Malignant Breast cancer Surgery
1/253
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
254 Terms
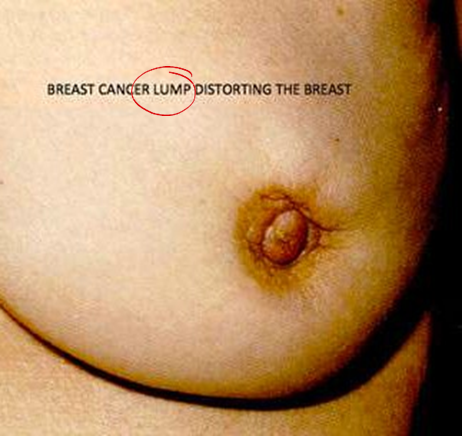
distoriting the breast
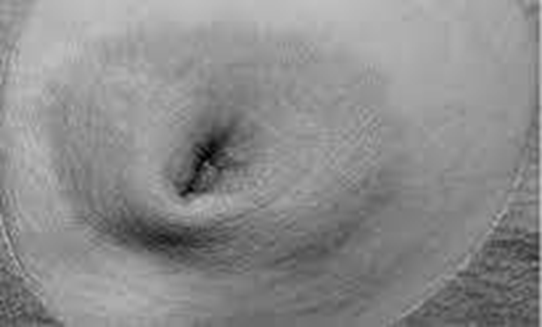
inverted breast
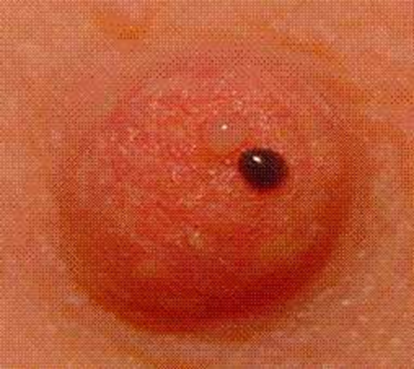
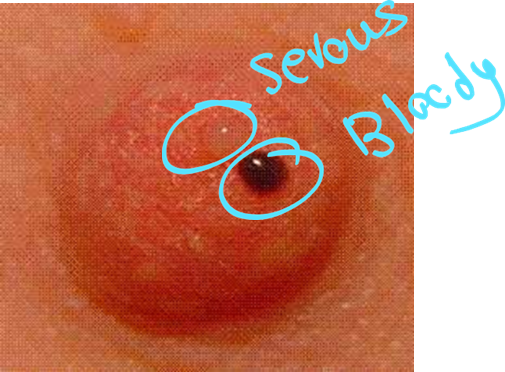
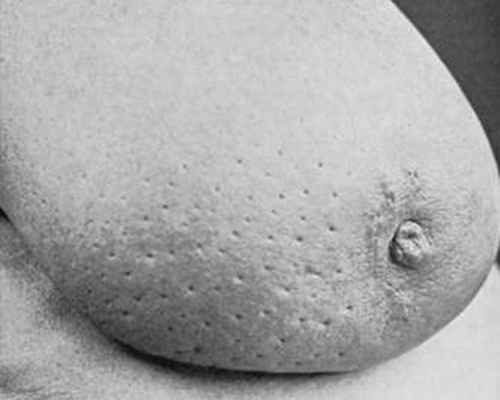
edema peau d orange
breast workup?
H&P–Diagnostic imaging–Tissue acquisition
How to work up a patient with breast complaint
History and physical examination are very very important!!
History breast cancer?
3 important aspects:
–Local symptoms
–Systemic symptoms
–Personal risk factor
–Local symptoms
–Lump
–Pain
–Nipple discharge?
–Color
–Unilateral vs bilateral
–Spontaneous vs induced
–Skin or nipple areola changes
correct
–Local symptoms
–Local symptoms
–Lump
–Pain
–Nipple discharge?
