KIN 167 Midterm 1 Review
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
What is sports psychology (SP)?
The study of people and behaviors within the context of sports and exercise
What are the roles of SP?
Teaching
Research
Consulting
What are the applied roles of SP?
Clinical sport psychology
Educational sport psychology
Define clinical sport psychology. Give one example.
A licensed psychologist who can detect and treat individuals with emotional disorders (i.e., depression, substance abuse, eating disorders)
Define educational sport psychology. Give one example.
A "mental coach" who educates athletes and exercisers about psychological skills and their development (i.e., anxiety management, improved communication, confidence development)
Which psychologist was interested in why cyclists rode faster in groups?
Norman Triplett
Who is the "father of american SP"?
Coleman Griffith
Who developed the 1st SP lab?
Coleman Griffith
Which psychologist developed the scientific SP?
Franklin Henry
Who was the first woman in SP to do both research and applied work?
Dorothy Yates
Which psychologist worked with relaxation techniques with boxers at SJSU?
Dorothy Yates
Who is the "Father of North American applied SP"?
Bruce Ogilvie
Dorothy Harris
1st American and 1st female member of ISSP
1st women awarded Fulbright Fellowship in SP
1st female president of NASPSPA
What is ISSP?
International society of SP
What is NASPSPA?
North American Society for the Psychology of Sport and Physical Activity
What is AAASP?
Association for the advancement of applied SP
What is APA?
American Psychological Association
What are the ethical SP standards?
Competence
Confidentiality
Integrity
Professional practice and scientific responsibility
Concern for the welfare of others
Social responsibility
Name the trends in the field of sport and exercise psychology
More graduate and undergraduate programs
More consulting opportunities
Greater emphasis on counseling and ethical training
Ethical issues
Specialization
Tension between academic SP and applied SP
Increase in qualitative research
Positive psychology (focus on a person's strengths)
Cultural SP
Multidisciplinary research
Technology
What is Psychological Skills Training (PST)?
the systematic and consistent practice of mental or psychological skills for the purpose of enhancing performance, enjoyment, and satisfaction
What are the 4 aspects of applied PST?
Mental
Technical
Tactical
Physical
What happens if an aspect is not fully devleoped?
Performance is off balance and not at its highest level
What are the myths of PST?
For "problem" athletes, only
For the elite and rich athletes
Quick fix
Not useful because its not scientific
Why is PST often neglected?
Lack of knowledge
Lack of time
Misunderstanding/trust
What are the phases of a PST program?
Education
Acquisition
Practice
What is self-regulation in PST?
Ability to work toward a person's short or long-term goals by effectively monitoring and managing one's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
What are the stages of self-regulation in PST?
Problem identification
Commitment to change
Execution
Environmental management
Generalization (sustaining efforts over time)
Which is the primary stage of self-regulation in PST?
Execution
When is the most effective time to implement a PST program?
During the off-season
3x week, 10-15 min meetings
Identify the vast array of psychological skills related to sport performance
Foundation skills
Performance skills
Personal development
Team skills
What are the common problems implementing a PST program?
Lack on conviction
Lack of time
Lack of sports knowledge
Lack of follow-up
What is outcome goals?
Result of event, but depends on the opponent's behavior
What is performance goals?
Achieving performance objects independently from other competitors
What is process goals?
Actions one must do to achieve performance goal
Identify numerous priniciples of effective goal setting
Set specific goals
Moderately difficult
Short and long term goals
Performance, process, and outcome goals
Record goals (strengthen goals)
Practice goal support
Provide feedback
Set mastery-approach goals
What is the first stage to design a goal setting system?
Preparation and planning
What is the second stage to design a goal setting system?
Education and acquisition
What is the third stage to design a goal setting system?
Implementation and follow up and eval
What are SMART goals?
Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, Timely
Identify common problems in goal setting
Being convinced goal setting is worthwhile
Vague goals
Too many goals too soon
Failure to adjust goals
Not recognizing individual differences
Lack of follow-up and eval
Goals unrealistically high or very low
Define arousal
physiological and psychological activations
Define stress
Imbalance between perceived demands and resources
Define anxiety
Negative emotional state characterized by nervousness, worry, and apprehension
Is arousal negative or positive?
Neither
Is stress negative or positive?
Both
Is anxiety negative or positive?
Negative
What are the types of anxiety?
Trait anxiety
State anxiety
Define trait anxiety. Give an example.
Personality and generally more anxious
Example: general anxiety disorder
Define state anxiety. Give an example.
