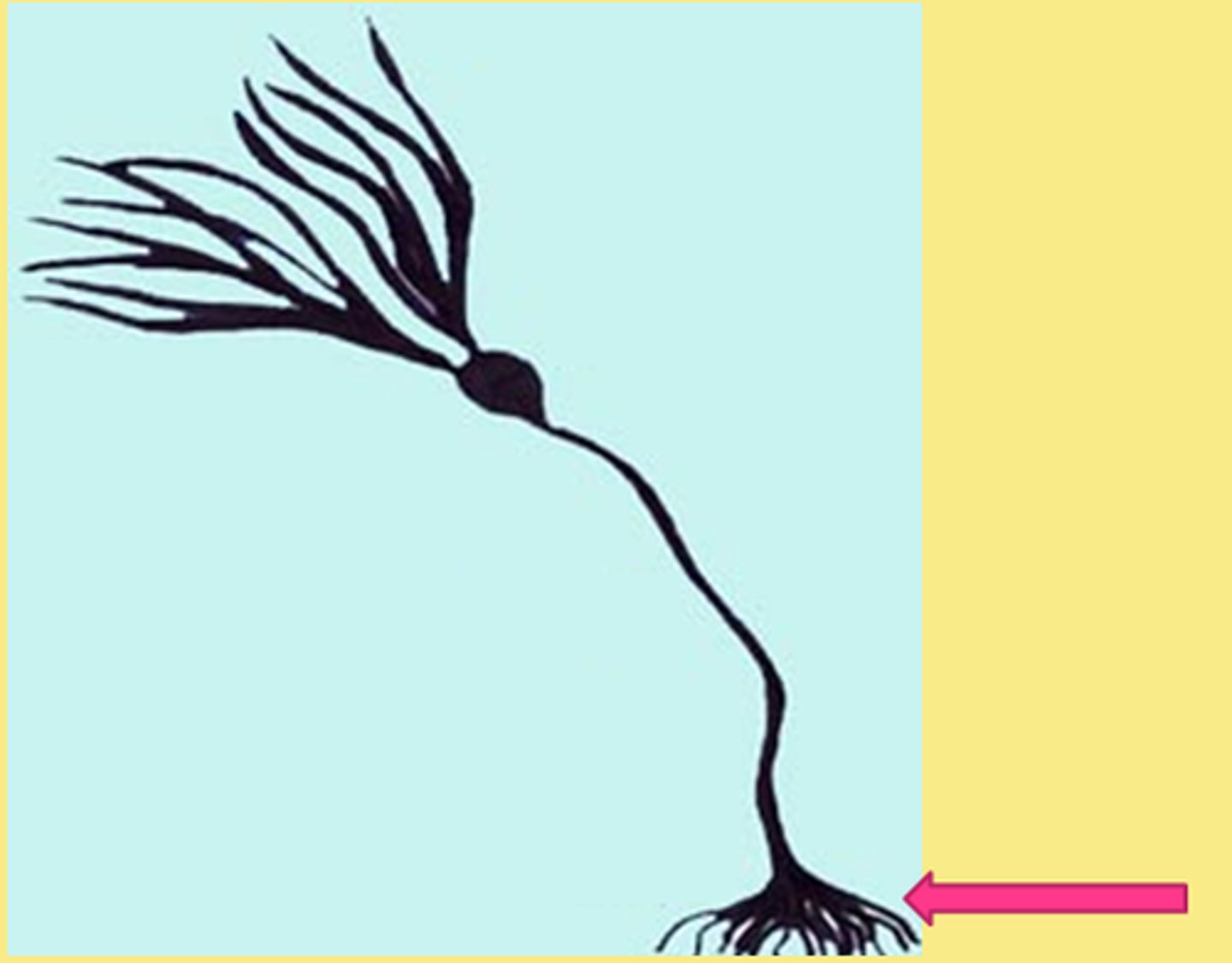

Sessile colony
A colony that uses holdfasts to anchor itself to an object.
Extracellular digestion
Digestion that takes place outside of the cell.
Mycelium
The part of the fungus responsible for extracellular digestion and absorption of the digested food.
Hypha
A filament of fungal cells.
Chitin
A chemical that provides both toughness and flexibility.

Zygospore
A zygote surrounded by a hard, protective covering.
Membrane
A thin covering of tissue
Botany
study of plants

Alternation of generations
the alternation between the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte in a plant's life cycle
Vascular tissue
system of tube-shaped cells that branches throughout a plant and transports water, mineral nutrients, and organic molecules between roots and shoots
Dominant generation
In alternation of generations, the generation that occupies the largest portion of the life cycle
Pollen
A fine dust that contains the sperm of seed-producing plants

