Blood/Tissue Parasites
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Malaria, Babesia, Hemoflagellates, filarial worms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
malaria characteristics
complications (P. falciparum)
temp spikes 7-10 days after Anopheles mosquito bite
fever episodes: short cold → longer hot period
hemolytic anemia (destroys rbc)
liver & kidney failure
cerebral malaria: dec cerebral blood flow, hypoxia , cytokines → nitrous oxide → consciousness depressor
resp failure
black water fever: rbc’s burst → Hgb into urine → kidney failure
malaria symptoms
paroxysm = cycle of chills, fever & sweating every
3rd day = P. vivax & P. ovale
4th day = P. malariae
36-48h = P. falciparum
malaria recurs after treatment for 3 reasons
recrudescence: when prs not cleared by treatment
reinfection: indicates complete clearance w new infn established from a separate infective mosquito bite
relapse: specific to P. vivax/ovale → re-emergence of blood stage prs from latent hypnozoites in the liver
giant plt
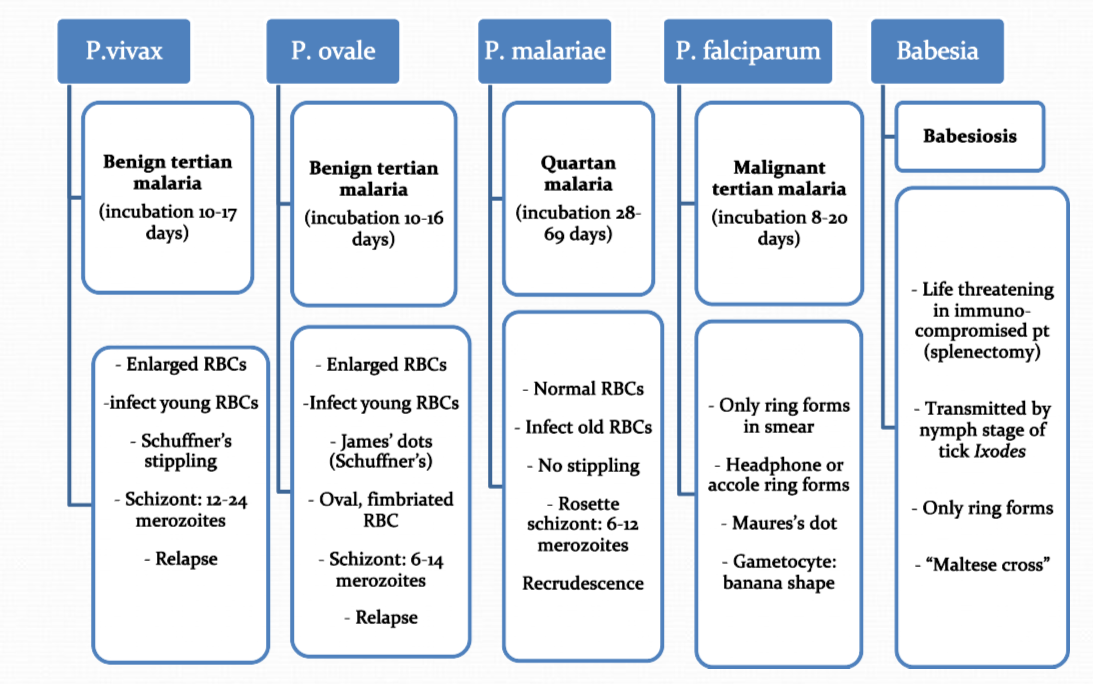
Plasmodium sp compared
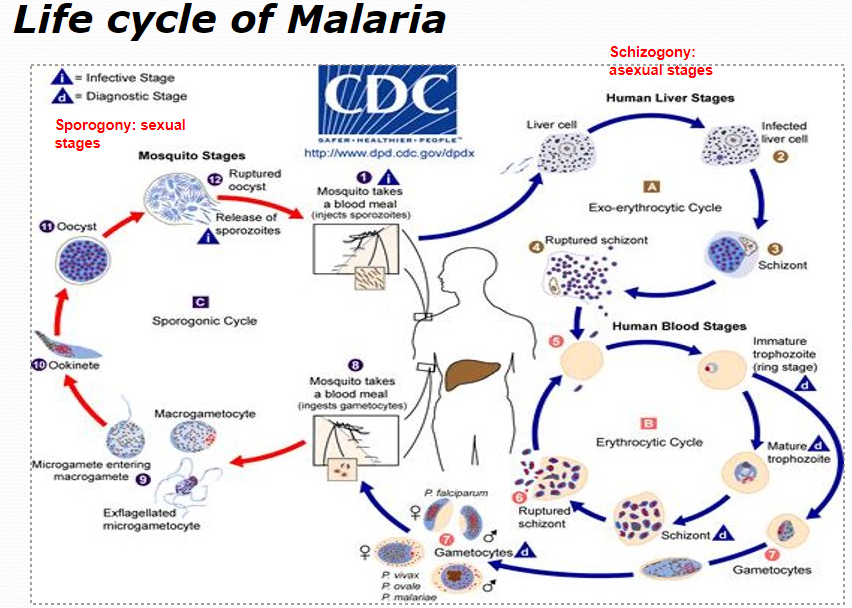
LC of malaria
IS / DS?
