Reproductive System
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Reproductive Development
It begins at the moment of conception and continues through life.
Gonad
a body organ that produces the cells necessary for reproduction (the ovary in females, testes in males)
Oocytes
cells that will develop into eggs through out the womanʼs mature years.
Puberty
stage of life at which secondary sex changes begin
Adrenarche
the awakening of the adrenal gland.
adrenal gland
responsible for making hormones including androgens — sex hormones that cause changes such as the development of pubic hair, oily skin, oily hair, and body odor.
Androgenic hormones
hormones responsible for muscular development, physical growth and the increase in sebaceous gland secretions
Thelarche
beginning of breast development
Menarche
onset of the reproductive phase in a young female (first menstruation). At menarche the first egg matures and is released out of the body if not fertilized. It occurs at an average of 1213 years.
Secondary sex characteristics
any physical characteristic developing at puberty which distinguishes between the sexes but is not directly involved in reproduction
Vulva or pudenda
refers to the entire female genitalia
Mons Pubis/ Mons Veneris
a pad of fats that protect the symphysis pubis
Labia Majora
these are two thick folds of adipose tissue originating from mons pubis and terminating in the perineum. It provides covering to external organ located under it.
Labia minora
these are two thin folds of adipose tissue that joins anteriorly to form a prepuce and posteriorly to form the fourchette. It is fragile, it is torn during delivery
Clitoris
it is erectile tissue situated under the prepuce of the labia minora. It is highly sensitive: touch and temperature. Known as "seat of womanʼs sexual arousal and orgasm. Supplied with sebaceous gland that produce cheese-like secretions called smegma
Fossa Navicularis
it is the space between the fourchette and vaginal introitus that is usually obliterated during childbirth.
Vestibule
triangular space between the labia minora where vaginal introitus, urethral meatus, Bartholinʼs gland and skeneʼs gland are located.
Bartholinʼs gland
pair of glands located at the side of the vagina which secretes mucus that keeps vaginal introitus lubricated. Its alkaline nature enhances sperm survival. It is known as vulvovaginal gland, paravaginal gland or major vestibular gland
Skeneʼs gland
located at inner side of urethral meatus. Also known as para urethral gland and minor vestibular gland. Its secretions increase with sexual stimulation to provide lubrication to the vagina to facilitate coitus
Vaginal orifice (introitus)
it is the external opening of the vagina located just below the urethral meatus.
G-spot (Granfenberg)
located at inner anterior surface of the vagina
Hymen
it is a thin circular membrane made of elastic tissue situated at the vaginal opening . It separates the female internal and external reproductive organ.
Urethral meatus
located just below the clitoris. It is where the urine flows
Pudendal Artery
main source of blood supply to the female external genitalia.
inferior rectal artery
Branch of the internal pudendal artery. where a portion of the vulvar blood supply also comes from
pudendal vein
Where venous return from the external genitalia occurs. During pregnancy, pressure from the fetal head on this vein can cause back pressure, leading to varicosities in the labia majora and legs.
ilioinguinal and genitofemoral nerves (L1 level).
anterior vulva is innervated by
pudendal nerve (S3 level).
posterior vulva and vagina are supplied by
Vagina
hollow, membranous organ located in front of the rectum and behind the bladder. contains numerous folds or rugae, allowing expansion
anterior wall is 6-7 cm long, posterior wall is 8-9 cm
Measurement of the anterior and posterior vaginal wall
bulbocavernosus muscle
circular muscle at the external opening of the vagina acts as a voluntary sphincter
6.8-7.2.
