Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PEBC
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
HSV
causes cold sores and genital herpes
2 types:
HSV-1:
Causes Herpes labialis (oral cold sores)
transmitted via saliva through oral to oral contact OR through oral to genital contact
HSV-2:
causes genital herpes
transmitted via sexual contact through contact with genital surfaces, skin, sores or fluids of infected individual
Asymptomatic viral shedding = pt can be asymptomatic and shed the virus unknowingly
HSV stays in the ganglia —> lifelong latency and recurrence
can be reactivated any time
assessment
Primary infection
1st episode with no antibodies for HSV present
may be asymptomatic or present as more severe disease
longer duration (7-18 days) and more severe signs and symptoms (fever, swollen lymph nodes, flu like)
Non-Primary infection
1st episode in patient who HAS ANTIBODIES for 1 type of HSV and acquires the other type of HSV
shorter duration and less severe signs and symptoms than primary infection → due to partial protection of antibodies
Recurrent Episode:
latent HSV reactivated (recurrence greater with HSV2)
less severe than primary and non-primary
prodromes = tingling, itching, pain prior to symptoms
clinical presentation
severity of sx depend on:
previous exposure = primary, nonprimary, recurrent
type of virus: HSV-1, HSV-2
site of infection: oral, genital, ocular, nervous system
immune status: immunocompromised
complications
herpes gladiatorum = skin infection
herpetic whitlow = finger infection
keratoconjunctivitis = conjunctival infection
herpes encepahilitis = neurological effects
risk factors
RF:
physical contact with infected person
kissing
sexual contant
sharing utensils (cold sore)
multiple sexual partners
Female
immunocompromised
recurrence triggered by:
stress/ fatigue
infection/ fever
immunosuppression
hormonal changes
menstruation
physical trauma/ dental extractions/ surgery
sun exposure
temperature extremes
HSV1 (herpes labialis)
cold sore or fever blister
diagnosis = clinical presentation of lesion
no cure or treatment to eradicate
lays dormant in ganglia until recurrence
begin treatment when prodrome sx occur
takes 1-2 weeks for cold sores to fully resolve w/o therapy
referral:
immunocompromised
patients with recurrent, persistent cold sores (≥6x/yr)
moderate to severe primary infection (systemic symptoms)
lasts >2 weeks
signs of secondary bacterial infection
treatment is most beneficial if started early: within 48 hrs of symptom onset
clinical presentation (cold sore: primary infection)
1st infection = primary herpes gingiovostomatitis
lasts 1-3 weeks
asymptomatic (commonly)
symptoms:
painful blisters around mouth (can crack, release clear, sticky liquid and then crust over)
Lymphadenopathy
red, swollen gums
sore throat
systemic fever, malaise, myalgia
clinical presentation (recurrent infection cold sores)
recurrent infection → reactivated
lasts 8-10 days
asymptomatic shedding
prodrome sx = tingling, itching, burning before blisters and sores
signs and symptoms:
painful blisters around the mouth area
red and erythematous base
goals of therapy
Minimize pain or discomfort
minimize the duration of lesions and viral shedding
prevent autoinoculation —> you can transmit to yourself so dont touch it
prevent recurrences
prevent transfer of virus