IS = sporozoites from Anopheles mosquito
DS = ring stage, gametocyte
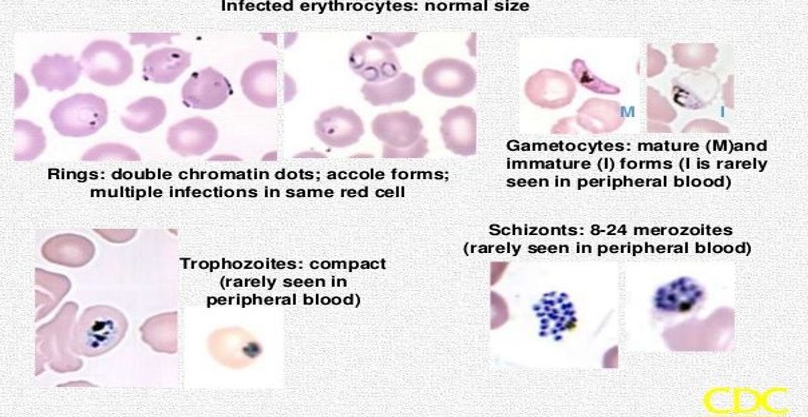
lab ID of malaria
EDTA (lavender top) tube of whole uncentrifuged blood, must receive w/in 1 hour of collection for sp ID on smear
thick blood smear (scratch method) = use to screen → Giemsa stain (lyses rbc → releases prs)
thin blood smear = to confirm Plasmodium sp → DifQuik stain
+malaria EIA
if past 2hr mark → only do EIA
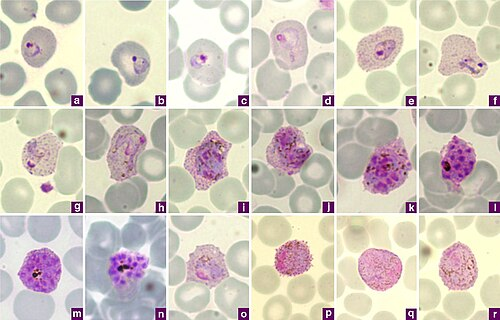
Plasmodium falciparum
how to ID?
normacytic rbc, multiple rings in rbc (headphone shape)
accole/applique form (rings plaster onto rbc membrane)
gametocyte: banana shape
schizonts: rarely seen in PBP
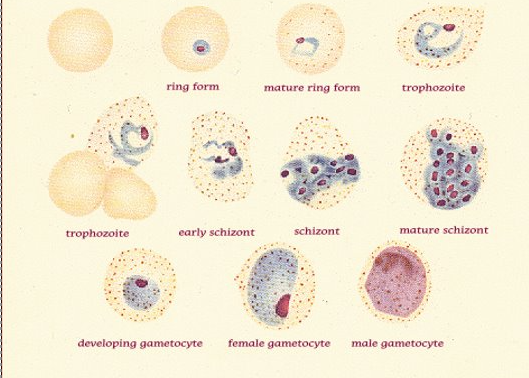
P. vivax
how to ID?