Vaginal pH before puberty
4.5 due to the activity of specific bacteria
Vaginal pH after puberty
Döderlein's bacilli
gram-positive bacteria that form part of the vaginal microbiome. These bacteria reproduce after a female reaches sexual maturity and secrete lactic acid, maintaining the vaginal pH. The secretion of lactic acid helps prevent the growth of pathogenic bacteria that can cause vaginitis
Ovaries
The development and maturation of the ovum (egg). 3 cm long, 2 cm in diameter, and 1.5 cm thick, with the shape and size of an almond. Grayish-white with pitted surfaces and minute indentations. Suspended near the ends of the fallopian tubes, held in place by three strong ligaments that attach to the uterus and the pelvic wall
Estrogen
Stimulates the development of female secondary sexual characteristics, Promotes endometrial proliferation, resulting in thickening of the uterine lining, Causes thinning of cervical mucus, aiding sperm movement, Stimulates growth of ductile structures in the breast, Regulates menarche (onset of menstruation) and the menstrual cycle, Inhibits FSH, regulating follicular development, Promotes ovum maturation
Progesterone
Has a thermogenic effect, increasing body temperature after ovulation, Relaxes uterine muscle, preventing contractions during pregnancy, Causes fluid retention, leading to weight gain, Contributes to Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) symptoms such as bloating and mood change, Causes tingling sensation and breast fullness before menstruation, Stimulates endometrial glands to secrete mucin and glycogen, preparing the endometrium for implantation
Ovulation
release of a mature ovum from the ovary, typically occurring around the middle of the menstrual cycle
Ovarian Ligament
A fibrous band of tissue that connects the ovary to the side of the uterus. Attaches to the ovary inferiorly and lies within the broad ligament. Joins the uterus just below the origin of the fallopian tubes
Suspensory Ligament of Ovary
A fold of peritoneum, sometimes considered part of the broad ligament that extends from the ovary to the lateral abdominal wall. Contains the ovarian vessels and nerves, including the ovarian artery, ovarian vein, ovarian nerve plexus, and lymphatic vessels.
Fallopian Tube
Arise from upper corner of the uterine body and extend outward and backward until each opens at its distal end, next to ovary. Approximately 10 cm long in a mature woman. Convey the ovum from the ovaries to the uterus and provide a place of fertilization of the ovum by sperm
infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus, interstitial segment
4 Parts of the Fallopian Tube:
Interstitial/Intramural
- thick walled, located inside the uterus
- 1 cm long
Isthmus
portion of the tube that is cut or sealed during tubal ligation (sterilization). 2cm long
Ampulla/Distal Third:
5 cm. The site where fertilization usually occurs
Infundibular
2 cm. The most distal segment, funnel shaped, and covered by fimbria (small hairs) that guide the ovum into the fallopian tube
mucosal layer, muscular layer, peritoneal layer
Layers of the Fallopian Tube:
Mucosal Layer:
Lubricates the tube. Contains cilia that help transport the ovum to the uterus.
Muscular Layer:
Responsible for peristaltic movement, which is strongest during ovulation.
Peritoneal Layer:
The outermost layer. Attaches to ligaments that maintain the position of the fallopian tube
Uterus
hollow, muscular canal resembling an inverted pear, located in the lower pelvis, posterior to the bladder and anterior to the rectum. Receives the ovum from the fallopian tube. Provides a site for implantation and nourishment of the fertilized egg. Protects and supports a growing fetus
Body/Corpus, Isthmus, Cervix
Divisions of the Uterus:
Body/Corpus
uppermost and largest part of the uterus. The fundus is located between the points of attachment of the fallopian tubes and is the portion that is palpated to assess uterine growth, contractions, and postpartum recovery
Isthmus
A short segment between the body and the cervix. 1-2 mm (nonpregnant). Common site for Caesarean incision during childbirth
Cervix
The lowest portion of the uterus. Approximately 25 cm long
perimetrium, myometrium, endometrium
Layers of Uterus
Endometrium (Inner Layer)
A mucous membrane composed of two layers
Basal layer and Glandular layer
Layers of endometrium
Basal Layer
Closest to the uterine wall. Remains stable and is not influenced by hormones
Glandular Layer
Grows and thickens each month under the influence of estrogen and progesterone. If pregnancy does not occur, this layer is shed as menstrual flow
Myometrium (Middle Muscle Layer)
Composed of three interwoven layers of smooth muscle arranged in longitudinal, transverse, and oblique directions. Expands, contracts, and constricts.
