The Cardiac Cycle/Physiology
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
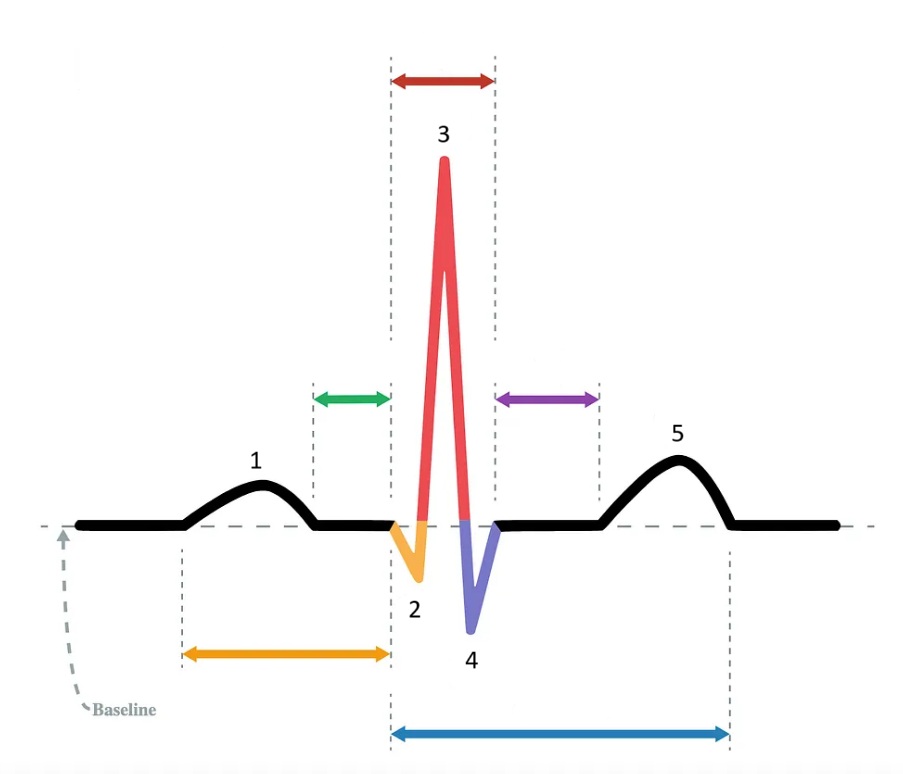
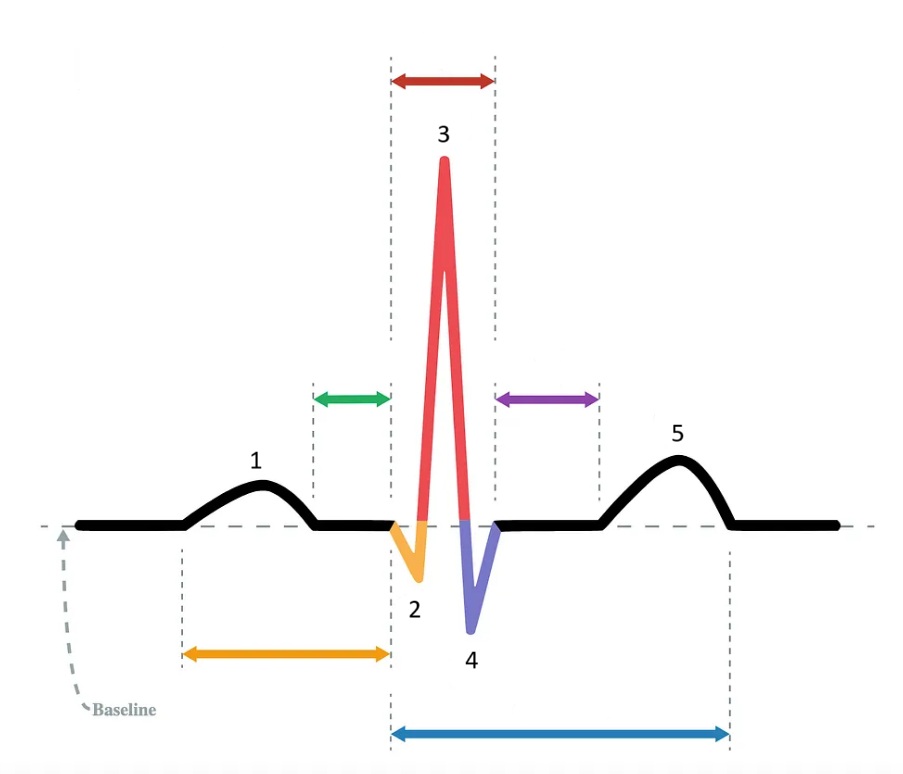
the P wave
What does “1” represent on the diagram?
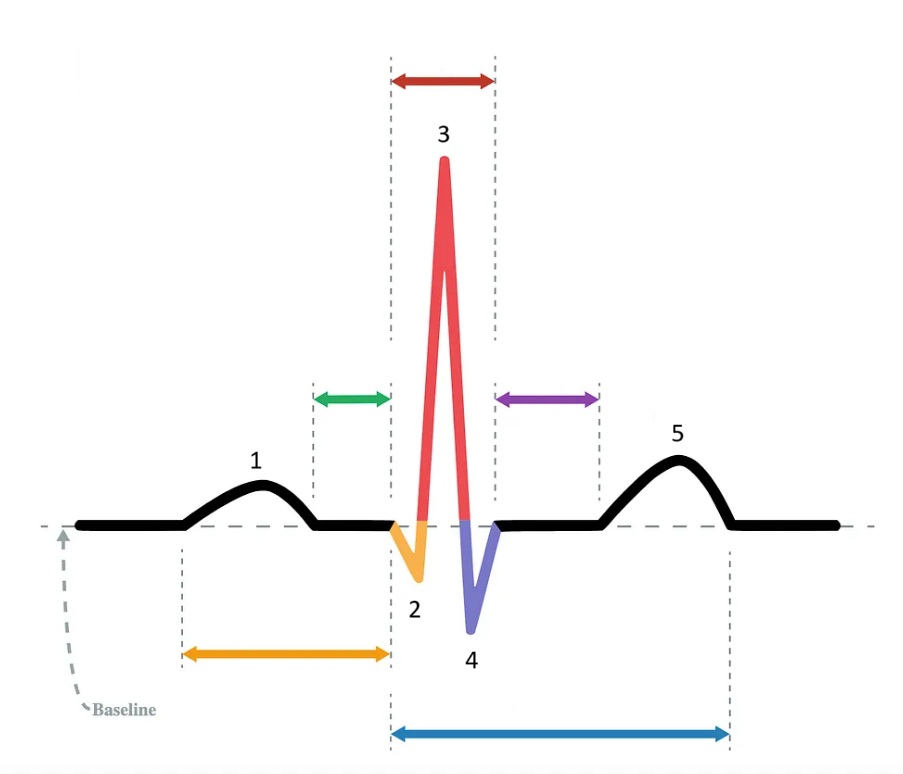
the Q wave
What does “2” represent on the diagram?
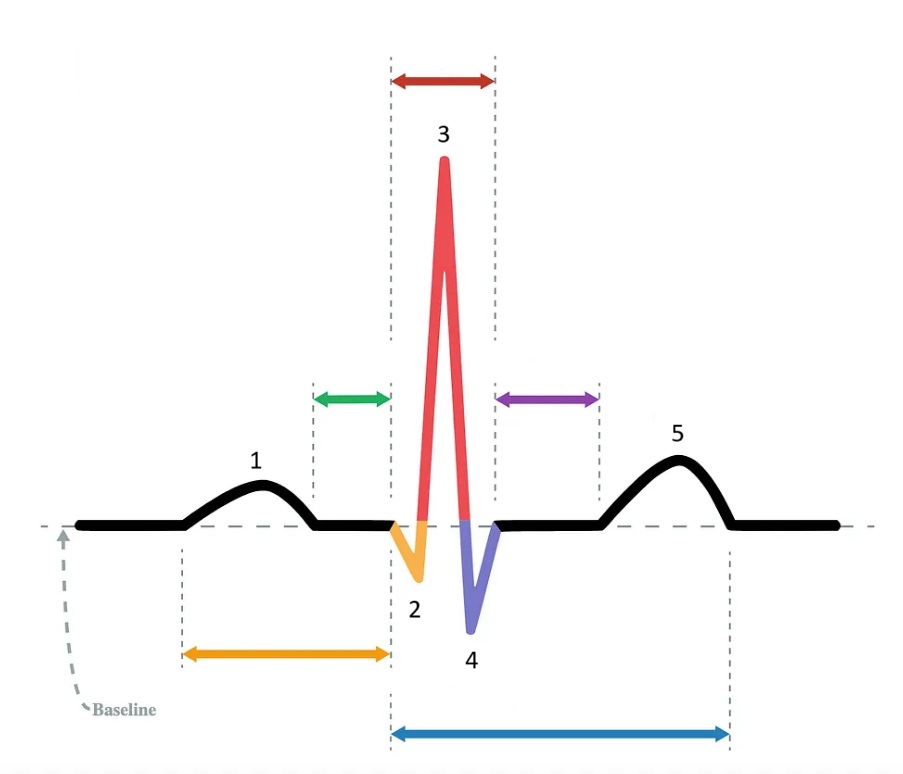
the R wave
What does “3” represent on the diagram?
