Chapter 6 DNA Structure, MITOSIS, Cell Cycle, and Chromosome Basics (2 of 2 sets for CH 6)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
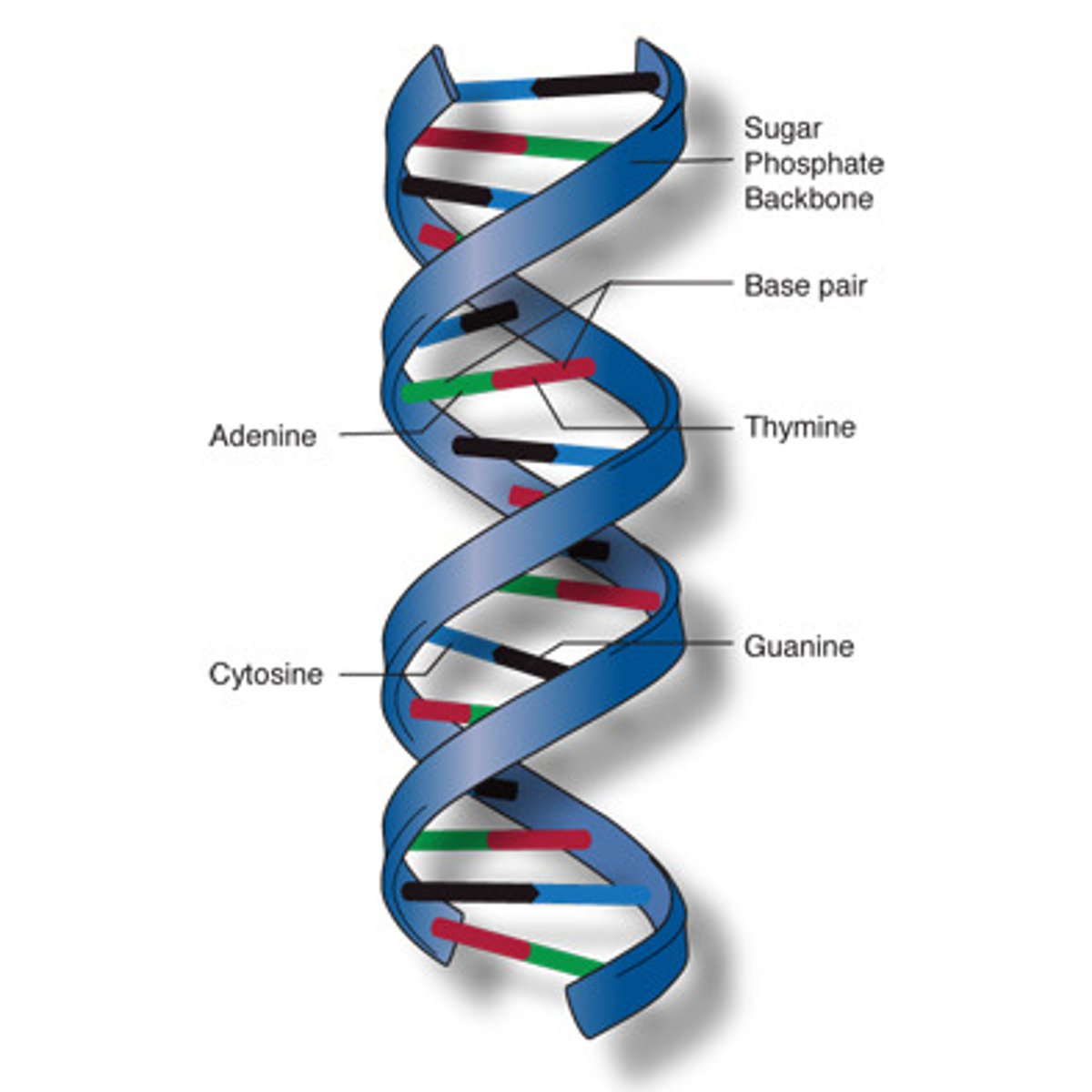
A Double Stranded Molecule containing Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, & Thymine
DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid
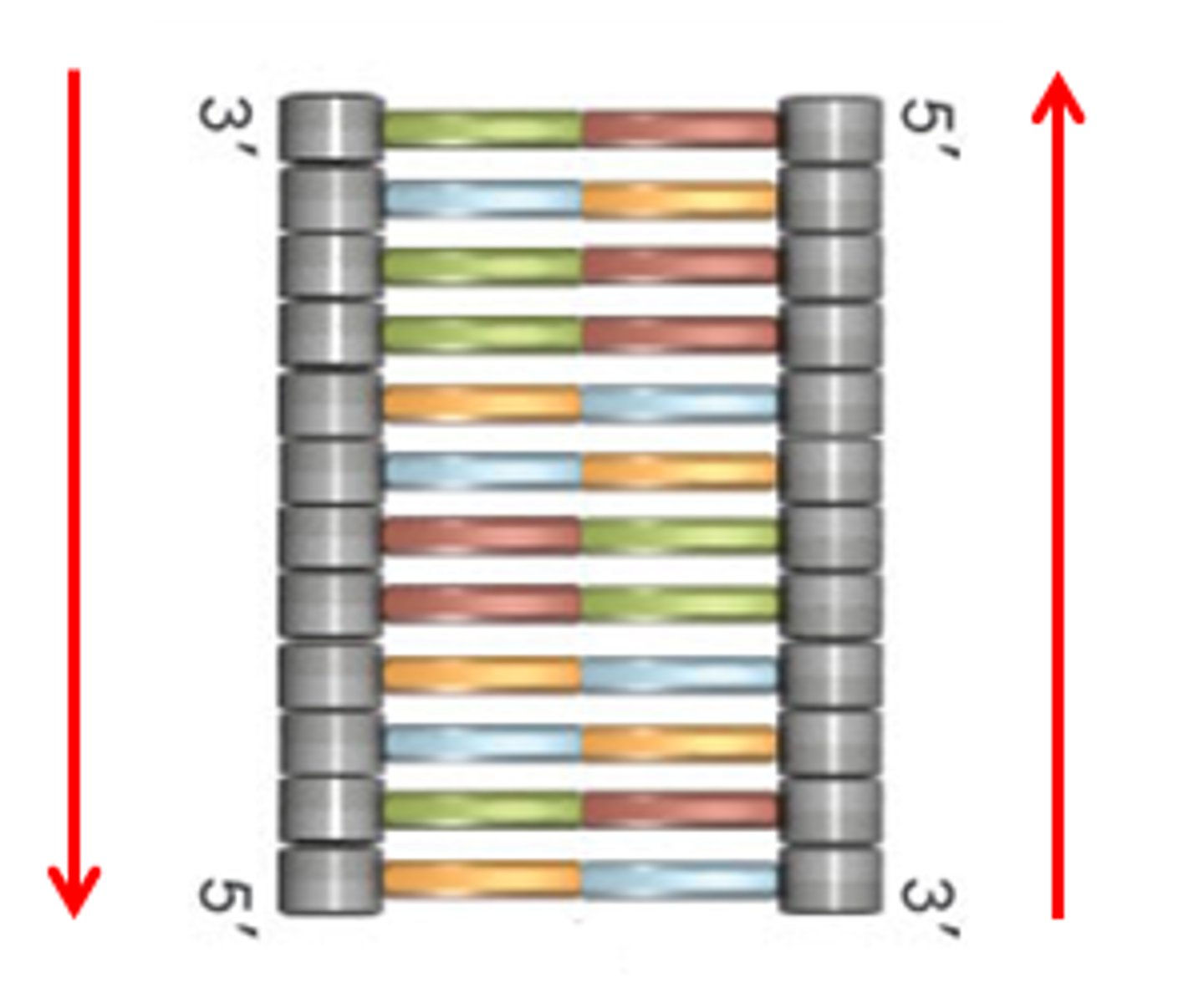
DNA "runs" in a 5' 3' /3' 5' direction. What is this called?
Antiparallel
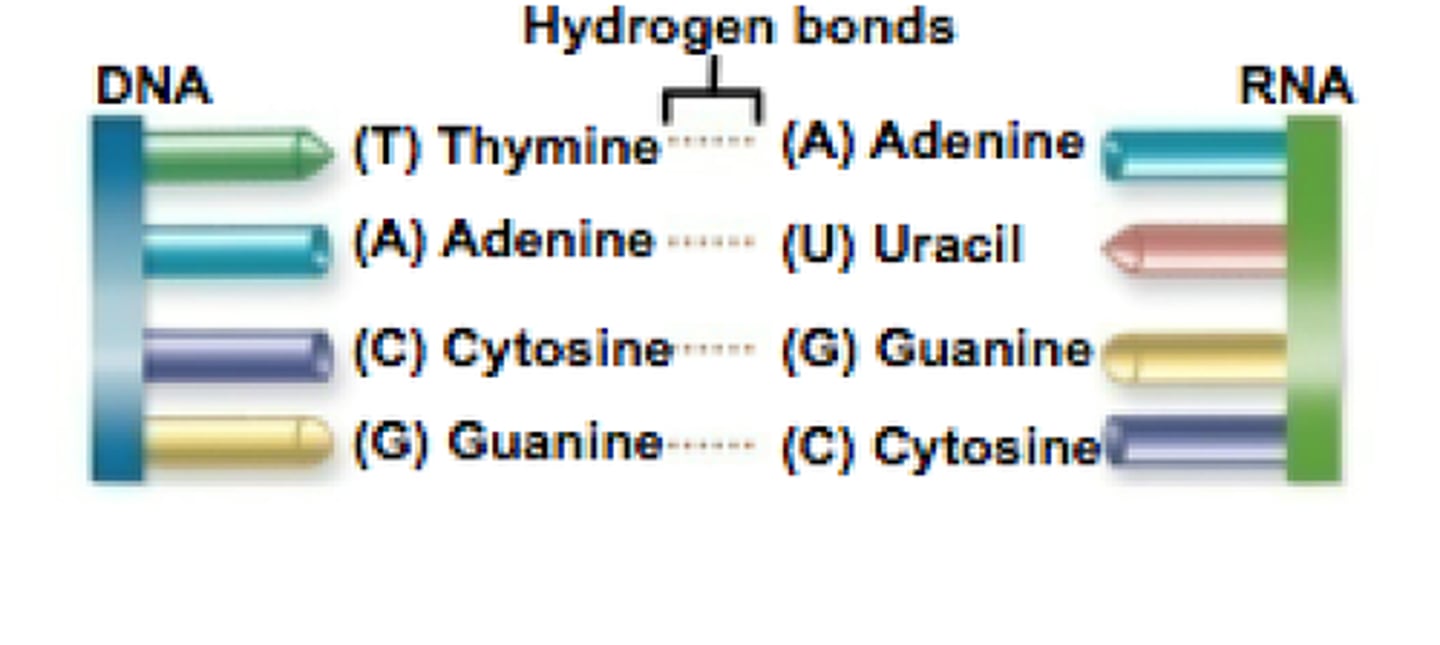
what are the Base Pairings in DNA vs RNA
A-T DNA; A-U RNA; C-G Both DNA & RNA
ALL the cell's DNA
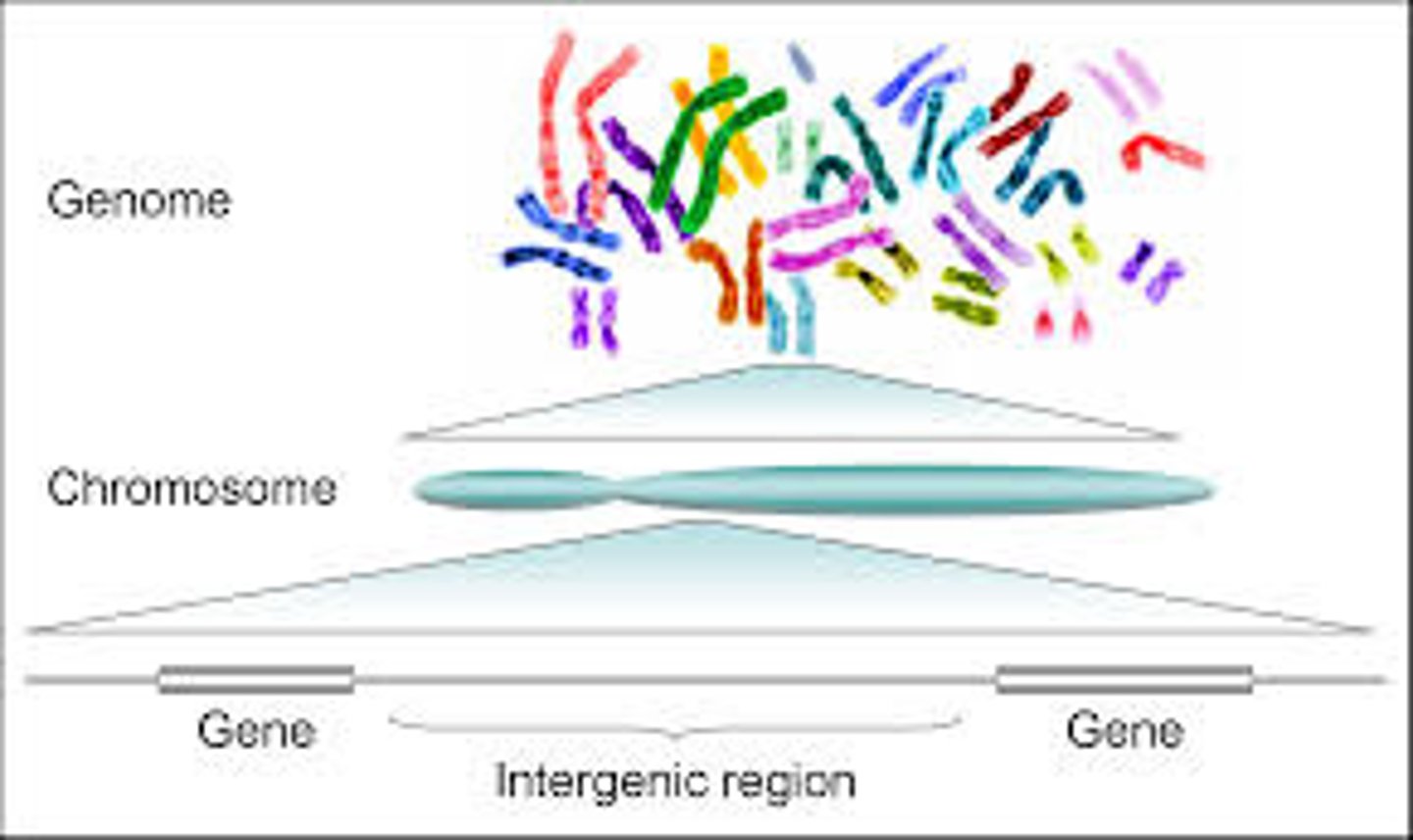
Genome
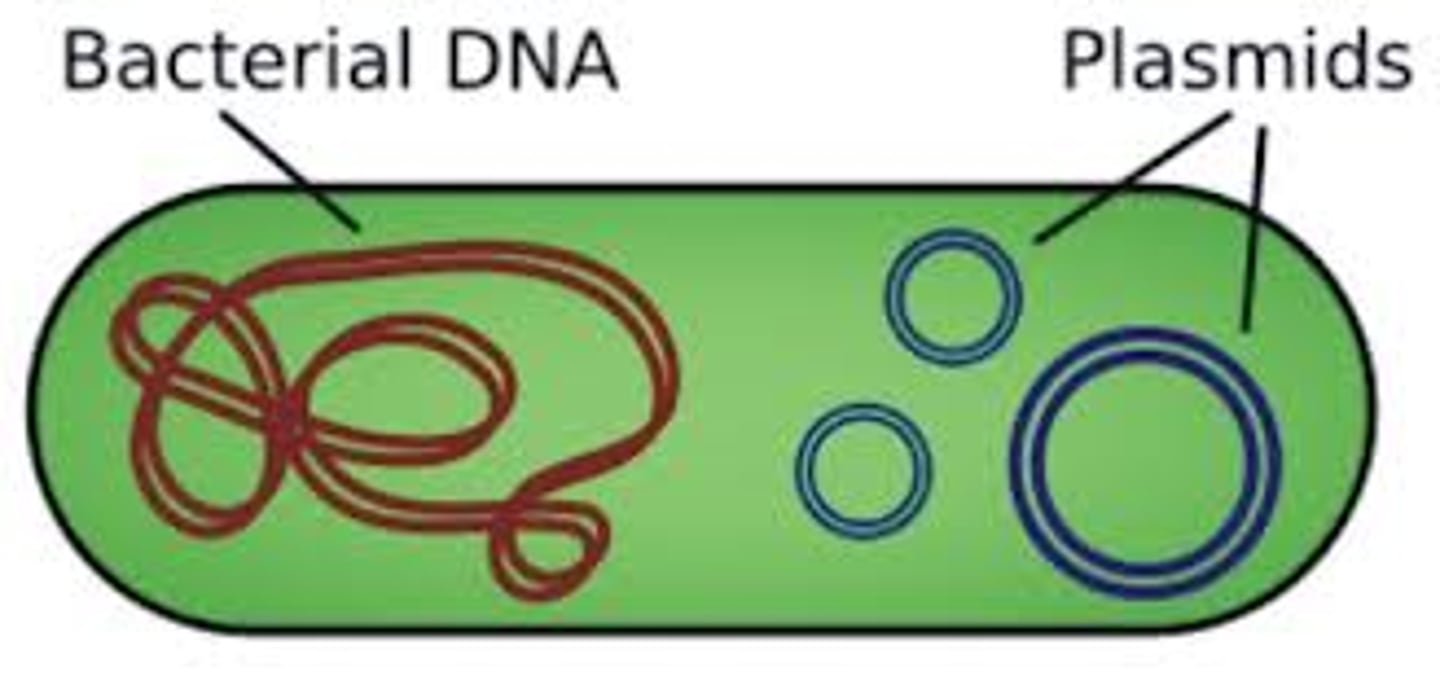
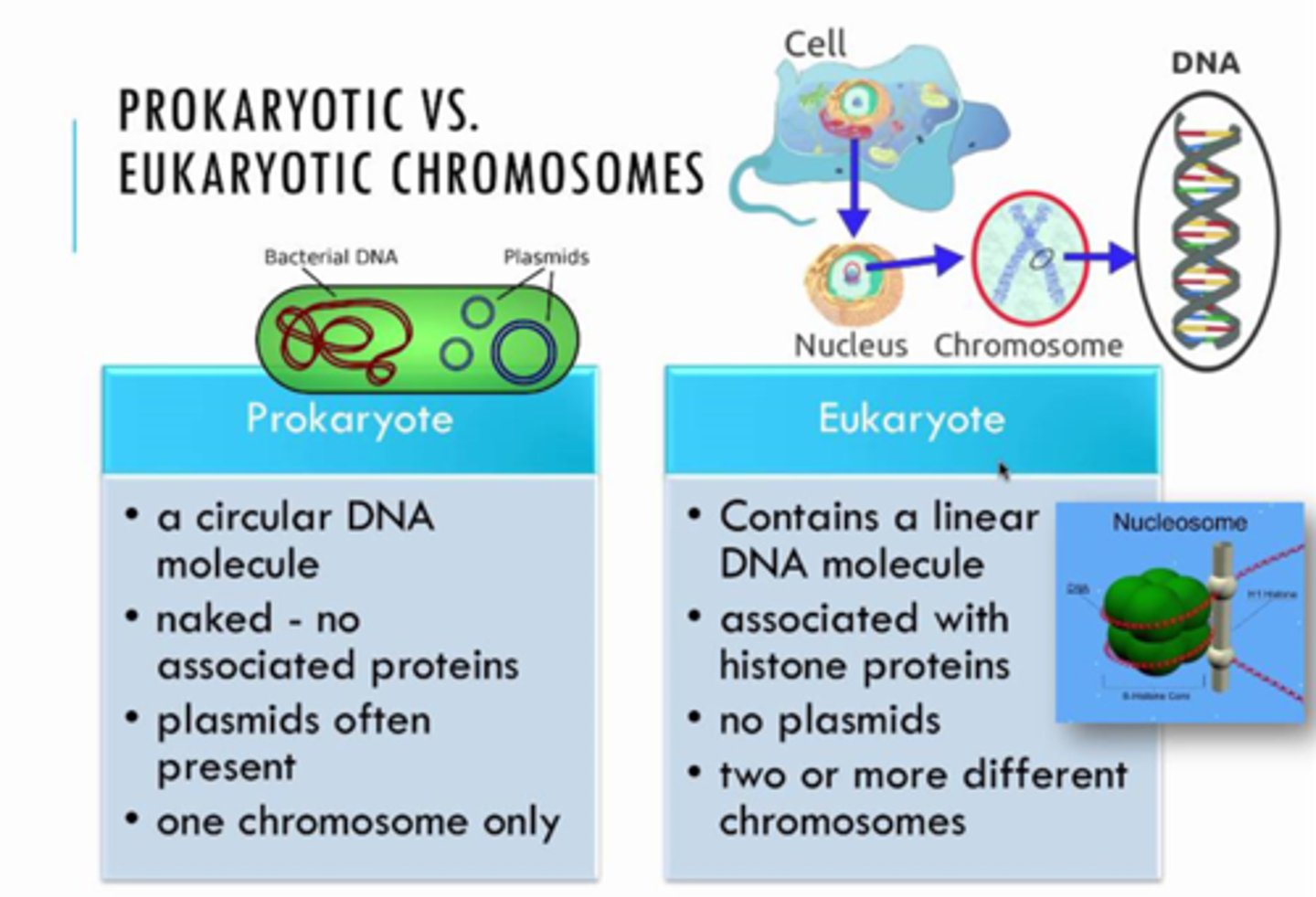
The _____________________________ consists of a single, circular double-stranded DNA molecule contained in the nucleoid. Some also have plasmids, which are smaller loops of DNA not essential for growth.
Prokaryotic Genome
The _____________________________ consists of several double-stranded linear DNA molecules, typically found in pairs.
