W4L1: Electrophilic addition reactions: the basics
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
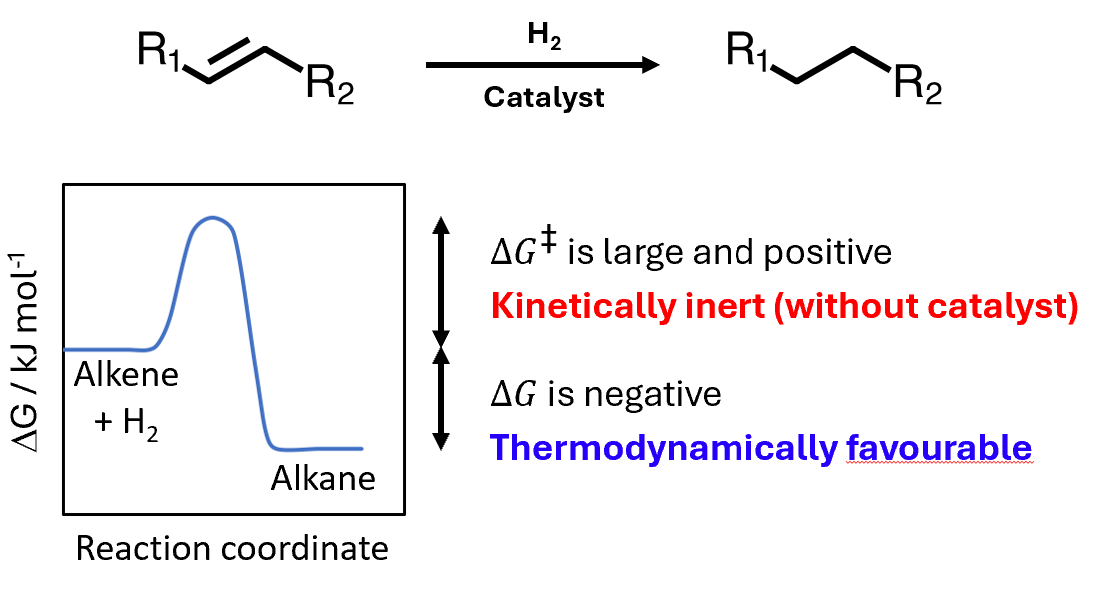
Addition of hydrogen to alkenes makes alkanes
Alkene is reduced and hydrogen is oxidised - redox reaction
Overall delta G is negative - favourable, barrier is very high and requires a catalyst
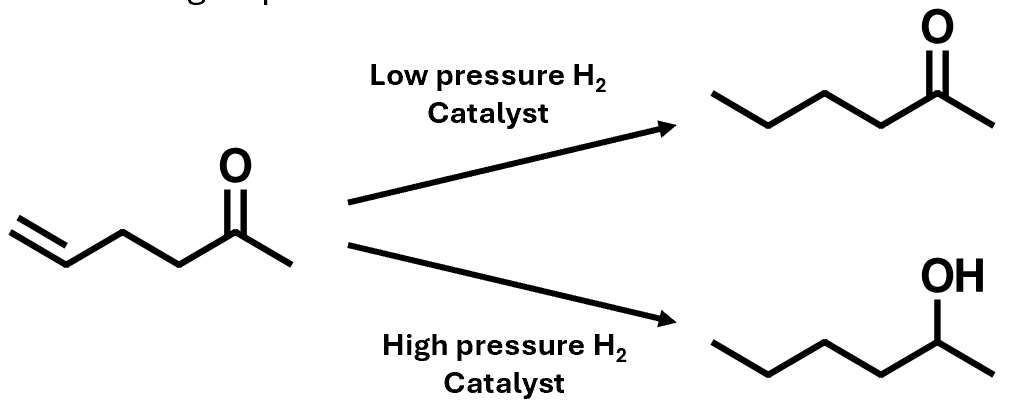
Hydrogenation: chemoselectivity
Alkenes can be hydrogenated in the presence of other functional groups
This is called chemoselectivity – the selection of one functional group over another