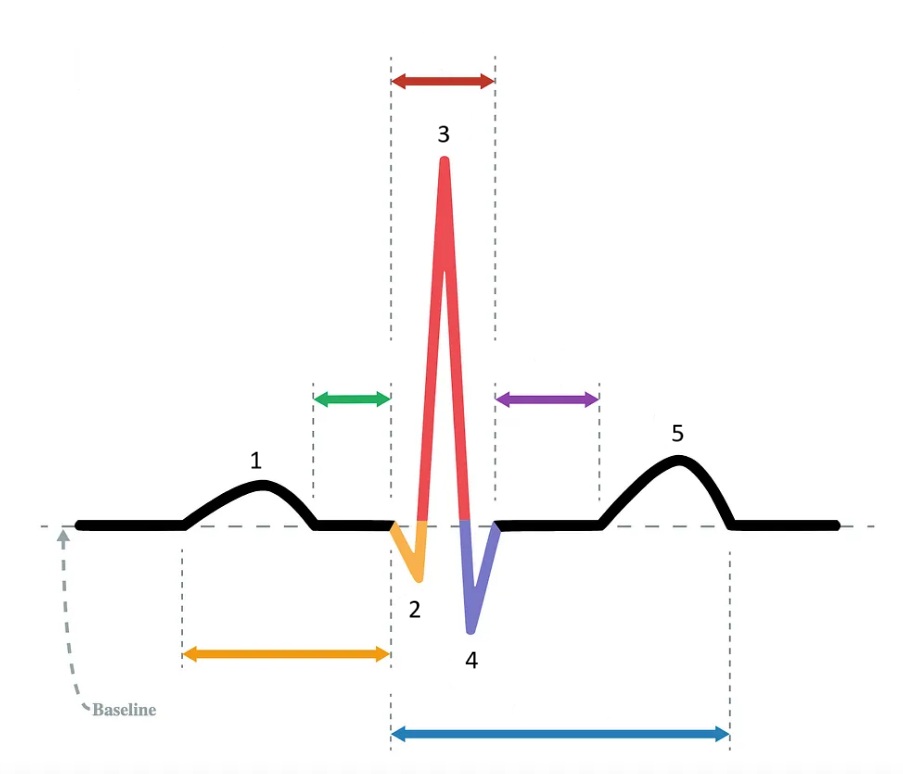
the S wave
What does “4” represent on the diagram?
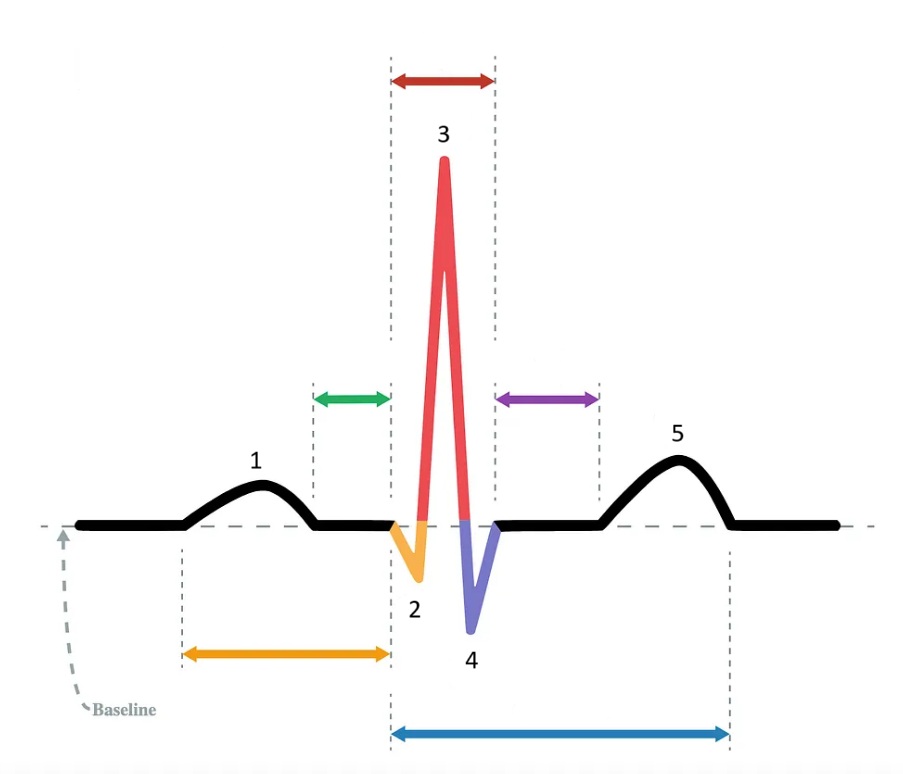
the T wave
What does “5” represent on the diagram?
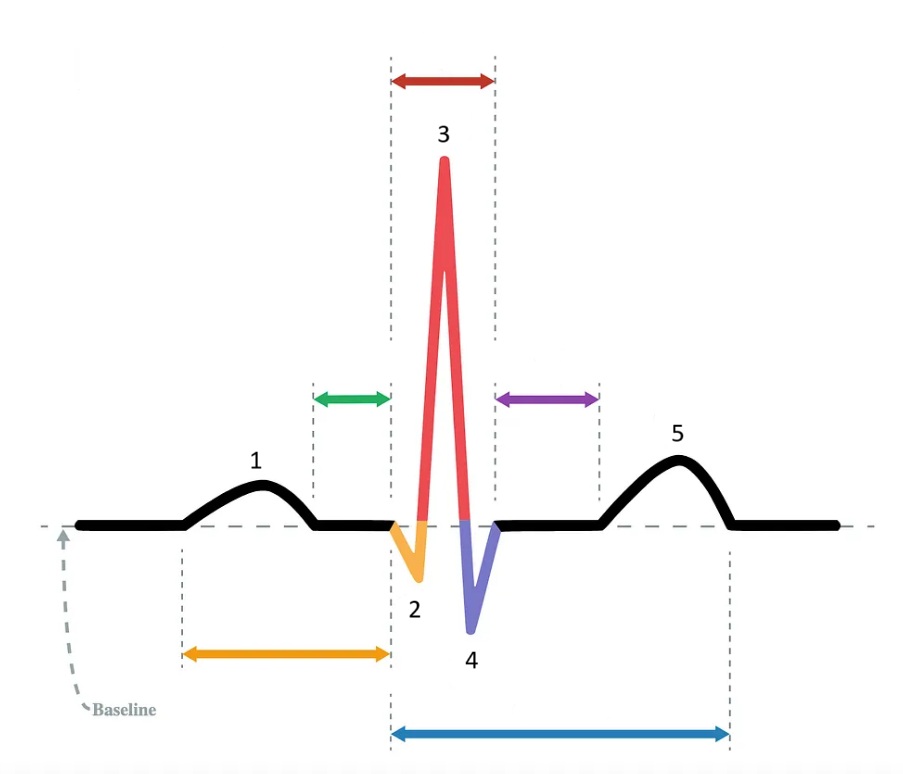
PR interval
Which segment does the orange arrow represent?
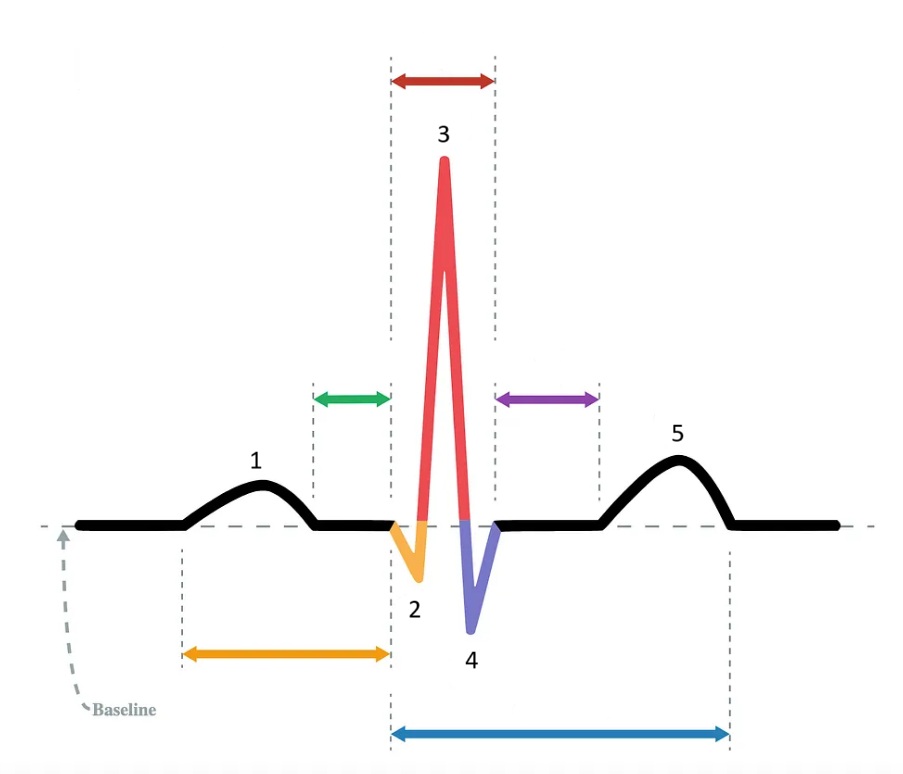
PR segment
Which segment does the green arrow represent?
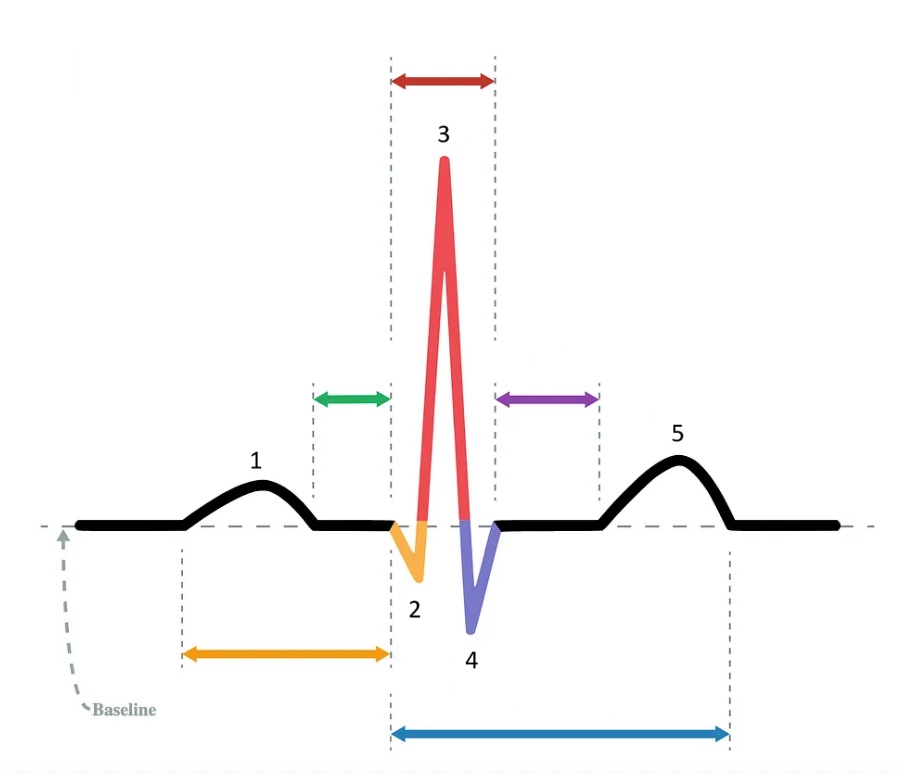
QRS complex
Which segment does the red arrow represent?
