Microbial Diseases
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
What type of microorganisms are seen on our skin?
Gram +, Salt-tolerant, Staphylococci/Micrococci
Corynebacterium xerosis
aerobes on the skin
Propionibacterium acnes
anaerobes in the hair follicles
Does S. aureus have catalase and coagulase?
yes
S. aureus survives in the ___________________
phagolysosome
Folliculitis
inflammation of the hair follicles
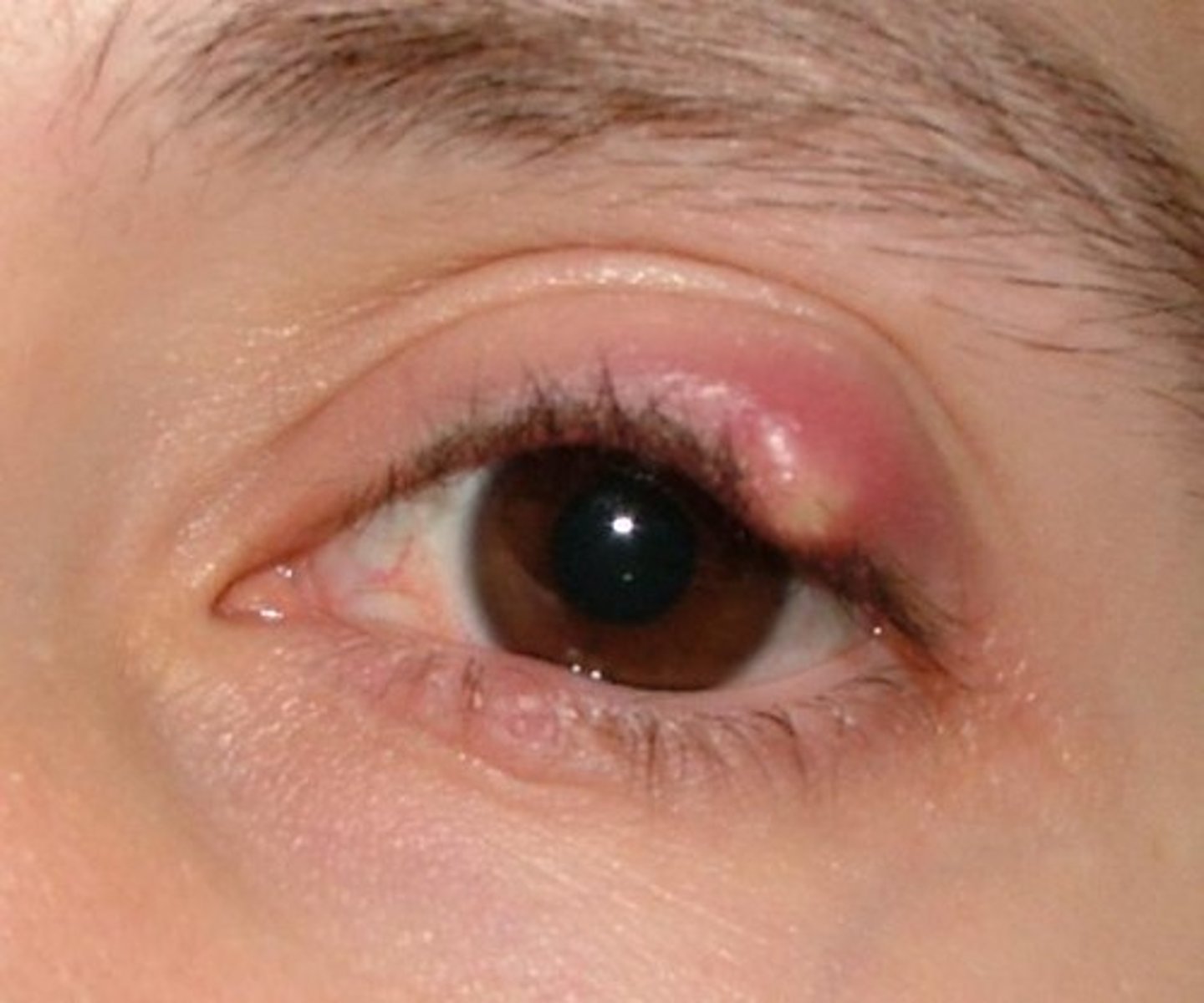
Sty
folliculitis of an eyelash