macrocytic rbc, amoeboid trophs (gets indented by other rbc)
Schuffner’s dots
ring forms
schizonts: 12-24 merozoites clusters
gametocytes: large, circular
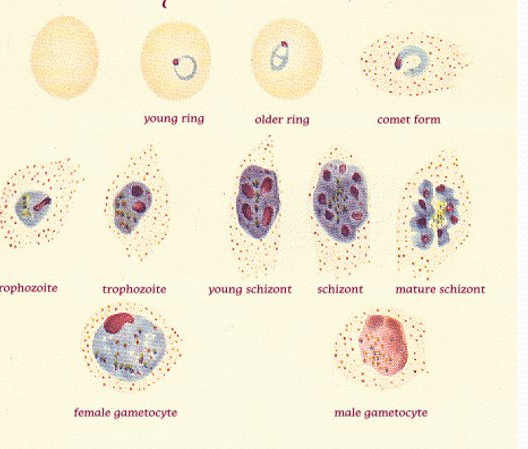
P. ovale
macrocytic rbc, fimbriated (comet) rbc
James stippling dots
schizont: 6-14 merozoites
GC: round
ok to say P. vivax / P. ovale bc
same treatment
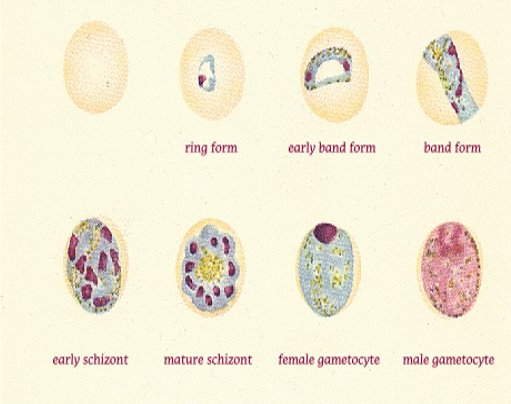
P. malariae
normocytic rbc, “bird’s eye kinetoplast”
band form
no dots
schizont: 6-12 merozoites (rosette)
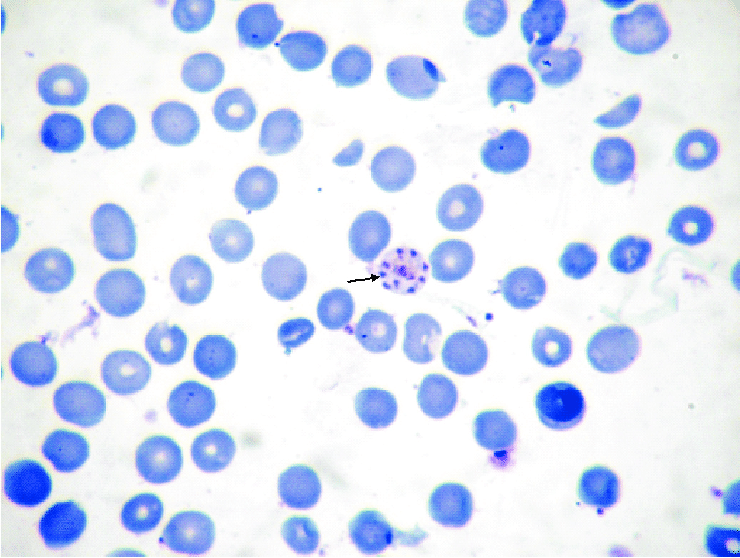
Babesiosis
vector = tick (Ixodes, spreads Lyme disease also) blood transfusion, IV drugs
B. microti = causes infn in E. US
B. divergens = Europe
febrile illness like malaria but not cyclic → resolves in month unless i-compromised