Limited to specific situations
Example: test anxiety
What are the dimensions of anxiety?
Cognitive
Somatic
What is cognitive anxiety? Give an example.
Thoughts
Example: negative self-talk
What is somatic anxiety? Give an example.
Physical
Example: sweaty palms, nausea, fidgety
What are the types of stress?
Distress
Eustress
What is distress?
Negative stress
What is eustress?
Positive stress
What are the stages of stress?
Environmental demands
Perception of demand
Emotional and physical response
Behaviors and Consequences
Define environmental demands stage of stress
Some type of demand that is placed on an individual, demand might be physical or psychological
Define perception of demand stage of stress
Individual's perception of the physical or psychological demand
Define emotional and physical response stage of stress
Stress response of the individual's physical or psychological response to a perception of the situation
Define behaviors and consequences stage of stress
Behavior/outcome of the individual under stress
Identify the various sources of stress
Event importance
Uncertainty
Trait anxiety
Self-esteem
Social physique anxiety
Name of models/theories of arousal/anxiety performance
Drive theory
Inverted U-hypotheses
Catastrophe model
Individualized zone of optimal functions (IZOF)
Multidimensional anxiety theory
Reversal theory
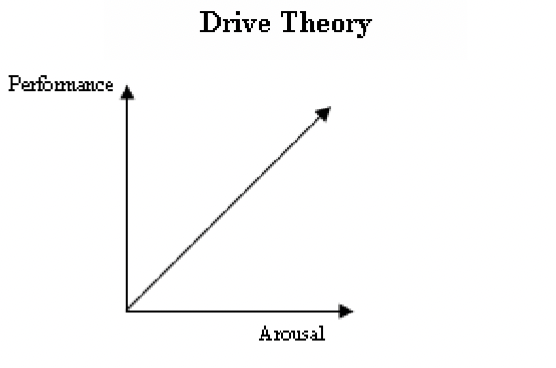
Define the drive theory model
as an individual's arousal or state of anxiety increase, so does their performance
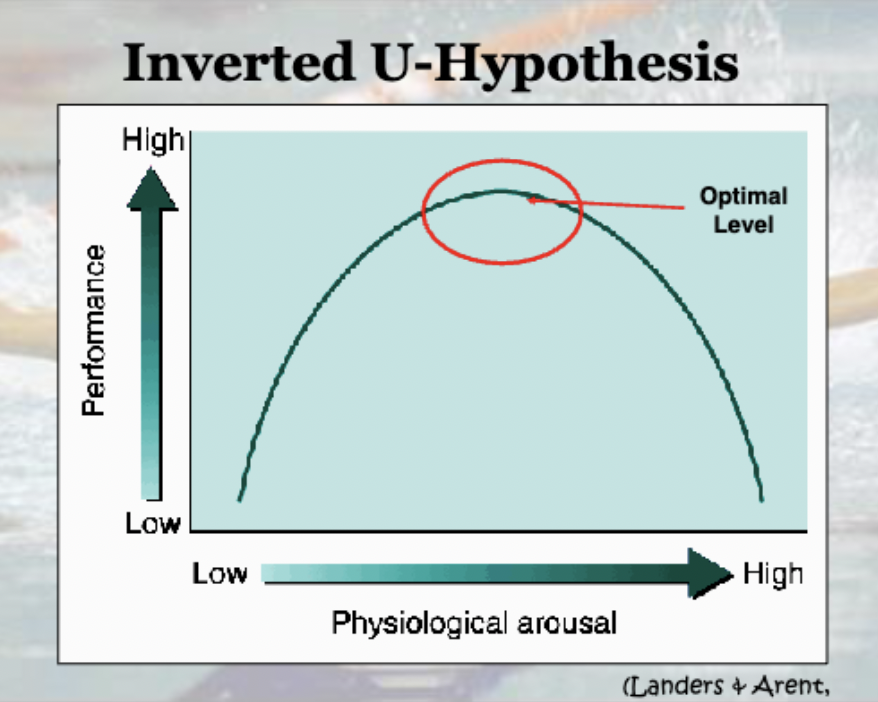
Define the inverted U-hypotheses model
At low arousal levels, performance will be below par; the exerciser is not psyched up.