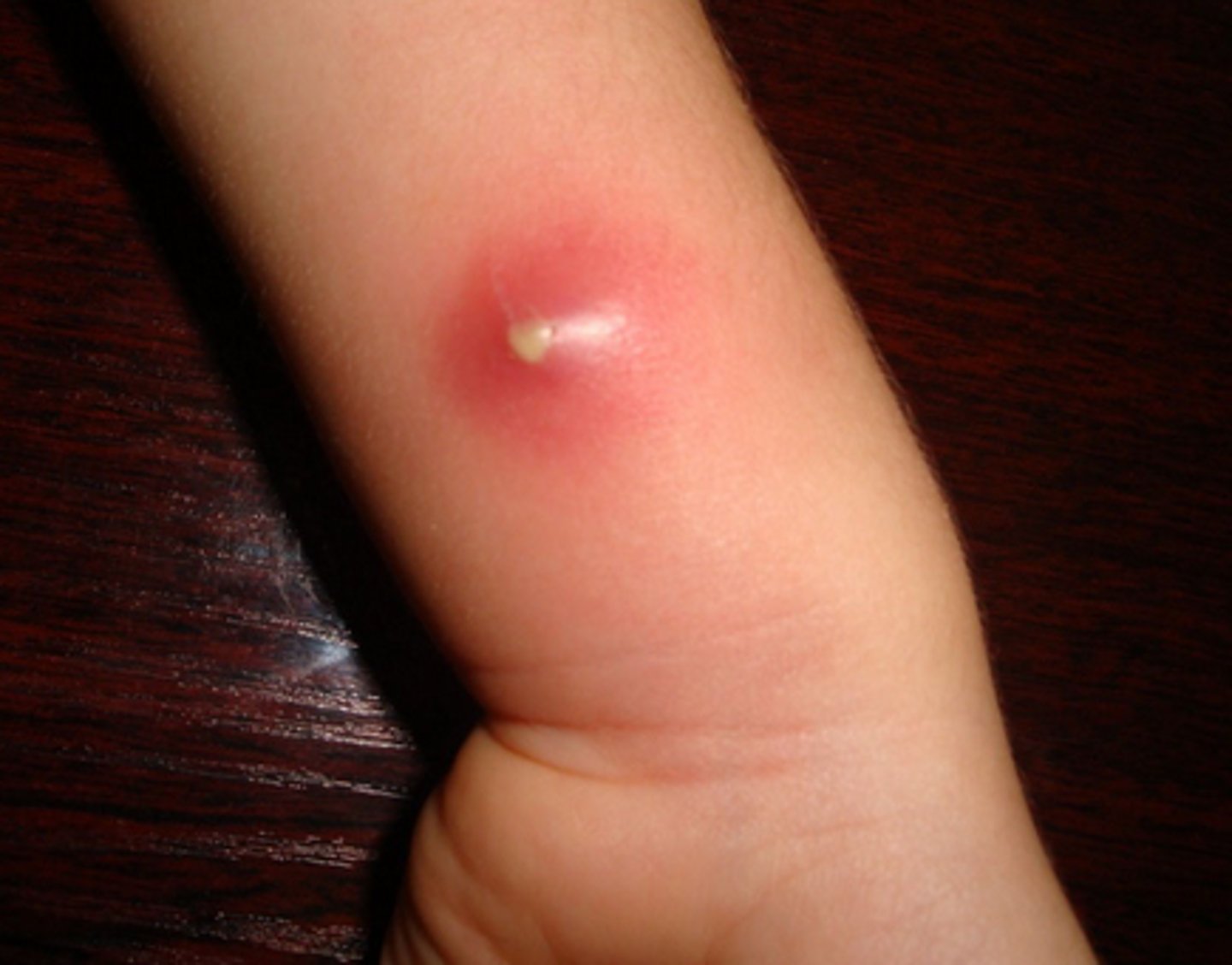
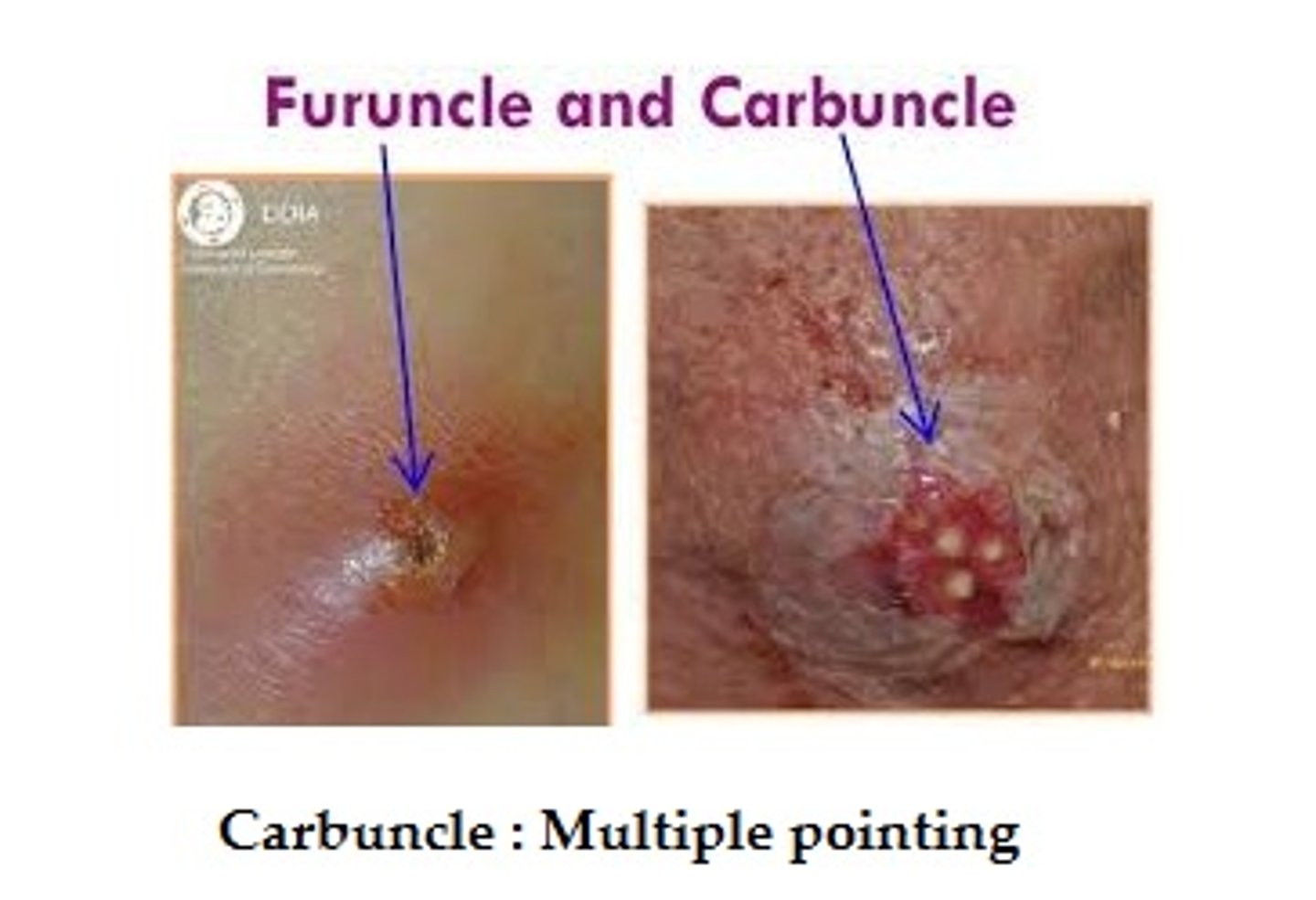
Furuncle
Abscess; pus surrounded by inflamed tissue
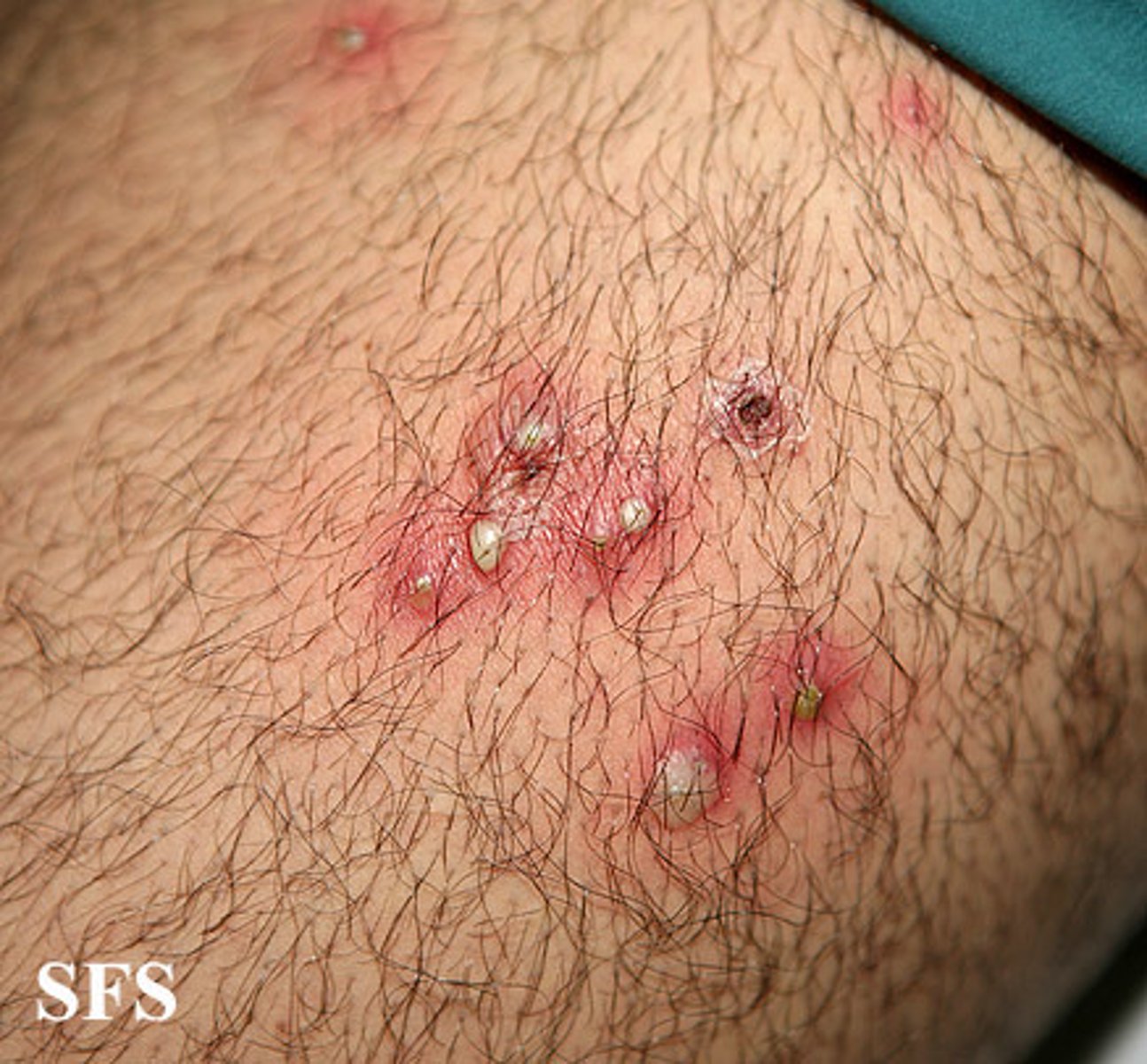
Carbuncle
Inflammation of tissue under the skin
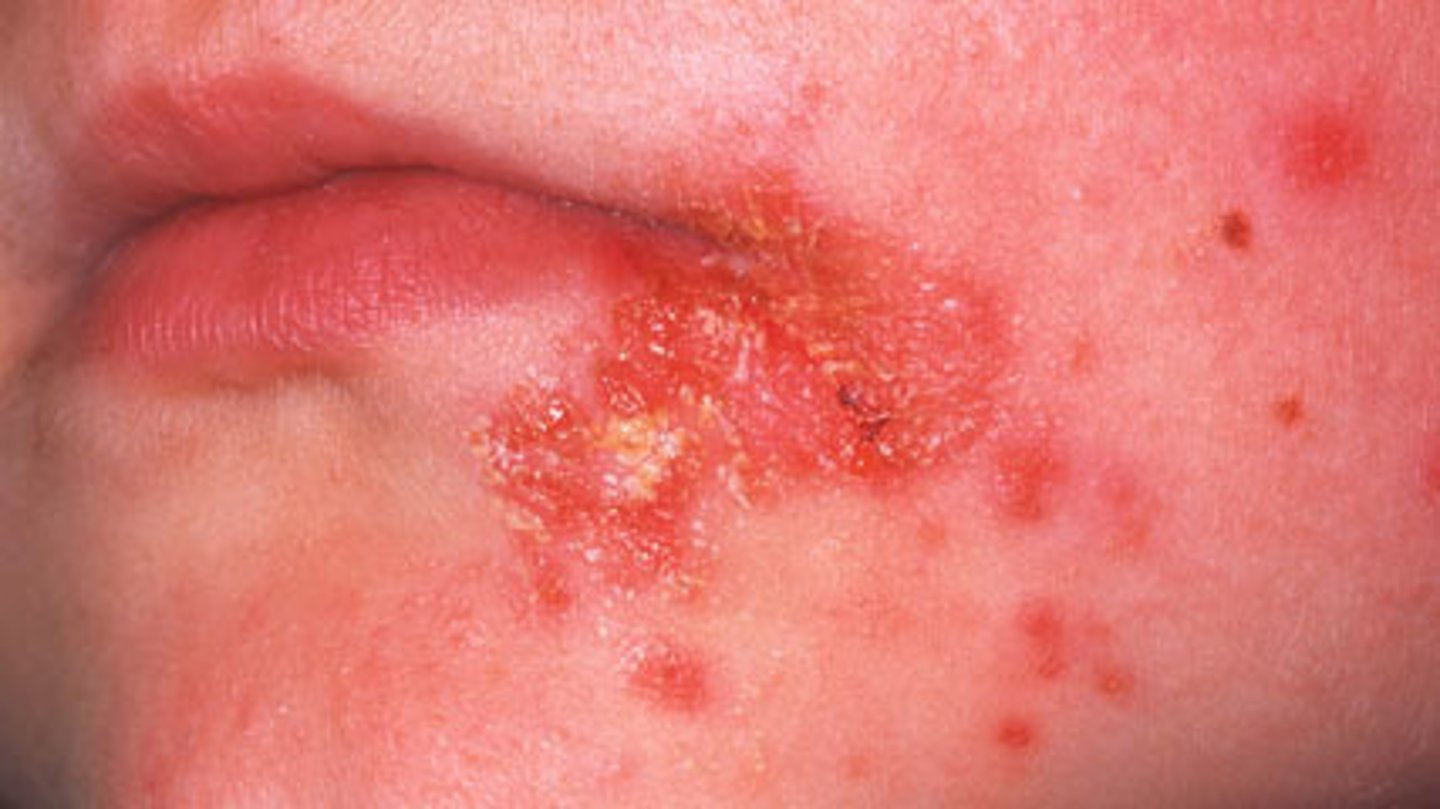
Impetigo
crusting sores, spread by autoinoculation
A mannitol salt agar plate is used to distinguish different species of...
staphylococci
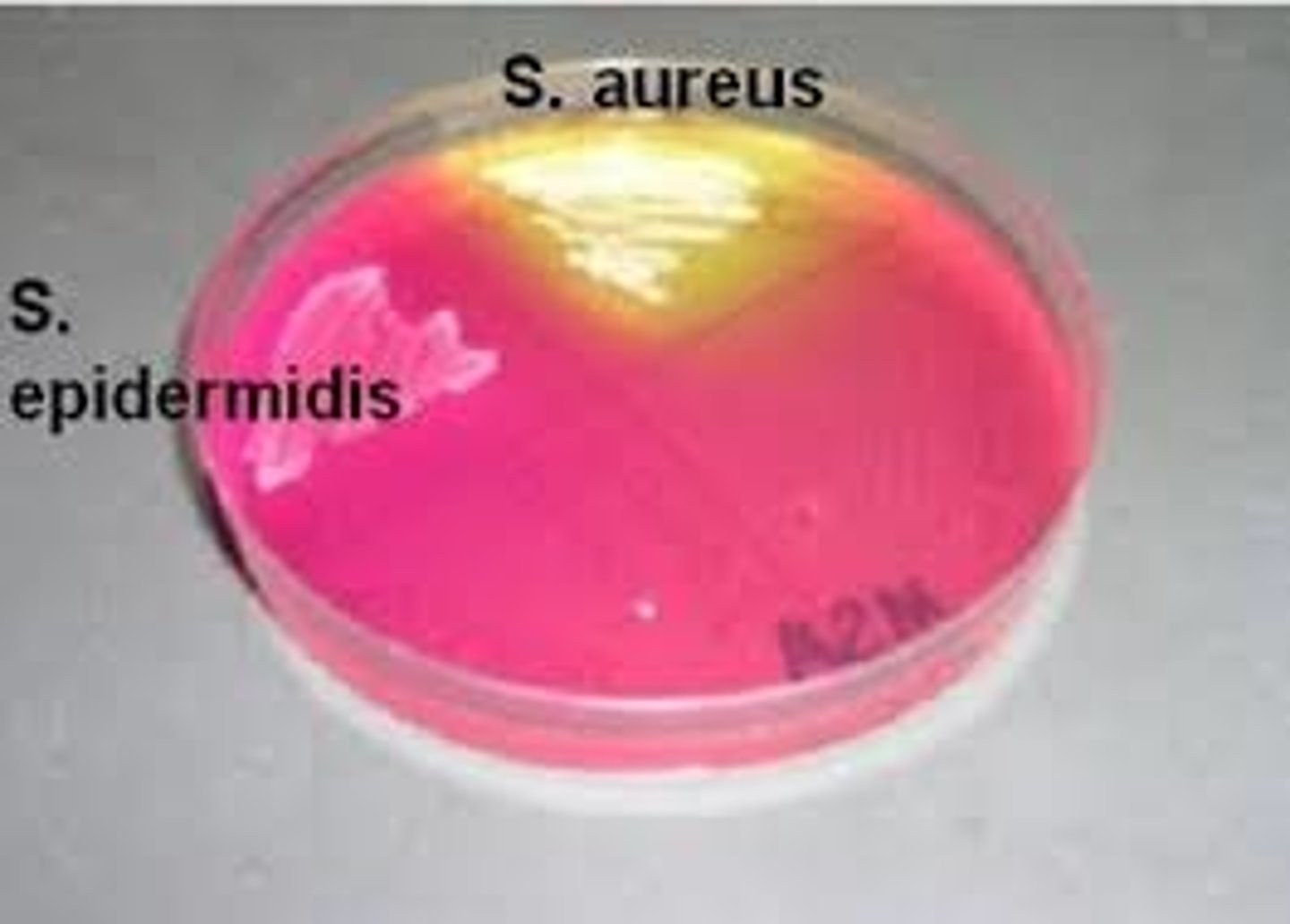
What does S. aureus produce that changes the color to yellow on the MSA plate?