Cotyledon
A "seed leaf" which develops as a part of the seed. It provides nutrients to the developing seedling and eventually becomes the first leaf of the plant.
Perennial plants
Plants that grow year after year
Annual plants
Plants that live for only one year
Biennial plants
Plants that live for two years
Perfect flowers
Flowers with both stamens and carpels
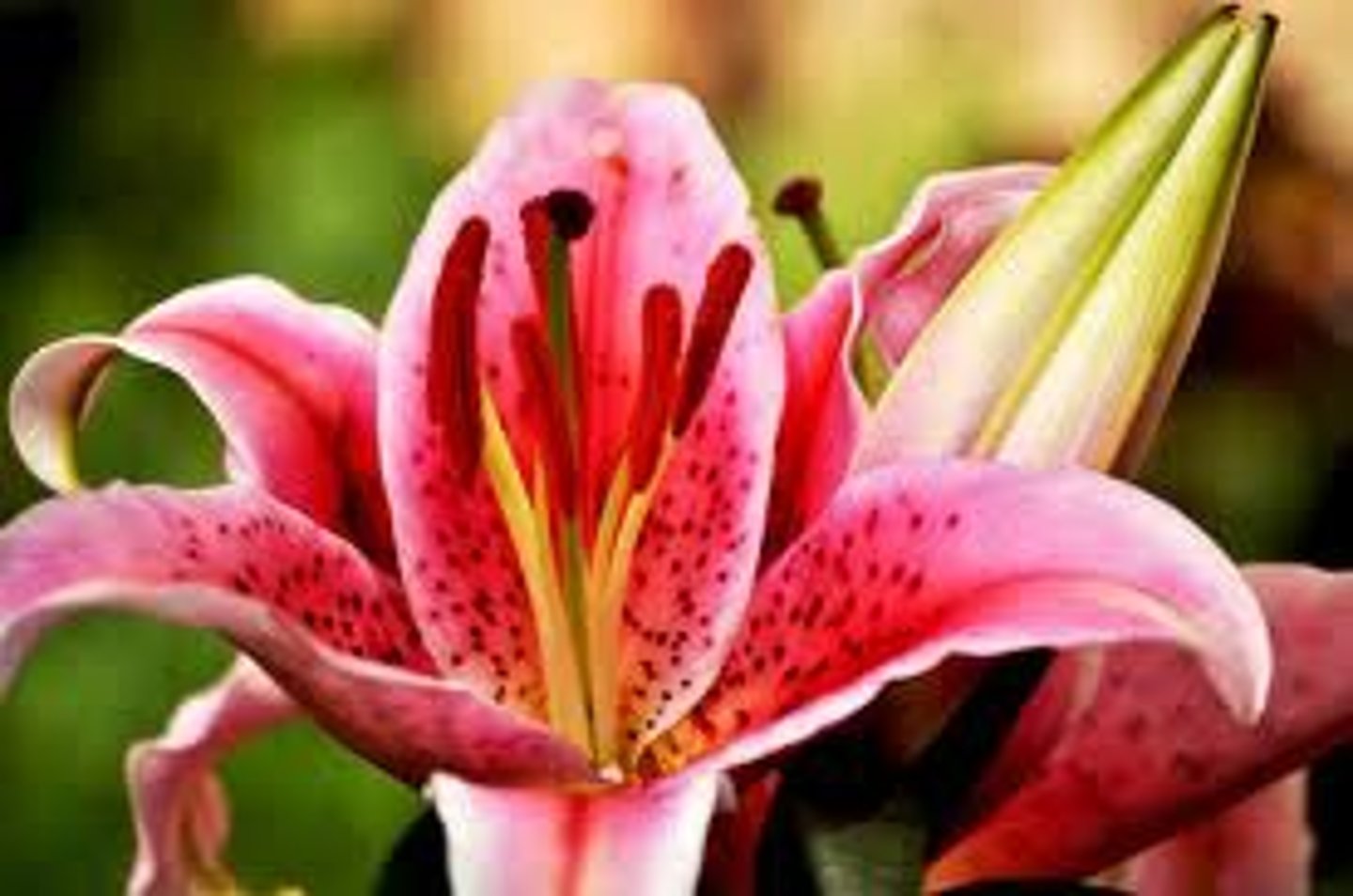

Imperfect flowers
Flowers with either stamens or carpels, but not both
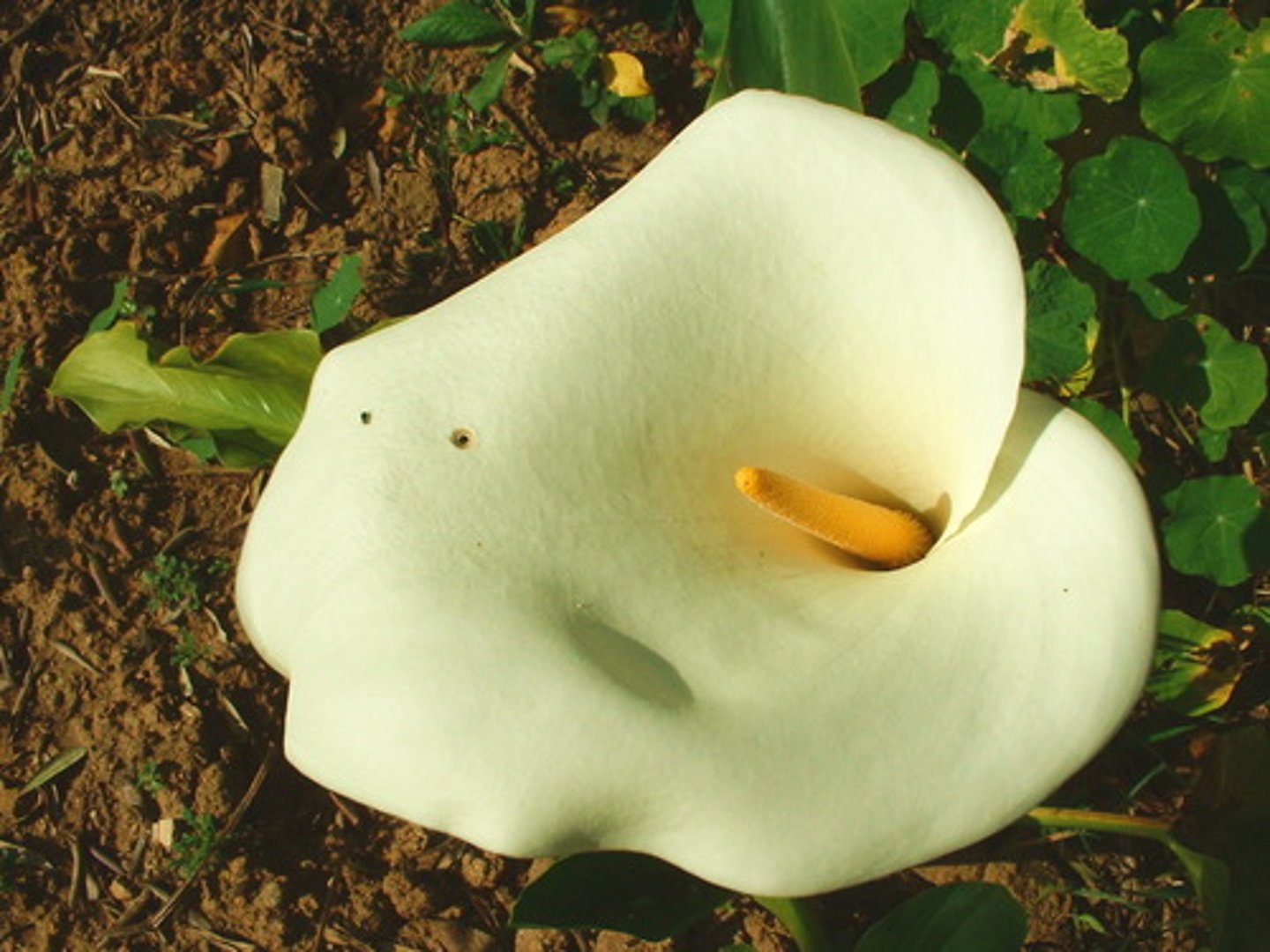

