2.1.2 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES SUPERSTACK
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms
What are some of the most abundant elements in living organisms?
Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P) and Sulfur (S)
What are elements distinguished by?
Number of protons in their atomic nuclei
How many bonds can carbon atoms form?
4 bonds
How many bonds can nitrogen atoms form?
3 bonds
How many bonds can oxygen atoms form?
2 bonds
How many bonds can hydrogen atoms form?
1 bond
What type of bond involves sharing a pair of electrons?
Covalent bond
What is an ion?
An atom/molecule where total electrons ≠ total protons
What is a cation?
An atom/molecule that loses electrons → net positive charge
What is an anion?
An atom/molecule that gains electrons → net negative charge
What holds ionic bonds together?
Electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions
What are ions in solution called?
Electrolytes
Role of (Ca²⁺)?
Nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction
Role of (Na⁺)?
Nerve impulse transmission, kidney function
Role of (K⁺)?
Nerve impulse transmission, stomatal opening
Role of (H⁺)?
Catalysis of reactions, pH determination
Role of (NH₄⁺)?
Production of nitrate ions by bacteria
Role of (NO₃⁻)?
Nitrogen supply to plants for amino acid and protein formation
Role of ions (HCO₃⁻)?
Maintenance of blood pH
Role of (Cl⁻)?
Balance positive charge of sodium and potassium ions in cells
Role of (PO₄³⁻)?
Cell membrane/ bone formation
nucleic acid and ATP formation
Role of (OH⁻)?
Catalysis of reactions, pH determination
Symbol for calcium ion
(Ca²⁺)
Symbol for sodium ions
(Na⁺)
Symbol for potassium ions
(K⁺)
Symbol for hydrogen ions
(H⁺)
Symbol for ammonium ions
(NH₄⁺)
Symbol for nitrate ions
(NO₃⁻)
Symbol for hydrogencarbonate ions
(HCO₃⁻)
Symbol for chloride ions
(Cl⁻)
Symbol for phosphate ions
(PO₄³⁻)
Symbol for hydroxide ions
(OH⁻)
Is water polar or non polar?
It’s a polar molecule
What bond holds hydrogen and oxygen atoms within a water molecule?
Polar covalent bond
What bond forms between adjacent water molecules?
Hydrogen bond
Why is water a polar molecule?
Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen
creating partial charges (δ+ and δ−)
What property gives water a high boiling point and high specific heat capacity?
Hydrogen bonding
Why is water described as a solvent?
It dissolves ionic and polar molecules by surrounding them
Why is water important as a solvent in biology?
Allows chemical reactions to occur in solution
and transport of dissolved substances
What is meant by water being cohesive?
Water molecules stick together due to hydrogen bonding
Why is cohesion important in plants?
Allows water to move up xylem in a continuous column
(transpiration stream)
What is meant by water being adhesive?
Water molecules stick to other polar molecules/surfaces
How does adhesion help water movement in plants?
Helps water molecules attach to xylem walls, aiding capillary action
Why does water have a high specific heat capacity?
Hydrogen bonds absorb lots of energy
resisting temperature change
Why is high specific heat capacity important for all organisms?
Buffers temperature changes
maintaining stable environments for enzymes
Why does water have a high latent heat of evaporation?
Energy is required to break hydrogen bonds before molecules can escape as vapour
Why is high latent heat of evaporation useful in biology?
Provides cooling effect
(e.g. sweating, transpiration) without large water loss
Why is ice less dense than liquid water?
Hydrogen bonds hold molecules apart in open lattice when frozen
Why is the lower density of ice important for life?
Ice floats, insulating water below, allowing aquatic life to survive in cold conditions
Why is water a metabolite?
It is involved directly in metabolic reactions
(e.g. hydrolysis, condensation, photosynthesis)
Give 3 examples of water as a metabolite.
Hydrolysis, Condensation and Photosynthesis
Why is water described as transparent?
It lets light pass through
Why is transparency important for organisms?
Allows aquatic plants to photosynthesise; light reaches retina in animals
DNA is one of many substances which will dissolve in water. Explain why water is a good solvent [2 marks]
molecules are polar (1)
enabling water molecules
to, attract / bind to, solute molecules
Outline the properties of water which make it an ideal habitat for an amphibian. (4 marks)
solvent ✓,
high specific heat (capacity) /temperature stability
(high) density (so frog floats /buoyant) ✓
ice is less dense than water ✓
What is cohesion? plus an example
attraction between water molecules (due to hydrogen bonding).
e.g, maintains continuous column water column in xylem (capillary action)
What is adhesion?