acid, due to mannitol fermentation
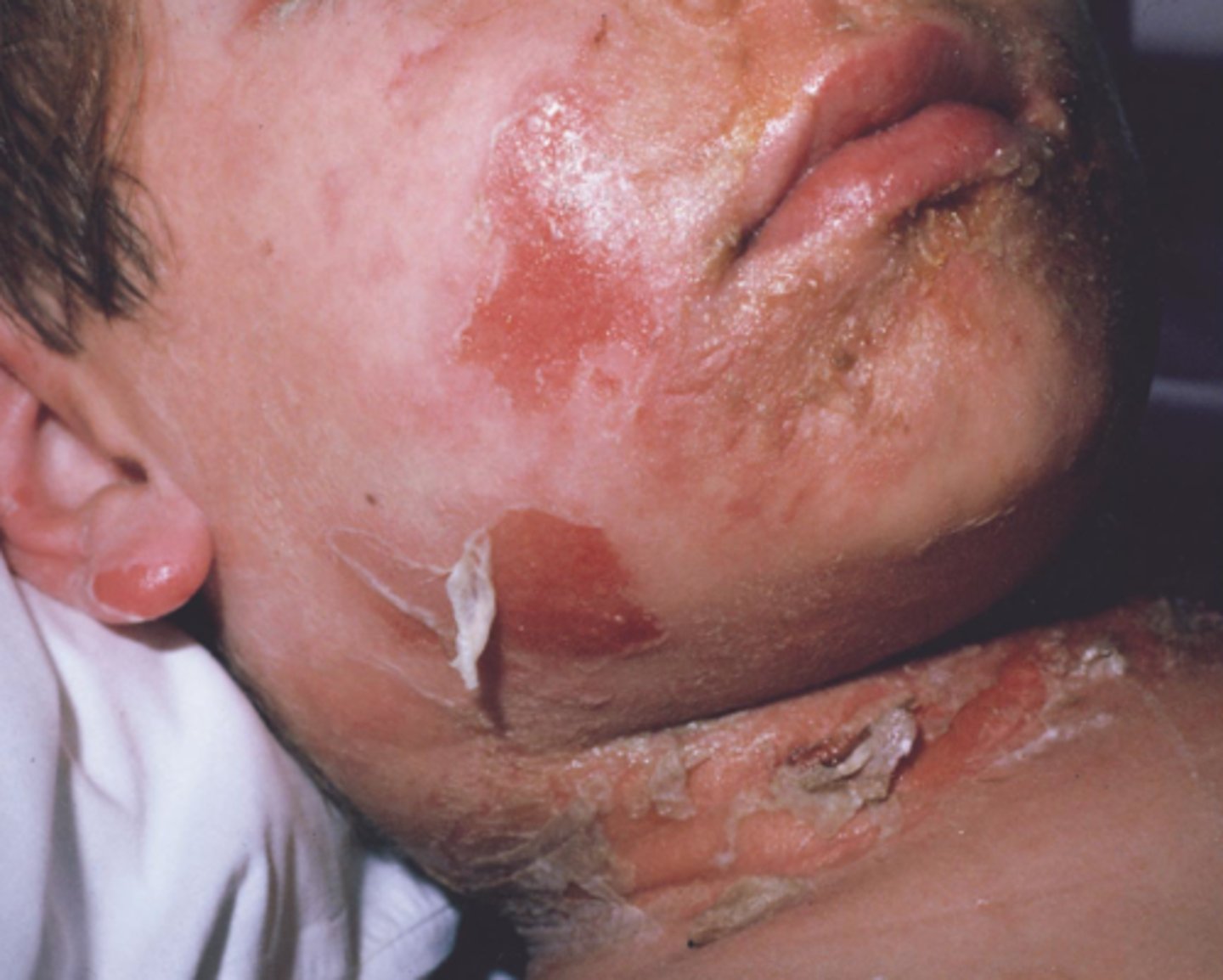
SSSS (staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome)
results in large regions of peeling, dead skin
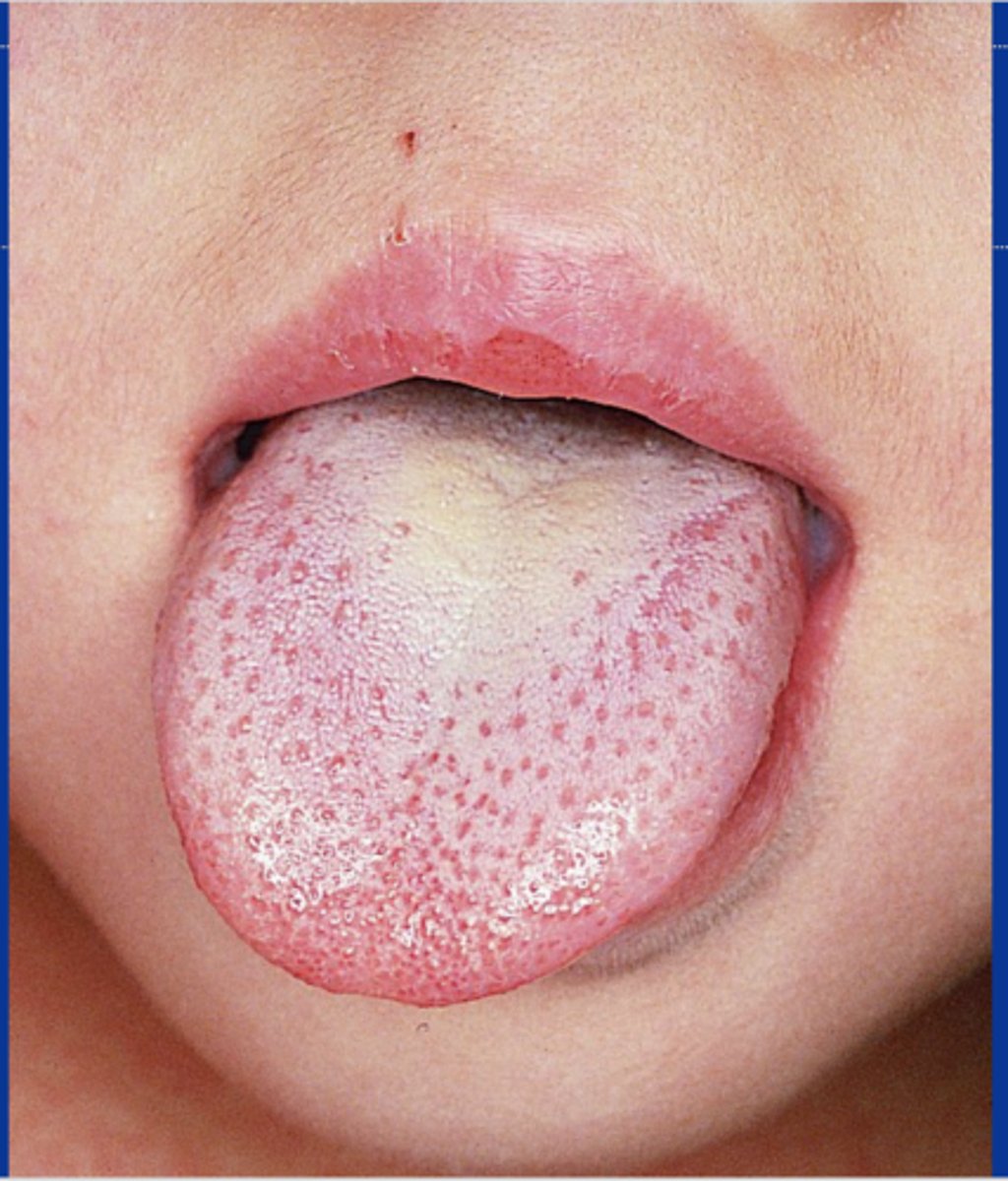
Toxic Shock Syndrome
Extremely serious condition that can be quickly fatal if not treated appropriately. abrupt onset of high fever, hypotension, a diffuse erythematous rash swollen "strawberry tongue."
Comedonal Acne (mild)
Sebum channels blocked with shed cells
Propionibacterium acnes is known to cause...
inflammatory acne (moderate)
Nodular Cystic Acne (severe)
Inflamed lesions with pus deep in the skin
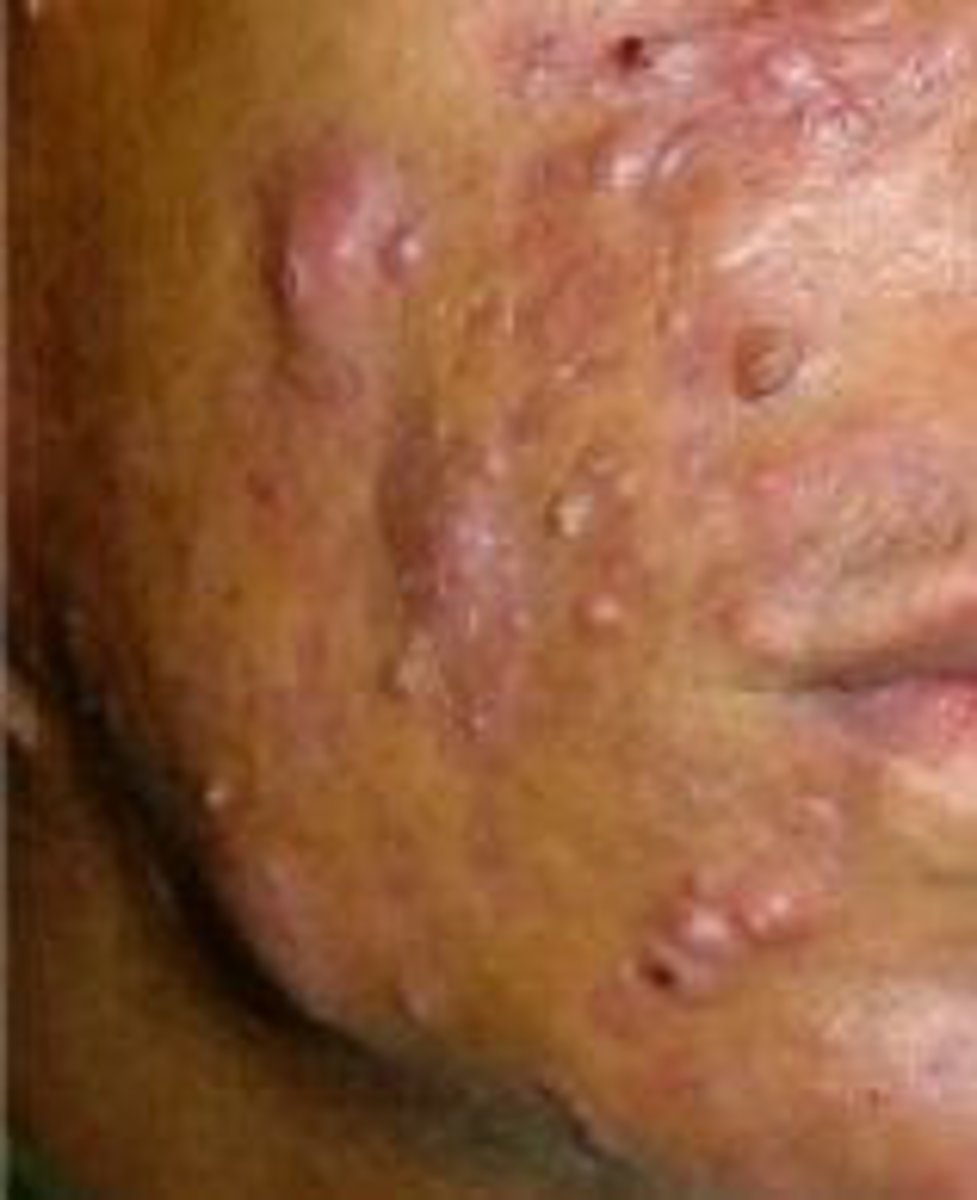
What medication is used to treat nodular cystic acne?
isotretinoin
Streptococcus pyogenes is a type of...