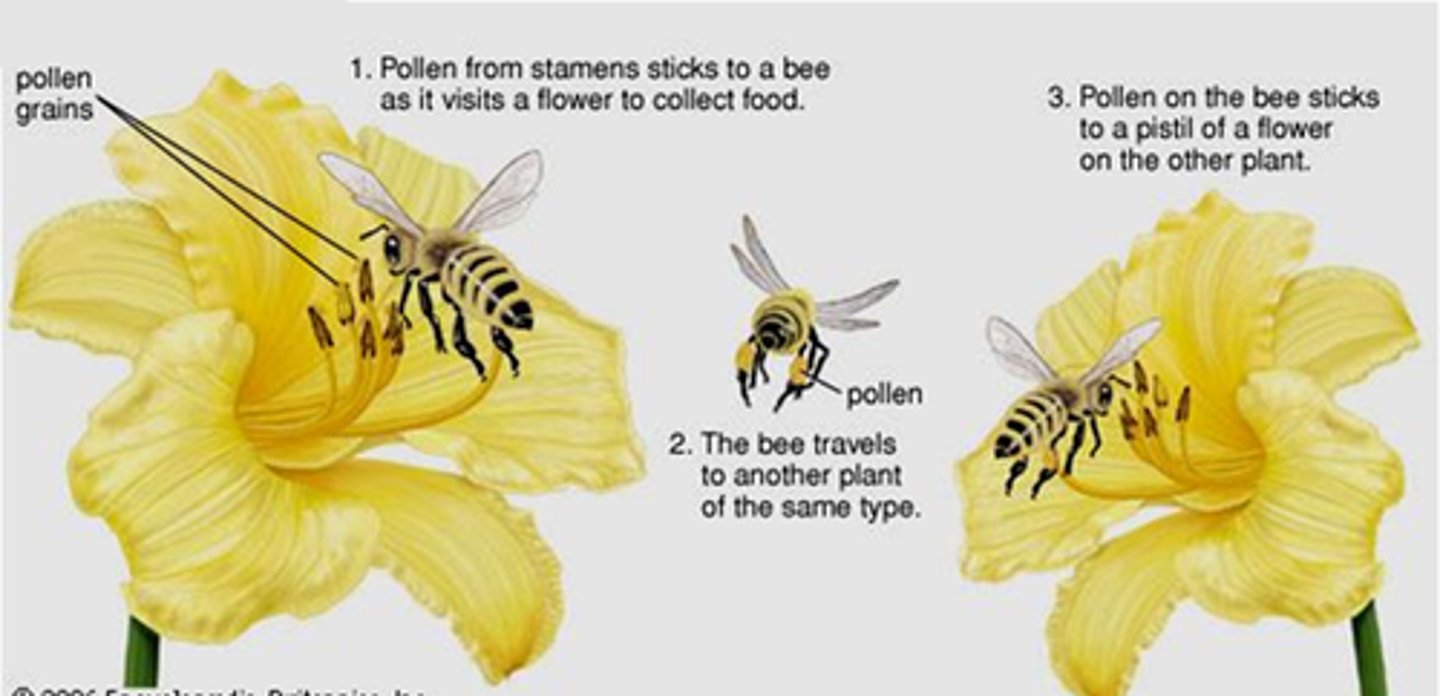
Pollination
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the carpel in flowering plants

Double fertilization
A fertilization process that requires two sperm to fuse with two other cells
Seed
An ovule with a protective coating, encasing a mature plant embryo and a nutrient source
Fruit
A mature ovary that contain a seed or seeds
Physiology
The study of life processes in an organism
Vegetative organs
The parts of a plant (such as stems, roots, and leaves) that are not involved in reproduction
Reproductive plant organs
The parts of a plant (such as flowers, fruits, and seeds) involved in reproduction
Undifferentiated cells
Cells that have not specialized in any particular function
Xylem
Nonliving vascular tissue that carries water and dissolved minerals from the roots of a plant to its leaves
phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant
Girdling
The process of cutting away a ring of inner and outer bark all the way around a tree trunk
Deciduous plant
A plant that loses its leaves for winter
Nastic movement
A plant's response to a stimulus such that the direction of the response is preprogrammed and not dependent on the direction of the stimulus