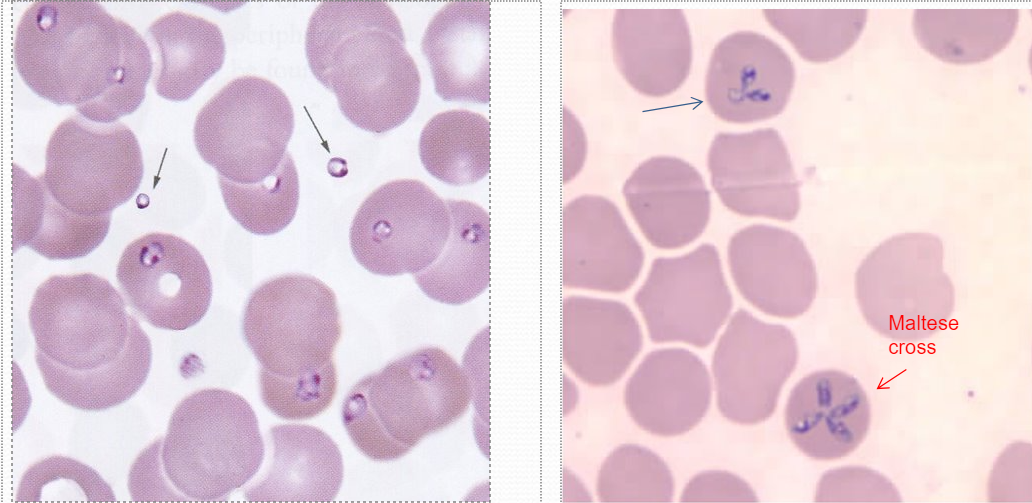
Babesia lab ID
typically lots of reticulocytes in smear bc lyses many rbc (see at 10x)
chromatid dots inside & out of rbc
bunny ears or maltese cross
must r/o malaria still
blood/tissue flagellate anatomy
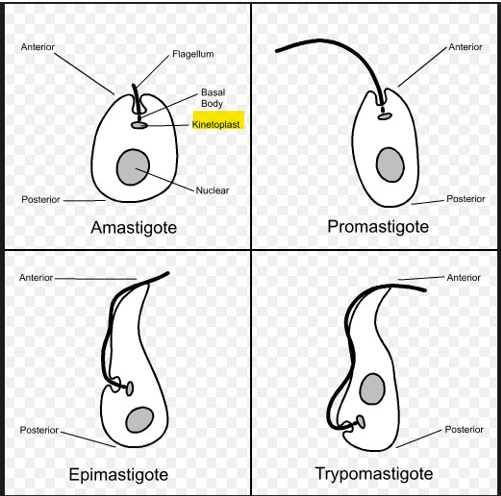
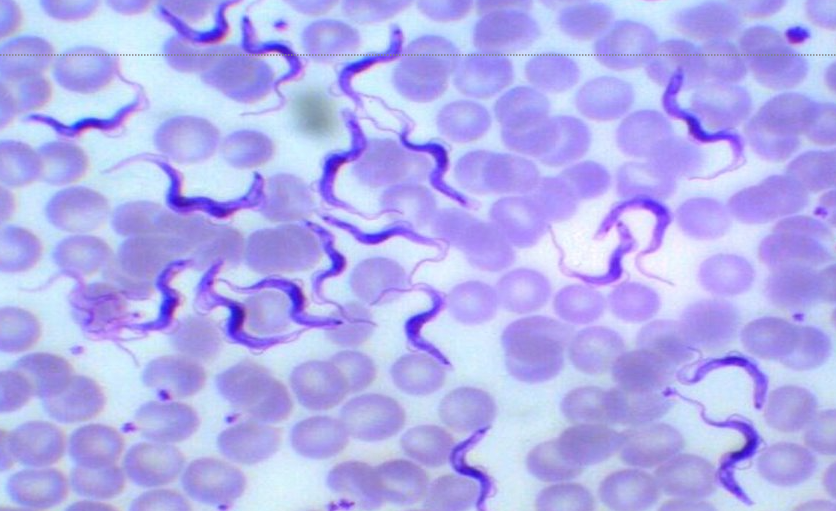
Trypanosoma brucei subspecies rhodesiense vs ssp gambiense
vector
IS
dx
rhodesiense = E. African sleeping sickness → more rapid onset, death
gambiense = W. African sleeping sickness → recurring fever w lymphadenopathy, Winterbottom sign
vector = tsetse fly
IS = metacyclic trypomastigotes
dx: see trypomastigote (pic’d) in body fluid, tissue, LN, blood → if dx, must examine CSF for CNS involvement