skin infection
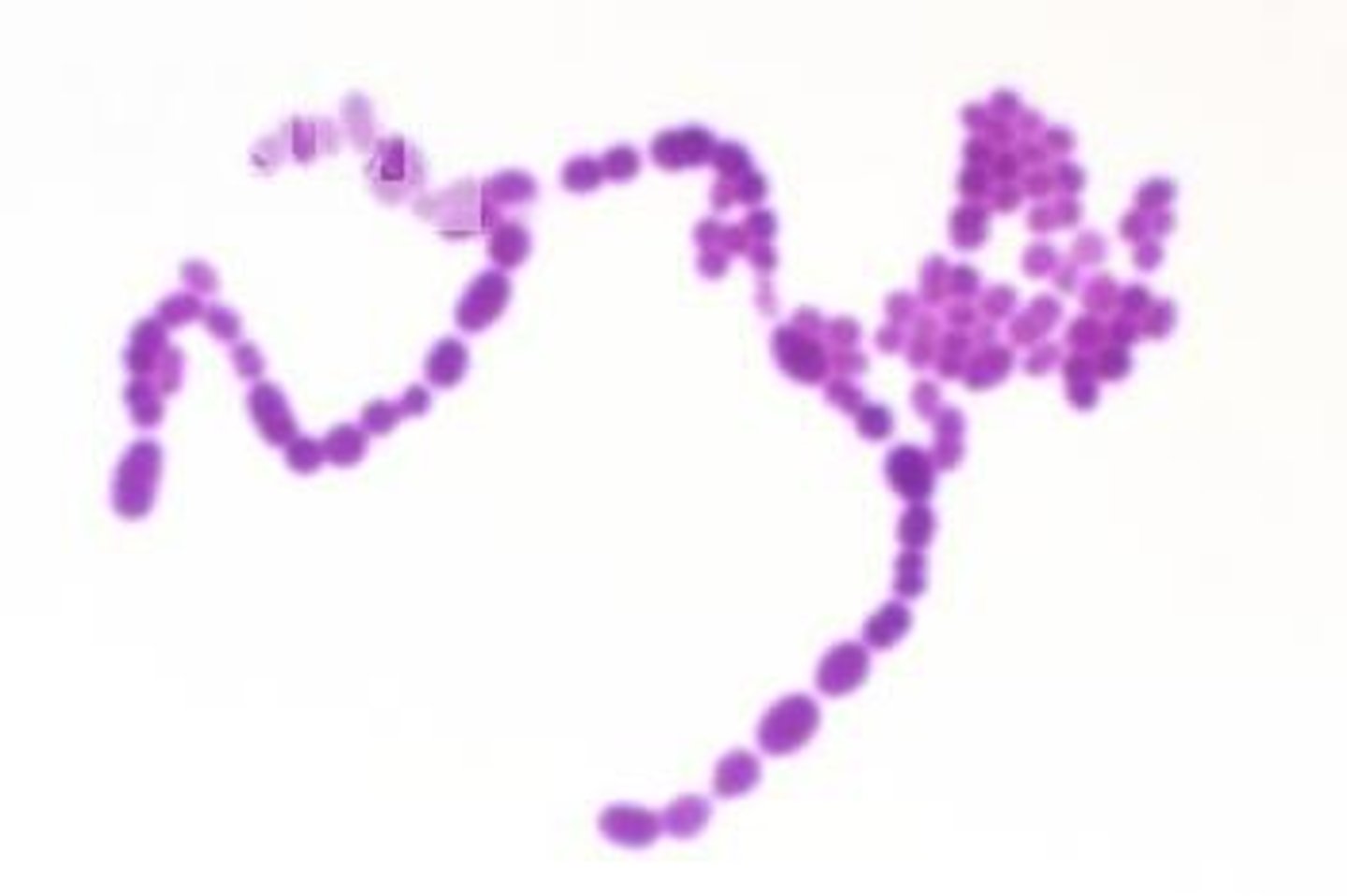
_____________________ is a group A beta-hemolytic streptococci
S. pyogenes
Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome
-M proteins
-Complex with fibrinogen
-Binds to neutrophils
-Activates neutrophils
-Release of damaging enzymes
-Shock and organ damage
Cellulitis, Erysipelas, and Erythema nodosum is mainly caused by...
S. pyogenes
What organism causes necrotizing fasciitis?
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcal Pharyngitis
Strep throat caused by Streptococcus pyogenes.
Warts are caused by what virus?
papillomaviruses
Plantar Warts
warts that develop on the soles of the foot, grow inward, and can become painful
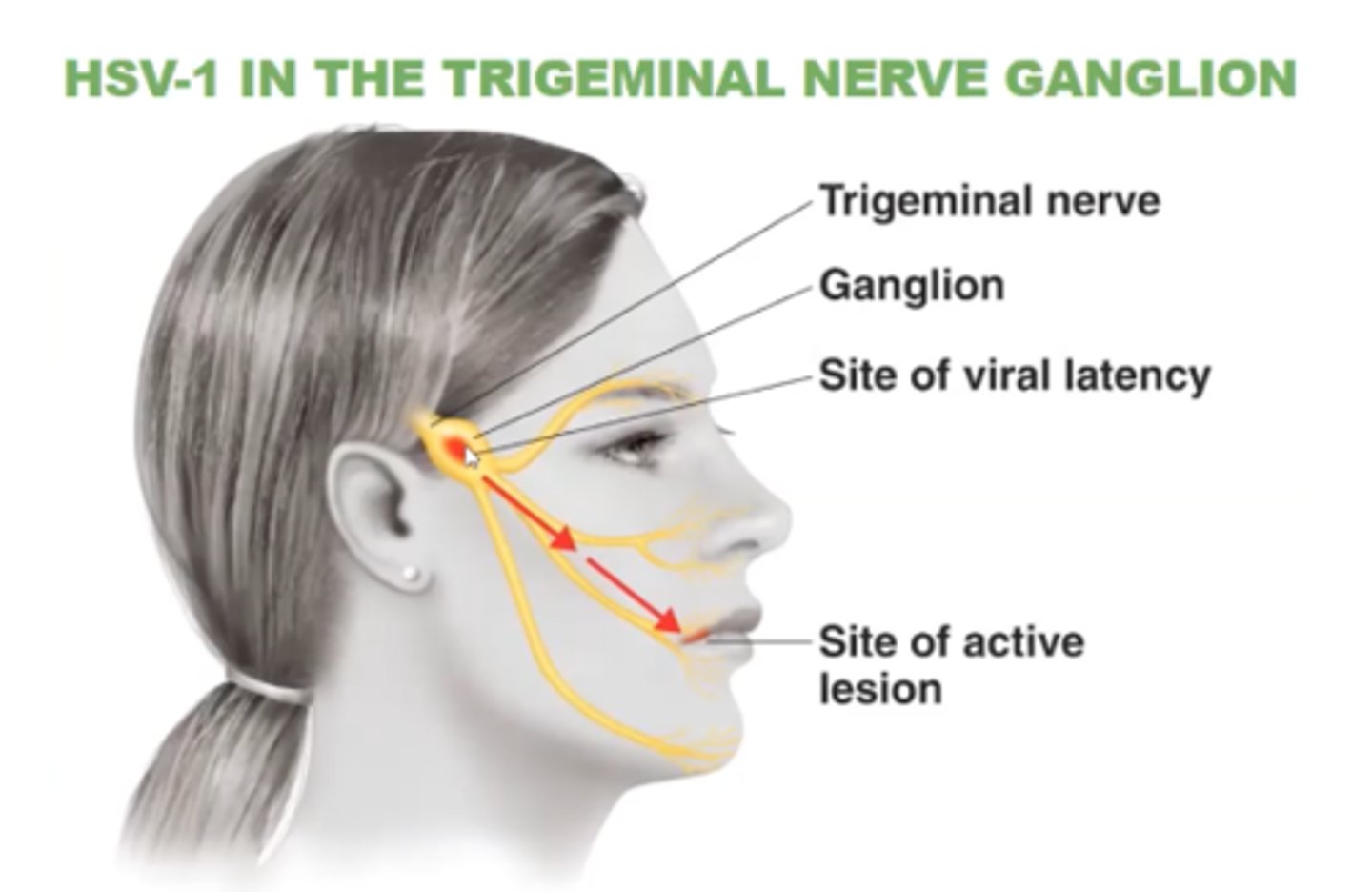
Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1)
This virus causes fever blisters/ cold sores
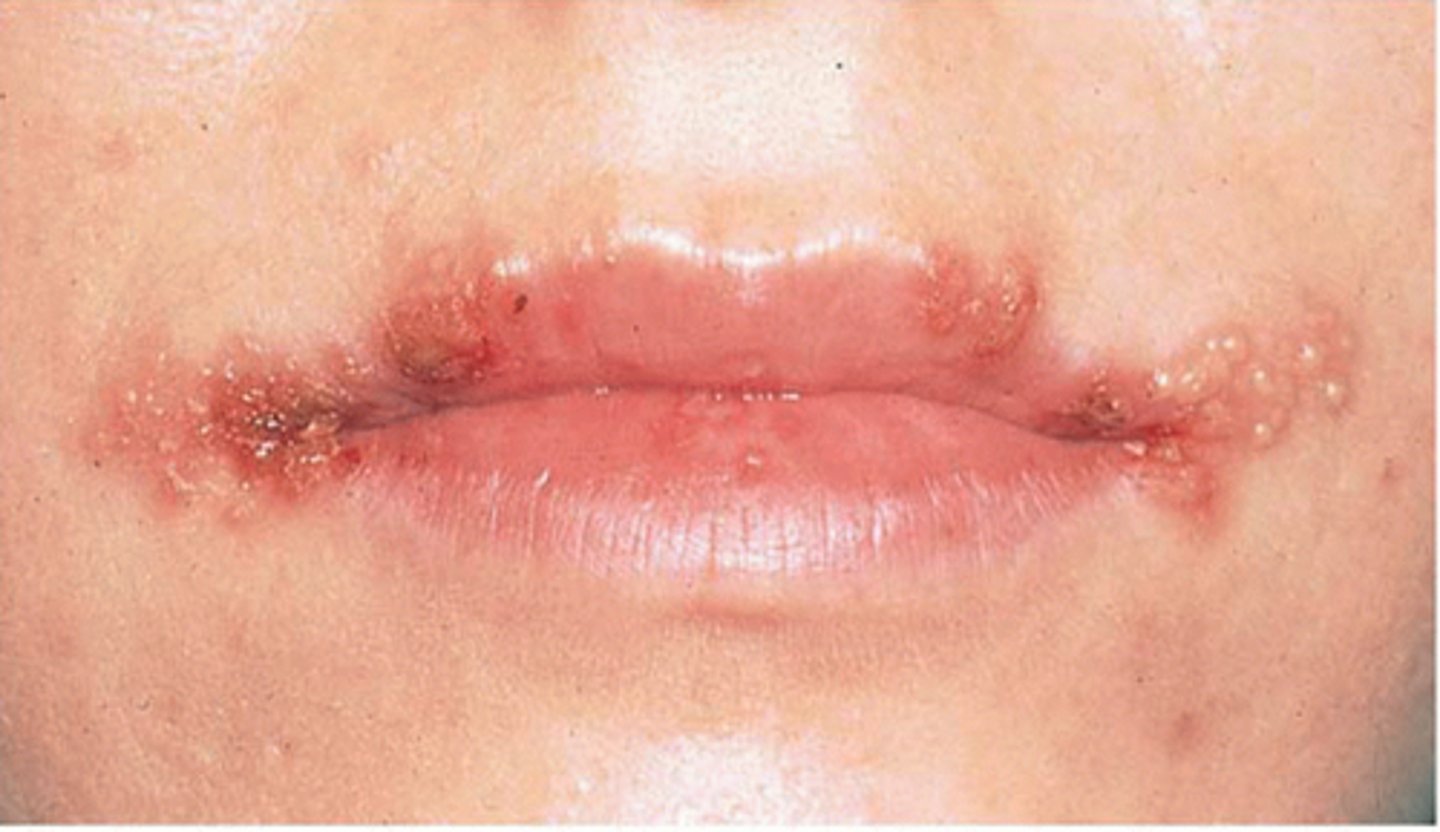
HSV-1 can remain latent in the....
trigeminal nerve ganglia
Herpes gladiatorum
vesicles on the skin
Herpetic whitlow
vesicles on fingers
Rubella is also known as
German measles
Rubella virus causes...
