MAN 3025 Exam 2 (Modules 6-9)
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
188 Terms
What three factors work in alignment to support strategic implementation?
Organizational culture
Organizational structure
HR practices
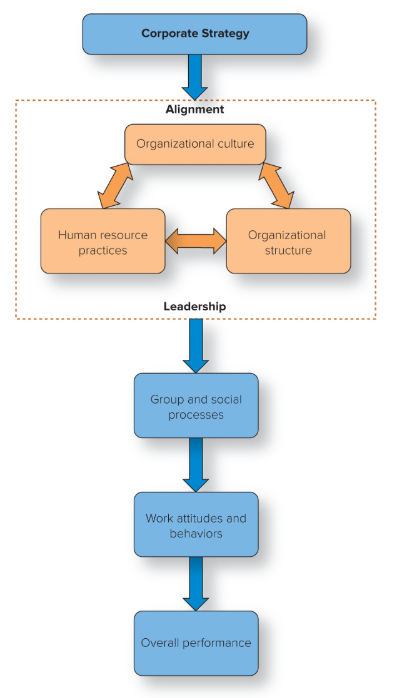
organizational culture
The shared assumptions that affect how work gets done
organizational structure
Formal system of task and reporting relationships
HR practices
All of the activities an organization uses to manage its human capital
3 Levels of Organizational Culture
Observable artifacts
Espoused values
Basic assumptions
observable artifacts
Physical manifestations of culture
espoused values
Explicitly stated values and norms preferred by an organization
enacted values
Values and norms actually exhibited in the organization
basic assumptions
Core values of the organization
How employees learn culture
Symbols
Stories
Heroes
Rites and rituals
Organizational socialization

hero
A person whose accomplishments embody the values of the organization
rites and rituals
The activities and ceremonies, planned and unplanned, that celebrate important occasions and accomplishments in organizational life
organizational socialization
The process by which people learn the values, norms, and required behaviors to be a member of an organization
4 Types of Organizational Culture
Clan
Adhocracy
Market
Hierarchy
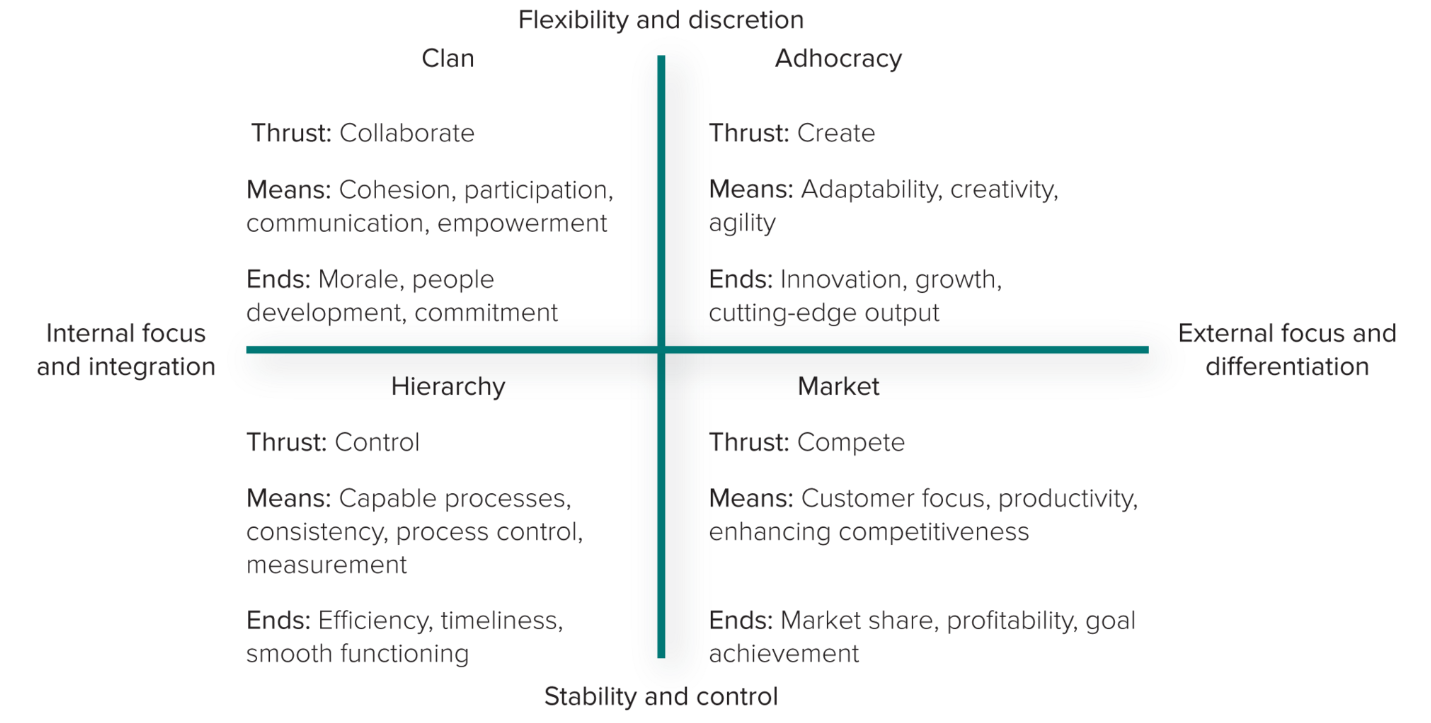
CVF horizontal dimension
Inward or outward focus?
Internal dynamics and employees (internal focus and integration) vs external environment and customers and shareholders (external focus and differentiation)
CVF vertical dimension
Flexibility or stability?
