Exploring Atomic Models and Theories in Science
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Dalton's Atomic Theory
He pictured atom as solid, indestructible with a mass like a billiard ball. His contribution: foundation of modern physical science.
Dalton's Atomic Theory Postulates
Matter is made of small, indivisible atoms. Elements have identical atoms, different from other elements. Compounds contain atoms in fixed ratios. Chemical reactions rearrange atoms, no creation or destruction.
Joseph John Thomson
Experimented with a vacuum tube. Discovered the negatively charged electron using the cathode ray tube.
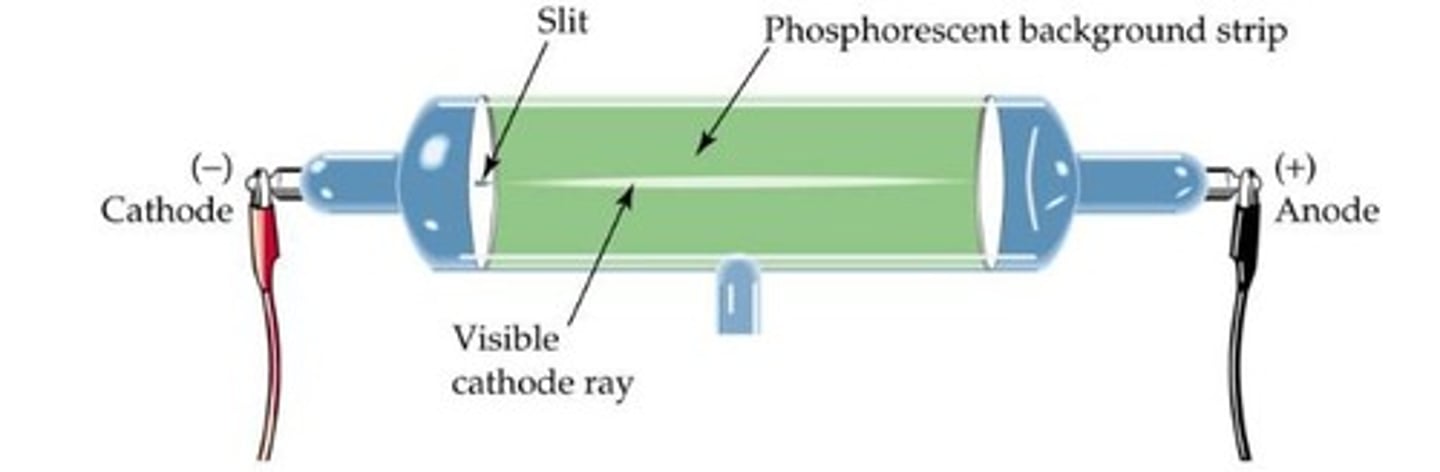
Joseph John Thomson's Theory
Proposed that atoms consist of subatomic particles with electric charges. Described the electron as embedded in a positively charged mass, like raisins in bread.
Ernest Rutherford
Tested Thompson's theory using a thin sheet of gold foil. Discovered that most α (alpha) particles passed through the foil, while some were deflected.