macular rash and fever
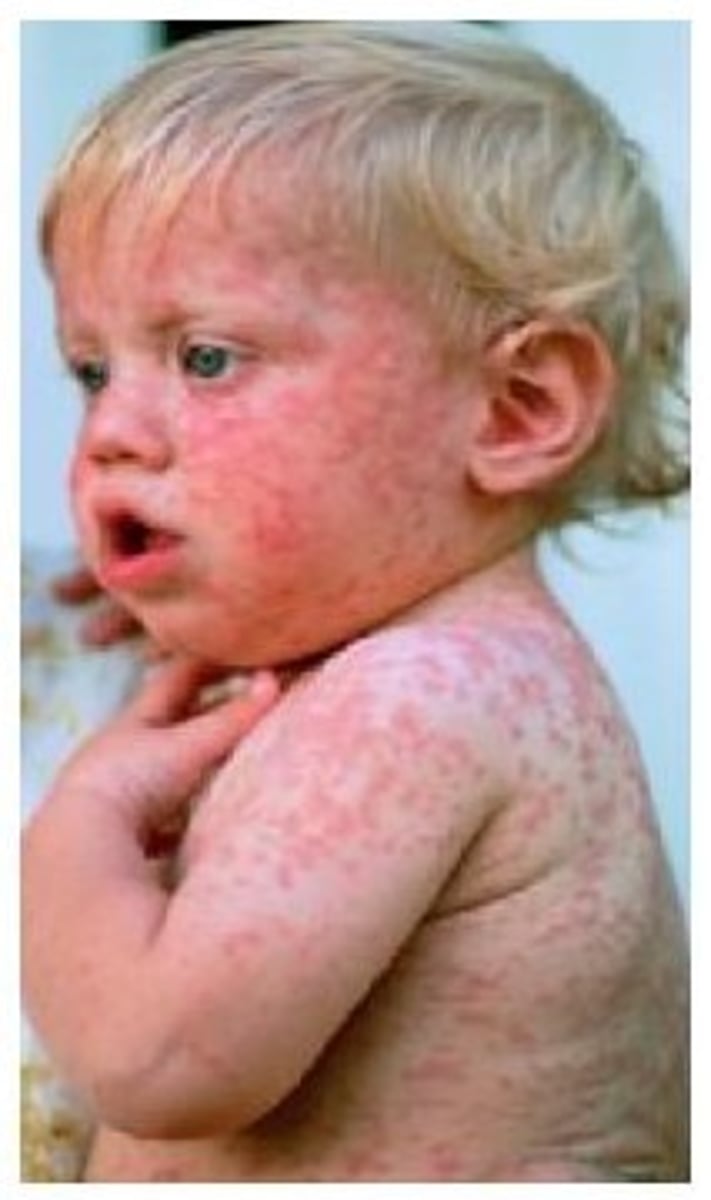
Congenital rubella syndrome
causes severe fetal damage
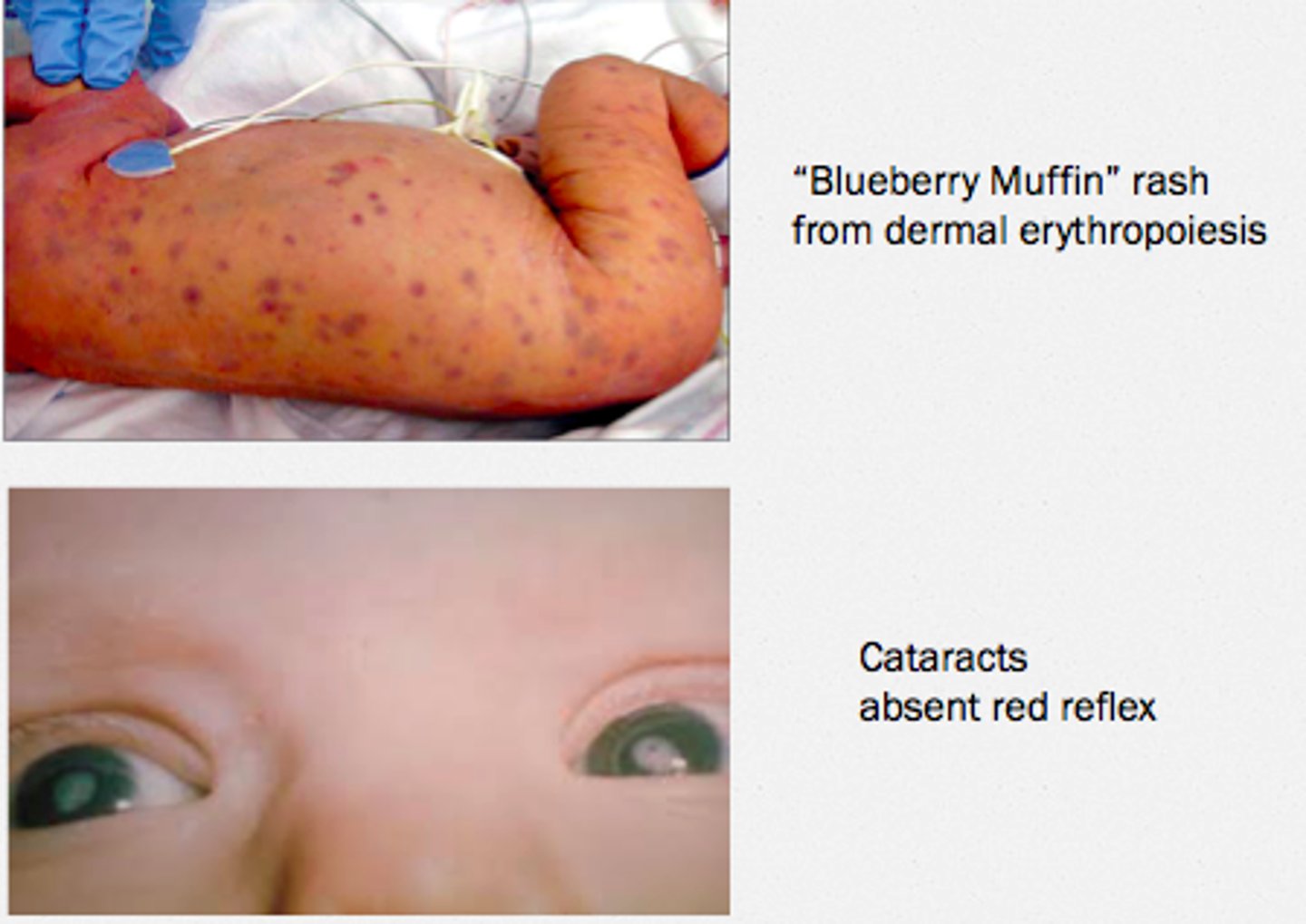
What virus is Chickenpox caused by?
varicella zoster virus (human herpesvirus 3)
Can Chickenpox remain latent in the dorsal root ganglia?
yes
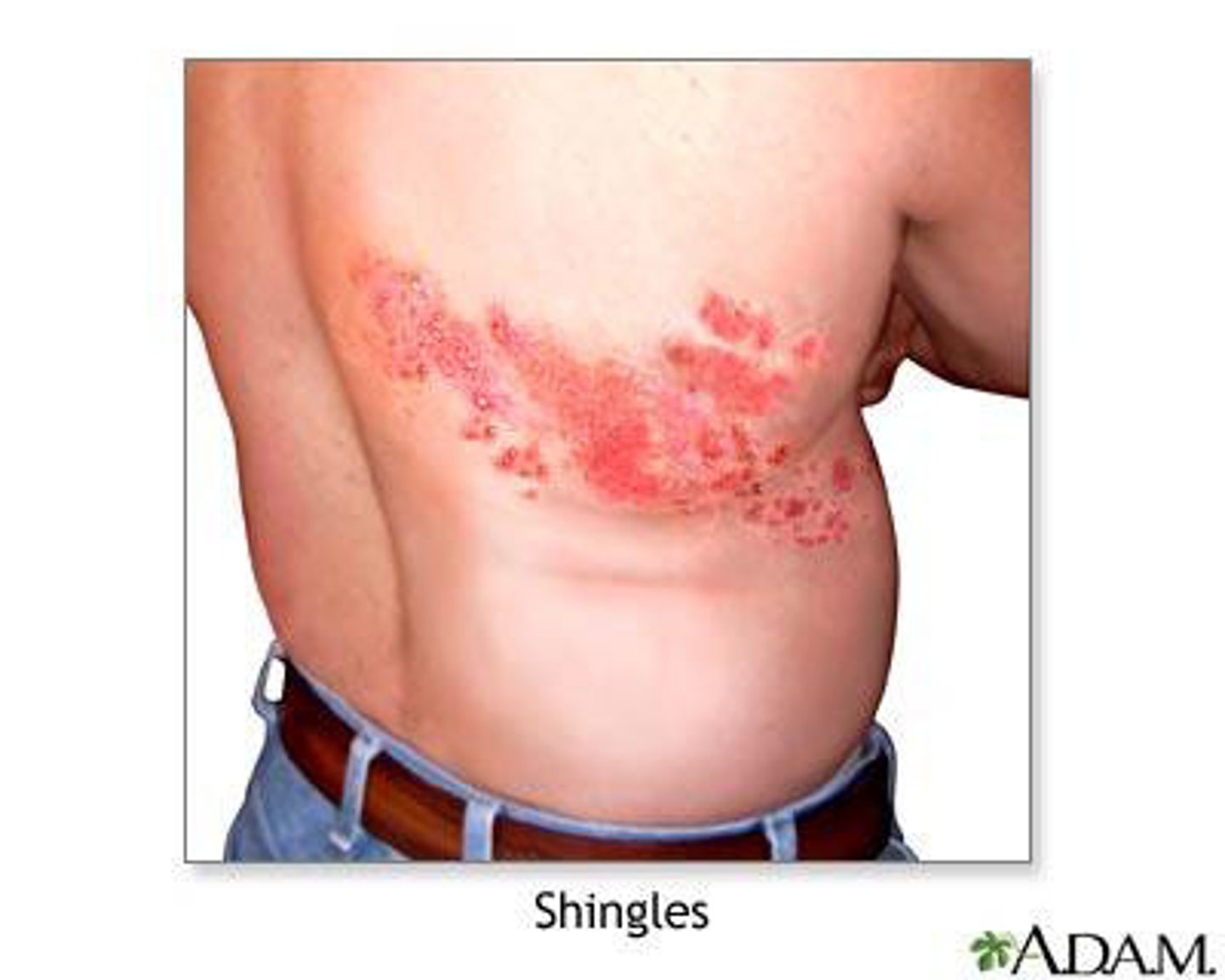
Shingles
reactivation of latent HHV-3 (chickenpox) releases viruses that move along peripheral nerves to skin
The top part of the skin, which is exposed to the environment is called:
the epidermis
All of the following are normal microbiota of the Skin EXCEPT
Streptococcus
A deep lesion that develops from multiple boils is called a:
carbuncle
Which bacterial genus is commonly associated with acne?