–Color
–Unilateral vs bilateral
–Spontaneous vs induced
–Skin or nipple areola changes
Systematic symptoms:
–Weight loss
–Loss of appetite
–Bony pain
–Neurological symptoms (headache or visual changes
correct
Systematic symptoms:
Systematic symptoms:
–Weight loss
–Loss of appetite
–Bony pain
–Neurological symptoms (headache or visual changes
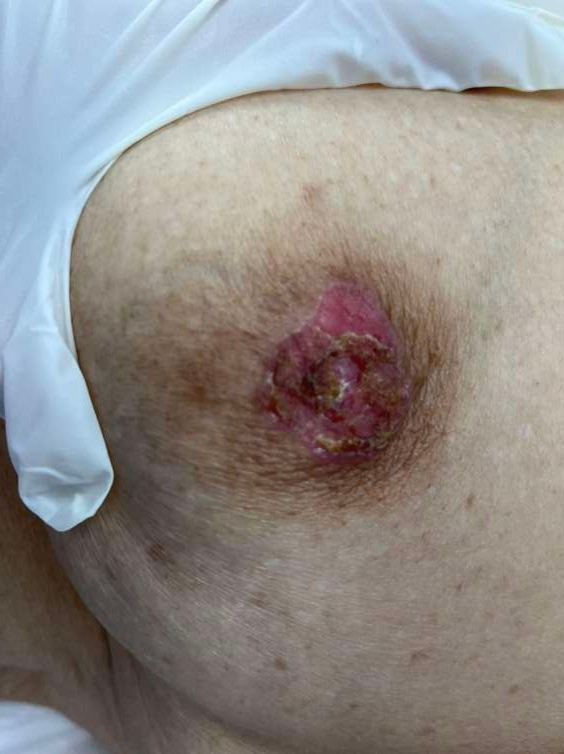