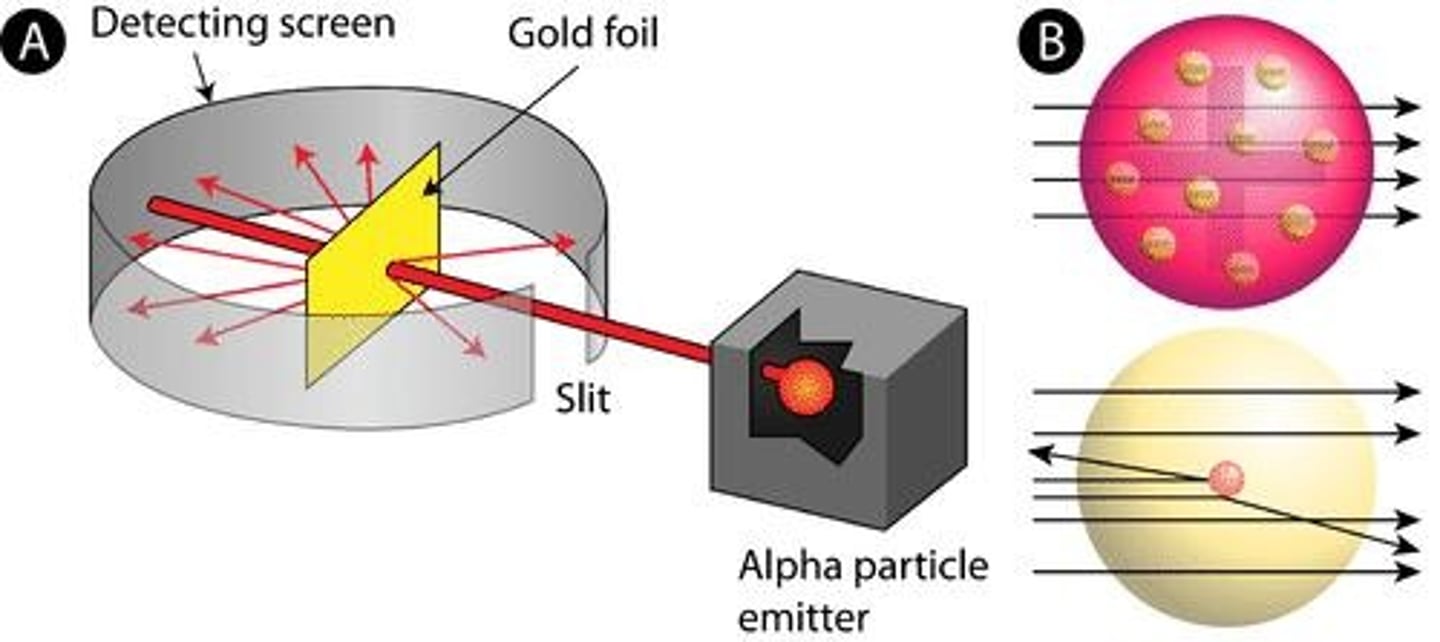
Ernest Rutherford's Conclusion
Concluded that atoms are mostly empty space with a positive nucleus. Coined the term 'nucleus' for the central core of an atom.
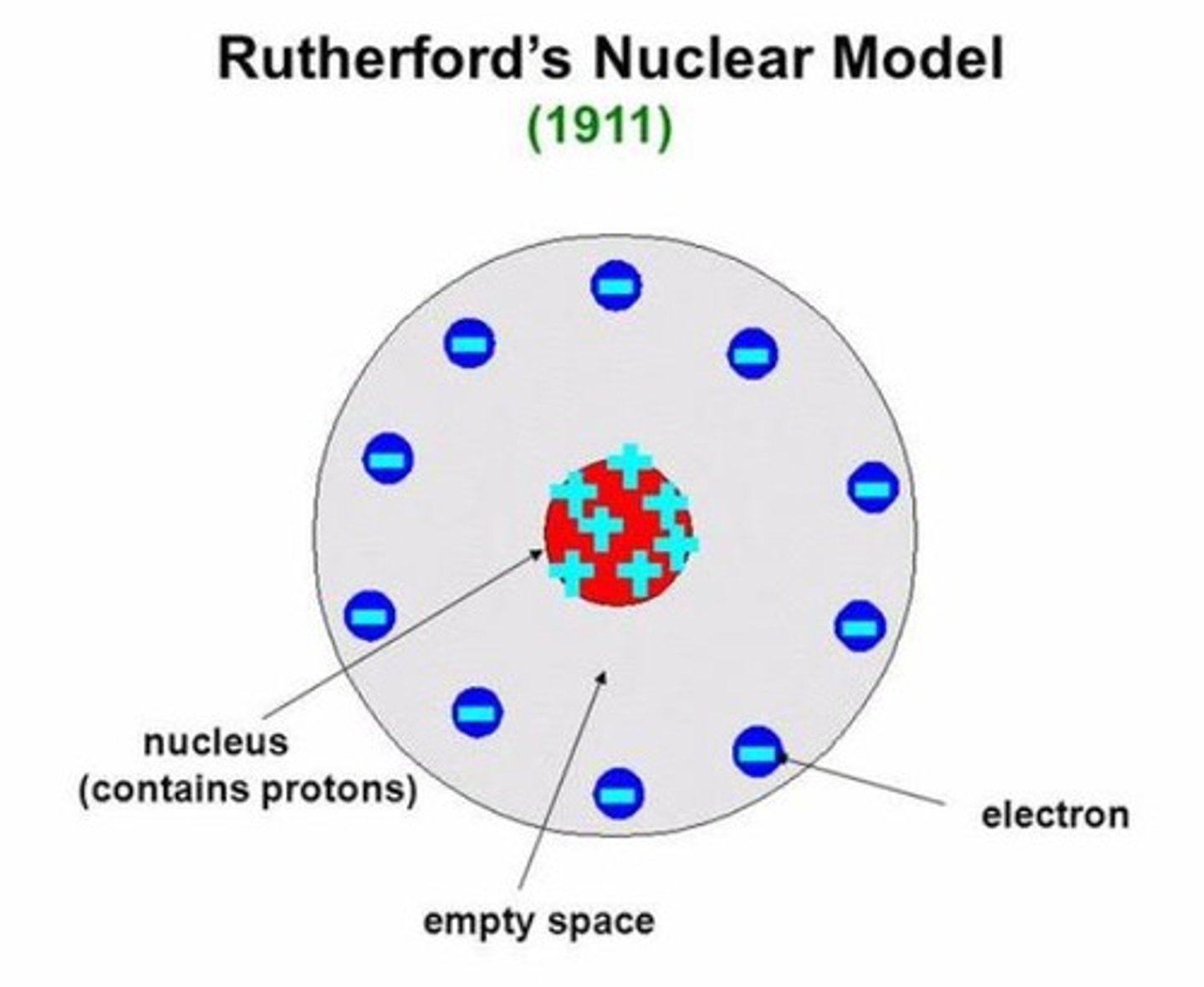
Ernest Rutherford
Proposed a model where electrons orbit the nucleus, resembling a miniature solar system.
Nuclear Model of an Atom
Called the nuclear model due to the discovery of the nucleus.
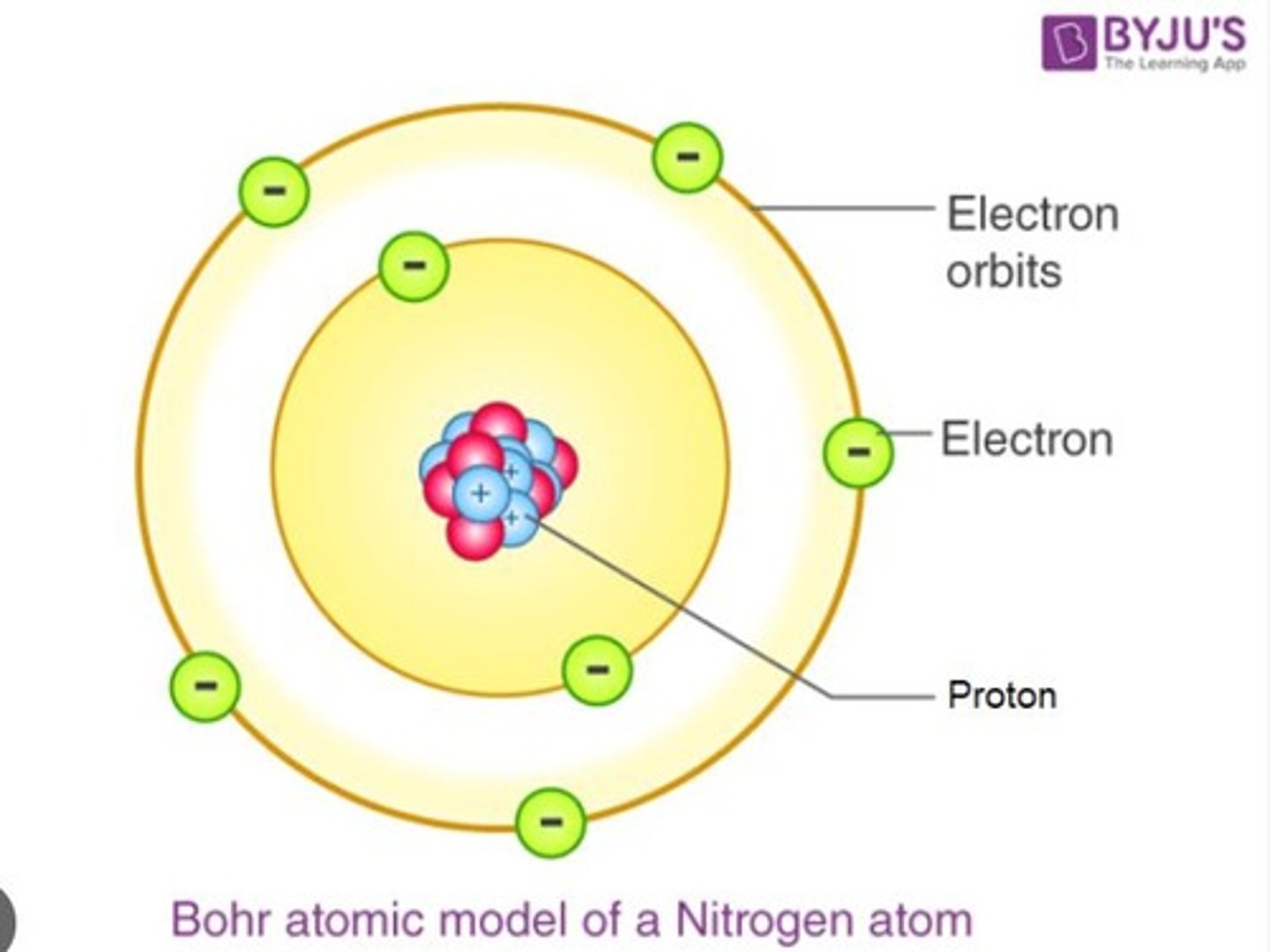
Niels Bohr
Danish Physicist who proposed that electrons in an atom can travel in specific orbits without radiating energy.
Quanta
Discrete energy packages that electrons can gain or lose to change orbits.
Planetary Model of an Atom
