Topic 8 - Space Physics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
the sun lies at the centre of our solar system it is ….
heliocentric
what galaxy is our solor system part off?
milky way
what are planets made of (small and big)
small planets are made mainly of rock
big planets are made mainly of gas
all planets orbit the sun …
on the same plane
all planets rotate but …
they have different speeds
some planets rotate in the opposite direction due to past collisions
why do larger planets have rings?
because their gravitational field is so strong it attracts debris
explain the geocentric model
the earth was the centre and everything orbited it in perfect circles
with a fixed background of stars
then 600 years later the heliocentric model was made because..
mars retrograde motion → earth obits the sun faster than mars, so we undertake it so it appears in reserve in the sky
Galileo observing moons orbiting Jupiter showed not everything orbited Earth
Kepler showed that the planets orbited in ellipses not circles
as planets orbit the sun …
the gravitational force causes the planet to change direction constantly
its velocity is always changing
the force causes the planet to accelerate without it increasing speed
for a stable orbit:
if the planet moves closer to the sun the gravitation attraction to the sun increases (forces and acceleration increases)
so orbital speed of planet increases
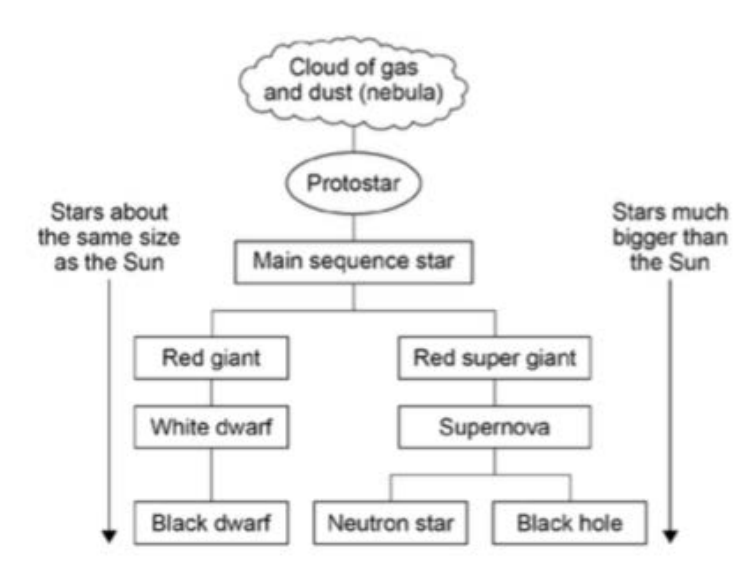
Life cycle of a star (start to star)
the gravitational pull between dust and gas particles draw them together
the cloud becomes more concentrated as the particles get closer
the temperature and pressure of the cloud increases as particles get pushed together eventually they can fuse together
fusion occurs releasing a large amount of energy
the cloud collapses due to gravity forming a star
fusion
occurs as the light (hydrogen) nuclei fuse together to form helium nuclei
creating a large amount of energy
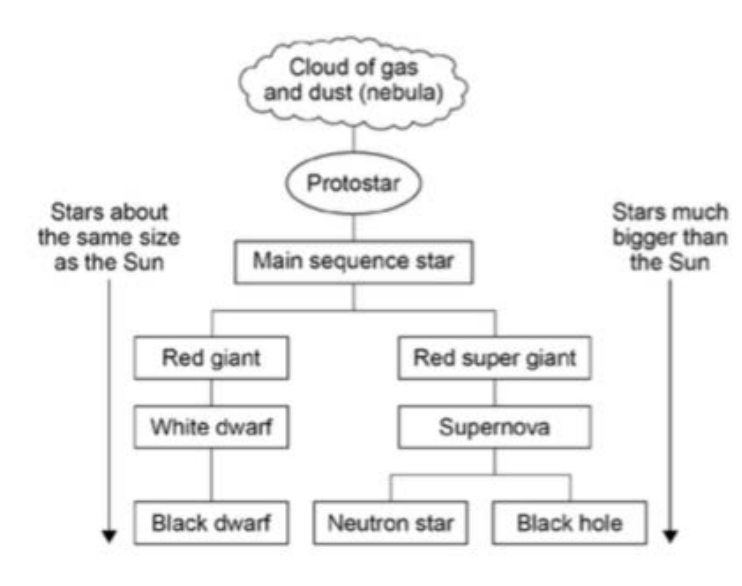
life cycle of a star (super giant)
eventually the star runs out of gas to fuse so it collapses
if its a red super giant the star will increase pressure and temperature of the core meaning heavier elements can fuse
it then becomes unstable because it is so big,
it then collapses, rebounds on its centre and produces a supernova
then it turns into a neutron star or a black hole
life cycle of a star (normal sized)
eventually the star runs out of gas to fuse so it collapses
less fusion occurs
the star collapses produces a nebula (lower scale supernova)
and a white dwarf remains
light appears red shifted from galaxies ….
moving away from earth
how do we know the universe is expanding
the change with distance of each galaxys speed
as wavelengths appear to get larger (more red) …
frequency decreases as the source is further away
what does red shift show?
the universe is expanding
initially it was formed from one point
Cosmic microwave background radiation
When the universe was very young, everything, the first stars and rock, would be very hot, and should have emitted lots of short-wavelength radiation
This radiation, as the universe expanded over time, would have been stretched to become microwaves
Which proves that the hot young universe has cooled and expanded since
why is the big bang the most accepted model?
it accounts for all the experimental evidence