Eukaryotic Genome

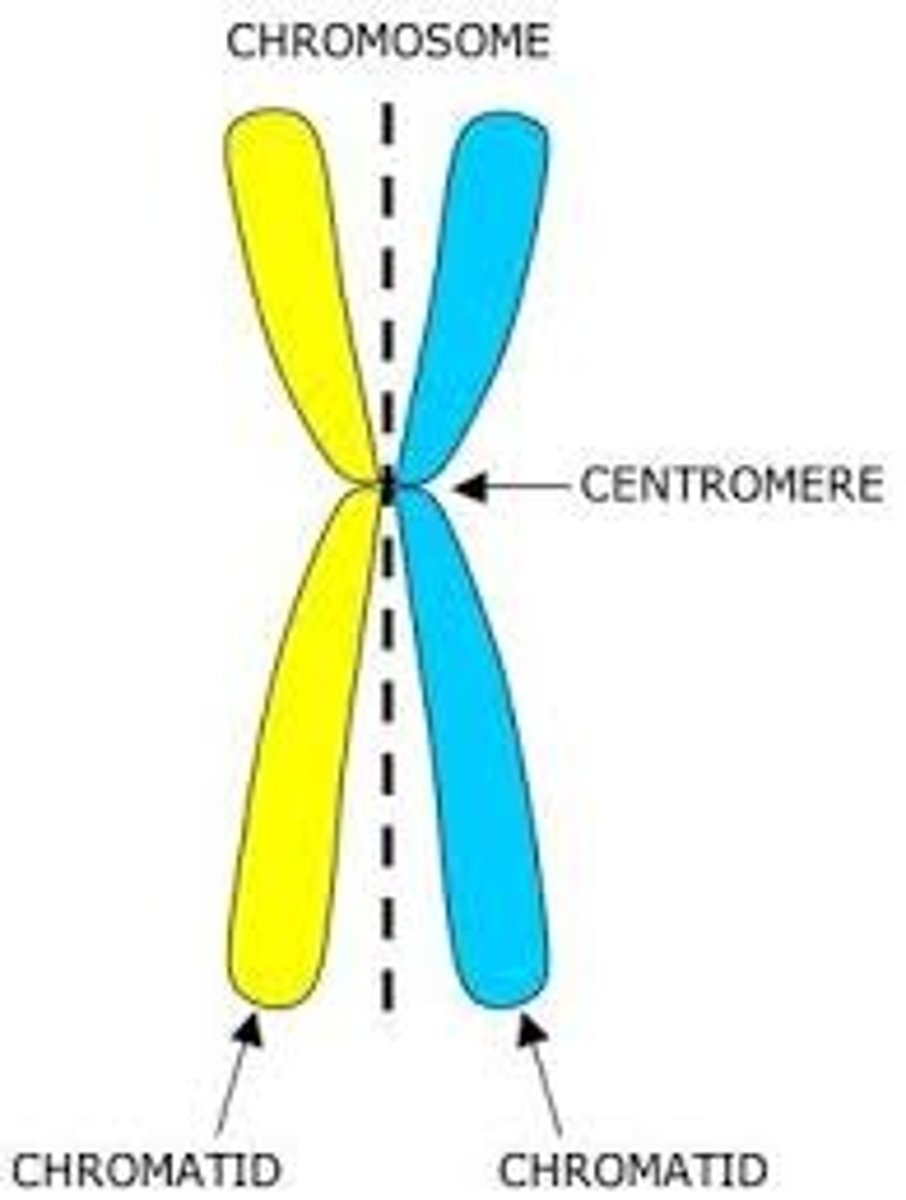
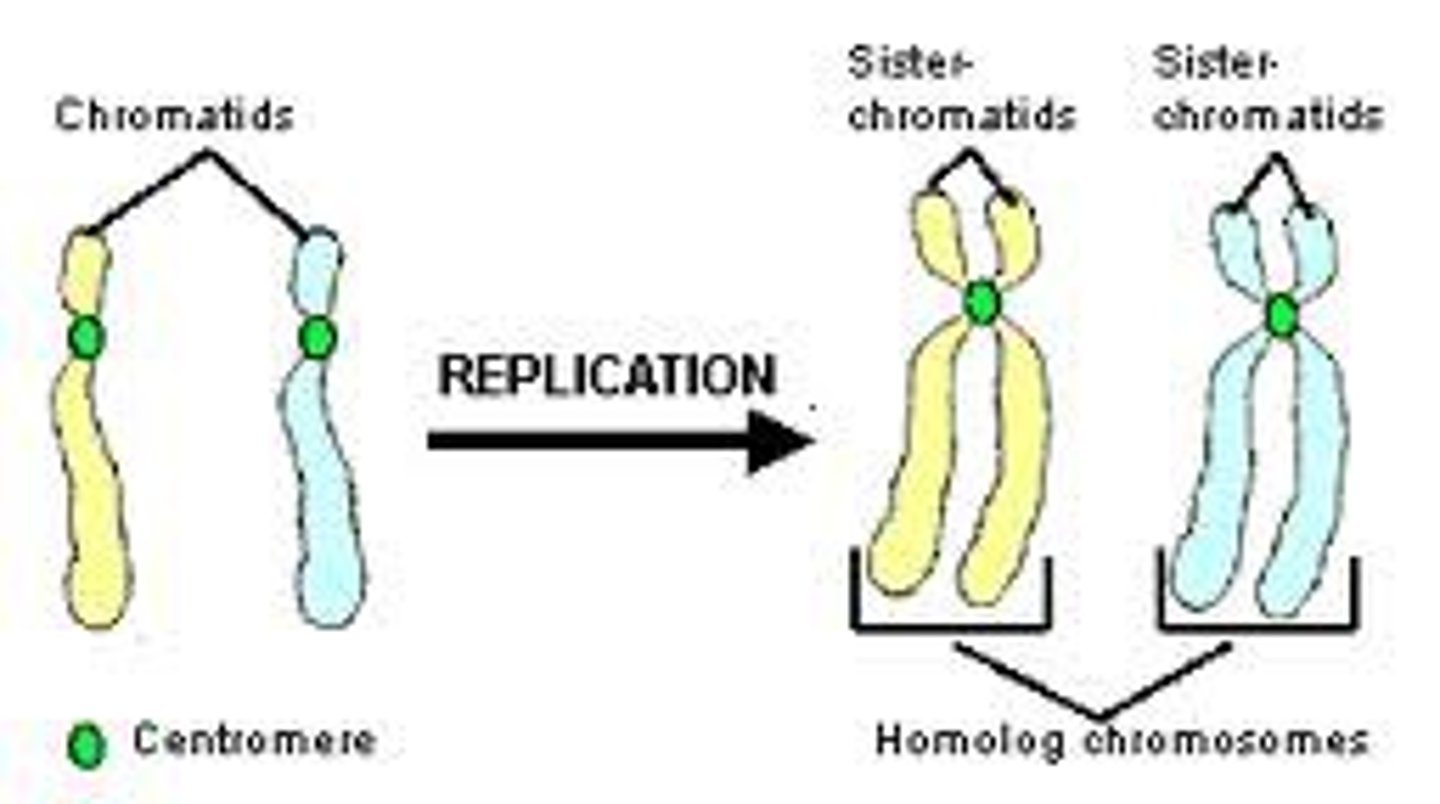
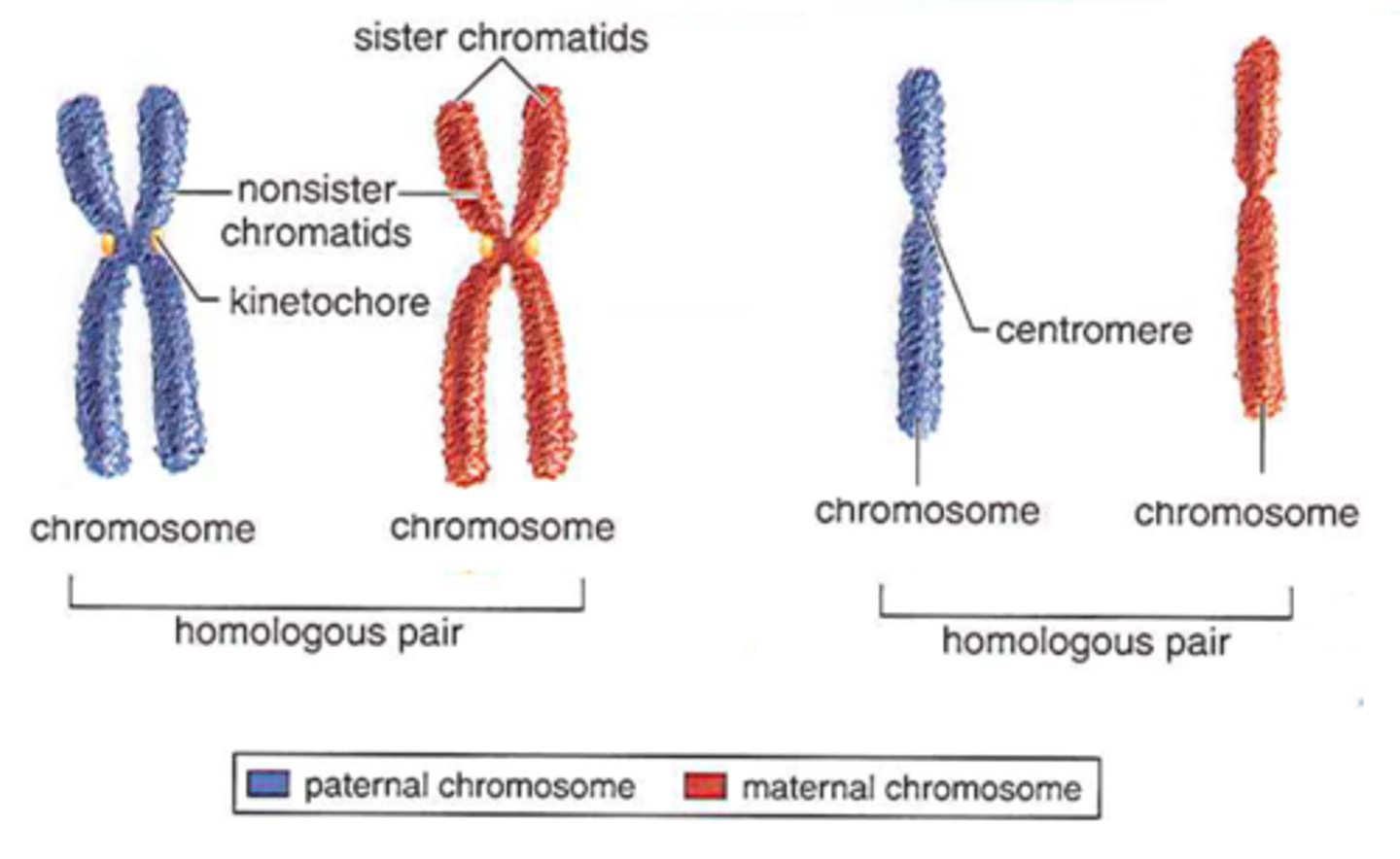
The region of a chromosome to which the microtubules of the spindle attach, via the kinetochore, during cell division.
Centromere
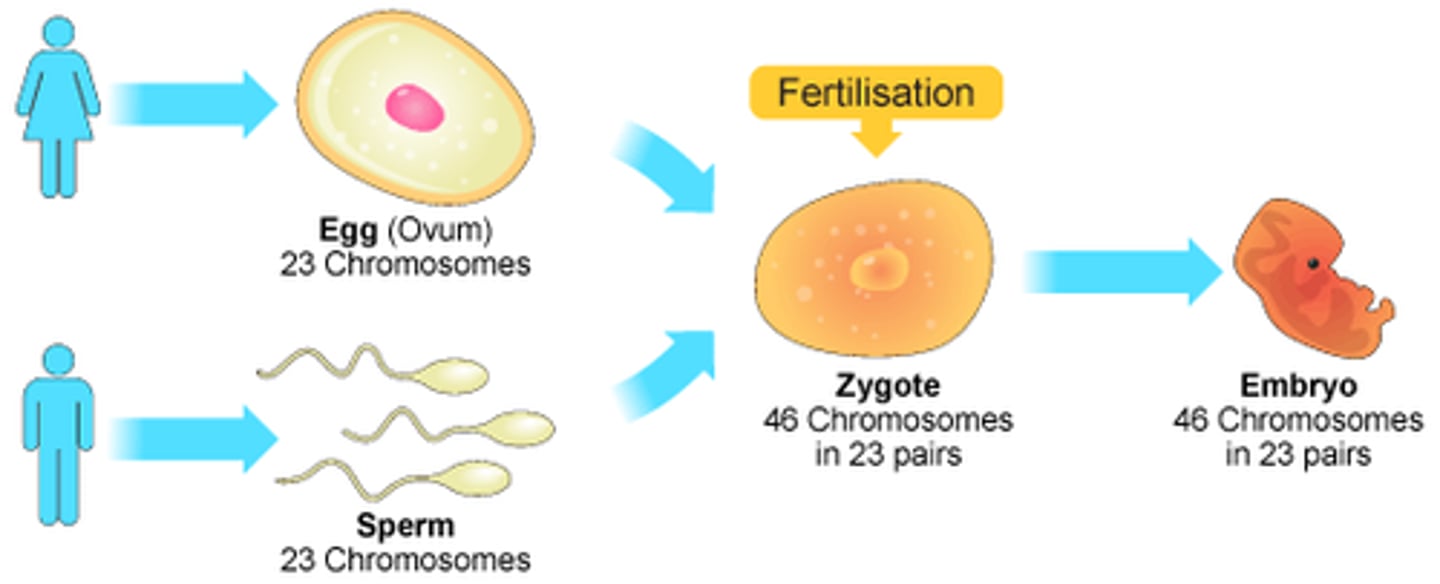
A somatic human cell has 2 sets of chromosomes—one set from the mother and one set from the father. These cells are ________ (2n), meaning they have 46 chromosomes (2 × 23).
Diploid Cells
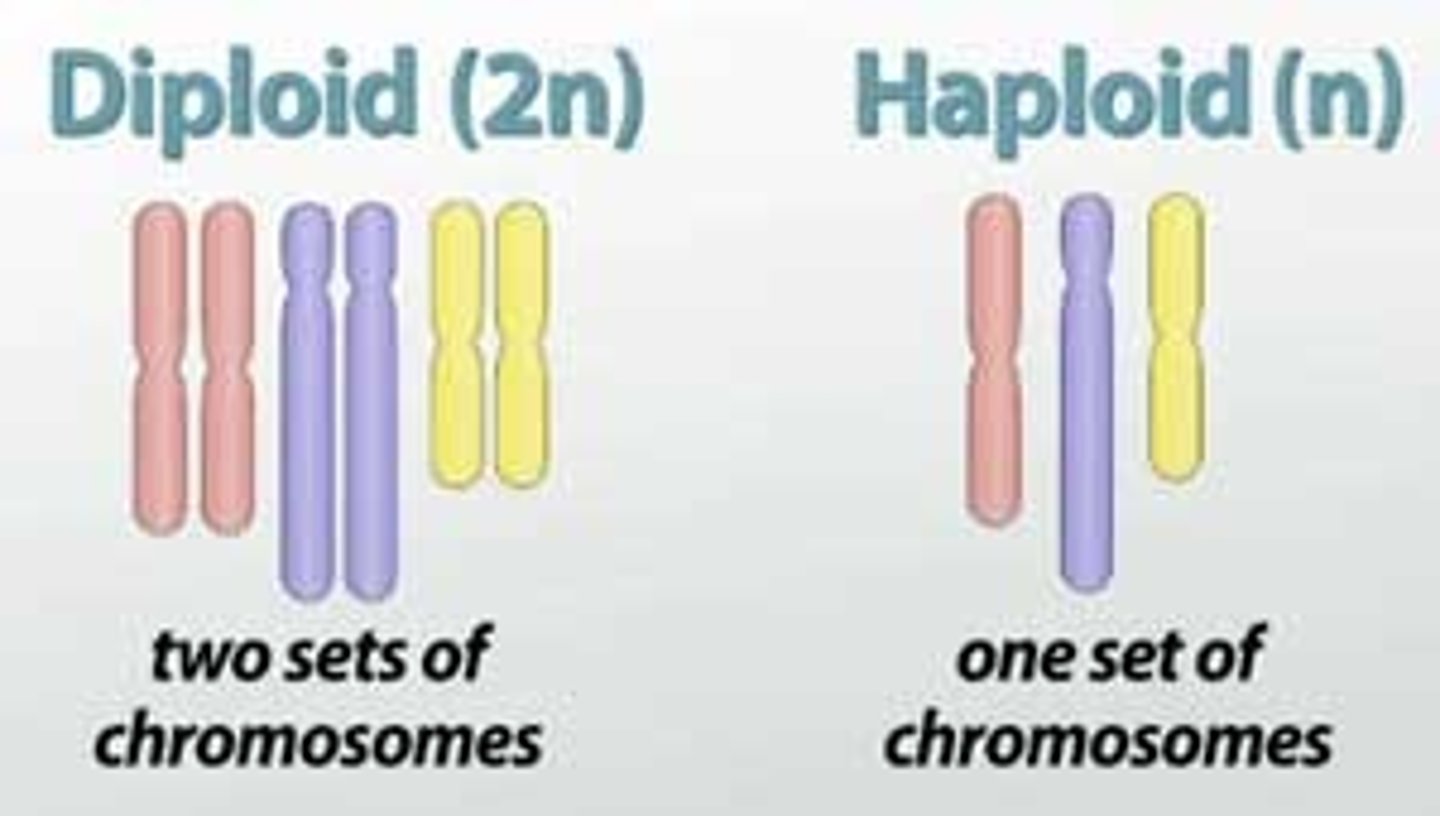
Reproductive cells (egg and sperm) have only one set (n), making them __________ with 23 chromosomes.
Haploid Cells
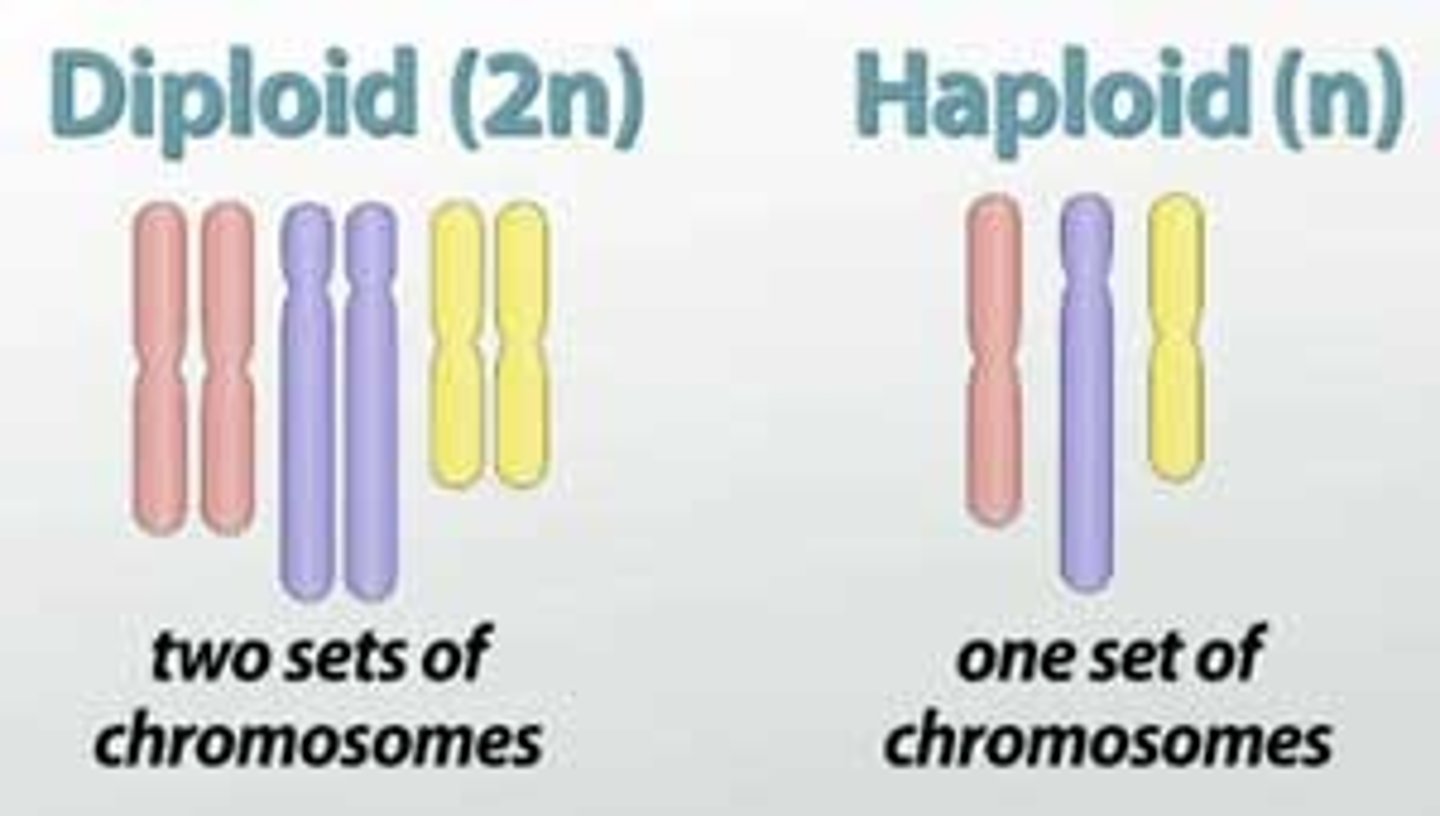
_______________________________ have the same length and centromere position but are NOT identical. They contain genes controlling the same characteristic at the same position.
Homologous Chromosomes
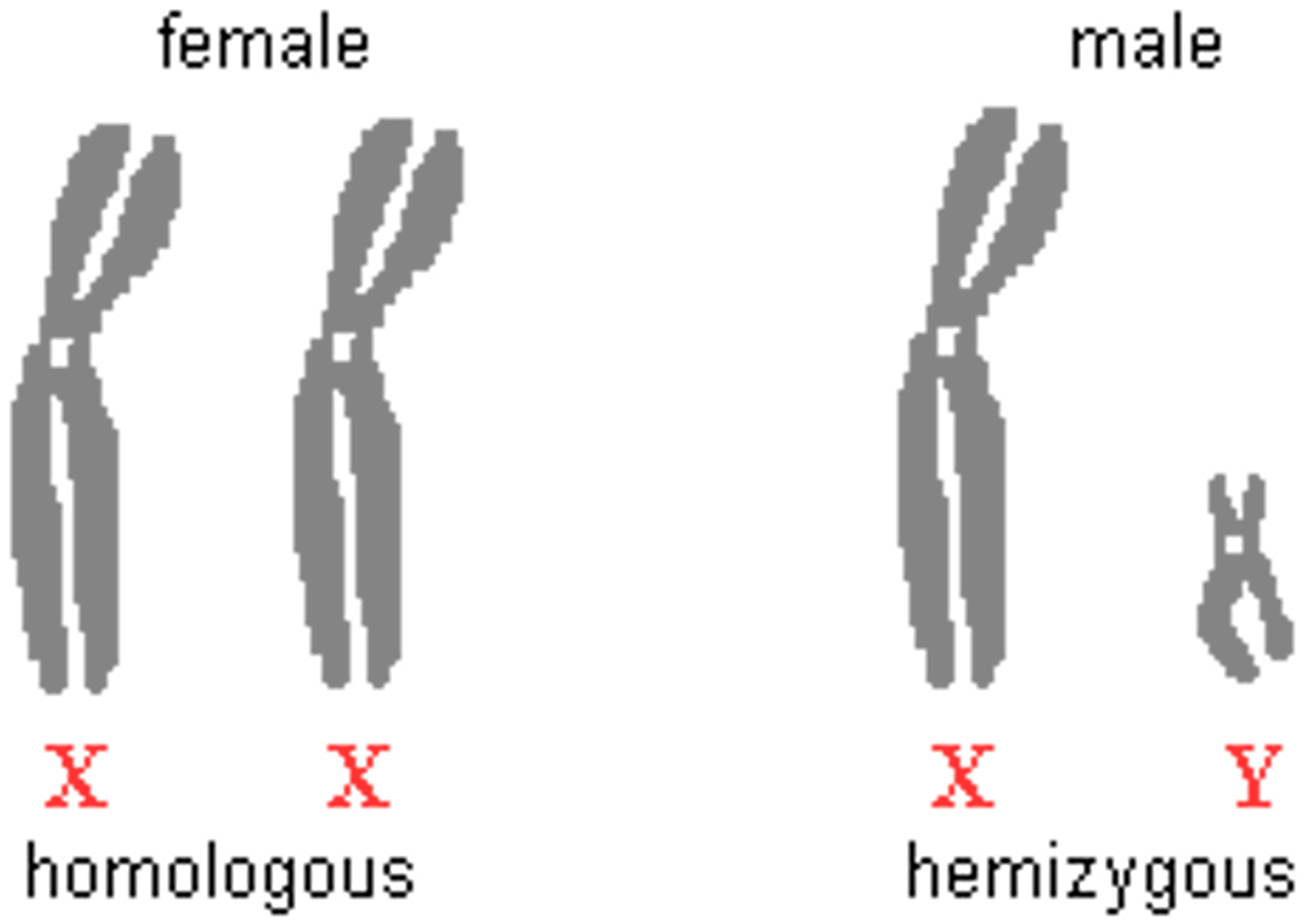
Chromosome 23 are the _____________________: XY = Male, XX = Female.
Sex/Reproductive Chromosomes in Humans
____________________ chromosomes are circular, and these cells typically have only one (n) whereas _________________chromosomes are linear and usually exist in pairs, making these cells diploid (2n).
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Chromosomes
Human __________ cells: Diploid (2n) = 46 chromosomes (23 pairs). Human ______________ cells (egg and sperm): Haploid (n) = 23 chromosomes.
somatic; reproductive/sex
Produces 2 identical cells (mitosis in eukaryotic cells, binary fission in prokaryotic cells).
Asexual Reproduction
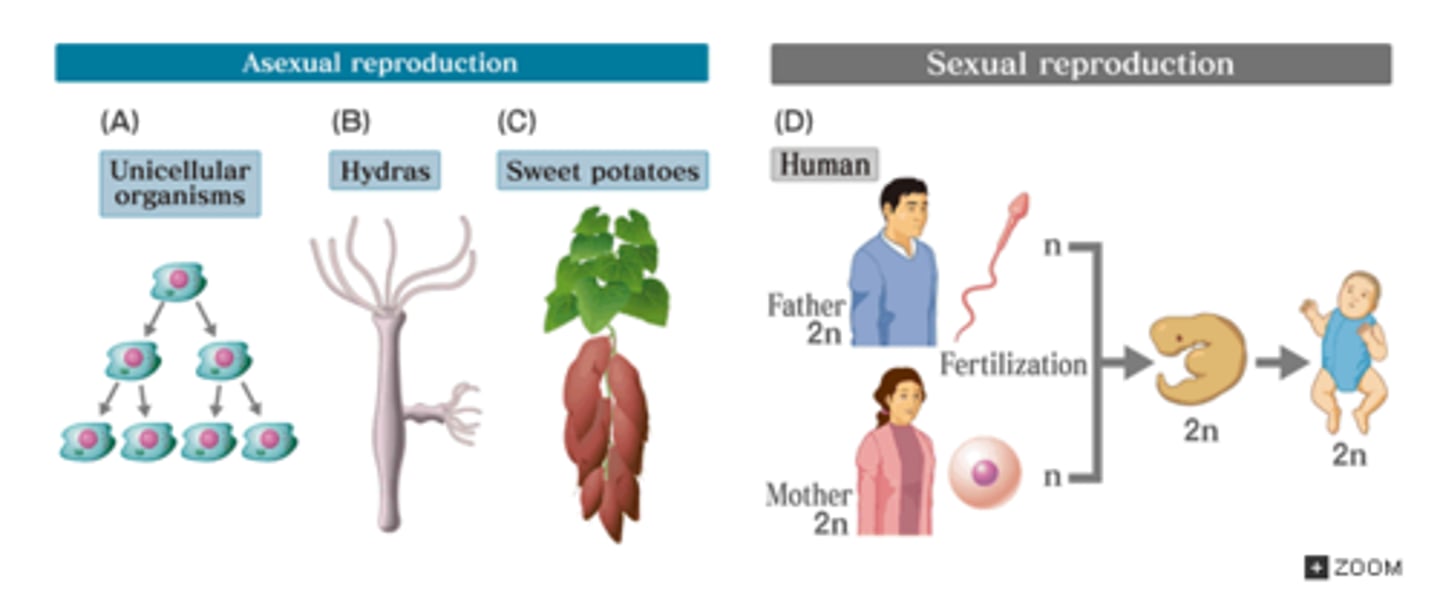
Produces 4 non-identical cells (meiosis - in eukaryotic cells only).
Sexual Reproduction
Bacteria propagate by ________________, resulting in two identical cells. No mitosis needed since there is only a single circular chromosome.