The molecule containss both an alkene and a ketone, then under mild conditions can hydrogenate the alkene while leaving the ketone untouched. If, however, we run the reaction under more forcing conditions, by increasing the pressure, then we can reduce the ketone also
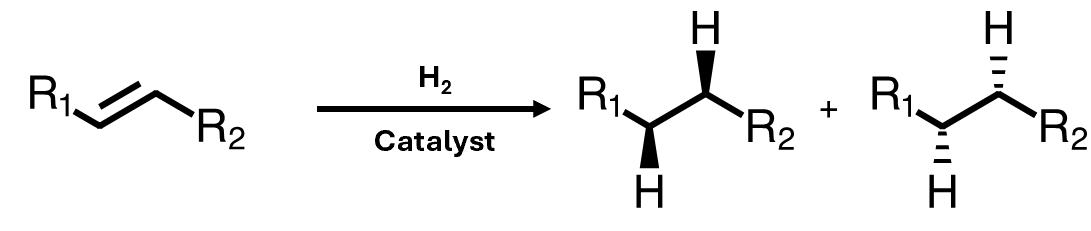
Hydrogenation: stereospecificity
The two hydrogen atoms always add syn to one another
This is called stereospecificity – the reaction mechanism only allows a specific stereochemical outcome
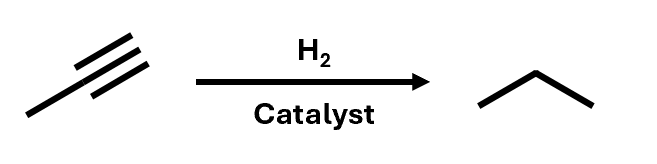
Alkynes can be hydrogenated to alkanes
