ch 8 science test
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
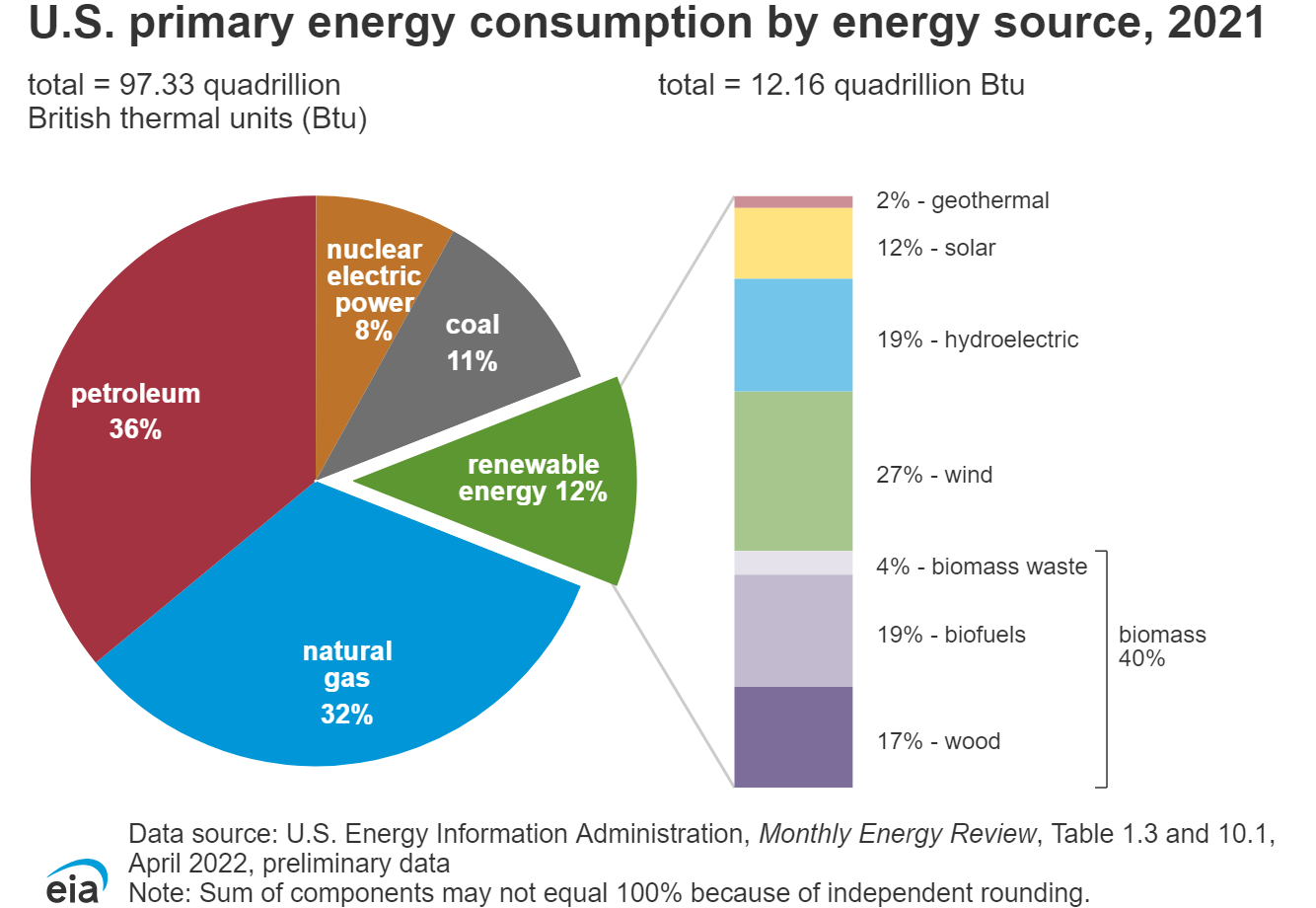
energy use in US
how coal forms
Coal forms over millions of years from the remains of dead plants in swampy environments. When plants die, they sink and are buried by layers of sediment, and the resulting pressure and heat from deep burial transform the plant matter into peat and then coal.
how oil (petroleum) forms
Petroleum forms over millions of years from the remains of ancient marine plants and animals, which are buried under layers of sand, silt, and rock. Intense heat and pressure from these overlying layers transform the organic material into a mixture of hydrocarbons.
how natural gas forms
when ancient remains of plants and animals are buried under layers of sediment, and subjected to millions of years of heat and pressure deep within the Earth. This immense heat and pressure transforms the organic matter into hydrocarbons, primarily methane, which becomes trapped in porous rock formations.
what are the uses of coal
to generate electricity, critical fuel for producing steel, coal is used in the production of cement, and its by-products are used to create a variety of chemicals and products, including dyes, soaps, plastics, and some medicines.
what are the uses of oil (petroleum)
transportation fuels like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel; heating and electricity generation
what are the uses of natural gas
electricity generation, heating homes and buildings, and cooking
how do power plants produce electricity from fossil fuels
burning the fuel to create heat, which turns water into high-pressure steam. This steam spins a turbine, and the turbine's rotation drives a generator to produce electricity through electromagnetic induction.
combustion reactions
a chemical process where a substance, the fuel, reacts rapidly with an oxidant, usually oxygen, to produce heat and light. When a hydrocarbon fuel (containing carbon and hydrogen) undergoes complete combustion, the products are carbon dioxide and water.