Stimulus
An environmental change that triggers a response
Pore spaces
Spaces in the soil that determine how much water and air the soil can hold
Loam
A mixture of gravel, sand, silt, clay, and organic matter
Translocation
The process by which organic substances move through the phloem of a plant
Hormones
Chemicals that circulate throughout multicellular organisms, regulating cellular processes by interacting with specifically targeted cells
Phototropism
A growth response to light
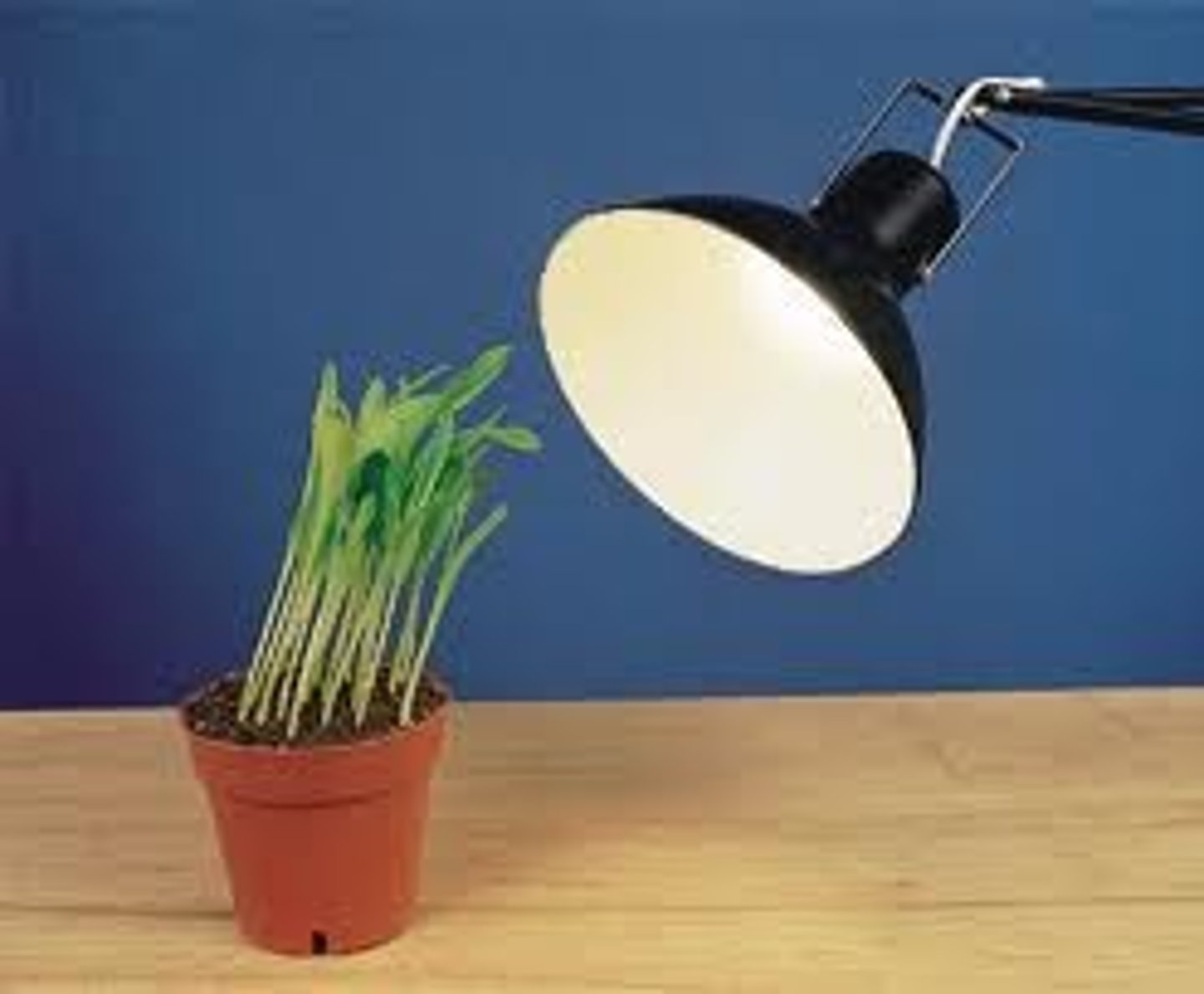

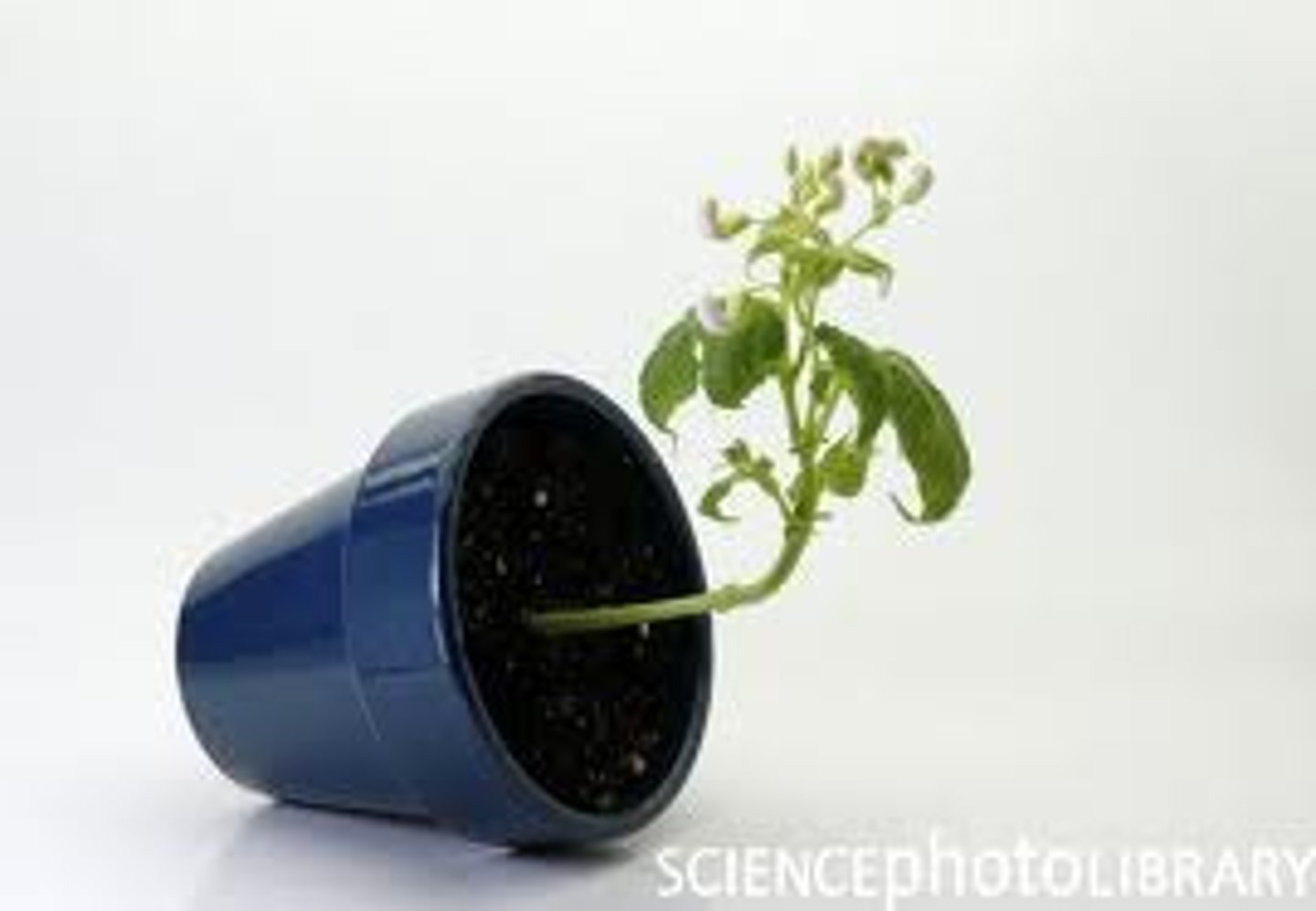
Gravitropism
A growth response to gravity

