MCAT stuff to review (this will be long)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms


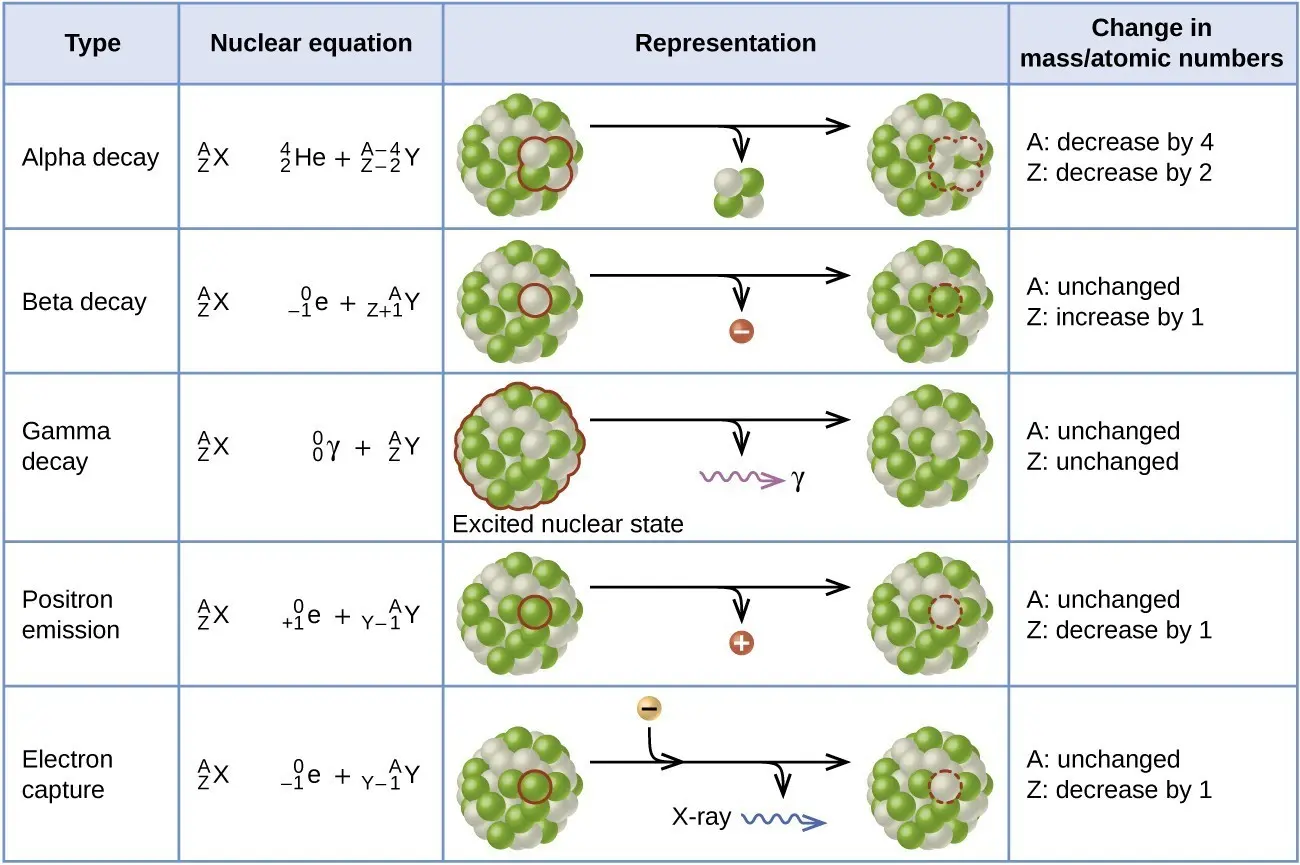
what are the different types of decay
What are the 5 stages of the Demographic Transition Model, and what happens to birth & death rates in each?
Stage 1 – Pre-industrial
High birth rate, high death rate
Little to no population growth
Stage 2 – Transitional
High birth rate, falling death rate
Rapid population growth
Stage 3 – Industrial
Falling birth rate, low death rate
Population growth slows
Stage 4 – Post-industrial
Low birth rate, low death rate
Stable population
Stage 5 – Declining
Birth rate < death rate
Population decline
Key rule: Death rate drops first, birth rate drops later.
What is a feedback loop, and what is the difference between positive and negative feedback?