Binary Fission
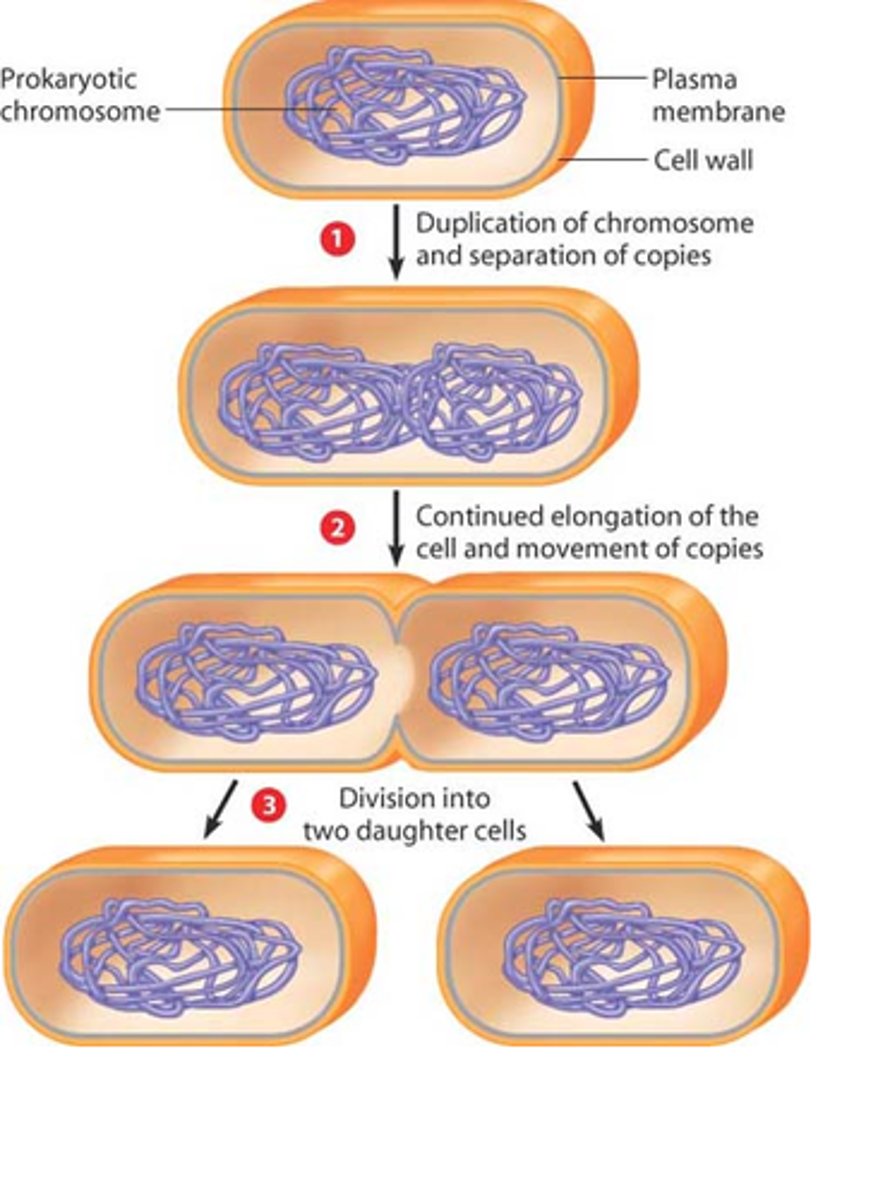
Binary Fission Steps include: Chromosomal DNA is copied & the cell _____________ (begins with an 'e'), Copied chromosomes move away from one another. A _____________ furrow forms. A _______________ is built & divides the cell while plasma membrane & cell wall are formed. Finally the cell pinches into 2 identical ___________ cells!
elongates; cleavage; septum; daughter
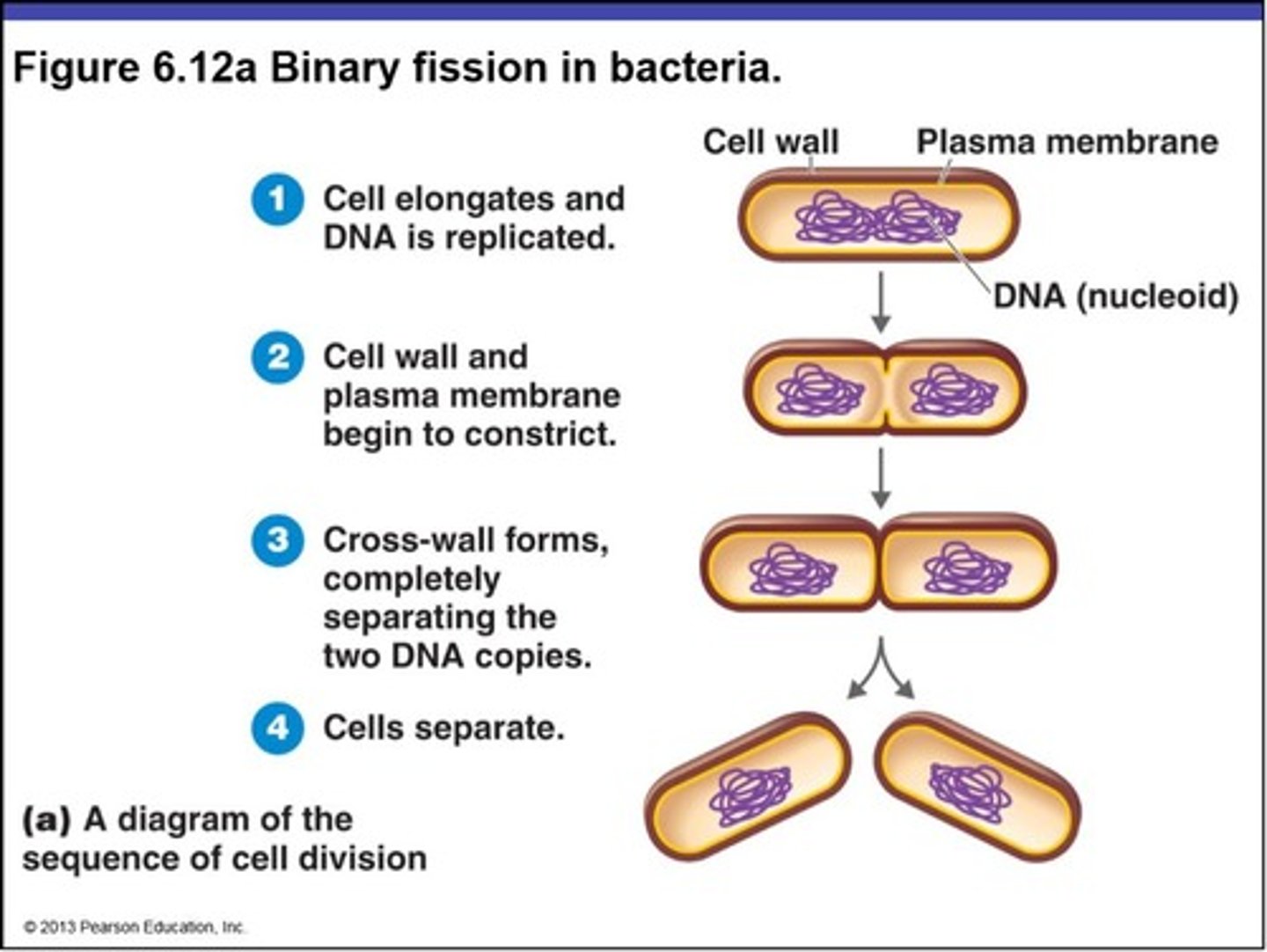
Asexual or Sexual? Results in two identical cells.
Asexual Cell Division
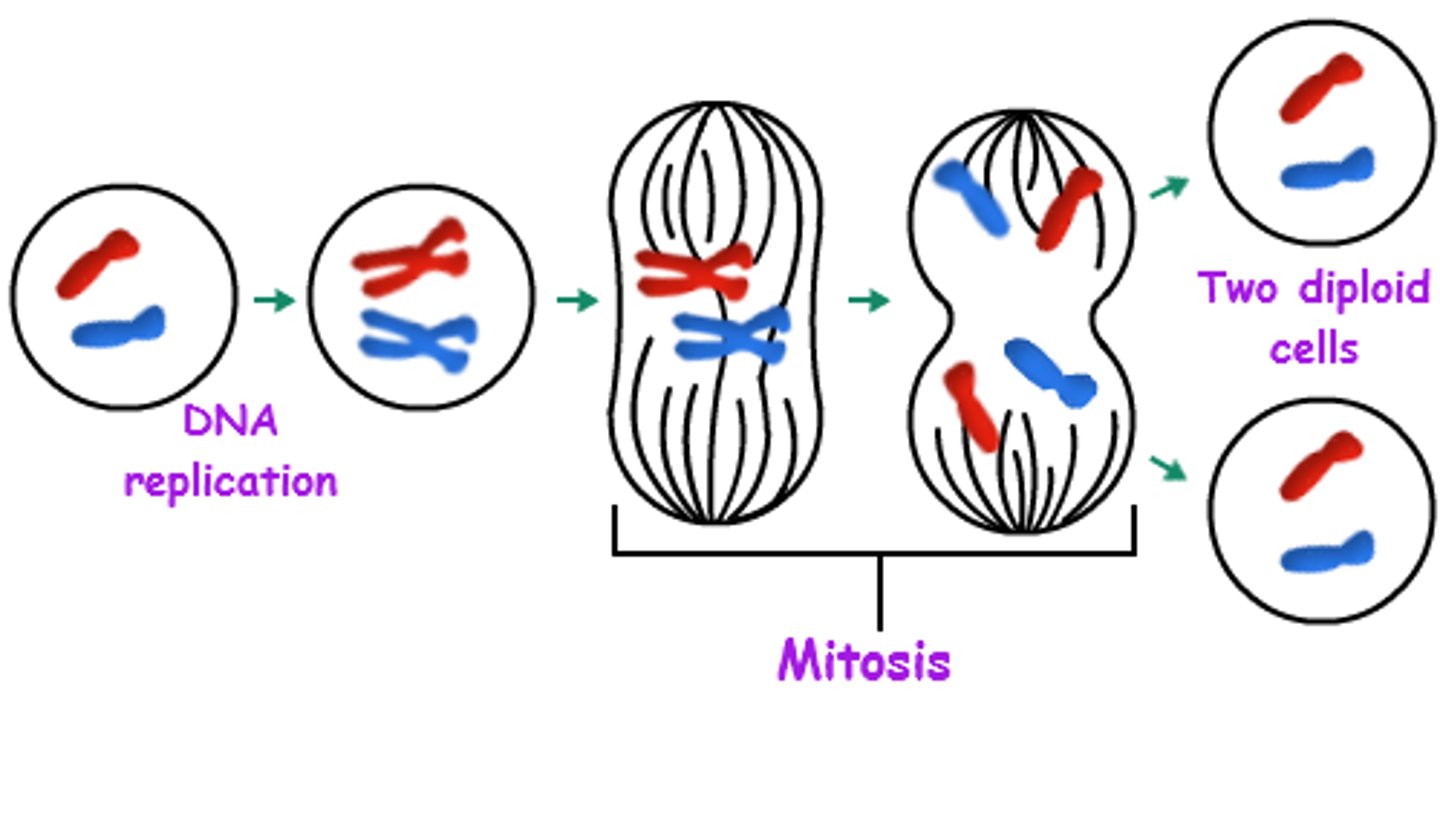
The orderly sequence of events from a single parent cell dividing into two daughter cells and their subsequent division.
Cell Cycle
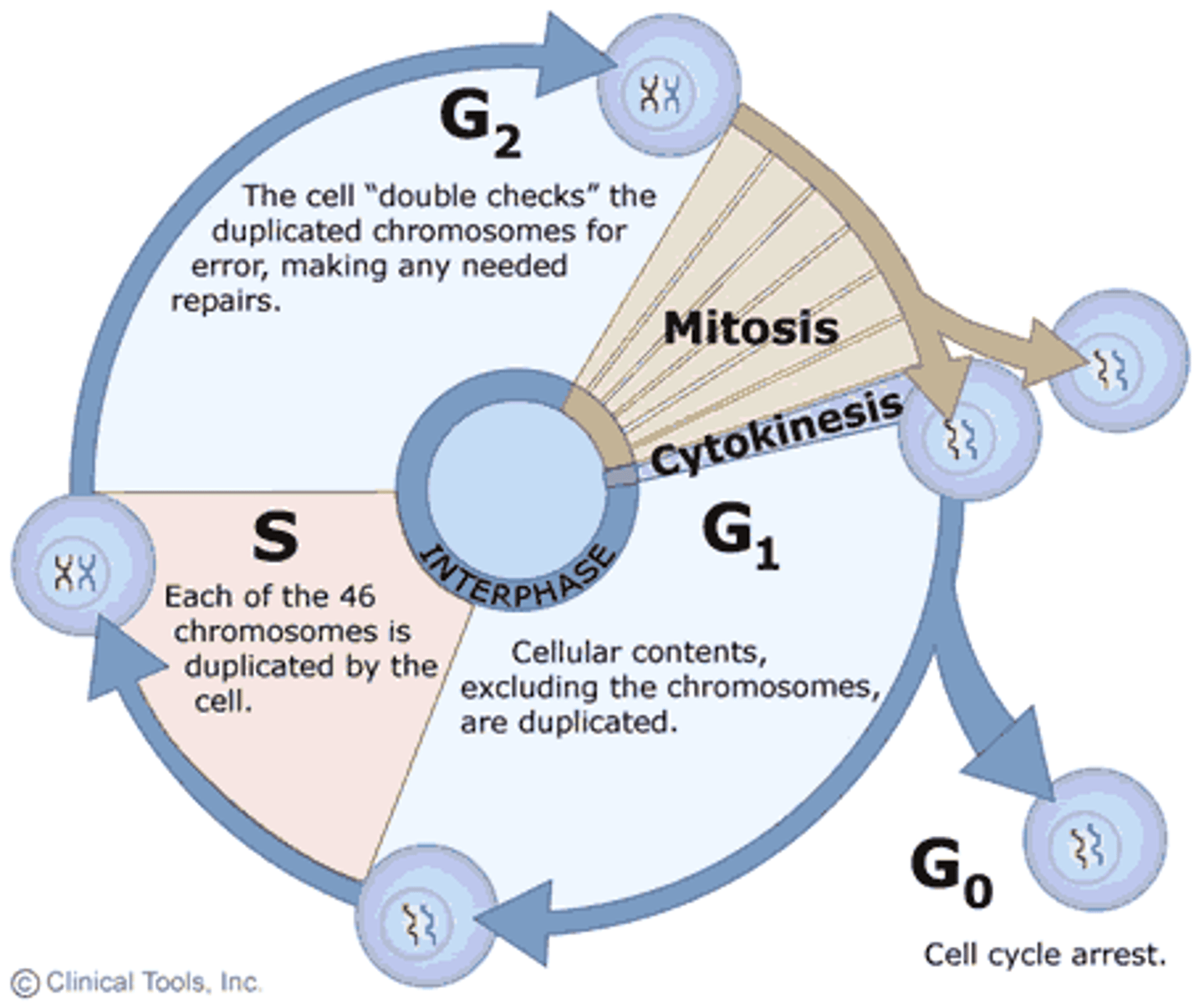
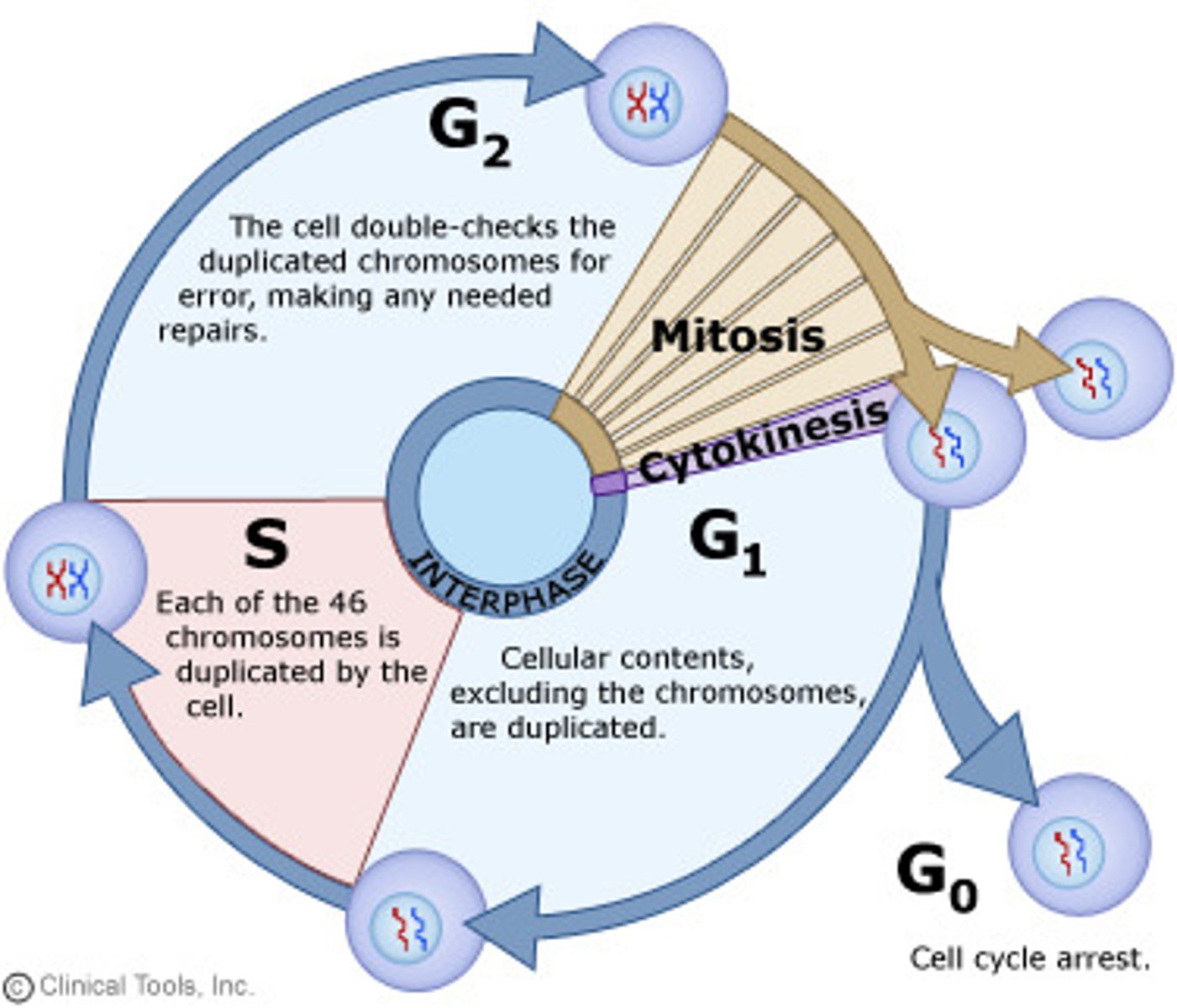
90% of cell cycle - Cell grows, DNA duplicates, prepares for division.
Interphase
One of the 2 MAIN "Phases" of the cell cycle where duplicated chromosomes are segregated into daughter nuclei & cytoplasm is also divided.
Mitotic Phase
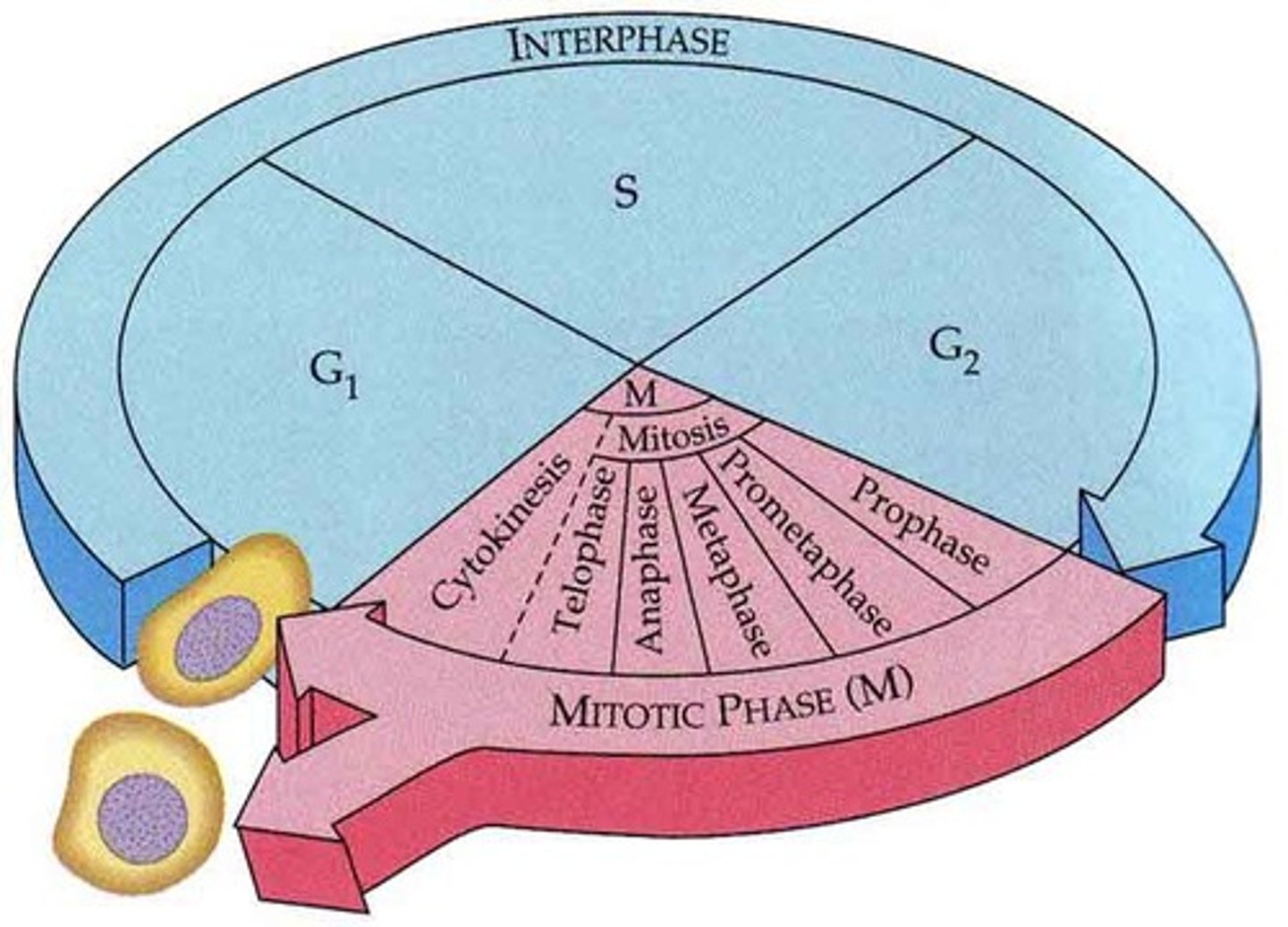
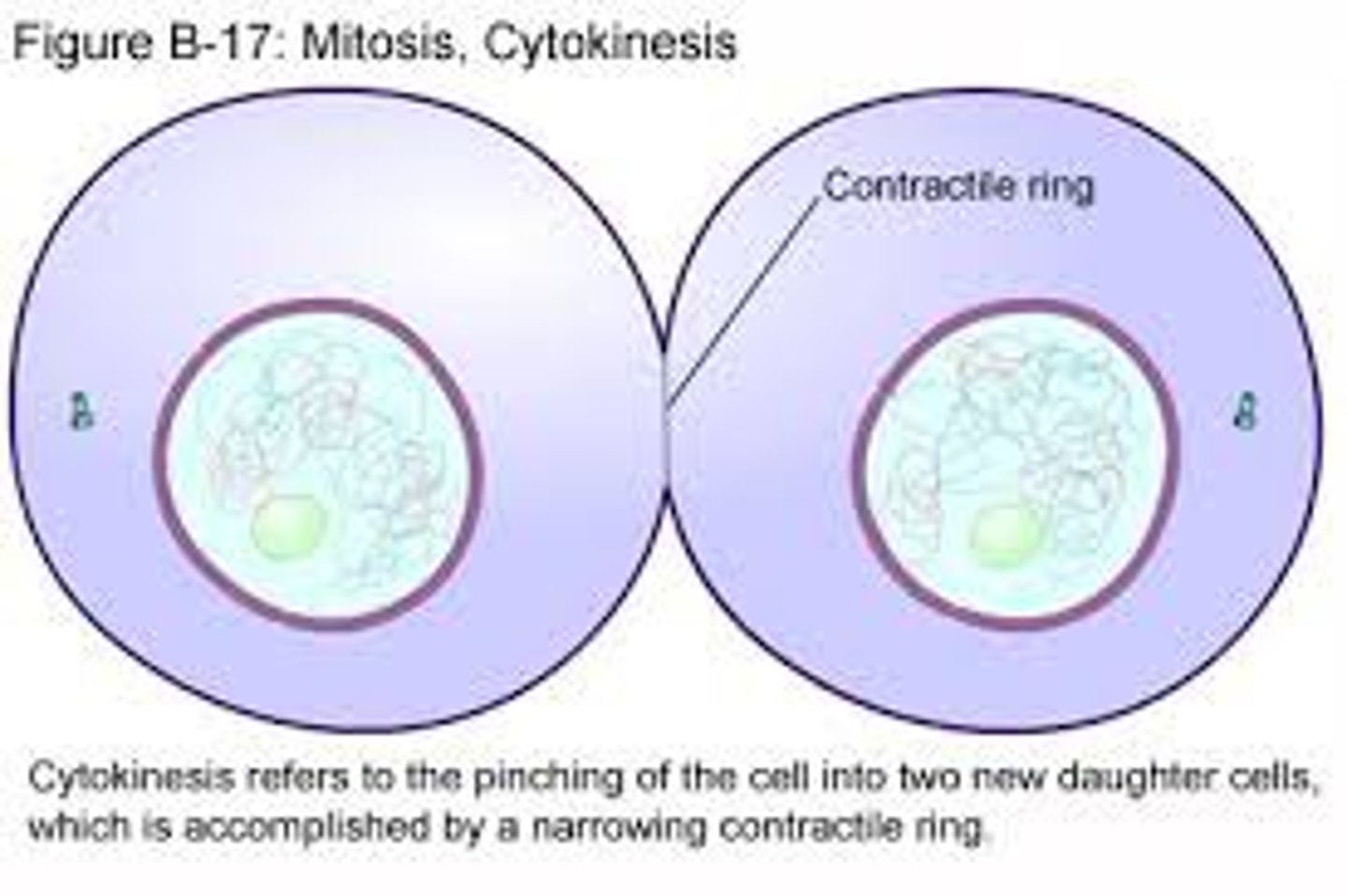
Division of the cytoplasm.