What are the products and reactants of a combustion reaction?
the reactants are a fuel and an oxidizer, which is almost always oxygen. The products of complete combustion are carbon dioxide and water
balancing combustion reactions
start by balancing the carbon atoms, then the hydrogen atoms, and finally the oxygen atoms
using control rods
fusion vs fission
Fission splits heavy atoms, releasing energy and producing long-lived radioactive waste, while fusion joins light atoms to form a heavier one, releasing even more energy with less radioactive waste
nuclear fuel
enriched uranium, is a substance used to generate energy in nuclear reactors through controlled nuclear fission
How a nuclear power plant produces electricity
through a process called nuclear fission, where the heat from splitting atoms is used to create steam that spins a turbine. This is a three-step process: First, a nuclear reactor heats water through controlled fission to create steam. Second, the steam turns a turbine, which is connected to a generator. Third, the generator spins to produce electricity.
Why are control rods so important?
they are essential for controlling the nuclear fission rate in a reactor, which allows them to safely regulate power and shut down the reactor in emergencies
advantages and risks of nuclear power
advantages: a reliable, low-carbon energy source
risks: challenge of radioactive waste disposal and the potential for severe accidents
how solar energy works
the suns rays beat down onto solar panels. The panels harness the energy and powers a generator
how hydroelectric dams generate electricity
by using the force of falling or flowing water to spin turbines, which are connected to generators that convert the mechanical energy into electrical energy
how wind generate electricity
the wind blows and spins the turbines on the wind turbines that powers a generator.
how tidal power produces energy
the rising and lowering tides spin underwater turbines which generate electricity
how biomass generates electricity
through direct combustion, where burning the organic material heats water to create high-pressure steam. This steam then spins a turbine, which is connected to a generator that produces electricity
how geothermal power generates electricity
using heat from the Earth to spin a turbine connected to a generator
where can solar energy be used
any place that has constant exposure to the sun during the day
where can hydroelectric tidal be used
in flowing bodies of water that can sustain a turbine
where can tidal energy be used
in places along the coast
where can wind energy be used
in windy places that have wide open fields
where can biomass energy be used
heating and electricity generation for residential, commercial, and industrial buildings, as well as producing liquid biofuels for transportation
where can geothermal energy be used
countries like Iceland, El Salvador, and the Philippines producing a significant portion of their electricity from it, while applications like heating buildings and greenhouses are common in many places, including the United States
natural greenhouse effect
gases in the atmosphere like CO2, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor trap heat from the sun and make Earth livable
human enhanced greenhouse effect
even more major greenhouse gases: H2O (water vapor), CO2 (carbon dioxide), CH4 (methane), O3 (ozone), N2O (nitrous oxide) are released into the atmosphere making the air warmer
surfaces with high albedo
fresh snow, ice, light-colored sand, and urban surfaces like white roofs and new concrete.
surfaces with low albedo
dark surfaces like forests, oceans, asphalt, and soil
carrying capacity
the maximum population size of a species that an environment can sustainably support over time
pollutants in agriculture
nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus from fertilizers, various pesticides, sediment from soil erosion, and pathogens and waste from livestock
effects of deforestation
loss of biodiversity, contributing to species extinction and habitat loss for countless plants and animals. It also causes climate change, soil erosion and degradation, disrupts water cycles, and can lead to flooding and drought.
water pollution
harms human health through diseases like cholera and typhoid and long-term issues like cancer, hormonal disruptions, and organ damage
ocean acidification
ongoing decrease in the ocean's pH due to the absorption of excess atmospheric carbon dioxide from human activities, primarily fossil fuel burning. This process lowers the pH and reduces the availability of carbonate ions, which are essential for many marine organisms to build shells and skeletons, threatening food chains and marine ecosystems.
air pollution
causing respiratory and cardiovascular diseases like asthma, bronchitis, heart attacks, and strokes, and can lead to premature death. It also harms the environment by damaging ecosystems, contributing to climate change, and reducing visibility
photochemical smog
a type of air pollution that forms when nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds react in the atmosphere with sunlight. This process creates a brownish haze over cities, particularly during warm, sunny days with little wind.
CFCs and Ozone interaction
(CFCs) react with ozone in the stratosphere through a catalytic chain reaction initiated by ultraviolet (UV) radiation that breaks the CFC molecule into chlorine radicals. The chlorine radical then repeatedly destroys ozone molecules by converting them to oxygen and regenerating itself, leading to the depletion of the protective ozone layer.
causes of ocean acidification
absorption of excess atmospheric carbon dioxide from human activities like burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and agriculture. When CO2cap C cap O sub 2𝐶𝑂2 dissolves in seawater, it forms carbonic acid, which then releases hydrogen ions, lowering the ocean's pH and making it more acidic. This process also reduces the availability of carbonate ions, which are essential for marine organisms to build shells and skeletons.
what impacts does it have on marine life
reduces the availability of carbonate ions, which are essential for marine organisms to build shells and skeletons, resulting in weaker, smaller shells of marine organisms.
what is one example on a sea animal impacted
sea urchins
will warmer or colder oceans become more acidic
Colder oceans become more acidic
because cold water can absorb more dissolved carbon dioxide than warm water