Propionibacterium
A highly contagious infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes that causes vesicles, pustules, and bullae which form encrusted sores is called:
Impetigo
What is the prevention method for shingles?
live attenuated vaccine
Vitreous Humor
sterile part of the eyeball
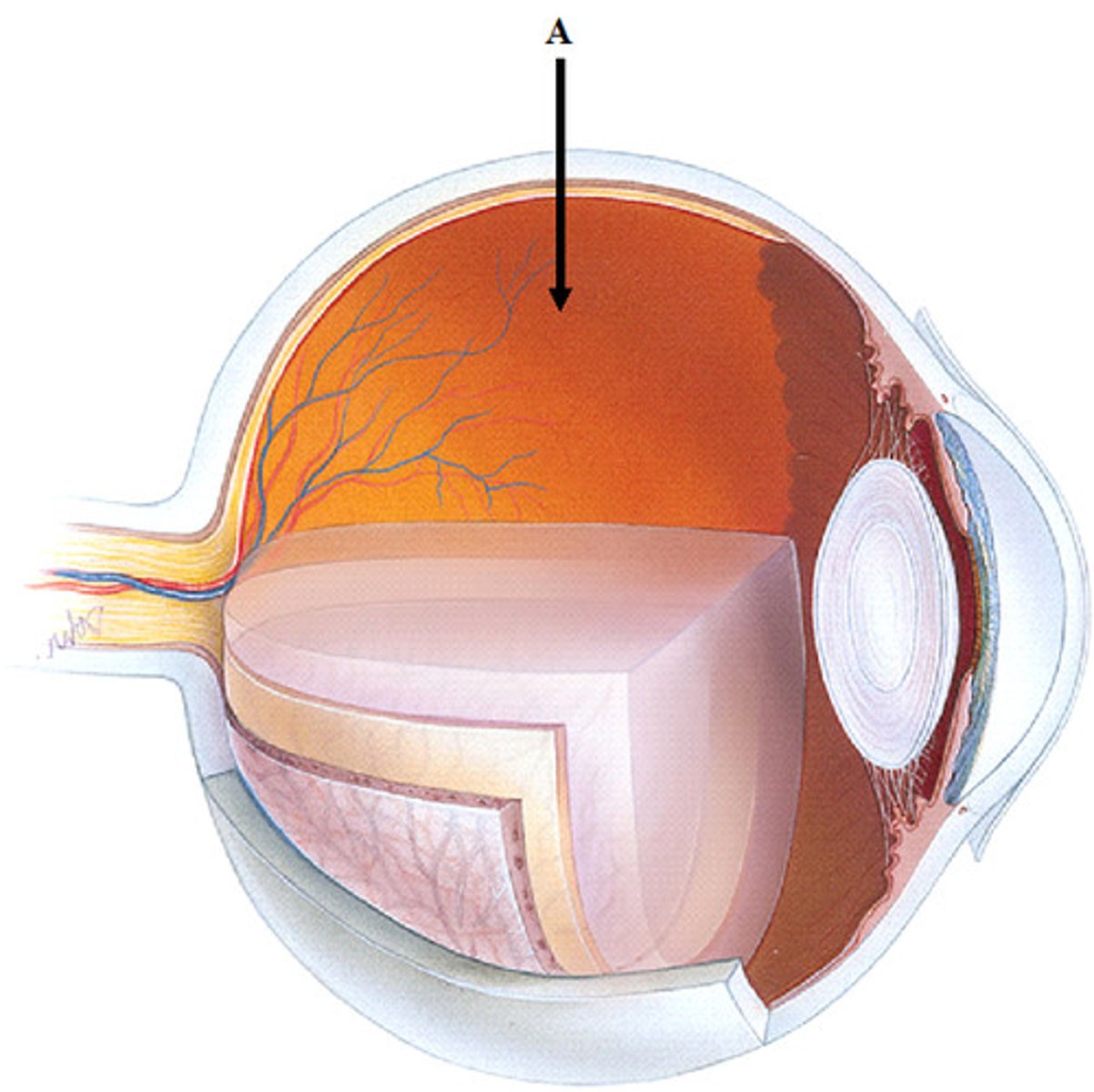
Conjunctiva
mucous membrane that lines the eyelids and outer surface of the eyeball
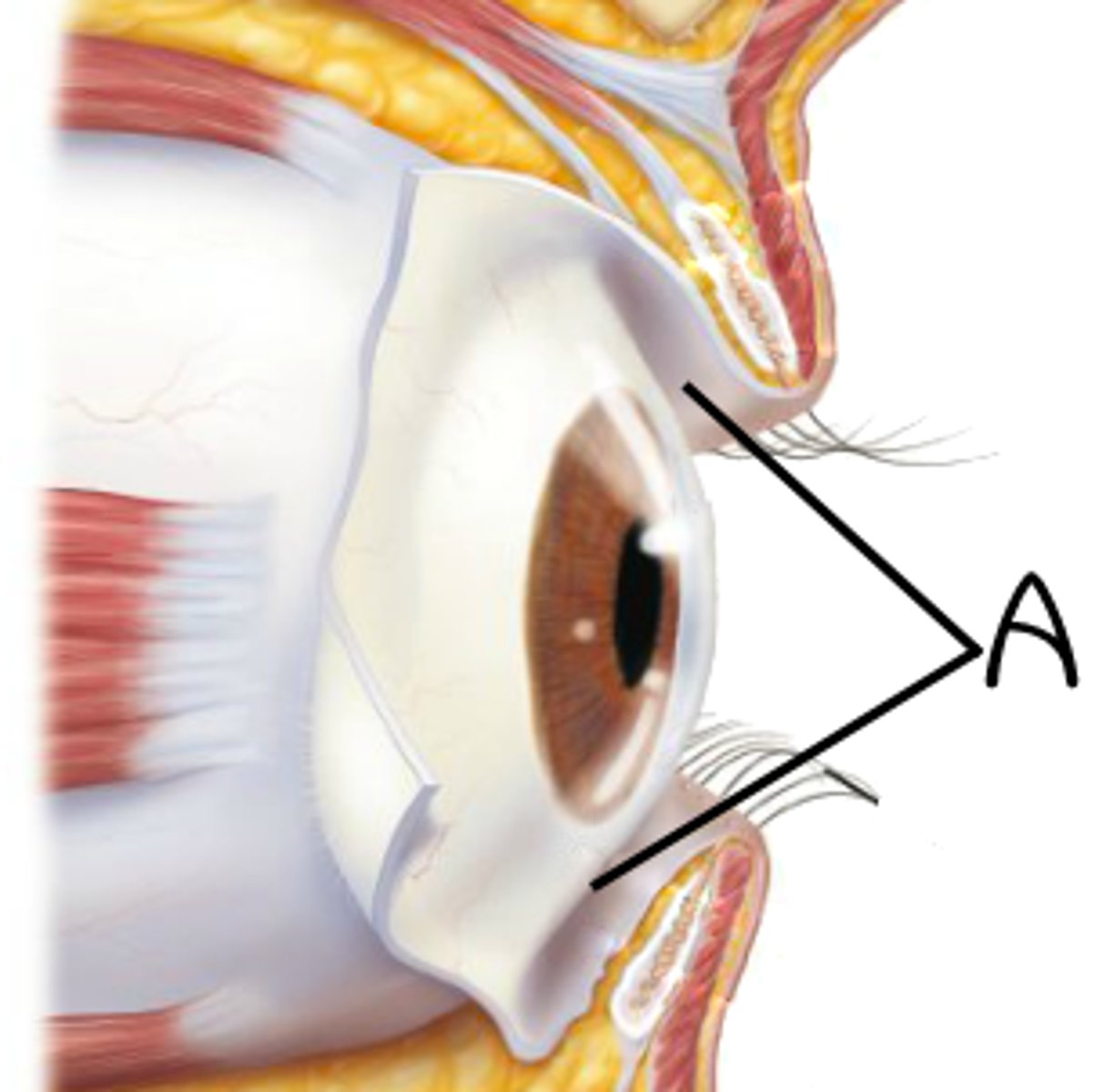
True or False? Microbes do not live on the conjunctiva
False, microbes do live on the conjunctiva
Conjuntivitis (pink eye)
inflammation of the conjunctiva
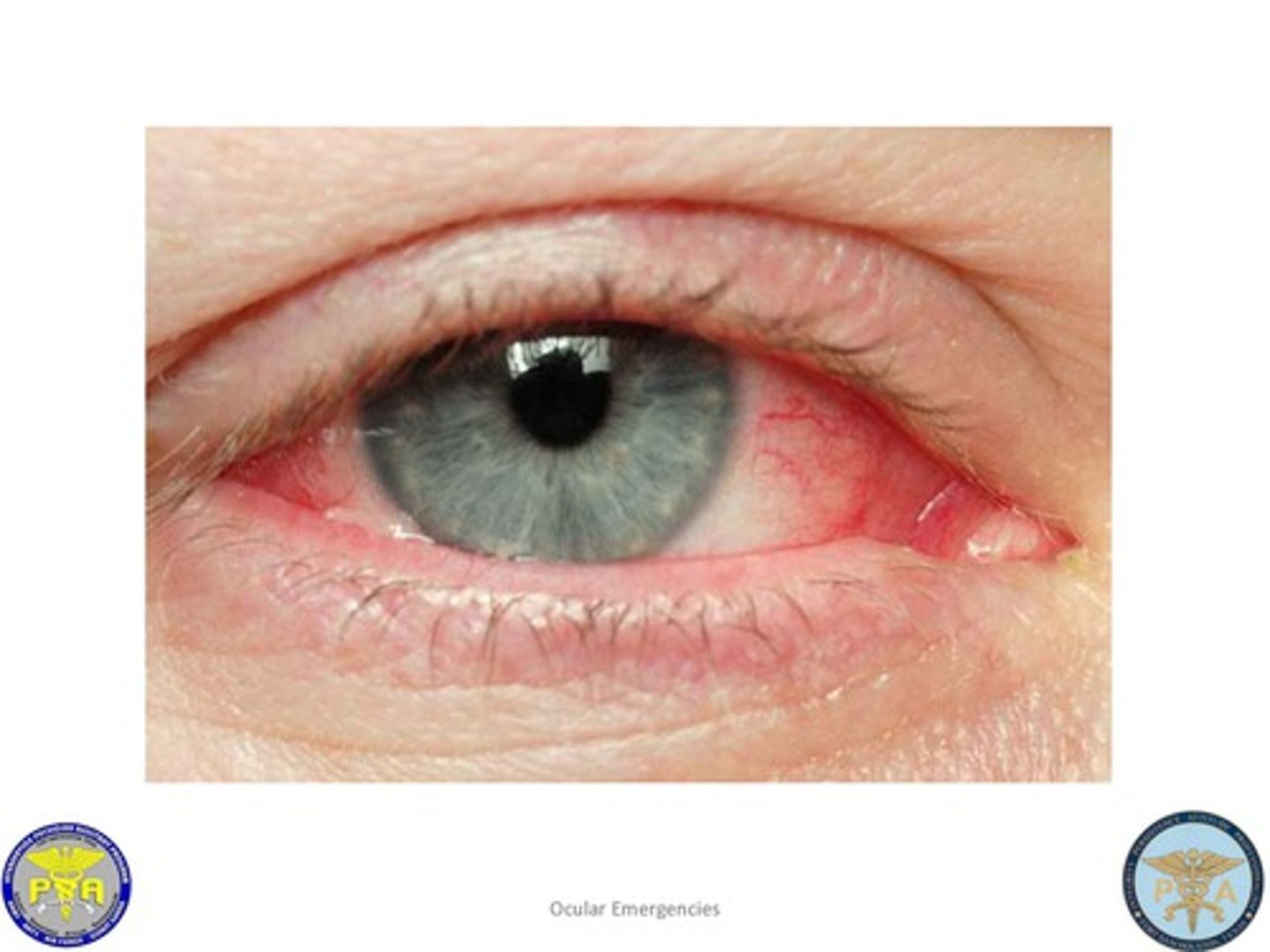
Haemophilus influenzae commonly causes...
pink eye
What is conjunctivitis associated with?