the attraction between water molecules and other, different molecules, caused by water's polar nature
Water is essential for survival and has many properties to ensure that living organisms survive. Outline how it is a good solvent. [4 marks]
water is a polar molecule (1)
can form hydrogen bonds with other polar molecules or ions (1)
can dissolve ionic and polar substances(1)
allows transport of dissolved substances in organisms (1)
Explain why water is able to make a temperature-stable aquatic environment
For FEATURE:
Water has a high specific heat capacity. (1)
ANY of (for EFFECT):
Water doesn’t change temperature readily. (1)
Water doesn’t allow sudden temperature changes. (1)
When we exercise our body temperature increases, and blood vessels dilate to encourage more blood to flow closer to our skin for heat to be released. Outline how sweat cools us down based on the properties of water. (4 marks)
Water has a high heat of vaporisation. (1)
This means that water molecules require a lot of energy to break down the hydrogen bonds present in between water molecules. (1)
When sweat evaporates from our skin, a lot of energy is used up (1)
and this cools our body down to regulate our body temperature. (1)
What is a monomer?
A small, basic molecular unit that can join with others to form a polymer (e.g. glucose, amino acids, nucleotides).
What is a polymer?
A large molecule made up of many monomers joined together (e.g. polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids).
What reaction forms polymers?
Condensation reaction – joins monomers with covalent bonds, releasing a water molecule.
What reaction breaks down polymers?
Hydrolysis reaction – breaks covalent bonds using water, splitting polymers into monomers.
Which elements make up carbohydrates?
Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O).
Which elements make up lipids?
C,O,H
Which elements make up proteins?
C,O,H,N,S
Which elements make up nucleic acids?
C,H,O,N,P
What is glucose?
A hexose monosaccharide (C6H12O6), main energy source in respiration.
What is a hexose sugar?
A monosaccharide with 6 carbon atoms (e.g. glucose, galactose, fructose).
What is a pentose sugar?
A monosaccharide with 5 carbon atoms (e.g. ribose, deoxyribose).
What is ribose?
A pentose monosaccharide found in RNA, ATP, and NAD.
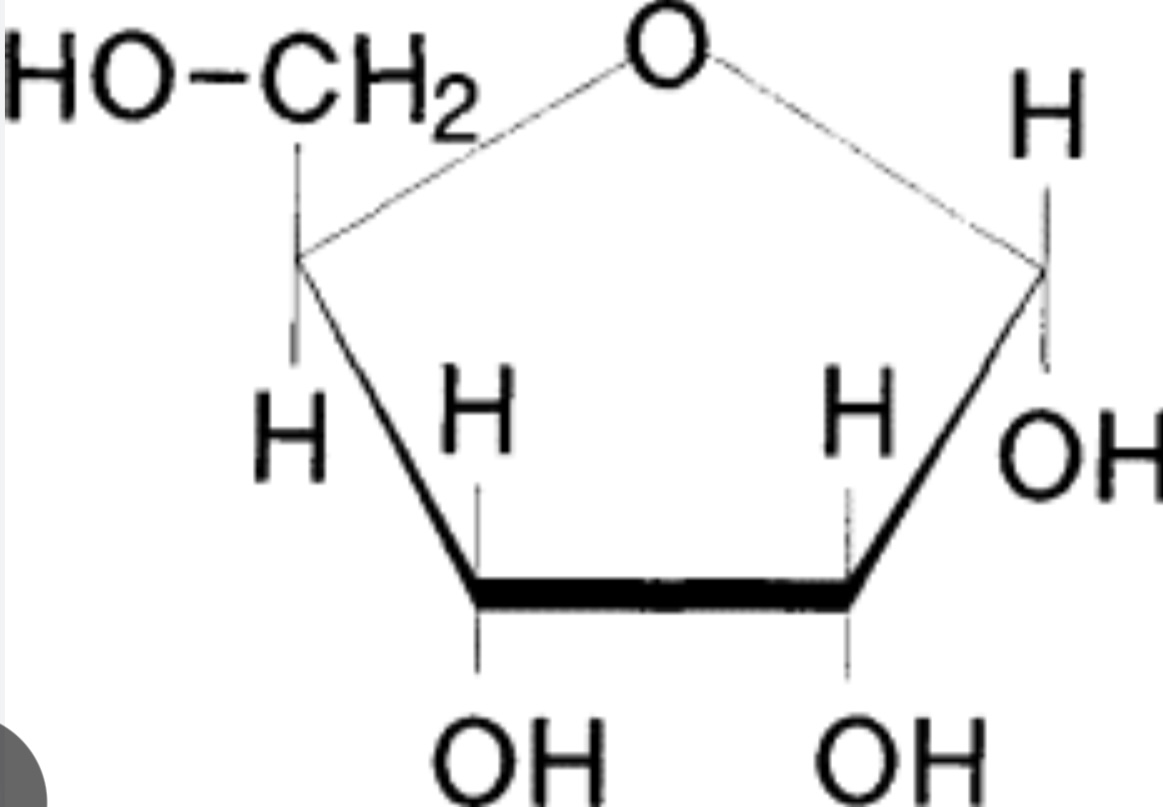
What is deoxyribose?