Decentralized decision making (flexibility and discretion) vs Centralized authority (stability and control)
clan culture
Internal focus and values flexibility rather than stability and control

adhocracy culture
External focus and values flexibility

market culture
Strong external focus and values stability and control

hierarchy culture
Internal focus and values stability and control over flexibility

person-organization (PO) fit
Extent to which your personality and values match the climate and culture in an organization
12 Levers for Organizational Culture Change
Formal statements
Slogans and sayings
Rites and rituals
Stories, legends, and myths
Leader reactions to crises
Role modeling, training, and coaching
Physical design
Rewards, titles, promotions, and bonuses
Organizational goals and performance criteria
Measurable and controllable activities
Organizational structure
Organizational systems and procedures

organization
A group of people who work together to achieve some specific purpose
7 Major Features of Organizations
Common purpose
Coordinated effort
Division of labor
Hierarchy of authority
Span of control
Authority—accountability, responsibility, and delegation
Centralization versus decentralization of authority
4 Features of Organizations Proposed by Schein
Common purpose
Coordinated effort
Division of labor
Hierarchy of authority
common purpose
Unifies employees or members and gives everyone an understanding of the organization’s reason for being
coordinated effort
The coordination of individual efforts into a group or organizationwide effort
division of labor
Work specialization; the arrangement of having discrete parts of a task done by different people
hierarchy of authority