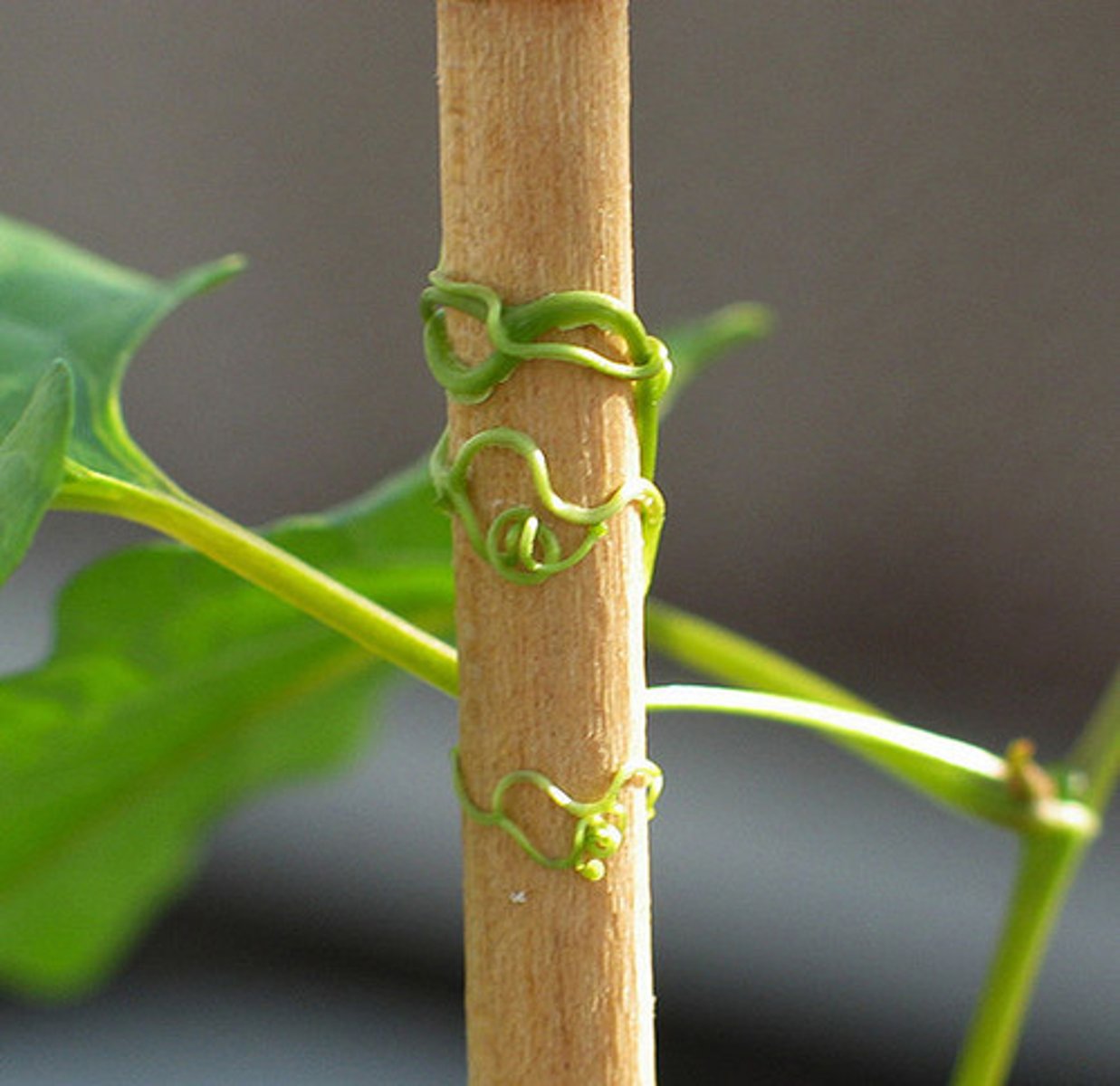
Thigmotropism
A growth response to touch