As arousal increases, so does performance - but up to an optimal point where the best performance results
A further increase is arousal can cause performance to decline
High performance with the optimal level of arousal and lesser performance with either low or high arousal
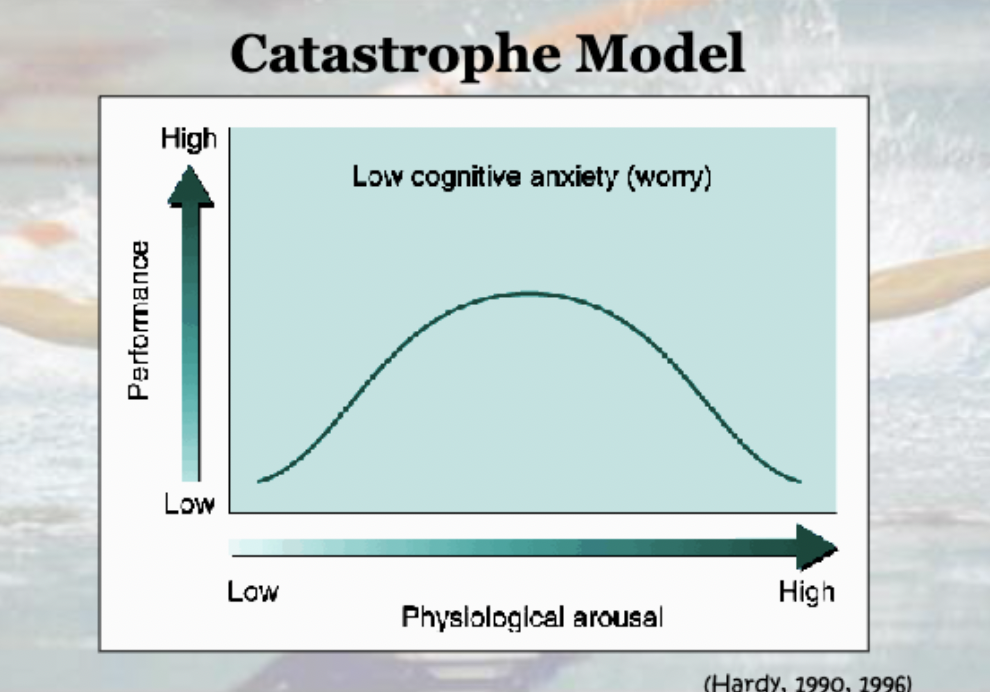
Define the catastrophe model
Predicts that physiological arousal is related to performance in an inverted U fashion, but only when an athlete is not worried or has a low cognitive state of anxiety
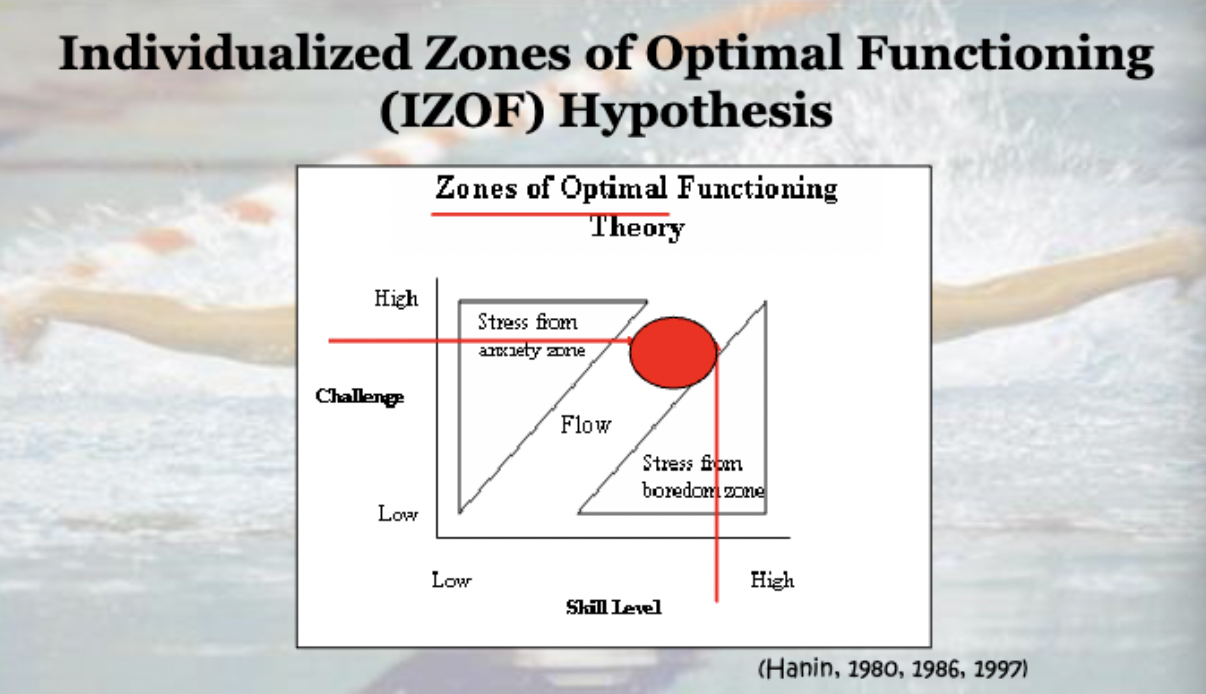
Define the individualized zone of optimal functions (IZOF)
model
Every person had their own optimal level of arousal. Different people perform best at different levels of arousal, and peak performance occurs in a small zone (as opposed to a single point)
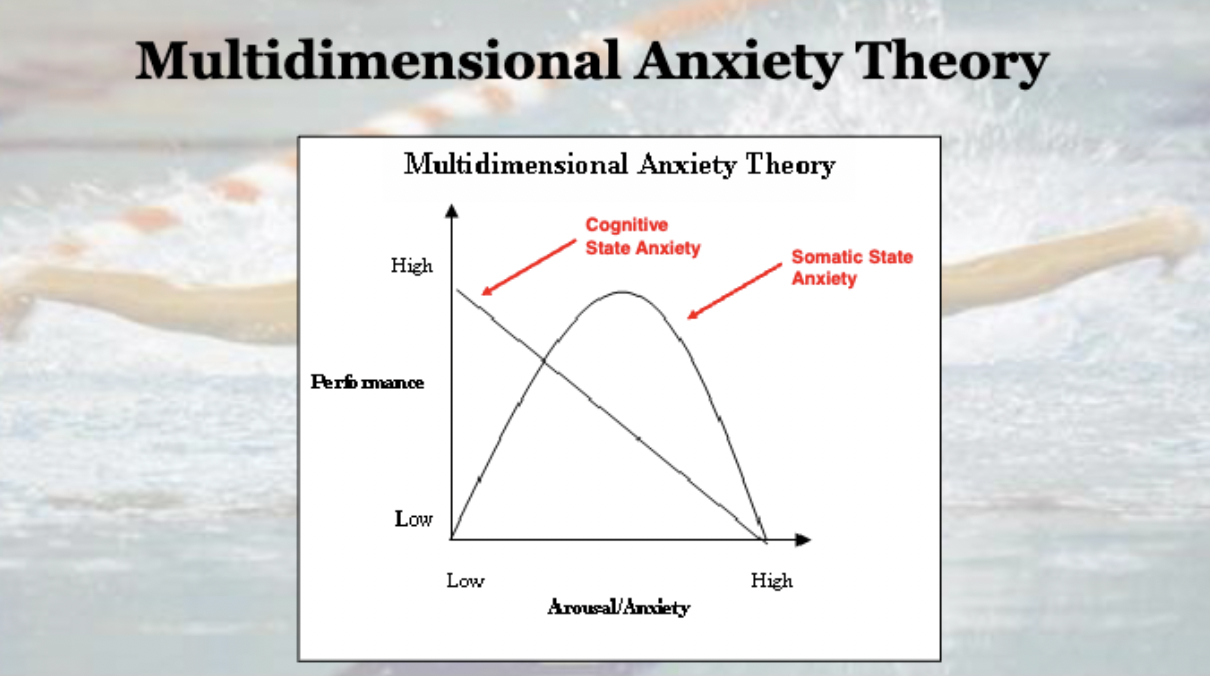