propyne to propane
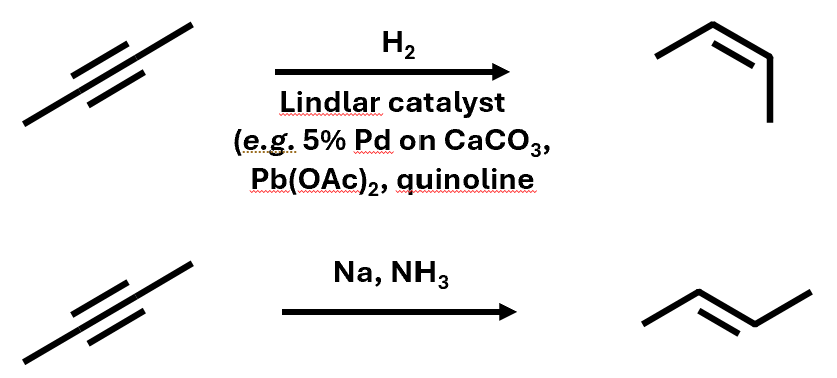
Alkynes can be partially hydrogenated to alkenes
Can get cis or trans product with different reactants
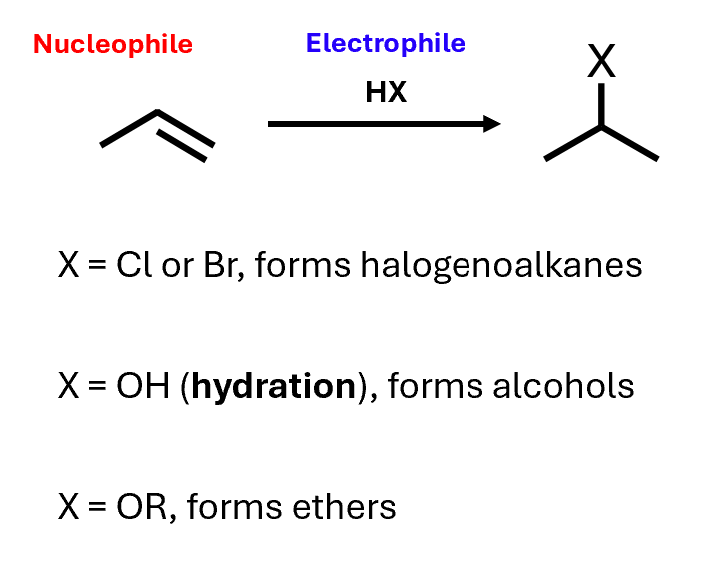
Electrophilic addition to alkenes
Alkenes can act as nucleophiles, and suitable electrophiles can add to them
Can react with HCl or HBr to form halogenoalkanes
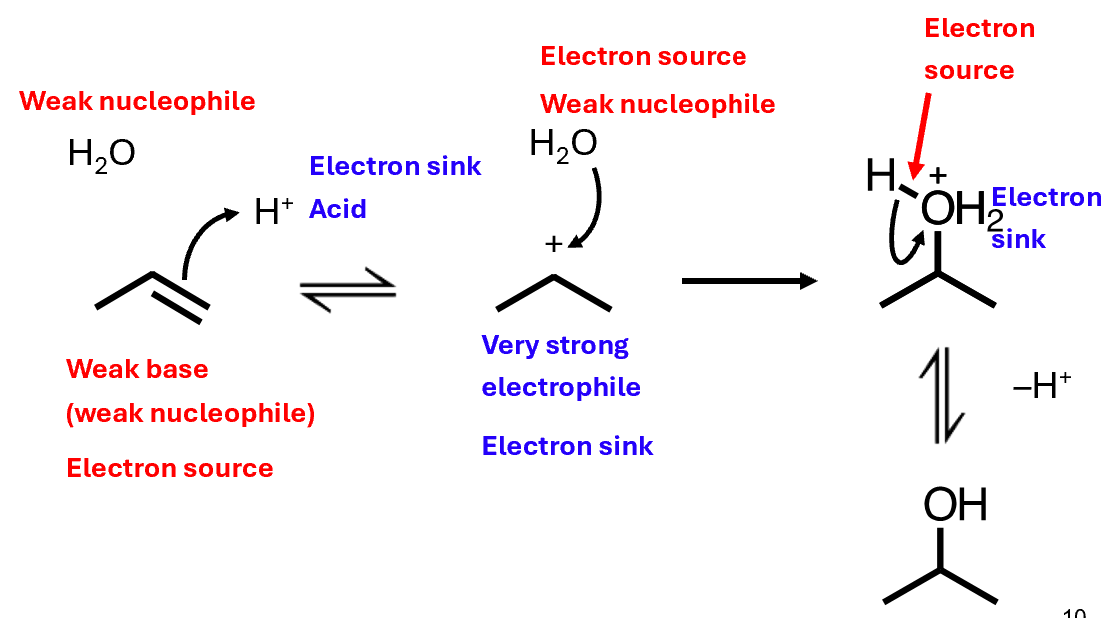
React with water to form alcohols
React with alcohols to form ethers
Electrophilic addition because the species that adds to the alkene initially acts as an electrophile