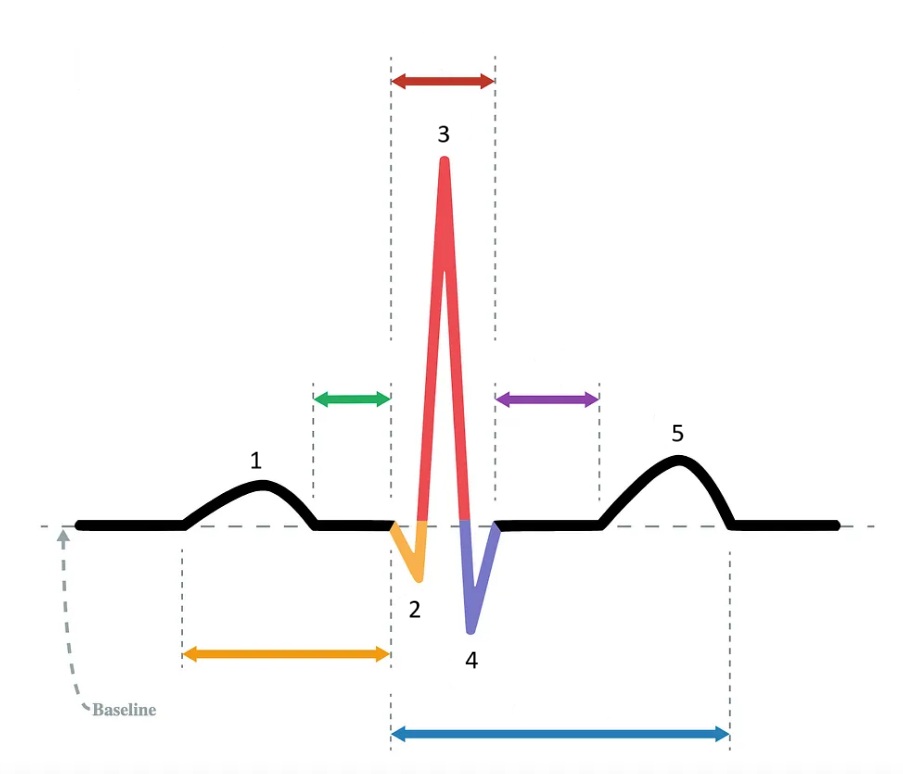
ST segment
Which segment does the purple arrow represent?
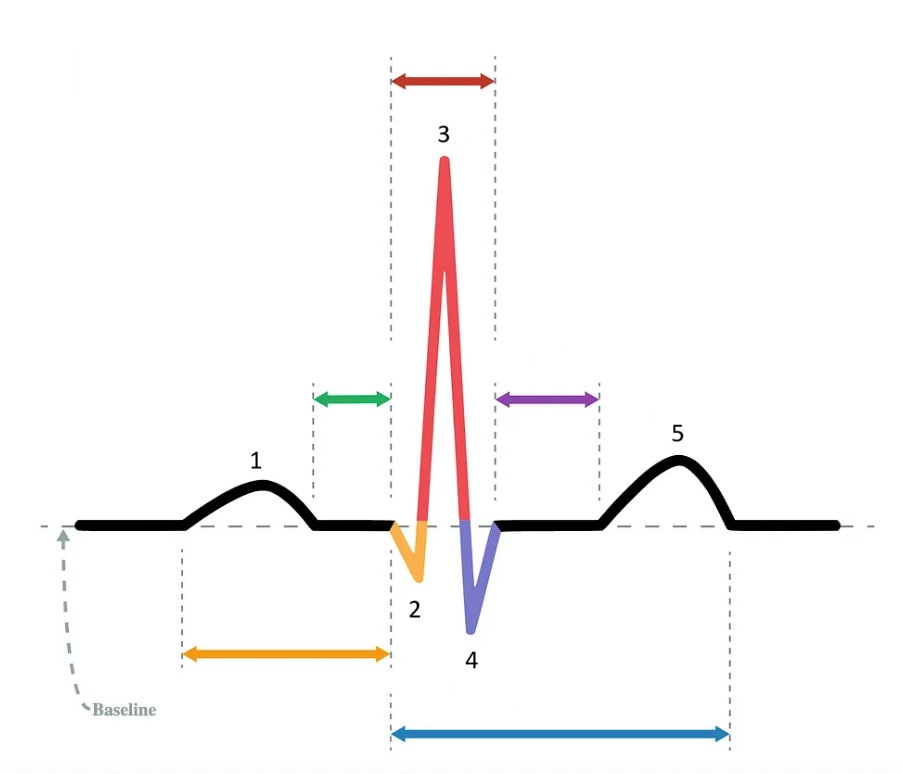
QT interval
Which segment does the blue arrow represent?
pulmonary circulatory system / systemic circulatory system
The right heart is associated with the ______ and the left heart is associated with the _______.
>25
Pulmonary artery pressure _______ mmHg at rest signifies pulmonary hypertension.
Capillaries
_______ are responsible for the exchange of nutrients and oxygen with the tissues.
75 / 98
In the adult, normal oxygen saturation in the right heart is _______% and normal oxygen saturation in the left heart is _______%.
arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins
The blood travels from the aorta to the ______.
inferior, rotates anterior, with a leftward direction
The apex is positioned _______.
superior, rotates posterior, with a rightward direction
The base of the heart is positioned _______.
posterior atrioventricular groove
The coronary sinus is positioned along the _______.
left anterior descending artery
The great cardiac vein travels along the _______, collects blood from the anterior myocardium, and drains into the coronary sinus.
infundibulum
The _______ is another name for the right ventricular outflow tract.
eustachian valve
The _______ is a normal embryologic remnant at the junction of the inferior vena cava and the right atrium.
left subclavian artery and ligamentum arteriosum
The aortic isthmus is located between the _______.
left subclavian artery
The aortic arch branches include the brachiocephalic artery, left common carotid artery, and _______.
end-diastolic volume
The largest volume in the heart during the cardiac cycle is known as the _______.
across the mitral valve during systole
Where/when is the largest normal pressure gradient within the heart?
(EDV - ESV) x HR
Cardiac output = _______
preload / afterload
Fluid overload increases _______ and pressure overload increases _______.
SA node / SVC and RA
The _______ is the primary pacemaker of the heart; it is located at the border of the ______.
endocardium to epicardium and apex to base
What is the sequence of depolarization?
epicardium to endocardium
What is the sequence of repolarization?
P wave
At what point in the EKG does atrial depolarization take place?
QRS complex
At what point in the EKG does ventricular depolarization take place?
T wave
At what point in the EKG does ventricular repolarization take place?
1 / P wave
Identify the part of the diagram where atrial depolarization takes place.
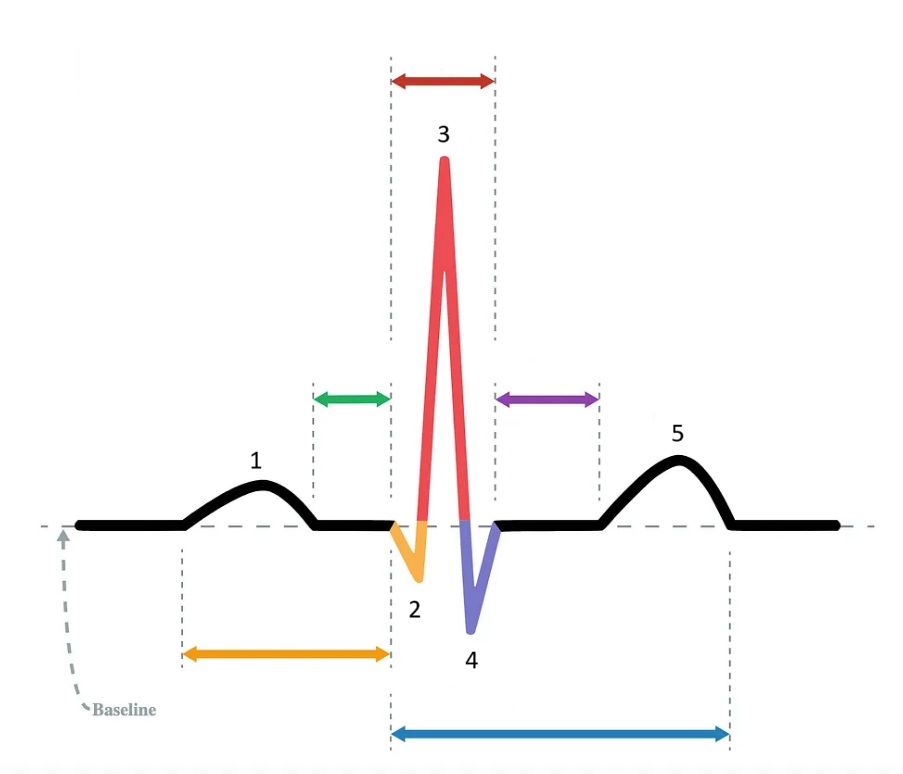
red arrow / QRS complex
Identify the part of the diagram where ventricular depolarization takes place.