A pentose sugar in DNA with one fewer oxygen atom than ribose.
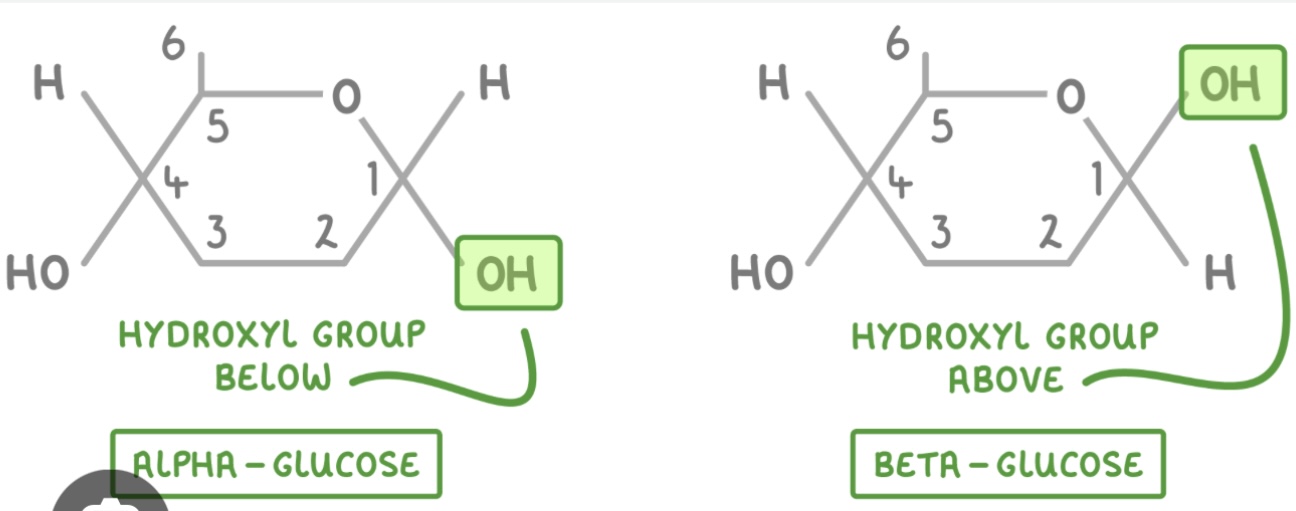
What is the structural difference between α-glucose and β-glucose?
In α-glucose, the OH on carbon 1 is below;
in β-glucose, the OH on carbon 1 is above.
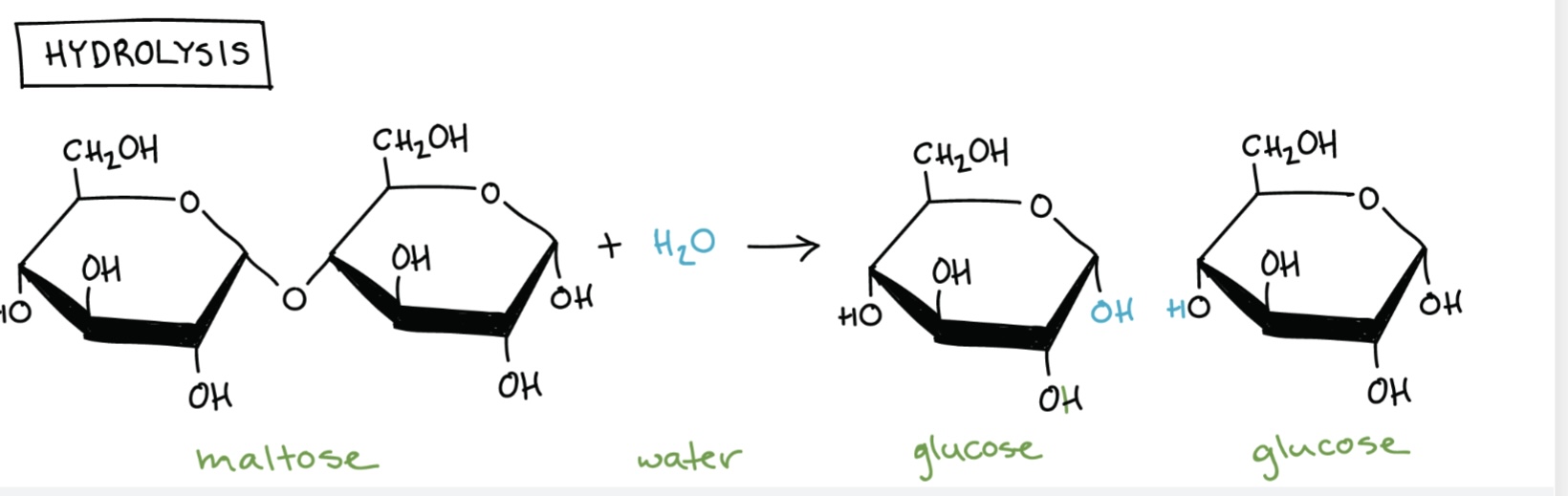
What is a disaccharide?
