32 - Digestion of the proteins and absorption of the amino acids in gastrointestinal tract. Nitrogen balance and final excreted products of nitrogen metabolism. General reactions of amino acids metabolism – transamination, oxidative deamination, trans-deamination, decarboxylation. Biologically active amines (biogenic amines) – examples and function. Clinical significance of transaminases.
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
sections
proteins
physical digestion
chemical digestion
absorption
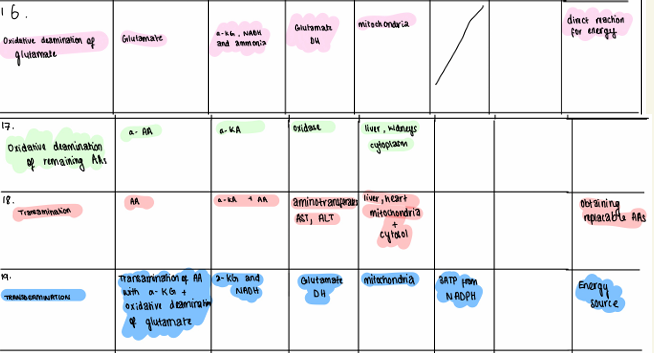
oxidative deamination
transamination
decarboxylation
oral box
proteins
chains of amino acids
amino terminal + hydroxyl terminal
physical digestionb
mouth
chemical digestion
stomach → pepsinogen → pepsin
pepsin breaks down peptide bonds
stomach cells secrete pepsinogen in presence of food
simultaneously HCL is secreted, triggers conversion of pepsinogen to pepsin
Polypeptide enters small intestines
duodenum main site for digestion + absorption
pancreas secretes trypsinogen + chymotrypsin
enterokines convert trypsinogen → trypsin (hydrolyses polypeptide bonds, helps convert chymotrypsinogen)
large polypeptides are broken into small polypeptides
Brush border enzymes digest small polypeptides to amino acids
absorption
small peptides absorbed through co-transporter with H+ then hydrolysed to amino acids
AAs carried theough blood to liver
AAs absorbed with Na+ then gets into blood
Leads to absorption of Na+ (by Na/K pump) so water also absorbed
AAs go into liver
oxidative deamination
removal of amine functional group + replacing it with ketone group
Ammonia into urea cycle
Occurs in glutamic acid as it is end product of transamination
localised in liver
transamination
transfer of amine group of 1 molecule to another
catalysed by transaminases
results in transfer of amine group of one acids and ketone of another acid
major keto acid - alpha KG
decarboxylation
splitting off of COOH as CO2
Catalysed by - decarboxylases
oral box