NGR6172 Pharmacology Midterm (Week #1-7) Latest exam with complete verified solutions 2025-2026
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics is the study of the action of drugs in the body including absorption, distribution, metabolism and elimination. What the body does to the drug.
Absorption: How the drug leaves its site of administration. Bioavailability is important; f-value (portion of drug that reaches systemic circulation).
Distribution: Transport of a drug in body fluids from bloodstream.
Metabolism: Biotransformation; chemical inactivation of a drug through conversion to a more water-soluble compound that can be excreted from the body (e.g., liver, lungs, GI tract).
Elimination: Process by which drugs and their metabolites are removed from the body (e.g., liver and kidneys).
Routes of administration: PO, topical, subqut, IM, IV, rectal (PR), intradermal (ID), sublingual (SL), buccal, intaartivularm inhalation, intravaginal, ophthalmic, aural
Fastest route?Intravenous
Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics is the study of the biochemical and physiological effects of drugs and the mechanisms of their actions; the effect of the drug on the body.
Inhibitor: A drug that causes INHIBITION in the enzyme metabolization of another drug. IF DRUG A (IS AN INHIBITOR) + DRUG B = THIS RESULTS IN A DECREASED METABOLISM OF DRUG B, A DECREASED ELIMINATION OF DRUG B, AND AN INCREASED AMOUNT OF DRUG B IN THE BLOODSTREAM
Substrate: Drug that is affected by a change in its enzyme metabolism.
Inducer: A drug that causes ACCELERATION in the enzyme metabolization of another drug. IF DRUG A (IS AN INDUCER) + DRUG B = THIS RESULTS IN AN INCREASED METABOLISM OF DRUG B, AN INCREASED ELIMINATION OF DRUG B, AND A DECREASED AMOUNT OF DRUG B IN THE BLOODSTREAM
Metabolizer: Break down of a drug.
Adverse Effect
Common: Expected; should not stop patient from taking medication.
Severe: May incapacitate pt or interfere with patient's ability to work or complete ADLS; may be life threatening and result in death.
Drug Interactions
- Risk vs benefit of drug
-Increased risk with elderly and pts with comorbidities
Contraindications
Factors that prevent the use of a drug or treatment
Prescriptive authority
A. Independent vs Dependent practice: Independent means NP can prescribe alone. Dependent means physician retains ultimate authority through countersignature of prescriptions and or by a written agreement between the NP and physician.
B. Meaning of delegable authority: Requires nurse to perform under a physician; without it nurses cannot legally prescribe medications under any circumstances but can recommend nonprescription medications.
C. Prescriptive authority regulation: Many states practice dependent authority. Independent authority is restricted still in many states (e..g, excluding controlled substances, limiting drugs to those listed in a formulary, etc.)
NP scope of practice
A. DEA registration for NP: Registration of all NPs who are authorized by state law to prescribe controlled substances; mid-level providers (MLPs) differentiate NP DEA numbers from that of physicians.
B. Issues common to all NPs: Prescribing controlled substances, dispensing privileges.
c. Prescribing controlled-substances: MLPs DEA number. Varies from state to state; specific state restrictions.
(Narcotic vs non-narcotic controlled substances: Family members, drug prescribing etiquette)
D. CDC guidelines (not on exam) but review CH. 43
Special populations: Geriatrics
Changes that affect drug therapy?
Common concerns regarding medication use in elderly patients?
Absorption - Passive; little to no change in absorption.
Distribution - Decline in total body weight, decrease body mass, decrease serum albumin all lead to enhanced drug effect and/or toxicity.
Metabolism - Loss of hepatic reserve/decreased flow so lower doses may be needed.
Excretion - Age related changes in renal function, decreased creatinine clearance (i.e., use modified Cockcroft-gault equation)
Common concerns?
-Adverse drug reactions, adherence
Special populations: Pediatrics
Calculation of pediatric dosages?
Package insert provided by the manufacturer is the best source for pediatric dose recommendations. If not available, based on weight, age or surface area.
Pediatric dosage rule based on weight
Clark's Rule = Dose x (weight (kg)/70)
Pediatric dosage rule based on age (not as accurate as weight based)
Special populations: Pregnant and nursing
Determinacy of teratogenicity: Timing of drug exposure important; most critical period to avoid drug exposures is weeks 3 to 8.
Counseling pregnant patient about drug use: Benefit vs risks.
Drugs contraindicated in the first trimester: ACE inhibitors (e.g., enalapril, lisinopril) , ARBs (e.g., valsartan, losartan), statins
Components of the traditional prescription
Name and address of the patient, date the perception is written, age and weight of patient, drug (full name, strength or concentration), signature, any refills, DEA number, if generic substitutions are okay or not.
Clinical decision-making components
Judging, evaluating, critical thinking
Drug prescribing etiquette
Can not write prescriptions for narcotics for themselves or family members, caution with excessive narcotic prescription writing.
Pain Management:
NSAIDS and ASA
Can you use ASA in children? Use acetaminophen, NOT aspirin in children.
Patients with chronic gastritis - ASA and NSAIDs cause GI bleeding!
TYLENOL
Antipyretic/analgesic
Combined with many medicinal products including OTC and Rx (e.g., codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, etc.); potential for overdose
THERAPEUTIC USES:
-Osteoarthritis - mild pain
-Drug of choice for FEVER; direct action on hypothalamic heat-regulating center
-Drug of choice for children with viral infections or chickenpox
ACTIONS OF APAP:
Does NOT inhibit peripheral prostaglandin synthesis; weak or absence of anti-inflammatory and platelet-inhibiting effects in comparison to ASA
SIDE EFFECTS/ CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Distinguish between Reye's Syndrome and hypersensitivity reactions (urticarial rash to APAP):
Reye's syndrome associated with ASPIRIN use; vomiting and altered mental status - Use acetaminophen, NOT aspirin in children.