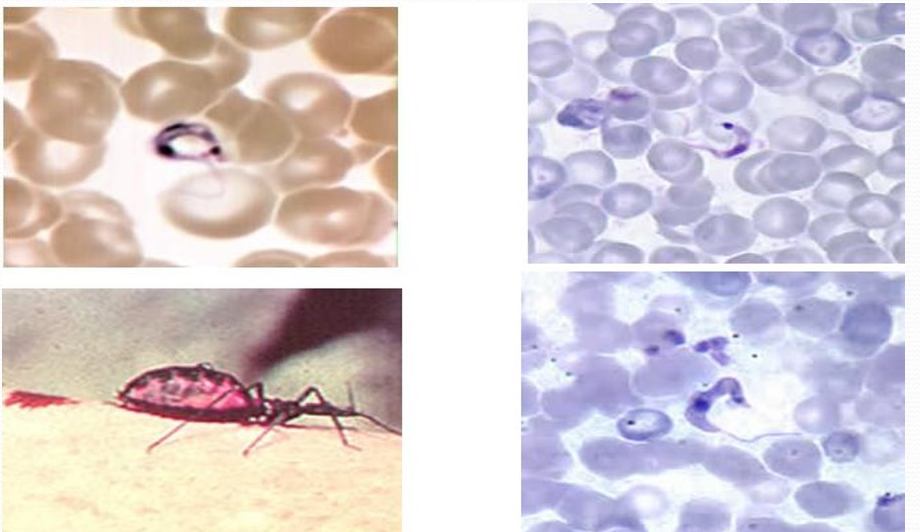
American trypanosomiasis (Chagas disease)
vector, IS
caused by Trypanosoma cruzi
vector = Triatomine bugs (kissing bugs) in rural areas of Latin America
IS = inf’d kissing bug takes blood meal → poops metacyclic trypomastigotes in feces near wound
dx: trypomastigotes in blood (larger kinetoplasts comp to T. brucei), ELISA, IFA, EIA, pt hx
Chagas disease pathology
acute: Chagoma, Romana’s sign (swollen eyelid), fever, hepatosplenomegaly
chronic: heart damage, megacolon, enlarged esophagus
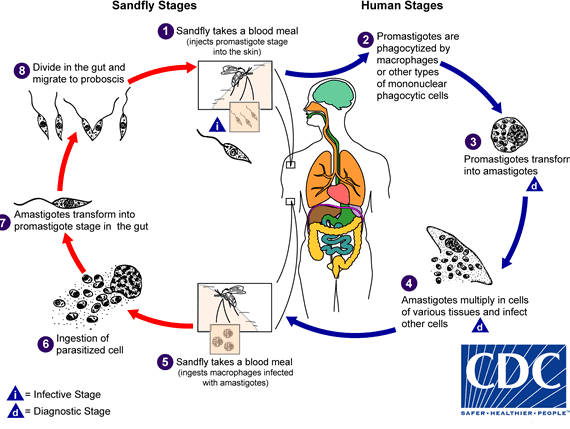
Leishmaniasis
GD
vector
IS
m/c forms
subtropic, tropics, southern Europe
v = female phlebotomine sand flies, promastigotes (IS)
m/c form = cutaneous (skin sores), visceral (spleen, liver, BM)