Cytokinesis
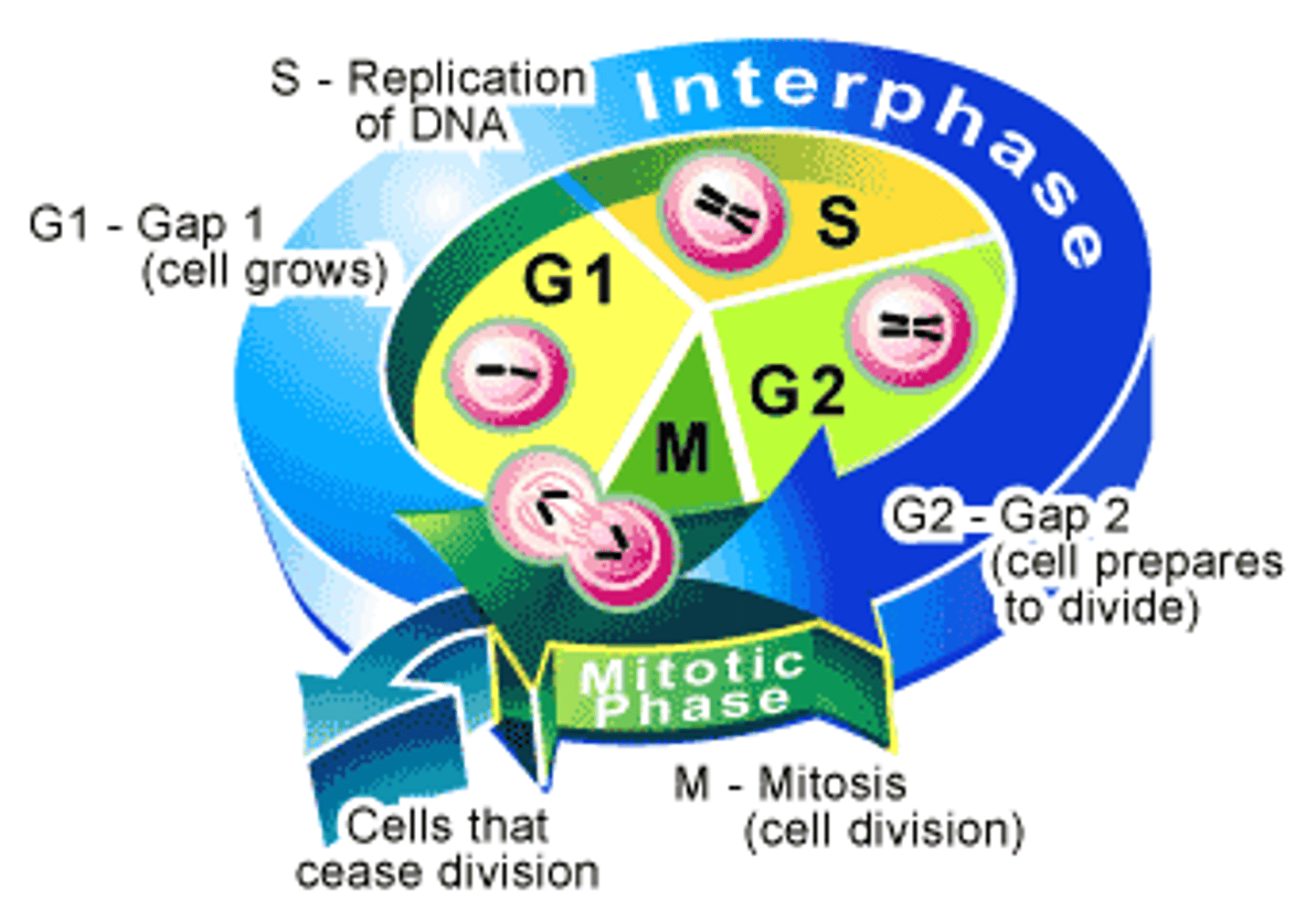
What are the Interphase Subphases & what do they generally do?
G1 phase - Cell grows and performs normal function. S phase - Chromosomes duplicate. G2 phase - Cell prepares other components for division.
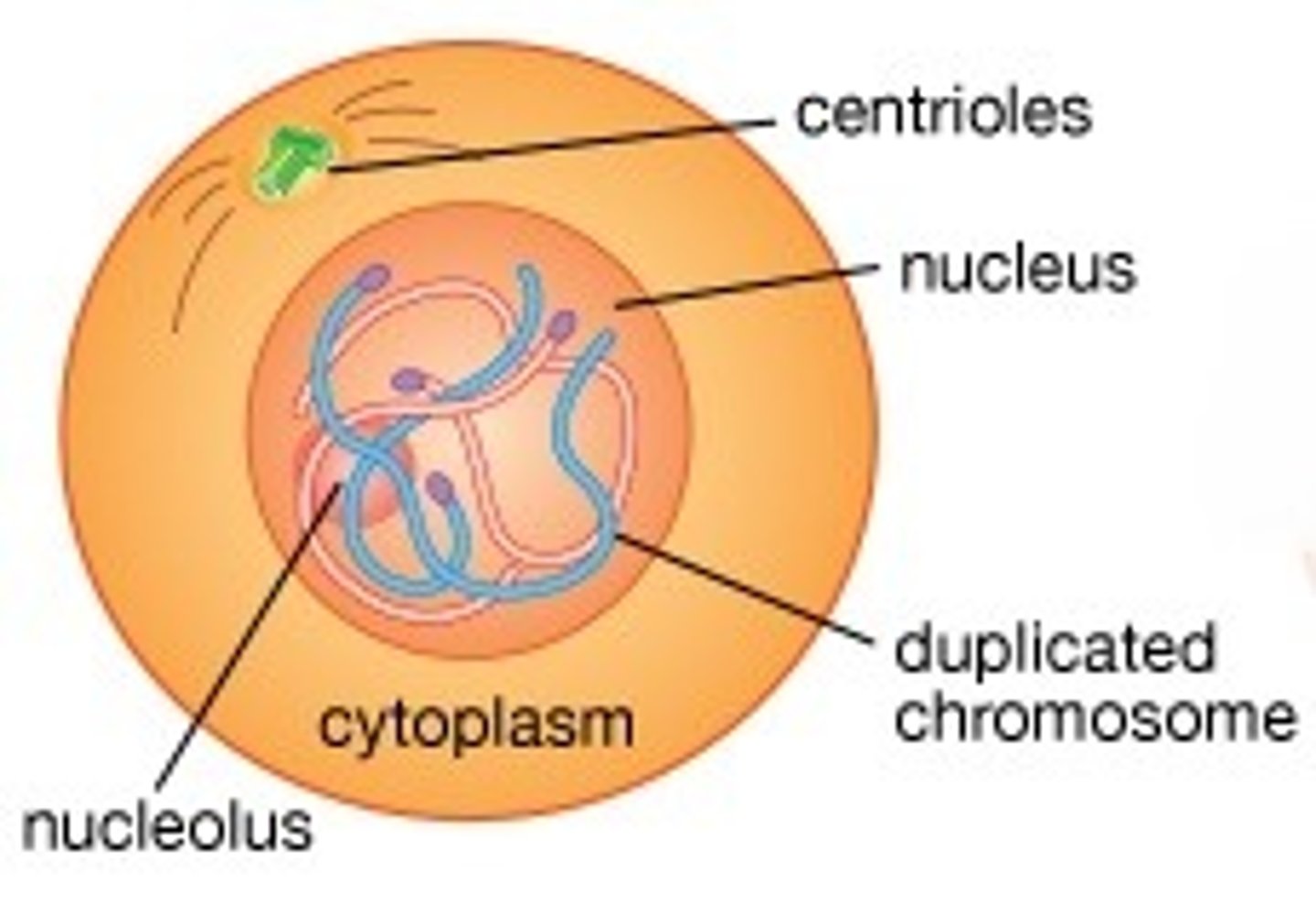
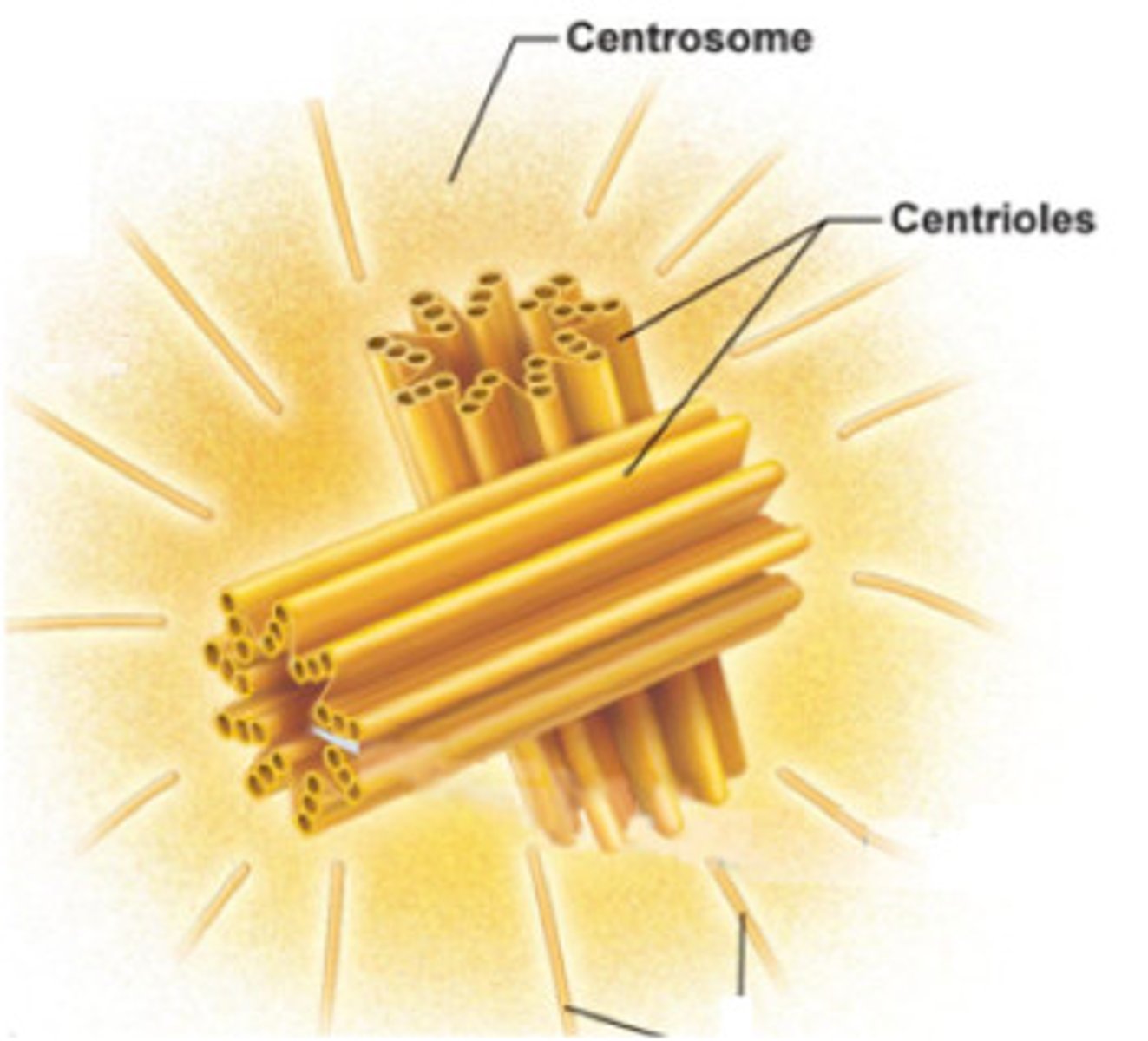
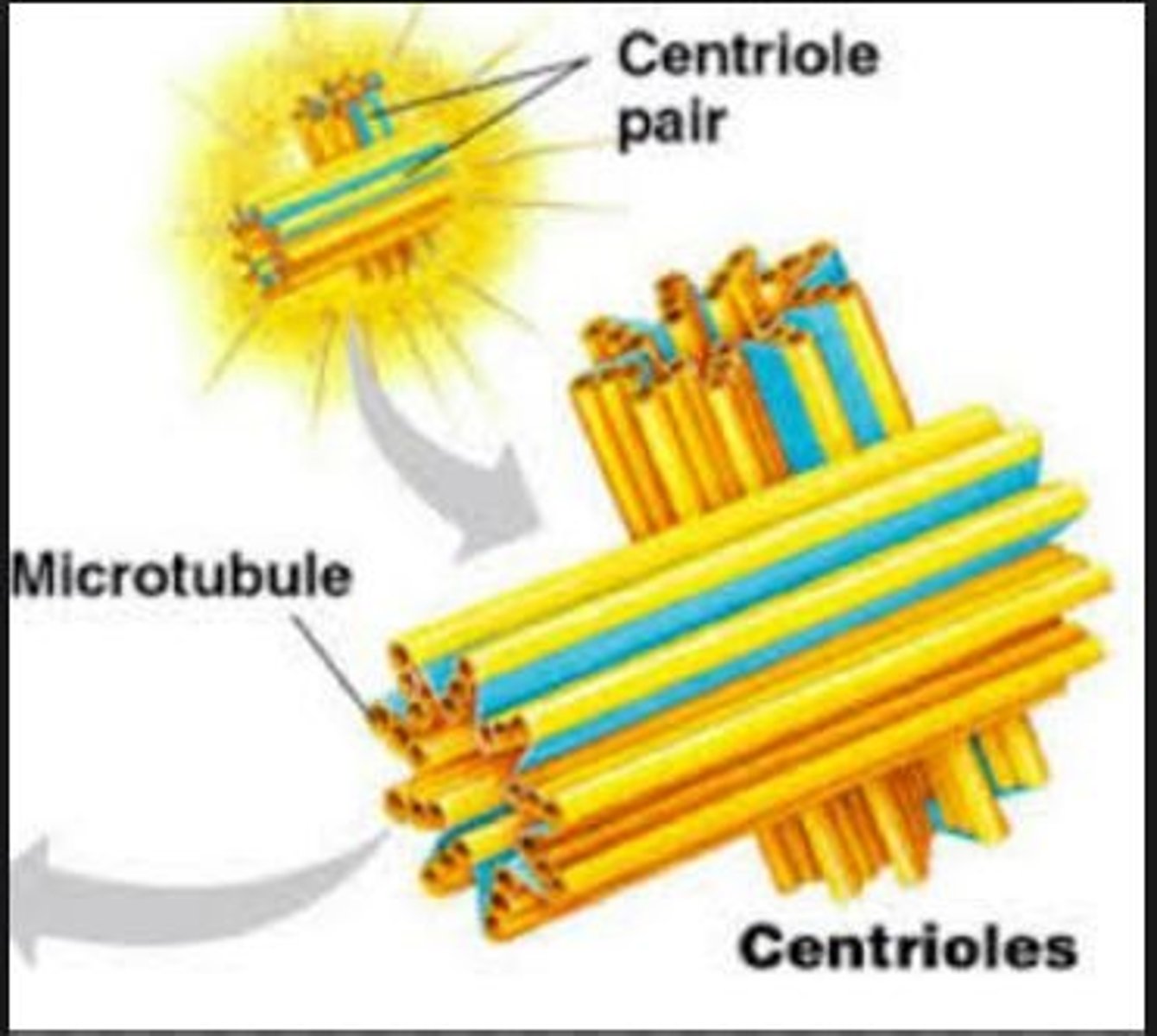
Composed of two centrioles. Organizes microtubules of the spindle apparatus.
G2 Centrosomes
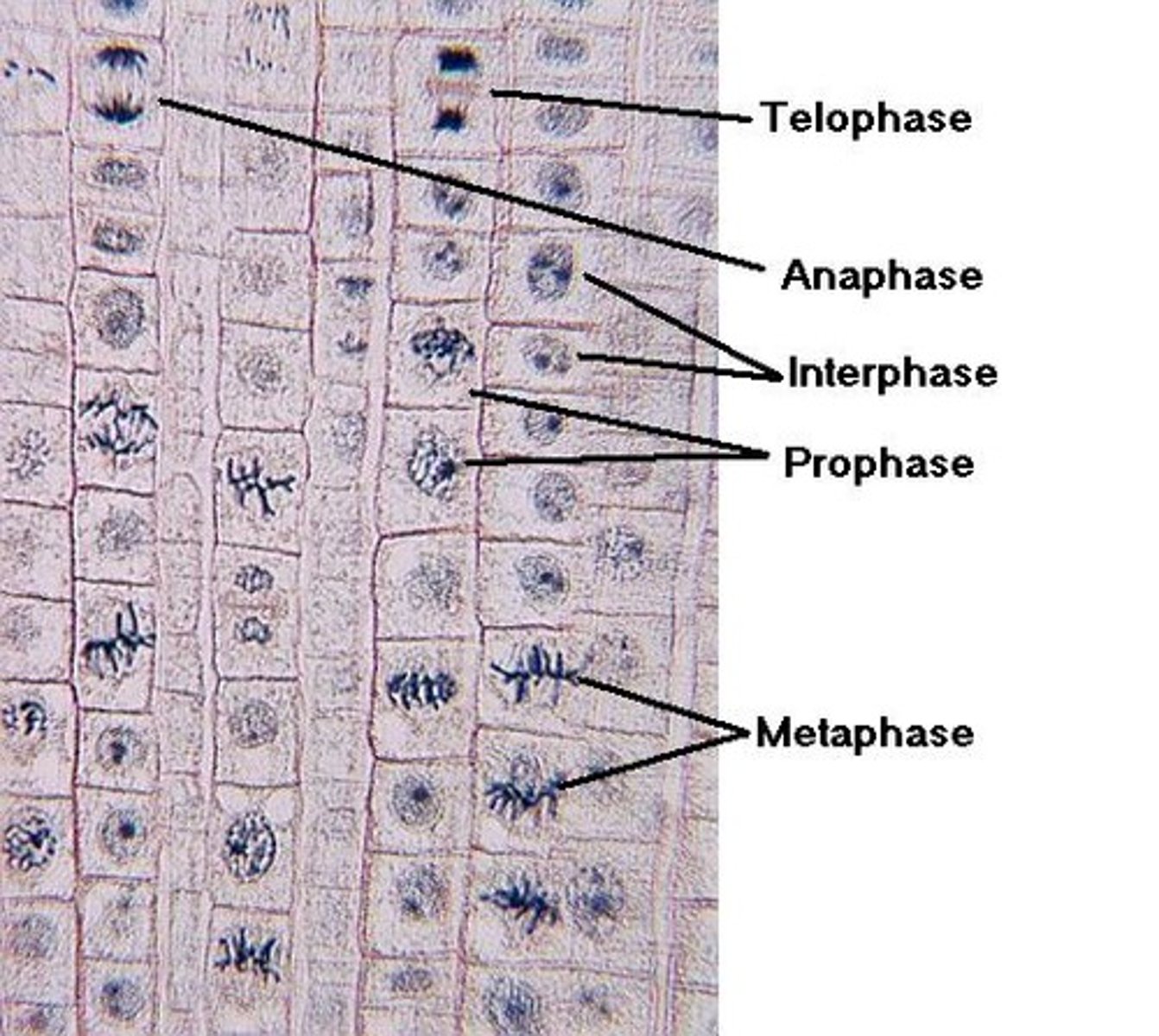
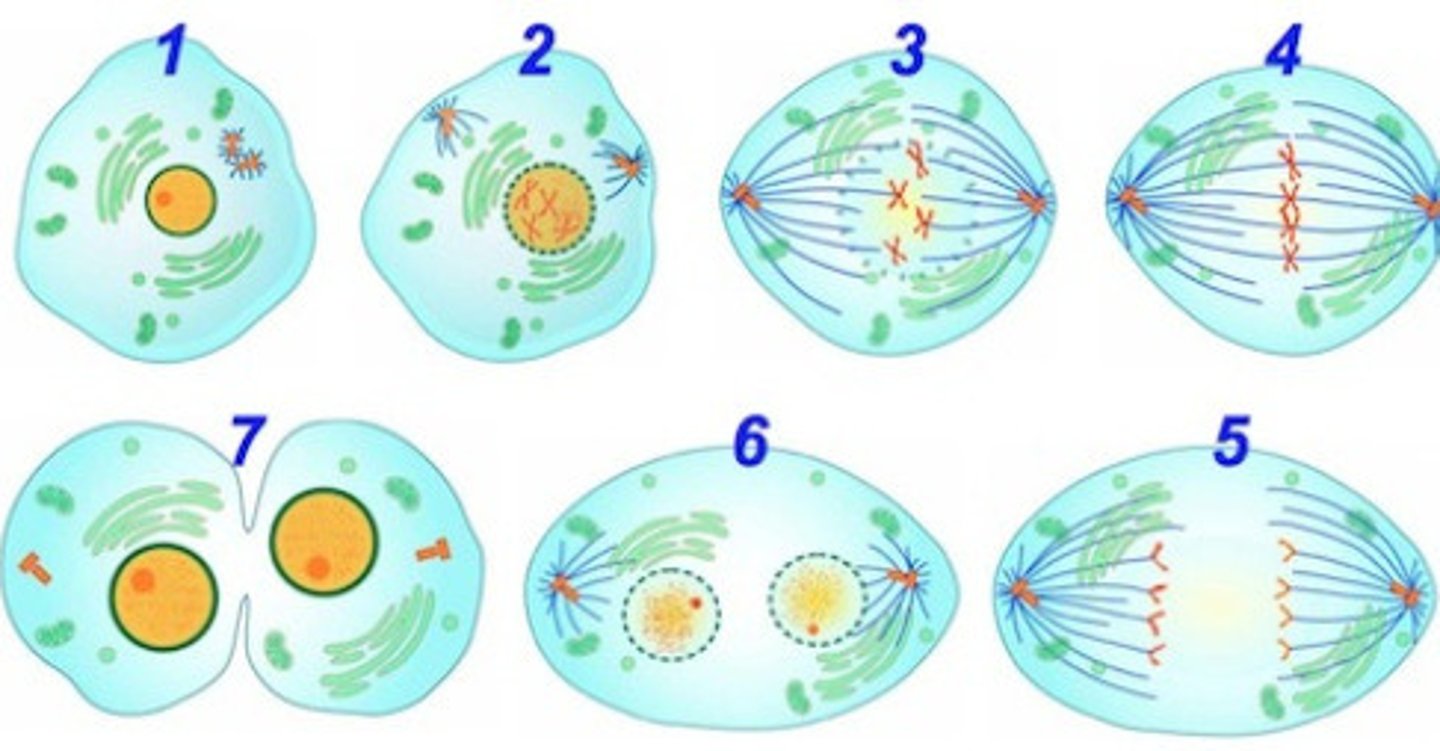
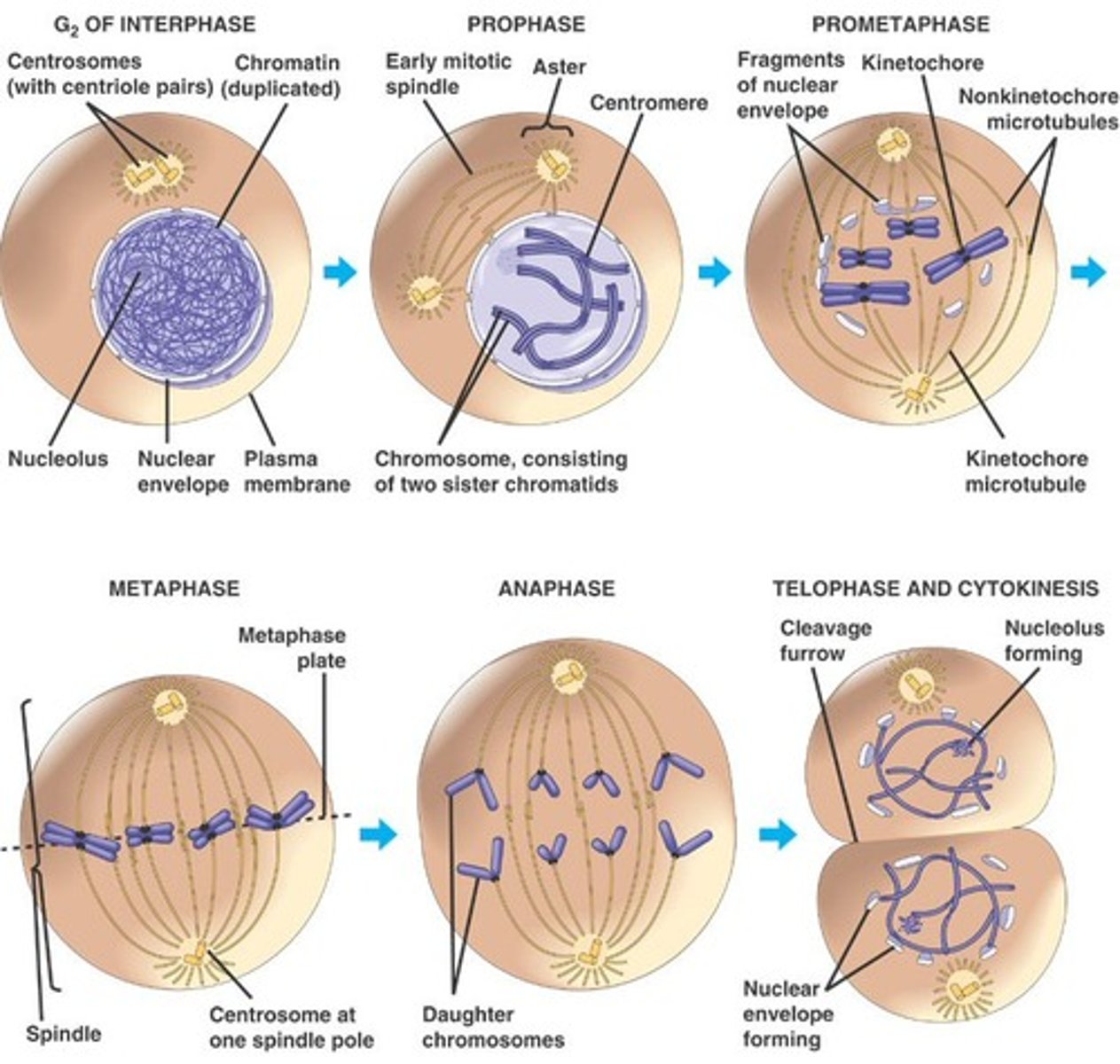
Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase.: These stages are part of __________________
Mitosis
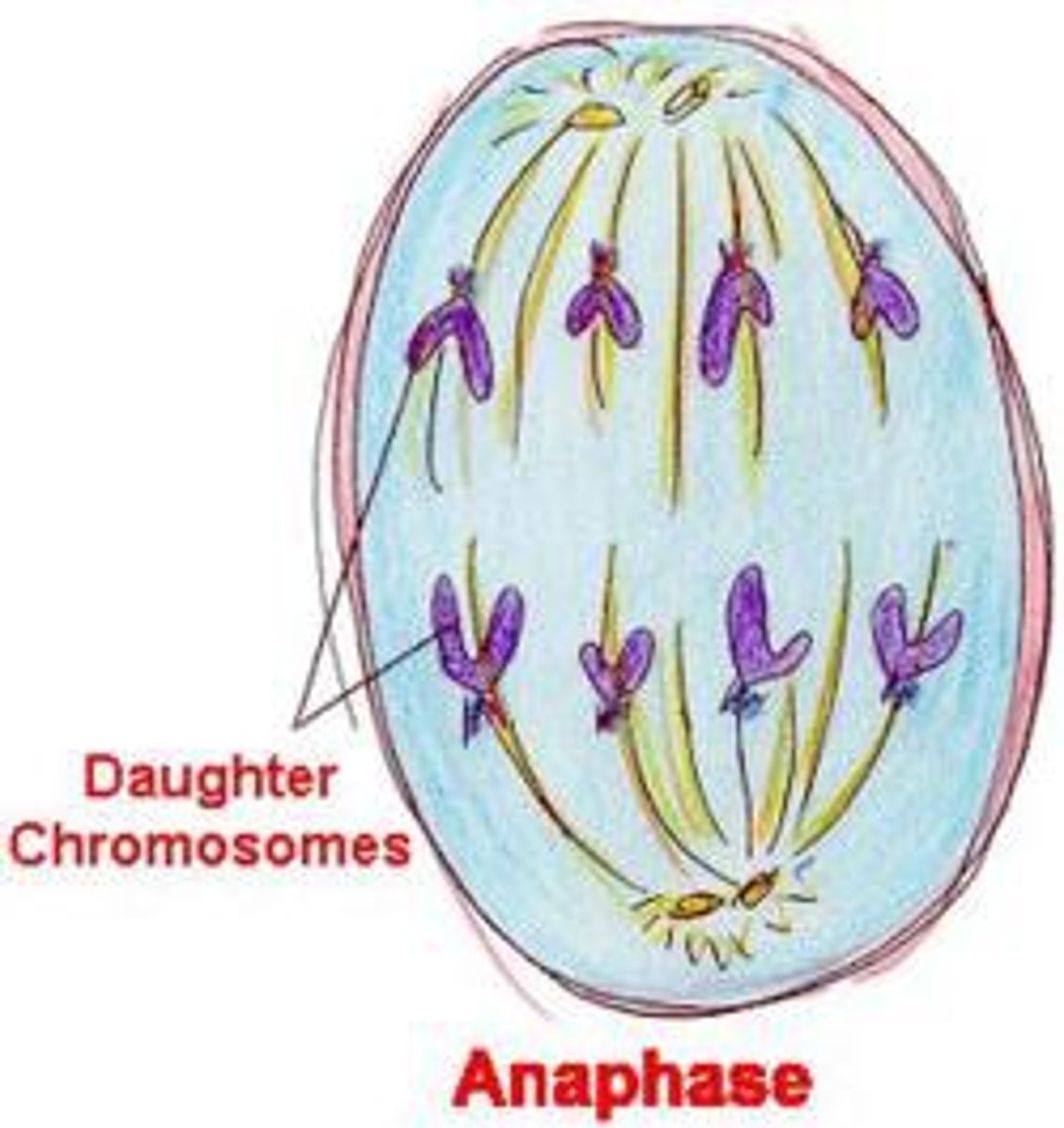
Sister chromatids separate and migrate to opposite poles of the cell during ________.