Explains the stability of atoms by incorporating Max Planck's quantum theory.
Energy Loss in Rutherford's Model
Addressed by Niels Bohr in his atomic model.
Restricted Orbits
Electrons can travel around the nucleus without radiating energy, provided they remain in certain restricted orbits.
Bohr-Sommerfeld Atomic Model
Enhanced Bohr's original model by introducing the concept of elliptical orbits.
Arnold Sommerfeld
German theoretical physicist who contributed to the Bohr-Sommerfeld model.
Elliptical Orbits
Electrons move in elliptical, rather than circular orbits, as introduced by Sommerfeld.
Bohr-Sommerfeld Atomic Model
This atomic model expanded upon the Bohr model and introduced the concept of elliptical orbits for electrons.
Nuclear Model of an Atom
Ernest Rutherford's atomic model, which is based on the discovery of the nucleus.
The Discovery of the Electron
The main discovery of J.J. Thomson's experiments with cathode rays.
Niels Bohr
Whose atomic model introduced the concept of electron energy levels or shells.
John Dalton
According to this physicist, atoms are indivisible and cannot be broken down into smaller parts.
Planetary Model of an Atom
Another name for Niels Bohr's atomic model.
Dalton's Atomic Theory
The theory that describes atoms as indivisible particles.
Joseph John Thomson's Theory
Also known as the Raisin Bun Model.
Ernest Rutherford
Physicist known for the Nuclear Model of an Atom.