NP IMPLICATIONS:
1) Preventing toxicity - Patients with hepatic disease, viral hepatitis, or a history of alcoholism; use proper formulation for age of the child; geriatric patients (at risk for APAP toxicity; use lower doses and increase intervals)
2) Max daily dose = 4 g (4000 mg)
3) Antidote = N-acetylcysteine
Review CH 43, TABLE 43-6
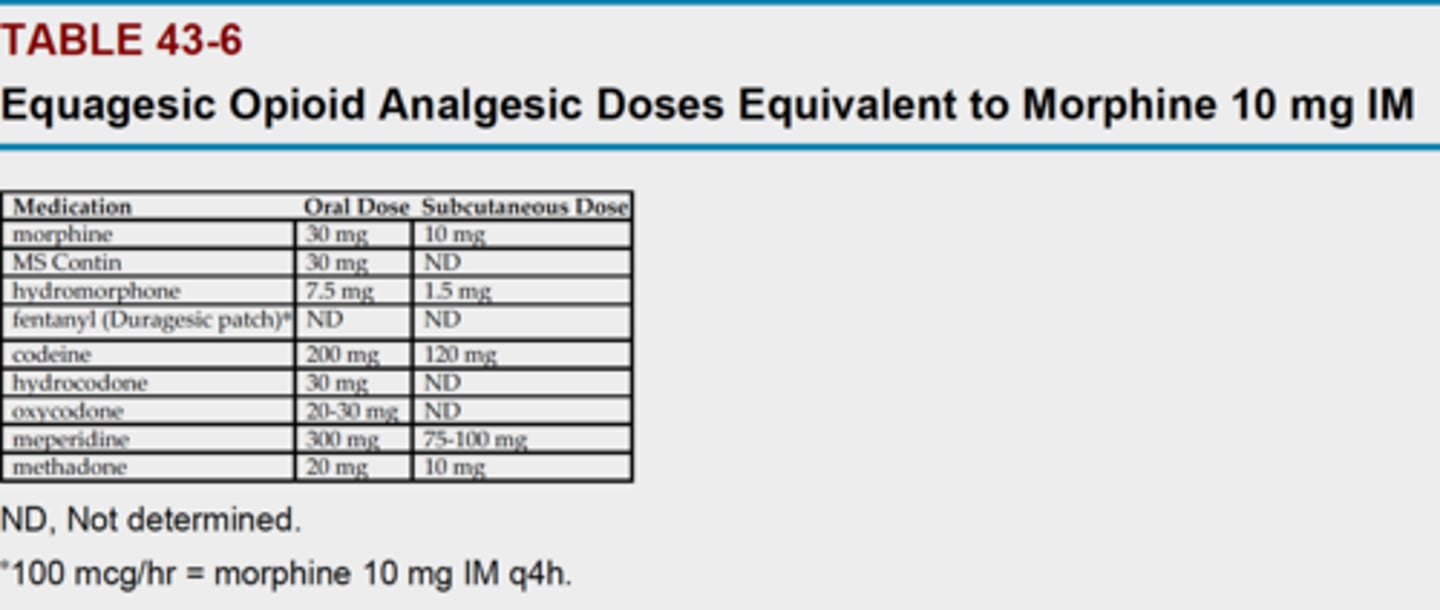
Opioids usage
MOA = Thought to inhibit painful stimuli in the substantia gelatinosa of the spinal cord, brainstem, reticular activating system, thalamus, and limbic system
SIDE EFFECTS: Constipation, confusion, dizziness, N/V, pruritis, respiratory depression, sedation
Respiratory depression = RR less than 12 breaths/min; irregular and shallow respirations
Fatal overdose = ER form is chewed, crushed, or diluted
Hydrocodone available in combination with antihistamines, decongestants, and expectorants
Codeine for persistent cough
Tramadol - DEA Schedule IV drug
Understanding the difference between addiction vs tolerance vs dependence
Addiction = Psychologic dependence; overwhelming obsession with obtaining and using a drug for non-medically approved purpose.
Tolerance = Decreasing drug effect over time; more drug needed to produce the same effect.
Dependence = Physiologic development of abstinence syndrome or withdrawal syndrome when a drug is discontinued or an antagonist is given.
Gout
MOA:
Increase excretion of uric acid (uricosuric)
Decrease synthesis of uric acid (allopurinol, febuxostat)
Decrease or stop inflammatory response (NSAIDs, colchicine)
Acute gout attack preferred initial tx:
NSAIDs used first (e.g., naproxen); colchicine is used for prophylaxis
Migraine
MOA: Beta blockers - Inhibit NE release by blocking prejunctional β-receptors, reduction in enzyme activity, delayed reduction of locus ceruleus neuron firing
CCBs - Block intracerebral vasconstriction
Tricyclic antidepressants - Increasing availability of synaptic NE or serotonin downregulation of 5-HT receptors and β-receptor density
SSRIs - Prevent vasconstrictive effects of decreased serotonin levels during headache
Coffee and NSAIDS: Abortive migraine medications. Can cause transformed migraine (long lasting headache from overuse of pain and migraine medication).
Pts with CVD or HTN: First line agent drug for migraines Triptan has contraindication in significant cardiovascular disease - can lead to MI or infarction or other adverse cardiac events; must obtain EKG
Different migraine headaches: Migraine with aura, migraine without aura, complicated migraine (divided into ophthalmoplegic, hemiplegic, basilar type). Transformed migraine.
Drugs used for prophylaxis of migraine headaches: Beta blockers (e.g., propranolol), CCBs (verapamil), antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline), SSRIs, anticonvulsants, NSAIDs.
Pts with nausea and vomiting: Triptan in nasal spray or injection (in unable to take oral products). Other commonly used antiemetics include prochlorperazine (Compazine), trimethobenzamide (Tigan), and metoclopramide (Reglan) (use caution as Reglan has potentially serious side effects).
Table 53-3 Making Treatment Decisions in Type 2 Diabetes
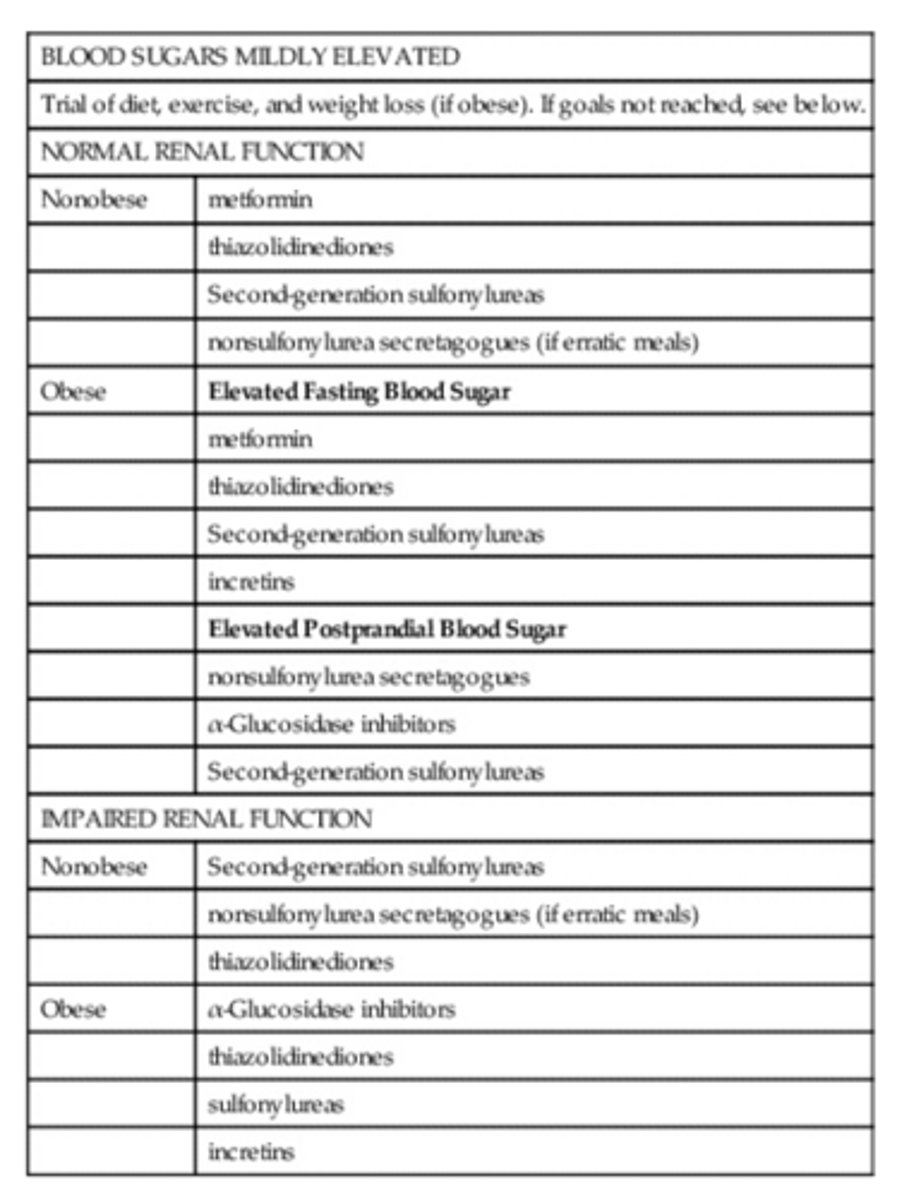
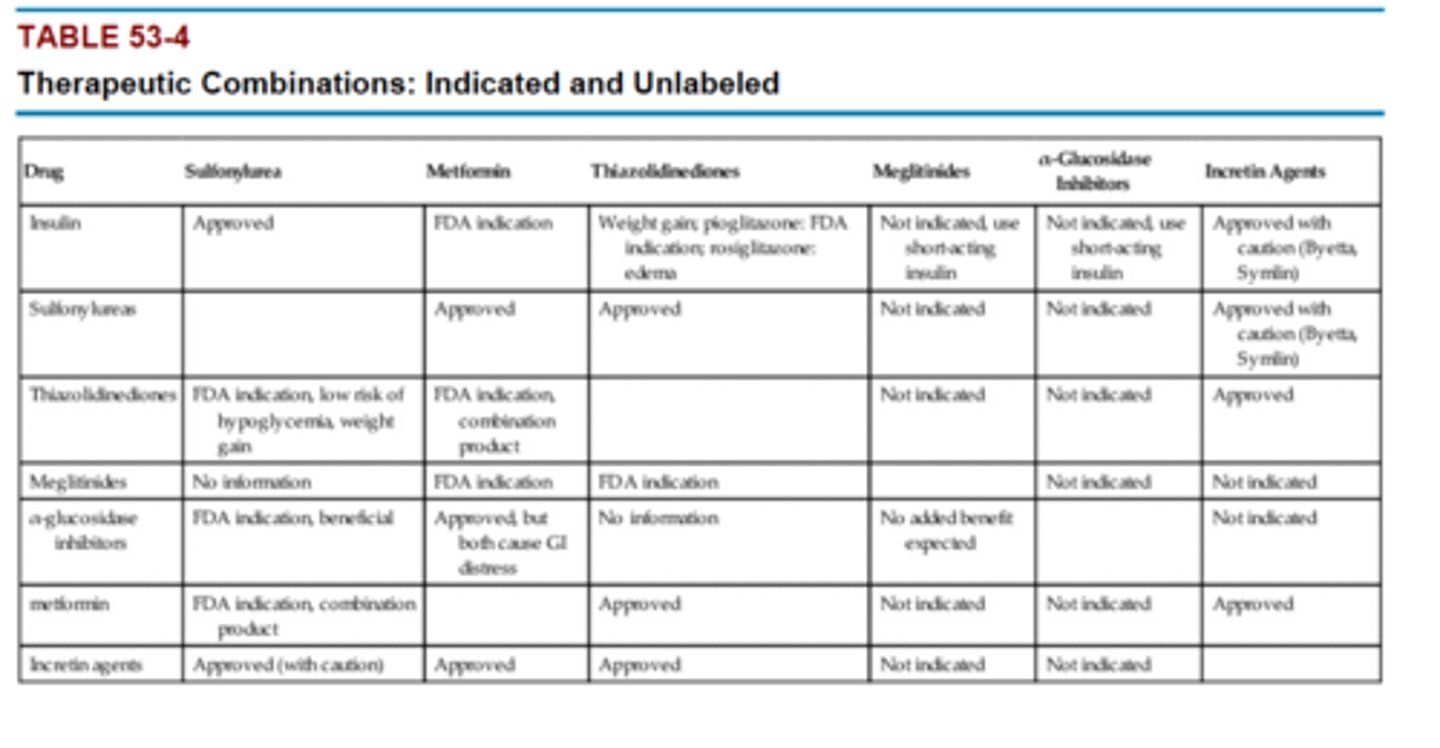
Table 53-4 Therapeutic Combinations: Indicated and Unlabeled
Osteoporosis
Class/MOA/Dosage/Adverse Effects:
1) alendronate, risedronate - BIPHOSPHATE: Inhibit activity of osteoclasts, result in indirect increase in bone mineral density.
alendronate - 10 mg PO daily or 70 mg once weekly (treatment) or 5 mg PO daily or 35 mg once weekly (prevention)
risedronate - 5 mg PO daily or 35 mg PO once weekly (tx and prevention); 35 mg once weekly on day 1 then 500 mg calcium once daily with food on days 2-7 of each week
S/E: Subtrochanteric fx and GI upset (abdominal pain, nausea, heartburn, irritation of esophagus), osteonecrosis (rarely)
Patient counseling:
2) raloxifene - Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) - Reduces reabsorption of bone and decreases overall bone turnover
60 mg PO once daily (osteoporosis)
S/E: Hot flashes, leg cramps, increased risk of VTE events
3) denosumab - Biologic and immunologic agents (monoclonal antibody)- Binds to receptor activator of RANKL, essential to formation, function, and survival of osteoclasts
60 mg SUBCUT every 6 months (all patients should also receive 10,000 mg calcium and at least 400 IU of vitamin D daily)
S/E: Infection, osteonecrosis of jaw, may produce secondary malignancy
Patient counseling:
- Calcium and vitamin and general good nutrition in diet
-Weight bearing exercise and modification of risk factors (smoking, alcohol)
-Fall precautions in elderly
-Take alendronate and risedronate at least 30 min before first food, drink or medication taken with full glass of water. Avoid laying down for 30-60 min after taking.
AACE 2010 treatment guidelines:
First line agents - alendronate, risedronate, zoledronic acid, denosumab, teriparatide
second line - ibandronate or denosumab
second or third line - raloxifene
Tx for high fx risk pt when biphosphate has failed - teriparatide
Combined oral contraceptive pills (COCPs)
Risks of OC use: Thromboembolism. stroke, MI, HTN, hepatic neoplasia, gallbladder disease.
Common side effects, particularly during initial tx: Breakthrough bleeding, headache, nausea, breast tenderness most common in first 3 months of use.
Backup method of contraception, when do you recommend it?:
Use a backup method for at least 48 hours when a progestin only OC is taken more than 2 to 3 hours late.
Table 54-5
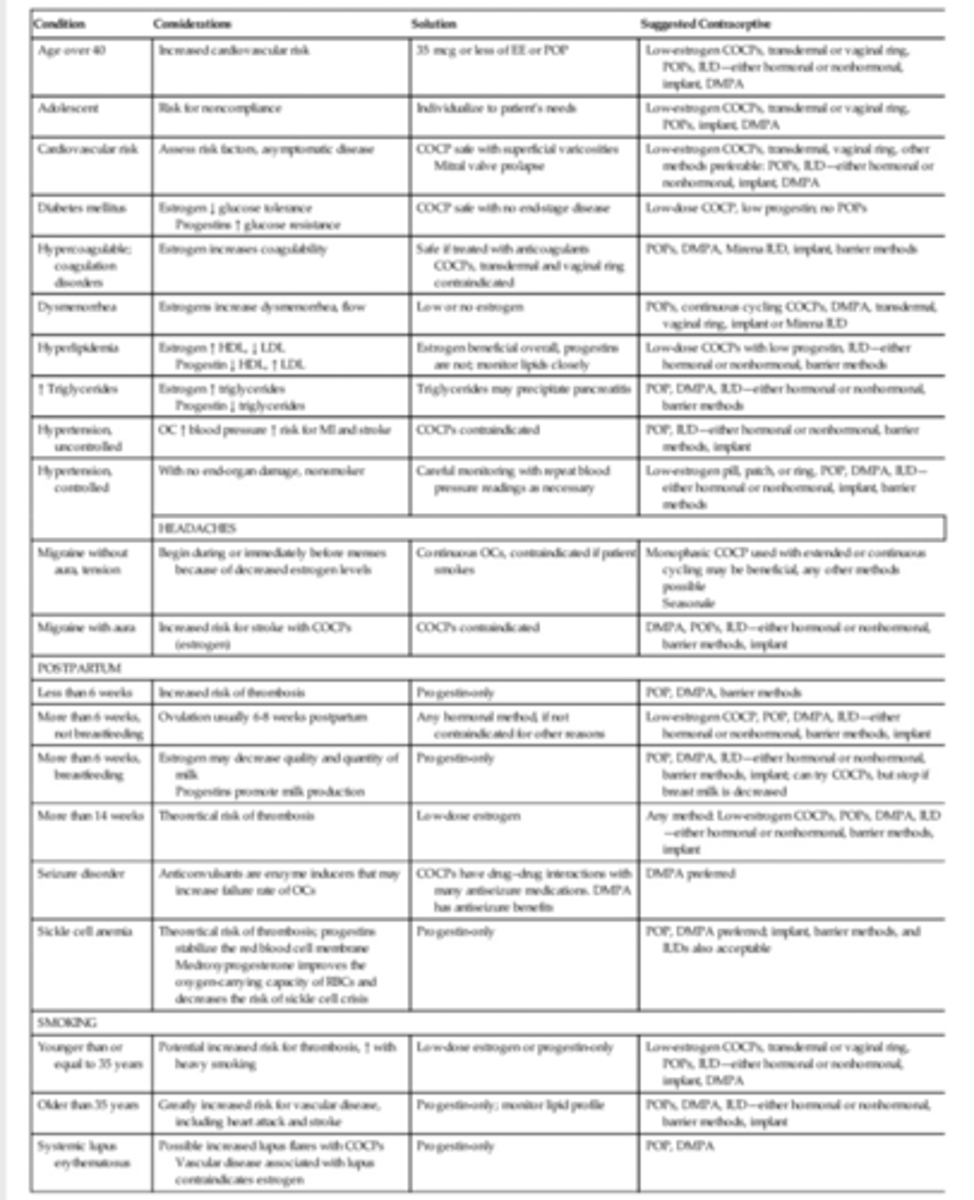
Contraceptives: Transdermal system
-Bypasses the liver, eliminating first pass effect
-Convenient, weekly application
- 99% effective and less side effects than OCs
-Applied once a week for 3 weeks, followed by a 1 week patch free interval
-Risks: Skin irritation, redness or rash; double the risk of blood clots compared to OCs
Box 54-1

HRT or HT
HRT for women: Hormone replacement therapy - estrogens, progesterones (postmenopausal symptoms and prevent osteoporosis)
When to initiate tx?:
At the time of menopause vs 5 years or more before menopause
Risk of breast cancer/CHD:
Timing hypothesis - initiating HT at time of menopause - less likely to develop CHD and have some beneficial effect against developing CHD
Gap hypothesis - initiating HT 5 years or more after menopause - no or little increase in risk for breast CA
Drug effects in menopause:
-Treat hot flashes decreasing frequency and severity.
-Decreased atrophic vaginitis.
-Estrogen + progesterone use = Increased higher incidence of CHD, stroke, PE
- Estrogen therapy may increase risk of breast CA
-HT slows or halts progression of bone loss and osteoporosis
-Possibly reduces Alzheimer's and possibly increases dementia risk
-Progesterones reduce risk of endometrial CA
-Cholecystitis predisposition
Box 55-1

Upper respiratory agents
Know your drug classes:
Decongestants, antihistamines, intranasal corticosteroids....
Pharmacological tx:
Mild, moderate severe symptoms
Which class should be avoided in pregnancy, especially during first trimester? Decongestants
Side effects;
Which drug is associated with rebound rhinitis? phenylephrine
Diabetes which drugs work together?
Combination;
which drugs work together?
insulin + metformin
insulin + thiazolidinediones
thiazolidinediones + sulfonylureas
thiazolidinediones + metformin
meglitinides + metformin
meflitinides + thiazolidinediones
alpha glucoside inhibitors + sulfonylureas
metformin + sulfonylureas
GOLD 2017
-Management of symptomatic COPD pts focus on risk factors (e.g., smoking) and inhaled drugs mostly - LABAs and LAMAs for pts with occasional dyspnea/first line treatment of symptomatic COPD pts regardless of exacerbation risk
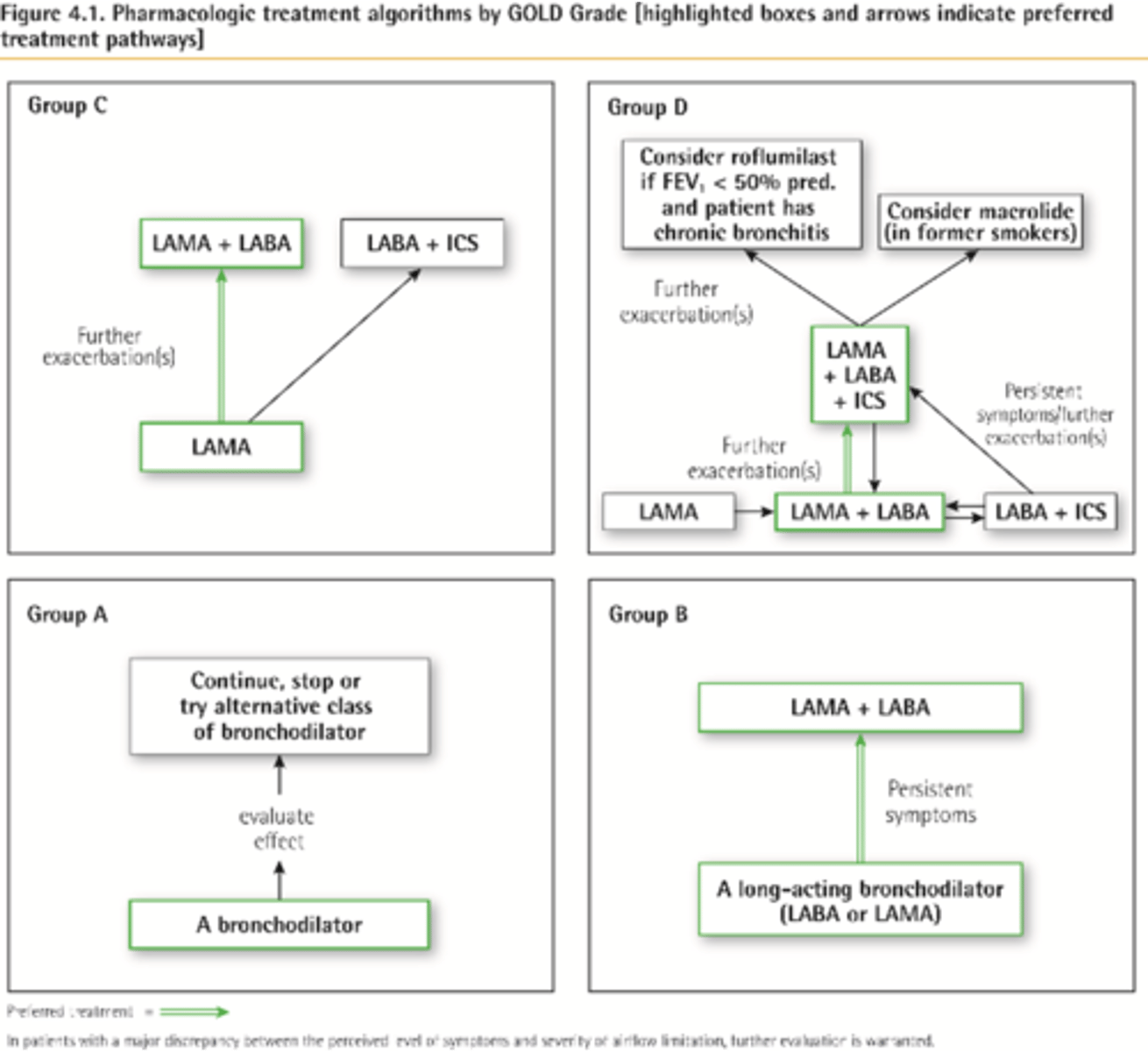
Prostate tx (MOA)
FIRST LINE TX =
Alpha1A selective blockers for patients without HTN = TAMSULOSIN
Long acting alpha1 antagonists for pts with HTN = DOXAZOSIN, TERAZOSIN
5-alpha reductase inhibitor SHRINKS size of prostate (6 months required to achieve effect) = FINASTERIDE
Combination therapy with both a1 antagonist + 5-a reductase inhibitor
*Finasteride is teratogenic = pregnant women should NOT touch pill and no semen contact with man taking this drug either
phenylephrine HCl (Sudafed)
Class: Decongestants
MOA: Vasoconstrictor that has a decongestant effect by stimulating alpha receptors of respiratory tract
Indications: Congestion in URI, sinusitis, allergic rhinitis; can be oral or inhaled or topical
S/E: REBOUND NASAL CONGESTION and rhinitis may occur. Common side effects include insomnia, tachycardia, palpitations, headache, dizziness, nausea, nervousness, excitability, agitation, weakness, tremor, HTN.
NP Implications:
-Avoid caffeine (increases insomnia, restlessness)
-Risk for misuse
-Contraindicated in cocaine use and MAOI in last 2 weeks
albuterol
Class: Short-acting relatively selective beta adrenergic agonist (SABA/RABA -rapid acting) bronchodilator
MOA: Sympathomimetic - smooth muscle relaxation - bronchodilator reduces airway resistance
Indication: SABAs have role in asthma therapy to provide relief of bronchospasm during exacerbation or pretreatment before exercise
S/E: Palpitations, tachycardia, increased BP, cough, dry throat, chest tightness, N/V, GI distress, headache, insomnia, dizziness, vertigo, nervousness, hyperactivity, heartburn, nasal congestion
salmeterol xinofoate
Class: Long acting beta2 agonists (LABA)
MOA: Bronchodilator- long acting
Indication: Asthma; NOT for acute bronchospasm - onset of action is 10 to 20 minutes
NP Implications:
-Take 30 to 60 min before exercise to prevent exercise induced bronchospasm
-Inhalation powder NOT to be used with spacer
-LABA should NEVER be used without an accompanying corticosteroid (increased risk of death)
First line tx of asthma and COPD
-RABAs (SABAs) and LABAs
-Increased use of RABA indicates need for additional drug therapy
-Inability to achieve adequate response with a beta2 agonist during exacerbation may indicate need for addition of a short term corticosteroid (inhaled or PO)
theophylline
Class: methylxanthines
MOA: Bronchodilation by inhibiting phosphodiesterase the enzyme that degrades cAMP, so increases cAMP level.
Indication: Add on therapy in asthma and COPD
NP Implications:
-Monitor serum levels (normal level 5-15 mcg/ml)
-Pregnant women may have to d/c breastfeeding as drug can cause serious toxicity in infants
-Avoid caffeine
-Notify if s&s toxicity (N/V, insomnia, jitteriness, headache, rash, severe GI pain, restless, convulsions, irregular heartbeat)
ipatropium bromide
Class: anticholingerics
MOA: Blocks cGMP, a mediator of bronchoconstriction
Indication: COPD, asthma
cromolyn sodium
Class: mast cell stabilizers
MOA: Inhibit type 1 immediate hypersensitivity rxns IgE; anti-inflammatory effect only
Indication: Allergic rhinitis
S/E: Dizziness, headache, cough, sore throat, rhinitis (minimal symptoms over all with this drug)
beclomethasone
Class: Aerosol corticosteroids
-NOT FOR ACUTE ASTHMA ATTACK
-Monitor for hypercorticism and HPA axis suppression, if it occurs, discontinue drug gradually
montelukast
Class: Leukotriene modifiers
MOA: Inhibition of airway CysTLs receptors
-NOT for acute asthma attack
S/E: Rare - may include headache, dizziness, N/V
sildenafil, tadalafil
Class: PDE5 inhibitors
Indication: Erectile dysfunction
MOA: Inhibit cGMP and this allows for increased blood flow to penis, to allow for erection :)
S/E: Headaches, flushing, dyspepsia
NP Implications:
-NEVER use with nitrates = DEATH
-Tadalafil has longer duration of action than sildenafil
oxybutynin chloride
Class: anticholinergic
Indication: Urinary incontinence
S/E: Drug mouth, constipation, headache, diarrhea, dizziness, anxiety, vision changes, fatigue, sinusitis, dysuria, somnolence
Antitubercular Agents
isoniazid (NIH)
-Bacteriostatic
-Nervous system and liver adverse reactions
-Monitor renal and hepatic fx
-EYE EXAMS annually
pyrazinamide (PZA)
-Bacteriostatic or cidal
-S/E: Mild, non gouty arthralgia, myalgia most common
-Monitor LFTs, baseline uric acid measurement, collect BGLs (may be difficult to control in DM pts)
rifampin (RIF)
-Suppresses RNA synthesis
-GI symptoms (N/V, epigastric discomfort), hepatitis
-May cause red-orange discoloration of body fluids
streptomycin (SM)
-Bacteriostatic abx
-S/E: Ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity
-Audiogram before starting tx and at 2-3 months
-NOT recommended for use in children
FIRST-LINE AGENTS: INH, RIF, PZA, ETHAMBUOL
Antifungal agents
ketonazole
-imidazoles
-S/E: Photophobia
-Can cause clinically significant even fatal hepatitis
fluconazole
-triazoles
-Less hepatotoxicity than other antifungals
-Reduce dose in renal impairment
itrazonazole (Sporanox)
-Azoles
-Contraindicated in CHF
terbinafine
-Not recommended for patients with acute or chronic liver disease
amophotericin B
-Monitor for nephrotoxicity
Antiviral agents
acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir
-Anti herpetic agents
-S/E: Headache, diarrhea, N/V
-Drink a lot of fluids, excreted through kidneys
-Caution in underlying neuropathy dx
oseltamivir, zanamivir
-Neuraminidase inhibitors
-zanamivir generally not recommended in COPD or asthma
-Begin within 2 days of exposure (prophylaxis) or 2 days of onset of symptoms (treatment)
-oseltamivir (PO) and zanamivir (inhaled)
hydrocortisone
-Short-acting glucocorticoid
-2 weeks or less
glucocorticoids in general:
-S/E: mood changes, euphoria, anxiety, depression, increased risk for infection
-Preferred agent for long term therapy: prednisone...less suppression of HPA axis; use short acting steroid every other day.
-Monitor weight, BP, BGL, potassium, vitamin D, bone mineral density, growth in children
-Sudden discontinuation leads to adrenal insufficiency (e.g., fatigue, weight loss, nausea, diarrhea, dyspnea, dizziness).
-NO live vaccines
levothyroxine sodium (Synthroid)
-Thyroid supplement
-DOC in hypothyroidism
-Monitor for thyrotoxicosis (e.g., insomnia, nervousness, irritability, palpitations); should be decreased in dose or temporarily d/c for 5-7 days
-Monitor TSH
-Take before breakfast
insulin lispro (Humalog), insulin aspart (Novolog), insulin glargine (Lantus), insulin detemir (Levemir)
insulin lispro (Humalog), insulin aspart (Novolog)
-RAPID ACTING
-Duration 3 to 5 hours; given 1-3x daily
insulin glargine (Lantus), insulin deter (Levemir)
-LONG ACTING
-Lantus duration median 24 hours; Levemir 7.6 to 24 hours
-Lantus given once daily, Levemir twice daily or once daily with evening meal or at bedtime
glipizide
-Second generation sulfonylurea
-Enhance insulin secretion; increased muscle glucose uptake
metformin
-Biguanide
-Decrease hepatic glucose production
-Lowers triglycerides and LDL, raises HDL
rosiglitazone, pioglititazone
-Thiazolidinediones
-Increase sensitivity in the muscle and liver by improving control of glycemic utilization, leading to decrease circulating insulin levels
-Functioning Beta cells required for these meds to work
-Increased MI risk, bladder cancer associated with use more than 1 year
acarbose
Class: alpha glucose inhibitor
MOA: Delays glucose absorption and lowers postprandial hyperglycemia
-Watch for hypoglycemia
liraglutide (Victoza), sitagliptin phosphate (Januvia)
Class:
Incretin agents
MOA: Stimulate insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells and restore insulin release
-Watch for hypoglycemia when combined with insulin or sulfonylureas
sitagliptin/metformin (Janumet)
Combination agents
aspirin
-Salicylates
-Cardioprotective
-Prevention of MI and stroke
-Irreversible inactivation of COX
ibuprofen
-NSAIDs
-Caution with prior hx of GI disease; increased risk of GI bleeding
celecoxib (Celebrex)
-NSAIDs
-Fewest adverse reactions - especially GI and renal
-Can be used everyday in chronic arthritis pain
-Do NOT use if allergic to sulfonamides
-Caution in CVD due to increased risk of CV mortality
colchicine
Gout medication
Acute attack and prevention.
-First dose: Monitor weekly for signs of toxicity (N/V, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort)
-LFTs q 3-6 months if long term tx
-Monitor B12 levels (may cause reversible malabsorption of b12)
probenecid
-Uricosuric agent
-Increase excretion of uric acid
-Less GI effects
oxycodone, fentanyl
-Opioid agonists
-S/E: Constipation.
-Watch for respiratory depression, sedation.
sumatriptan, ergotamine tartrate
-Abortive migraine agents
-Activation of 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors leading to constriction
-Risk of MI, infarction or other CV events; do NOT give to pts with cardiac risk
-Monitor EKG periodically and cardiac enzyme lab work
levonorgestrel (Mirena)
-Progestin-only contraceptive
-Effective for 5 years and additional indication for heavy menstrual bleeding
-Contraindicated in uterine abnormalities, acute PID, women at high risk for STDs, etc.
methyltestosterone (AndroGel)
-Androgens
-Promote weight gain, increase muscle mass, stimulate RBC production in certain forms of anemia
-Monitor for hepatotoxicity
-Common S/E are headache, hot flushes, insomnia, increased BP, increased hmg or hct
Provision of Primary Health Care by the Nurse Practitioner include the following functions (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY):
Prevention
Diagnosis
Prescription
Treatment
Prevention
Diagnosis
Prescription
Treatment
Which of the following are common components found on a prescription for a controlled substance? (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY):
Full Name of Drug
Strength or Concentration
DEA Number
Directions for use
Full Name of Drug
Strength or Concentration
DEA Number
Directions for use
When discussing new drugs with pharmaceutical representatives, the ARNP should ask about direct comparison head-to-head studies with older, standard drugs in comparable doses.
True
False
True
For each term, please provide the correct description.
Absorption, bioavailability, f value, distribution
Absorption = how the drug leaves it site of administration
Bioavailability = How much of the drug that is administered reaches its site of action
f value = The fraction of the drug that reaches systemic circulation
Distribution = The transport of a drug in body fluids from the bloodstream
Which of the following correctly describes an age-related physiologic alteration that affects the pharmacokinetics of medication in geriatric patients?
Decline in creatinine clearance with an increase in age
The NP is getting ready to start a 75 year old client on a highly protein-bound drug (e.g., phenytoin). Review of the client's record reveals a recently obtained laboratory report with albumin 2.5 g/dL, as the only out of range value. With this in mind, the NP will prescribe the needed highly protein-bound drug in:
Reduce doses for patients with low serum albumin values
Pharmacokinetics of the drug therapy in the pediatric population is dynamic and is known to change for each of the age groups that compromise the pediatric category In safely prescribing medications to the pediatric population, the NP must clearly remember the ages of each group. All of the are groups listed below are correct EXCEPT:
Infants (30 days-12 months)
Toddlers (2-5 years old)
Children (5-12 years old)
Adolescents (13-17 years old)
Toddlers
As it relates to the determinants of teratogenicity, the NP explains to the client who just received news of being pregnant, that the most critical period in which drug exposures should be avoided is the:
fetal period (week 9 through term)
embryonic period (week 3-8)
preconception period (10-30 days prior to conception)
ovulation period (14-17 days port last menstrual cycle)
embryonic period (week 3-8)
A patient who has BPH is on finasteride (Proscar) to shrink the size of the prostate is asking the NP "what is the expected time to achieve maximum benefit of taking 5-alpha reductase inhibitors for prostate size reduction." The primary care NP should advise this client that
6 months of therapy is required to achieve maximum benefit
An NP sees a patient who needs to be treated for the management of allergic rhinitis. Which of the following are preferred antihistamines that the NP can recommend? Select all that apply
Fexofenadine, loratidine, cetirizine
A NP prescribes to a patient an anti-tussive syrup medication containing guaifenesin with codeine. Which common side effects may this patient experience?
Nausea/vomiting, Dizziness, Drowsiness
According to the CDC video, when using a metered-dose inhaler (in mouth), you should do the following (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY):
Hold inhaler upright
Press down on inhaler one time, breathe in QUICKLY, and then hold breath for 5 - 10 seconds
Put inhaler in your mouth, above your tongue, and between your teeth.
Shake inhaler 10 - 15 times
Hold inhaler upright
Put inhaler in your mouth, above your tongue, and between your teeth.
Shake inhaler 10 - 15 times
Match the following medications with their corresponding class:
Xopenex
Short-Acting B2-adrenergic Agonists
Serevent
Long-Acting B2-adrenergic agonist
Dulera
Long-Acting B2-adrenergic agonist/Corticosteroid Combination
Spiriva
Long-Acting Anticholinergic
Xopenex
Short-Acting B2-adrenergic Agonists
Serevent
Long-Acting B2-adrenergic agonist
Dulera
Long-Acting B2-adrenergic agonist/Corticosteroid Combination
Spiriva
Long-Acting Anticholinergic
According to GOLD 2017 guidelines, ICS-containing regimens are NOT recommended as initial maintenance treatment for COPD of any severity.
True
False
True
Mr. Smith is a 53 year old patient that has been diagnosed with COPD using Spirometry. Further assessment results show his FEV1 is 28% of predicted, CAT score of 12, and he had 1 exacerbation in the past year leading to hospital admission. Based on your knowledge of the refined ABCD assessment tool (GOLD 2017), the NP should labelled this patient as follow:
GOLD grade 3, group D
GOLD grade 4, group D
GOLD grade 2, group B
GOLD grade 4, group B
GOLD grade 4, group D
Mrs. Gomez is a 45 year old female diagnosed with COPD using Spirometry. She has been a smoker for over 20 years. Her FEV1 is 48% of predicted, she has a CAT score of 8, and she had more than 3 exacerbations in the past year. Based on the GOLD 2017 guidelines and Mrs. Gomez COPD assessment results, the NP should initiate treatment with:
Flovent (fluticasone)
Serevent Diskus (salmeterol xinafoate)
Ventolin (albuterol)
Spiriva (tiotropium bromide)
Spiriva (tiotropium bromide)
A patient that tested positive for Covid-19 was experiencing mild flu-like symptoms that included congestion, sore throat, and cough. He was treated for his symptoms with an antihistamine, a decongestant, and a cough suppressant. After 3 days of treatment the patient complaint of a worsening of his nasal congestion. Which of the following medications most likely cause the rebound congestion?