Anaphase (Mitosis)
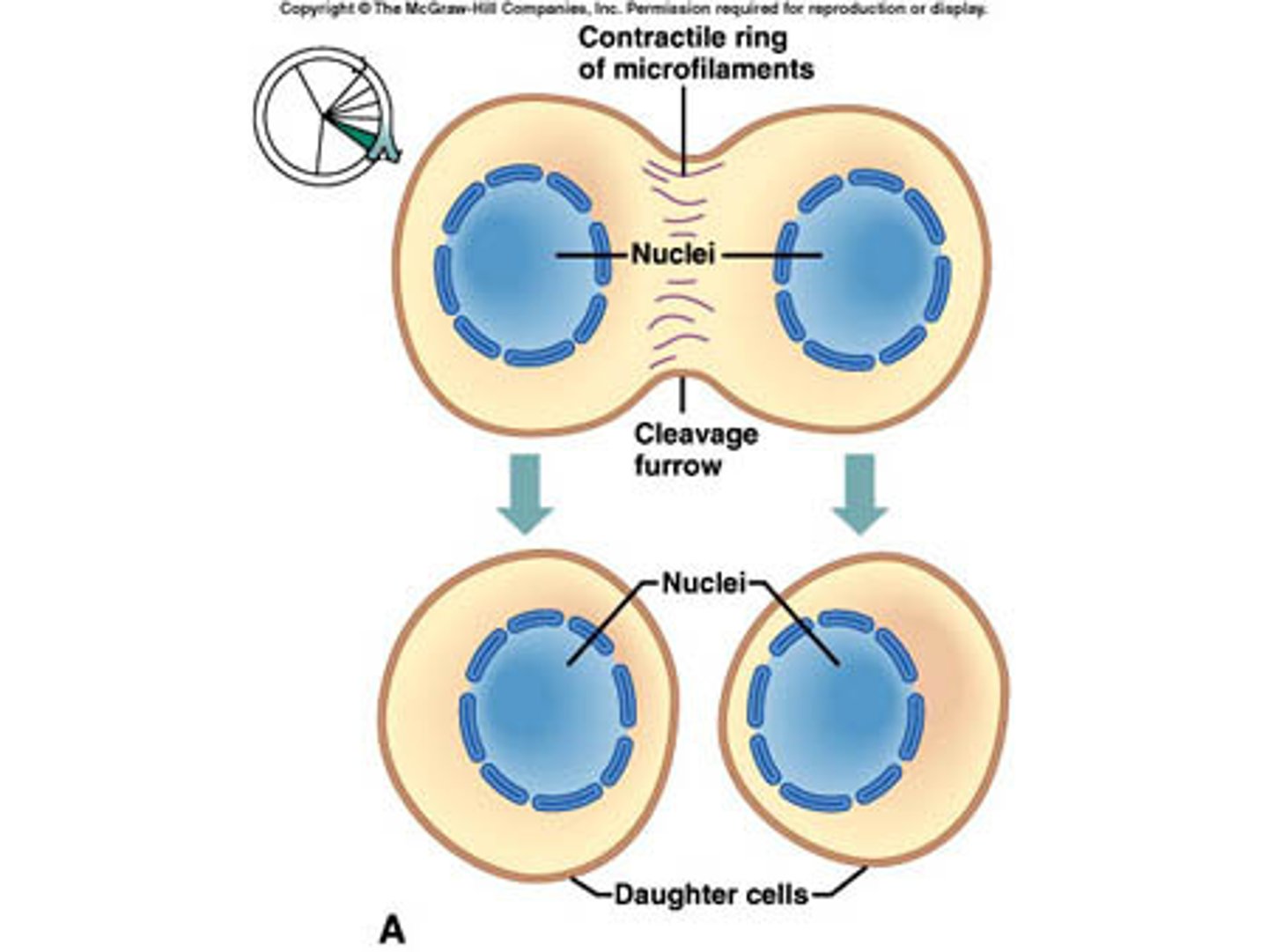
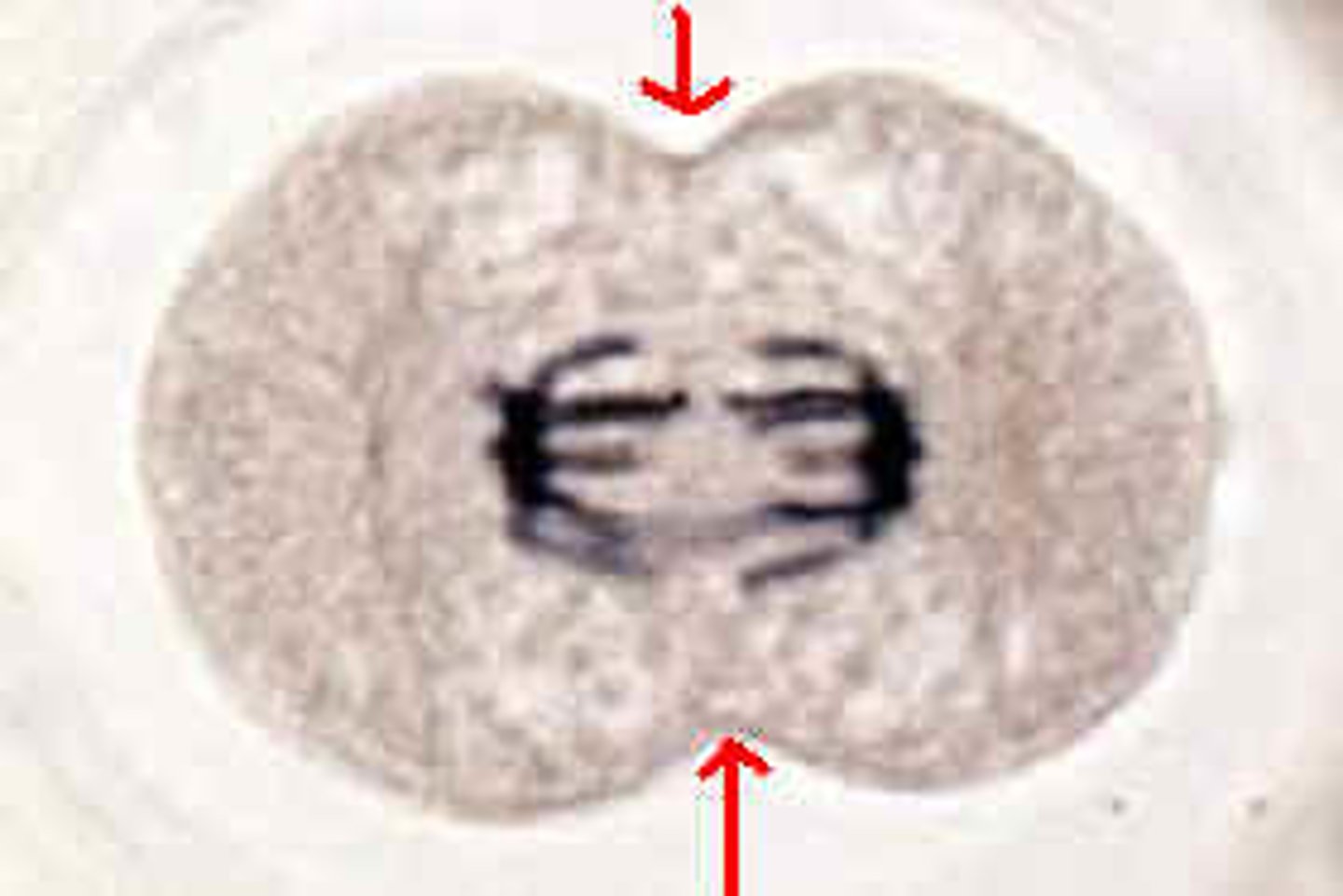
Occurs via cleavage (since animal cells lack a cell wall). A cleavage furrow forms, dividing the cell in two. A 'belt' of microtubules tightens until the cell is pinched apart.
Cytokinesis in Animal Cells
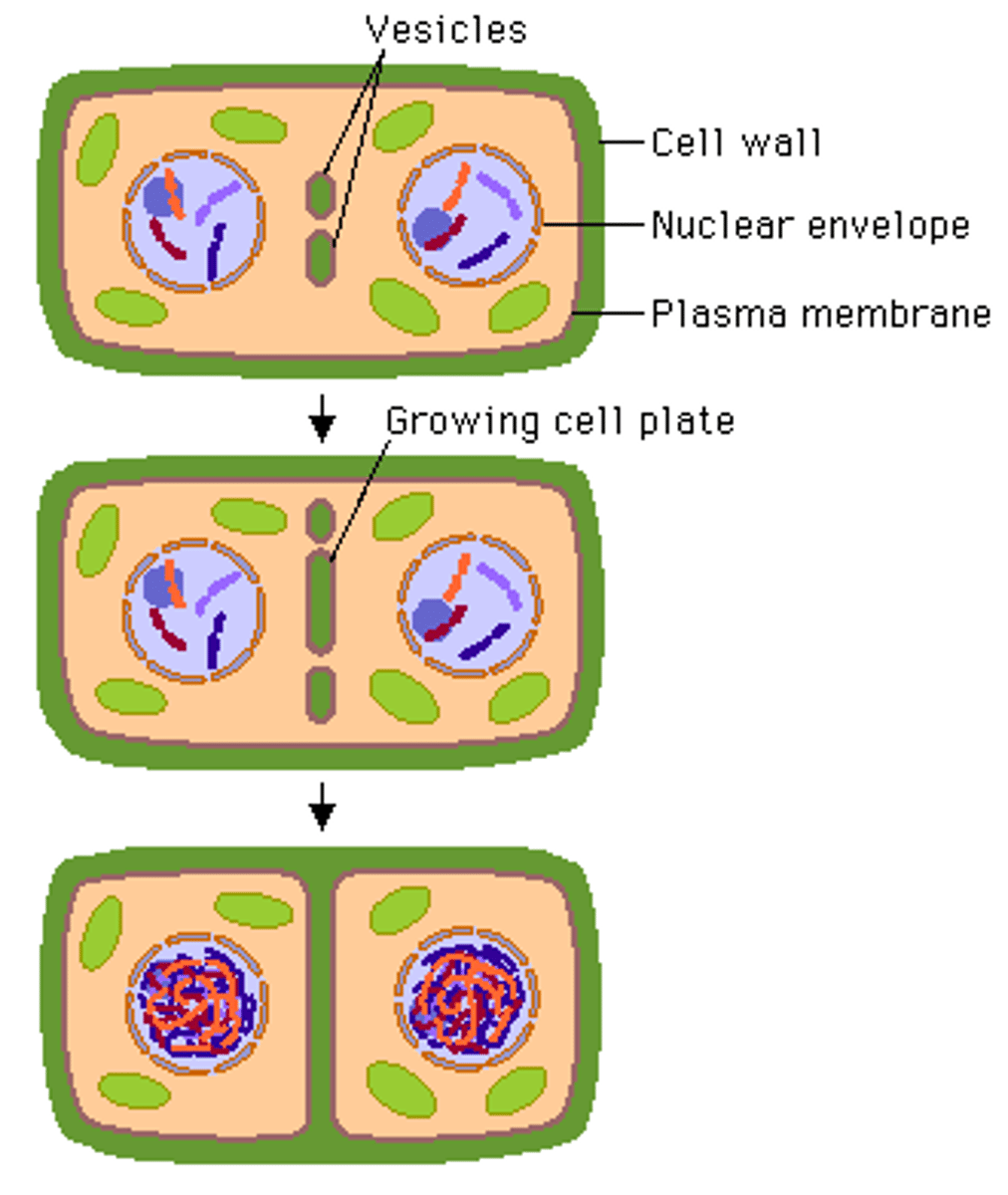
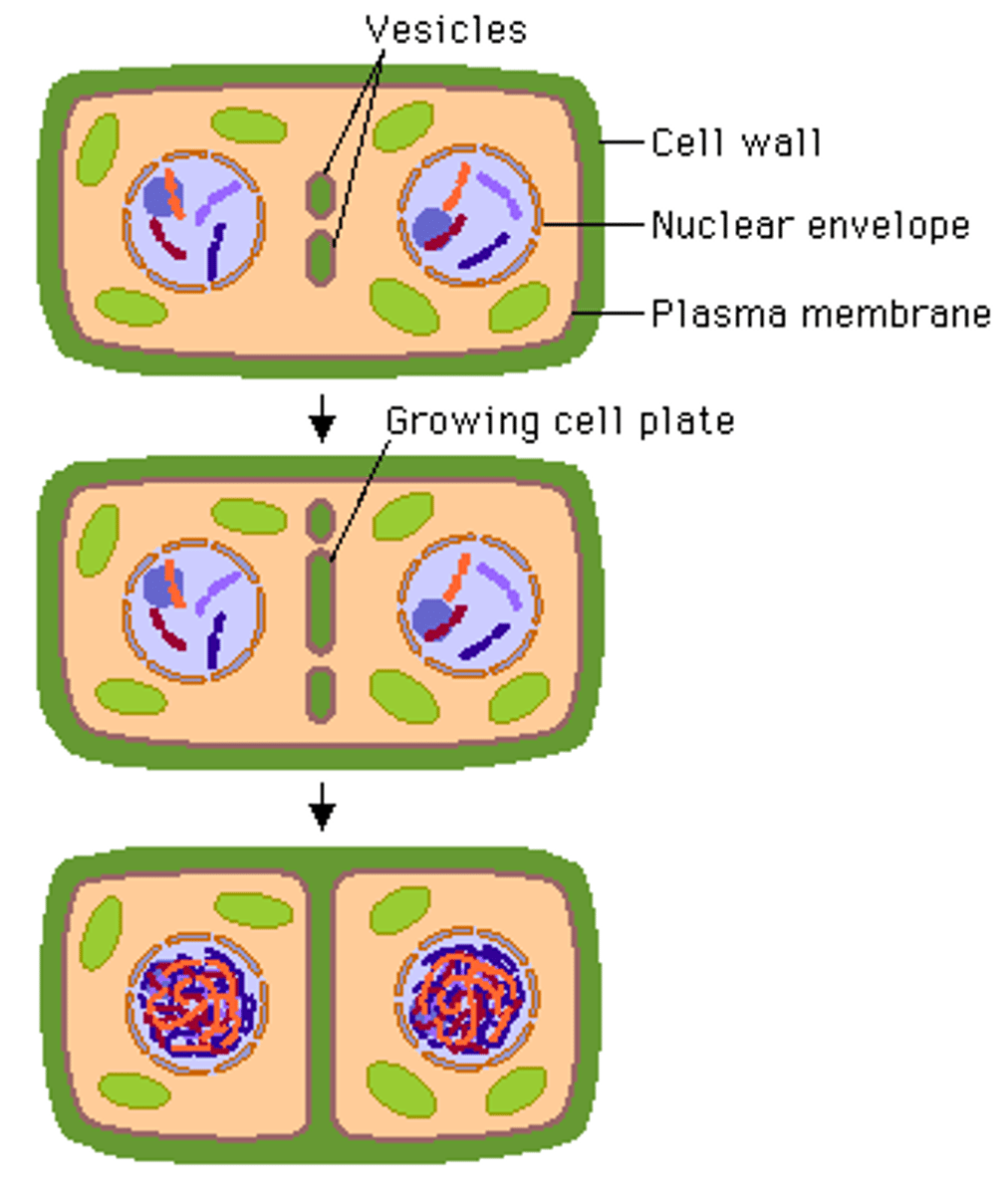
Occurs via formation of a cell plate (since plant cells have a cell wall). The cell plate grows progressively longer. Eventually, the cell plate fully divides the two new cells.
Cytokinesis in Plant Cells
Also known as Nuclear division ....is divided into five phases: Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase.
Mitosis
Simple process called binary fission. No nucleus, only a single circular chromosome. Results in two identical daughter cells.
Cell Division in Prokaryotes
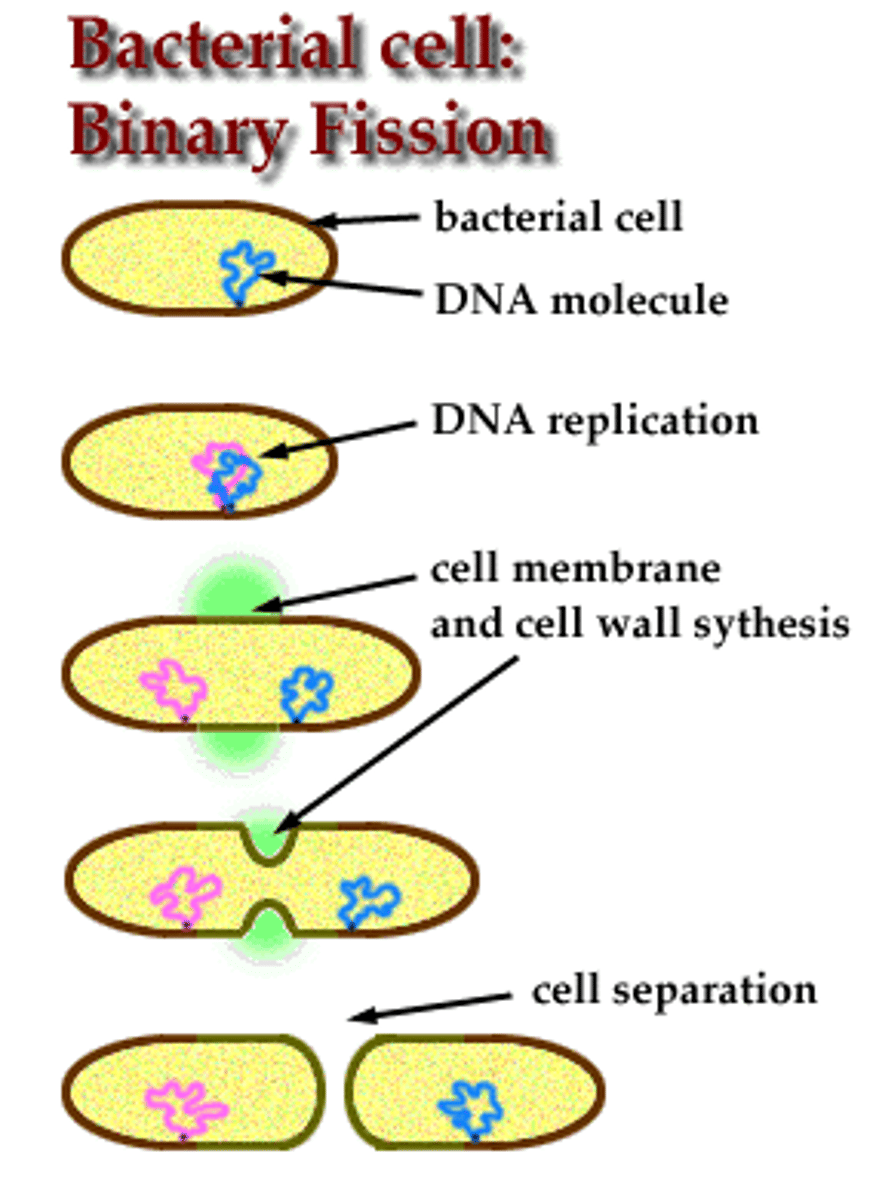
In binary fission, the _________________ of prokaryotes must be replicated and allocated into daughter cells to ensure they have the necessary genetic material for life.