Chain of command; control mechanism for making sure the right people do the right things at the right time
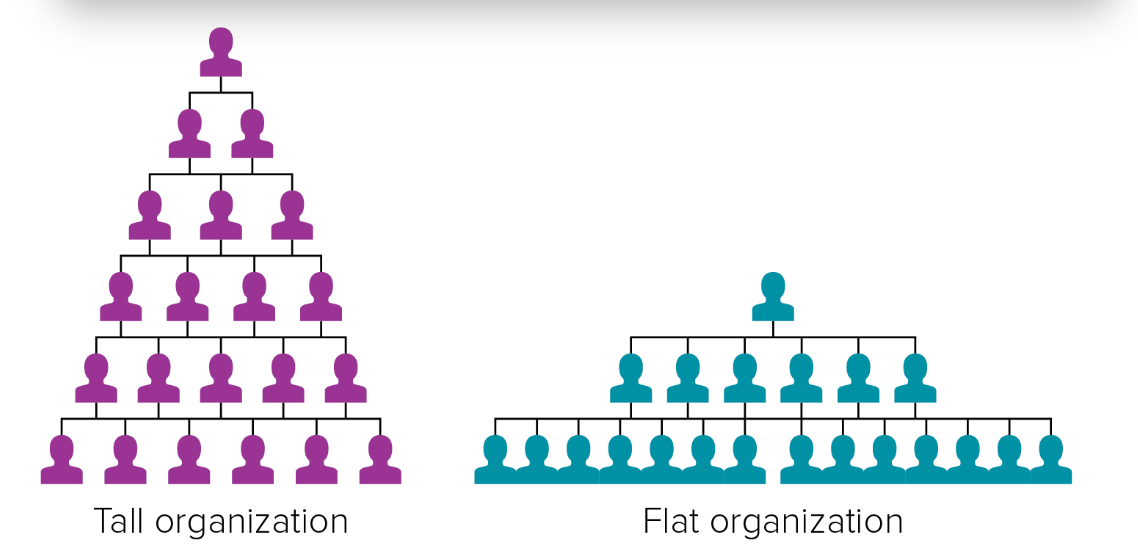
flat organization
Organizational structure with few or no levels of middle management between top managers and those reporting to them
unity of command
Principle that an employee should report to no more than one manager to avoid conflicting priorities and demands
span of control
The number of people reporting directly to a given manager; narrow (or tall) and wide (or flat)
authority
The rights inherent in a managerial position to make decisions, give orders, and utilize resources
accountability
Managers must report and justify work results to the managers above them
responsibility
The obligation one has to perform the assigned tasks
delegation
Process of assigning managerial authority and responsibility to managers and employees lower in the hierarchy
centralized authority
Important decisions are made by higher-level managers
decentralized authority
Important decisions are made by middle-level and supervisory-level managers
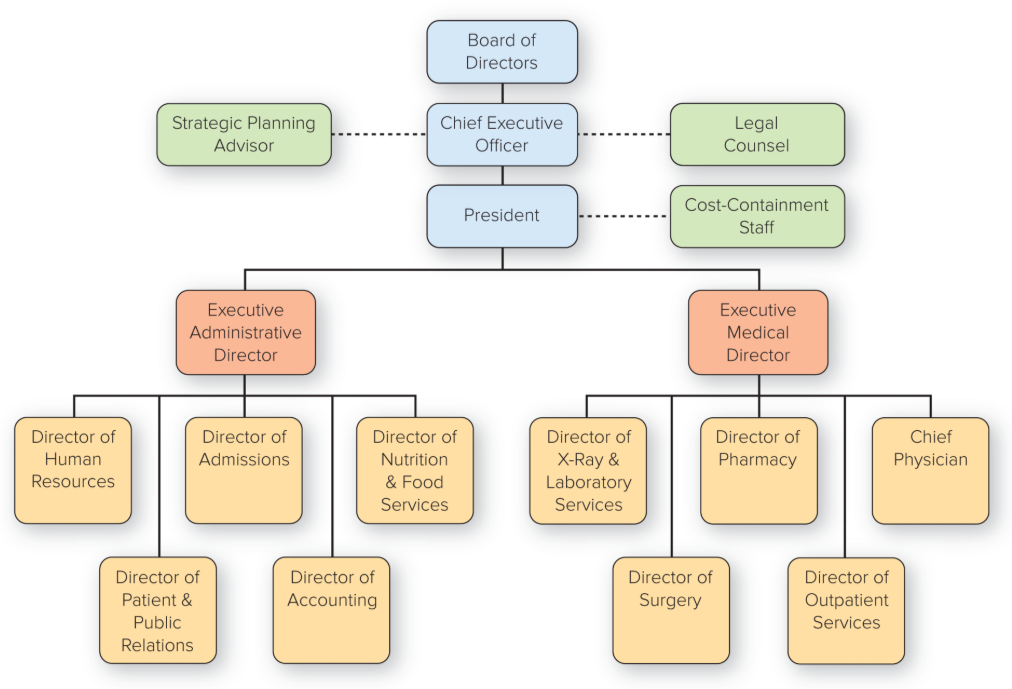
organization chart
Box and line illustration showing the formal lines of authority and the organization’s official positions or work specializations
8 Types of Organizational Structures
Simple
Functional
Divisional
Matrix
Horizontal
Hollow
Modular
Virtual
simple structure
Authority centralized in a single person, a flat hierarchy, few rules, and low work specialization

functional structure
People with similar occupational specialties are put together in formal groups
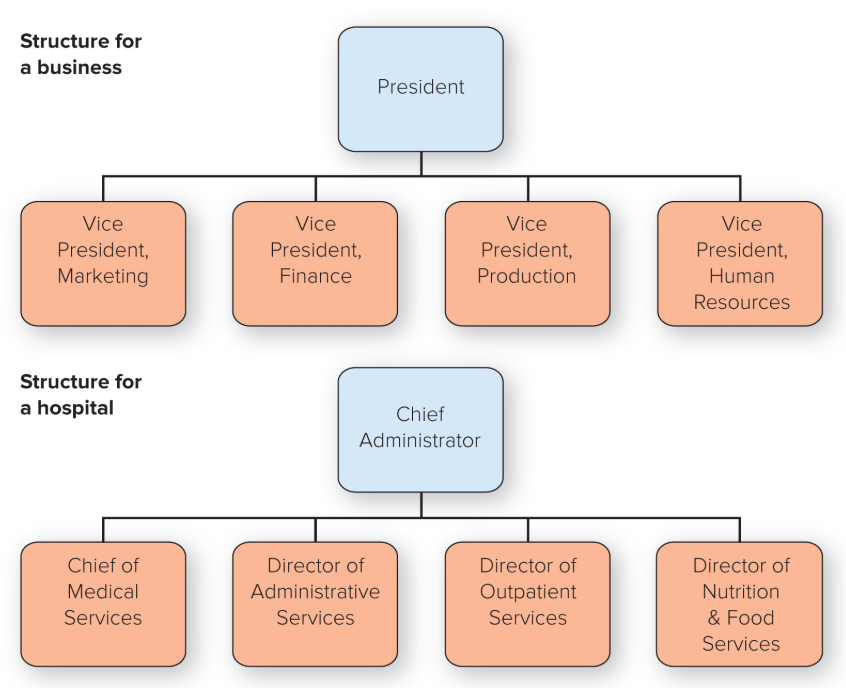
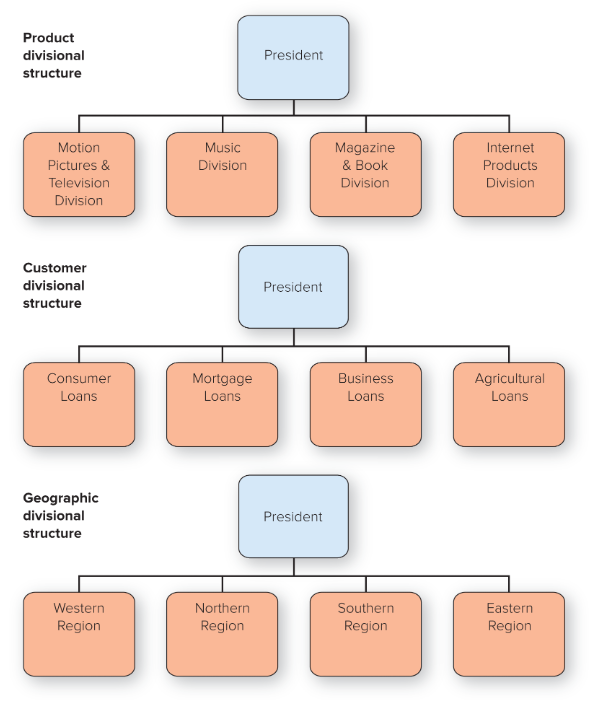
divisional structure