Define the multidimensional anxiety theory model
Predicts that cognitive state anxiety (worry) is negatively related to performance, and an increase in cognitive state anxiety leads to a decrease in performance
Theory predicts that somatic state anxiety is related to performance in an inverted U and that increases in anxiety facilitate performance up to an optimal level, beyond which additional anxiety causes performance to decline
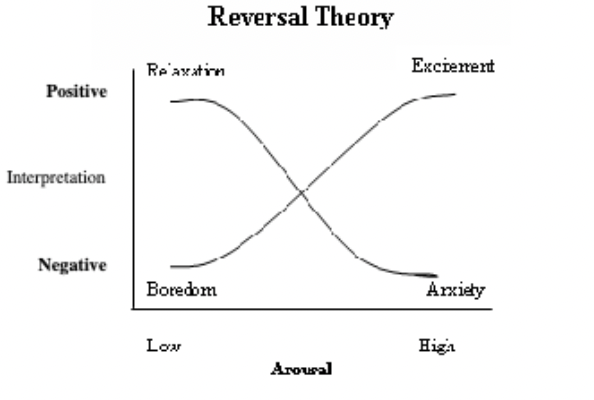
Define the reversal theory model
The way in which arousal affects performance depends on the individuals interpretation of his or her arousal level
How does high arousal or anxiety levels undermine performance
Increase muscle tension, which decreases coordination (affects performance and injury)
Attention and concentration changes
Describe somatic anxiety reduction technique. Give an example.