unsanitary contact lenses
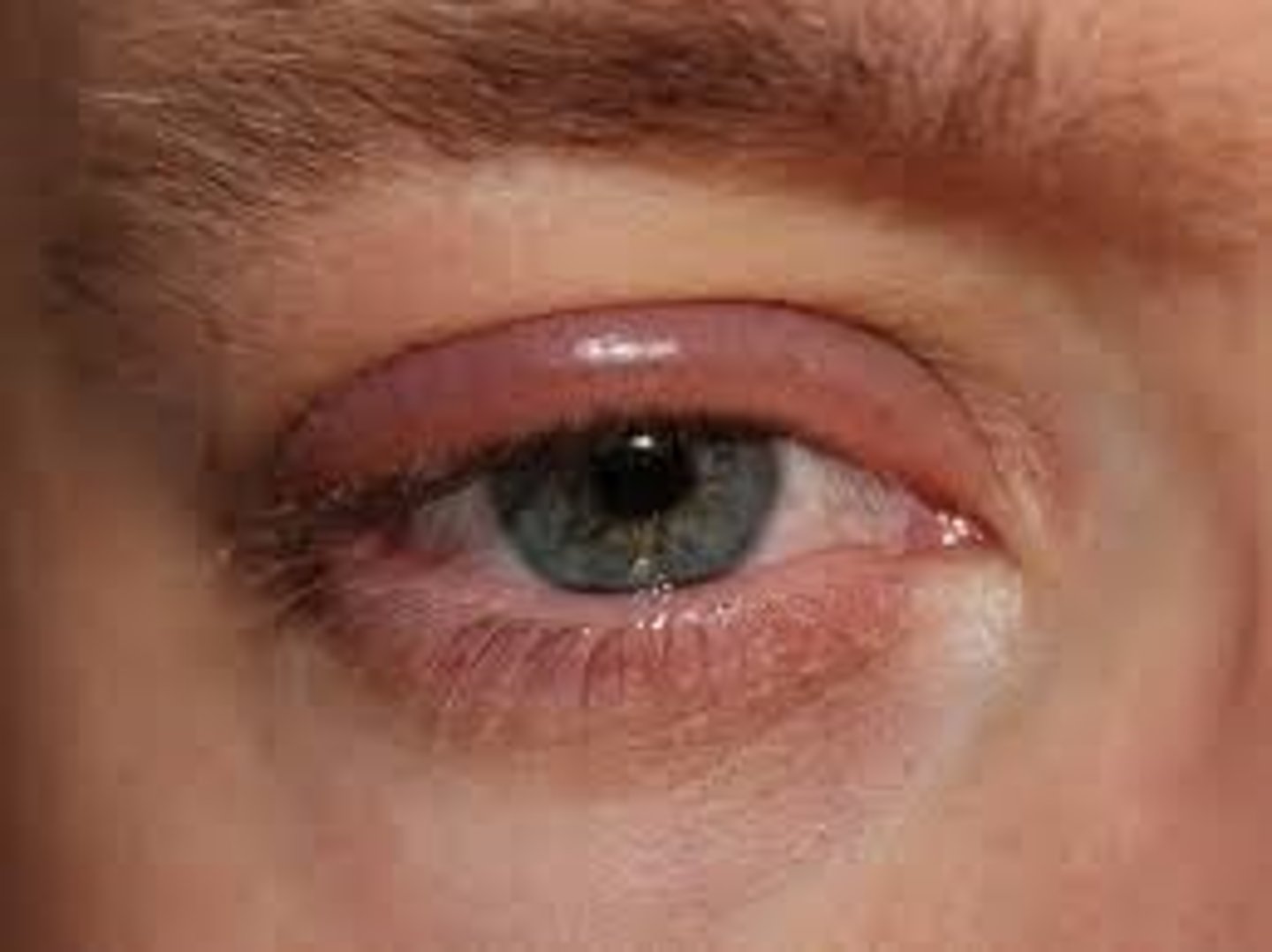
Blepharitis
inflammation of the eyelid
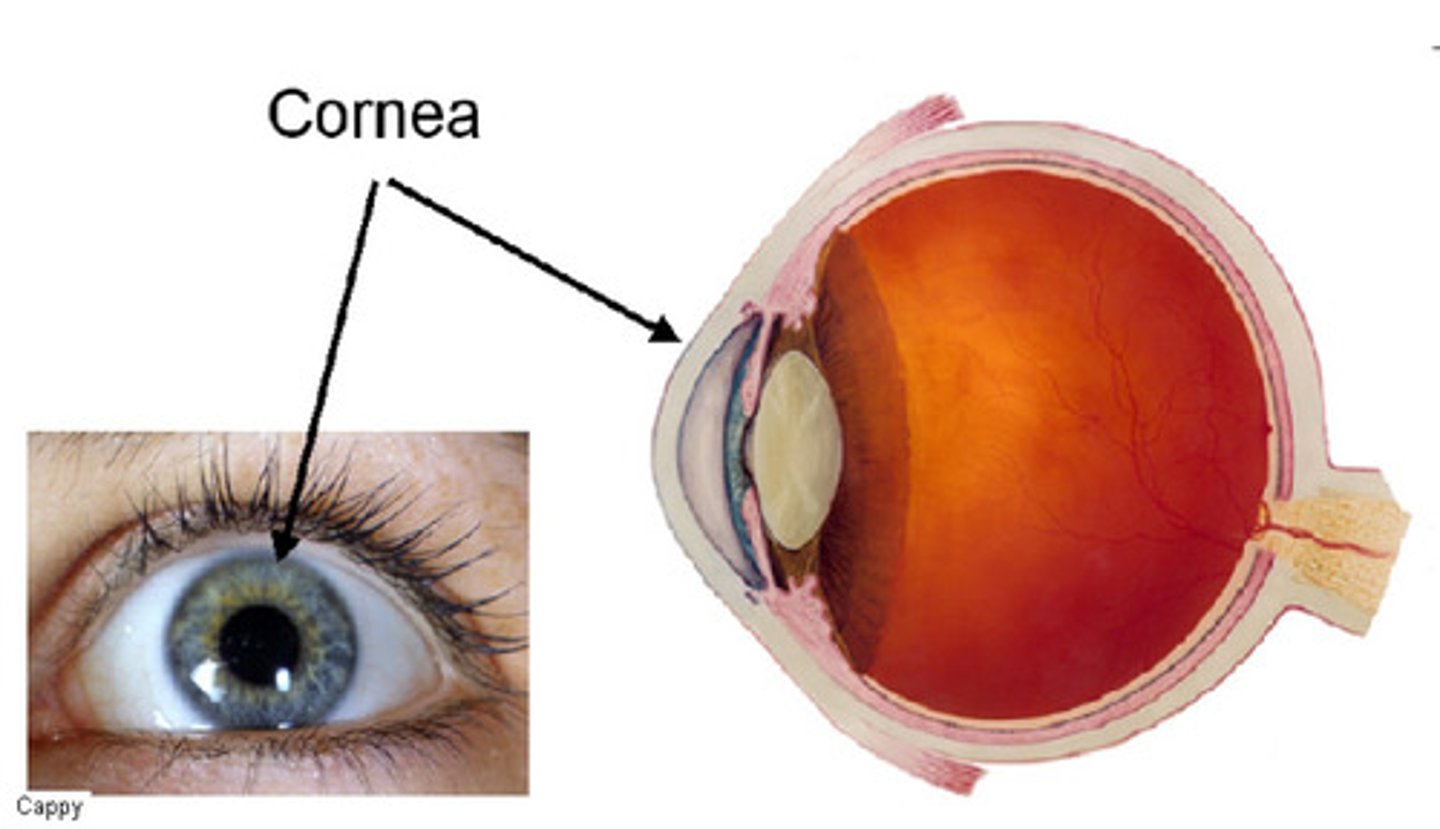
Keratitis
inflammation of the cornea
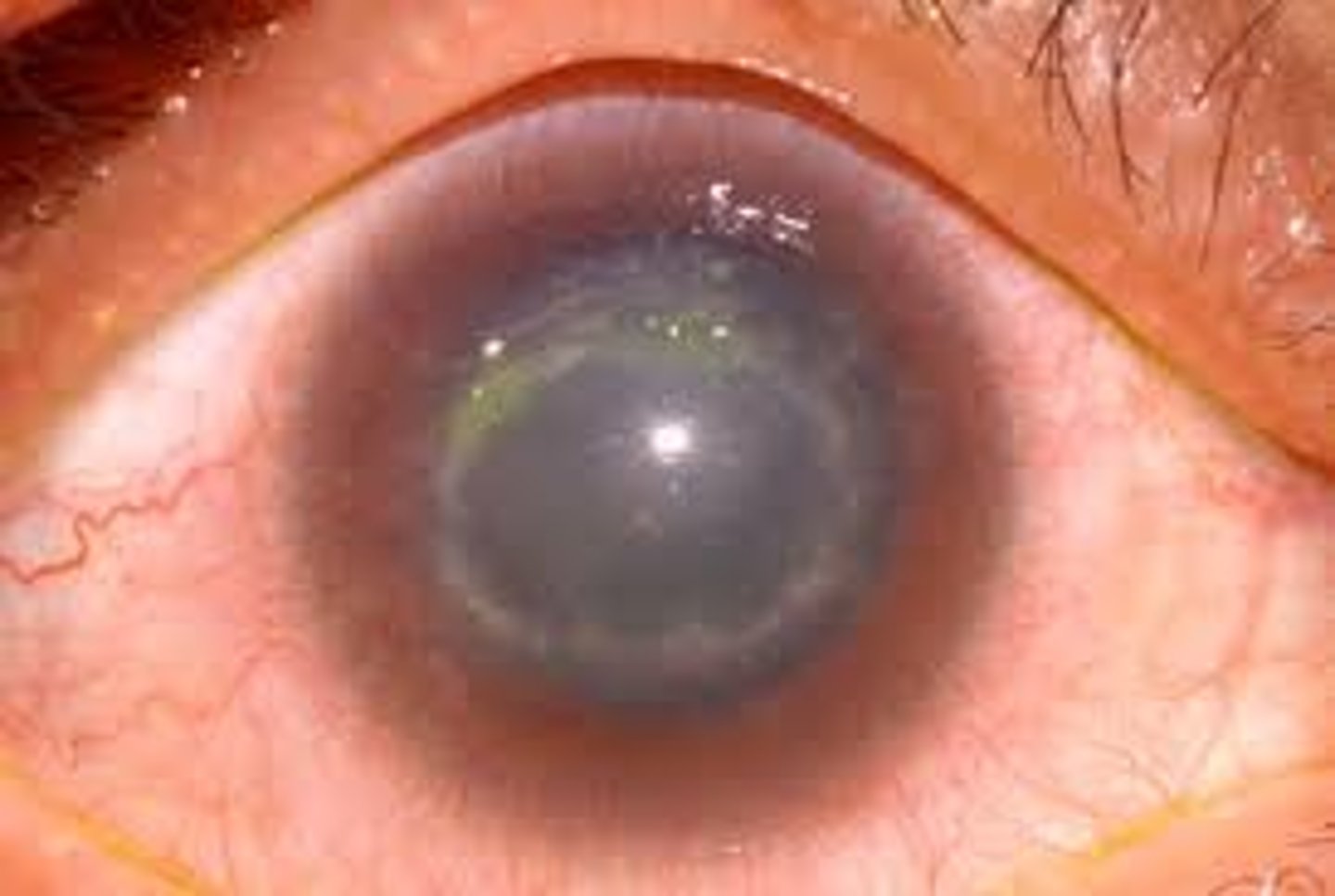
Bacterial Keratitis is most frequently caused by __________________ or ___________________
S. epidermidis, P. aeriginosa
Ophthalmia neonatorum
conjuctivitis of the newborn. Neisseria gonorrhoeae present in the birth canal infect the eyes of the baby. Silver nitrate or tetracycline is used for treatment.