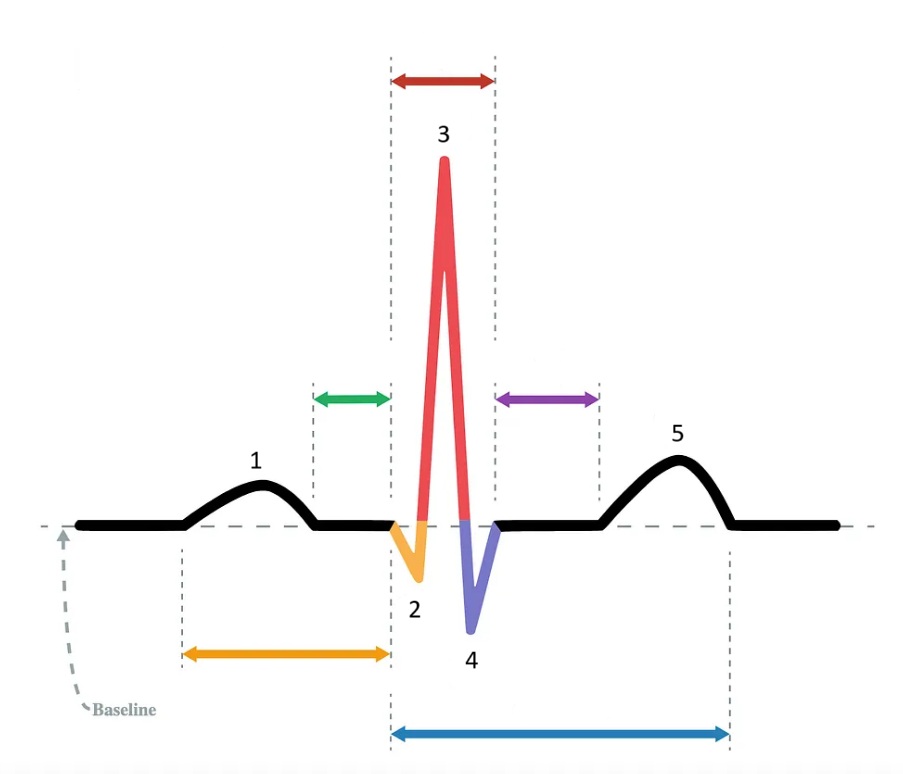
5 / T wave
Identify the part of the diagram where ventricular repolarization takes place.
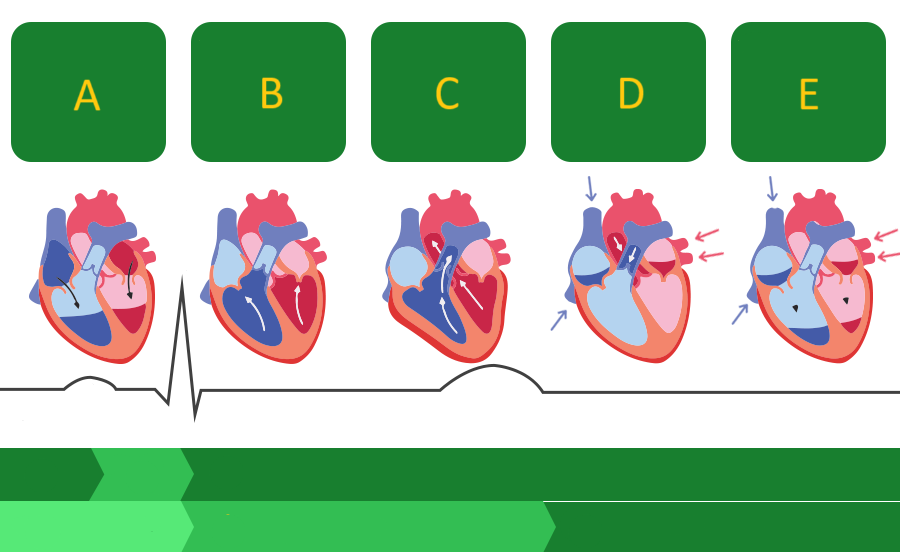
systole
During _______, the PV and AOV are open.
systole
During _______, the TV and MV are closed.
diastole
During _______, the TV and MV are open.
diastole
During _______, the PV and AOV are closed.
Isovolumic Contraction Time (IVCT)
Which part of the cardiac cycle is being described:
All four valves are closed. Ventricular volume is constant. Ventricular pressure and wall thickness increase.
Isovolumic Relaxation Time (IVRT)
Which part of the cardiac cycle is being described:
All four valves are closed. Ventricular volume is constant. Ventricular pressure and wall thickness decrease.
Systole
Which part of the cardiac cycle is being described:
The SL valves open and blood is forcefully ejected out of the ventricles through the open PV and AOV into the great vessels.
Diastole
Which part of the cardiac cycle is being described:
The AV valves open, the blood leaves the atria, passed through the open MV and TV, and fills the relaxed and compliant ventricles.
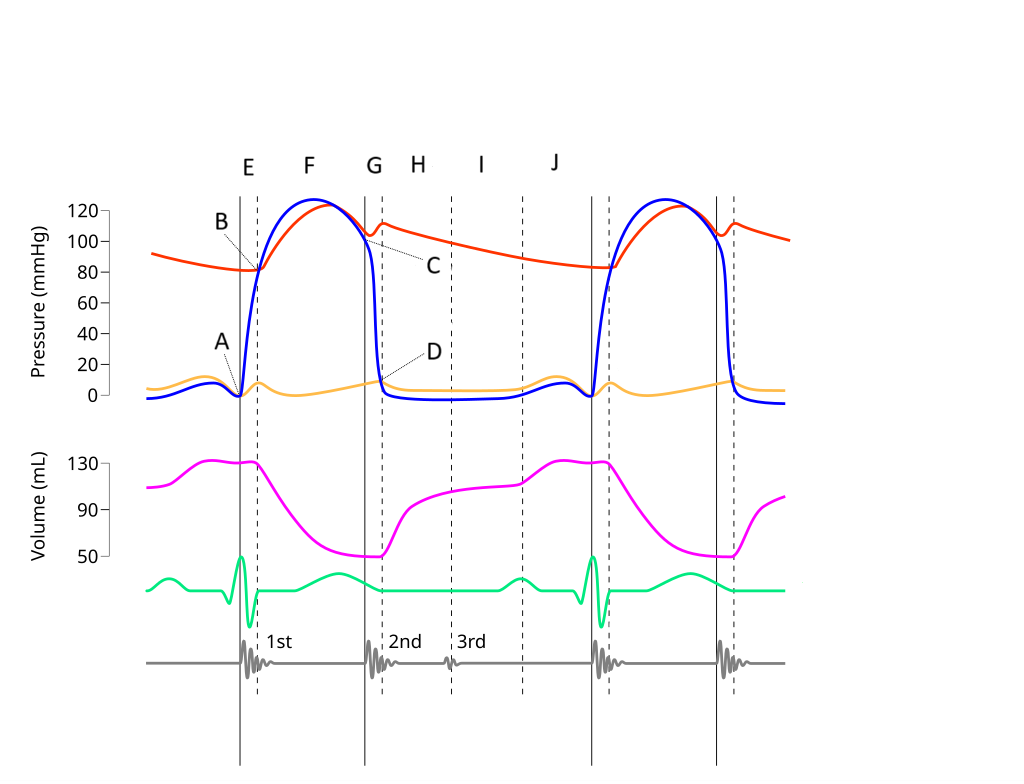
E
Where on this Wiggers diagram does isovolumic contraction take place?
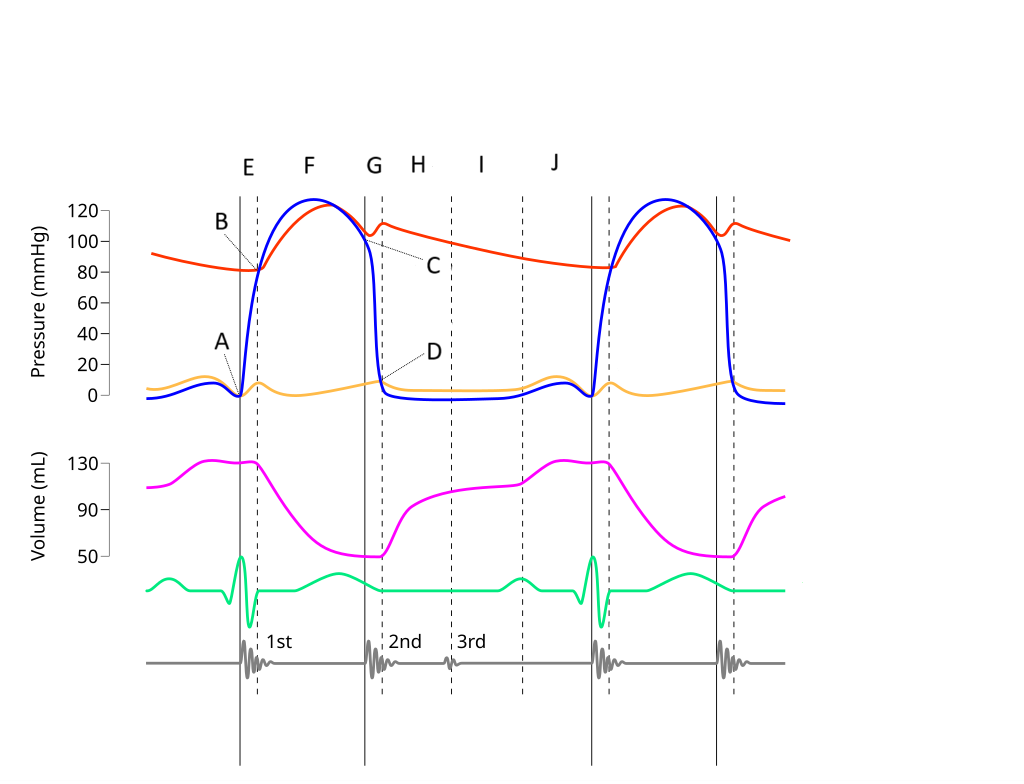
G
Where on this Wiggers diagram does isovolumic relaxation take place?
I
Where on this Wiggers diagram does diastasis take place?
