BIO 111 Exam 1 Practice
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/97
Last updated 4:28 AM on 1/17/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
1
New cards
The Culture of Science
Science is an intensely social activity, both collaboration (cooperation) and competition characterize scientific culture
2
New cards
All living things share 5 fundamental characteristics
(2 as of now)
(2 as of now)
1\.) All organisms are made up of Cells
4\.) All organisms acquire and use Energy
4\.) All organisms acquire and use Energy
3
New cards
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
The form of chemical energy that is required for reactions to take place inside of the cell.
4
New cards
Cell Theory
The understanding of cells
5
New cards
Theory
a rigorously tested and supported explanation (pattern + process)
6
New cards
Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
all organisms are made of cells (pattern) and all cells come from preexisting cells (process)
7
New cards
3 theories form the framework for modern biological science:
\- The cell theory (Bio. 111) - The theory of evolution by natural selection (Bio.112 and Bio. 211)- The chromosome theory of inheritance (Bio. 111)
8
New cards
How is hereditary information transmitted from one generation to the next?
DNA, chromosomes and genes
9
New cards
Two main types of cells:
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes
10
New cards
Prokaryotes
Domains: Archaea and Bacteria
* single-celled
* “before kernel”
* not membrane-bound
* ten times smaller than eukaryotes
* DNA is not enclosed in the nucleus; in the region called the nucleoid
* single-celled
* “before kernel”
* not membrane-bound
* ten times smaller than eukaryotes
* DNA is not enclosed in the nucleus; in the region called the nucleoid
11
New cards
Eukaryotes
Domain: Eukarya
* single-celled or multicellular
* “true-kernel”
* membrane-bound nucleus and organelles
* provides more S.A. to move quickly in a large volume
* complicated exoskeleton
* single-celled or multicellular
* “true-kernel”
* membrane-bound nucleus and organelles
* provides more S.A. to move quickly in a large volume
* complicated exoskeleton
12
New cards
Broadest phylogenetic classification
Domain
13
New cards
Cell Characteristics
* Move,
* Metabolize (acquire and use energy),
* Respond to the environment,
* Reproduce, and
* Descend from pre-existing cells, and over time these lineages of cells evolve
* Metabolize (acquire and use energy),
* Respond to the environment,
* Reproduce, and
* Descend from pre-existing cells, and over time these lineages of cells evolve
14
New cards
Nucleic acids
what chromosomes are made of (genetic information)
15
New cards
Proteins
made by ribosomes that are either free in the cytoplasm or attached
16
New cards
Carbohydrates
provide energy, carbon, identity/ recognition
17
New cards
Lipids
make up the plasma membrane and other structures
18
New cards
Kernel
nucleus
19
New cards
Nucleoid
The central region in a prokaryotic cell where the DNA is located. It is not enclosed by a membrane and is responsible for controlling the cell's activities.
20
New cards
symbiotic
living together with another organism
21
New cards
mutualism
A type of symbiotic relationship where both species benefit from each other's presence.
22
New cards
Plasma membrane
A selectively permeable barrier that surrounds the cell, controlling the movement of substances in and out.
23
New cards
Plasmid
It can replicate independently from the chromosomal DNA and can transfer genetic material between different bacteria. Plasmids often carry genes that provide advantages to the bacteria, such as antibiotic resistance.
24
New cards
Cytoplasm
A gel-like substance found inside cells. It holds organelles in place and facilitates cell processes.
25
New cards
Cell wall
Structure outside the cell membrane that provides support and protection to plant cells.
26
New cards
Ribosome
A cellular structure responsible for protein synthesis. It translates genetic information from DNA into proteins.
27
New cards
NPC,L
* Nucleic Acids
* Proteins
* Carbohydrates
* Lipids
* Proteins
* Carbohydrates
* Lipids
28
New cards
The Nucleus
* The central part of a cell that contains genetic material
* makes up the rRNA for transport and use in the cytoplasm
* double membrane (nuclear envelope)
* semi-permeable
* loosely packed chromosomes
* makes up the rRNA for transport and use in the cytoplasm
* double membrane (nuclear envelope)
* semi-permeable
* loosely packed chromosomes
29
New cards
Chromosomes
* coiled
* only 1
* Inside the nucleus with DNA that carries genetic information
* made of chromatin
* Shape changes as the cell divides
* only 1
* Inside the nucleus with DNA that carries genetic information
* made of chromatin
* Shape changes as the cell divides
30
New cards
Supercoiled Chromosomes
DNA structure where the double helix is twisted upon itself, forming a tightly coiled shape. (90% of the time)
31
New cards
Relaxed Chromosomes
DNA structure where it is in a linear form. (10% of the time)
32
New cards
Chromatin
The complex of DNA and proteins found in the nucleus of a cell, which condenses to form chromosomes during cell division.