Paget disseae
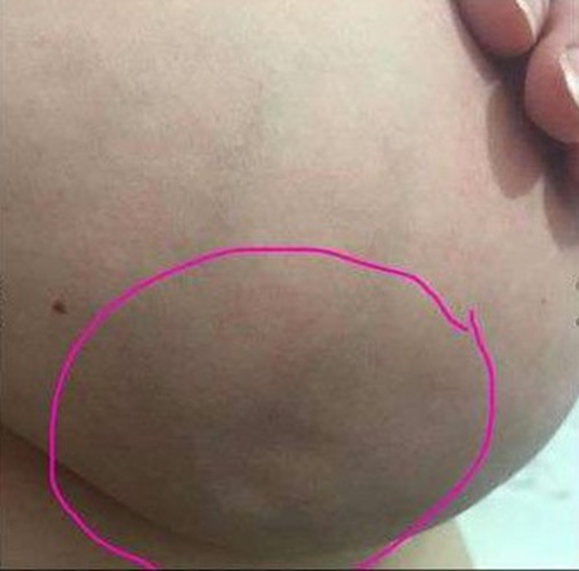
skin tethering
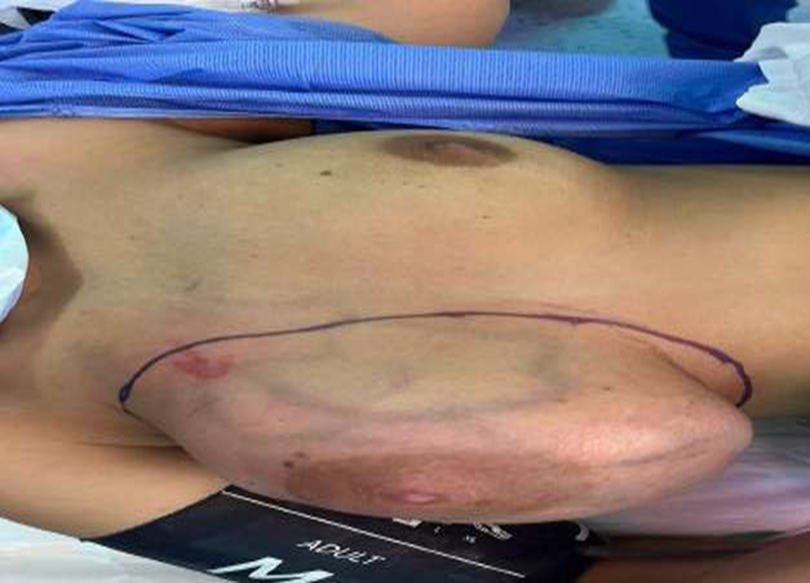
mass
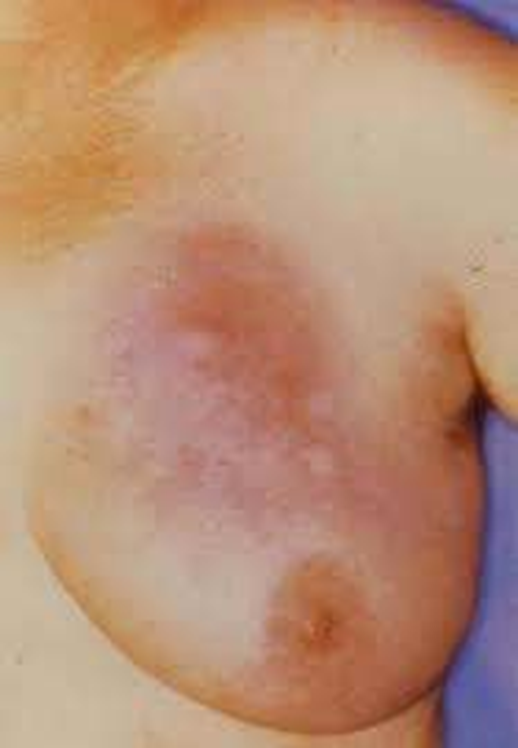
erythema inflammatory (breast cancer)
cancer metastasis
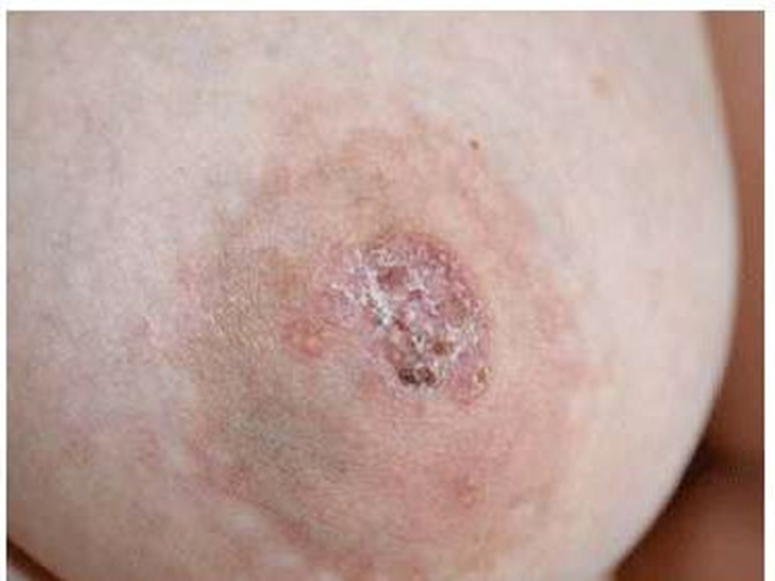
paget disease
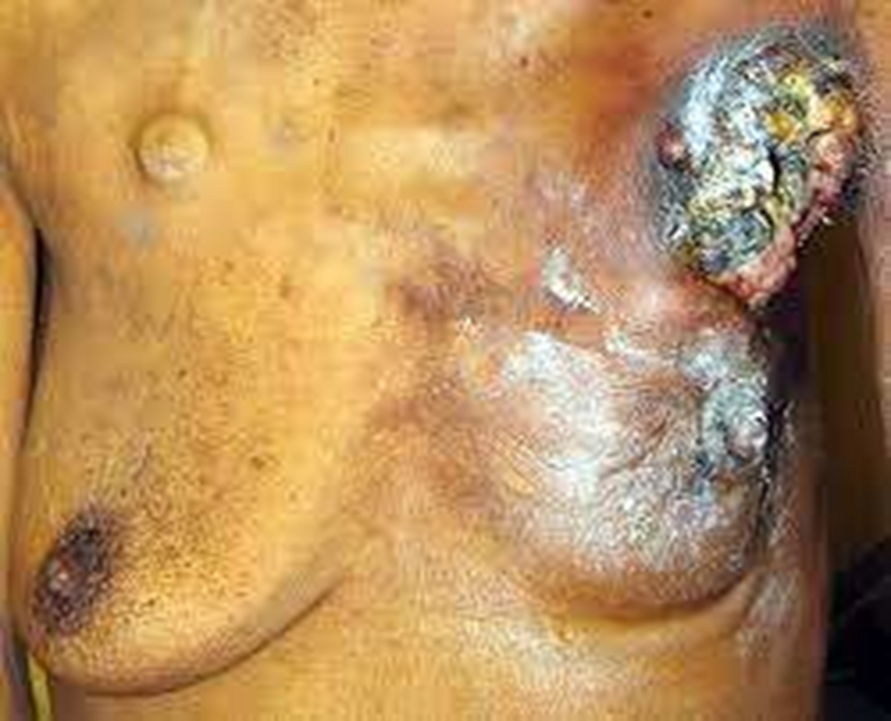
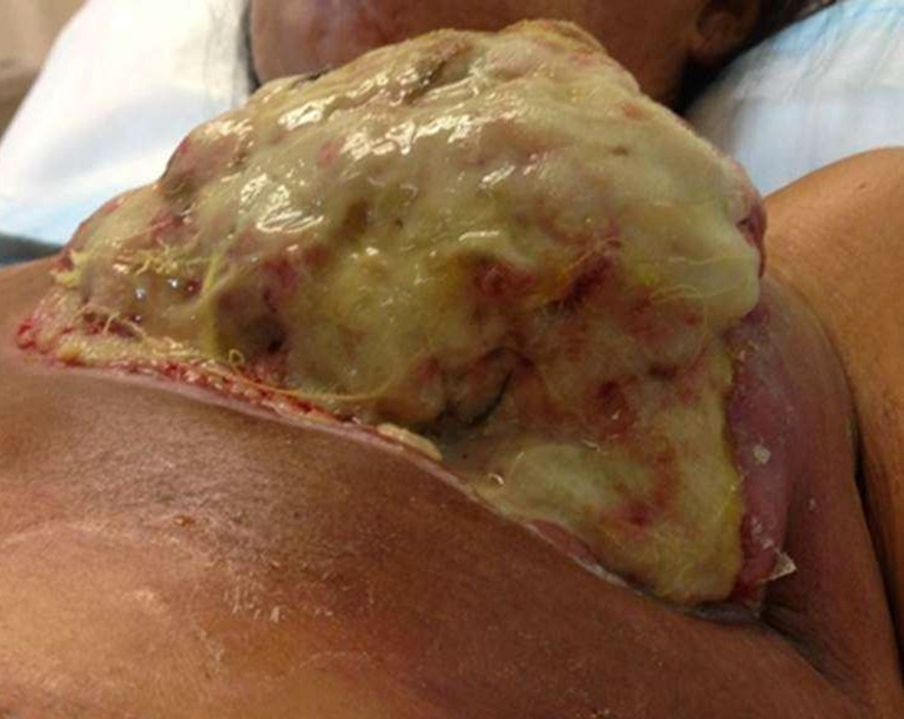
fangating breast cancer
3 imaging for the breast?
US
MRI
mammogram
correct
3 imaging for the breast?
3 imaging for the breast?
US
MRI
mammogram
breast cancer mammogram is in which plane?
1- medial lateral oblique MLO ( pectoralis muscle and axillary vessels)
2- cranio-caudal
correct
breast cancer mammogram is in which plane?
breast cancer mammogram is in which plane?