Body to mind
Breath control (diaphragmatic breathing)
Progressive muscular relaxation
Biofeedback
Describe cognitive anxiety reduction technique. Give an example.
Mind to body
Relaxation response (meditation)
Autogenic training (self-hipnosis)
Self-talk techniques
Imagery
Describe multimodal anxiety reduction technique. Give an example.
Holistic (combo of somatic and cognitive)
Systemic desensitization and stress inoculation (STI)
Cognitive-affect stress management training
Hypnosis
What is systemic desensitization?
Steps to exposure of what cause anxiety
What is stress inoculation (STI)?
Working on anxiety
Define coping
What we do to shift the balance
What is problem-focused coping? Give an example.
Used when a situation is perceived as controllable.
Example: nervous about a midterm = study
What is emotion-focused coping? Give an example.
Used when a situation is perceived as uncontrollable.
Example: gets angry easily = go to anger management
Name effective coping strategies
Thought control
Task focus
Rational thinking and self-talk
Positive focus and orientation
Social support
Precompetitive mental preparation and anxiety management
Time management
Training hard and smart
Name the arousal-inducing techniques
increasing breathing rate
Act energizes
Listen to music
Use energizing imagery
Use cue words and positive statements
Light precompetitive workout
What are the components of concentration?
Focusing on relevant cues in the environment (selective attention)
Maintaining attentional focus over time
Maintaining situational awareness
Shifting attentional focus when necessary
Define focusing on relevant cues in the environment (selective attention)
When the environment changes rapidly, attentional focus must also change rapidly. Thinking of the past or the future raises irrelevant cues that often lead to performance errors.
Define maintaining situational awareness
Ability allows players to size up game situations, opponents, and competitions to make appropriate decisions based on the situation, often under acute pressure and time demands
Define shifting attentional focus when necessary
Ability to alter the scope and focus of attention as demanded by the situation
Name the attentional focus processes
Attentional selectivity
Attentional capacity
Attentional alertness
Define attentional selectivity
Letting some information into the information-processing system while screening out or ignoring other information
Define attentional capacity
Refers to the fact that attention is limited in that one can process only so much information at one time
Define attentional alertness
Related to the notion that increases in emotional arousal narrows the attentional field because of a systemic reduction in the rnage of cues that a performer considers in executing a skill
Describe the relationship between concentration and optimal performance
Athletes need to foucs on only the relevant cues in the athletic environment and to eliminate distractions
What are the common internal problems with concentration
Attending to past or future events
Choking
Overanalyzing body mechanics (form)
Fatigue
Inadequate motivation
What are the common external problems with concentration
Visual
Auditory
Name the techniques to improve self-talk
Thought stopping
Cognitive restructuring
What is thought stopping?
Involves concentrating on the undesired thought briefly and then using a cue or trigger to stop the thought and clear your mind
What is cognitive restructuring?
Redirects focus
Negative thought > reinterpret > positive statement
Name the exercises for improving concentraion
Learning to shift attention
Learning to maintain focus
Searching for relevant cues
Identify on-sight techniques for improving concentration
Simulations in practice
Cue words
Nonjudgemental thinking
Establish routines
Develop competition plans
Over learn skills
What are the types of attentional focuses?
Broad
Narrow
External
Internal
Define broad attentional focus. Give an example.
Allows a person to perceive several occurrences simultaneously
Example: basketball player running a fast break and multiple occurrences happening simultaneously
Define narrow attentional focus. Give an example.
Occurs when you respond to only one or two cues
Example: tennis player focusing on the ball and how to servre it focusing on those 2 cues
Define external attentional focus. Give an example.
Directs attention outward to an object or to an opponent's movements
Example: a basketball player focuses on someone else's wrist movements when he shoots
Define internal attentional focus. Give an example.
Directed inwards to thoughts and feeling
Example: high jumper mentally thinking about their run up, but not actually performing it physically