33
New cards
Ribosomes
* Made of rRNA and proteins
* 1 large and 1 small sub-unit. (come together to make proteins)
* synthesize proteins in two different locations
* free (cytoplasm)
* attached (\[ER\] ore the nuclear envelope)
* 1 large and 1 small sub-unit. (come together to make proteins)
* synthesize proteins in two different locations
* free (cytoplasm)
* attached (\[ER\] ore the nuclear envelope)
34
New cards
Endomembrane System
* ER - rough and smooth
* Golgi apparatus
* Lysosomes (animals only)
* Continuous or connected by vesicles
* Golgi apparatus
* Lysosomes (animals only)
* Continuous or connected by vesicles
35
New cards
Rough ER
* Ribosomes bound to it
* proteins from ribosomes finish folding here
* proteins from ribosomes finish folding here
36
New cards
Lumen
Inside space within the cells organelles
37
New cards
Smooth ER
* No attached ribosomes
* Synthesizes lipids
* Testes and ovaries need lots of this for hormone production
* Synthesizes lipids
* Testes and ovaries need lots of this for hormone production
38
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
* shipping and receiving center
* made of sacs called cisternae
* Functions:
* the receiving cis side gets vesicles from the ER, forming new cisternae
* modifies and manufactures
* the shipping trans side sorts and packages materials with molecular barcodes
* made of sacs called cisternae
* Functions:
* the receiving cis side gets vesicles from the ER, forming new cisternae
* modifies and manufactures
* the shipping trans side sorts and packages materials with molecular barcodes
39
New cards
Cisternae
Membrane sacs found in the ER and Golgi apparatus. They play a crucial role in the processing, modification, and transport of proteins and lipids within the cell.
40
New cards
Lysosome
* (animals only)
* interior is acidic for digestion
* interior is acidic for digestion
41
New cards
Vacuole
* (plants and fungi only)
* storage of water and ions
* huge, in a fixed place in the cell
* can sometimes digest
* storage of water and ions
* huge, in a fixed place in the cell
* can sometimes digest
42
New cards
Peroxisomes
Organelles in which oxidation reactions occur sequestering H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide)
43
New cards
Mitochondria
* energy powerhouse of the cell
* can make their own proteins because of the DNA and ribosomes it contains
* in all eukaryotic cells (fungi, plants, animals, and protists)
* double membrane system
* produces ATP and oxygen through cellular respiration
* can make their own proteins because of the DNA and ribosomes it contains
* in all eukaryotic cells (fungi, plants, animals, and protists)
* double membrane system
* produces ATP and oxygen through cellular respiration
44
New cards
Chloroplast
* (plants only)
* convert sunlight energy into chemical bond energy in the form of carbohydrates
* can make their own protein b/c DNA and ribosomes it contains
* multiple membranes
* convert sunlight energy into chemical bond energy in the form of carbohydrates
* can make their own protein b/c DNA and ribosomes it contains
* multiple membranes
45
New cards
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein filaments that give shape, support, and movement to cells. Made up of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments.
46
New cards
Actin Filaments
(smallest)
* responsible for cytokinesis and cell crawling
* responsible for cytokinesis and cell crawling
47
New cards
Intermediate Filaments
Maintain cell shape and also anchor the nucleus
48
New cards
Microtubule Filaments
(largest)
* move chromosomes by building and falling apart at the other end (railroad)
* move chromosomes by building and falling apart at the other end (railroad)
49
New cards
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Electrons pass through the sample, creating a detailed 2D image
50
New cards
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Electrons bounce off the sample, creating a 3D sample
51
New cards
Polymerize
to combine or cause to combine to form a polymer.
* actions or α and β coming together to form filaments.
* actions or α and β coming together to form filaments.
52
New cards
Depolymerize
break (a polymer) down into monomers or other smaller units.
* actions or α and β coming breaking apart
* actions or α and β coming breaking apart
53
New cards
Centrosome
(only in animal cells)
* organize the microtubules
* organize the microtubules
54
New cards
Microtubule Transport
transport membrane vesicles and organelles through the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.
* ADP releases
* ATP enters
* ADP - Pi (hydrolyze)
* (repeats)
* ADP releases
* ATP enters
* ADP - Pi (hydrolyze)
* (repeats)
55
New cards
Centriole
help to arrange the microtubules that move chromosomes during cell division to ensure each daughter cell receives the appropriate number of chromosomes.
56
New cards
ATP Bond Break
Massive amounts of energy are released when one bond is broken in the phosphate group and one inorganic phosphate is released. This results in ADP
57
New cards
ADP
Adenosine Diphosphate
58
New cards
Aquaporins
A type of protein is a part of facilitated diffusion, where lots of water molecules pass through the cell membrane so osmosis can occur faster.
59
New cards
Endosymbiosis
A symbiotic relationship where one organism lives inside the other
60
New cards
The benefit of engulfing a Mitochondrion
Gains energy/ ATP for survival
61
New cards
The benefit of engulfing Chloroplast
Photosynthesis provides sugar, making it advantageous to absorb to engulf to have a food source for the cell.