Perimetrium (Outer Layer)
Composed of connective tissue. Provides strength and structural support to the uterus
Broad Ligaments
Two folds of peritoneum that cover the uterus anteriorly and posteriorly, extending to the pelvic sides to help stabilize the uterus.
mesometrium, mesosalpinx, mesovarium
3 parts of broad ligament
Mesometrium
Surrounds the uterus; the largest subsection. Runs laterally to cover the external iliac vessels, forming a fold over them. Encloses the proximal part of the round ligament of the uterus
Mesovarium
Associated with the ovaries. Projects from the posterior surface of the broad ligament, attaching to the hilum of the ovary and enclosing its neurovascular supply. Does not cover the surface of the ovary itself.
Mesosalpinx
Originates superiorly to the mesovarium, enclosing the fallopian tubes.
Superior Aspect
Supported by the broad ligament and round ligaments
Middle Aspect
Supported by the cardinal, pubocervical, and uterosacral ligaments.
Inferior Aspect
Supported by pelvic floor structures, including the levator ani, perineal membrane, and perineal body
Round Ligaments
Fibrous muscular cords that originate at the uterine horns and attach to the labia majora, passing through the inguinal canal to insert into the fascia of the vulva. Pulls the uterus forward, helping maintain an anteverted position
Cardinal Ligaments:
Also known as lateral, transverse cervical, or Mackenrodtʼs ligaments. Located along the inferior border of the broad ligament; house the uterine artery and uterine veins. Arise from the cervix and lateral fornix of the vagina, providing extensive attachment to the lateral pelvic wall.
Pubocervical Ligaments:
Bilateral structures that attach the cervix to the posterior surface of the pubic symphysis. Function to support the uterus within the pelvic cavity.
Uterosacral Ligaments:
Bilateral fibrous bands that attach the cervix to the sacrum; also known as recto-uterine ligaments or sacrocervical ligaments. Function to support the uterus and keep it in place
Congenital Uterine Anomalies
Congenital malformations of the female reproductive tract. These anomalies may also affect the fallopian tubes, cervix, and upper vagina. Can lead to infertility or complications during pregnancy.
Didelphys Uterus
Double uterus, double cervix, double vagina
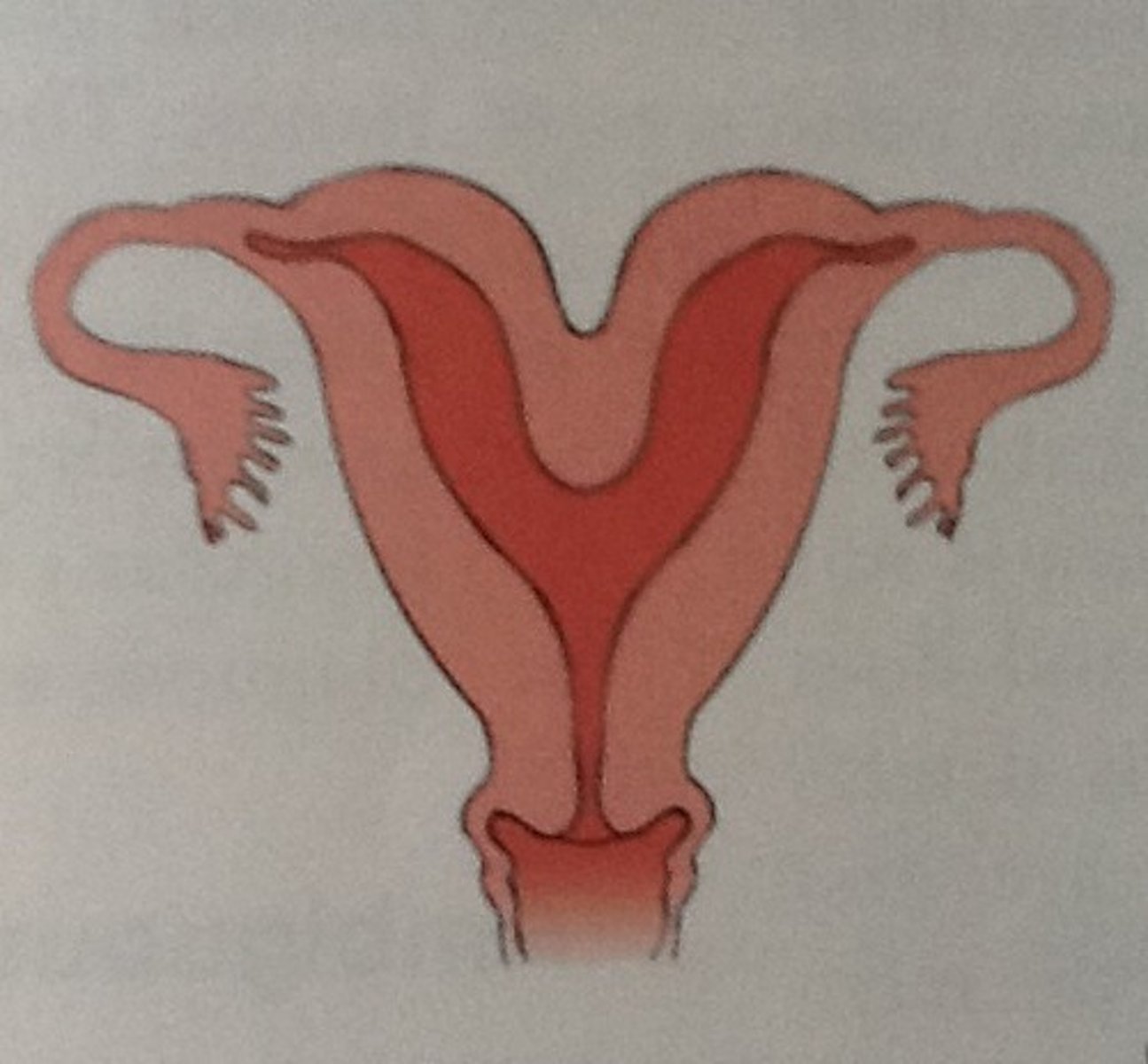
Arcuate Uterus
Uterus with a dent on the top part
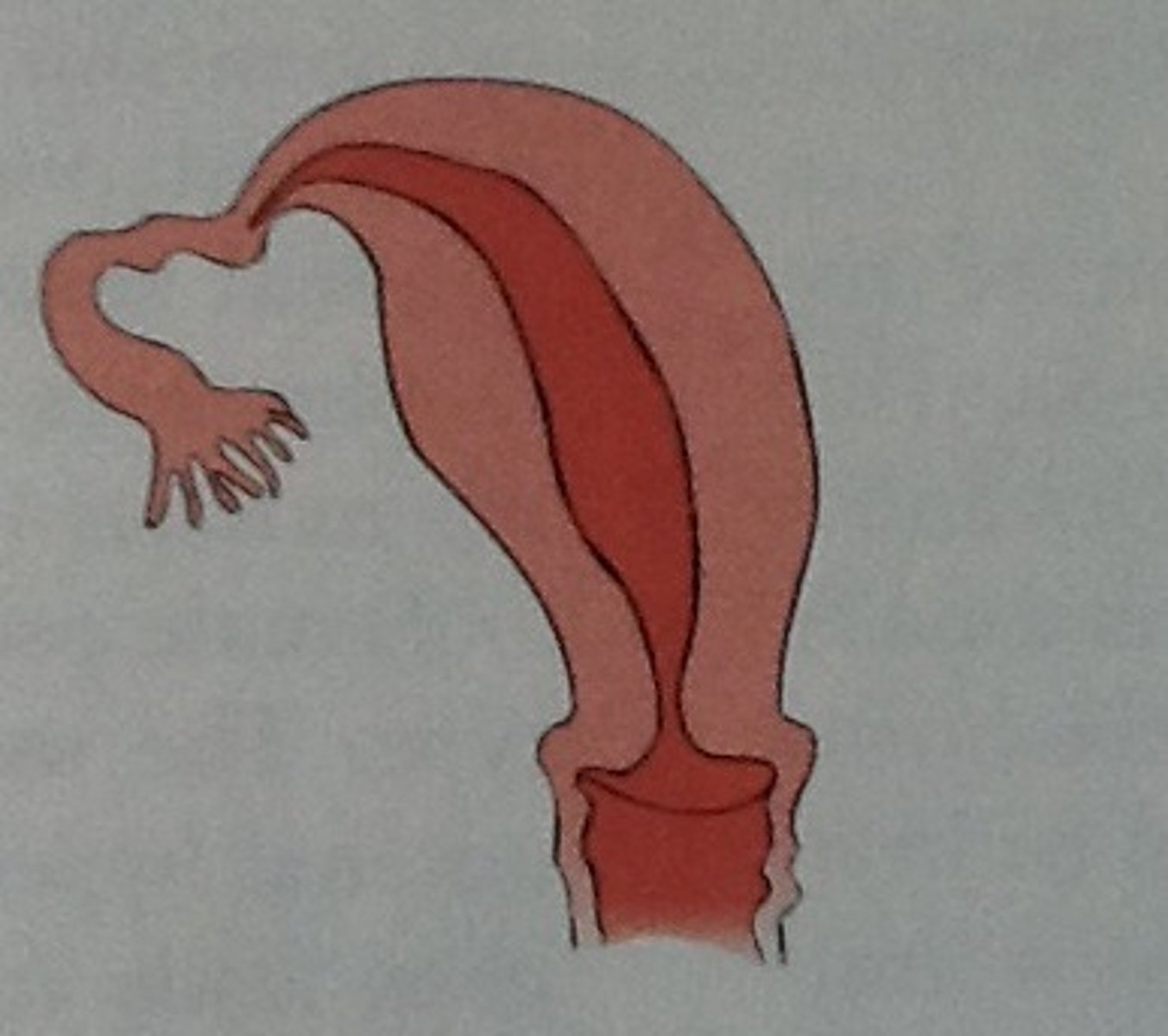
Unicornuate Uterus
One-sided uterus.
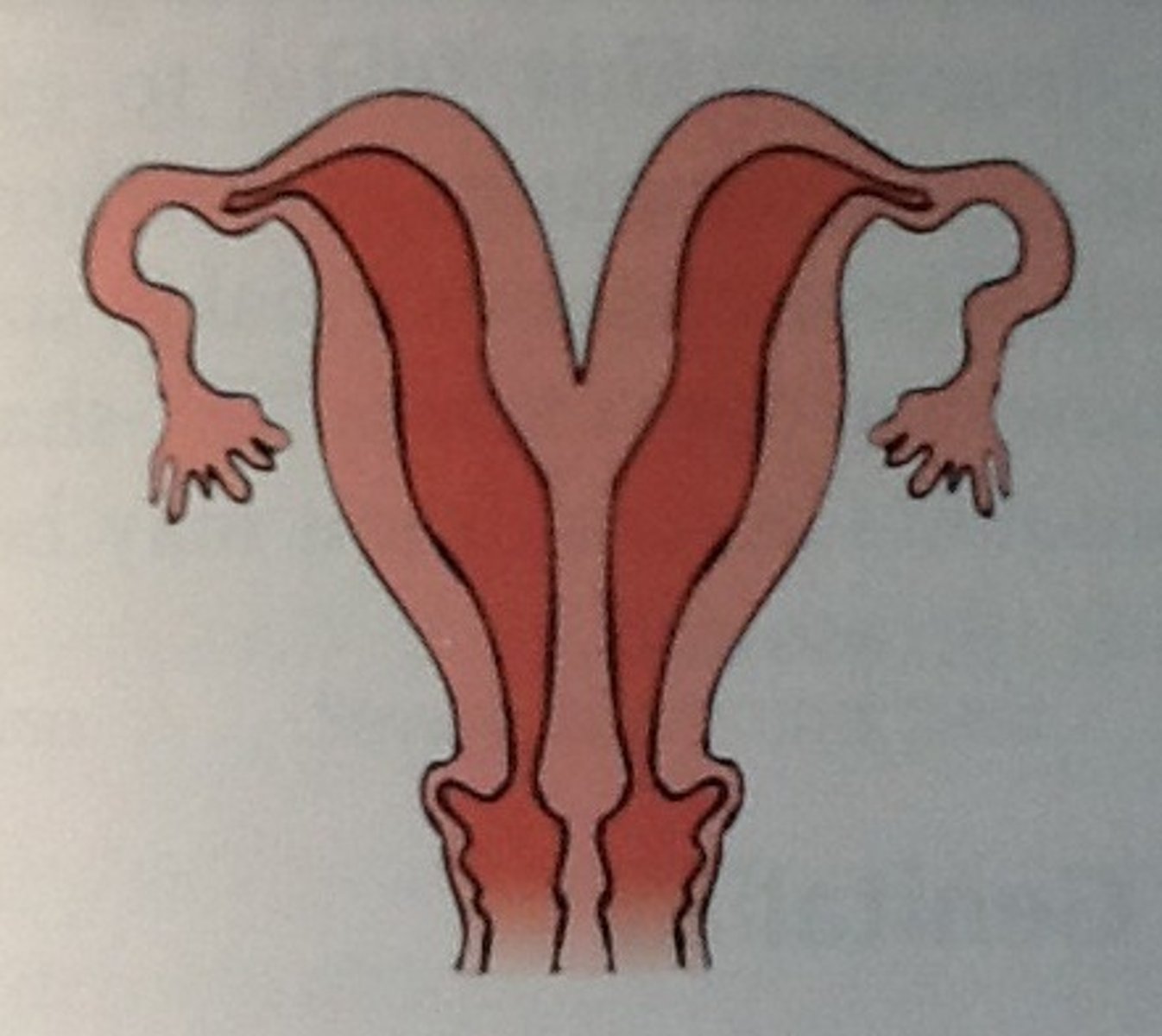
Bicornuate Uterus
uterus with two horns, Heart-shaped uterus.
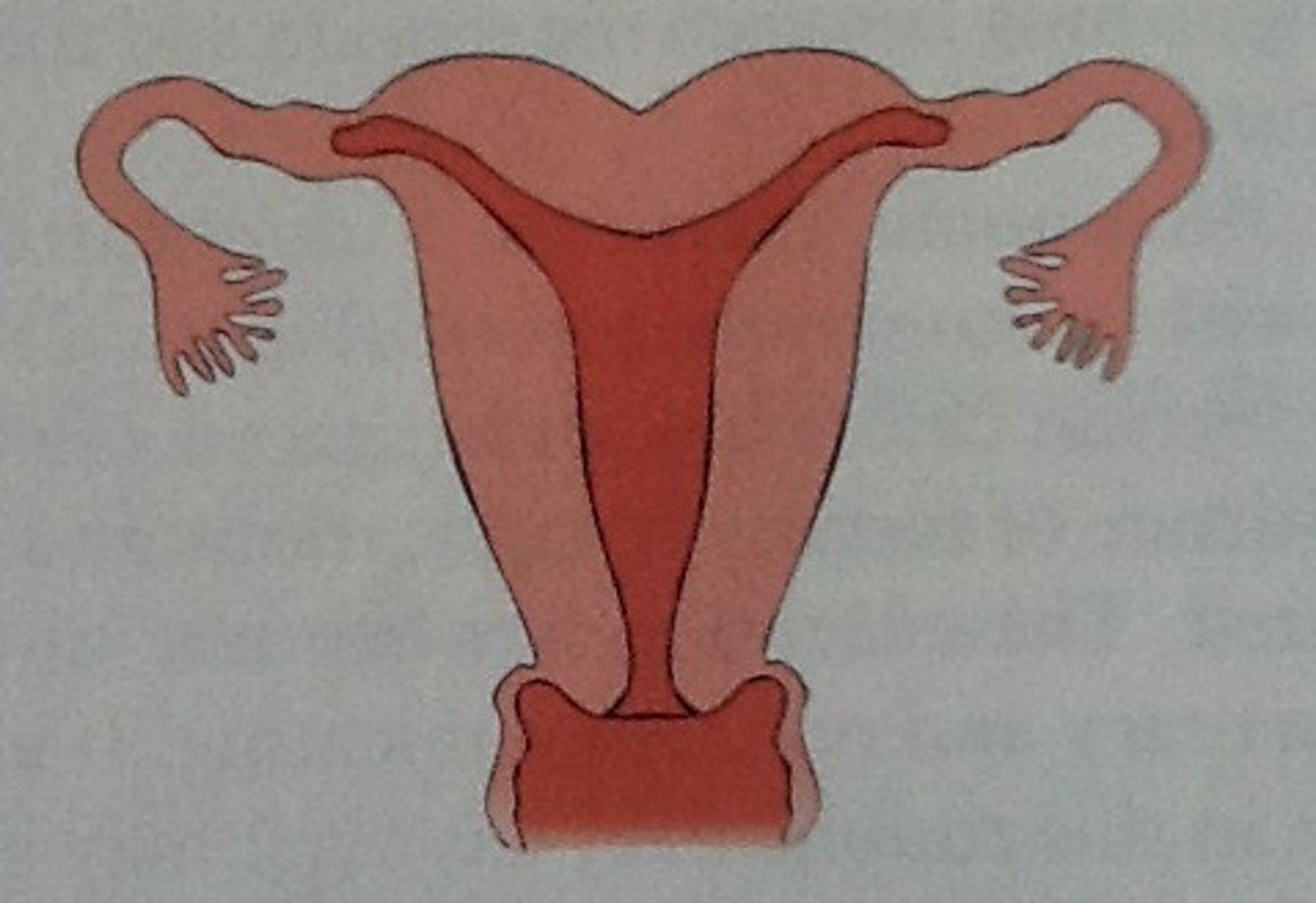
Septate Uterus
Uterus with a partition in the middle.
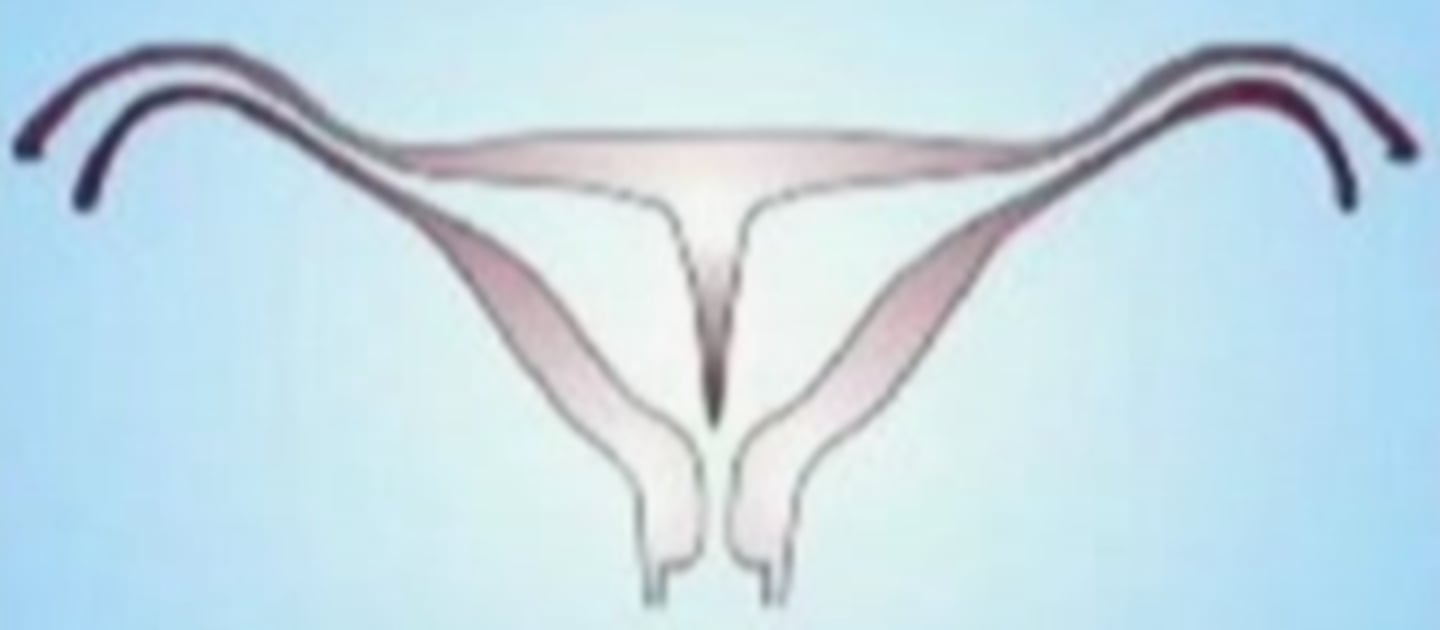
Absent Uterus
Complete absence of the uterus
anteverted position
typical position of the uterus, where the uterus tips forward at the cervix