Alkenes are electron-rich, so they can act as nucleophiles
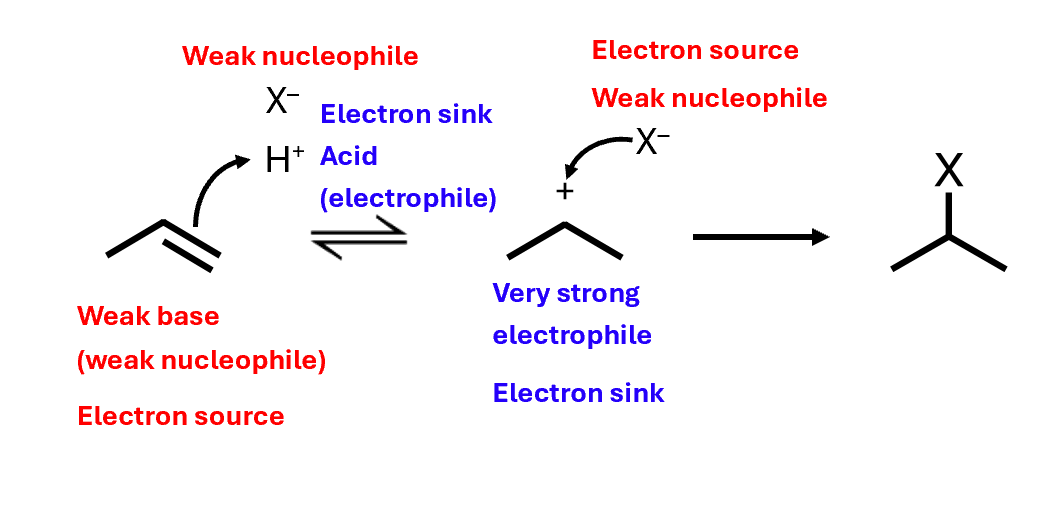
Electrophilic addition: mechanism
Not stereoselective - forms a racemic mixture
Electrophilic addition: selectivity
The acid always adds to form the more stable carbocation
This is called regioselectivity – the selection of one region of the molecule over another
More stable secondary carbocation is more likely to form - more of the 2-halogenopropane is formed
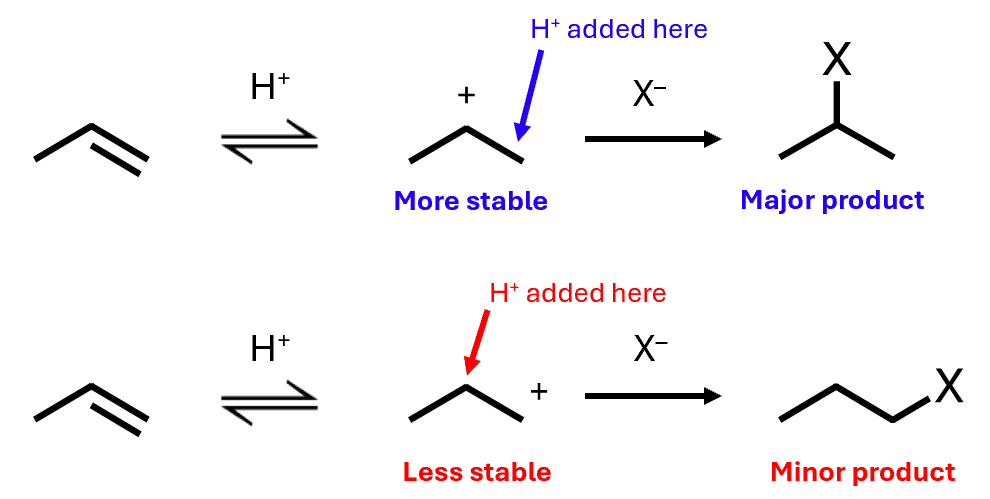
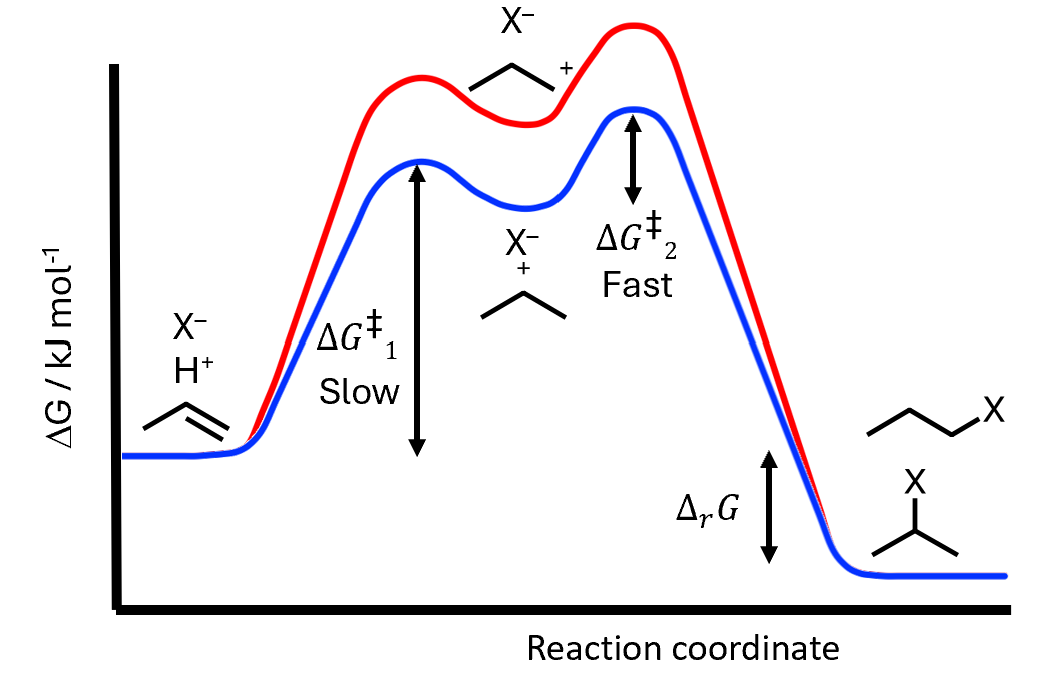
Electrophilic addition: energies