Claritin (Loratadine)
Afrin Nasal Spray (Oxymetazoline)
Codeine with Guaifenesin
Flonase Nasal Spray (fluticasone)
Afrin Nasal Spray (Oxymetazoline)
Which of the following drugs is a LABA/ICS combination and would be most appropriate for a patient who is having compliance issues?
Symbicort Aerosol
Anoro Ellipta
Spiriva
Breo Ellipta
Breo ellipta
Based on the Gold 2017 guidelines and COPD assessment results, Mr. Scott was prescribed a LAMA medication to treat his COPD symptoms. However, a few months later, Mr. Scott's symptoms continue to be persistent and he has further exacerbations. Which of the following drugs is the next preferred treatment the NP should initiate:
SYMBICORT AEROSOL
FLOVENT DISKUS
ANORO ELLIPTA
BREO ELLIPTA
Anoro ellipta
A patient is taking pyrazinamide, rifampin, and streptomycin to treat TB. The primary care NP should routinely perform:
serum glucose and liver function tests (LFTs).
bone marrow density and ophthalmologic tests.
CBC, LFTs, hearing, and serum glucose tests.
CBC, color vision, serum glucose, and LFTs.
CBC, LFTs, hearing, and serum glucose tests.
A patient with CHF will receive oral treatment for a tinea pedis infection. The NP may use any of the following antifungal agents, except:
Terbinafine
Itraconazole
Griseofulvin
Fluconazole
itraconazole
An NP will start treating a patient for TB. Which of the following drugs are considered first-line anti-TB agents approved by the FDA? Select all that apply.
isoniazid, pyrazinamide
A patient has been diagnosed with a systemic mycoses infection and will start treatment with intravenous Amphotericin B. Which of the following is true about Amphotericin B? Select all that apply
Can be either fungicidal or fungistatic, may cause renal insufficiency
Which of the following statements are true regarding the drug Trulicity (dulaglutide)? (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY):
It is a GLP-1 agonist
It is recommended as a first-line agent
Can be used in combination with Novolog
Once-daily dosing
It is a GLP-1 agonist
Can be used in combination with Novolog
A patient with type 2 diabetes and CV disease has been treated with Metformin for several months. After re-evaluating the patient, the NP adds Jardiance (empagliflozin) to the patient's drug regime. The patient inquires about Jardiance. Which of the following statements is true regarding Jardiance? (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY):
It is the first diabetes med approved to reduce risk of CV death in patients with type 2 diabetes and CV disease.
It is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitor
It is a selective sodium-glucose transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor
It works by reducing glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, thereby increasing urinary glucose excretion
It is the first diabetes med approved to reduce risk of CV death in patients with type 2 diabetes and CV disease.
It is a selective sodium-glucose transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor
It works by reducing glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, thereby increasing urinary glucose excretion
A patient with continuous uncontrolled diabetes, HbA1c of 7.7%, will be initiated with basal insulin therapy in combination with oral agents. The NP explained to the patient that she will be prescribing a newer long-acting insulin that is use once daily at the same time every day. Which of the following insulins is the NP most likely referring to?
Basaglar (insulin glargine)
Tresiba (insulin degludec)
Humalog
Novolin R
Basaglar (insulin glargine)
Unless contraindicated, the pharmacological management of mild osteoarthritis pain is to begin with:
aspirin
flexeril
ibuprofen
acetaminophen
acetaminophen
In comparing the effect of Acetaminophen vs NSAIDS, Acetaminophen is known to have (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY):
Strong antipyretic effect
Strong analgesic effect
Weak antipyretic effec
Strong anti-inflammatory effect
Weak analgesic effect
Weak anti-inflammatory effect
Strong antipyretic effect
Strong analgesic effect
Weak anti-inflammatory effect
Several agents are effective in reducing the frequency and severity of migraine attacks. The NP is educating a client on the different choices available to provide prophylactic treatment and identifies the following drug classes as FIRST LINE treatment agents (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY):
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs; i.e. paroxetine)
Anticonvulsants (i.e. gabapentin)
Tricyclic Antidepressents (TCAs; i.e. amitriptylline)
Beta Blockers (BBs; i.e. propranolol)
Tricyclic Antidepressents (TCAs; i.e. amitriptylline)
Beta Blockers (BBs; i.e. propranolol)
The 12 recommendations provided by the CDC on the Opioid Prescribing Guidelines (2016) are grouped into the following conceptual areas, EXCEPT:
Assesing risk and addressing harms of opioid use
Determining when to initiate or continue opioids for chronic pain
Reducing the increasing number of opioid dependency in America
Opioid selection, dosage, duration, follow-up, and discontinuation
Reducing the increasing number of opioid dependency in America
Nonpharmacologic therapy and non-opioid pharmacologic therapy are preferred for chronic pain management.
True
False
True
The NP understands that when opioids are needed to manage acute pain, the following principles should give the prescription of opioids (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY):
Prescribe at least 2 additional days than expected just in case the patient does not get a prompt follow up appointment
Re-evaluate patients with severe acute pain that continues longer than the expected duration to confirm initial diagnosis
Prescribe the lowest effective dose.
Prescribe ER/LA opioids for best treatment of acute pain
Re-evaluate patients with severe acute pain that continues longer than the expected duration to confirm initial diagnosis
Prescribe the lowest effective dose.
Clinicians should continue opioid therapy for at least 2 additional weeks when there is no clinically meaningful improvement in pain and function that outweighs risks to patient safety during the first 30 days of treatment.
True
False
False
For its potential for abuse, the drug Tramadol (Ultram) was changed to a Schedule IV drug by the DEA in recent years.
True
False
True
A patient experiencing an acute overdose with a narcotic such a morphine may display the following signs and symptoms: (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY)
Hypothermia
Respiratory rate less than 60 breaths/min
Profound respiratory depression
Stupor or coma
Hypothermia
Profound respiratory depression
Stupor or coma
Clonazepam is the only benzodiazepine indicated for muscle relaxation because of its direct muscle relaxant effects.
True
False
False (its diazepam lol)