1- medial lateral oblique MLO ( pectoralis muscle and axillary vessels)
2- cranio-caudal
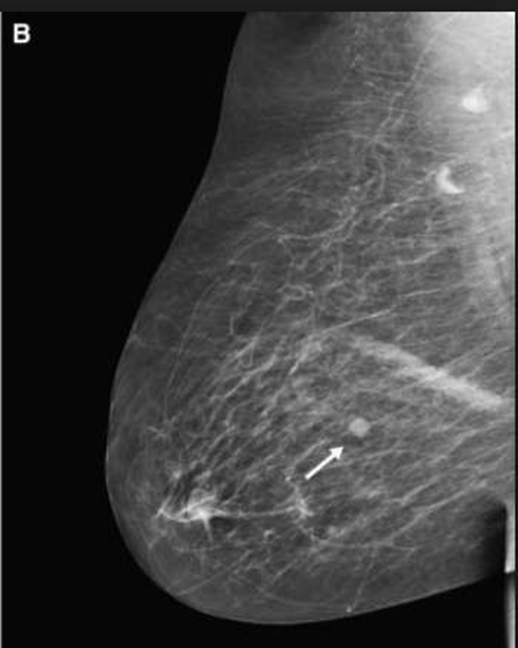
medial lateral oblique MLO
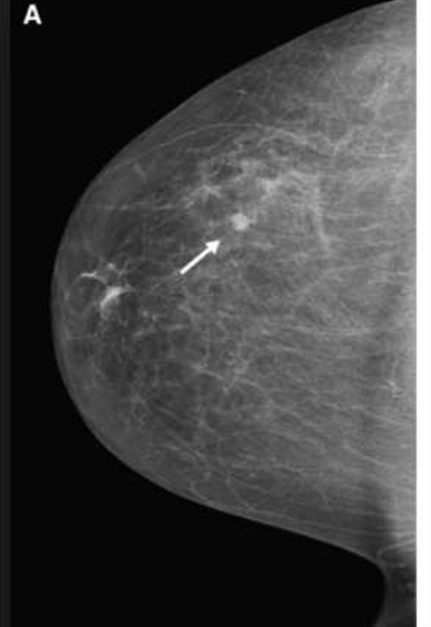
CC
craniocaudal
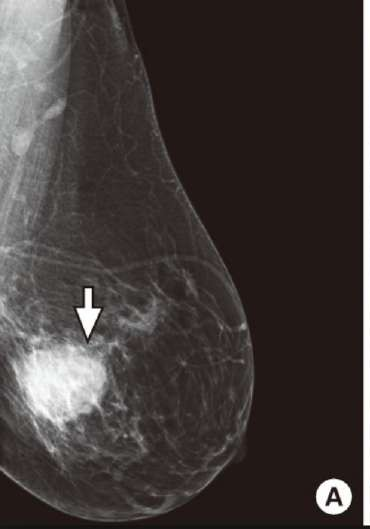
round well defeined
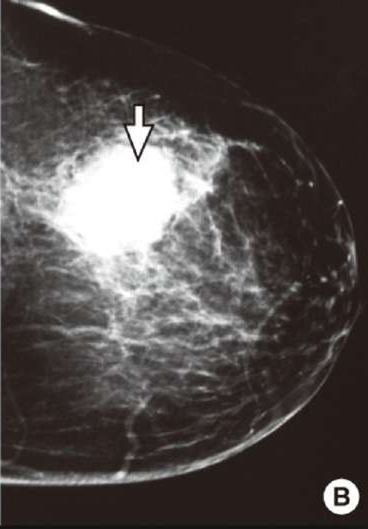
irrigular shape mass
speculated margin
– 3% of pts have synchronous bilateral breast ca; ≥ 50% of them are non-palpable lesions.
correct
–MICROCALCIFICATION
DCIS
The typical high-risk finding will be a speculated mass with abnormal architecture & asymmetry, with clustered micro- calcification
correct
The typical high-risk finding will be a ___________ mass with _________ architecture & _________ , with clustered micro- calcification
The typical high-risk finding will be a speculated mass with abnormal architecture & asymmetry, with clustered micro- calcification
breast cancer means:
irregular margin
speculated mass
ultrasound in the breast used for whaT?
used to assess the vessels of the breasts
- deifferentiate between solid and cyst
ultrasound in the breast used for whaT?
used to assess the vessels of the breasts
- deifferentiate between solid and cyst
what is used for used to assess the vessels of the breasts
- deifferentiate between solid and cyst?
