Topic 2.1 Western Expansion (1803-1834)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Western Expansion Theme
it begins as goal to expand agrarianism, not yet abt business
Decision on how to take land (negotiate or take): who are we taking from?
what will power the U.S. economically?
Who inhabits western American
Native Americans + Indigenous
English Settlers in Canda
French Settlers in Canada and the Louisiana Territories
Spanish Settlers in the Spanish Colonies
Russian Interest in modern-day Alaska
Thomas Jefferson + Jeffersonian Foreign Policy
1800-1808: Democratic-Republican
Tho came to power determined to limit fed gov, foreign affairs = inc fed gov
America's sucess as a democratic experimental republic of farmers was linked to foreign policy
America as Model: America exceptionals, Louisiana Purchase 1803 = double size of US, 530 mil acres for $15mil (3 cents per acre, .84 cents today -> value tdy is 2.2 $trillion = counter to Hamilton + industry economy
Louisiana Purchase
Louisiana Purchase 1803 = double size of US, 530 mil acres for $15mil (3 cents per acre, .84 cents today -> value tdy is 2.2 $trillion = counter to Hamilton + industry economy
In 1803 President Jefferson bought the Louisiana territory from France
France was losing control of its empire following the Napoleonic Wars (1799-1815) and the Haitian Revolution of 1791-1803 (lost control of Hati)
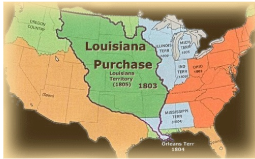
Jefferson wanted Louisiana purchase because
Would bring more land into the American democratic experiment
Would give more land to farmers to live on as democratic agrarians
Would help American farming economically by giving access to the Mississippi River and ports in the Gulf of Mexico
James Madison and the War of 1812
The US viewed a series of British actions as a threat to American sovereignty: bc they were treated like kids, questioned US independence
President Madison declared war on Great Britain (First US declaration of war)
U.S. army unprepared; British sack and burn Washington, D.C. in 1814 (when guy writes national anthem)
Control of the war teetered between the British and the Americans
Treaty of Ghent
1814: ended war of 1812
War of 1812 significance
3 fold:
War confirmed the sovereignty of the US
Weakened European involvement in North America
Changed US-Native American relationship bc Europe’s gone
War confirmed the sovereignty of the US
Solidified American Independence -> Often called the Second War of Independence
Helps build nationalism
Weakened European involvement in North America
America can expand in North American w/o real European opposition
Weakened France: w/ sake of Louisiana Territory = scales back involvement in North America
Weakened Spain: With wars for independence breaking out in Latin America, Spain’s role in North America was also weakening
Weakened Britain: With its loss in the War of 1812, the British were becoming less involved in North America (at least south of Canada)
Changed the US-Native American relationship
America can expand in North America w/ the possibility of success despite Native American opposition
As American migration occurred between the late 1700s and early 1800s, many Native Americans experienced white encroachment
= many Native American tribes sought to form alliances with European nations who also wanted to prevent American encroachment into their North American Colonies
War of 1812 ended alliances
Signaled to Europeans that conflict with the US could result in defeat = European nations were less likely to work with Native Americans to agitate against the United States
Native Americans lost their allies and were left to deal with the United States on their own (now with significantly less manpower and resources)
Florida pre 1819 - Aquisition
Florida was a Spanish colony
Spain largely neglected Florida because it was preoccupied with its struggles in Latin America
Florida was populated by:
Floridanos (Spanish colonists)
Seminole Indians (Indigenous to FL)
American farmers
Runaway American slaves
Given safe harbor in Seminole communities
+ Spain had stopped extraditing runaway slaves to the US in 1794
Seminole Indians Attack America + America Responds
There are a series of border conflicts between the Seminoles and Americans along the Florida/Georgia/Alabama border
Americans are going into Florida to reclaim their slaves and the Seminoles resent that they are going into Seminole territories and communities to do this Attacks Seminoles: raids, invasions, mass killings thru communicates
Attacks Spanish: captures forts + cities
Spain can’t get a handle on the situation
President James Monroe authorized U.S. Army General Andrew Jackson to invade Florida in order put down the Seminole attacks
Jackson is given the “full power to conduct the war in the manner he may judge best”
For Jackson, the invasion of Florida was an opportunity to:
Quell Seminole invasions, but also Native American resistance more broadly
Get the Spanish out of Florida and make a play for the colony
First Seminole War (1817-1819)
General Andrew Jackson leads:
Attacks on Seminoles: raids, invasions, mass killings thru communicates
Attacks on Spanish: captures forts + cities
Adams–Onís Treaty
Aquisition of Florida 1819
The US proposes a treaty with Spain: We will not expand our invasion west into New Spain if you give us Florida
The Monroe administration signed a treaty with Spain in which the US purchased Florida from Spain for $5 million ($120 million in 2024)
The treaty also created a fixed Western border between the United States and New Spain
President James Monroe, General Andrew Jackson, and the Acquisition of Florida (1819) Significance
Aquisition of Florida =
Spain: Revealed to be a weak nation who the US can challenge
Might the US be able to take Spanish control over other areas of New Spain?
