BioPsych Exam 2
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Health Psychology
is about 40 years old
We now have a longer life expectancy BUT
we’re now living long enough to see ourselves fall apart
What is the leading cause of death in America
Heart Disease
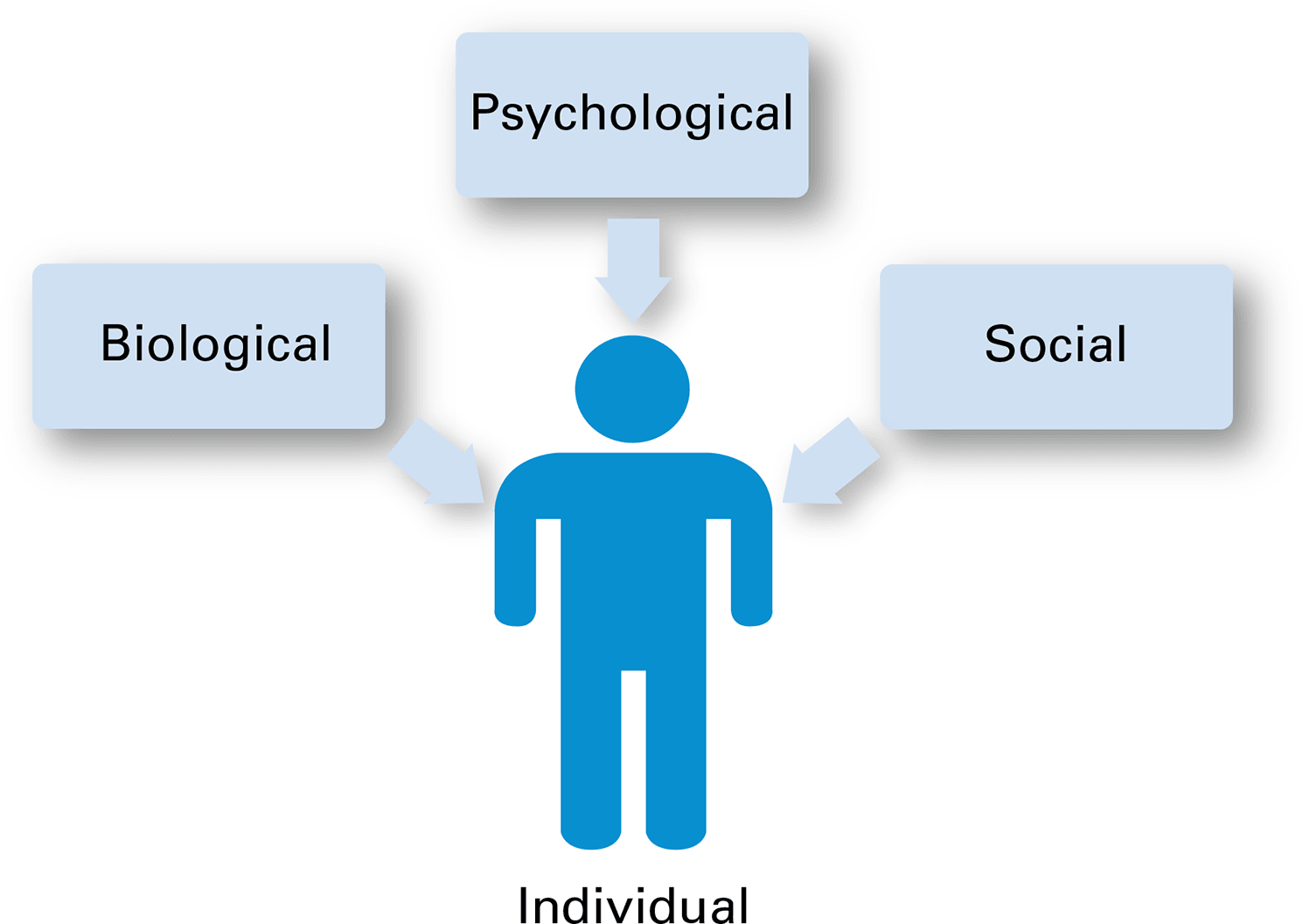
Biological factors
genetics
infectious agents
environmental toxins
immune responses
Psychological factors
personality
attitudes
stress levels
behavioral habits
coping strategies
reactions to illness
Lifestyle Behaviors can be:
health defeating OR promoting behaviors
Wellness is defined as
“a way of life oriented toward optimal health and well-being”
Illusion of Vulnerability
the tendency for people to underestimate their vulnerabilities
Optimism Bias
the belief that bad things only happen to others
Bio Social Model
health professionals take recent life stressors into account
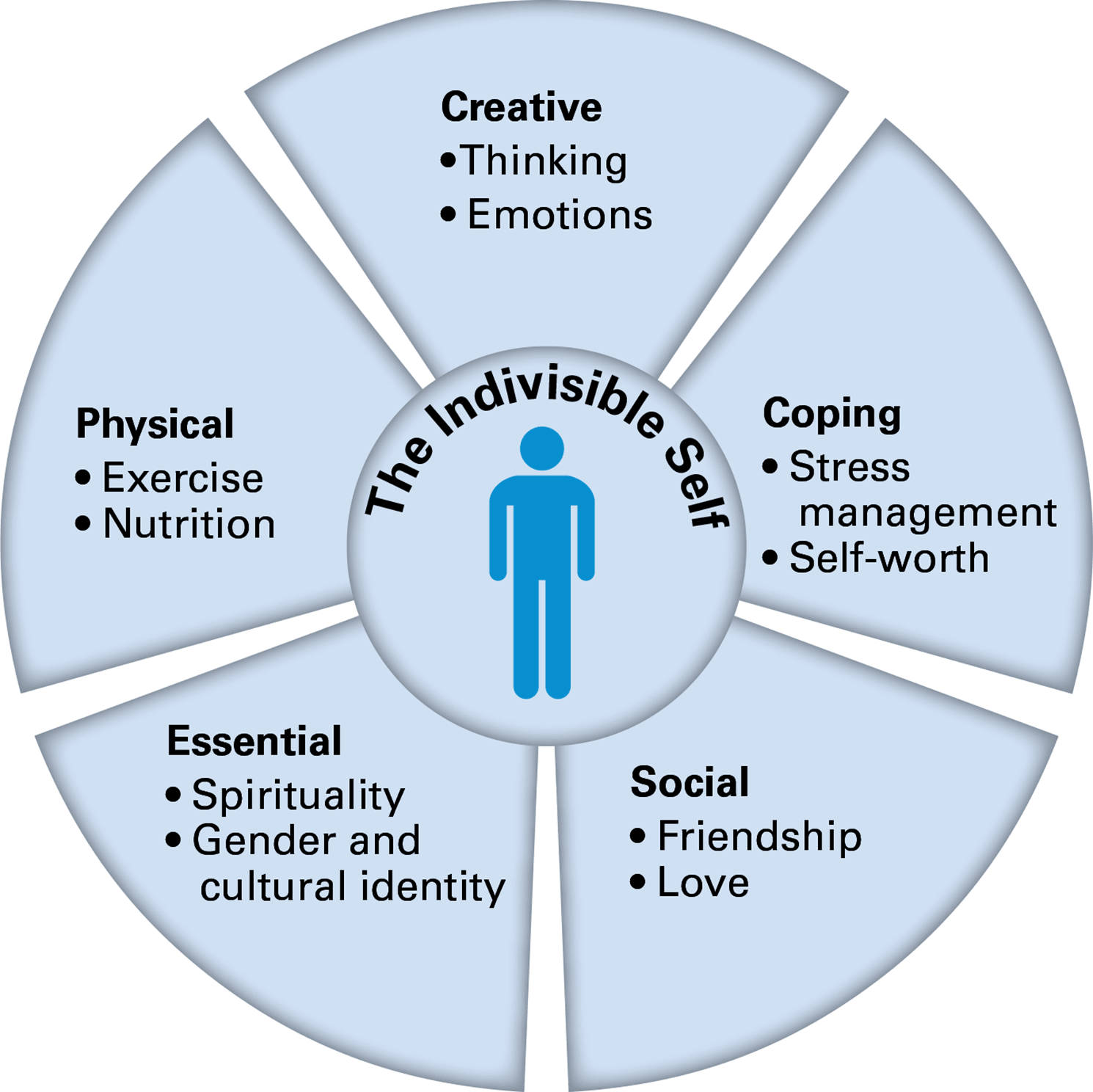
Wheel of Wellness
Social Ecology Model (SEM)
how peoples environment influences them
Placebo Effect
when a treatment/substance brings relief because the person believes it will
can be prescribed
works best if pills are yellow and expensive 💵
Nocebo Effects
unwelcome side effects of a placebo
Psychosomatic disorders
physical symptoms or disorders that may have neural causes
Classical conditioning
when a natural response is triggered by a formally neural stimulus
General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
Hans Selye
3 stages that happen when the body is exposed to stress
What are the 3 stages that happen when the body is exposed to stress
Alarm stage
body responds to the initial threat of stress
Resistance stage
body heightens resistance to illness
Exhaustion stage
resistance levels drop and body becomes vulnerable
Autonomic Nervous System
the part of the peripheral nervous involuntary neurons that control bodily functions and operate below consciousness
Sympathetic Nervous System
½ of the Autonomic Nervous system that is turned ON
🧠 → spine → goes out branching out to every organ
Epinephrine, norenephrine, and DA are important neurotransmitters for sympathetic “arousal”
NE and DA turn on the amygdala and off in the prefrontal cortex
Parasympathetic Nervous System
½ of the Autonomic Nervous system that is OFF
it’s chill 😎
Glucocorticouds
classic stress hormone
released from the HPA
classic steroid hormone
great for mobilizing energy
When the nervous system is triggered what is released
Glucagon
Prolactin
ADH
endorphins and enkephalins
When the nervous system is triggered what is inhibited
Reproductive hormones
Two exact stressors can…
cause different responses
the response depends on how a stressor is appraised
What are the different ways a threat could be appraised
threat vs challenge (primary)
coping possibility (secondary)
How chronic stress creates CVD
the stress response causes sympathetic arousal
increases in heart rate (HR)
increases in blood pressure (BP)
chronic stress + hypertension (raised BP) =
CVD
High BP is
when blood forcefully pushes through veins to the ❤
What happens if high BP (chronic stress) happens frequently
smaller blood vessels bulk up 💪 → causes blood flow problems (vascular resistance)
Blood SLAMMING into the left ventricle results in
left ventricle hypertrophy
What is left ventricle hypertrophy
an enlargement of the heart that causes:
irregular heartbeat
not enough blood for bigger ❤
Development of plaques
due to small tears in points of bifurcation
where branch points of the vessels further ➗ inflammatory response
pulls in extra cells (like cholesterol)
Plaques _____ the vessel
narrow
What’s the problem when vessels narrow
it’s harder for blood to get through
If part of plaques breaks off…
a clot is formed (thrombus)
What happens if a clot gets to the ❤
heart attack
What happens if a clot gets to the 🧠
stroke
Left ❤
pumps blood to the peripheral organs
Right ❤
pumps blood through the 🫁
A cardiovascular stress response causes
increase in HR
increase in force
decreased blood flow to kidneys
What happens to blood when a stress response is triggered
blood is distributed to places that need it
arteries to muscles dilate so more blood is available
Chronic stress causes ____ to happen frequently which is ____ for the body
increases, bad
No cell in your body is less than 5 cells away from a ______ but the ______ takes up only 3% of body mass
blood vessel, circulatory system
______ is better at predicting CVD than cortisol
C-reactive protein (CRP)
Angina Pectoris
chest pain or discomfort that keeps coming back
The immune system has 2 main characteristics:
the ability to differentiate self from non-self
exhibit specificity and memory
What are the 2 types of T-cells
Helper T’s
help with immune responses
Cytotoxic
help with your own cells being altered by things like Cancer
B-cells
produce antibodies
Macrophages
destroy some antigens
help T and B cells combat antigens too
PNI was started by:
a behavioral psychologist (Dr. Ader) studying classical conditioning
you can _____ immune responses
condition
immune cells have receptors for:
E
NE
DA
etc
cortisol
E, NE, etc, and cortisol are
released as part of the stress response
What are some important studies in PNI
Rats and control
stressor and cancer
Girl with Lupus
Cytoxan
Sensory coding
physical energy from the world → electrical signals → 🧠
Transduction
sensory neurons transform physical energy → neural impulses
Just noticeable difference (difference threshold)
smallest amount of change we can detect
Absolute threshold
smallest amount of sensation we can detect
Sensory threshold
smallest amount of sensory stimulation to activate sensory neurons
Weber’s Law
idea that a new stimulus must differ by a constant fraction from the original to be detected
Signal detection theory
idea that the deduction of a sensory stimulus involves some amount of decision making
Sensory areas of the brain
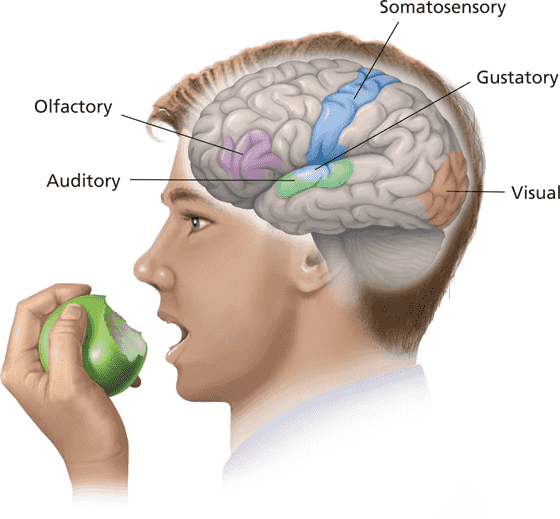
Olfactory
smell
Somotosensory
touch
Auditory
hearing
Gustatory
taste
Visual
sight
Bottom-up processing ↑
information flows from sensory receptors ↑ smarter processing in the 🧠
Top-down processing ↓
information flows from higher-level brain structures ↓ lower-level brain structures
Sensory compensation
enhancement of 1 or more sense after losing one
Synesthesia
occurs when stimulating one sense triggers another
Trichromatic
a theory of color vision based on the eyes’ red, green, and blue sensitive cones
Opponent-process theory
information about color is processed through signals in the visual receptors in an incompatible manner
Auditory receptors
detect sound waves
Conductive hearing loss