dx: amastigotes inside macrophages in BM or tissue
cutaneous Leishmaniasis
oriental sore = L. tropica complex (urban Middle East, Africa, Mediterranean, Asia Minor, India)
Chiclero ulcer = L. mexicana complex (L America, US)
mucocutaneous Leishmaniasis
espundia = L. braziliensis (Columbia, Ecuador, Brazil)
visceral Leishmaniasis
Kala-azar = L. donovani complex (Asia, Africa, Middle East, Mediterranean, S. America)
hepatosplenomegaly, skin lesions usually not present
dx = splenic or liver biopsy, BM → secondary infn → high mortality rate
Leishmania LC
IS = promastigote
vector = sandfly
Wuchereria bancrofti
GD
vector
warm region: Asia, L. America
v = Culex sp, Aedes sp., L3 larva (IS)
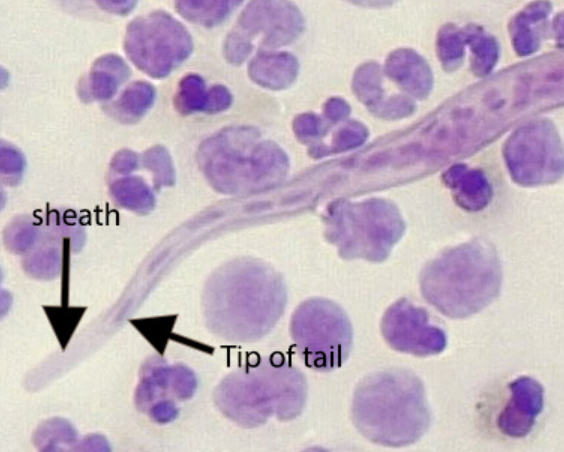
dx: sheathed microfilariae (MF) in blood
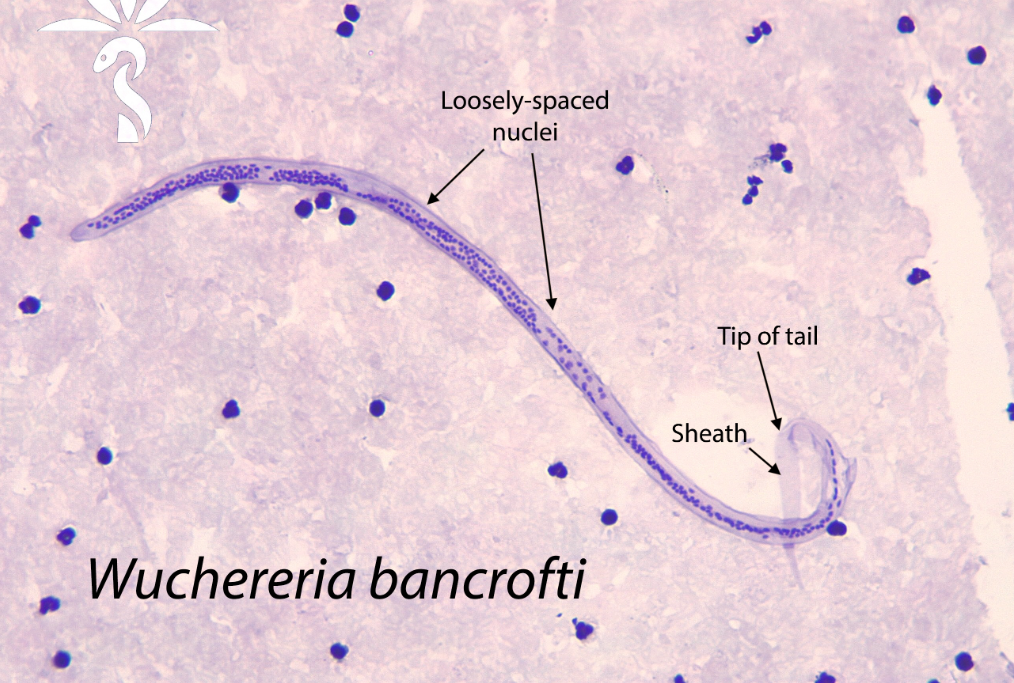
W. bancrofti pathology
acute: fever, lymphangitis
chronic: enlarged lower extremities via obstruction of lymph tract from dead worms → elephantiasis of legs, scrotum, etc
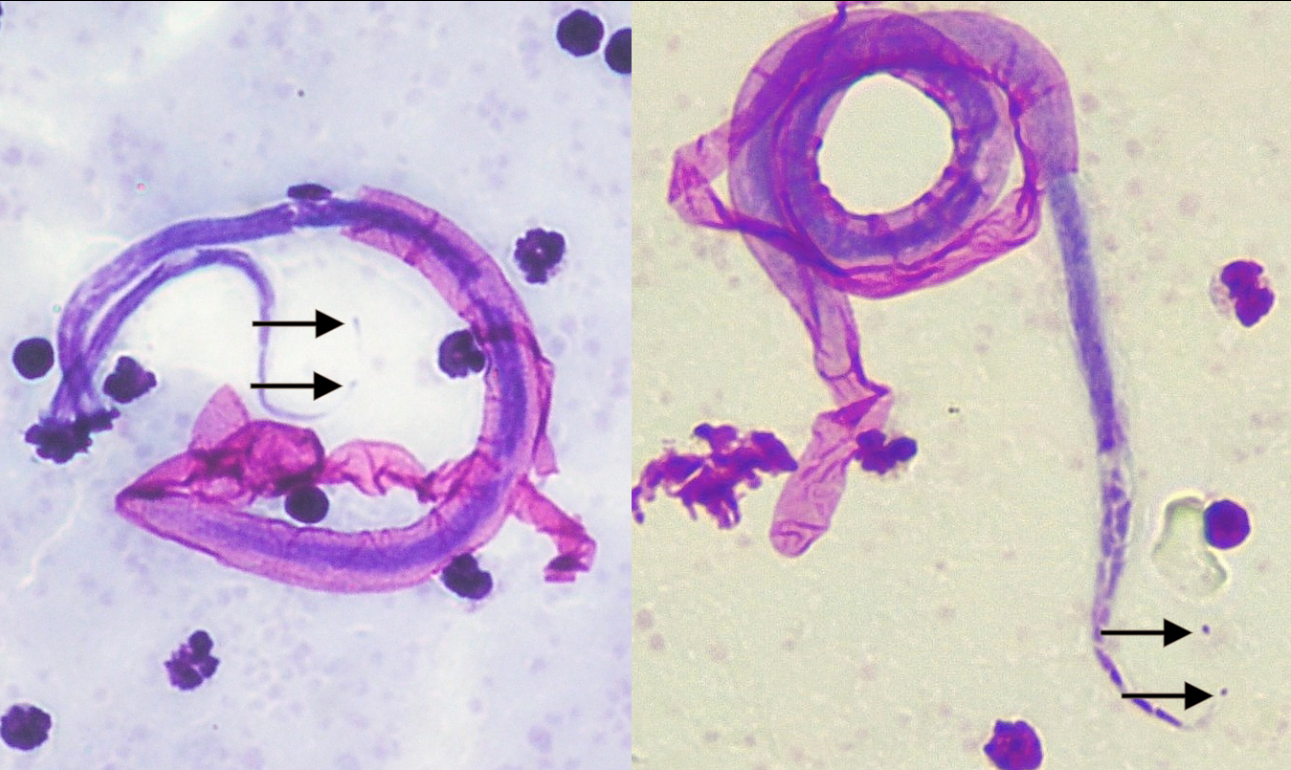
Brugia malayi
GD
vector/IS
dx / disease
SE Asia, Asia, India
v = Anopheles mosquito, L3 larvae (IS)
dx: sheathed MF in PB
enlarged upper extremities ie arms
Onchocerca volvulus
GD
v/IS
pathology /dx
Africa, Mexico, Guatemala, Venezuela
v = blackfly (simulium), L3 larvae (IS)
dx: skin scraping to see MF, adult females prefer to ball in subdermis → nodule (walnut sized)
adult worms lodged in lymphatic vessels in subcut tissue → tumors, eyes
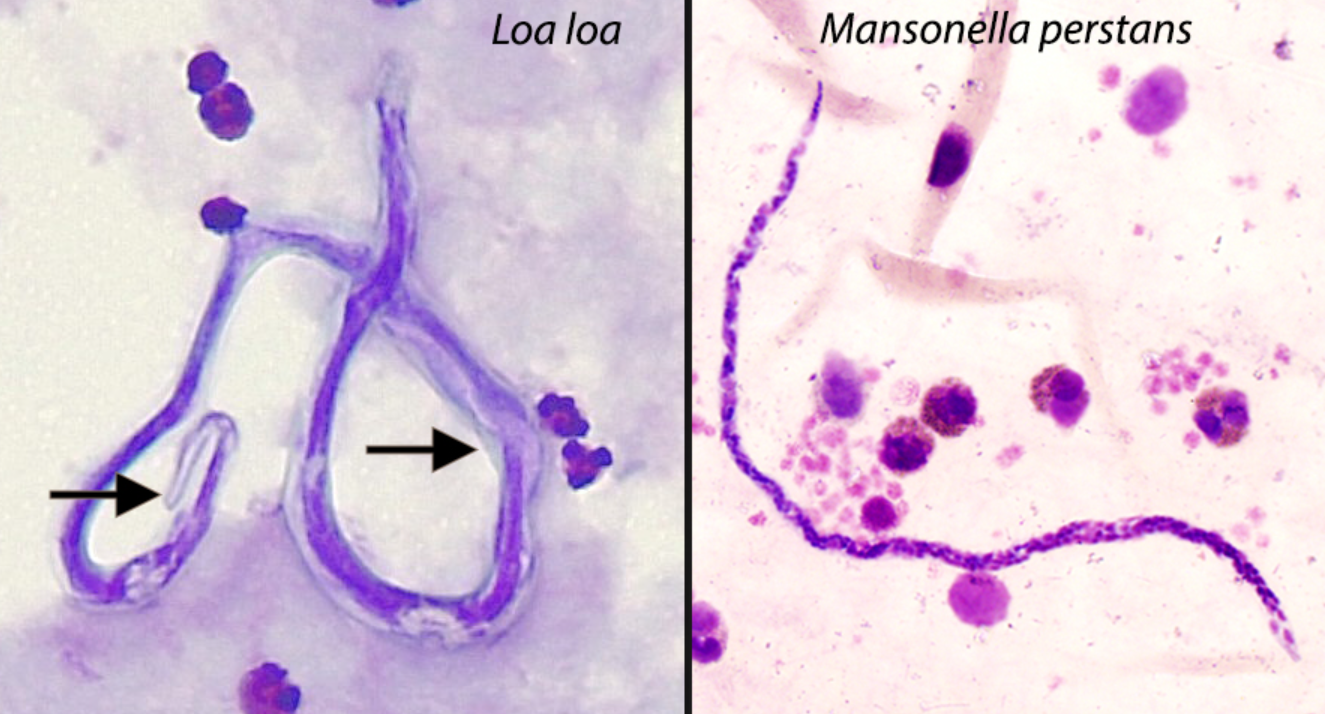
Loiasis
caused by Loa-loa (African eye worm), assoc’d Calabar swellings
v = deerflies in West & Central Africa; L3 larve (IS)
dx: MF found in CSF, urine, sputum, blood, feeling across nose bridge, crosses eyeball
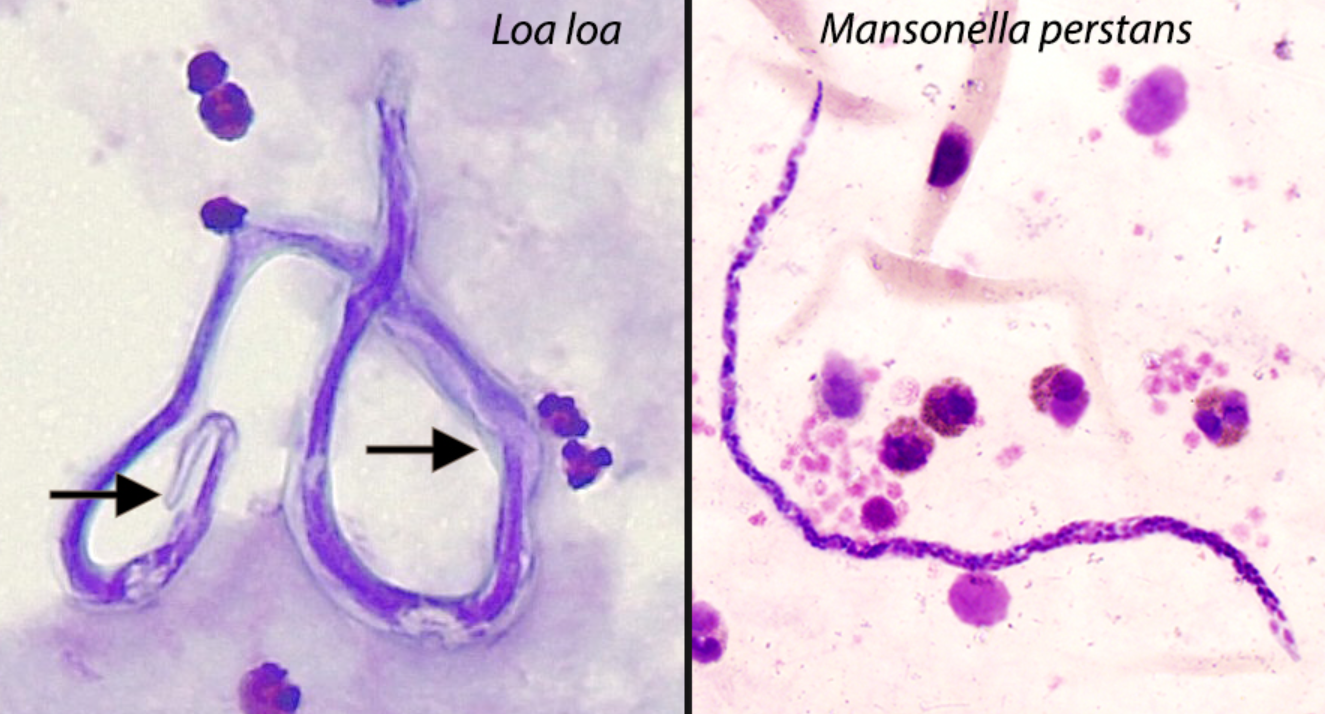
Mansonella perstans
GD
v/IS
Latin America, Africa
v = biting midge, L3 larvae (IS)
mostly asympto
dx: MF in PB
Dracunculiasis (Guinea worm disease)
caused by Dracunculus medinensis
v = L3 inf’d-copepods in stagnant water ingested
dx = L1 emerge from lower extremities in water
P. vivax
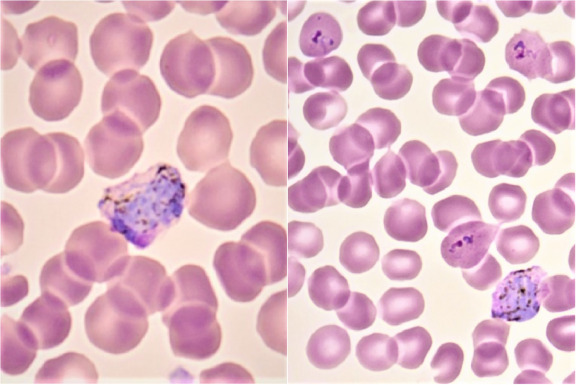
P. ovale
P. malariae
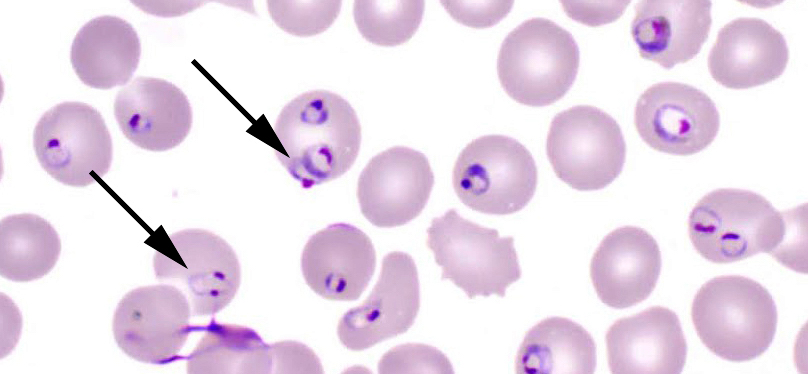
P. falciparum
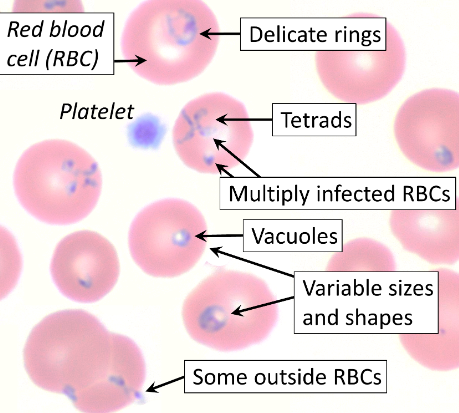
Babesia microti