genomic DNA
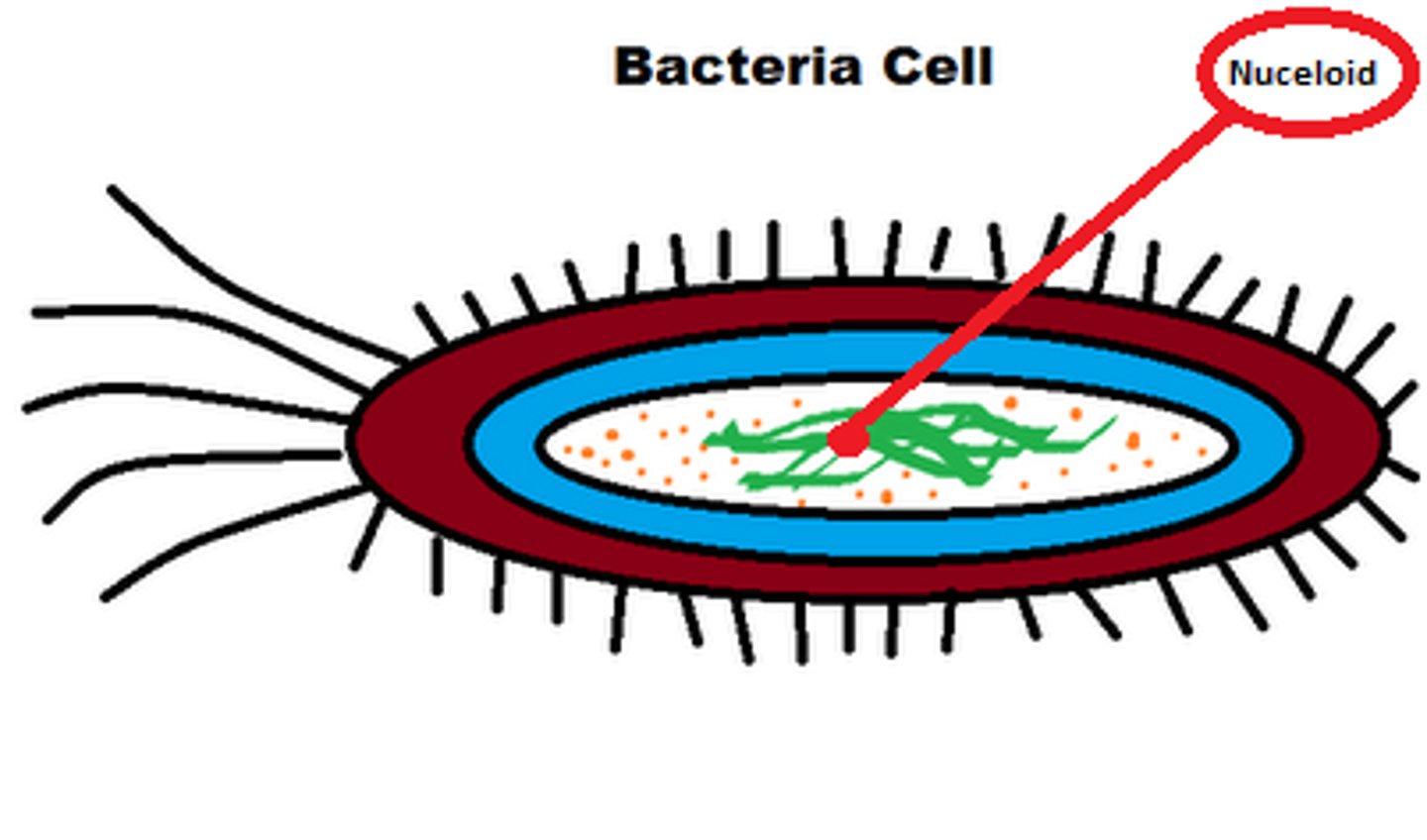
bacterial chromosome is located where within the cell?
nucleoid
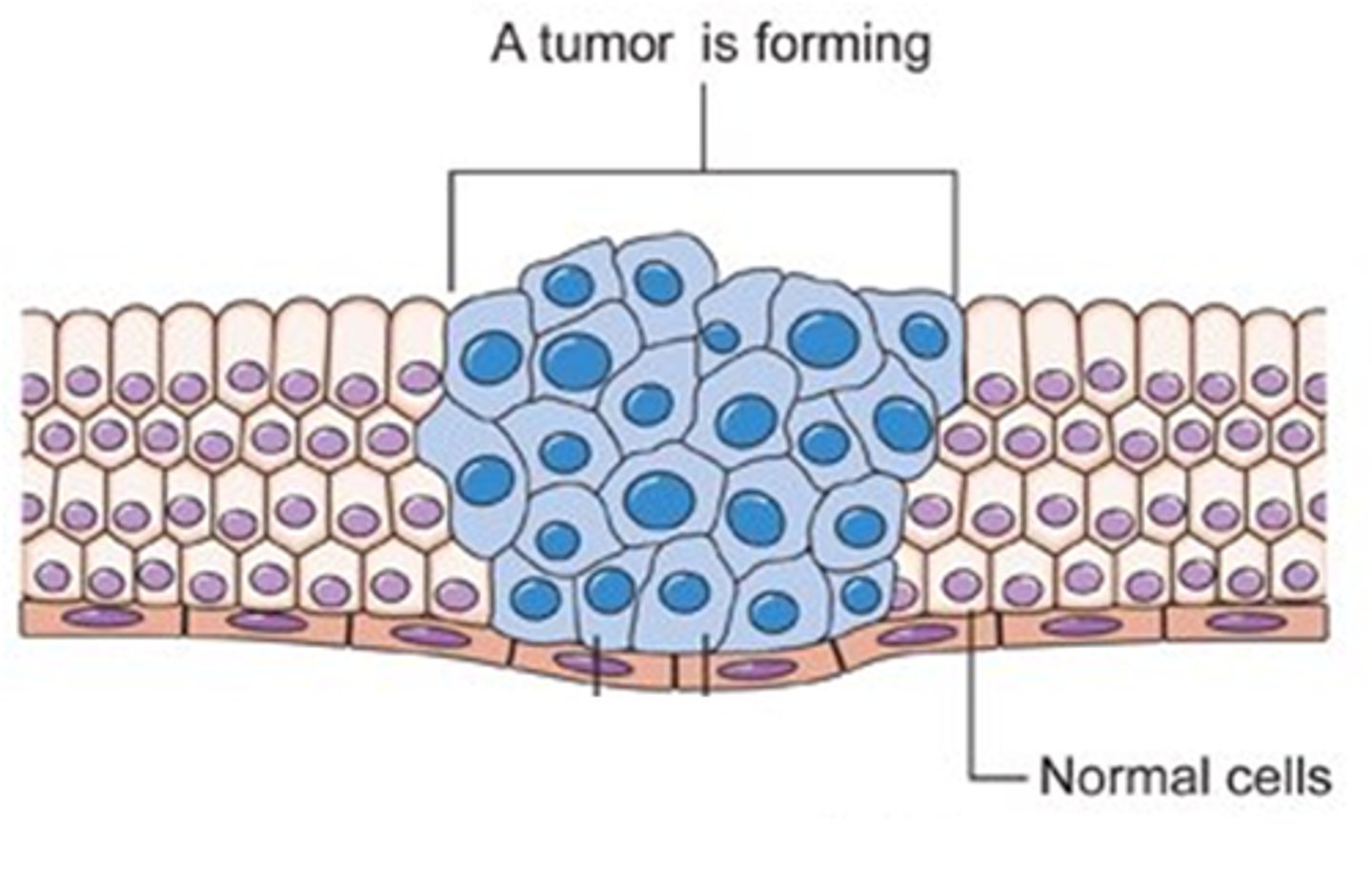
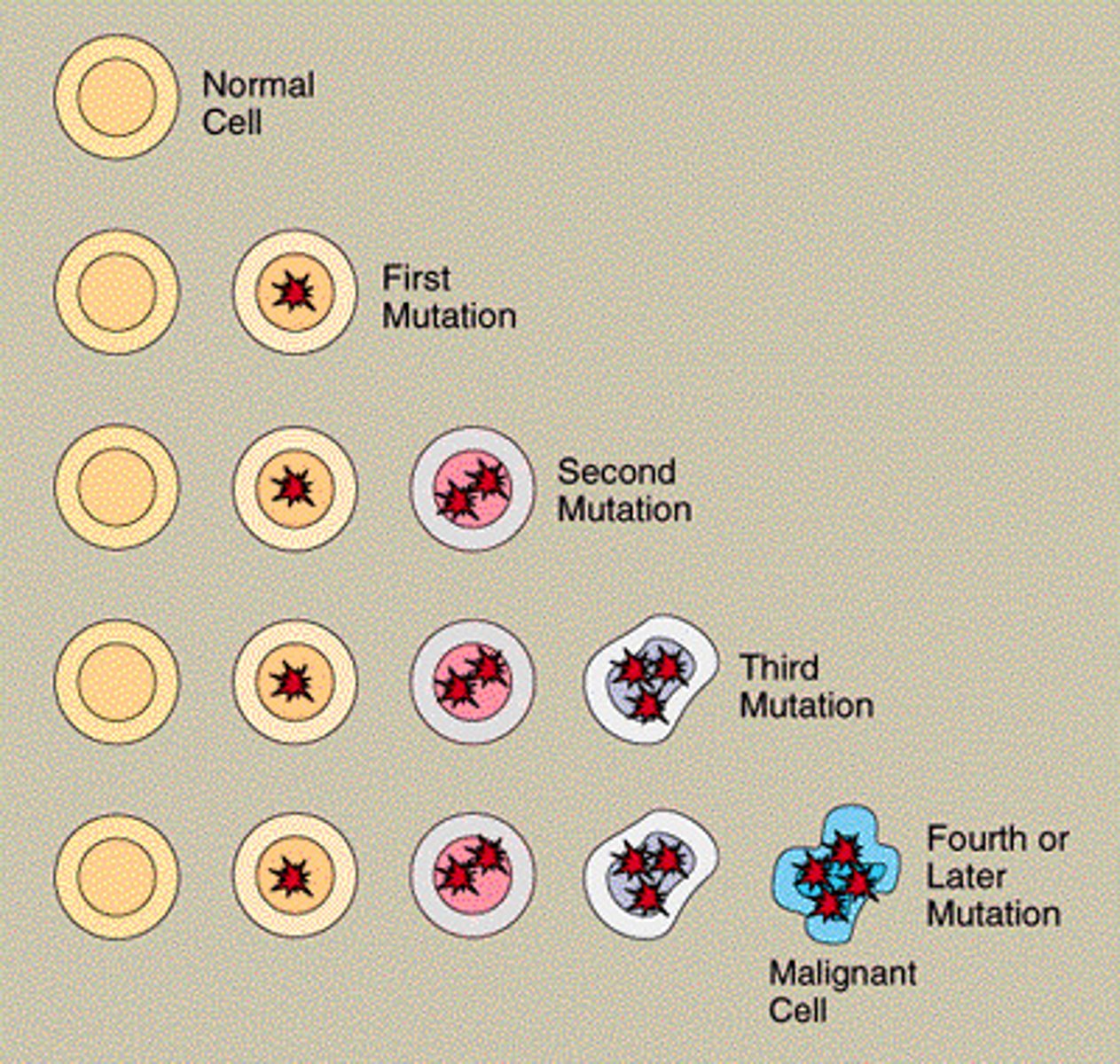
An abnormal mass of tissue formed by uncontrolled cell growth.
Tumor
Molecules that stimulate or inhibit cellular processes.
Hormones
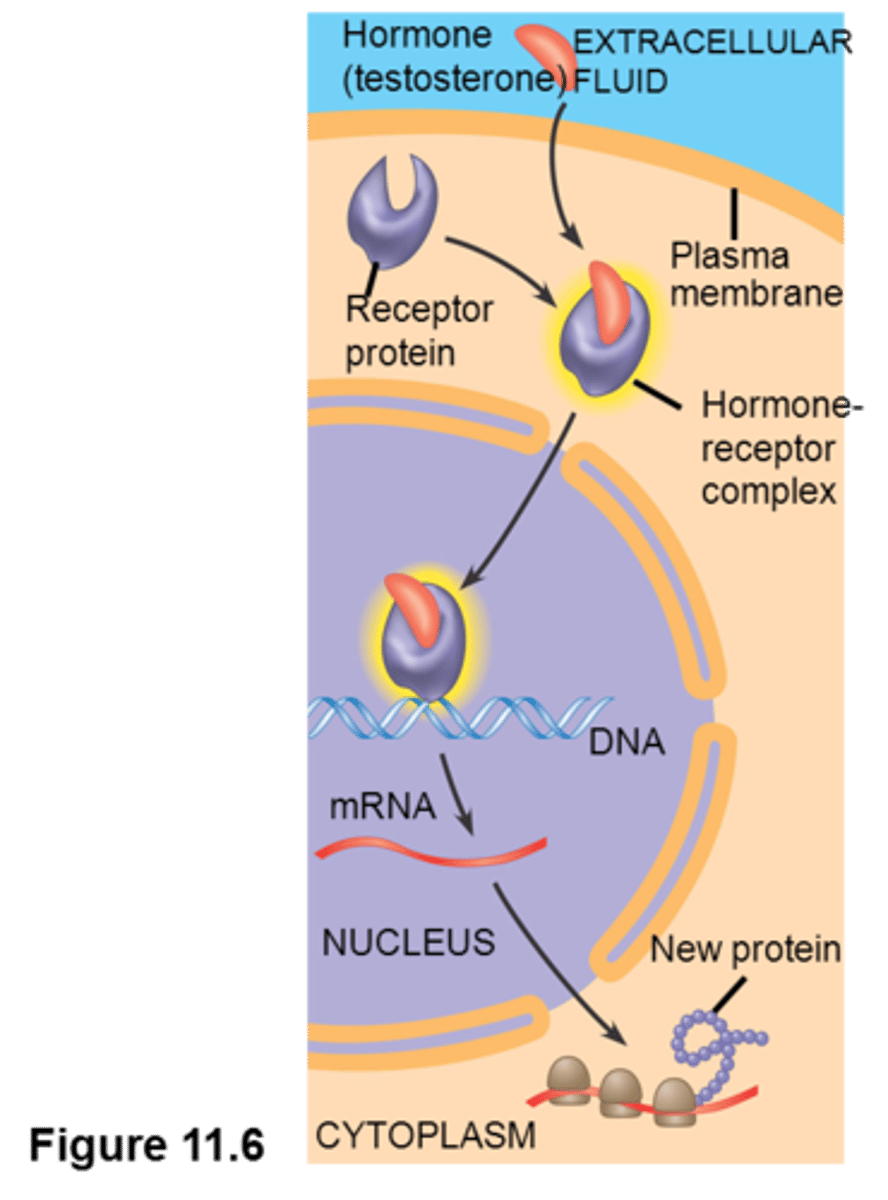
A disease characterized by uncontrolled cell division.
Cancer
Units of heredity that encode proteins regulating the cell cycle.
Genes
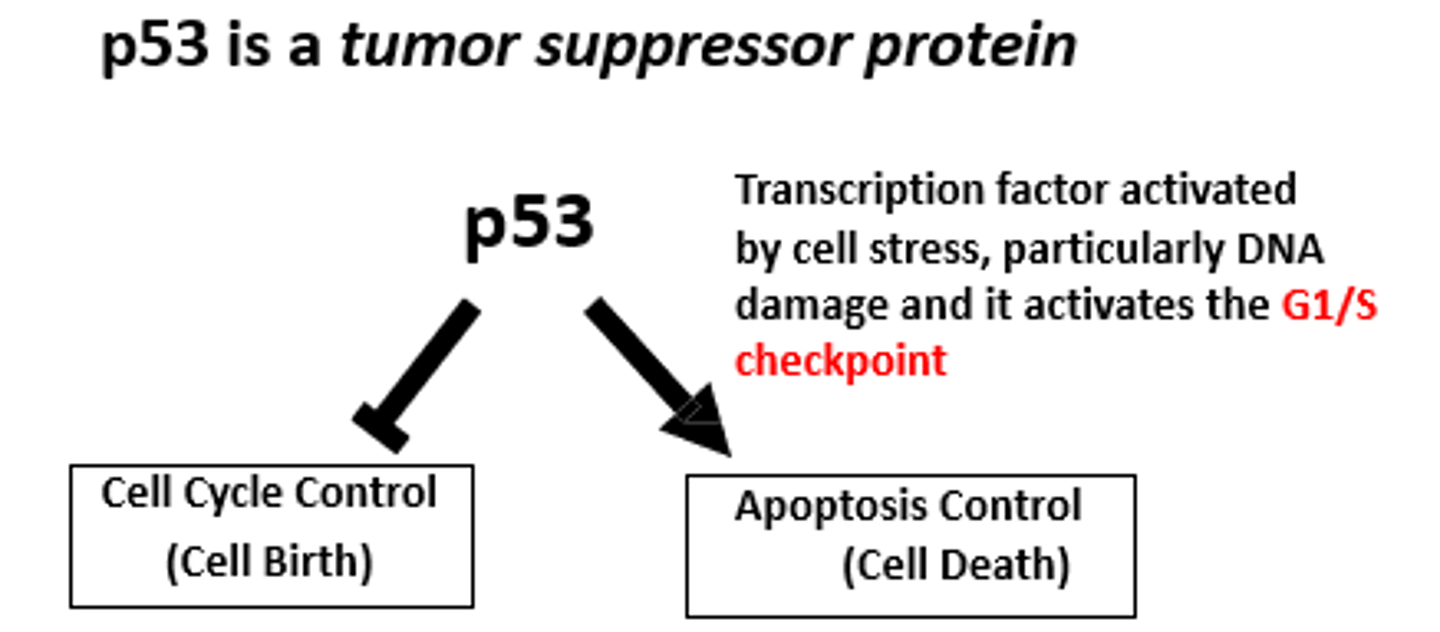
The main role of ________ is to stop genes that promote cell growth and activate genes that control the cell cycle. It helps regulate gene activity to let cells quickly adapt to changes in their environment.
p53
To change or alter the structure of genes.
Mutate
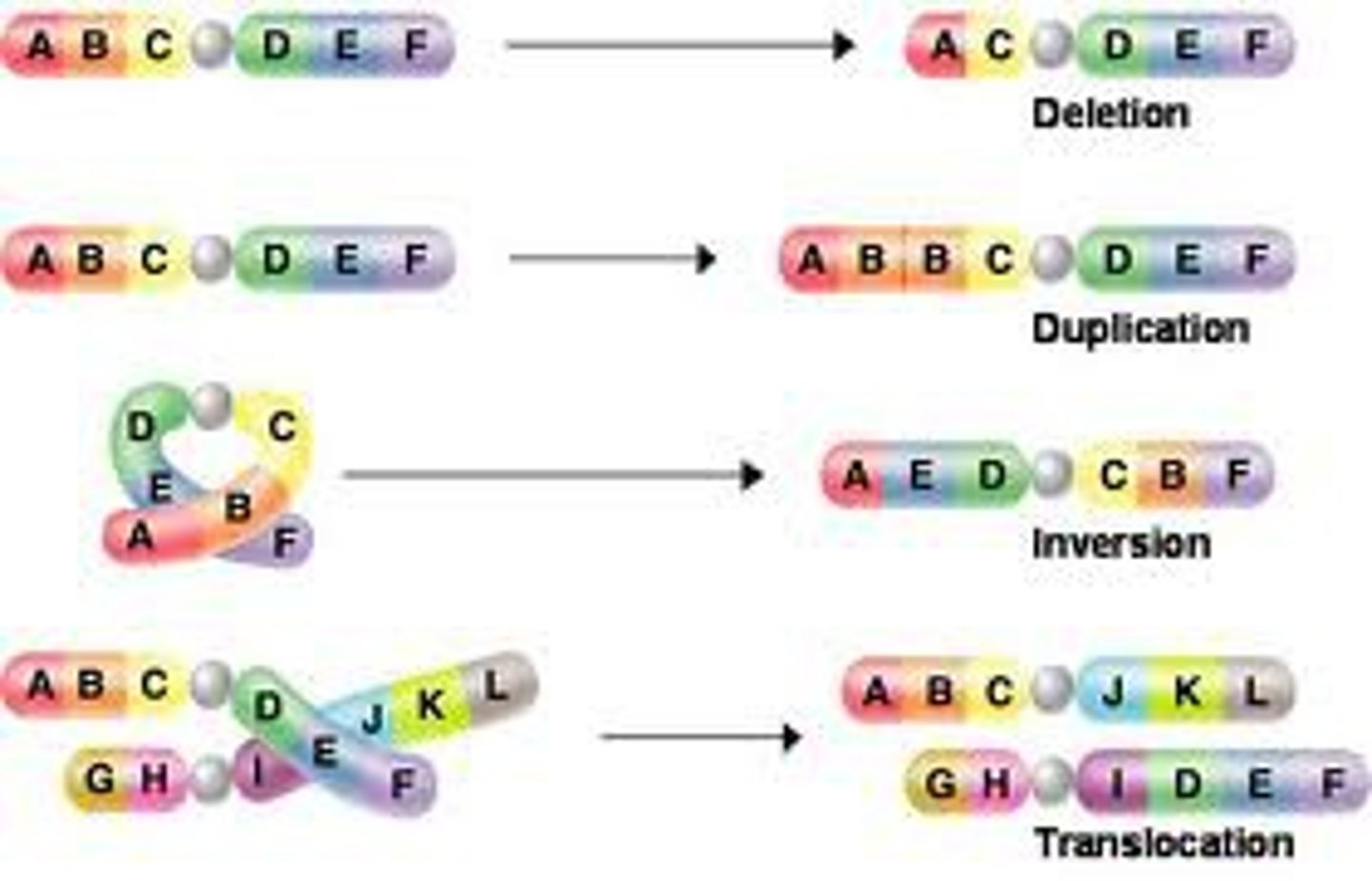
Proteins that regulate the cell cycle by activating the CDK enzymes.
Cyclins

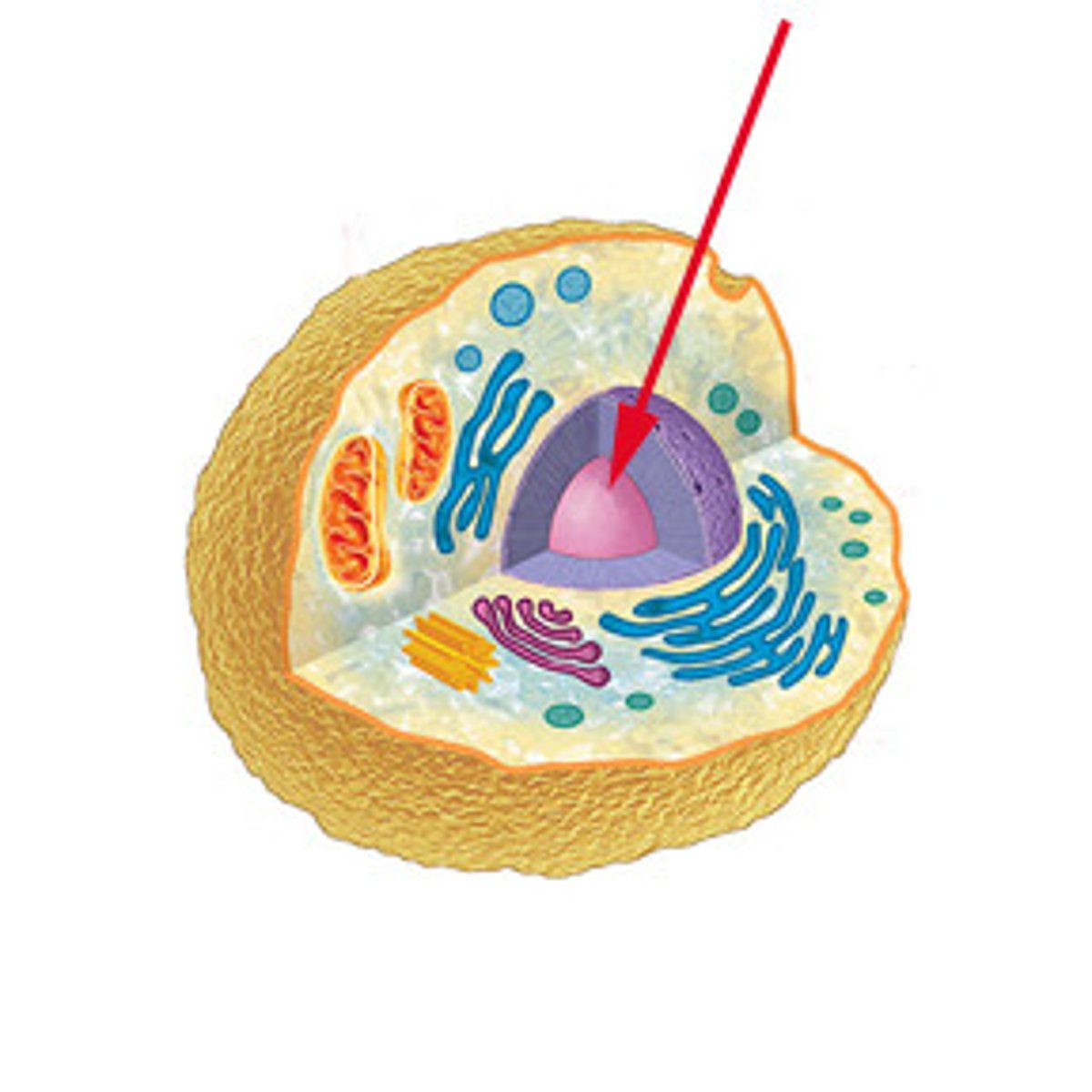
Where do eukaryotic cells store their genetic information?