People with diverse occupational specialties are put together in formal groups by similar products or services, customers or clients, or geographic regions
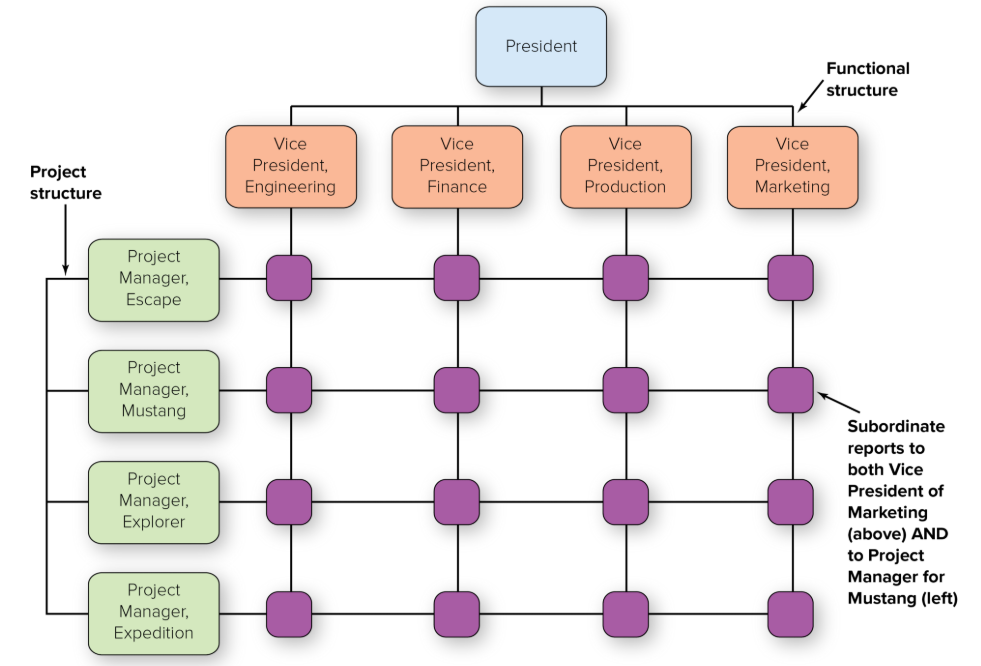
matrix structure
Combines functional and divisional chains of command in a grid so that there are two command structures—vertical and horizontal
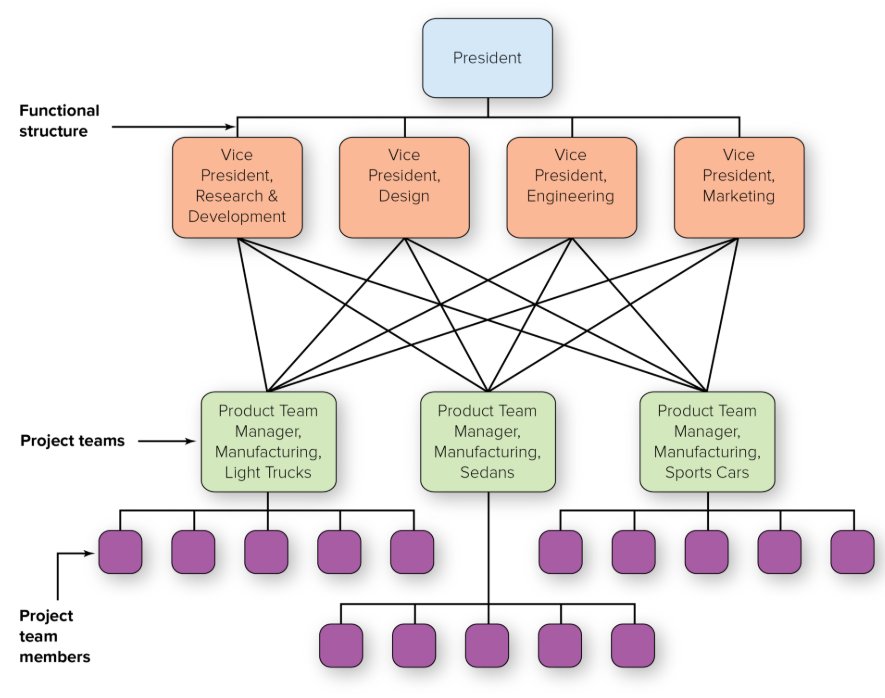
horizontal structure
Also called team-based design, teams or workgroups, either temporary or permanent, are used to improve collaboration and work on shared tasks by breaking down internal boundaries
boundaryless organization
A fluid, highly adaptive organization whose members, linked by information technology, come together to collaborate on common tasks
Includes hollow, modular, and virtual structures
hollow structure
Network structure; the organization has a central core of key functions and outsources other functions to vendors
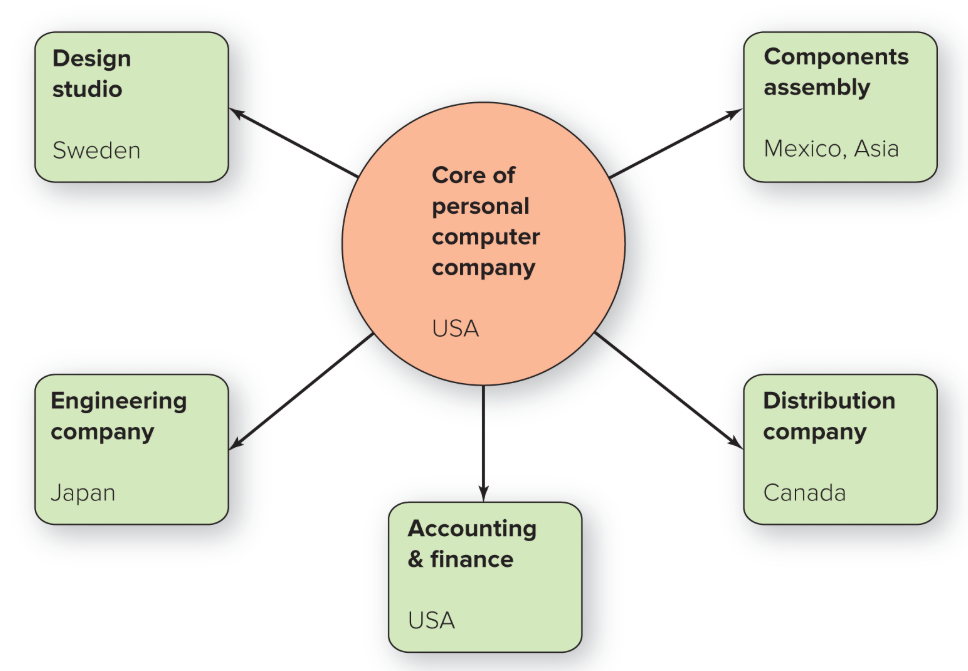
modular structure
A firm assembles product chunks, or modules, provided by outside contractors
virtual structure
An organization whose members are geographically apart and connected through the internet and remote work software
6 Supertrends shaping the future of business
The marketplace is becoming more segmented and moving toward more niche products
More competitors are offering targeted products, requiring faster speed-to-market
Some traditional companies may not survive radical change
Offshore suppliers are changing the way we work
Knowledge, not information, is becoming the new competitive advantage
Employment landscape is shifting

reactive change
Change in response to problems or opportunities as they arise
proactive change
