Economics: Scarcity, Opportunity Cost, and Trade-offs
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is economics?
The study of human choices in a world of scarcity, where resources are limited.
What does scarcity mean?
Not enough resources to satisfy all of society's wants.
What is a resource in economics?
An input used to produce goods and services, including natural, physical, human, and time.
Give an example of scarcity in the Western United States.
Regular droughts and high demand have made water very scarce.
What is the 'tragedy of the commons'?
A situation where individuals overconsume a shared resource, leading to its depletion.
What is the difference between scarcity and shortage?
Scarcity is a natural fact of limited resources, while a shortage is a market phenomenon where demand exceeds supply at current prices.
What is opportunity cost?
The value of the next best alternative when making a decision.
What happens when demand is greater than supply at the current price?
A shortage occurs, which can be addressed by increasing prices.
Why is the concept of scarcity important in economics?
It forces individuals and societies to make choices about resource allocation.
How does urbanization affect resource scarcity?
It increases demand for resources like water, leading to greater scarcity.
What is a common misconception about scarcity?
That scarcity can be resolved simply by increasing prices, which is not true as it is a natural limitation.
What should each person produce to maximize efficiency?
The good with the lowest opportunity cost.
What is specialization in economics?
The practice of focusing on a specific task or good to maximize productivity.
What is comparative advantage?
The ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than others.
What is the division of labor?
Breaking a large task into smaller tasks completed by specialists to increase efficiency.
What are economies of scale?
The reduction in average cost of production as the volume of production increases.
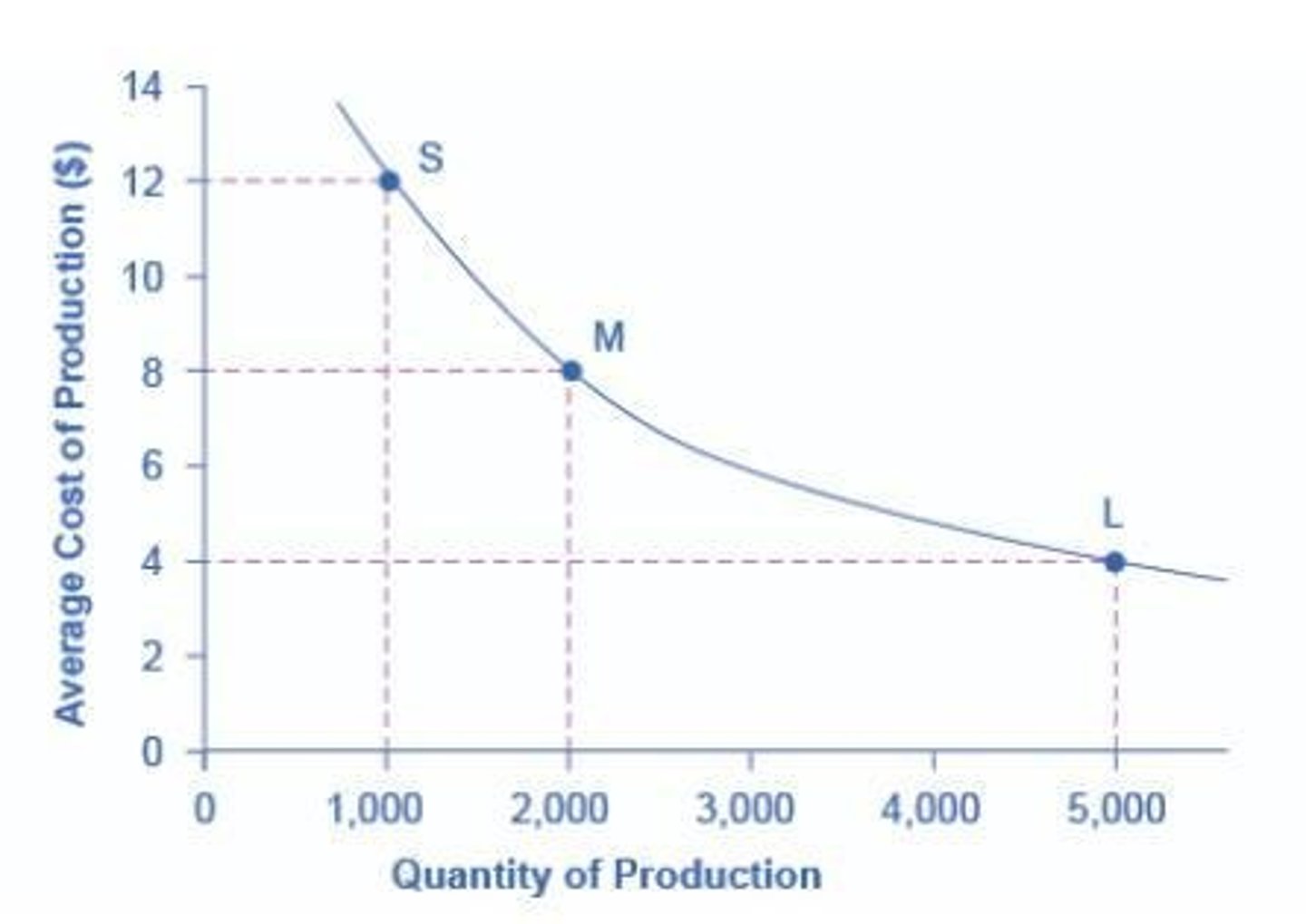
What are the three main reasons for economies of scale?
1. Learning by doing, 2. Bulk purchases of materials, 3. Technical improvements in production.
How does international trade relate to opportunity costs?
It allows everyone to specialize in their most efficient tasks, minimizing opportunity costs.
What are the winners of international trade?
1. Efficient industries gaining access to more markets, 2. Consumers facing lower prices and more options.
Who are the losers of international trade?
1. Inefficient industries losing business to foreign competitors, 2. Workers in those industries losing jobs.
What is allocative efficiency?
When the goods produced meet the needs of the economy (quantity supplied = quantity demanded).
What is productive efficiency?
The maximum level of production is reached using all available resources.
What are the three broad types of economic systems?
1. Market economies, 2. Command economies, 3. Mixed economies.
How are resources allocated in a market economy?
According to the price system, where prices indicate supply and demand.
What happens at an equilibrium price?
Consumers want to buy the exact amount provided by suppliers.
What characterizes a command economy?
A central government dictates all aspects of the economy and allocates resources.
What is a mixed economy?
An economy that allocates some goods through government provision and others through the market.
What is a market failure?
When markets do not reach efficient outcomes, often due to pollution, underproduction, or imperfect competition.
How can government intervention help in market failures?
By regulating to correct inefficiencies such as pollution or monopolistic practices.