nucleus
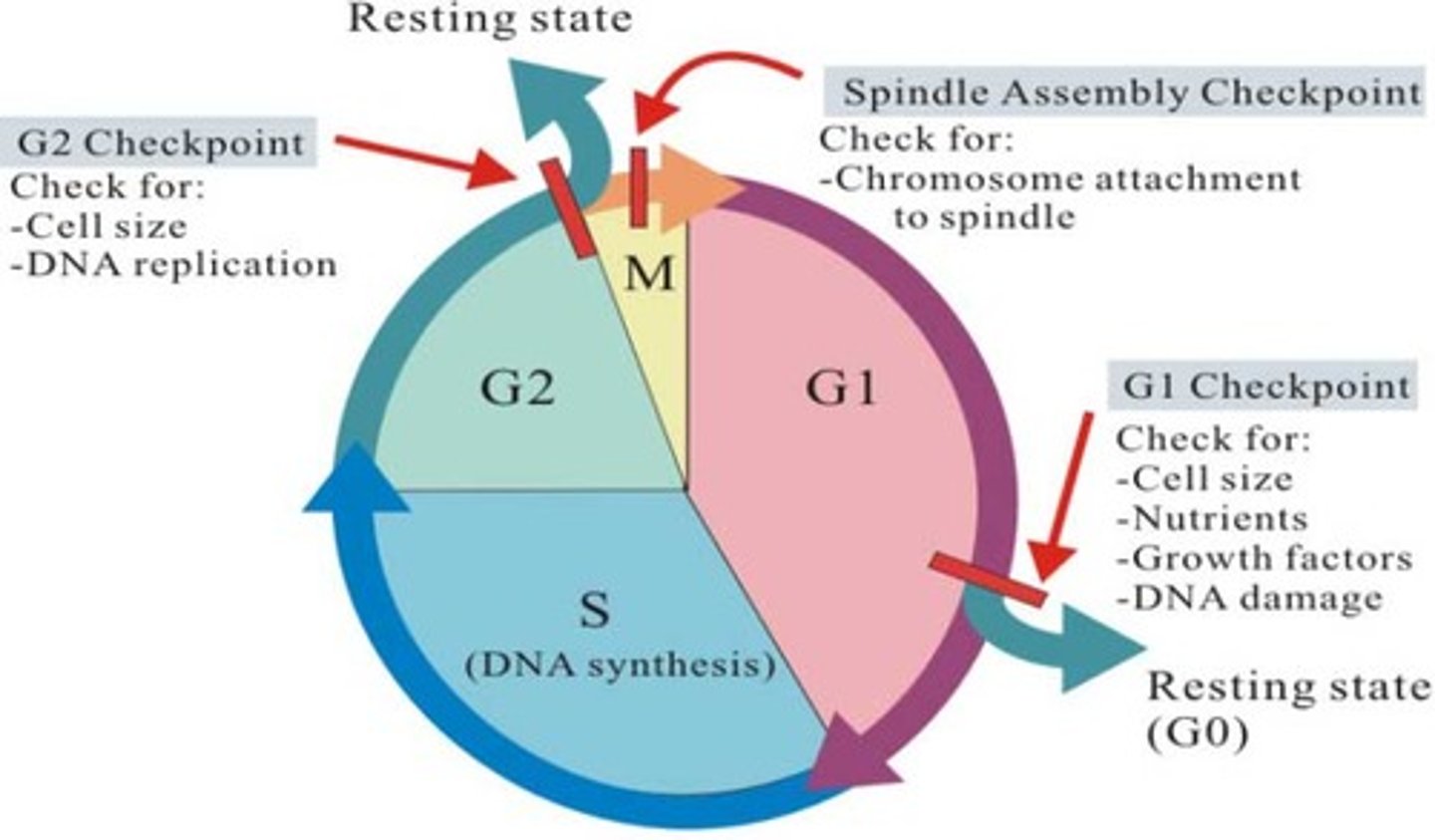
_________________ in the cell cycle assess the integrity of DNA, proper chromosome duplication, and the attachment of kinetochores to spindle fibers to prevent errors during cell division.
checkpoints
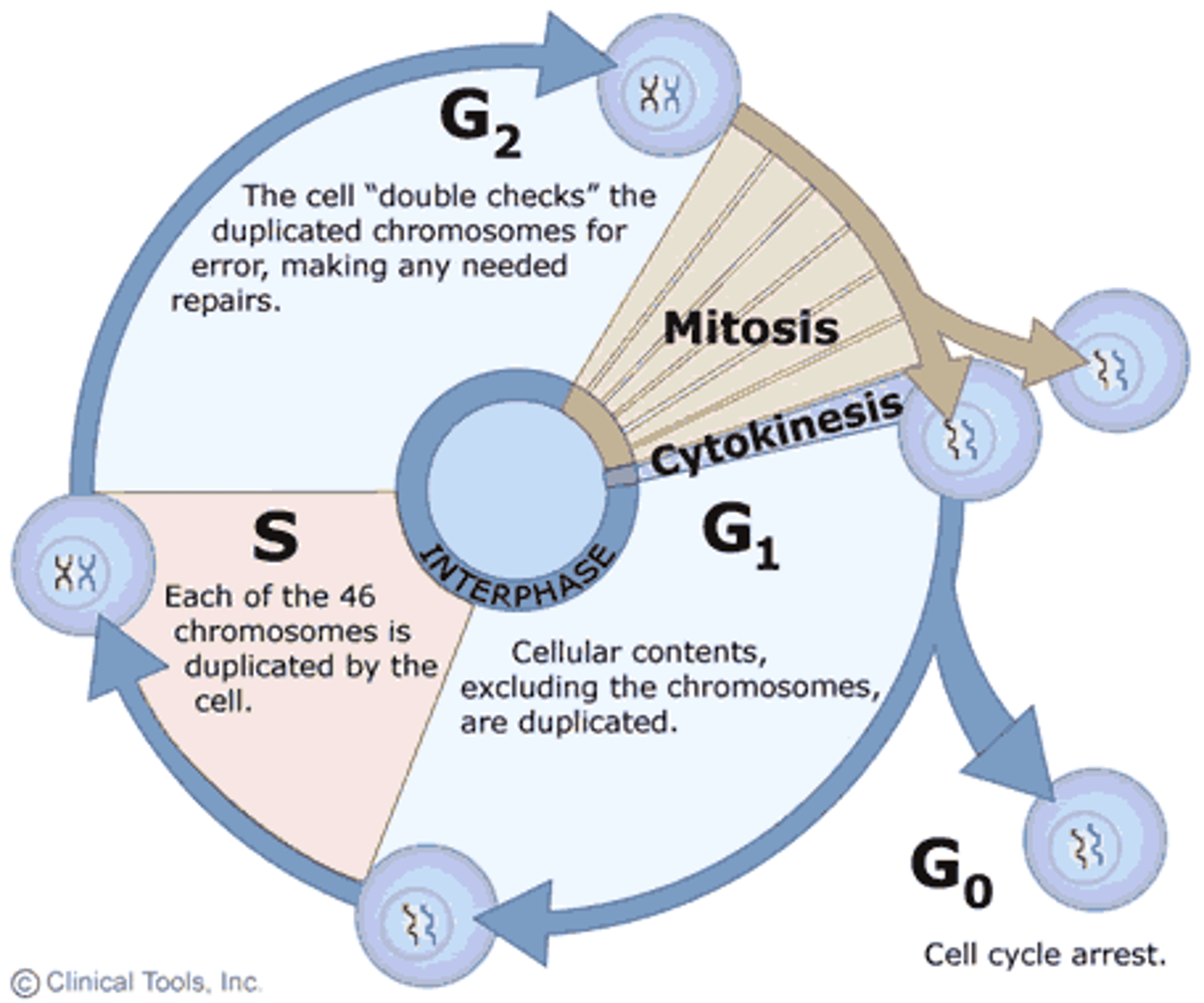
During the________________ of the cell cycle, DNA synthesis occurs, resulting in the duplication of chromosomes into sister chromatids.
S phase of the cell cycle
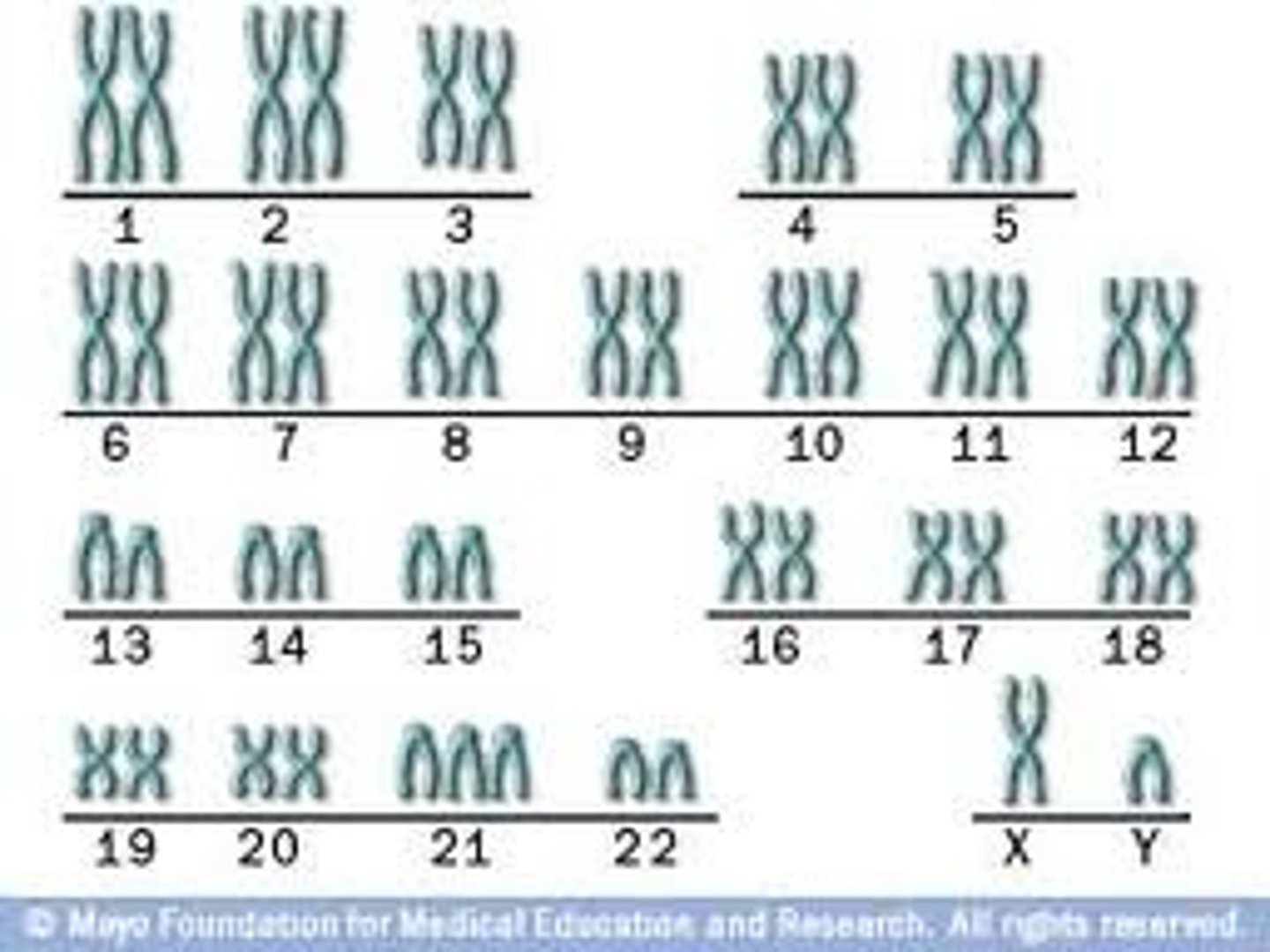
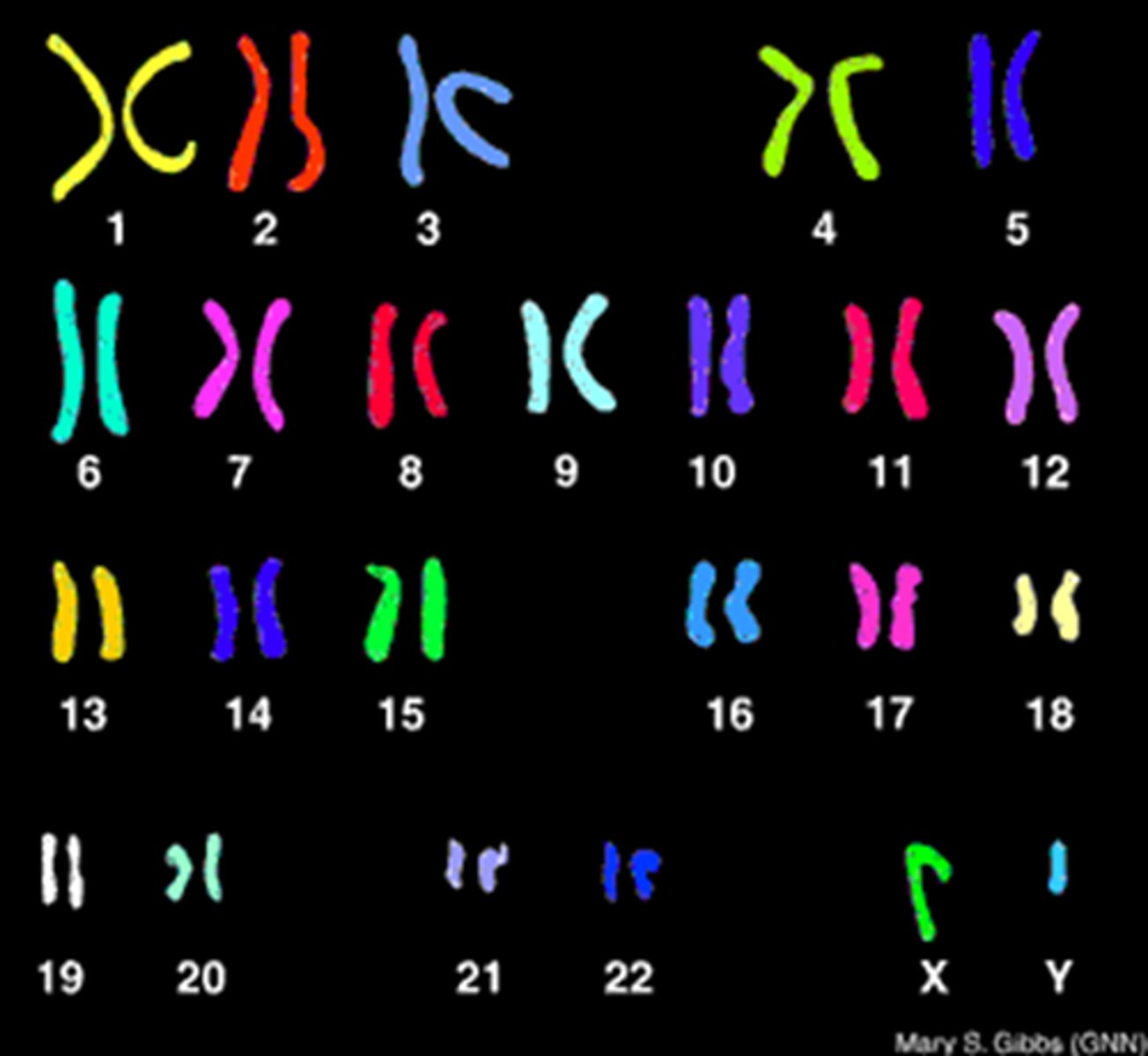
A ________________is an orderly arrangement of chromosomes that allows scientists to identify any abnormalities, such as missing or extra chromosomes.
Karyotype
Centrioles are OR are NOT?? not found in all eukaryotes.
NOT! They are present in animal cells and most protists, but they are absent in most plant cells and fungi.
The _____________________ is a resting or quiescent stage in the cell cycle where cells exit the cell cycle and do not actively divide, often performing specialized functions; some cells, like nerve and muscle cells, remain in G₀ permanently.
G₀ phase
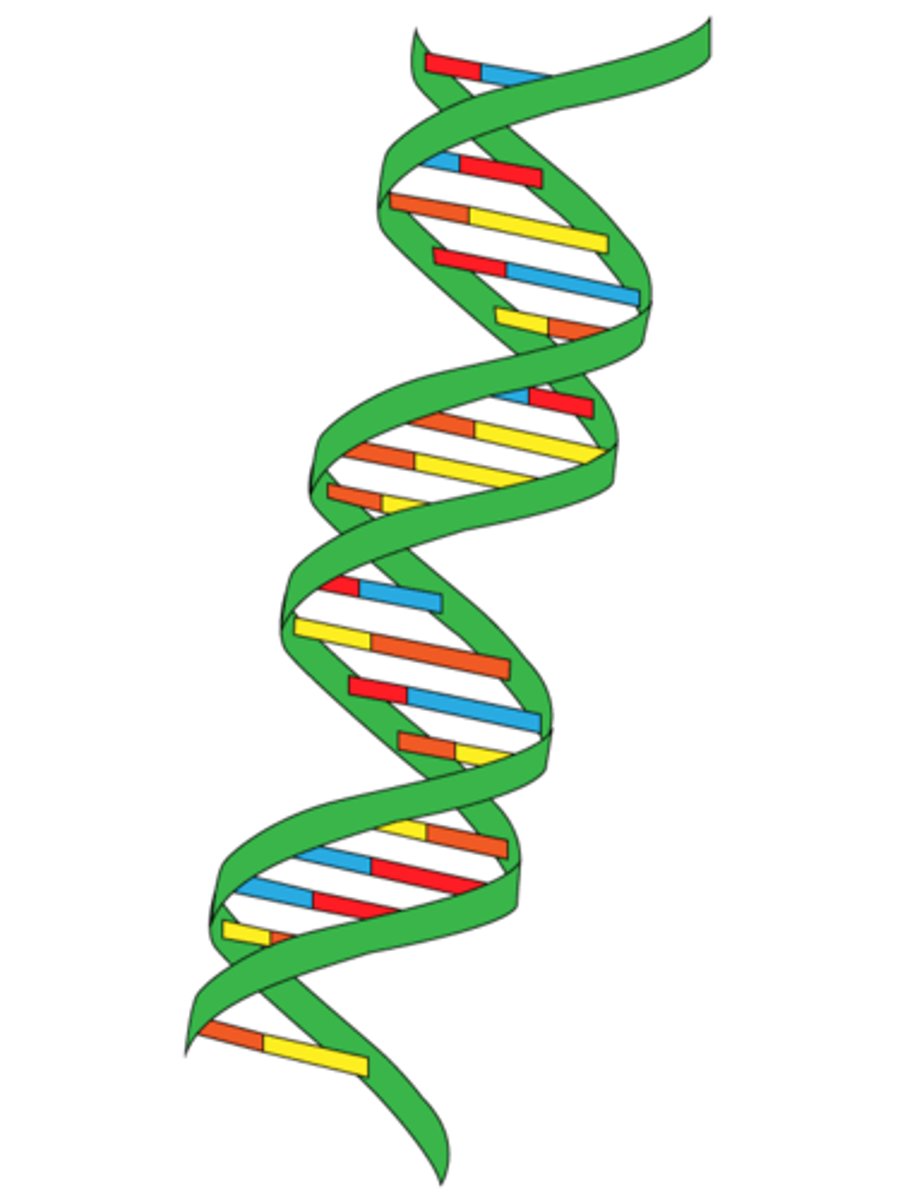
The opposite arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix.
antiparallel
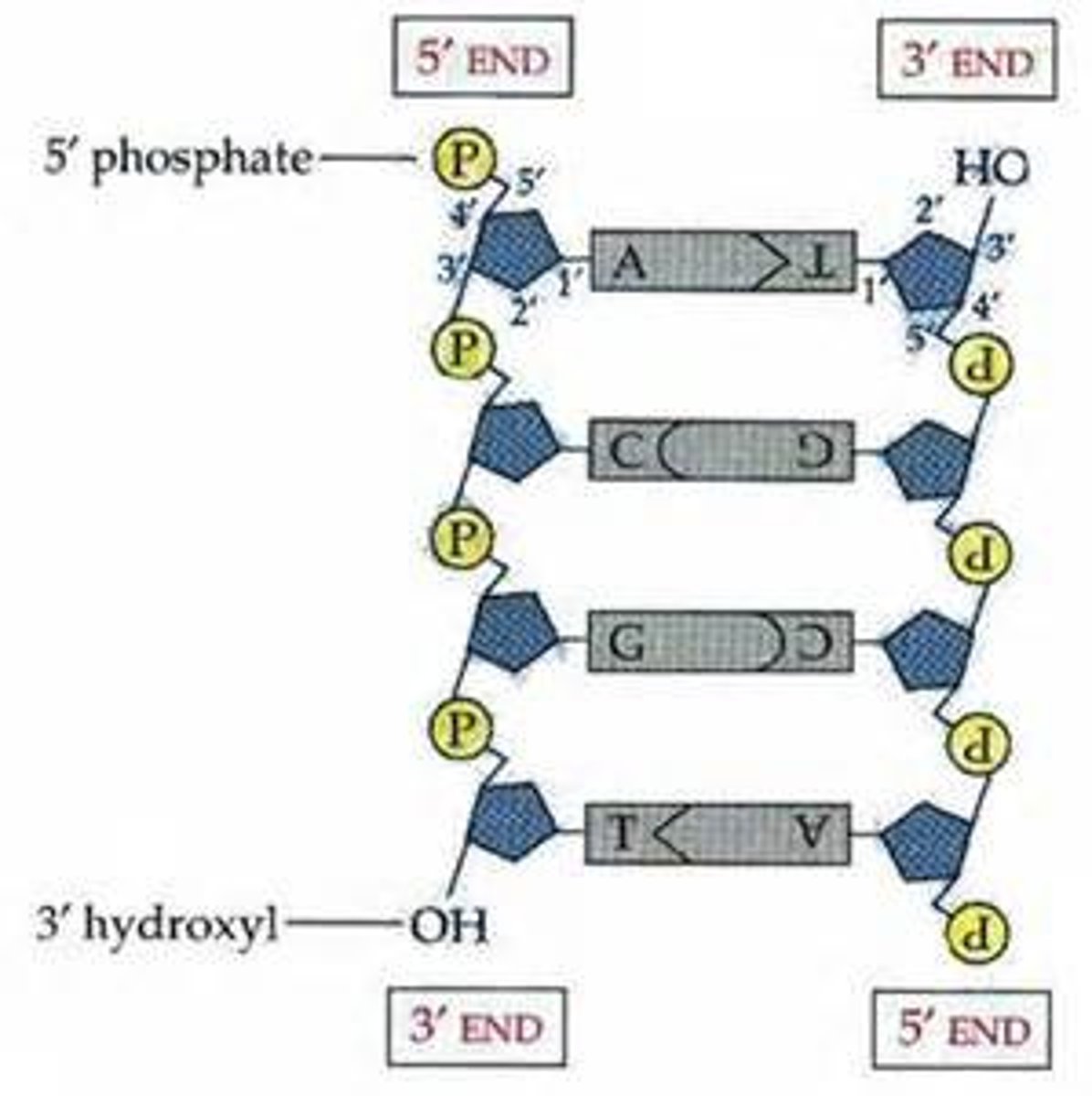
two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; structure of DNA
double helix
Replicated forms of a chromosome joined together by the centromere and eventually separated during mitosis or meiosis II.
sister chromatids
the division in animal cell cytoplasm caused by the pinching in of the cell membrane (a belt of microtubules)
cleavage furrow
In a plant cell, midline of dividing cells. Becomes the cell wall eventually.
cell plate
What are nucleic acids? What are the monomers (building blocks) of
nucleic acids?
o a) Proteins; amino acids
o b) Lipids; fatty acids
o c) Nucleic acids; nucleotides
o d) Carbohydrates; monosaccharide
c. nucleic acids; nucleotides
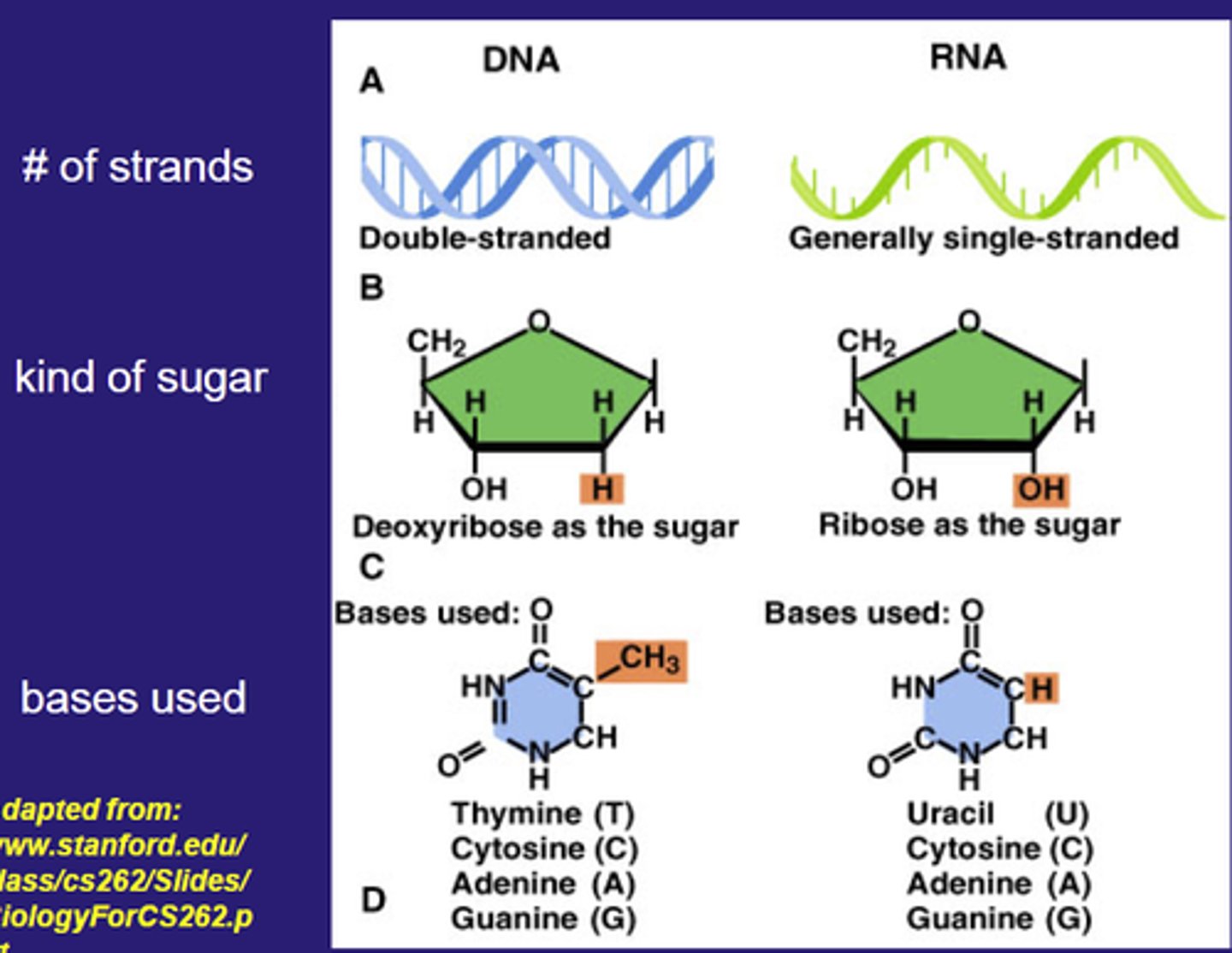
Name the two types of nucleic acids and give their functions.