62
New cards
Polar
partial charge due to unequal sharing of electrons
63
New cards
Nonpolar
no charge, electrons shared equally
64
New cards
Ions
full charge due to the actual GAIN or LOSS of electrons
65
New cards
Phospholipid Bilayer
Acts as a barrier to the passage of molecules and ions into and out of the cell.
* Size and charge can affect the diffusion rate across the membrane
* contains proteins
* Size and charge can affect the diffusion rate across the membrane
* contains proteins
66
New cards
Ground Substance
helps the cell resist compression
* a part of the extracellular matrix
* a part of the extracellular matrix
67
New cards
Fibers
helps the cell resist tension
* a part of the extracellular matrix
* a part of the extracellular matrix
68
New cards
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
The ECM provides structural and biochemical support to cells.
69
New cards
Collagen
provides strength and also regulates cell adhesion, supports chemotaxis and migration, and directs tissue development.
* **a part of the extracellular matrix**
* **a part of the extracellular matrix**
70
New cards
Diffusion
the movement of a substance traveling down its concentration gradient
* high to low concentration
* passive transport
* high to low concentration
* passive transport
71
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion
molecules going through a protein channel b/c they can’t pass through the semi-permeable membrane if they are charged ions or polar molecules.
72
New cards
Osmosis
Water molecules travel from an area of high concentration to a lower concentration.
* movement from low solute concentration to high solute concentration
* high water ψ potential → Low water ψ
\
* movement from low solute concentration to high solute concentration
* high water ψ potential → Low water ψ
\
73
New cards
Hypertonic
high solute concentration
74
New cards
Hypotonic
low solute concentraion
75
New cards
Isotonic
equal solute concentration
76
New cards
Water potential
measurement of potential energy in water
* solute and pressure potential
* formula - water ψ = pressure ψ + solute ψ
* solute and pressure potential
* formula - water ψ = pressure ψ + solute ψ
77
New cards
Homeostasis
Stable equilibrium maintained by all living systems
78
New cards
Active Transport
Force molecules to move against their concentration gradient by using ATP/ energy.
79
New cards
Sodium Potassium Pump
To pump sodium out of the cell and potassium onto the cell
* 3 sodium out
* 2 potassium in
* 3 sodium out
* 2 potassium in
80
New cards
Resting Membrane Potential
The electric potential energy that results from separating opposite charges across the membrane when those charges aren not stimulating the cell.
81
New cards
Electrochemical Gradient
allow cells to control the direction ions move across membranes
82
New cards
Adjacent Cell Connection (animal)
* Tight Junctions
* Desmosomes
* Gap Junctions
* Desmosomes
* Gap Junctions
83
New cards
Adjacent Cell Connection (Plant)
Plasmodesmata
* connect + direct communication
* smooth ER of two cells connect through cell wall
* connect + direct communication
* smooth ER of two cells connect through cell wall
84
New cards
Tight Junctions
forms an adhesion complex between two neighboring cells, serving as a tight seal between the cells
85
New cards
Desmosomes
mediate cell-cell contact and strong adhesion
* Requires
* membrane proteins
* anchoring proteins
* intermediate filaments
* Requires
* membrane proteins
* anchoring proteins
* intermediate filaments
86
New cards
Gap Junctions
Allows for direct connection and communication, creating open channels between cells.
* ex.)heart cells
* ex.)heart cells
87
New cards
Most common elements in humans
* Hydrogen - H
* Oxygen - 02
* Carbon - C
* Nitrogen - N2
* Oxygen - 02
* Carbon - C
* Nitrogen - N2
88
New cards

What is circled
Mass number (picture)
89
New cards
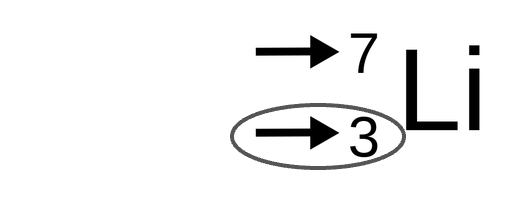
What is circled
Atomic number (picture)
90
New cards
Mass #
\# of protons + neutrons
91
New cards
Atomic #
\# of protons
92
New cards
Valence Electrons
electrons in the outermost shell of an atom
93
New cards
Covalent Bonds
a chemical bond that occurs when atoms share electrons to form electron pairs
94
New cards
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
atoms share electrons equally
95
New cards
Polar Covalent Bonds
atoms don’t share electrons equally
* one atom has more pull, or attraction
* one atom has more pull, or attraction
96
New cards
Electronegativity
how likely an atom is to attract electrons when forming a chemical bond
FON
FON
97
New cards
Ionic Bonds
made from atoms or ions with a charge
* electrons are gained or lost
* electrons are gained or lost
98
New cards
Hydrogen Bonds
An attraction between two atoms already in chemical bonds. One of the atoms is hydrogen, and the other atom can be any electronegative atom.