Invertebrates
animal that lacks a backbone
Vertebrates
animals that possess a backbone
Spherical symmetry
An organism possesses spherical symmetry if it can be cut into two identical halves by any cut that runs through the organism's center
Radial symmetry
An organism possesses radial symmetry if it can be cut into two identical halves by any longitudinal cut through its center
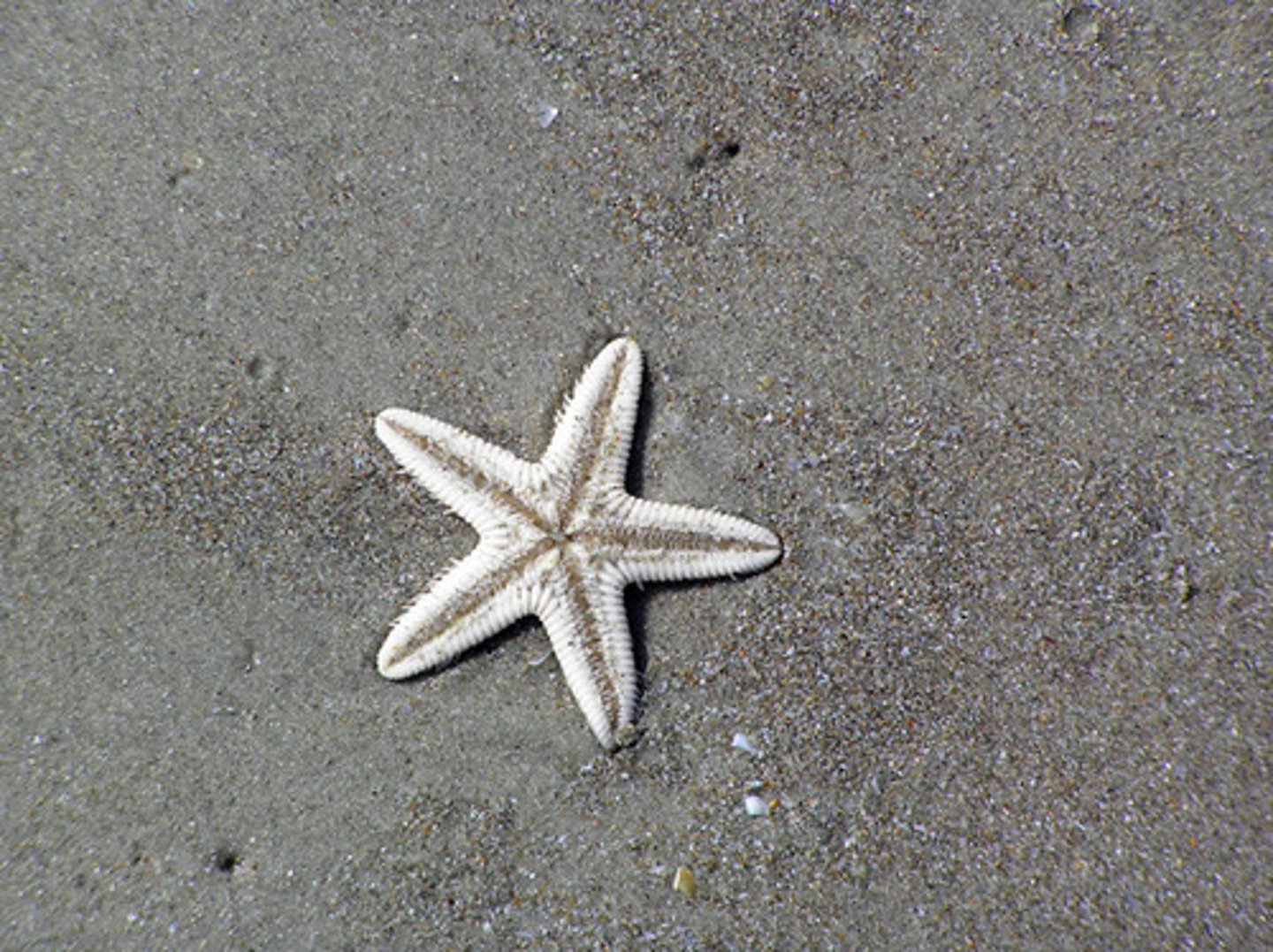