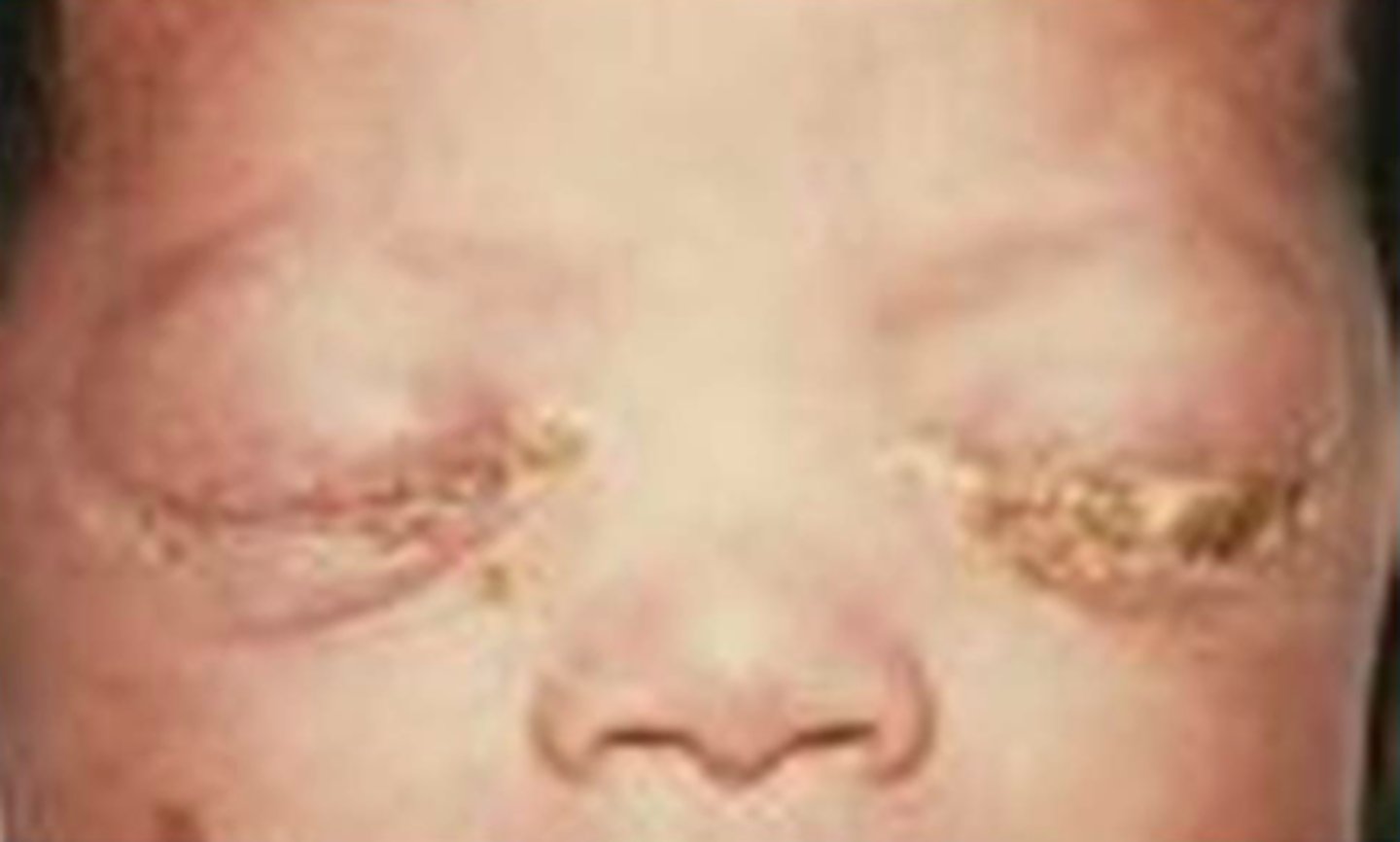
Chlamydia trachomatis (neonates)
causes inclusion conjunctivitis in neonates, transmitted during birth
Chlamydia trachomatis
causes trachoma or granular conjunctivitis
What disease is the leading cause of blindness worldwide?
Chlamydia trachomatis
What microbe causes the STD lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) and is common on college campuses?
Chlamydia trachomatis
Trichiasis
condition caused by eyelashes growing backward and coming in contact with the eye
Meningies
protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord
What are the three layers of meninges?
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
Dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
Arachoid mater
middle layer of the meninges
Subarachnoid space
a space in the meninges beneath the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Pia mater
Innermost layer of the meninges
Meningitis
inflammation of the meninges
Encephalitis
inflammation of the brain
Meningoencephalitis
inflammation of the meninges and brain
Bacterial Meningitis symptoms
Fever, headache, and stiff neck
Followed by nausea and vomiting
May progress to convulsions and coma
How is bacterial meningitis diagnosed?
gram stain and latex agglutination of CSF
_______________ and ______________ are sed to treat bacterial meningitis
Cephalosporins, Vancomycin
Neisseria meningitis is also called ____________ meningitis
meningoccocal
What percentage of people are healthy nasopharyngeal carriers of Neisseria (meningococcal) Meningitis?
10%
Vaccination (B, C, Y, W-135 capsule) is recommended for college students for which disease?
Neisseria (meningococcal) Meningitis
Streptococcal Pneumonia Meningitis is also called...
pneumococcal meningitis
What bacteria causes pneumococcal meningitis?
Streptococcus pneumoniae
What percentage of people are healthy nasopharyngeal carriers of pneumococcal meningitis?
70%
PCV13
pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
Haemophilus influenzae Meningitis
Occurs mostly in children (6 months to 4 years)
Gram-negative aerobic bacteria, normal throat microbiota
Hib Vaccine
Prevents Haemophilus influenzae meningitis
Tetanus is caused by...
Clostridium tetani
Characteristics of Clostridium tetani
gram +, endospore forming, obligate anaerobe
Tetanospasmin (lockjaw)
neurotoxin produced by clostridium tetani that causes rigid muscle paralysis
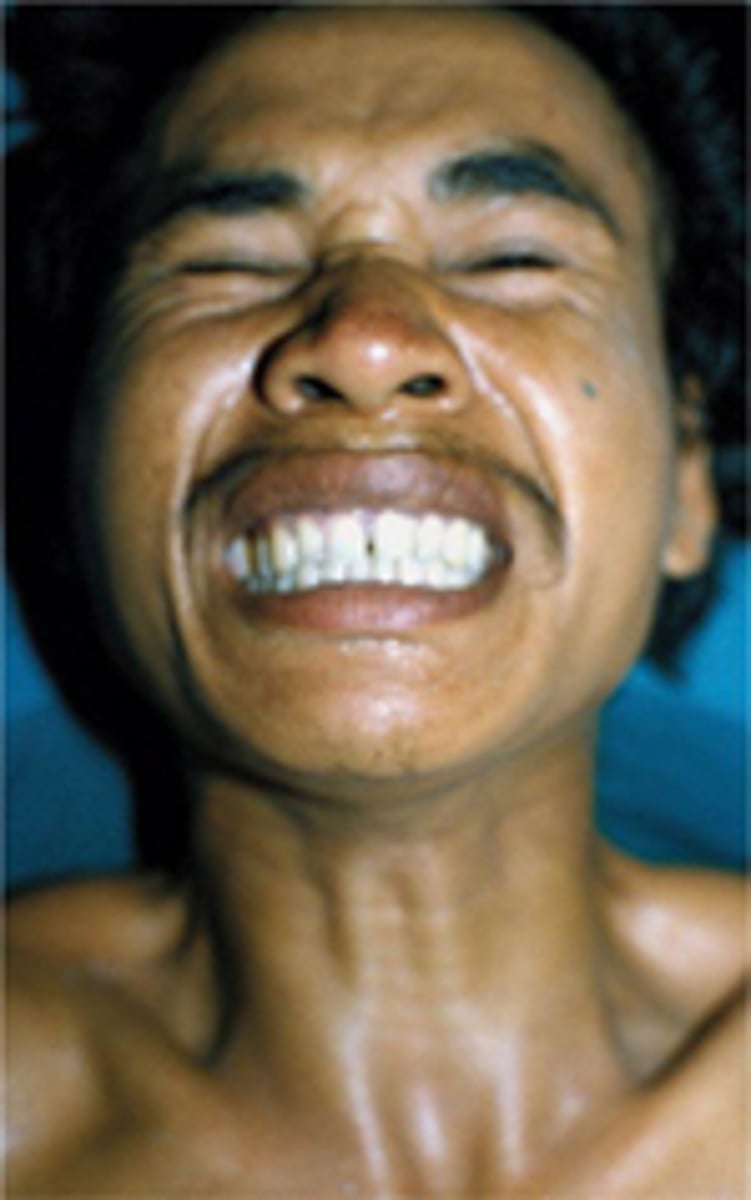
Tetanus toxoid (DPT)
vaccine that prevents tetanus
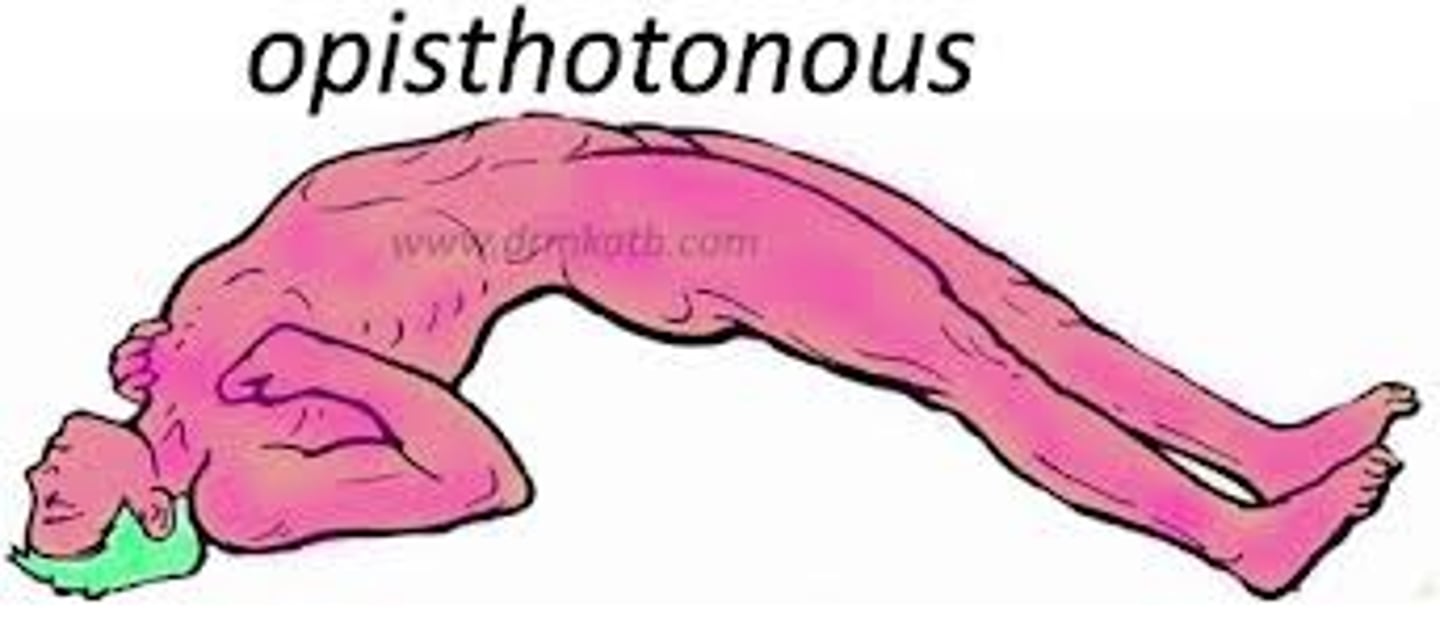
Opisthotonos
tetanic spasm in which the head and tail are bent dorsally and the back is arched
Clostridium botulinum causes...
botulism
Botulism intoxication comes from...
ingesting botulinal toxin
Botulinal toxin blocks release of neurotransmitter, causing ______________ ________________
flaccid paralysis
Two prevention methods for botulism
proper canning and Nitrites
Infant Botulism
C. botulinum growing in the intestines of infants due to a lack of intestinal microbiota
Associated with honey
Wound botulism
growth of C. botulinum in wounds
HSV-2
genital herpes
Which of the viruses can spread to the eye to cause keratitis?
HSV-1
What does it mean to say that HSV-1 is often latent?
it undergoes periods of inactivity when it resides in the trigeminal nerve ganglia and does not cause symptoms
Cornea
The clear tissue that covers the front of the eye
Trachoma or Granular Conjunctivitis affects what age group?
Adults
What age is pneumococcal meningitis most common in?
1mo-4 years
What age group does haemophilus influenzae meningitis effects?
6mo to 4 years
DPT vaccine
diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus
DPT vaccine
diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus