tRNA structure
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What’re the 2 important components of tRNA structure?
Acceptor domain
Anti codon loop
Where does amino acids attach to?
3’ OH on as it extends further than 5’ end
What does the acceptor domain do?
(3’-ACC) → amino acids is carried by the 3’ OH end of the tRNA
What does the anti-codon loop do?
(central loop) → contains 3 bases (anti codon) which determines placement of a specific amino acid into the growing polypeptide chain
Explain what occurs due to the 3’ end having unpaired CCA
Generally not encoded in the tRNA gene
Added sequentially one at a time by CCA adding enzyme Using CTP and ATP as substrates
Cognate amino acid covalently attached to A
What facilitates the linkage of correct amino acid to tRNA?
Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
Requires specific contacts made between regions of the tRNA and the synthetase
Explain what occurs in step 1 of the binding of amino acid to 3’ CCA end of tRNA (mediated by aminoacyl tRNA synthetase)
Activation of amino acid by reaction with ATP
Amino acid + ATP ←> aminoacyl- AMP + P-P (pyrophosphate PPi)
Aminoacyl intermediate formed remains bound to the tRNA synthetase until collision with the appropriate tRNA molecule
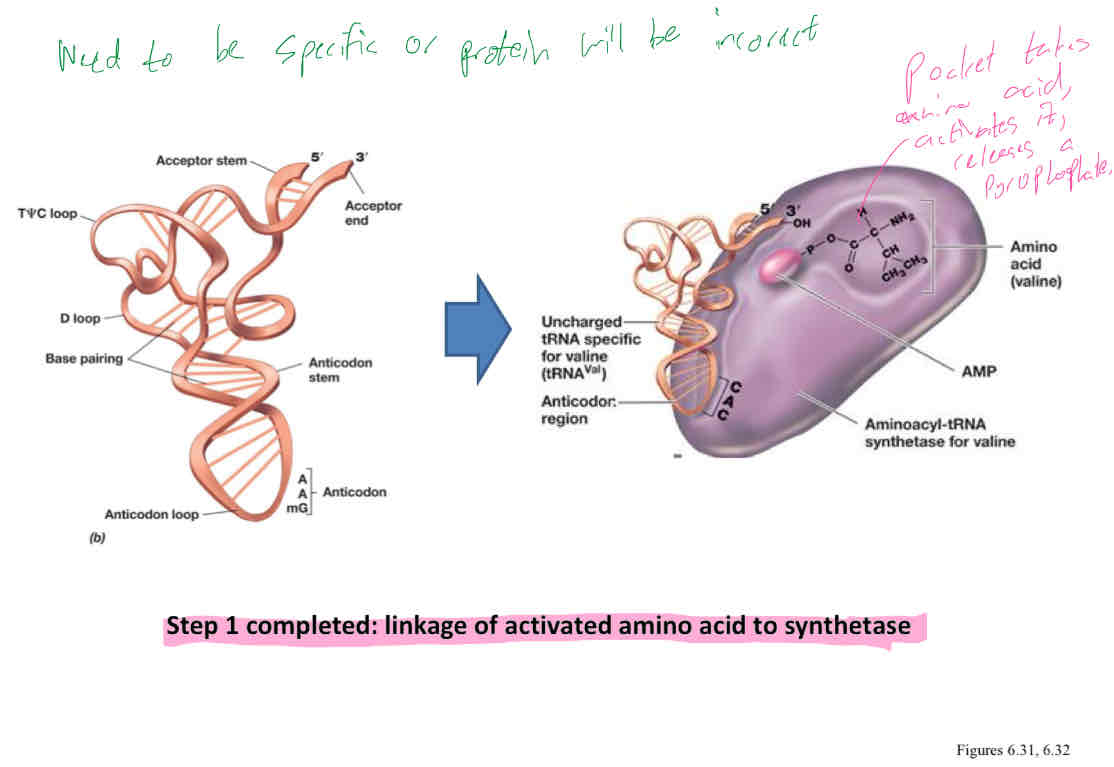
Explain what occurs in step 2 of the binding of amino acid to 3’ CCA end of tRNA
Activated amino acid is bonded to the CCA stem of its tRNA to form a charged tRNA
Aminoacyl-AMP + tRNA → aminoacyl-tRNA + AMP
Pyrophosphate (PPi) formed in first rxn is split into 2 molecules of inorganic phosphate cuz ATP used and AMP formed in these rxns, a total of 2 energy rich phosphate bonds are expended to charge a tRNA with its cognate amino acid
Amino-acyl AMP is now bonded to CCA stem of its tRNA and exits synthetase
Energy rich bond provides energy to incorporate amino acids into growing polypeptide chain
What does mRNA do?
Carries information about protein structure
~90% of genes in E.coli code for mRNA (structural gene)
MRNA has short life span
What are the 3 sections of mRNA?
Leader sequence
Coding sequence
Trailer sequence

What does leader sequence in mRNA do?
On 5’ end of mRNA transcript
Contains a specific ribosome binding site (shine dalgarno sequence)
What does coding sequence of mRNA do?
Info is organized in codons (ie sets of 3 nucleotides)
Each codon is complementary to an anticodon of a tRNA which specifies amino acid
Generally begins with AUG start codon encoding chemically modified methionine called N-formal methionine
Ends with stop (ie nonsense codon)
What does trailer sequence of mRNA do?
Transcribed to make the 3’ end of mRNA
Sequence of trailer determines stability of mRNA
Eg: degradation impeded by secondary structure, modulated by RNA binding proteins into response to environmental stress signals etc.
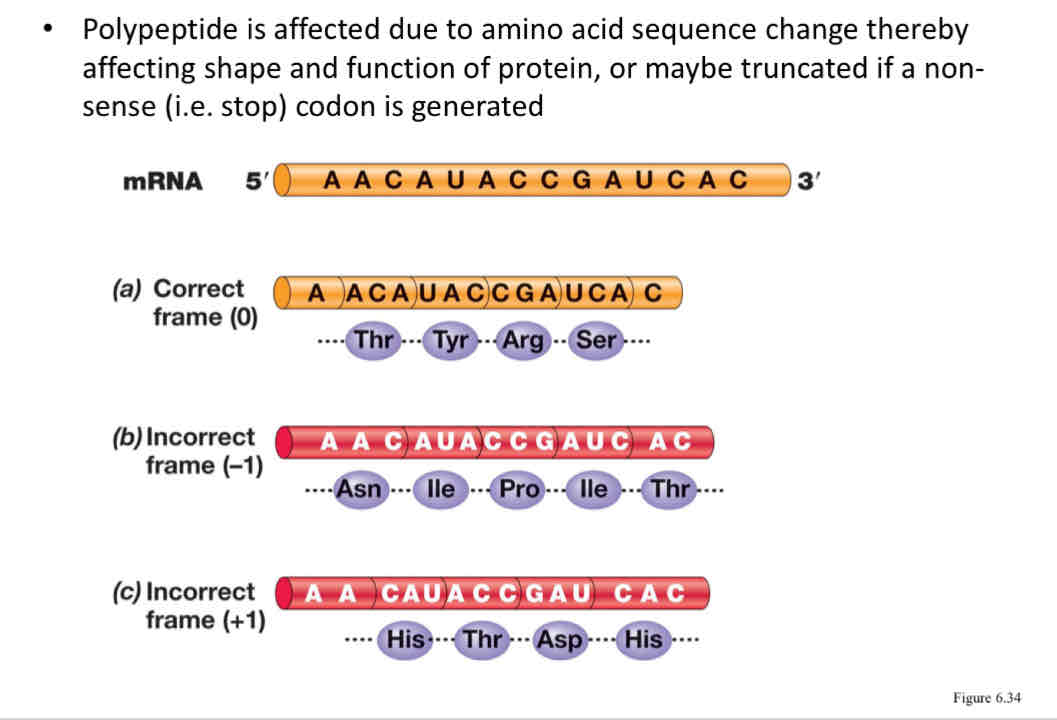
Explain the way the reading frame works
It starts from the start codon, the mRNA transcript is read “in frame” with each frame corresponding to a codon (set of 3 nucleotides) with no interruption between frames
What’s a frame-shift mutation?
Caused by addition of deletion of nucleotide in DNA sequence, when transcribed, can put the coding sequence “out of frame”
Explain what the polypeptide is affected by
Affected due to amino acid sequence change thereby affecting shape and function of protein, or maybe truncated if a non-sense (stop) codon is generated
What are the 3 types of proteins covered?
Catalytic proteins
Structural proteins
Regulatory proteins
What do catalytic proteins do?
Catalysts for chemical reactions that occur in the cell
What do structural proteins do?
Integral parts of the major structures of the cell (membranes, walls, ribosomes, etc)
What do regulatory proteins do?
Control cell processes by variety of mechanism including binding to DNA and affecting transcription (gene expression)
What are proteins polymers of?
Amino acids
An amino acid contains an amino group (NH2) and a carboxylic acid group (COOH) that are attached at the alpha carbon
What’s a peptide bond?
Linkage between the COOH group of one amino acid with the amino nitrogen of the second amino acid with the loss of one water molecule
What’s a dipeptide?
2 amino acids bonded by peptide linkage
What’s a tripeptide?
3 amino acids bonded by 2 peptide linkages
What’s a polypeptide?
Multiple peptide bond linked amino acids
Explain what happens as a result of a protein consisting of one or more polypeptides
Translation of a mRNA transcript will result in a polypeptide sequence which may be the final protein product or may be part of a final protein product (subunit)
Explain what primary protein structure is
Linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain that ultimately determines the folding pattern of the polypeptide, which in turn determines its biological activity
What affects primary protein structure?
As little as an amino acid change can affect primary structure affecting function
Explain secondary structure of polypeptides
Generated by hydrogen bonding between oxygen and nitrogen atoms of 2 peptide bonds to either form alpha helix or beta sheet
A polypeptide can contain regions of alpha helix and regions of beta sheet
Explain tertiary structure of polypeptides
Higher order of structures generated by interactions between the R groups of the amino acids in a polypeptide
3D form dependent of hydrophobic interactions, with lesser contributions from H bonds, ionic bonds and disulfide bonds
Many proteins consist of 2 or more polypeptides (subunits) and thus show quaternary structure stabilized by various interactions and also by disulfide bonds formed between cysteine residues in 2 diff subunits