Bilateral symmetry
An organism possesses bilateral symmetry if it can only be cut into two identical halves by a single longitudinal cut along its center which divides it into right and left halves.
Anterior end
head region
Posterior end
tail end
Epidermis
An outer layer of cells designed to provide protection
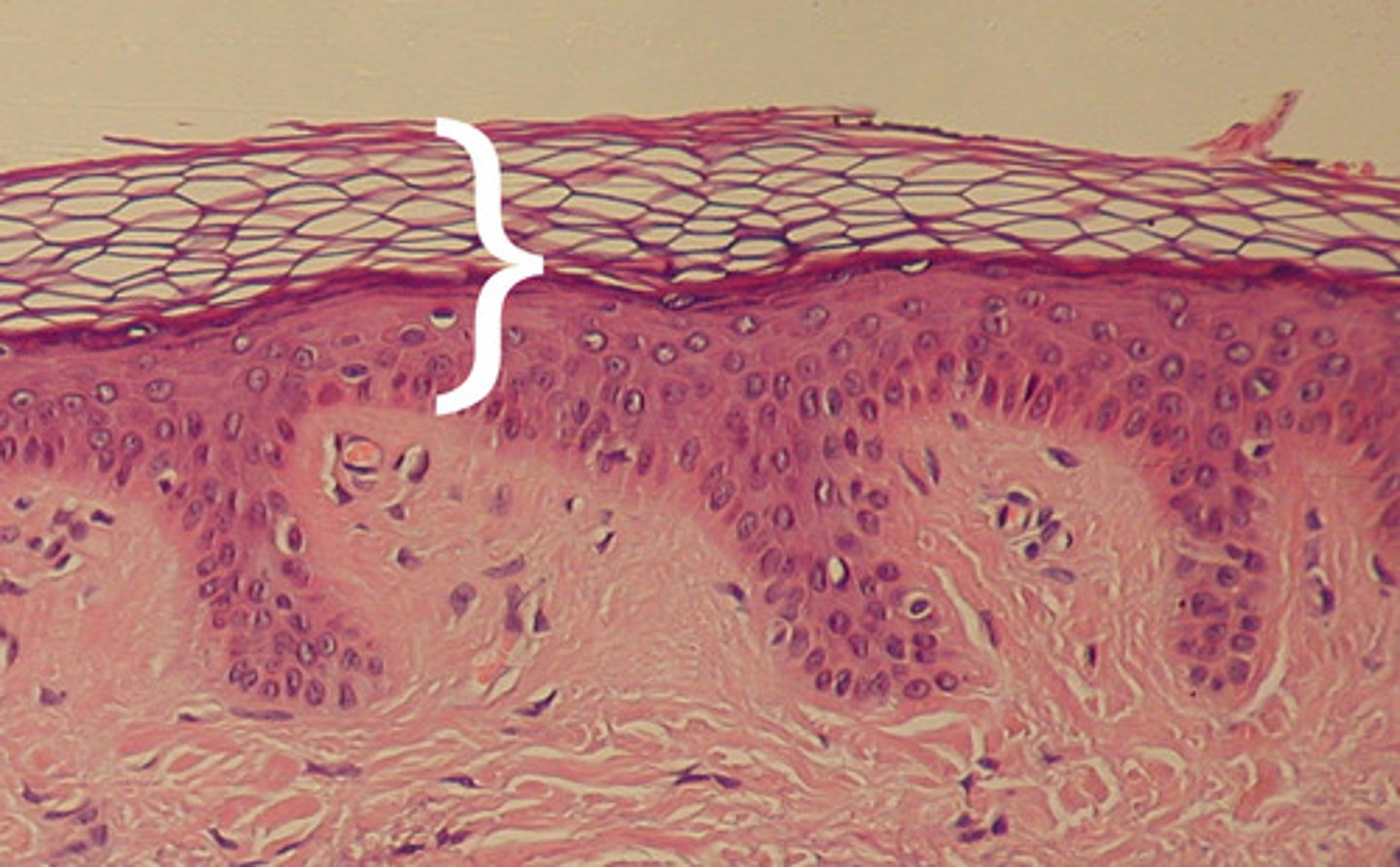
Endodermis
an inner layer of cells
mesenchyme
The jellylike substance that separates the epidermis from the inner cells in a sponge
Collar cells
flagellated cells that push water through a sponge
Amoebcytes
Cells that move using pseudopods and perform different functions in different animals
Gemmule
A cluster of cells encased in a hard, spicule-reinforced shell
Polyp
The sessile, tubular form of a cnidarian with a mouth and tentacles at one end and a basal disk at the other
Medusa
A free-swimming cnidarian with a bell-shaped body and tentacles
Epithelium
Animal tissue consisting of one or more layers of cells that have only one free surface, because the other surface adheres to a membrane or other substance
Mesoglea
The jellylike substance that separates the epithelial cells in a cnidarian
Nematocysts
Small capsules that contain a toxin which is injected into prey or predators

Testes
organs that produces sperm
Ovaries
Organs that produce eggs
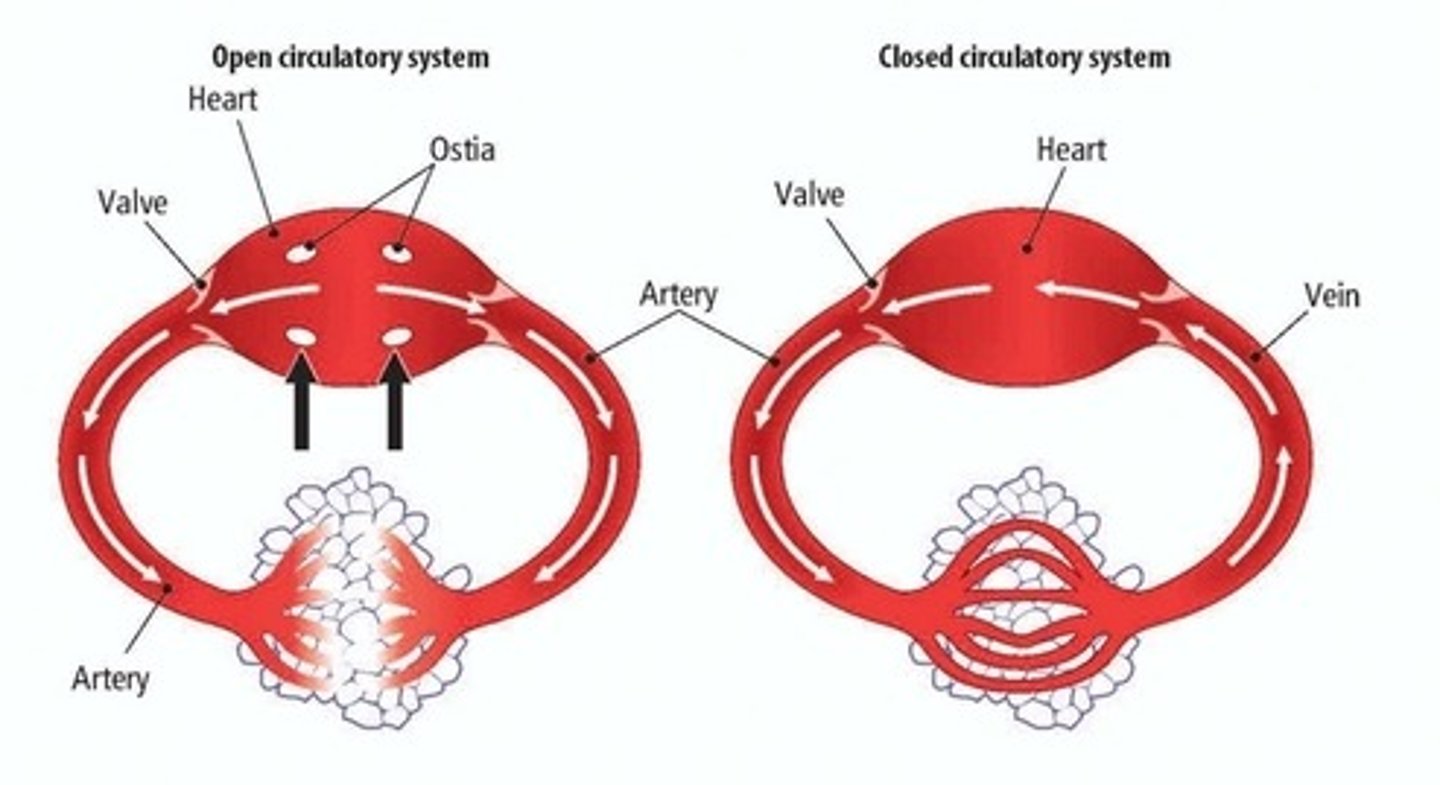
closed circulatory system
A system in which blood stays in vessels designed to transport food and other necessary substances throughout a creature's body
Nervous system
A system of sensitive cells that respond to stimuli such as sound, touch, and taste
Ganglia
Masses of nerve cell bodies
Hermaphroditic
possessing both the male ad female reproductive organs
Regeneration
The ability to regrow a missing part of the body
open circulatory system
a system in which blood is pumped through vessels into various chambers or body cavities where it comes in direct contact with cells, tissues, and organs
Mantle
A sheath of tissue that encloses the vital organs of a mollusk, makes the mollusk's shell, and performs respiration
Shell
A tough, multilayered structure secreted by the mantle, generally used for protection, but sometimes for body support