A sugar formed from two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond in a condensation reaction.
Name the disaccharides and their monomers.
Maltose = glucose + glucose
Sucrose = glucose + fructose
Lactose = glucose + galactose.
How are glycosidic bonds formed?
By condensation reactions between hydroxyl groups, releasing water.
How are glycosidic bonds broken?
By hydrolysis reactions, adding water to break the bond.
What is a 1,4 glycosidic bond?
A covalent bond formed between carbon 1 of one monosaccharide and carbon 4 of another.
What is starch?
A storage polysaccharide in plants made of α-glucose; a mixture of amylose and amylopectin.
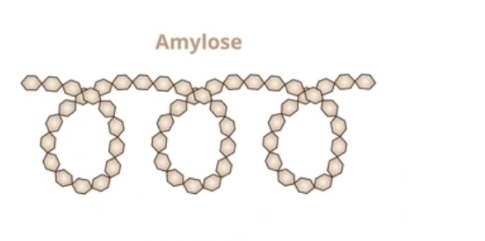
Structure and function of amylose?
Unbranched α-glucose chain
1,4 glycosidic bonds
coils into helix
compact for storage.
Structure and function of amylopectin?
Branched α-glucose chain
1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
branches allow rapid glucose release.
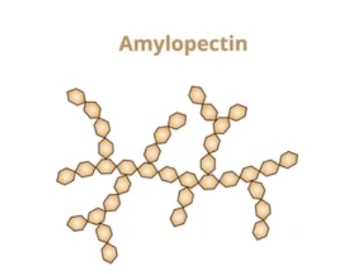
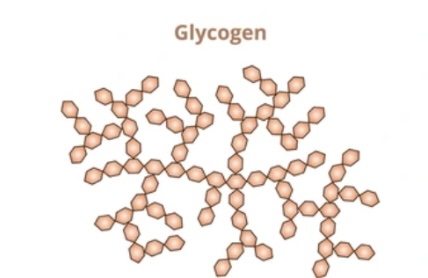
What is the structure glycogen?
Animal storage polysaccharide of α-glucose,
highly branched and compact,
allows rapid glucose release.
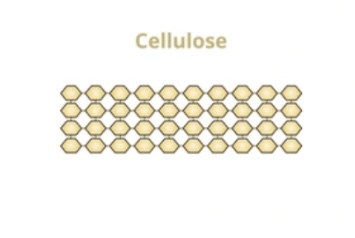
What is the structure of cellulose?
Structural polysaccharide of β-glucose,
straight unbranched chains linked by hydrogen bonds,
forming strong microfibrils in plant cell walls.
Why is glucose soluble?
Because of hydrogen bonding with water; allows transport in blood and cytoplasm.
Why is starch good for storage?
Compact, insoluble (does not affect osmosis)
large (does not diffuse out of cells)
branched amylopectin allows rapid glucose release.
Why is glycogen good for storage in animals?
Compact,
highly branched (faster glucose release to meet high metabolic demand),
insoluble so does not affect osmosis.
Why is cellulose strong?
β-glucose chains form straight structures, hydrogen bonds between chains form microfibrils, giving high tensile strength to plant cell walls.
Why are condensation and hydrolysis reactions important?
They allow the synthesis and breakdown of biological molecules for energy release, storage, and structural functions.
What is a condensation reaction?
A process two monomers join together to form a polymer
with the elimination of a water molecule
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
A chemical reaction that uses water to break the covalent bond
between 2 monomers to form polymers
What type of bonding does lactose include?
Beta-glycosidic bond
What type of bonding does maltose include?
Alpha-glycosidic
What elements are lipids made of?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen.
At room temperature, what is the difference between fats and oils?
Fats are solid, oils are liquid.
Why are lipids insoluble in water?
They are non-polar molecules (no regions of charge).
What type of macromolecule are lipids?
Non-polymeric macromolecules (not made of repeating monomers).
What is a triglyceride made from?
One glycerol + three fatty acids.
What type of reaction forms triglycerides?
Condensation reaction (esterification).
What bond is formed in a triglyceride?
Ester bond (between glycerol and fatty acid).