Unit 5: Forces and Motion
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Newton’s first law
States that an object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net external force.
Newton’s second law
F = ma
Fg
is the gravitational force acting on an object
Fn
is the normal force exerted by a surface on an object resting on it, perpendicular to the surface.
Ff
is the force that opposes the relative motion of two surfaces in contact.
Ft
is the tension force transmitted through a string, rope, or cable when it is pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends.
Fd
is the drag force acting opposite to the relative motion of an object moving through a fluid or gas
Fs
exerted by something stretchy trying to return to its original shape
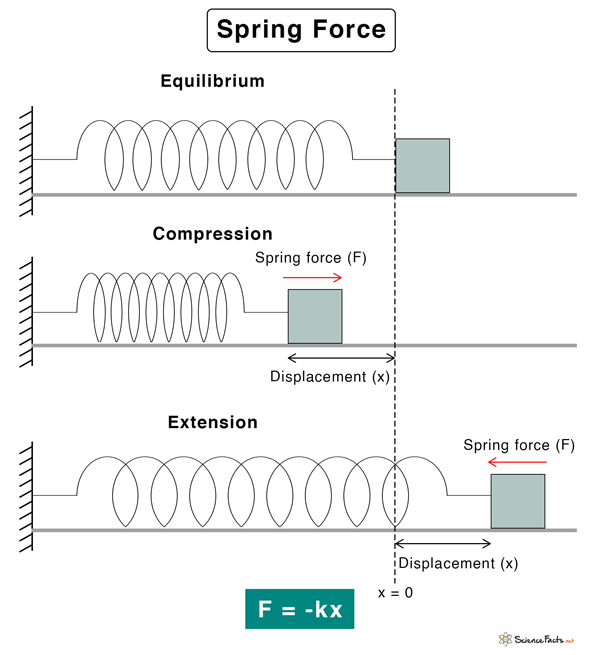
Fe
exerted b/w two charged objects. + and + or - and - will repel, + and - will attract
Fmag
exterted b/w two magnetic objects. N and N or S and S will repel, N and S will attract
Mass
amount of matter in an objects
Other word for mass
inertia
Weight
Force of gravity pulling on a mass (Newtons)
