Chem161, unit4
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Ionic vs Covalent Bonds
Ionic: Metal + Non-metal
Covalent: Non-metal + Non-metal
How is an empirical formula different from a molecular formula?
The molecular formula shows the actual number of each atom in a molecule, while the empirical formula shows the simplest ratio.
(Example: Glucose — molecular: C₆H₁₂O₆, empirical: CH₂O)
What is lattice energy, how to compare lattice energy?
Lattice energy (ΔHₗₐₜₜ) is the energy released when gaseous ions form an ionic solid, or the energy required to separate an ionic solid into gaseous ions.
Equation:E=k\frac{Q_1Q_2}{r}
r = is the sum of the ionic radii of the cation and anion in the compound
Q1 and Q2 = the charges of both ions
E = Lattice Energy
Radius trend in Periodic Table
Radius increase: Top—> Bottom
Radius decrease:Left—> right
radius exponentially increases (so radius differences are larger for atoms lower on the periodic table)
comparing radius of elements
1) We can use the period table radius trend, BUT..
If two elements are in a different row and column, the smallest is the one with less electrons
If two electrons are in a different row and column and have the same number of electrons, the smallest is the one with more protons
How do you name a binary ionic compound when the cation is multivalent(could be any charge)?
Back (Answer):
Identify the cation (metal) and its possible charges.
Identify the anion (nonmetal) and its charge.
Determine the charge of the cation that balances the anion.
Write the cation name first, followed by the anion name.
Indicate the cation’s charge with a Roman numeral in parentheses.
Example:
FeCl₂ → Iron(II) chloride
FeCl₃ → Iron(III) chloride
What are the charges of compounds typically?
they are formed to be neutral
(excluding the specific ones we are memorizing)
Elements that exist as a Diatomic Molecule
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2
How do we name elements?
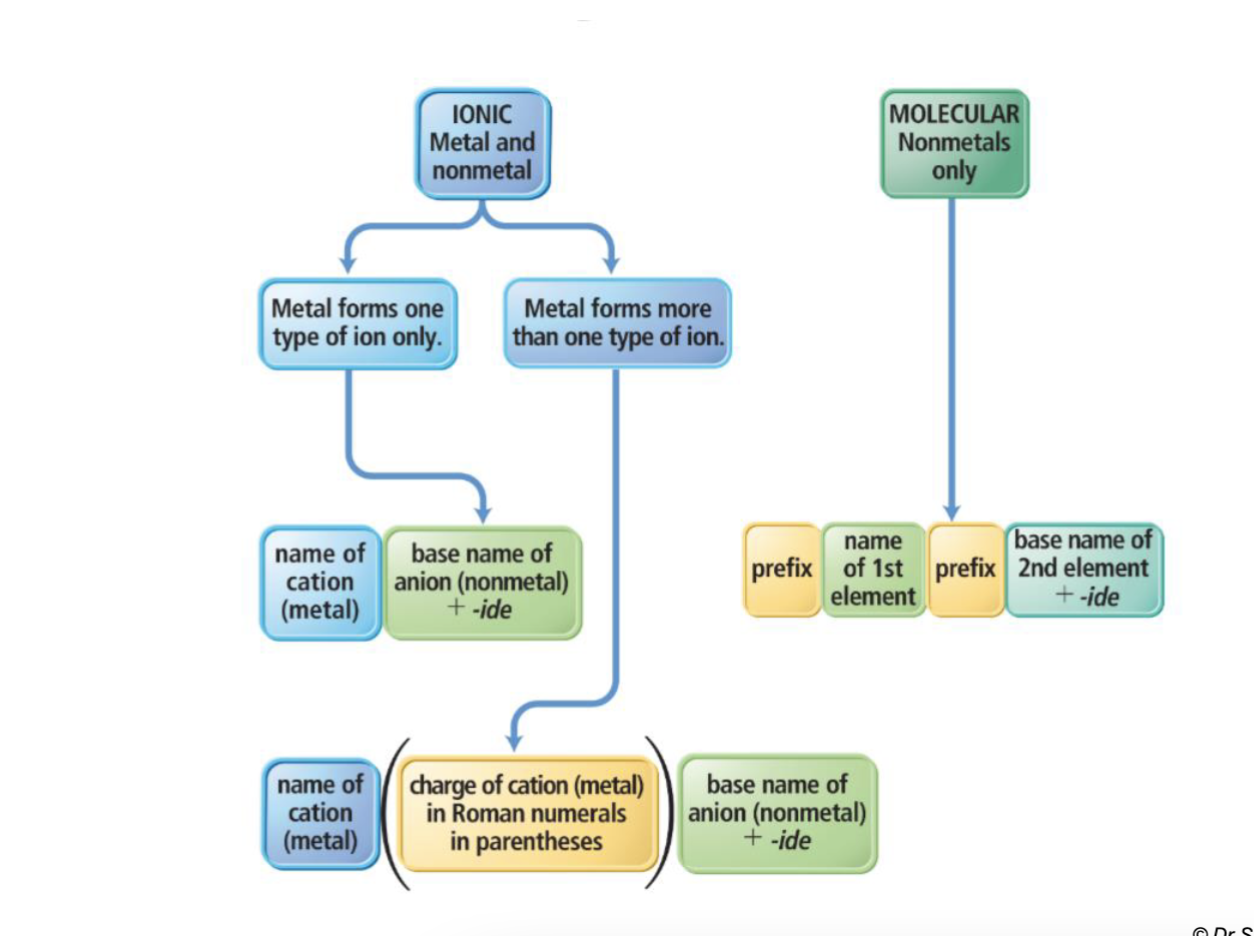
Molecular Compound Prefixes (Nonmetal + Nonmetal)
1 — mono- (omit “mono” on the first element)
2 — di-
3 — tri-
4 — tetra-
5 — penta-
6 — hexa-
7 — hepta-
8 — octa-
9 — nona-
10 — deca-
outliers for the roman numeral rule for ionic compounds
“Al, Zn, Sc — no Roman for me!”
aluminum
scandium
Zinc
main group elemtns that still use roman numeral
Tin(Sn)
Lead(Pb)
Antimony(Sb)
Bismuth(Bi)
How do you identify a hydrocarbon?
No oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or halogens present.
Molecular formulas look like CₓHᵧ.
Common types:
Alkane: single bonds only → CₙH₂ₙ₊₂
Alkene: one double bond → CₙH₂ₙ
Alkyne: one triple bond → CₙH₂ₙ₋₂
Aromatic (benzene rings): follow C₆H₆-type pattern
✅ Examples:
CH₄ → methane (alkane)
C₂H₄ → ethene (alkene)
C₂H₂ → ethyne (alkyne)
What’s the difference between organic and inorganic compounds?
✅ Organic Compounds:
Always contain carbon (C) (usually bonded to H, O, N, or S)
Often found in living organisms
Covalent bonding dominates
Examples: CH₄, C₆H₁₂O₆, C₂H₅OH
✅ Inorganic Compounds:
Usually do not contain carbon, or carbon isn’t bonded to hydrogen
Often from nonliving sources (minerals, salts, metals)
Often ionic bonding
Examples: NaCl, H₂O, CO₂*, NH₃
🟡 Note: CO₂, CO, and carbonates (like CaCO₃) are inorganic, even though they have carbon.
What are the main functional groups to identify?
✅ Alkene (C=C) → double bond between carbons
✅ Alkyne (C≡C) → triple bond between carbons
✅ Alcohol (R–OH) → hydroxyl group on carbon
✅ Carboxylic Acid (R–COOH) → carbon with C=O and O–H
✅ Amine (C-N, C-NH-C, C-NH²) → nitrogen attached to carbon/hydrogen
How can you quickly recognize these functional groups in a molecule?
Look for C=C → alkene
Look for C≡C → alkyne
Look for O–H → alcohol or acid
If C=O and O–H on the same carbon → carboxylic acid
Look for N attached to C/H → amine
what is a functional group?
–OH → Alcohols
–COOH → Carboxylic acids
–NH₂ → Amines
C=C → Alkenes
💡 Think of functional groups as the “active sites” of organic molecules — they decide how a molecule behaves.
formula mass
find the mass of the compound the give you… NOT THE MASS OF THE SIMPLEST RATIO VERSION OF THE COMPOUND
How do you determine a chemical formula given the ratios of each element?
Convert each percent to grams(multiply by 100 g)
convert to moles(via g/mol number for each element)
balance moles!
Combustion analysis procedure
find the number of C and H moles based on the H20 and C02 produces
(if Oxygen in compound) find the moles of Oxygen in the element by subtracting the mass of the C and O by the total mass of the compound and then use that number to find the moles of oxygen via g/mol of oxygen
balance the moles in the compound
Hydrocarbon
Definition: Compounds made only of carbon (C) and hydrogen (H).
Main Types:
Alkanes – single bonds only (CnH₂n₊₂)
Alkenes – at least one double bond (CnH₂n)
Alkynes – at least one triple bond (CnH₂n₋₂)
Aromatic – contain benzene rings (C₆H₆ type)