Planned change; making carefully thought-out changes in anticipation of possible or expected problems or opportunities
Forces for change outside and inside the organization
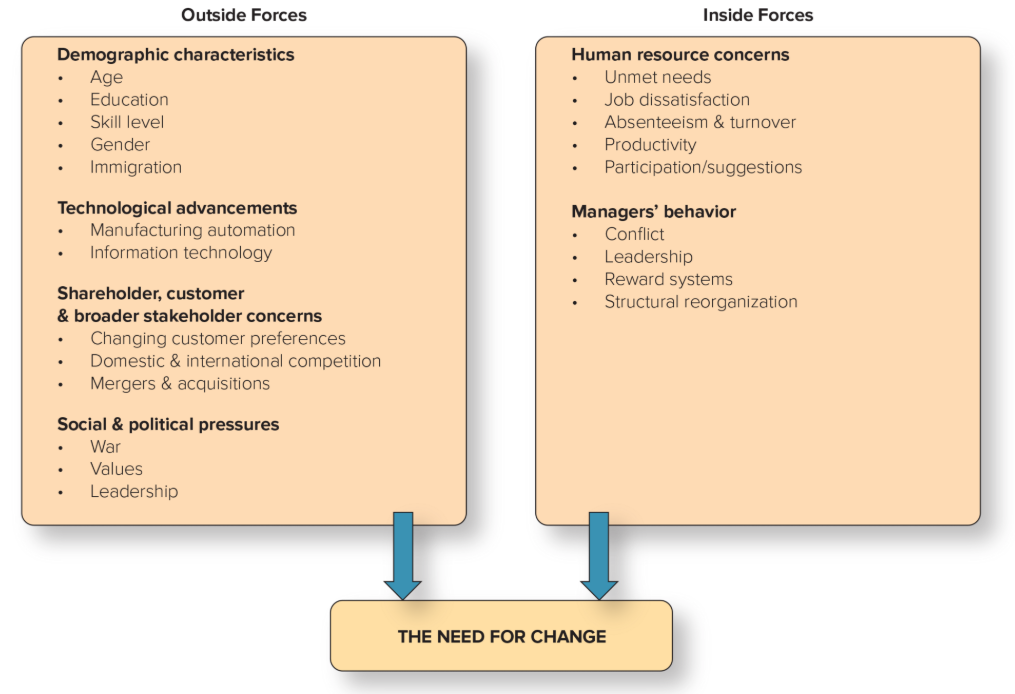
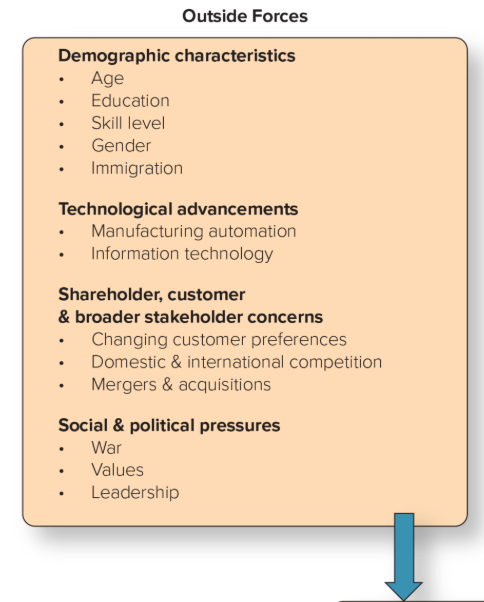
4 Outside Forces for Change
Demographic characteristics
Technological advancements
Shareholder, customer, and broader stakeholder concerns
Social and political pressures
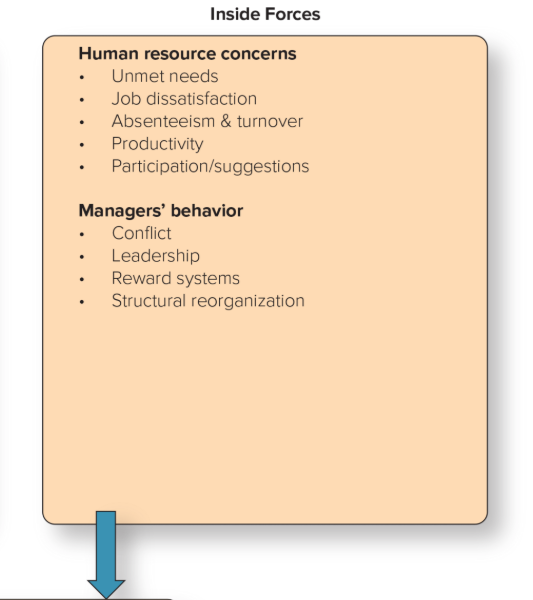
2 Inside Forces for Change
Human resource concerns
Managers’ behavior
3 Forms of Change
Adaptive change (least threatening)
Innovative change (somewhat threatening)
Radically innovative change (very threatening)

adaptive change
The reintroduction of a familiar practice
easiest to implement successfully
least threatening to employees
innovative change
The introduction of a practice that is new to the organization
moderately difficult to implement
somewhat threatening to employees
radically innovative change
Introduces a practice that is new to the industry
very difficult to implement
highly threatening to employees
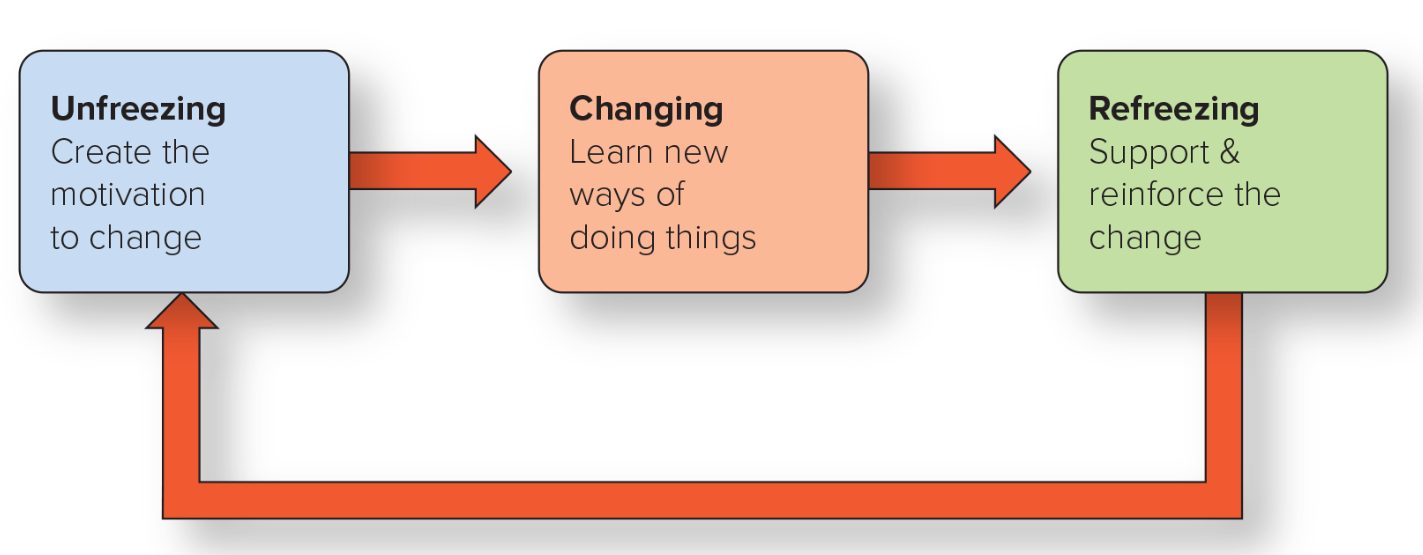
Lewin’s Change Model
Unfreezing - create the motivation to change
Changing - learn the new ways of doing things
Refreezing - support and reinforce the change
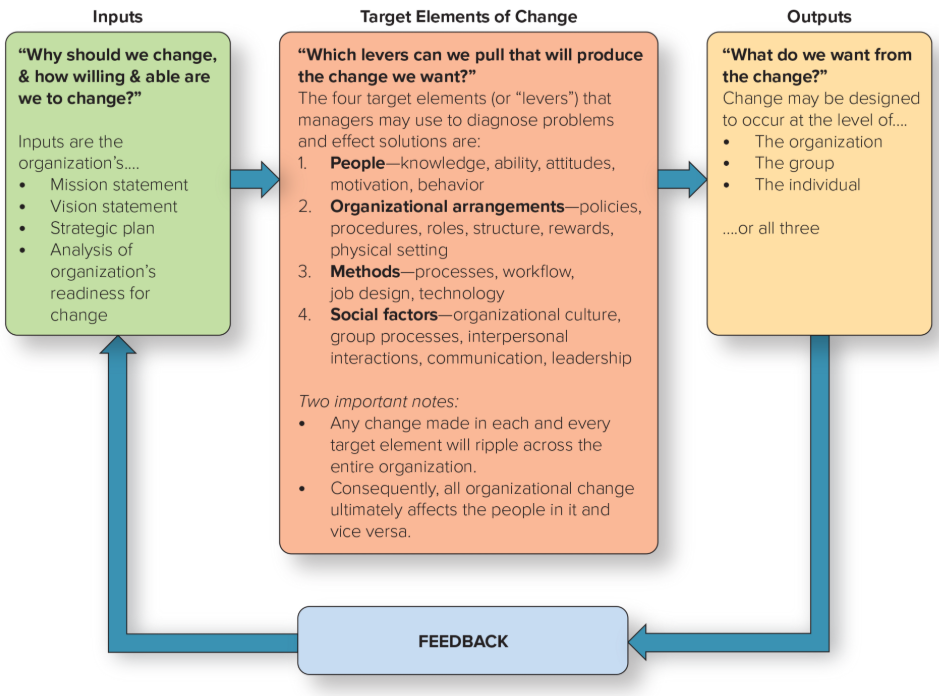
Systems Approach to Change
Change creates additional change
Consists of three parts:
Inputs
Target elements of change
Outputs
Feedback loop
force-field analysis
Technique to determine which forces could facilitate a proposed change and which forces could act against it
organizational development (OD)
A set of techniques for implementing planned change to make people and organizations more effective