Net force always has…
DIRECTION
Acceleration
Rate of change of velocityover time.
Acceleration ONLY is speeding up when the net force and velocity are in the _____ direction
same
how to calculate acceleration
\frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t}
Speeding up (positive direction): Pos. vs. Time
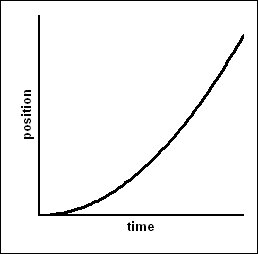
Speeding up (negative direction): pos vs time
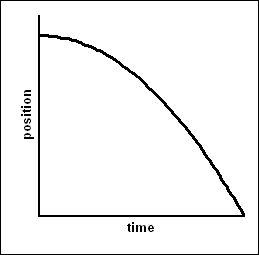
Slowing down (positive): pos vs time
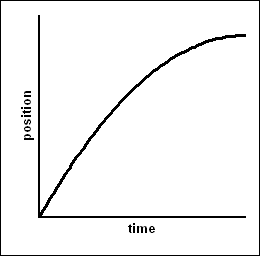
Slowing down (negative): pos vs time
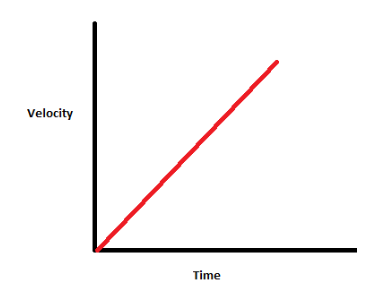
Speeding up (positive): velocity vs time
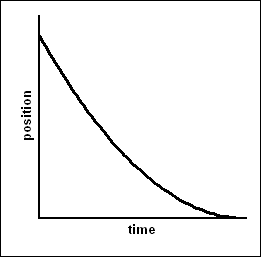
Speeding up (negative) velocity vs time
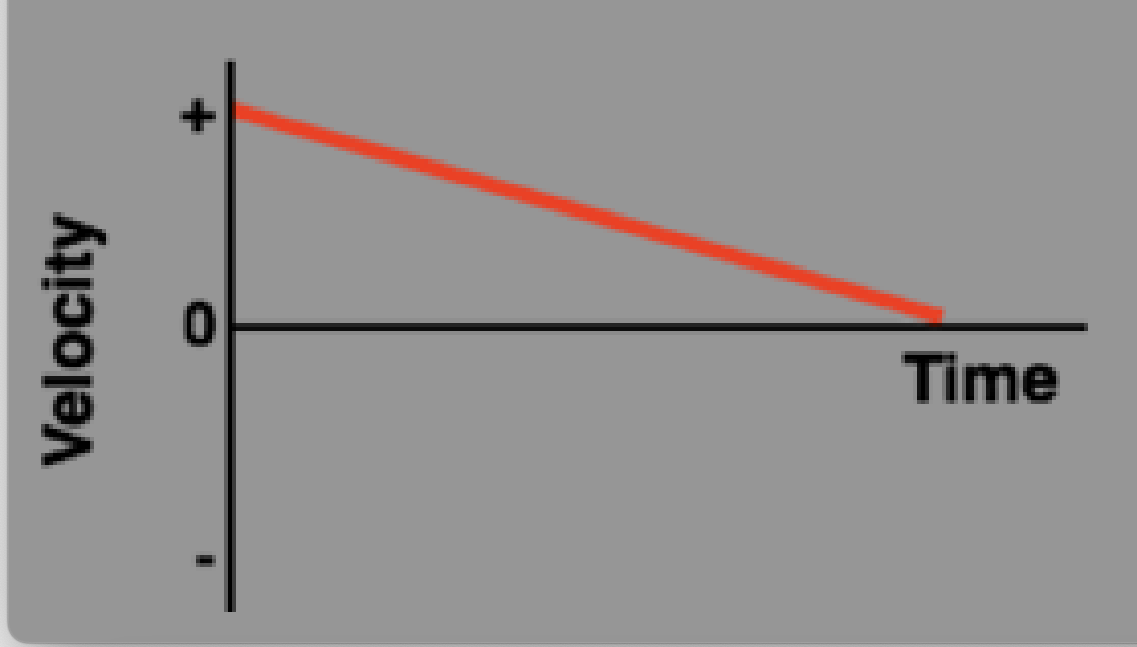
Slowing down (positive) velocity vs time
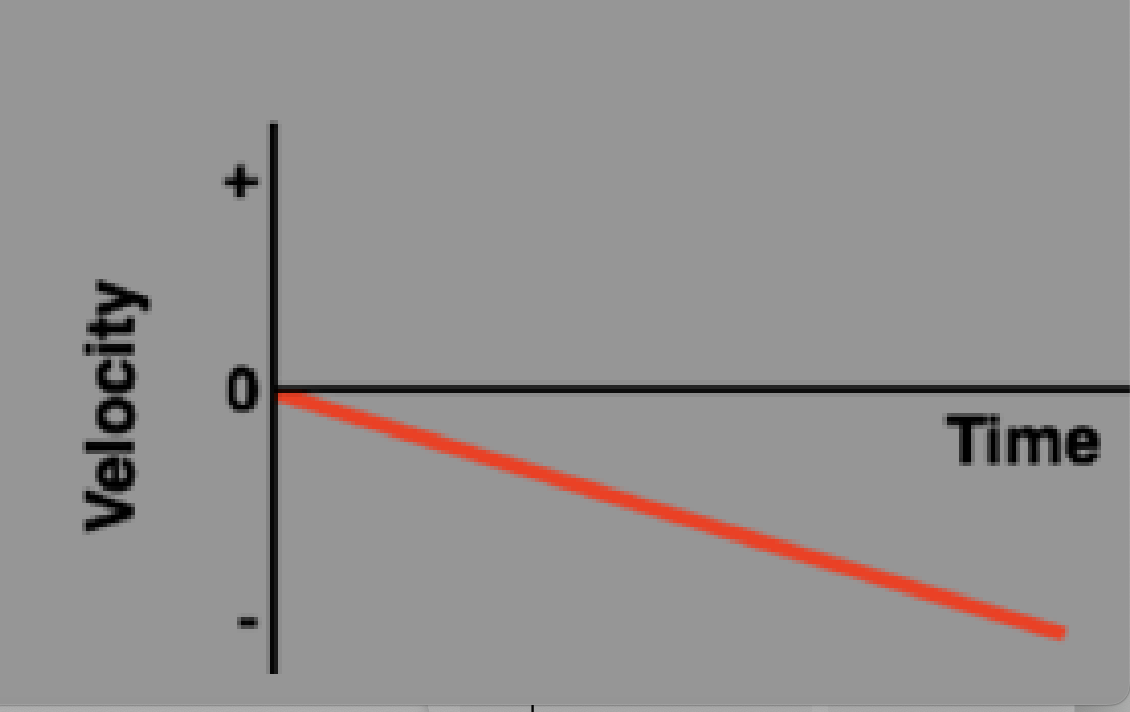
Slowing down (negative) velocity vs time
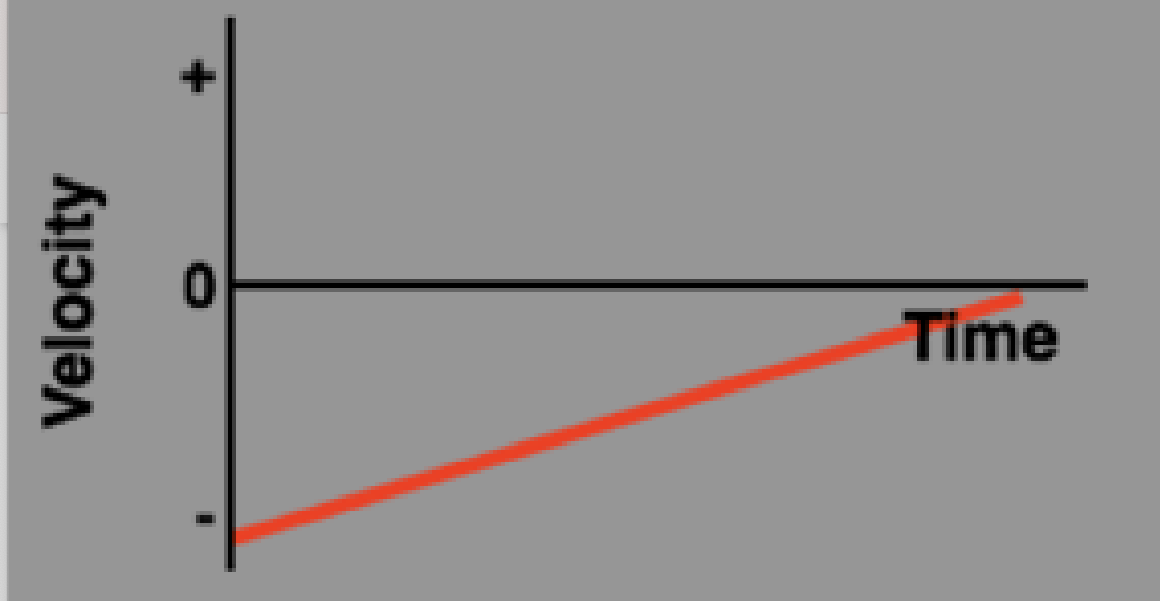

Speeding up (positive) acceleration vs time
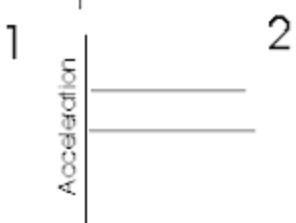
Speeding up (negative) acceleration vs time
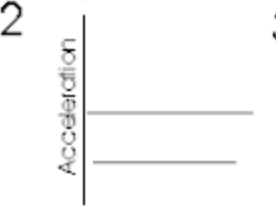