A feedback loop is a process where a system’s output feeds back into the system to regulate future activity.
Negative feedback loop:
Output reduces the original stimulus
Maintains homeostasis
Most common in the body
Example:
Body temperature regulation
Blood glucose regulation (insulin & glucagon)
Positive feedback loop:
Output amplifies the original stimulus
Pushes system away from equilibrium
Occurs until a specific endpoint is reached
Example:
Childbirth (oxytocin → contractions → more oxytocin)
Blood clotting
Key rule:
Negative = stabilize, Positive = amplify
What is actor–observer bias?
Attribute our own behavior to situational factors
Attribute others’ behavior to dispositional traits
Example:
Me: “I did poorly because the test was unfair.”
Them: “They did poorly because they’re lazy.”
Key cue: Me vs them
What is the fundamental attribution error?
The tendency to:
Overemphasize dispositional factors
Underemphasize situational factors
when explaining others’ behavior
Example:
“That driver is reckless.” (ignores situational context)
Key cue: Them only
What are the stages of Piaget’s cognitive development theory?
Sensorimotor (0–2): learning through senses & actions; object permanence
Preoperational (2–7): symbolic thinking; egocentrism, no conservation
Concrete operational (7–11): logical thinking about concrete objects; conservation
Formal operational (12+): abstract and hypothetical reasoning
Mnemonic:
Some People Can Fly
What are the effects of high vs low self-efficacy on behavior and outcomes?
High Self-Efficacy
↑ motivation & persistence
Takes on challenging tasks
Views failure as fixable
Better academic, health, and coping outcomes
Low Self-Efficacy
↓ motivation & effort
Avoids challenges
Attributes failure to lack of ability
↑ risk of anxiety, learned helplessness, poor performance
Key cue: High → try & persist; Low → avoid & give up
What are the main functions of the frontal lobe?
Executive function: planning, decision-making
Problem solving & reasoning
Motor cortex: voluntary movement
Broca’s area (usually left): speech production
Personality, impulse control, and social behavior
What are the main functions of the parietal lobe?
Somatosensory cortex: touch, temperature, pain
Spatial orientation & body awareness
Integrates sensory info for perception and navigation
What are the main functions of the temporal lobe?
Auditory processing & hearing
Wernicke’s area (usually left): language comprehension
Memory formation (hippocampus located here)
Emotion (amygdala located here)
What is the main function of the occipital lobe?
Visual cortex: processing visual info (color, shape, motion)
What are the main functions of the brainstem?
Basic life functions: heart rate, breathing, sleep-wake cycle
Reflexes: swallowing, coughing, vomiting
Relay: connects brain & spinal cord
What are the main functions of the limbic system?
Emotion: amygdala → fear & aggression
Memory: hippocampus → forming new memories
Motivation & reward: nucleus accumbens
Regulates autonomic responses
What are the 8 stages of Erikson’s psychosocial development, including age ranges, conflicts, and key outcomes?
Trust vs. Mistrust (0–1 yr) → world is reliable → hope
Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt (1–3 yr) → independence → will
Initiative vs. Guilt (3–6 yr) → assertiveness → purpose
Industry vs. Inferiority (6–12 yr) → competence, skills → competence
Identity vs. Role Confusion (12–18 yr) → sense of self → fidelity
Intimacy vs. Isolation (18–40 yr) → close relationships → love
Generativity vs. Stagnation (40–65 yr) → contribute to society → care
Integrity vs. Despair (65+ yr) → reflection on life → wisdom
Mnemonic for MCAT:
“Trust All Innocent Individuals In Generous Integrity”
What is cultural capital, and what are its main types?
Definition: Non-financial social assets that help a person gain social mobility (knowledge, skills, education, behaviors valued by society).
Types:
Embodied: skills, knowledge, habits, manners
Objectified: cultural goods, books, instruments, art
Institutionalized: formal credentials, degrees, titles
MCAT Tip: Think Bourdieu; often tested in context of social inequality & education.
What is social capital, and why is it important?
Definition: The networks of relationships among people that provide access to resources, support, and opportunities.
Key Points:
Includes connections, social networks, and community ties
Can enhance social mobility and improve health/outcomes
Complements cultural capital (knowledge/skills)
Often passed through family, community, or institutions
MCAT Tip: Think “who you know” vs “what you know”.