3 Uses for OD
Improving individual, team, and organizational performance
Transforming organizations
Adapting to mergers
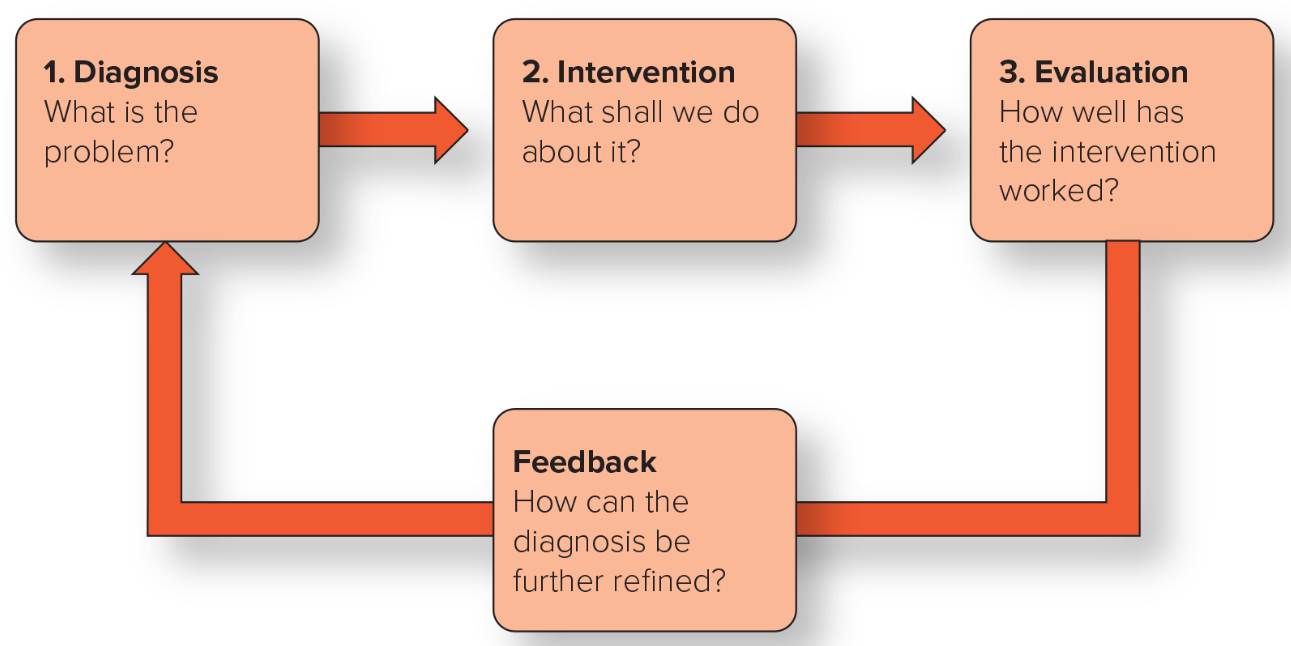
3 Steps of the OD Process
Diagnosis what is the problem?
Intervention what shall we do about it?
Evaluation how well has the intervention worked?
Feedback loop
4 factors that make OD successful
Multiple interventions
Top managers support the OD program
Goals are chosen wisely
Change agents understand how culture affects OD
Approaches to Innovation
Classified by crossing the type of innovation (product or process) with the focus of innovation (improvement or new-directions)
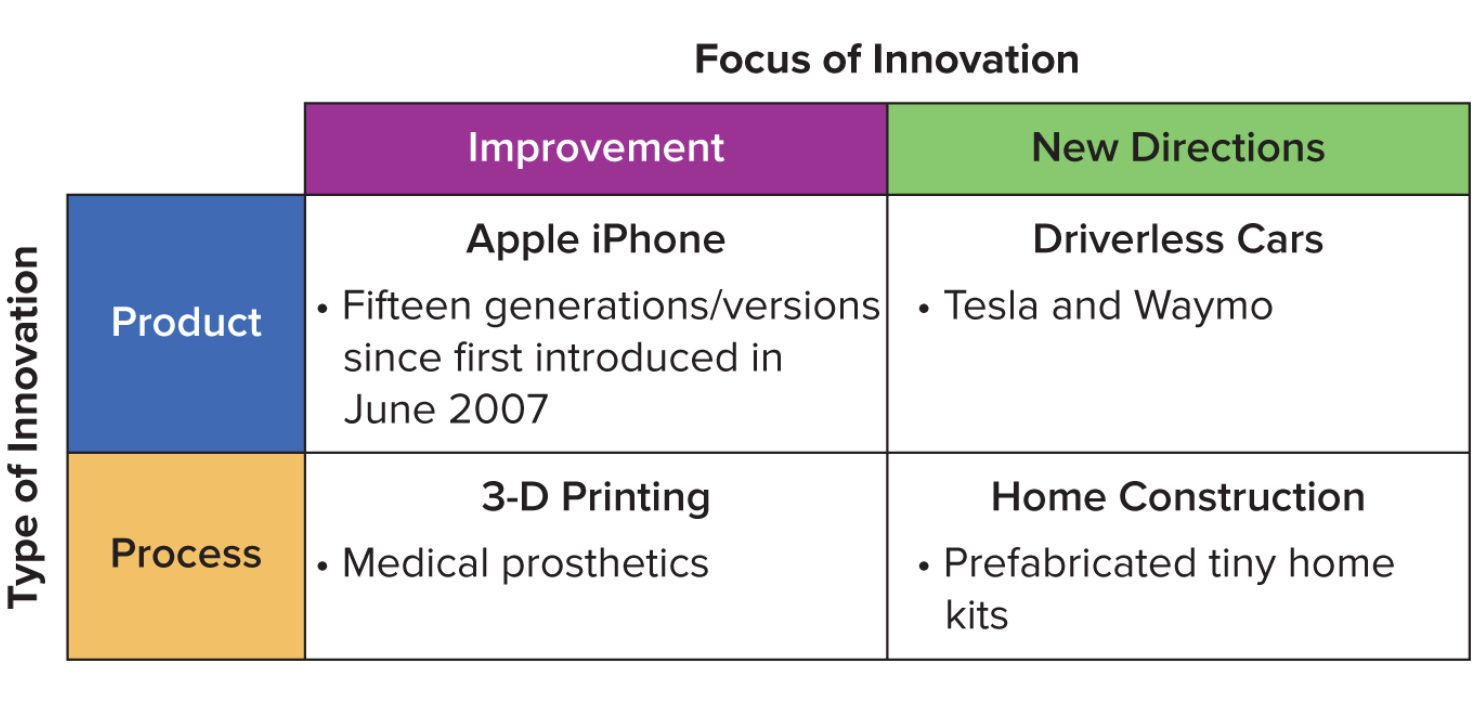
product innovation
Change in the appearance or functionality/performance of a product or service or the creation of a new one
process innovation
Change in the way a product or service is conceived, manufactured, or distributed
improvement innovations
Enhance or upgrade an existing product, service, or process
new-direction innovations
Take a totally new or different approach to a product, service, process, or industry
innovation system
A set of mutually reinforcing structures, processes, and practices that drive an organization’s choices around innovation and its ability to innovate successfully
7 Components of an Innovation System
Innovation strategy
Committed leadership
Innovative culture and climate
Required structure and processes
Necessary human capital
Human resource policies, practices, and procedures
Appropriate resources
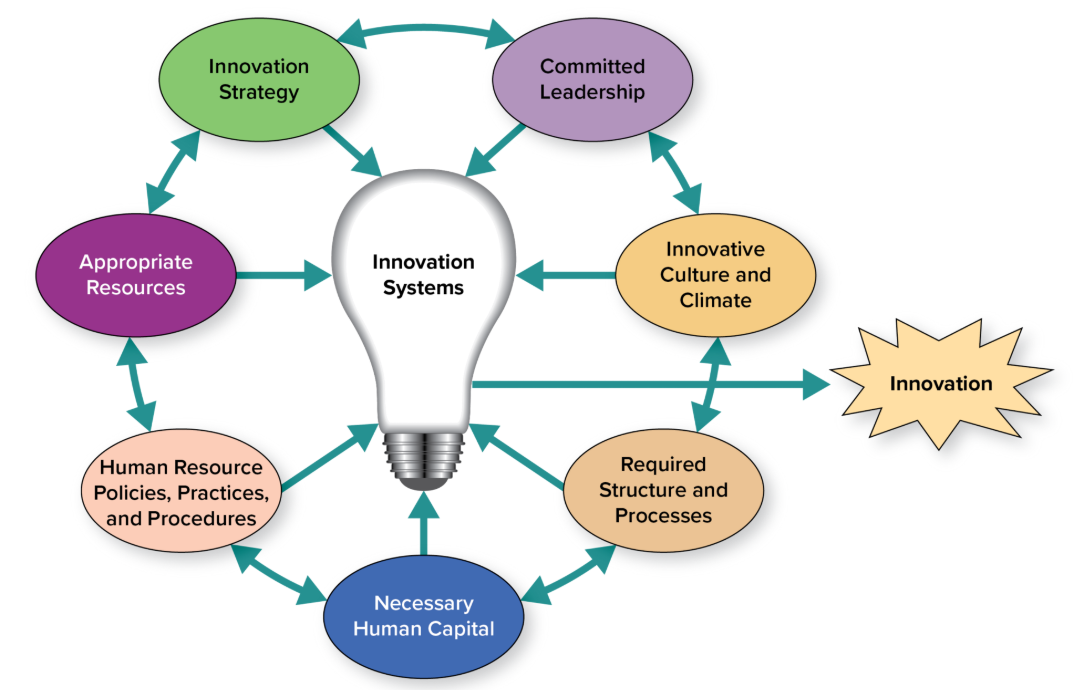
innovation strategy
A plan for being more innovative that requires a company to integrate its innovation activities into its business strategies