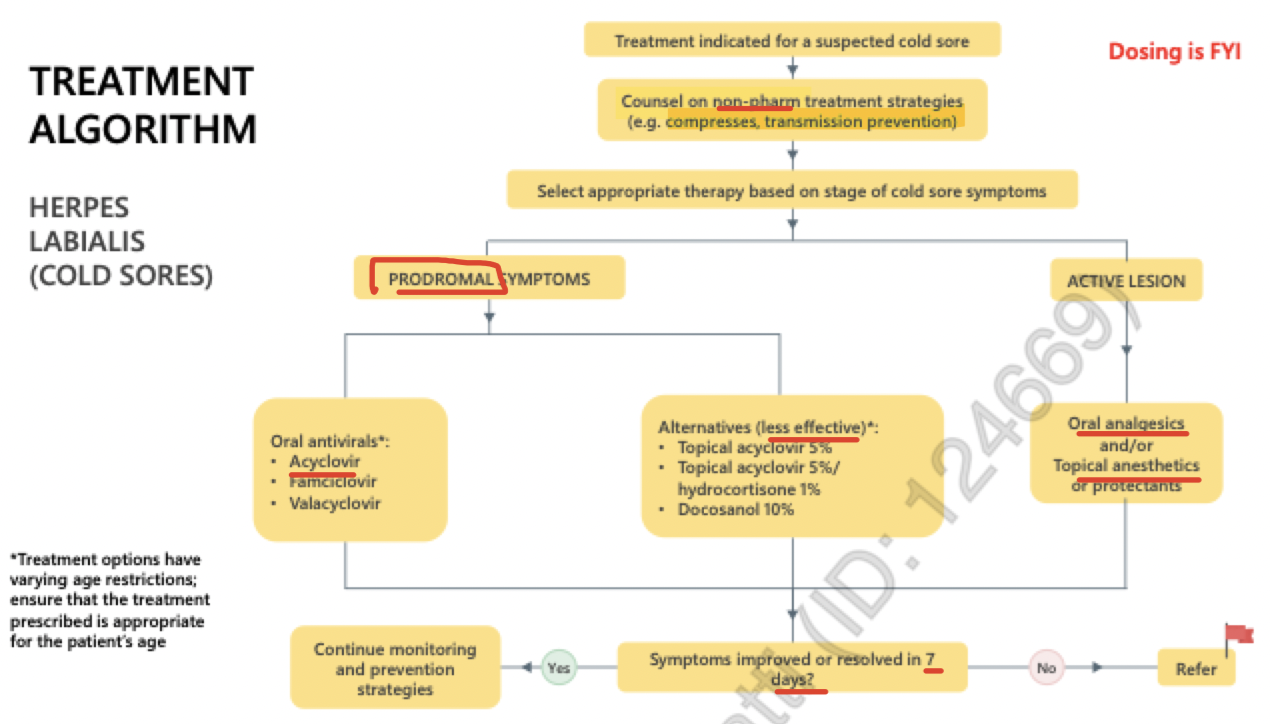
algorithm (cold sores)
Primary infections are treated longer
Recurrent infections are higher doses but shorter durations
Acyclovir is the active drug!! Valacyclovir and Famiciclovir are prodrugs so they are metabolized into acyclovir
Due to increase in bioavailability! And need less frequent dosing
non pharm (cold sores)
Prevention:
reduce stress (if trigger)
prevent sun induced recurrences → use sunscreen with SPF 30+ on affected areas
freq wash hands to prevent transmission of virus
avoid skin to skin contact until blister dried up and crusted over
clean area with soap and water
cool or warm compresses
cool = reduce inflammation
warm = relieve pain
topical protectants prevent blisters from drying out and breaking
petrolatum
cocoa butter
calamine
prevent autoinolculation
avoid oral sex, kissing and touching lesions until lesions competely healed
freq wash hands
OTC treatment (cold sores)
Antiviral = Abreva (Docosanol cream)
prevents HSV from spreading to healthy cells
apply at first sign of pain, itching, burning, redness or tingling
may decrease duration of painful symptoms and time to healing by 17-79 hrs
Pain relief/ protectants
mod - severe pain = acetaminophen or NSAIDs
Mild pain:
benzocaine (anbesol)
lidocaine/ prilocaine (EMLA)
camphor, menthol (blistex, anbesol cold sore)
lidocaine
pramoxine ← VERY GOOD
Zinc sulfate/ Heparin sodium (Lipactin)
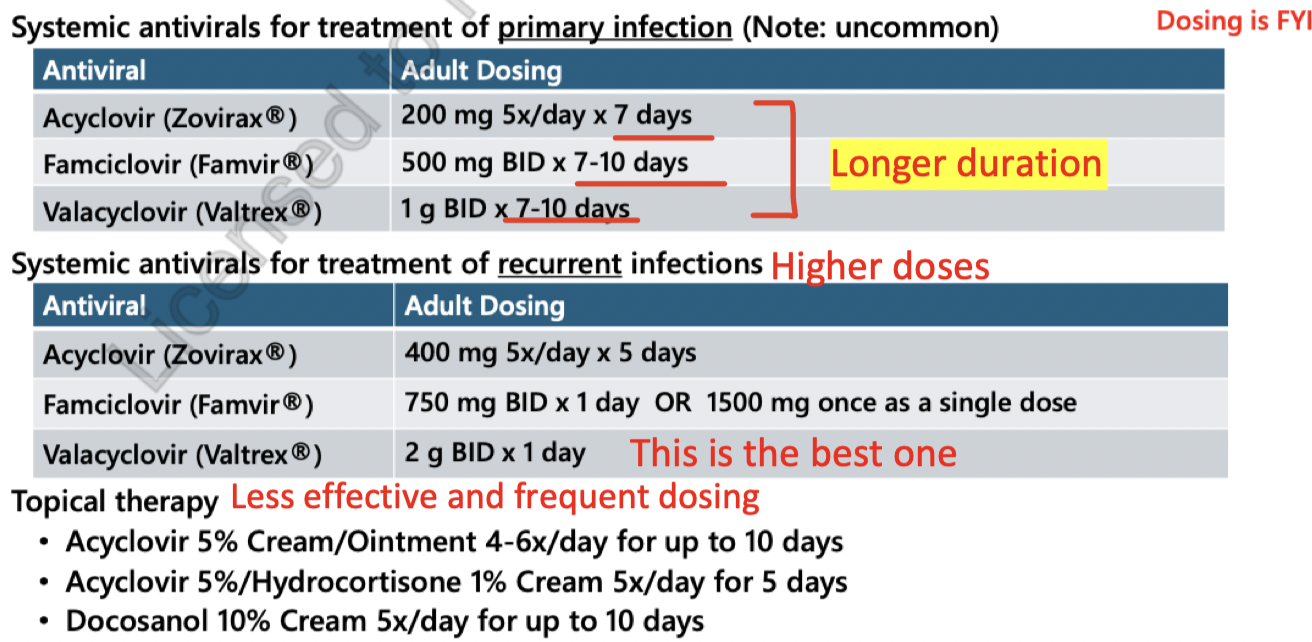
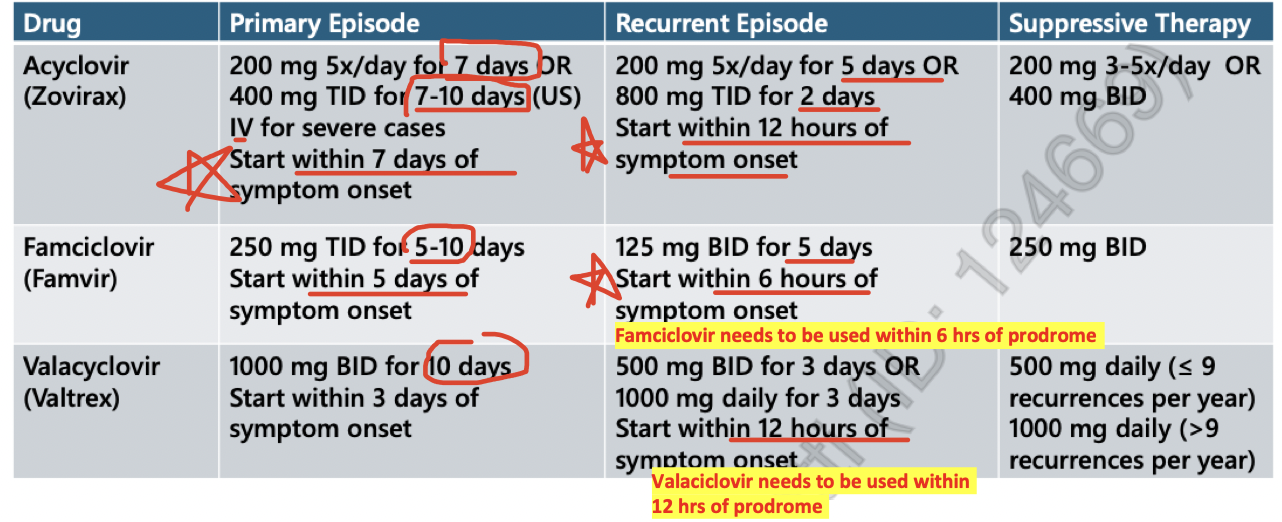
primary infection treatment (cold sore)
acyclovir = 200 mg 5x/day x 7 days
famicyclovir = 500mg BID x 7-10 days
Valacyclovir 1g BID x 7-10 days
s/e = Headache, nausea.