US
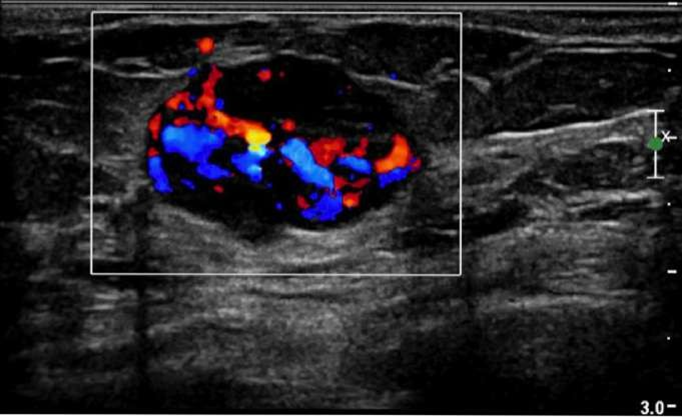
US
BIRADS →
0: Incomplete/Unable to evaluate· (US/MRI)
I: Negative·
II: Benign findings· → ROUTINE FOLLOW UP
III: Findings likely benign (~2% chance of ca; Repeat mammo in 6m+/- other radx investigation vs Bx)·
IV: Findings suspicious for malignancy (needs confirmatory tests & bx) TAKE BIOPSY
IV-A: mildly suspicious
IV-B: moderately suspicious
IV-C: highly suspicious
V: Highly suggestive of ca (>90% chance of ca)·
VI: known bx results of ca
CORRECT
BI-RADS stands for Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System, a classification system created by the American College of Radiology. It's designed to standardize mammogram reports and make it easier for nonradiologists to understand the findings.
COORECT
BI-RADS stands for Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System,
BI-RADS stands for Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System, a classification system created by the American College of Radiology. It's designed to standardize mammogram reports and make it easier for nonradiologists to understand the findings.
BIRADS →
0?
BIRADS →
0: Incomplete/Unable to evaluate· (US/MRI)
BIRADS →
I: ?
I: Negative·
BIRADS →
2
II: Benign findings· → ROUTINE FOLLOW UP
BIRADS →
3
BIRADS →
0: Incomplete/Unable to evaluate· (US/MRI)
I: Negative·
II: Benign findings· → ROUTINE FOLLOW UP
III: Findings likely benign (~2% chance of ca; Repeat mammo in 6m+/- other radx investigation vs Bx)·
IV: Findings suspicious for malignancy (needs confirmatory tests & bx) TAKE BIOPSY
IV-A: mildly suspicious
IV-B: moderately suspicious
IV-C: highly suspicious
V: Highly suggestive of ca (>90% chance of ca)·
VI: known bx results of ca
BIRADS →
4
BIRADS →
·
IV: Findings suspicious for malignancy (needs confirmatory tests & bx) TAKE BIOPSY
IV-A: mildly suspicious
IV-B: moderately suspicious
IV-C: highly suspicious
V: Highly suggestive of ca (>90% chance of ca)·
VI: known bx results of ca
BIRADS 4A
IV-A: mildly suspicious
BIRADS →
IV-B:
BIRADS →
IV-B: moderately suspicious
BIRADS →
IV-C:
BIRADS →
0: Incomplete/Unable to evaluate· (US/MRI)
I: Negative·
II: Benign findings· → ROUTINE FOLLOW UP
III: Findings likely benign (~2% chance of ca; Repeat mammo in 6m+/- other radx investigation vs Bx)·
IV: Findings suspicious for malignancy (needs confirmatory tests & bx) TAKE BIOPSY
IV-A: mildly suspicious
IV-B: moderately suspicious
IV-C: highly suspicious
V: Highly suggestive of ca (>90% chance of ca)·
VI: known bx results of ca
BIIRADS 5
BIRADS →
V: Highly suggestive of ca (>90% chance of ca)·
BIRADS 6?
VI: known bx results of ca
MOST COMMON TYPE OF BIOPSY IN breasts?
Core Biopsy
FNA fine needle aspiration:
- False negative rate of around 10%
–NEVER use it to diagnose BC
–Only for LN
correct
FNA fine needle aspiration:
FNA fine needle aspiration:
- False negative rate of around 10%
–NEVER use it to diagnose BC
–Only for LN
FNA can we use it to diagnose breast cancer?