Alkene and hydrohalic acid are reactants
Forms the intermediate carbocation and retains halide anion - slow
Second barrier to form product
Formation of alcohols and ethers is slightly more complex
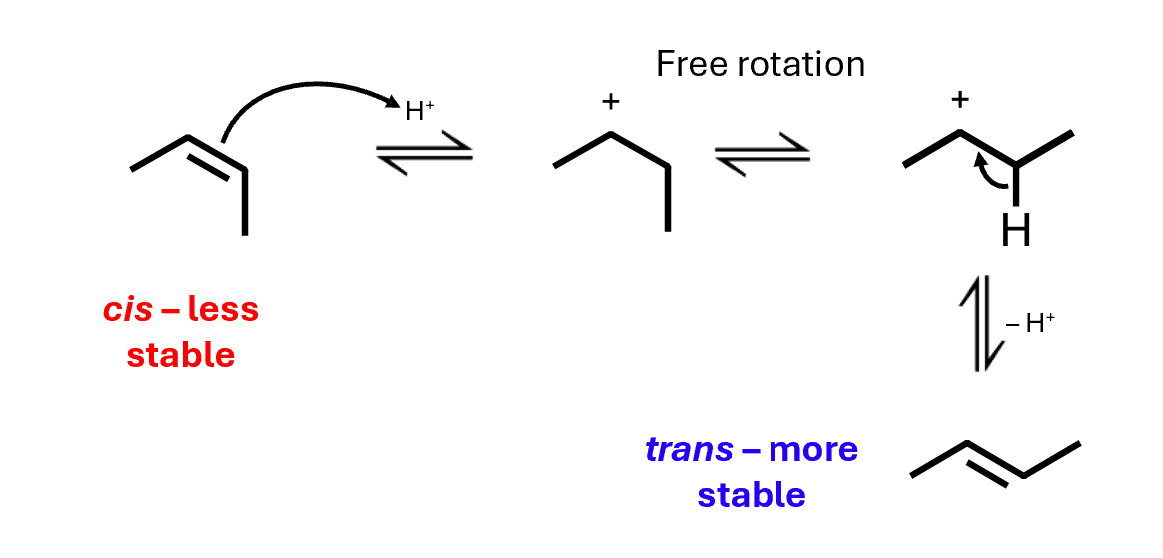
Alkene isomerisation
A low concentration of acid will isomerise a cis alkene, rather than adding to it:
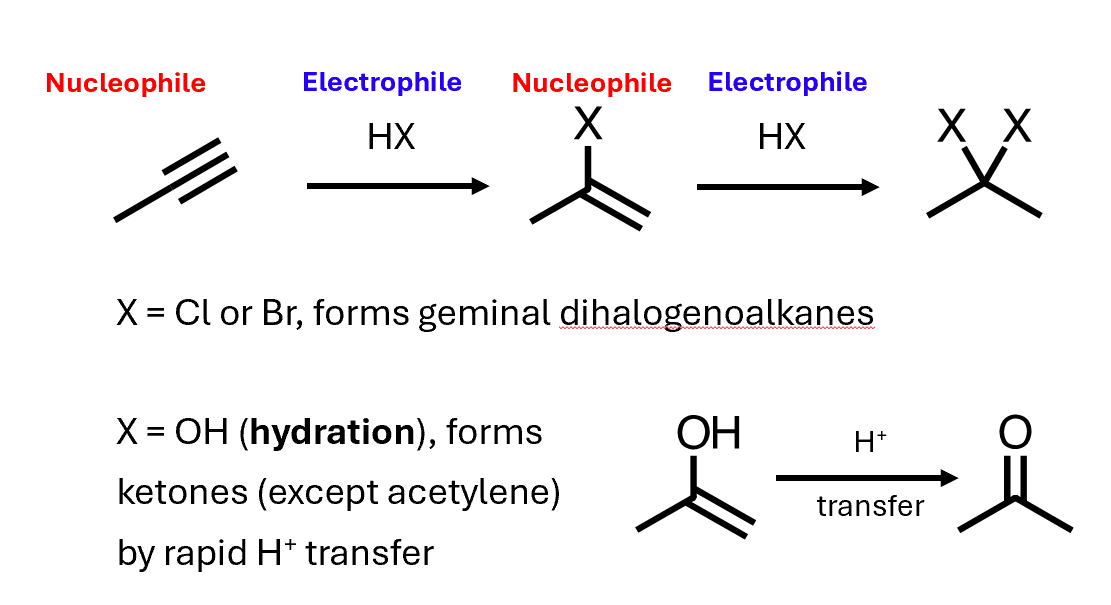
Electrophilic addition to alkynes
Alkynes can also act as nucleophiles, and suitable electrophiles can add to them
Germinal - compound with the functional groups on the same carbon atom