Slowing down (positive) acceleration vs time
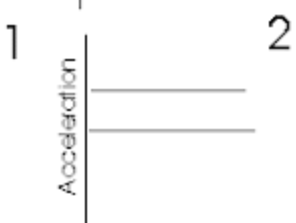
Slowing down (positive) acceleration vs time
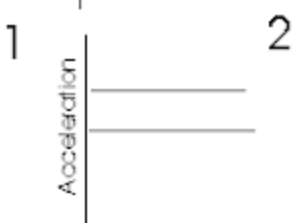
Work
change in energy of an object, W = Fd
When work is done on an object, energy is ___ or ___ from the system
Added or removed
newton’s third law
every action has an equal and opposite reaction
Force of gravity: if one mass doubles what happens to the force?
Doubles
Force of Gravity: When both masses double what happens to the force
4x
Force of Gravity: If one mass doubles and the other triples, what happens to the force?
5x
Force of Gravity: How does dist. affect force?
If dist. doubles = force does 2²x. if dist. halves, force divides by 2²
Difference b/w Fg, g, and G
Fg = force of gravity
g = gravitational force
G = universal grav. constant
Equation for Fg (Coloumbs law but not)
Fg = G(m1*m2/d²)
Coloumbs law
Fe = k(q1*q2/d²)
Displacement
Δx, how far an object moves from a starting position
Three ways to change acceleration
Increase speed, decrease speed, change direction
_____ is an object’s resistance to a change in its motion
inertia