FNA fine needle aspiration:
- False negative rate of around 10%
–NEVER use it to diagnose BC
–Only for LN
FNA used for?
LN
Core (Tru-Cut) Biopsy
rake real part of tumor
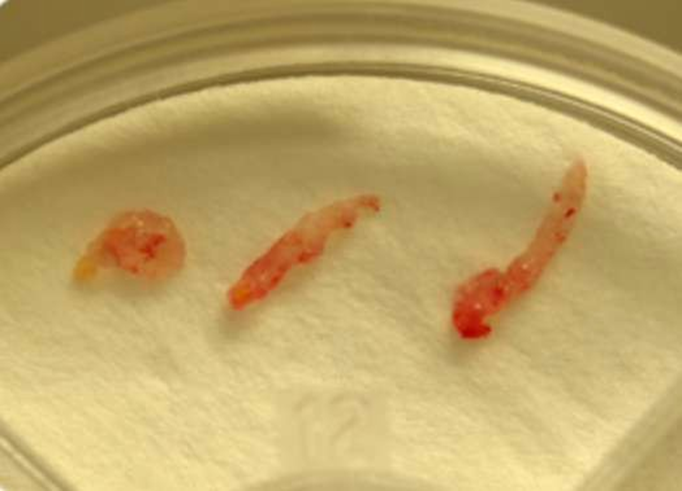
Core (Tru-Cut) Biopsy
most common mammary carcinoma?
invasive ductal
staging breast cancer by?
TNM
T1 < 20
T2 > 2 20 to 50
T3 > 50
T4a = attach to chest wall or breast skin
T4b = inflammatory BC
correct
T1 <
T2 >
T3 >
T4a =
T4b =
T1 < 20
T2 > 2 20 to 50
T3 > 50
T4a = attach to chest wall or breast skin
T4b = inflammatory BC
T4a =
T4a = attach to chest wall or breast skin
T4b =
T4b = inflammatory BC
N1 → Movable ipsilateral axillary
N2 → clinically fixed or matted or in clinically
detected ipsilateral internal mammary nodes
in the w/o axillary lymph node
N3 → Infraclavicular
Ipsilateral internal + Axillary
Supraclavicular lymph node
N1
Movable ipsilateral axillary
N1 →
N1 → Movable ipsilateral axillary
N2 → clinically fixed or matted or in clinically
detected ipsilateral internal mammary nodes
in the w/o axillary lymph node
N3 → Infraclavicular
Ipsilateral internal + Axillary
Supraclavicular lymph node
N2 →
N1 → Movable ipsilateral axillary
N2 → clinically fixed or matted or in clinically
detected ipsilateral internal mammary nodes
in the w/o axillary lymph node
N3 → Infraclavicular
Ipsilateral internal + Axillary
Supraclavicular lymph node
N3 →
N1 → Movable ipsilateral axillary
N2 → clinically fixed or matted or in clinically
detected ipsilateral internal mammary nodes
in the w/o axillary lymph node
N3 → Infraclavicular
Ipsilateral internal + Axillary
Supraclavicular lymph node
BREAST CANCER METASTASSI?
Lliver
Lungs
Bone
Bbrain
Tissue acquisistion: FNA
- False negative rate of around 10%
– NEVER use it to diagnose BC
corect
Tissue acquisistion: FNA
Tissue acquisistion: FNA
- False negative rate of around 10%
– NEVER use it to diagnose BC
BIRADIS score?
6
0 →Incomplete assessment-need additional
imaging evaluation or prior mammograms for
comparison
1→Negative-nothing to comment on; usually
recommend annual screening
2→ Benign finding -- usually recommend annual
corect
0 BIRADS?
0 →Incomplete assessment-need additional
imaging evaluation or prior mammograms for
comparison
1 BIRADS?
1→Negative-nothing to comment on; usually
recommend annual screening
2 BRAIDS?
2→ Benign finding -- usually recommend annual
BENIGN BRES?
2→ Benign finding -- usually recommend annual
Negative-nothing to comment on; usually
recommend annual screening
1
Prohably benign finding (<2% malignant)
initial short-interval follow-up suggested
flloow up in 6 months
3
BIRADS 3?
