MMD I: Week 8 (Shoulder Biomechanics/SE and OMs)
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 3 content
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
The primary function of the shoulder complex is…
Placement of the hand to manipulate our environment
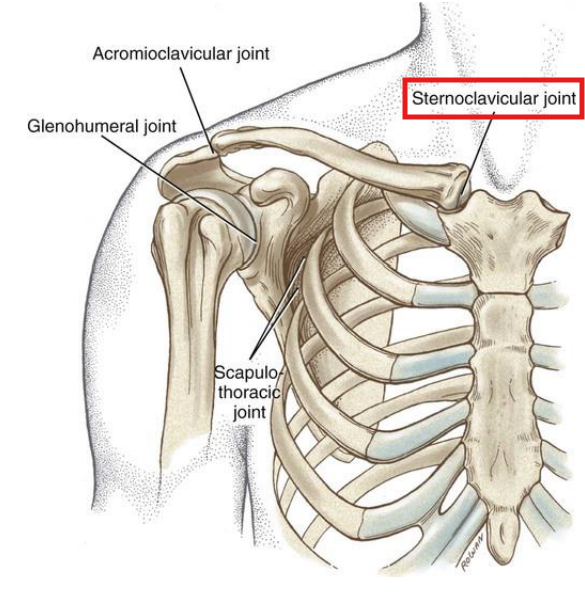
The only attachment point of the UE to the axial skeletion is through this joint…
The sternoclavicular joint
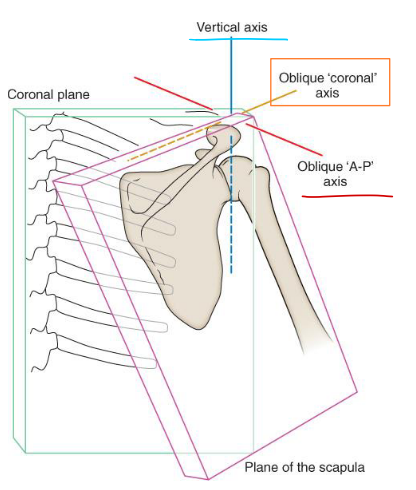
Describe the position of the scapula at rest
Internally rotated 35-45°
Upwardly rotated 5-10°
Anteriorly tipped 10-15°
Sits between T2-T7, 5-6 cm from SPs
Translatory scapular motions (couplings):
Elevation/Depression
Protraction/Retraction
Elevation/Depression: SC depression/elevation + AC anterior/posterior tilt + AC IR
Protraction/Retraction: SC protraction/retraction + AC IR/ER
What are the 4 passive restraints of the GH joint?
Bony geometry
Labrum
Capsule/Ligaments
Negative intra-articular pressure
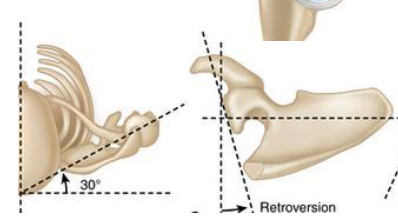
Describe the bony geometry of the glenoid fossa:
5° superior tilt
6 -7° retroversion from scapular plane
Scapular plane is 30° from the frontal plane
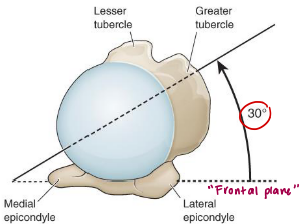
Describe the bony geometry of the humeral head:
~1/2 sphere shape
30° retroverted
Angle of inclination 130-150°
25-50% in contact with the glenoid
Inferior surface of HH is in contact with the glenoid at rest
What is the function of the labrum? What attaches to it?
The funciton of the labrum is to increase surface area and add stability. Attachments:
GH capsule
All glenohumeral ligaments
LH of the biceps tendon
Describe what happens to the GH joint capsule in the following positions: Rest. Abduction + ER
Rest:
Taut superiorly + Anterior/inferior slack
Abducted + Externally Rotated:
Anterior capsule becomes taut = closed pack position
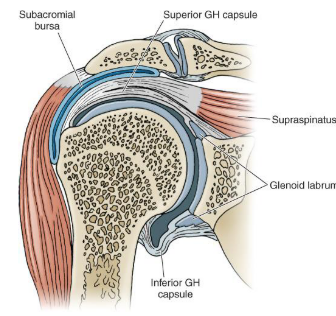
What is the weakest portion of the GH capsule?
The inferior portion, due to its folds to allow abduction
What is the open pack position for the GH joint?
30-40º scaption
What is the capsular patter for the GH joint?
Limitations in ER>ABD>IR>FLX
What are the functions of the superior GH ligament?
Prevents inferior translation of the humerus - with the arm at the side (PRIMARY STABILIZER)
Secondary: Limits EXT and ER
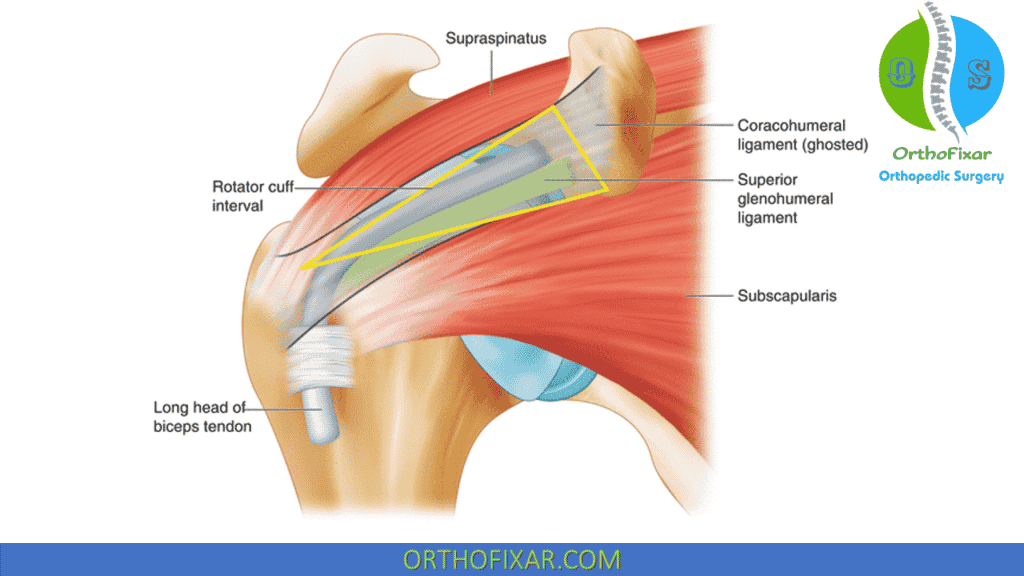
What are the components of the rotator interval capsule (RIC)?
Joint capsule
Coracohumeral ligament
Superior glenohumeral ligament
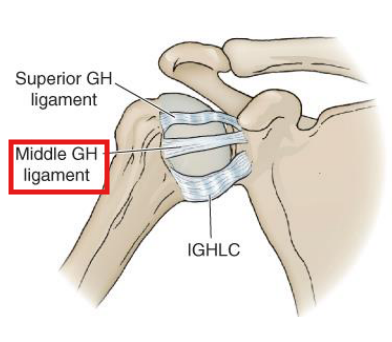
What are the functions of the middle GH ligament?
Limits ER in 45-75° ABD
Limits ANTERIOR humeral translation between 0-60˚ ABD
Resists INFERIOR humeral translation at rest
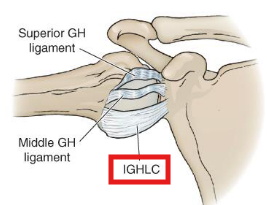
What are the functions of the inferior GH ligament?
• Pouch: Cradles the head; resists inferior translation
• Ant B: Limits ABD and ER; anterior/inferior translation
• Post B: Limits ABD and IR; posterior/inferior translation
Sulcus sign reflects pathology of the…
Superior GH ligament & loss of intra-articular negative pressure
Which ligament is primarily responsible for stabilizing the humerus for OH motions?
The inferior GH ligament
What is the vulnerable positon of the shoulder where dislocations typically happen?
Abducted and externally rotated (mainly limited by the AB of the IGHL and the MGHL)
What are the contents of the subacromial space?
Supraspinatus tendon
LH biceps
Subacromial bursa
What can cause a reduction in the subacromial space, potentially leading to impingment?
“Anything that occupies space may limit motion.” Like:
Hooked acromion
AC joint degeneration
GH instability
Tight posterior capsule
Lack of posterior tilting or upward scapular rotation
Elevation of humerus requires head to slide ______, while it rolls _______ on fossa. If not, will…
Elevation of humerus requires head to slide inferiorly, while it rolls superiorly on fossa. If not, will cause impingement on the coracoacromial arch
Center of rotation of the humeral head moves slightly superiorly during first ___ of elevation, then it stabilizes.
Center of rotation of the humeral head moves slightly superiorly during first 60°of elevation, then it stabilizes.
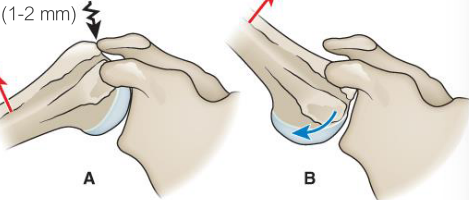
What is the purpose of the scapulohumeral rhythm?
Distributes motion between several joints
Increases stability by optimizing glenoid fossa orientation of humeral head
Maintains optimal length-tension of GH muscles
Scapulohumeral rhythm has a GH:ST ratio of _____, which becomes constant after…
Scapulohumeral rhythm has a GH:ST ratio of 2:1, which becomes constant after 30° of abduction or 60° of flexion
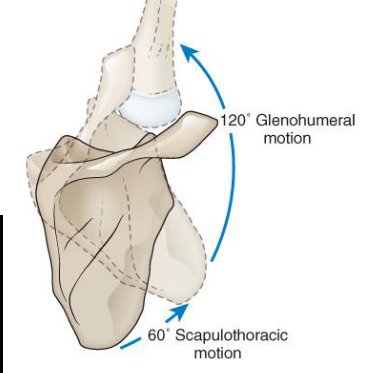
T/F: Upward rotation of the scapula can be influenced by the position of the thoracic spine
TRUE
During humeral elevation, normally the scapula should…
Upwardly rotate
Posteriorly tilt
Externally rotate
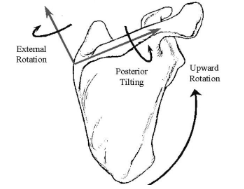
What are the 3 main muscles responsible for upward rotation of the scapula?
Serratus anterior (largest moment arm)
Upper trap
Lower trap
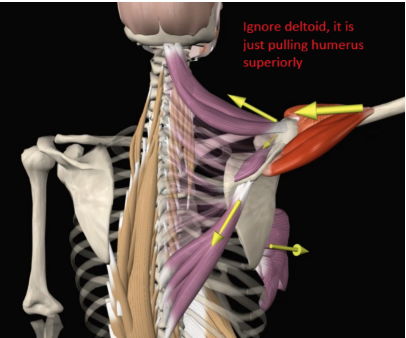
Describe the activity of serratus anterior during upward rotation of the scapula:
SA active through the FULL ROM of both ABD and FLX
Upper fibers: resist downward pull of gravity
Mid/low fibers: stabilize medial border to the thorax and inferior scapular angle (preventing winging and tipping)
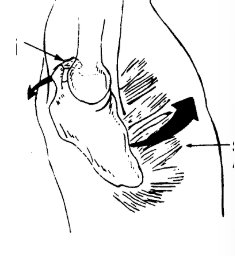
Describe the role of the muscles in the force couple for upward rotation:
First 30° of ABD:
Superior fibers of SA and UT
Last 30° of ABD:
Lower fibers of SA anf LT
Describe the role of the muscles in the force couple for abduction:
The trapezius is more important in ABD (compared to UR)
The middle trap functions primarily as a stabilizer
T/F: Complete shoulder FLEX is impossible with a denervated trapezius
FALSE. Complete shoulder FLEX is impossible with a denervated trapezius, but is weakened
T/F: With an intact trap & absent SA, active shoulder ABD is limited to about 75º
FALSE. The trap has a bigger role than the SA in this movement!!
The ______ trap functions primarily as a stabilizer due to its line of pull
Middle
The dynamic stabilizers of the GH joint provide _____ of abduction strength and ____ of ER strength
The dynamic stabilizers of the GH joint provide 50% of abduction strength and 80% of ER strength
T/F: The ability to abduct is lost in the absence of the deltoid
FALSE. You can still abduct the arm but it will be a little weaker
T/F: The supraspinatus is active throughout elevation and in all scapular planes of rotation
TRUE
Which muscles are considered GH compressors?
Supraspinatus (with the aid of gravity)
Infraspinatus
Teres Minor
Subscapularis
Deltoid (@ 90° of ABD)
LH of the biceps (@ 90° of ABD/FLX)
Which muscles counteract the superior translation moment of the deltoid?
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Subscapularis
Prime movers for ER with a BIG role in deceleration forces
Infraspinatus and Teres Minor
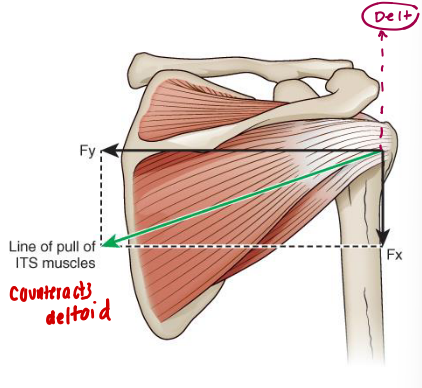
Restricted scapular upward rotation results in loss of _______ tension and _______ active GH ROM
Restricted scapular upward rotation results in loss of deltoid tension and decreased active GH ROM
The deltoid is most efficient in the…
Scapular plane
What movement impairments can be seen with a deficit in upward rotators? What if SA/traps were paralyzed?
The middle and posterior deltoid would take over and downwardly rotate the scapula (opposite of what we want)
In the complete loss of upward rotators, the arm can only raise 60-75°
What are the contributors to dynamic stability of the shoulder in the following positions: At rest, mid range, end range?
At rest:
Negative intra-articular pressure
Superior GHL
Maybe also supraspinatus
Mid range:
RTC and imuscular force couples
End range:
Capsular ligaments
What does the patient specific functional scale measure? How is it scored?
Measures up to 5 patient-selected activities — which MUST remain the same for reassessment
Measured by “difficulty with activity” for 0-10 (higher numbers better)
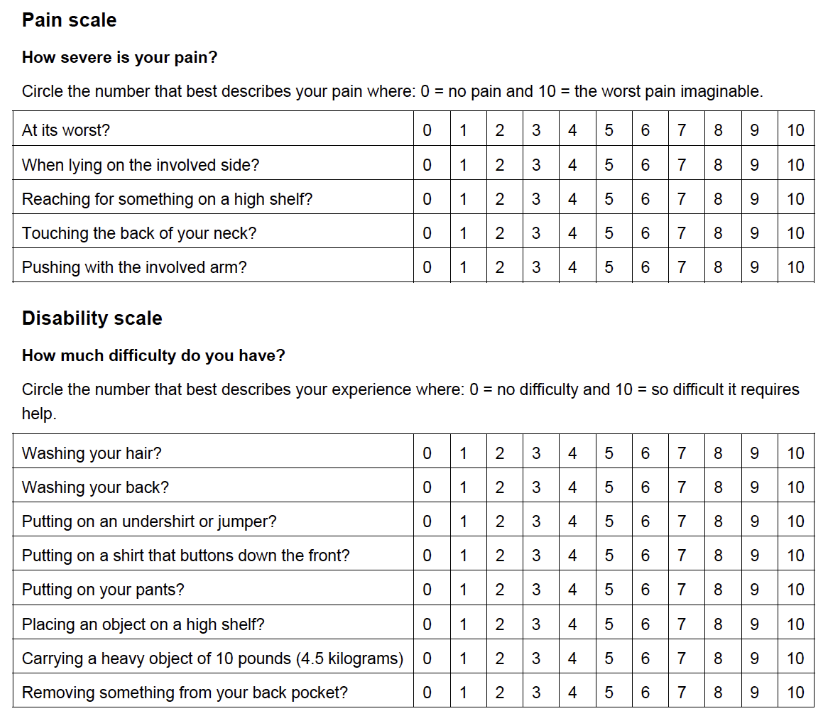
Shoulder Pain and Disability Index (SPADI) Overview — (Items, completion time, scales, scoring, clinical application)
13 items (5 pain, 8 function)
5-8 min
NPRS for pain & 10 pt (Likert) scale for function
0-100 (best to worst)***
Low scores=good (% of disability)
MDC: 18 / MCID: 8-13
Simple Shoulder Test (SST) — (Items, completion time, scales, scoring, clinical application)
12 items (all function)
<3 min
Yes/no scale
0-12 (worst to best)

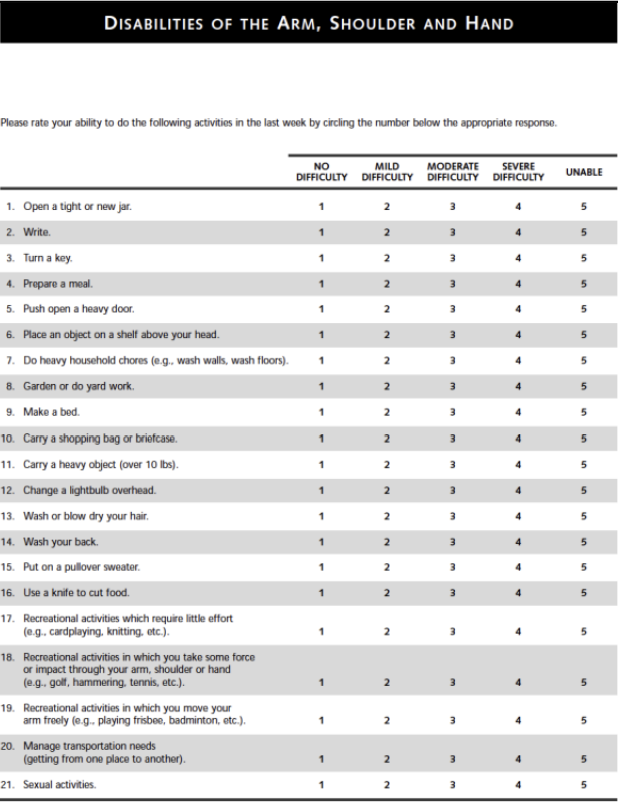
Disability of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) — (Items, completion time, scales, scoring, clinical application)
30 items
5 symptoms (pain, N/T, strength, stiffness)
24 function
1 sleep
5-8 min
5 pt Likert scale
0-100 (best to worst)***
Low scores=good (% of disability)
MDC: 10.5 / MCID: 10.2
Quick DASH — (Items, completion time, scales, scoring, clinical application)
11 items
2 symptoms (pain, N/T)
8 function
1 sleep
<3 min
5 pt Likert scale
0-100 (best to worst)***
Low scores=good (% of disability)
MDC: 12.8 / MCID: 15.9
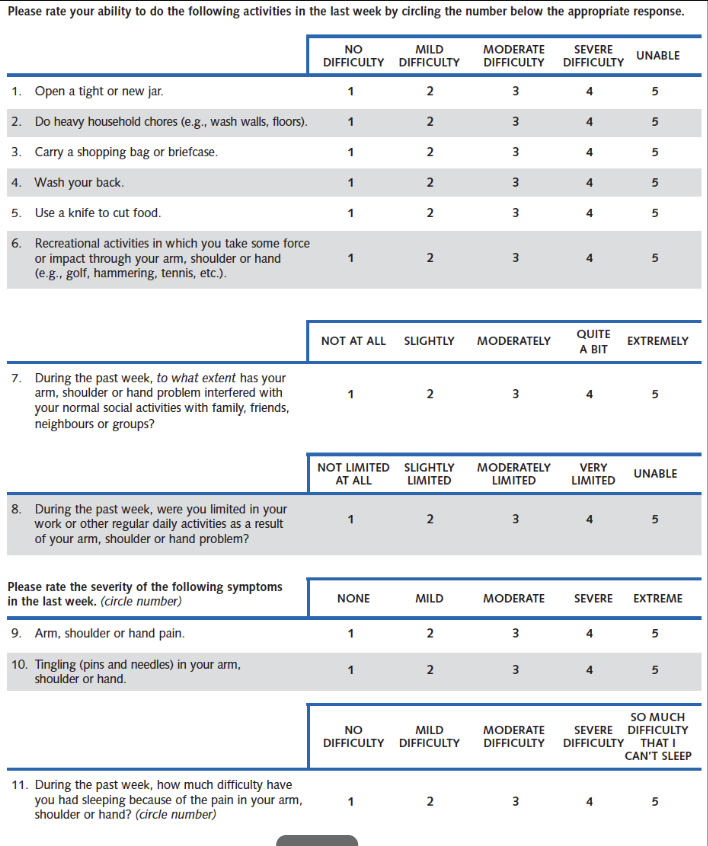
ASES Shoulder Score Overview — (Items, completion time, scales, scoring, clinical application)
11 items (1 pain, 10 function)
<5 mins
NPRS for pain & 4 pt scale (Likert) for ADLs
0-100 (worst → best)
MDC: 9.4 / MCID: 6.4

Match the type of pain to the possible structure resposnible for it:
Cramping, dull, aching →
Dull, aching →
Sharp, shooting →
Sharp, burning, stinging, bright, lightning-like →
Deep, nagging, dull →
Sharp, severe, intolerable →
Throbbing, pulsating, diffuse →
Cramping, dull, aching → muscle
Dull, aching → ligament, joint capsule
Sharp, shooting → nerve root
Sharp, burning, stinging, bright, lightning-like → nerve
Deep, nagging, dull → bone
Sharp, severe, intolerable → fracture
Throbbing, pulsating, diffuse → vascular
Frequency and pain nature
Intermittent → Mechanical
Constant, but varies w/ activity → Inflammatory & mechanical (related to movement & stress)
Constant, but does not vary → Acute disease or serious pathology
Match complaints to condition:
Anterior/lateral pain with overhead activity
Painful arc
Pain lying on that side
External Impingement/Bursitis/Tendonitis
Match complaints to condition:
Apprehension, pain with activity (ABD/ER)
Dead arm feeling, performance loss
Younger age (<35)
Instability/labral lesion
Match complaints to condition:
Age 40+, pain and weakness
RCT/degeneration
Match complaints to condition:
Fall onto that shoulder
Pain laying on that shoulder
AC Sprain
Match complaints to condition:
Poorly located, insidious onset, limited ROM
Age > 45, female
Adhesive Capsulitis
Match complaints to condition:
UE heaviness, numbness with prolonged postures and when lying on that sid
TOS/Cervical radiculopathy