crowdsourcing
The practice of obtaining needed services, ideas, or content by soliciting contributions from a large group of people typically via the internet
resistance to change
An emotional/behavioral response to real or imagined threats to an established work routine
3 Causes for Resistance to Change
Employee characteristics
Change agent characteristics
The change-agent employee relationship
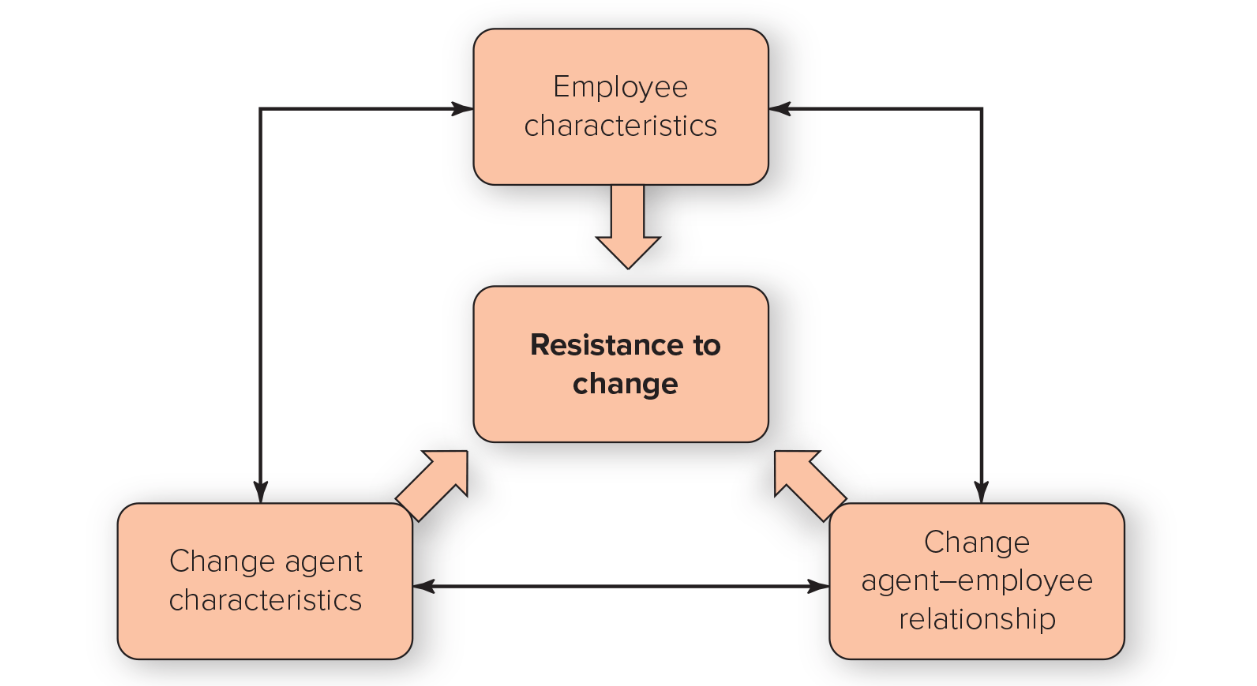
10 Reasons Employees Resist Change
Individuals’ predisposition toward change
Surprise and fear of the unknown
Climate of mistrust
Fear of failure
Loss of status or job security
Peer pressure
Disruption of cultural traditions or group relationships
Personality conflicts
Lack of tact or poor timing
Nonreinforcing reward systems

self-affirmations
Positive statements that impact your subconscious mind by drawing attention to your values and positive attributes and away from negative self-perceptions
human resource management (HRM)
The process of planning for, attracting, developing, and retaining an effective workforce
5 Human Resource Practices
Recruitment and selection
Compensation and benefits
Onboarding and L&D
Performance management
Employee relations
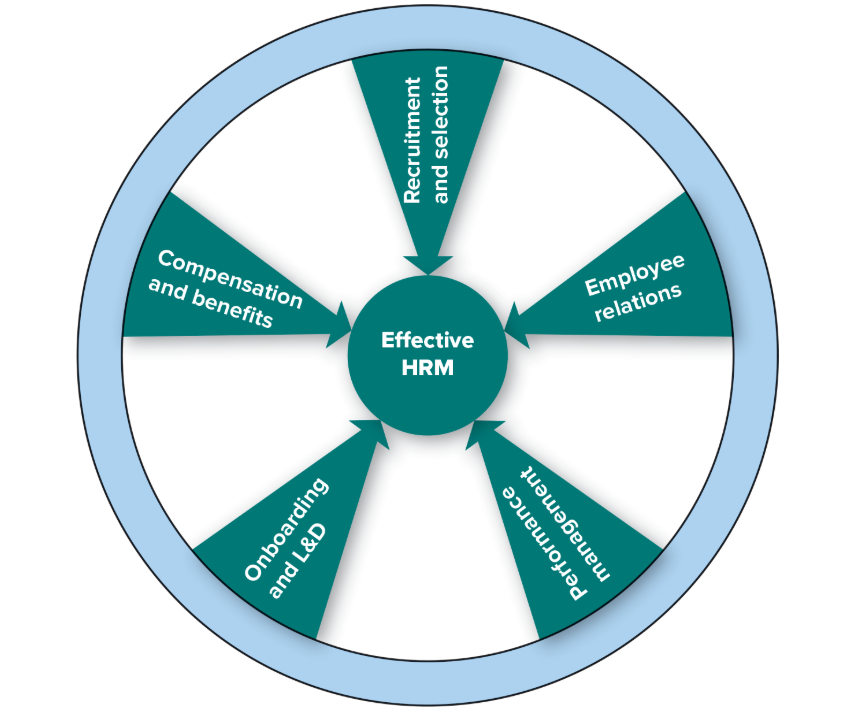
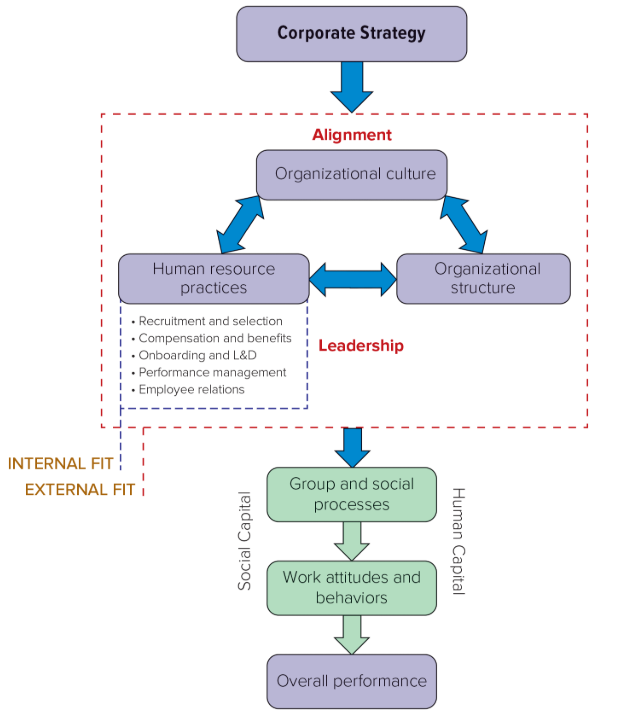
strategic human resource management
The process of designing and implementing systems of policies and practices that align an organization’s human capital with its strategic objectives
HRM vs. Strategic HRM
HRM is about managing people
Strategic HRM is about generating competitive advantages through people
internal fit
When all of the organization’s HR policies and practices reinforce one another
external fit
When the organization’s HR system as a whole aligns with its culture and structure in a way that supports firm-level strategy
human capital
The economic or productive potential of employee knowledge, experience, and actions
social capital
The economic or productive potential of strong, trusting, and cooperative relationships
Strategic HRM approaches
Talent management
High-performance work systems
talent management
strategic HRM approach that matches high-potential employees with an organization’s most strategically valuable positions
high-performance work system (HPWS)
strategic HRM approach that deploys bundles of internally consistent HR practices in order to improve employee ability, motivation, and opportunities across the organization
recruiting
The process of locating and attracting qualified applicants for job openings
internal recruiting
Hiring from the inside, or making people already employed by the organization aware of job openings
external recruiting
Attracting job applicants from outside the organization
talent marketplaces
Digital platforms that use AI to match existing employees with job openings, training opportunities, and mentoring relationships
employee referrals
Tap into existing employees’ social networks to fill open positions with outside applicants
boomerangs
Former employees who return to the organization
person-job fit
Extent to which a worker’s competencies and needs match a specific job
selection
The process of screening job applicants and choosing the best candidate for a position
legal defensibility
The extent to which the selection device measures job-related criteria in a bias free way
reliability
Represents the degree to which a test produces consistent scores