o a) DNA and RNA; store and transmit genetic information
o b) ATP and ADP; provide energy
o c) Proteins and enzymes; catalyze reactions
o d) Lipids and carbohydrates; store ener
a. DNA and RNA; store and transmit genetic information
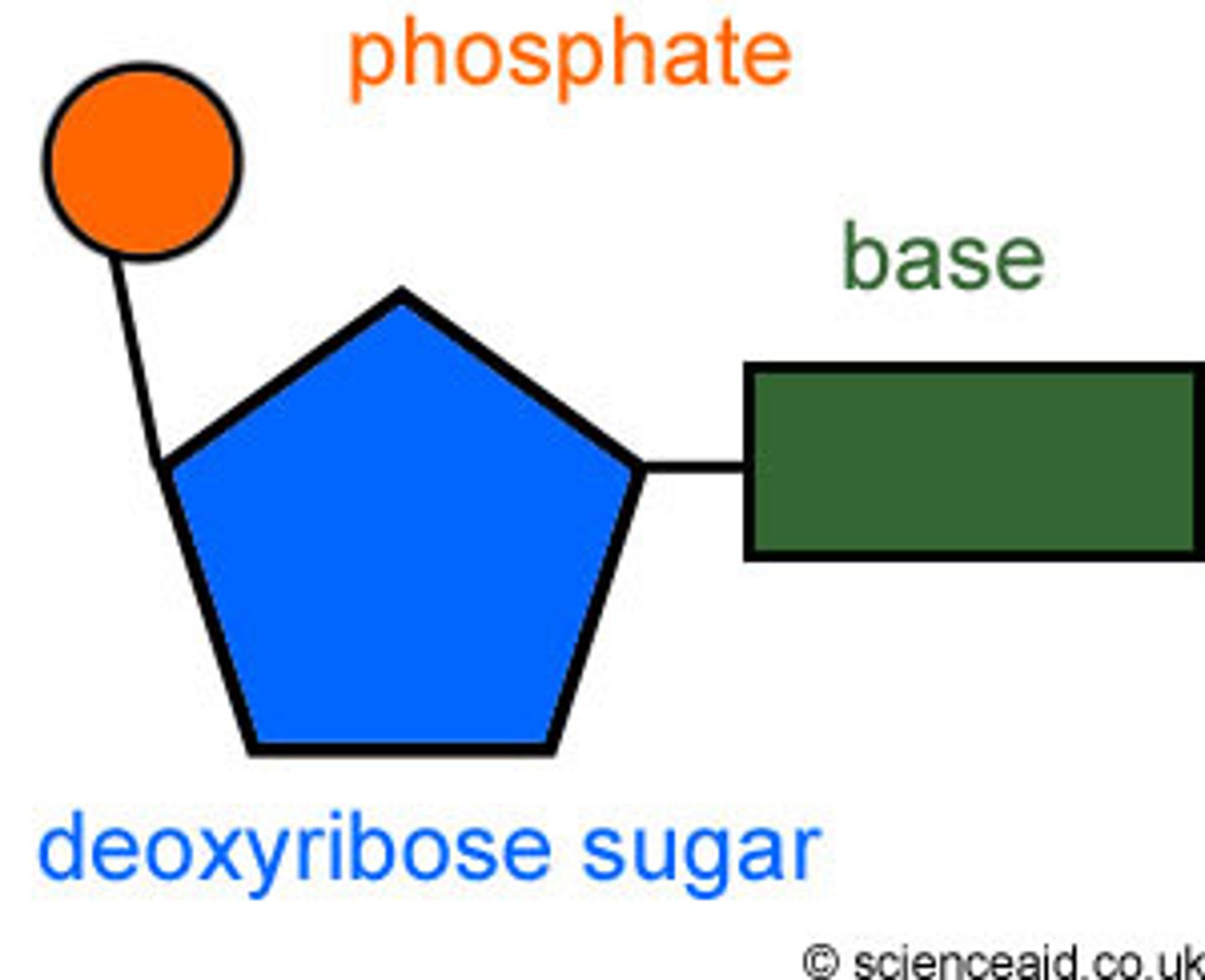
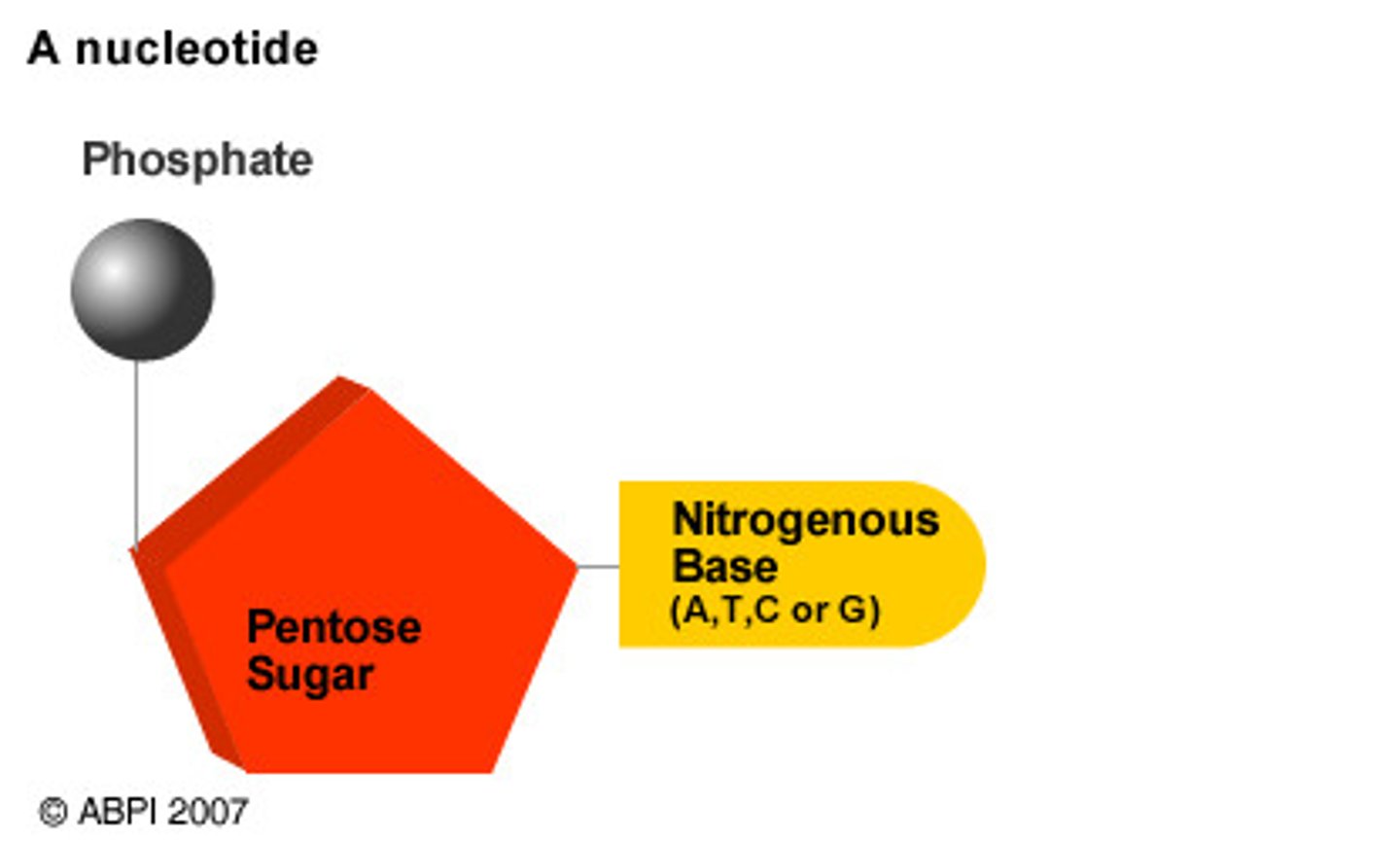
What are three important components of a nucleotide?
o a) Phosphate group, sugar, nitrogenous base
o b) Amino group, carboxyl group, R-group
o c) Fatty acid, glycerol, phosphate group
o d) Monosaccharide, polysaccharide, disaccharid
o a) Phosphate group, sugar, nitrogenous base
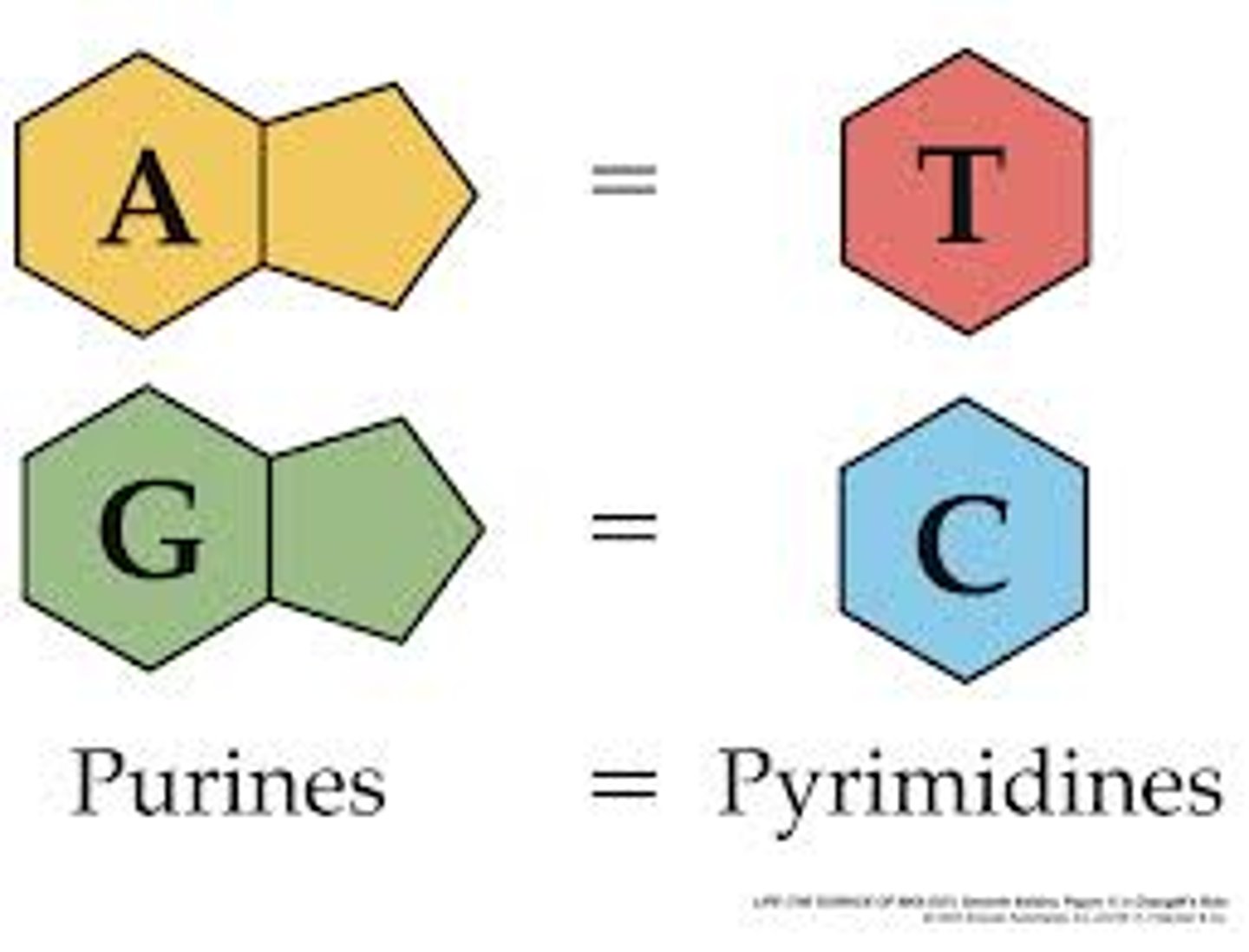
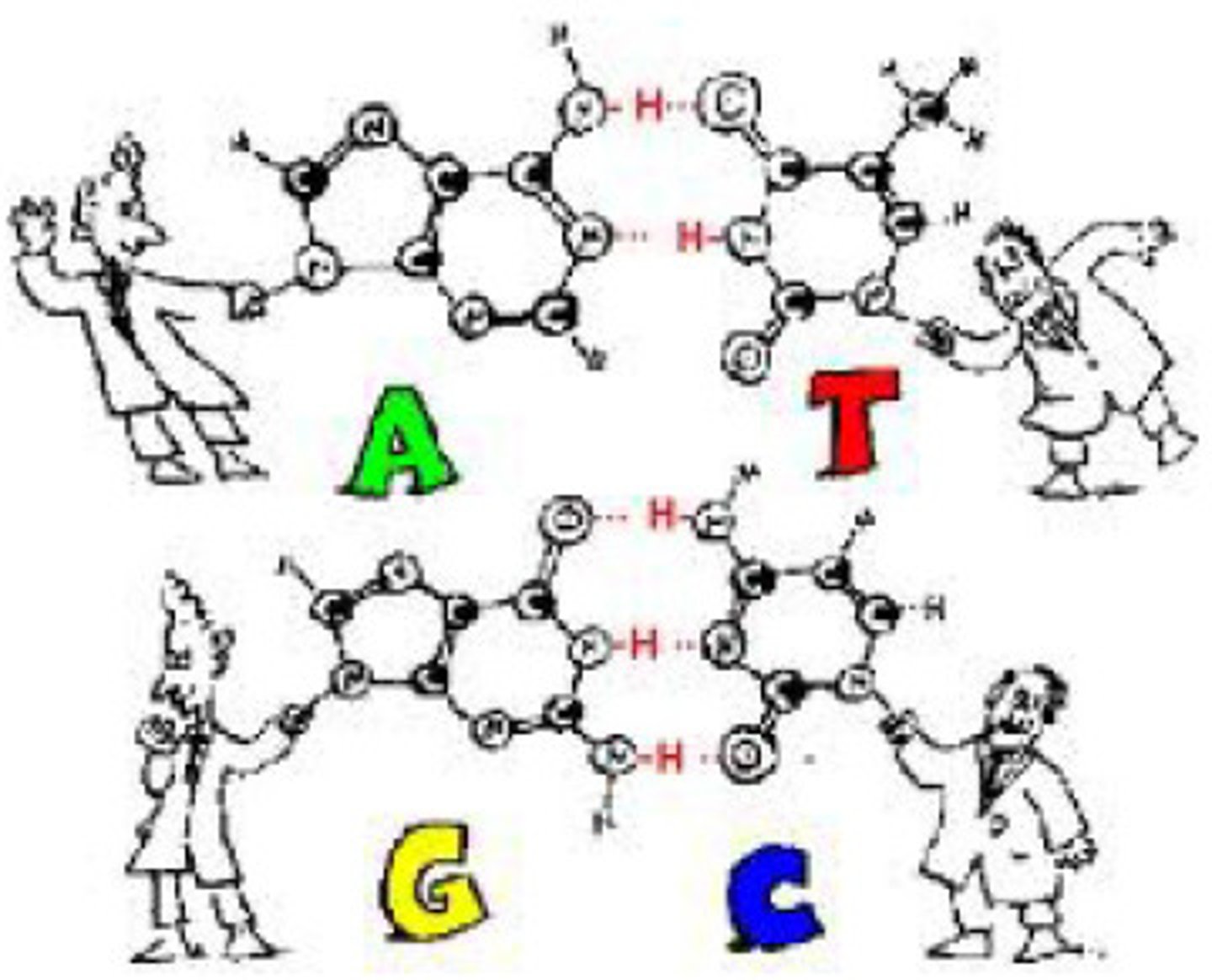
Name the 5 nitrogenous bases. Identify which ones are pyrimidines and which ones are purines, and which are found in DNA and RNA.
o a) Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine, Uracil
o b) Adenine and Guanine are purines; Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil are
pyrimidines
o c) DNA contains A, T, C, and G; RNA contains A, U, C, and G
o d) All of the above
b) Adenine and Guanine are purines; Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil are
pyrimidines
Which DNA nucleotides pair up when two DNA polynucleotides come together? (Base pairing rules)
o a) A-T and C-G
o b) A-G and C-T
o c) A-C and G-T
o d) A-U and C-G
o a) A-T and C-G
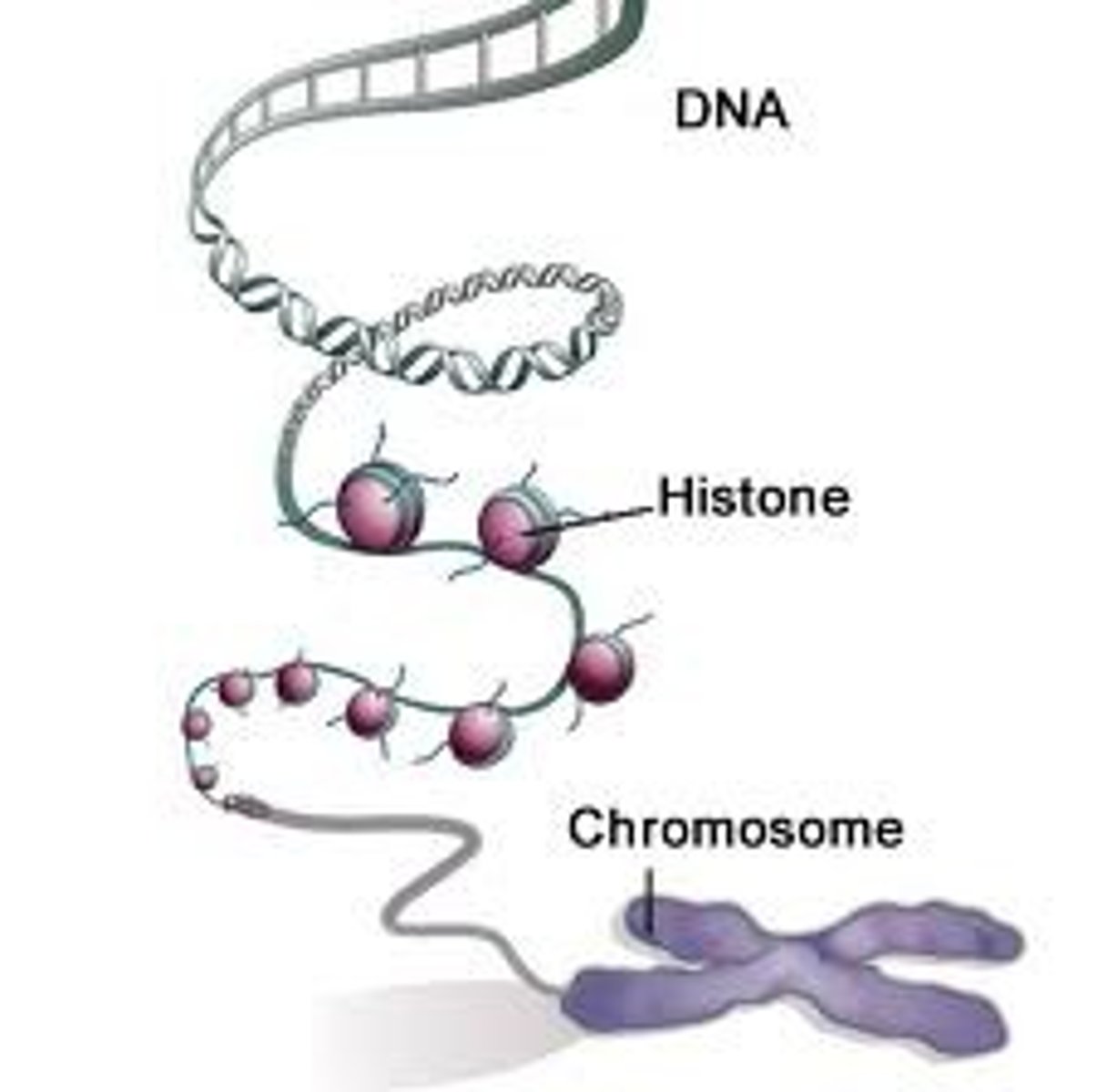
Explain how DNA condenses in chromosomes. Why does DNA have to become compact?
o a) DNA wraps around histones to form chromatin, which further condenses into chromosomes
o b) DNA condenses to fit within the nucleus and facilitate cell division
o c) DNA remains loose in the nucleus at all times
o d) Both a and b
Explain how DNA condenses in chromosomes. Why does DNA have to become compact?
o d) Both a and b
o a) DNA wraps around histones to form chromatin, which further
condenses into chromosomes
o b) DNA condenses to fit within the nucleus and facilitate cell division
o d) Both a and b
Draw & label Mitosis (for Bio 1210 @ AU)
I will provide you a piece of paper. You will draw mitosis and label it with terms that I provide. (alone or with up to 3 students)
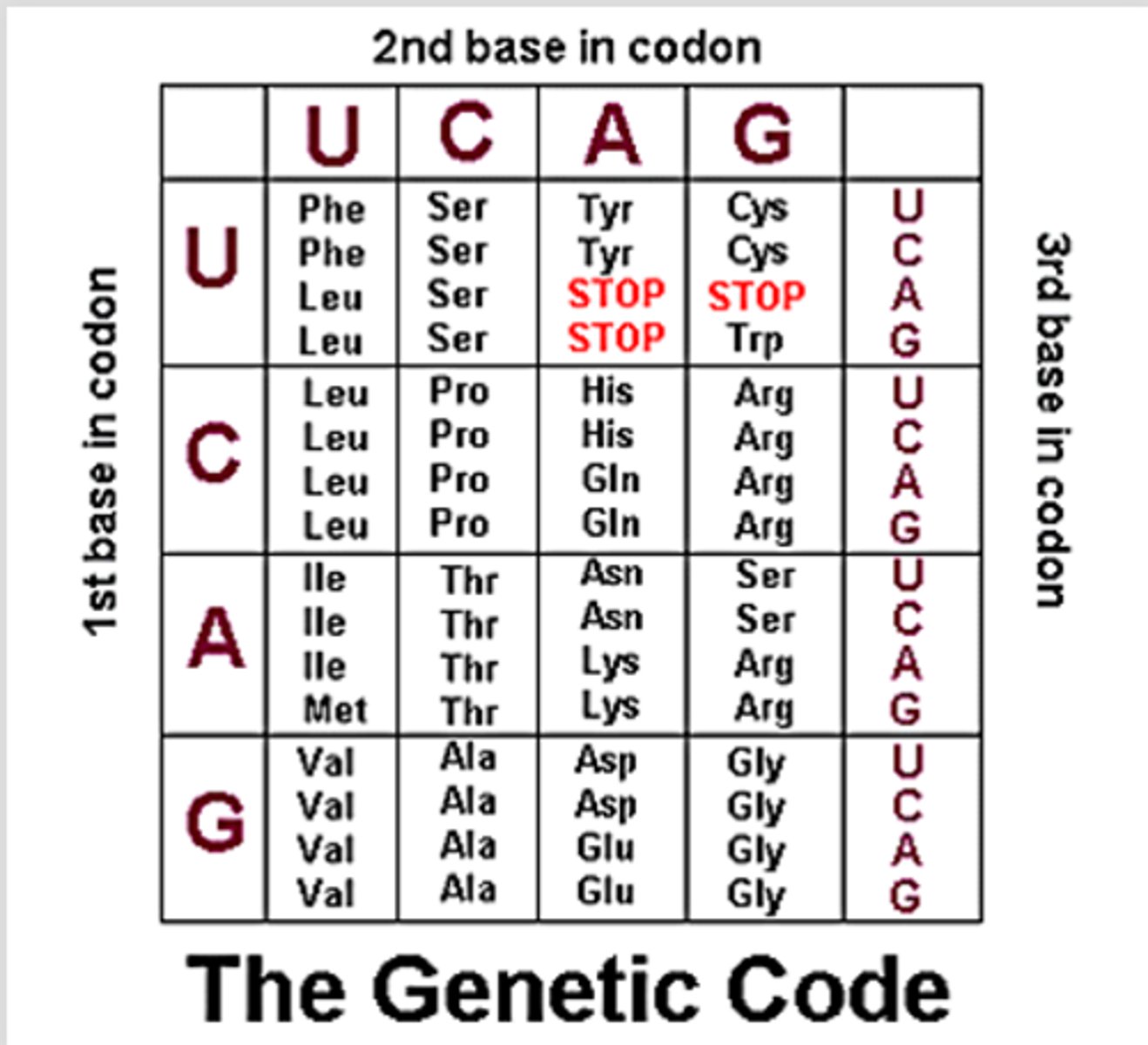
codon chart