Visceral hump
A hump that contains a mollusk's heart, digestive, and excretory organs
Foot
A muscular organ that is used for locomotion and takes a variety of forms depending on the animal
Radula
an organ covered with teeth that mollusks use to scrape food into their mouths
Univalve
An organism with a single shell
Bivalve
have 2 shells

Exoskeleton
A body covering, typically made of chitin, that provides support and protection

Molt
To shed an old outer covering so that it can be replaced with a new one
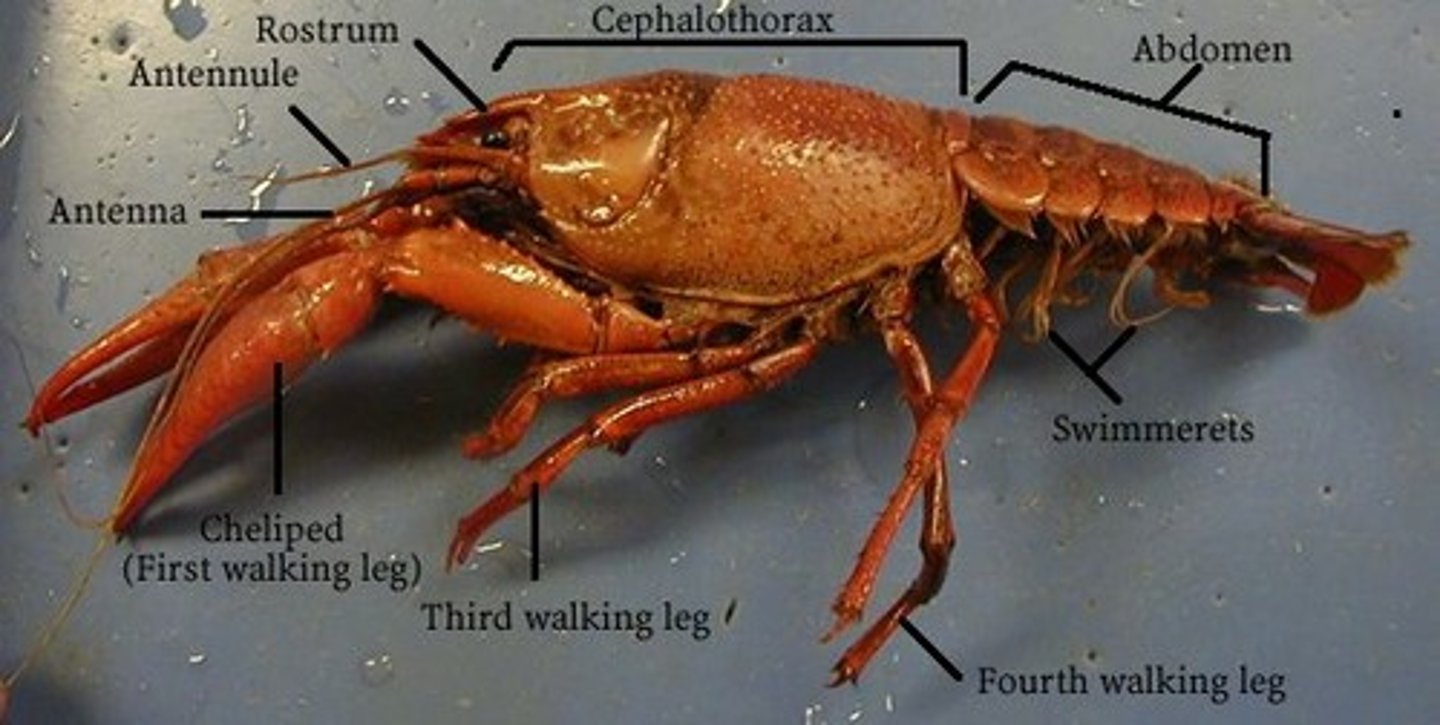
Thorax
The body region between the head and the abdomen.
Abdomen
The body region posterior to the thorax
Cephalothorax
A body region composed of the head and thorax fused together
Compound eye
An eye made of many lenses, each with a very limited scope
Simple eye
An eye with only one lens