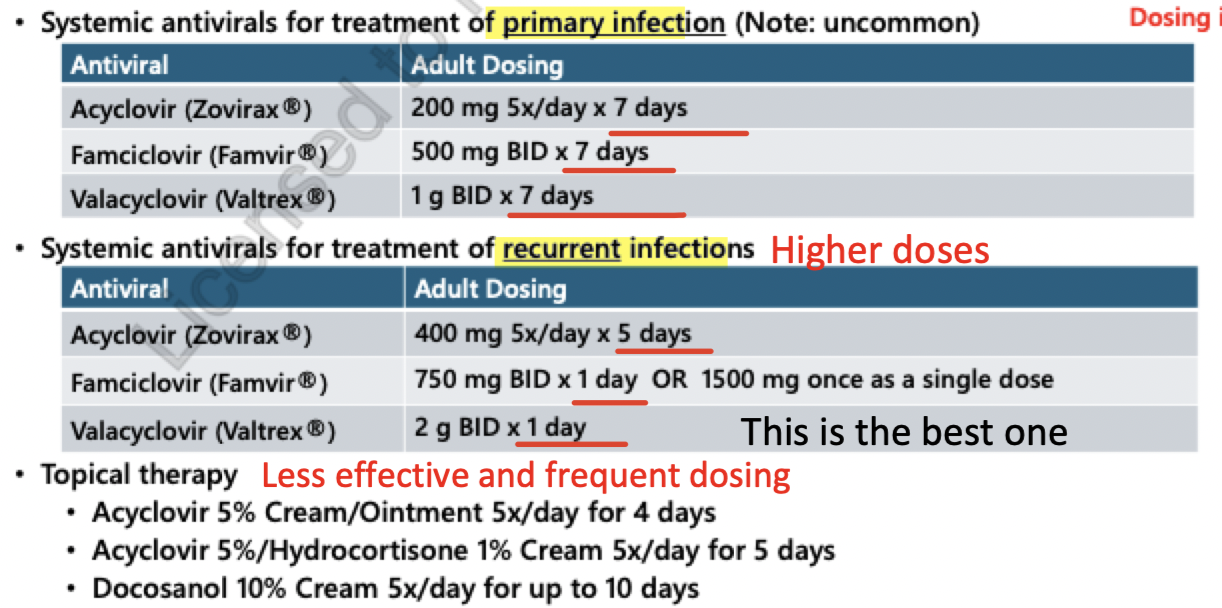
recurrent infection treatment (cold sores)
higher doses and shorter duration
Acyclovir = 400mg 5x/day 5 days
Famicyclovir = 750 mg BID x 1 day or 1500 mg x 1 dose
Valacyclovir = 2g BID x 1 day
s/e = Headache, nausea.
genital herpes
STI
increases the risk of contracting HIV
recurrence more likely to occur with HSV-2 infections
rate of recurrence decreased with increasing age
diagnosis = confirm with lab tests to exclude other STIs (chancroid)
PCR
Viral culture
Serology
clinical presentation (genital herpes)
primary infection
may be asymptomatic or unrecognized by patient
viral shedding lasts 12 days
lesions heal in 2-4 weeks
signs and sx:
painful, pustular lesions
local itching, tingling, pain
dysuria
lymphadenopathy: swollen glands
systemic symptoms = fever, myalgia, malaise
recurrent = milder and shorter duration
viral shedding = 4 days
lesions heal in 7-10 days
begin treatment during prodrome symptoms
suppressive therapy may be indicated if: (re-evaluate yearly)
is experiencing frequent recurrences (≥6 recurrences/yr)
experiencing complications from infection
is serodifferent or has serodiscordant parterns
multiple sexual partners
treatment (genital herpes)
all patients should be treated with antiviral!
primary = longer duration
recurrent = moderate doses and few days
suppressive = low doses
acyclovir = more complicated regimen but les expensive
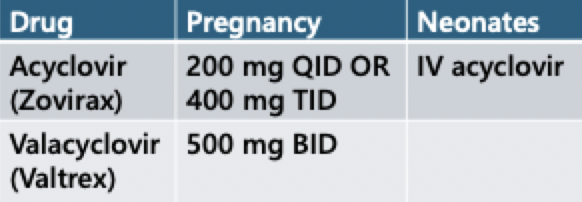
pregnancy
HSV can be transferred to neonate
greatest risk during primary infection = near term
caesarean required if active infection or prodrome symptoms present during delivery
if mother contracts HSV in 2nd and more in 3rd trimester = NEED CAESAREAN section
neonatal HSV = skin, eye, mouth (SEM) disease and can advance to CNS or disseminated disease (risk of morbidity and mortality)
suppressive antiviral management is recommended at 36 weeks
reduce risk of recurrence
c-section not needed
limited data on famiciclovir
CNS HSV
HSV encephalitis/meningitis = medical emergency
typically in elderly, immunocompromised
seizures, personality changes, fever, photophobia
HSV2 meningitis less severe than HSV encephalitis
rapid diagnosis and treatment = essential for reducing morbidity and mortality
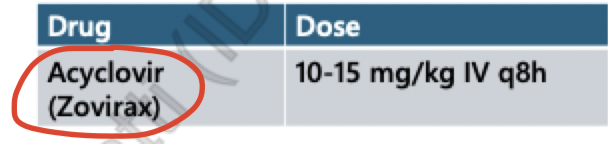
s/e IV Acyclovir:
injection site pain
nephrotoxicity
nausea
headache
IV acyclovir = drug of choice
HSV encephalitis = IV x 14-21 days
HSV meningitis = po x 10-14 days