Slavery: Growth and Protection
The Seminole's willingness to protect runaway slaves in their communities threatened slavery in the Southeast.
Now, runaway slaves wouldn’t have safe harbor in Florida (ideally they continue expanding west)
Florida would become a slave state when it entered the union in 1845 allowing the institution to expand further south
Native Americans: Subject of Formal Attack and Invasion by US Military
US military is now being used to attack and control Native Americans (done by Jackson as a General -> Indian Removal Act in presidency)
President James Monroe & The Monroe Doctrine (1825)
The Monroe Doctrine was a United States foreign policy position that opposed European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere.
Asserted by President James Monroe
Asserted two key ideas:
Warned European powers not to interfere in the Western Hemisphere (US gaining power as Europe losing power, wars, etc)
Told Europe that if it made new colonies or tried to overthrow newly independent republics, the US would consider this “dangerous to our peace and safety”
Monroe Doctrine was largely a warning to Spain (Europe's involvement in their colonies = threat to US)
Motivations of Monroe Doctrine
Ideological:
US is now a protector
The US is destined to protect the ideals of democracy wherever they are struggling to be achieved
Economic:
Agrarian/Slave-holding Interest:
Weaken Spain’s presence in North America and you can go after New Spain and expand slavery westward along the Continent (Spain took runaway slaves)
Supported by Democrats (pro-slavery)
Commercial/Buisness Interest:
Foster independence in Latin America and there will be access to new resources and new markets to send American goods to, from new developing nations
Supported by Federalists/Whigs (no Republican party yet…)
Significance of Monroe
The US declares itself the protector of the Western Hemisphere
Extension of Jefferson’s ideas: It is America’s obligation to protect and promote democracy
It argues that it has a strategic interest beyond its own national borders and that it has a role to play in shaping events and outcomes in the Western Hemisphere.
Clear economic motivations for expansion, but each party/region perceives a different economic value of expansion
President Andrew Jackson, Indian Removal Act, and The Trail of Tears 1830-1834 CAUSE
Americans come into Conflict with Native Americans in the Southeast 1812-1830
Hope of FF that slavery would fade out fails: Cotton makes more $, ban on import of slaves makes them more valuable
cotton boom in the South =desire for “easy” land
southeastern tribes had signed numerous treaties with the US in which their sovereignty was recognized, but Jackson refused to accept their independence and asked Congress to draft a law authorizing Native American removal
The Indian Removal Act 1830
Indian Removal Act authorized the forcible removal of Native Americans from several southern states.
Supreme Court overturns the act in Worcester v. Georgia 1832 bc even tho Georgia surrounds them, they r their own country, u must negotiate w/ them
Jackson disobeys court's ruling, checks and balances, judicial review
The Trail of Tears 1832-1834
U.S. soldiers forcibly march 15,000 Cherokee living in the South East off of their land
4,000 die in the process
Indian + Trial (2nd Seminole War) Significance
The War of 1812 and the First Seminole War of 1817-1819 both made the Trail of Tears possible
War of 1812: Drastically weakens Native American Resistance
First Seminole War: Shows a willingness to use the US military against Native Americans
Trail of Tears begins a decades-long process of the forcible relocation of Native Americans = big part of US Western expansion
Jacksonian Framework (Seminole wars)
Strategic Aim before was to protect democracy or economy for the whole = less willingness to use violence
Aim now whatever president wants = willingness to use other aims “I want this and that” = aggressive actions