Prohably benign finding (<2% malignant)
initial short-interval follow-up suggested
flloow up in 6 months
Suspicious abnormality (2%-95% malignant)-
biopsy should be considered
4 BIRADS
4 BIRADS?
Suspicious abnormality (2%-95% malignant)-
biopsy should be considered
Highly suggestive of malignancy (>95%
malignant)-appropriate action should be taken
Known biopsy-proven malignancy
5
5
Highly suggestive of malignancy (>95%
malignant)-appropriate action should be taken
Known biopsy-proven malignancy
6
Known biopsy-proven malignancy
RIGHT
6
6
Known biopsy-proven malignancy
Core (Tru-Cut) Biopsy
solid tumorr
Axillary LN Dissectio
I Lateral to pectoralis minor
– II Behind
– III Medial
The younger female females have more lobules , ducts and less fatty tissue[that’s why it’s not recommended for young females to do mammogram]
correct
The younger female females have more lobules , ducts and less fatty tissue[that’s why it’s not recommended for young females to do mammogram]
The younger female females have more lobules , ducts and less fatty tissue[that’s why it’s not recommended for young females to do mammogram]
The younger female females have more lobules , ducts and less fatty tissue[that’s why it’s not recommended for young females to do mammogram]
we use ultrasound
corect
)In older females have more adipose tissues mammogram
correct
Fibro cystic changes:
- It's not a disease so never do surgery or give medications
- Patient complain of:pain+lumpy breast+menstrual change
In Ex:no palpable mass تحسي فيه كلاكيع بس, tenderness
- In Hx:
The pain is presented bilateral but usually
one more than the other,
In Ex : General Lumpiness but not well defined
masses
-
orrct
Fibro cystic changes:
- It's not a disease so never do surgery or give medications
right
Fibro cystic changes:
Fibro cystic changes:
- It's not a disease so never do surgery or give medications
Patient complain of:pain+lumpy breast+menstrual change
In Ex:no palpable mass تحسي فيه كلاكيع بس, tenderness
- In Hx:
The pain is presented bilateral but usually
one more than the other,
In Ex : General Lumpiness but not well defined
masses
-
fibrocystic changes
fibrocystic changeS:
The condition previously referred to as fibrocystic disease represents a
spectrum of clinical, mammographic, and histologic findings and is
common during the fourth and fifth decades of life.
An exaggerated response of breast stroma and epithelium to a variety of circulating and locally produced hormones and growth factors is frequently characterized by the constellation of breast pain, tenderness, and
nodularity.
Management: conservative
fibrocystic changes:
Osmosis: Key words in cases:
· Premenopausal women (20-50)
· Premenstrual breast pain (Hallmark)
· Multiple lumps in upper lateral quadrant
· Association with menstrual cycle.
· Not high risk with cancer.
correct
pain of the breast in what in fibrocytic changes? hallmark?
· Premenstrual breast pain (Hallmark)
fibrocytic changes:
in what place lumps?
risk cancer?
menstural cycle?
→ · Multiple lumps in upper lateral quadrant
· Association with menstrual cycle.
· Not high risk with cancer.
→ · Multiple lumps in upper lateral quadrant
· Association with menstrual cycle.
· Not high risk with cancer.
hallmark of fibrocystic chages?
Premenstrual breast pain (Hallmark)
Mammogram and US will show radiological features of
fibrocystic changes
And biopsy to confirm pathologically > Microscopic distribution
and it's the Gold standard in diagnosis fibrocystic changes
correct
what is gold standard of the fibrocystic changes to be confirmed?
Mammogram and US will show radiological features of
fibrocystic changes
And biopsy to confirm pathologically > Microscopic distribution
and it's the Gold standard in diagnosis fibrocystic changes
2
Sclerosing Adenosis
microcalcifications
No palpable mass only detected while screening
No surgery just follow up
Sclerosing adenosis is the most common pathologic diagnosis in patients
undergoing needle-directed biopsy of microcalcifications.
- Sclerosing adenosis is frequently listed as one of the component lesions of fibrocystic disease; it is common and has no significant malignant potential.
correct