caused by damage to the ear drum or ossicles
prevents vibrations from reaching cochlea
Sensorineural hearing loss
caused by damage to middle ear
a result of an exposure to loud noise
About ____ of hearing problems are the result of damage to the ____
90%, inner ear
Chemical senses
smell and taste
Olfactory receptor cells
specialized nucleated cells of the mucous membrane of the nose that serve as the receptors for the smell
Olfactory nerve
registers smell by sending impulses for the sense of smell from 👃 → 🧠
Anosmia
loss of sense of smell
Papillae
taste receptors and taste buds
Chemosensation
ability to sense chemicals in the environment that are odorless and tasteless
Kinesthetic sense
a sense that tracks the position and orientation of your body parts
Proprioceptors
sensory receptors found in muscles, tendons, and joints that detect the motion or position
Vestibular sense
a sensory system involving the inner ear that registers the orientation of the head
Touch sensation
result of a number of different types of receptors
Congenital Insensitivity to Pain with Anhidrosis (CIPA)
an insensitivity to pain
Gate-control theory
a model that proposes a neutral gate in the spinal cord can modulate incoming pain signals
Pain can be
chronic
accute
Analgesis
painkillers
Accupuncture
temporarily releases pain with tiny needles
releases endorphins
sends messages through smaller nerve fibers that close senses to the spine
Figure-ground
the tendency to perceive objects as being either in the foreground or the background
What are the Gestalt principles
nearness
similarity
closure
continuity
Nearness
objects that are close together in space or time are grouped together
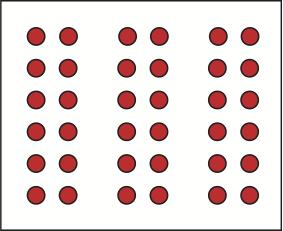
Similarity
objects that are similar to each other are grouped together
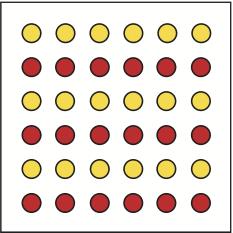
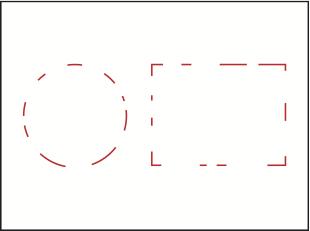
Closure
the brain will close gaps in order to show us the whole object
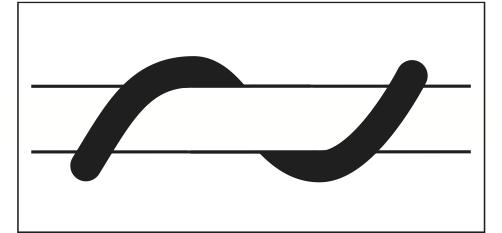
Continuity
the brain would prefer to see one continuous movement rather that broken up parts
Perceptual learning
long lasting changes to the brain’s perceptual systems that improve the ability to respond to the environment