Extreme abnormal flexion or version
positions may interfere with fertility due to sharp bends that can block the deposition or migration of sperm.
retroverted uterus
the entire uterus including the body and the cervix are tilted backwards; contrasts with anteverted, anteflexed, or mid-position uterus
anteflexion of the uterus
abnormal forward bending of the uterus
retroflexion of the uterus
condition in which the body of the uterus is bent backward, forming an angle with the cervix
Penis
Used for sexual intercourse, the penis consists of the root, body, and glans (head). The body contains sponge-like tissue that fills with blood during arousal, causing an erection. The penis expels semen during orgasm and blocks urine flow during this process.
Scrotum
sac of skin holds the testicles and acts as a temperature control system for sperm production, keeping the testicles cooler than body temperature by contracting or relaxing
Testicles (Testes)
These oval organs produce testosterone and sperm. Inside are seminiferous tubules, where sperm is generated
Epididymis
long, coiled tube located at the back of each testicle, the epididymis is responsible for transporting and storing sperm produced in the testes. facilitates the maturation of sperm, which are initially immature and unable to fertilize an egg. During sexual arousal, contractions push the mature sperm into the vas deferens
Vas deferens
long, muscular tube that carries sperm from the epididymis into the pelvic cavity, behind the bladder. transports mature sperm to the urethra in preparation for ejaculation
Ejaculatory ducts
These ducts are formed by the fusion of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicles. They empty sperm and seminal fluid into the urethra
Urethra
This tube carries both urine and semen out of the body. During sexual arousal and orgasm, the urethra is blocked from carrying urine, allowing only semen to be ejaculated
Seminal vesicles
Sac-like structures that produce a fluid rich in fructose, providing energy for the sperm. This fluid constitutes a significant portion of the ejaculatory fluid or semen
Prostate gland
A walnut-sized gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. Adds additional fluid to the semen, which helps nourish and protect sperm. The urethra passes through the prostate gland, carrying semen during ejaculation.
Bulbourethral glands Cowper's glands)
Pea-sized glands located on either side of the urethra, just below the prostate. These glands secrete a clear, lubricating fluid that helps neutralize acidity in the urethra from urine, ensuring a safer passage for sperm during ejaculation
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
sperm production (spermatogenesis)
luteinizing hormone (LH)
testosterone production.
Testosterone
crucial for sperm development and male characteristics, including muscle growth, voice changes, and sex drive