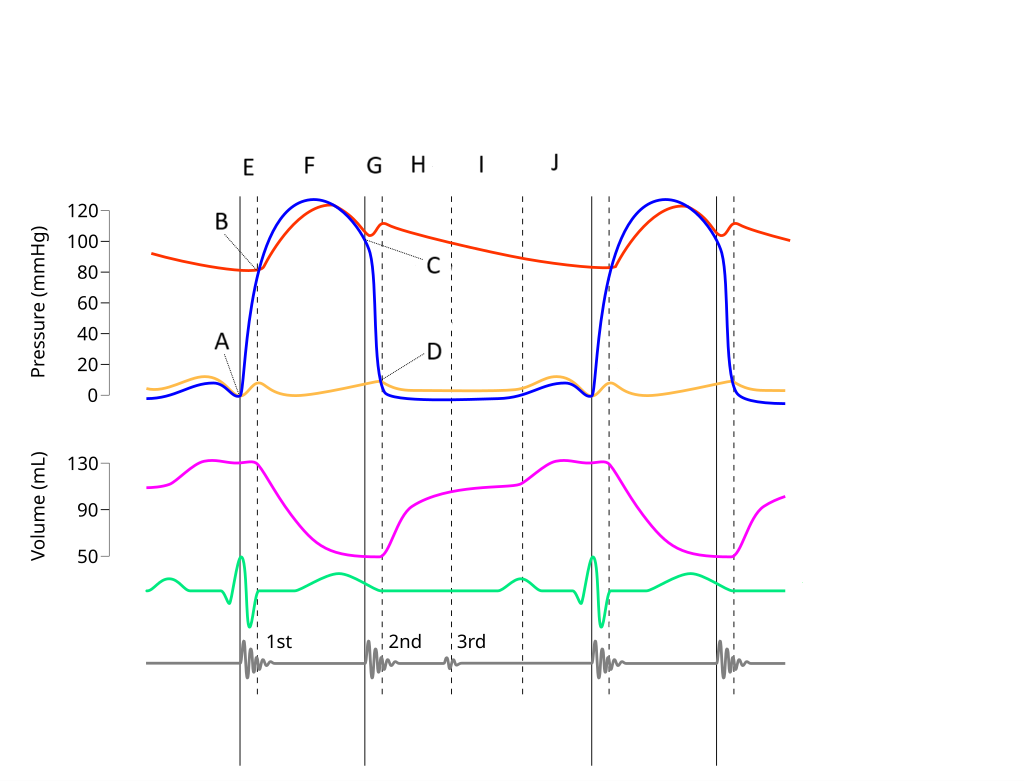
H
Where on this Wiggers diagram does rapid inflow take place?
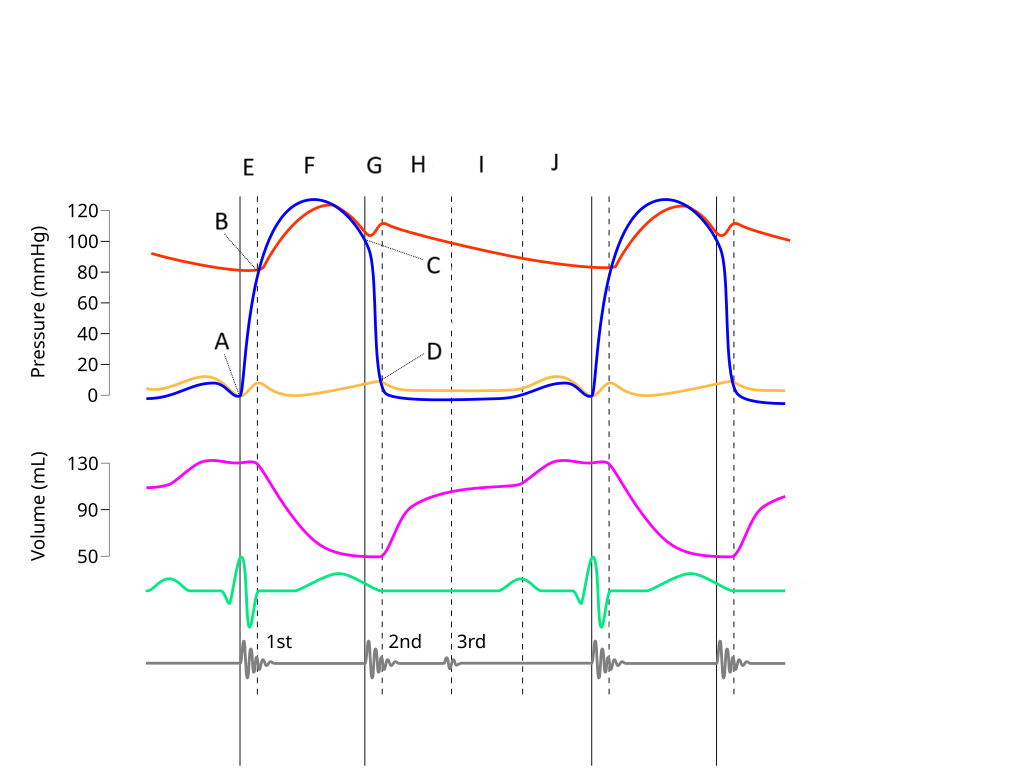
F
Where on this Wiggers diagram does ejection take place?
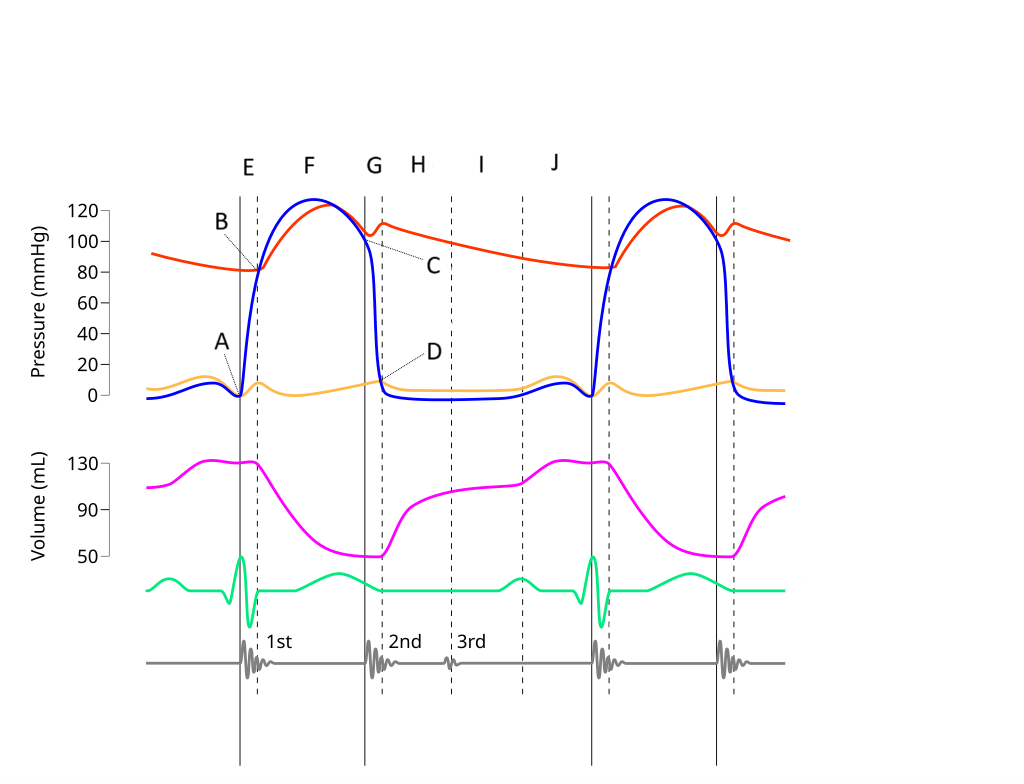
J
Where on this Wiggers diagram does atrial systole take place?
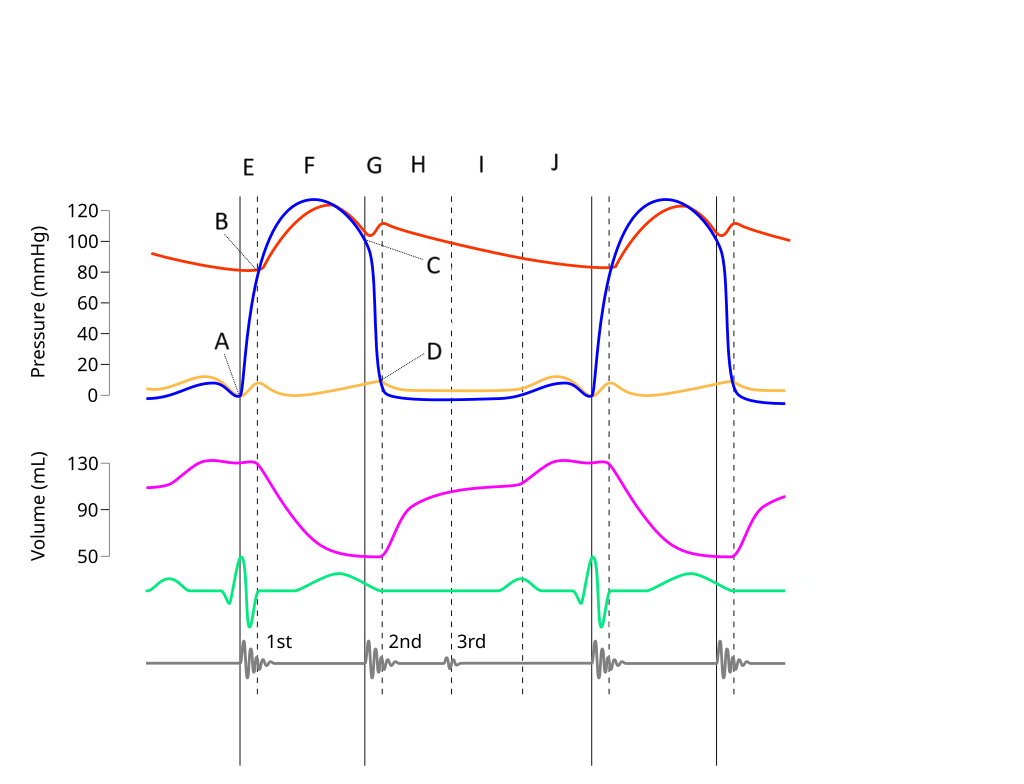
B
What part of this diagram represents the aortic valve opening?
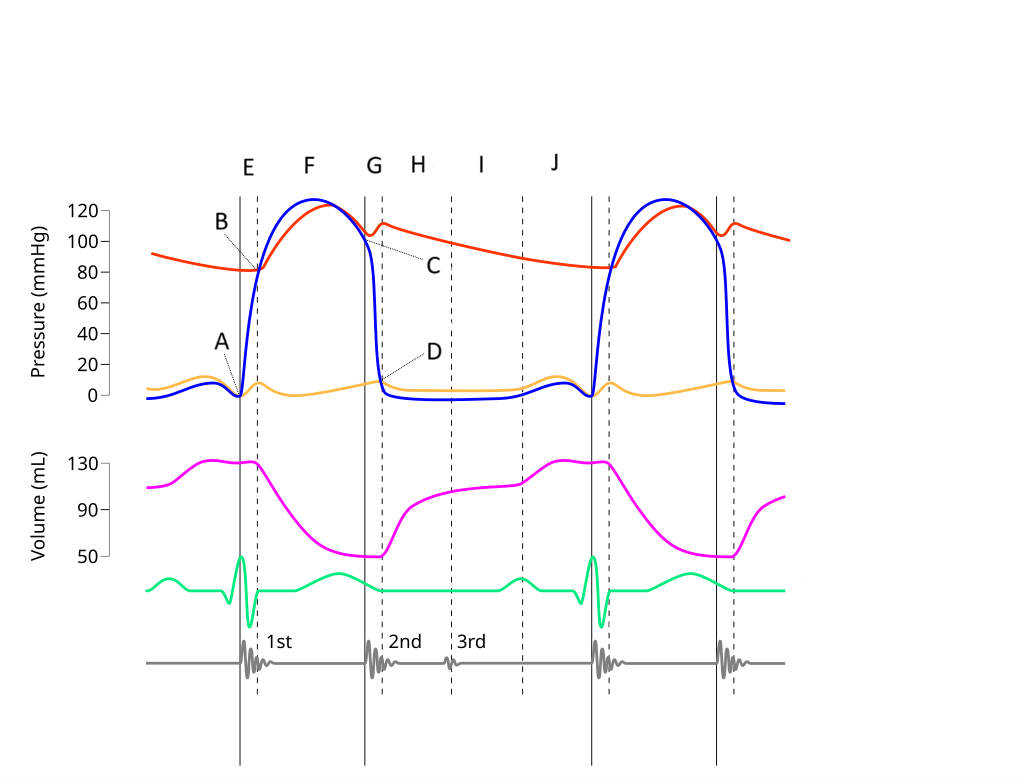
D
What part of this diagram represents the mitral valve opening?
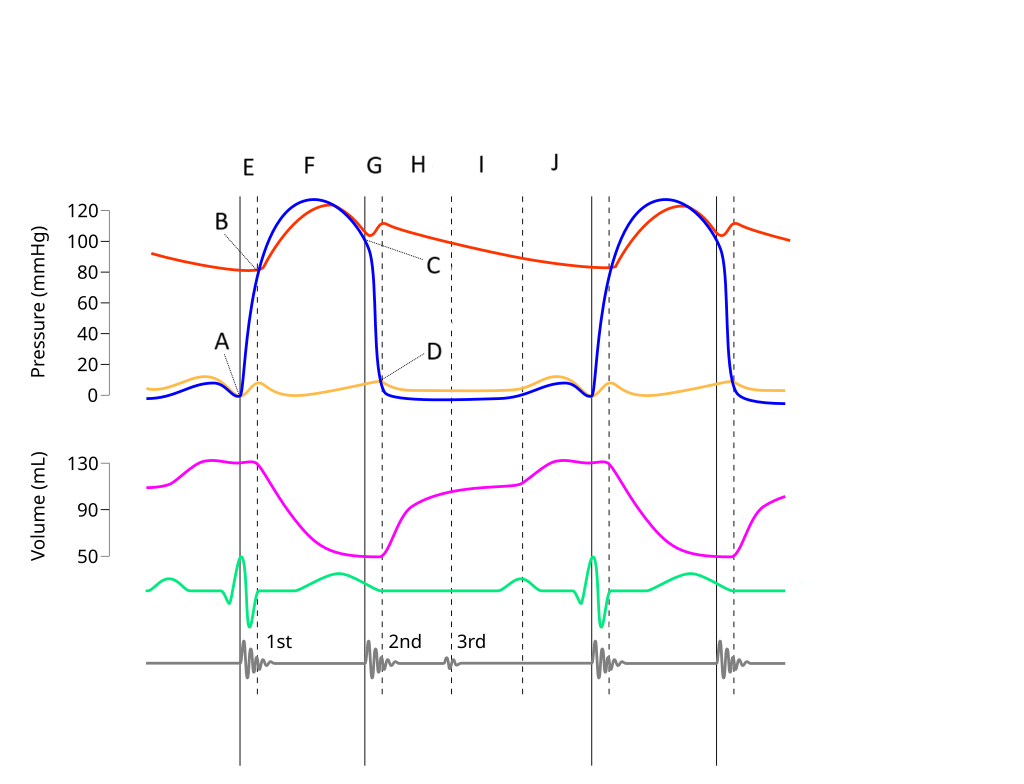
C
What part of this diagram represents the aortic valve closing?
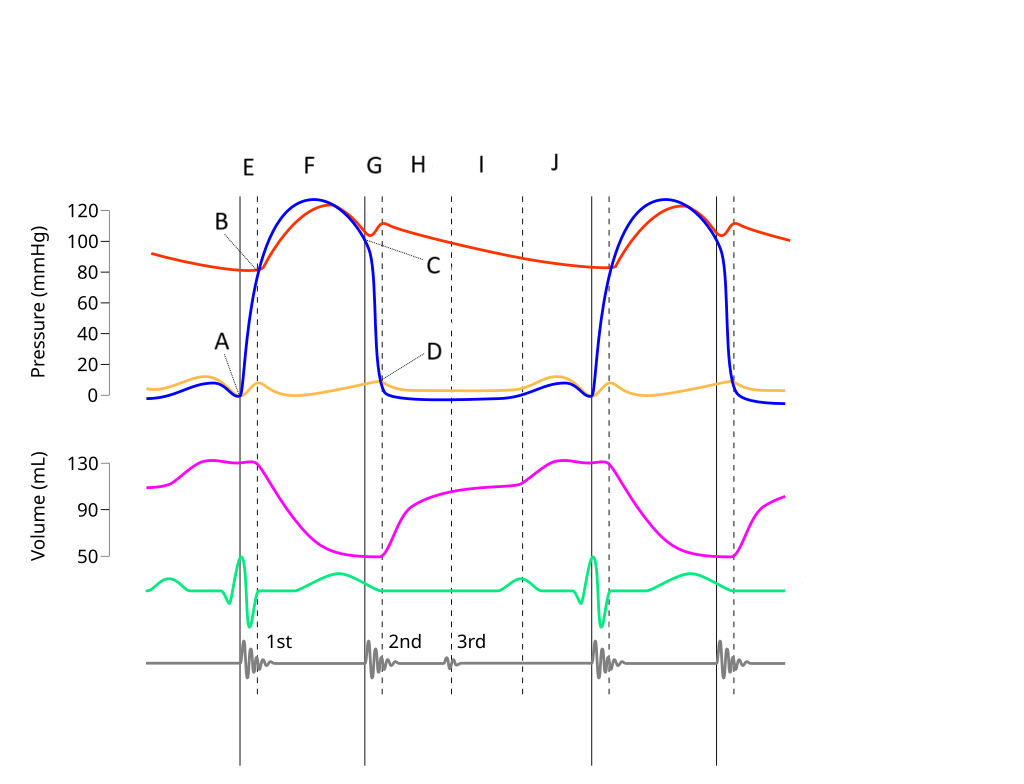
A
What part of this diagram represents the mitral valve closing?
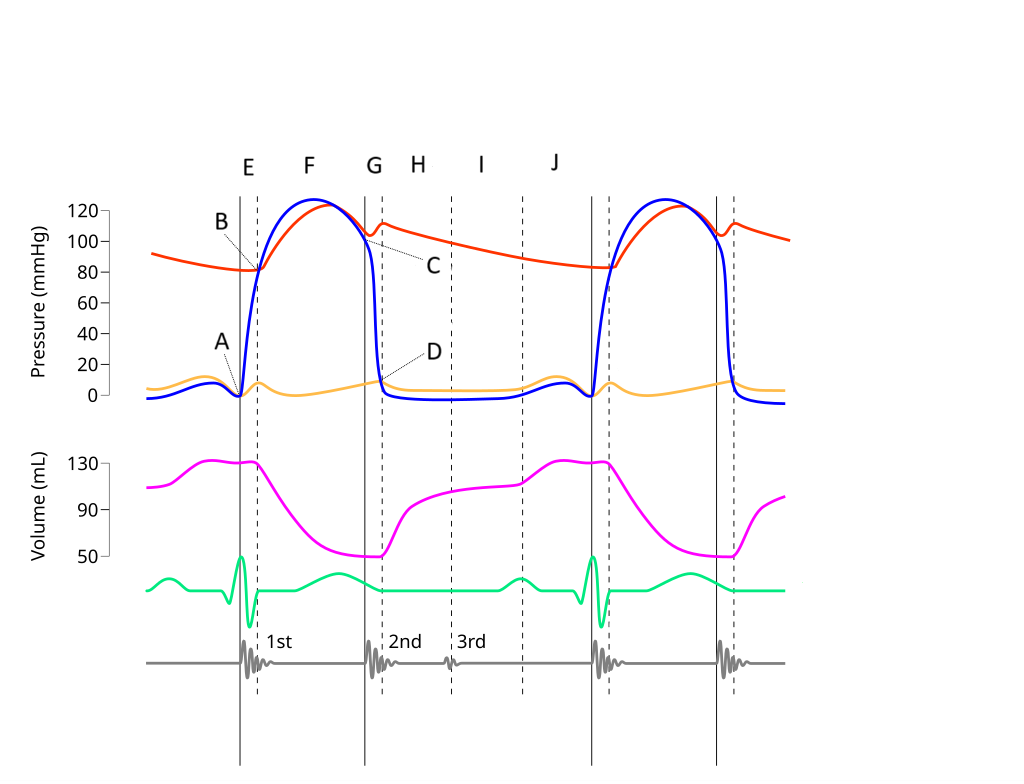
aortic pressure
What does the red wave on the diagram represent?
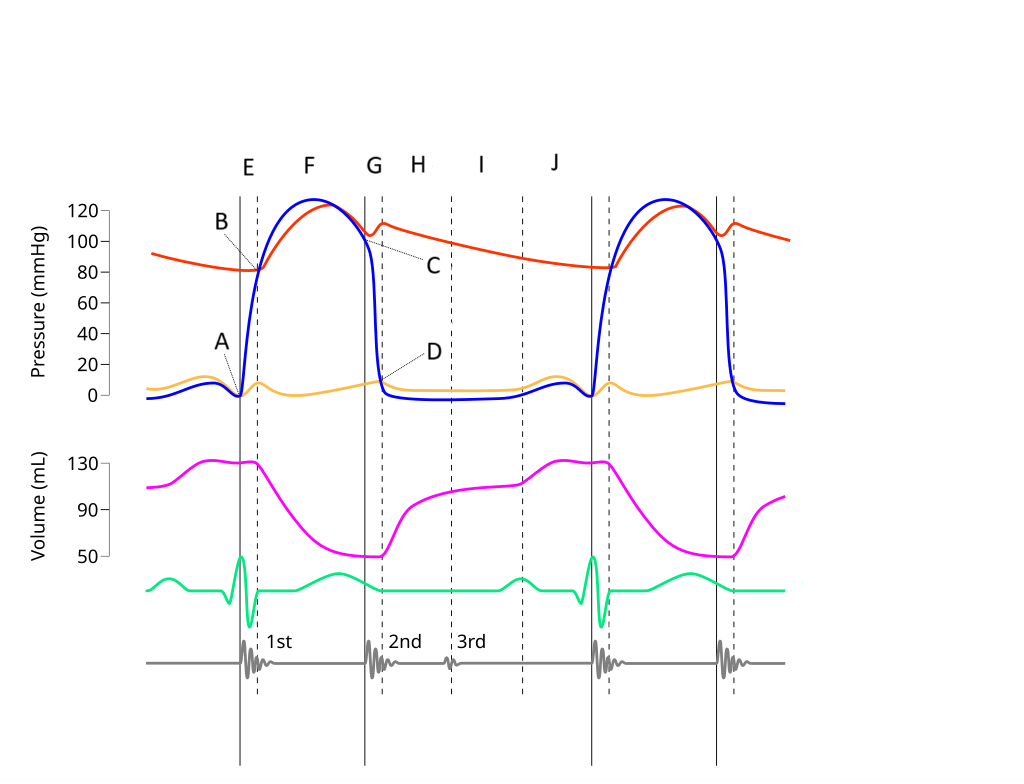
atrial pressure
What does the yellow wave on the diagram represent?
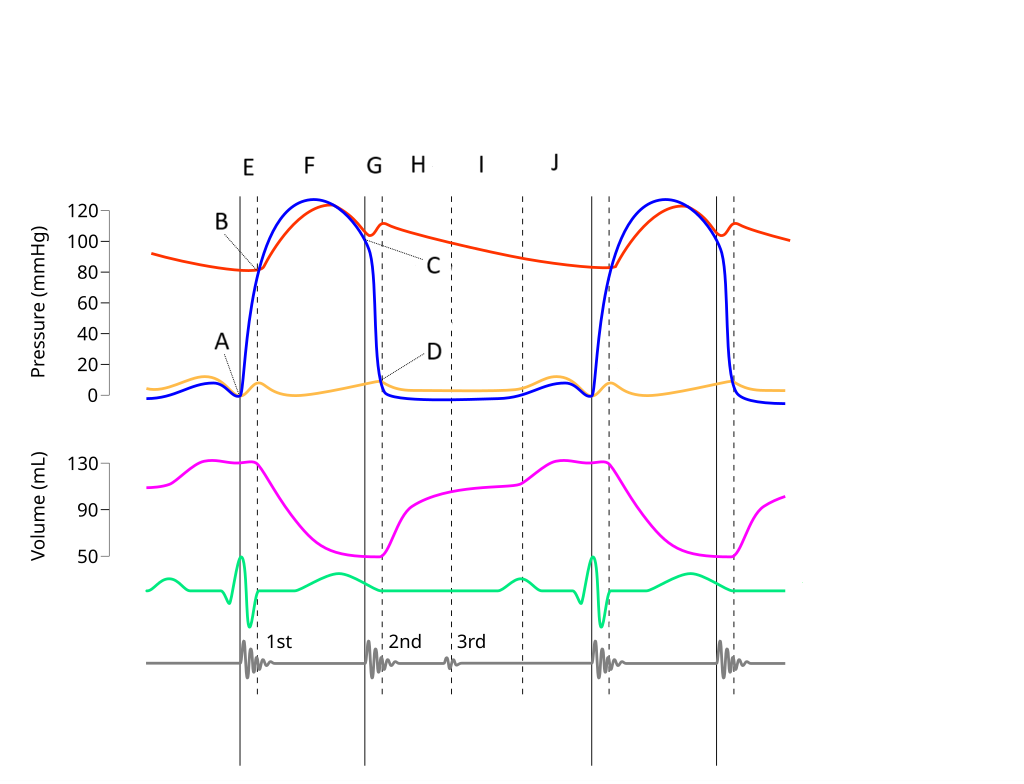
ventricular pressure
What does the blue wave on the diagram represent?
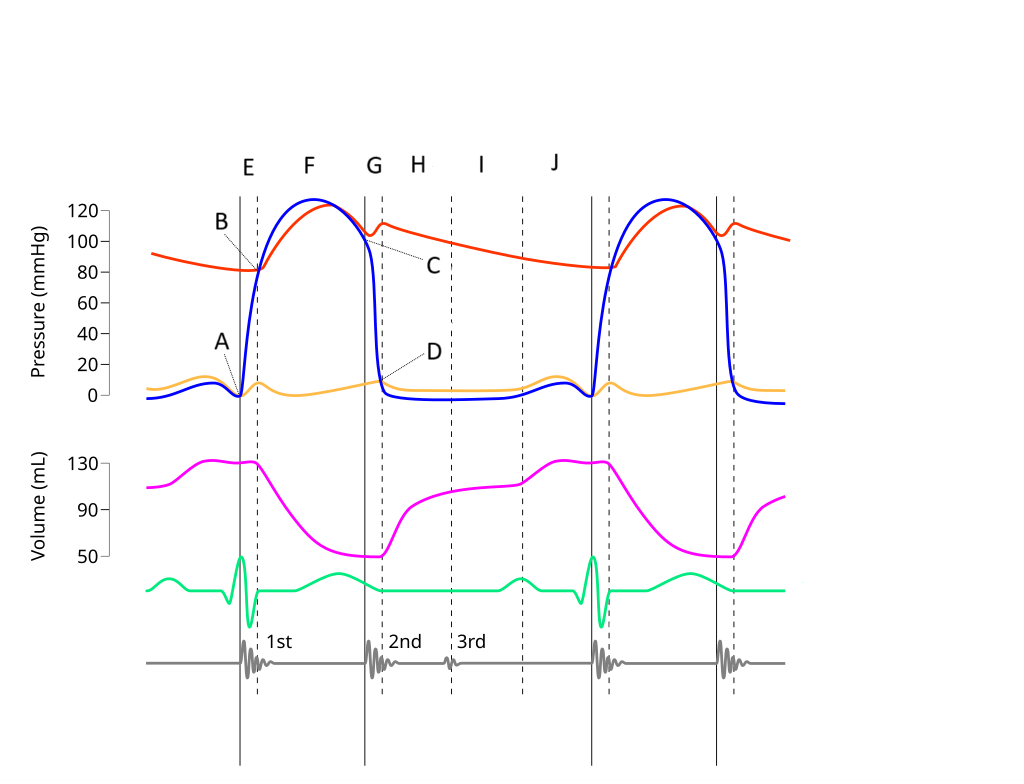
ventricular volume
What does the purple wave on the diagram represent?
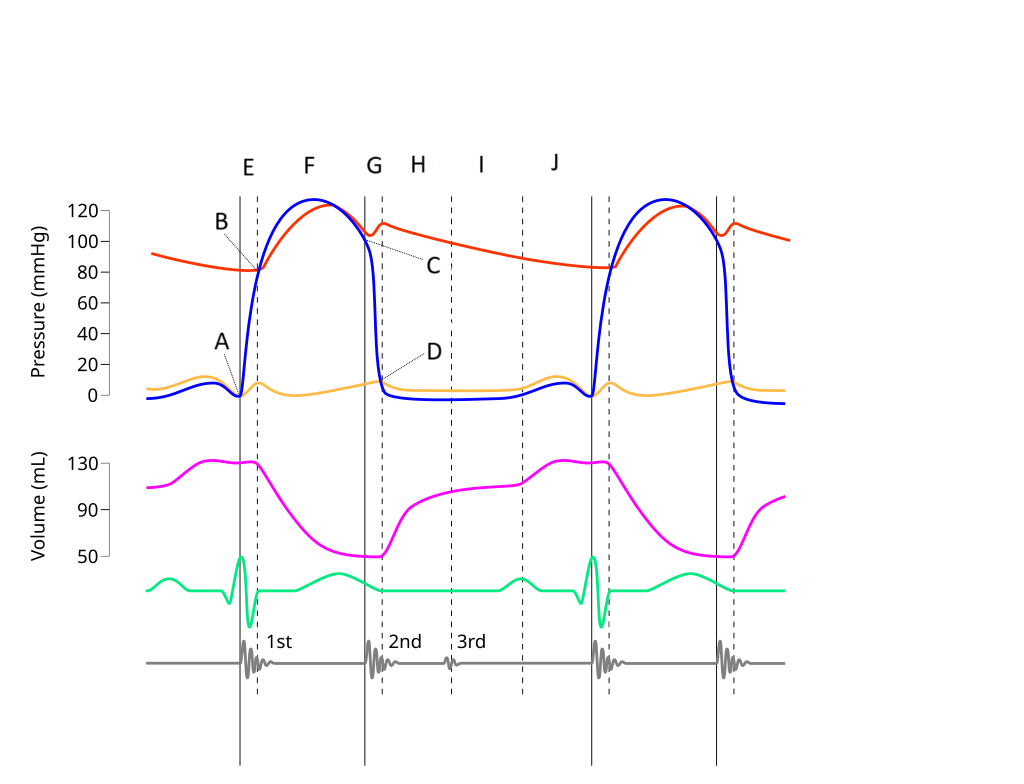
phonocardiogram (heart sounds)
What does the grey wave on the diagram represent?
A
Where on this diagram is atrial depolarization taking place?
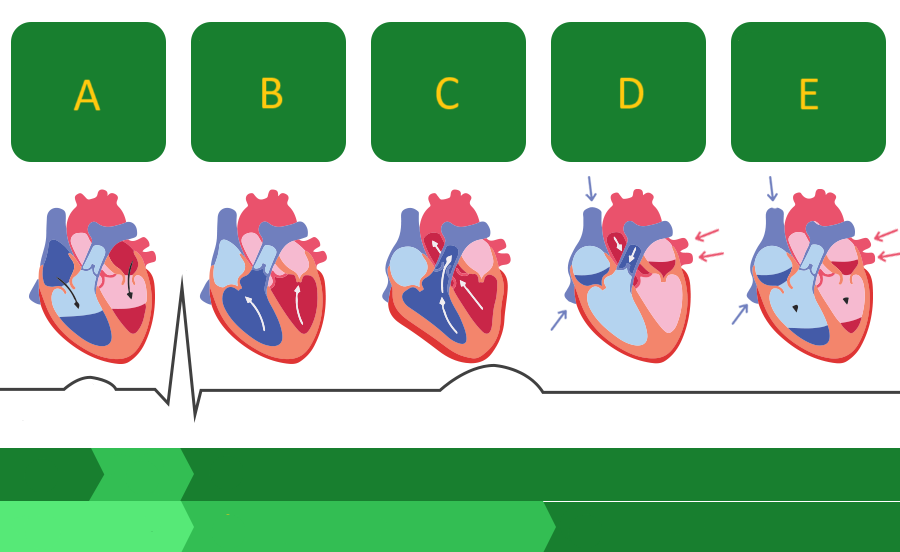
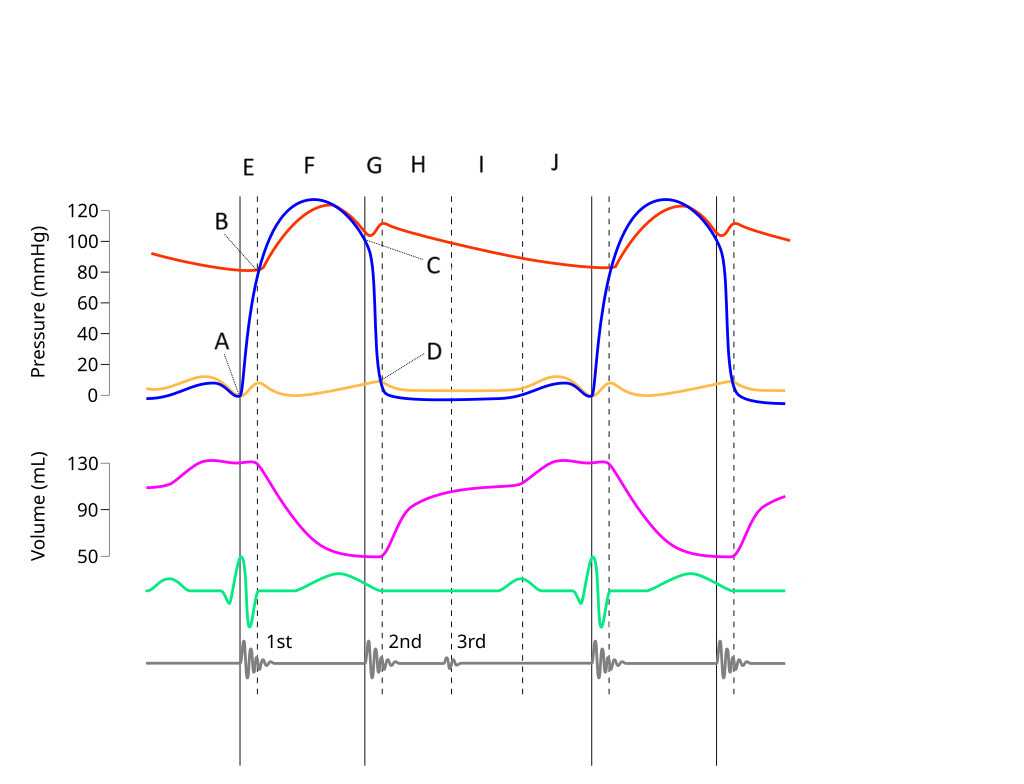
A - atrial systole
atrial contraction forces blood into the ventricles
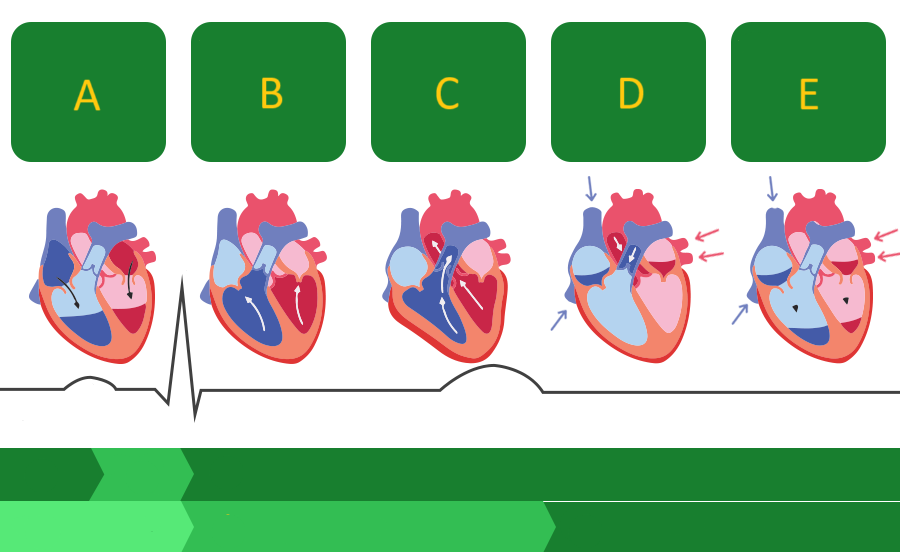
B - first phase of ventricular systole
ventricular contraction pushes the AV valves closed
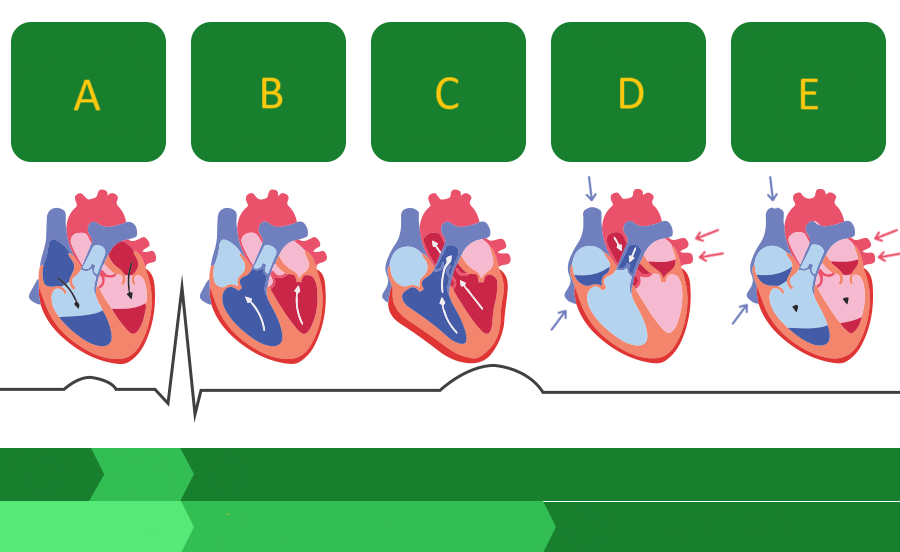
C - second phase of ventricular systole
the semilunar valves open and blood is ejected
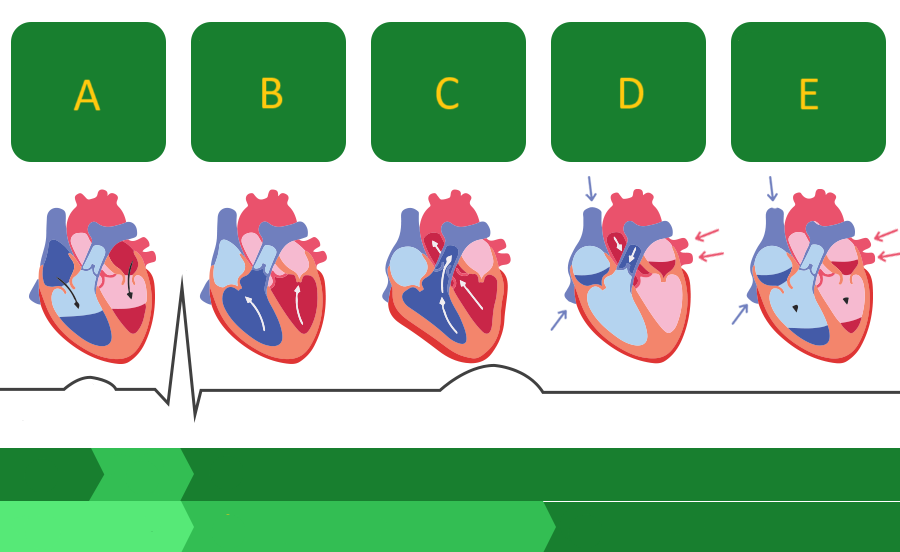
D - early ventricular diastole
the semilunar valves close and blood flows into the atria
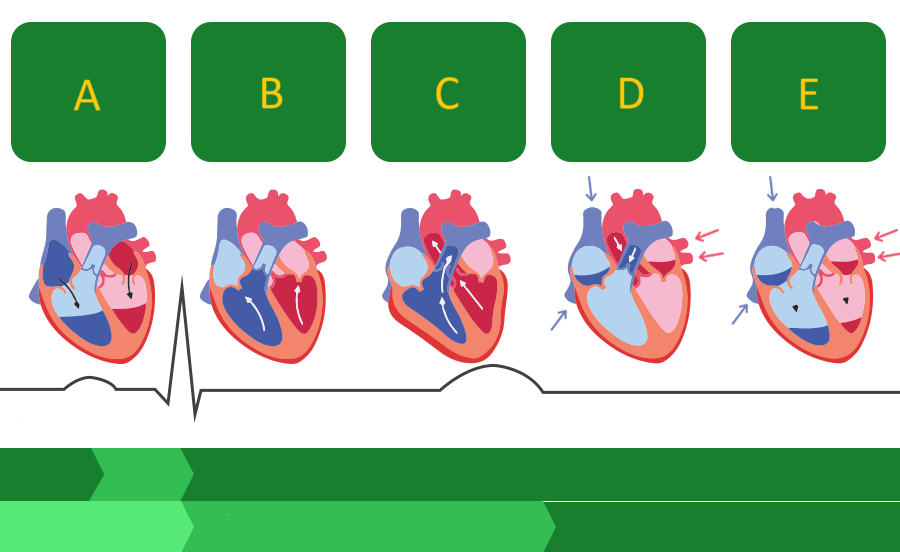
E - late ventricular diastole
the chambers relax and blood fills the ventricles passively