Histology Quiz 9
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
1
New cards
2 primary bronchi
what does the trachea branch into?
2
New cards
bronchi, conducting bronchioles, terminal bronchioles, terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, alveoli
how do bronchi narrow to conduct gas exchange?
3
New cards
carry air in and out of lungs and protection
bronchi function
4
New cards
respirtory epithelium, lamina propria, some MALT/ mucous glands/ hyaline cartilage, smooth muscle, adventitia
structure of bronchi
5
New cards
thinning of the epithelium, pseudostratified turns to simple columnar
major change between bronchi and bronchioles
6
New cards
thinning epithelium, lamina propria, smooth muscle
structure of bronchioles
7
New cards
clara cells
\- Specialized cells found in terminal and respiratory bronchiole epithelia \n • Clara cells have domed, non-ciliated apical surfaces \n • Cytoplasm includes secretory granules and SER
8
New cards
surfunctant production (prevents airway collapse), produce antimicrobial peptides, detoxification, stem cells
Functions of clara cells
9
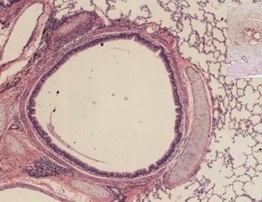
New cards
bronchus, cartilage in wall
bronchus or bronchiole? how is it identified?
10
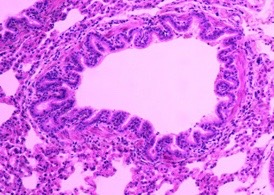
New cards
bronchiole, simple cuboidal epithelium with smooth muscle
bronchus or bronchiole? how is it identified?
11
New cards
respiratory bronchiole, alveolar duct, alveolar sacs, alveoli
what structures in lungs are capable of gas exchange and how do they branch?
12
New cards
thinner epithelium and increased capillary density
what allows gas exchange to occur as airways narrow?
13
New cards
alveoli
where does the most gas exchange occur?
14
New cards
simple cuboidal epithelium but without underlying smooth muscle
Respiratory bronchiole structure
15
New cards
thin with simple squamous epithelium and little underlying ct, lots of capillaries
Alveolar ducts and alveoli structure
16
New cards
type I alveolar cells
Very thin squamous epithelial cells, majority of cells in alveoli for gas exchange
17
New cards
type II alveolar cells
larger epithelial cells that produce surfactants
18
New cards
dust cells
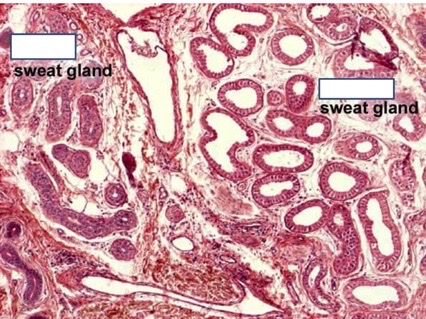
macrophages in alveoli that phagocytose inhaled particles and pathogens
19
New cards
terminal bronchiole, respiratory bronchiole, alveolar duct, alveoli
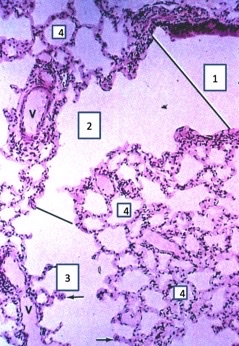
20
New cards
type I alveolar cells, type II alveolar cells, dust cells, capillaries
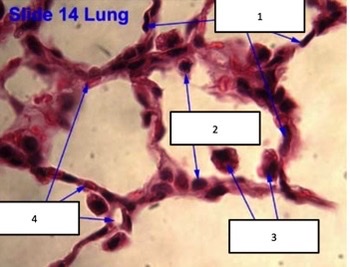
21
New cards
protection, sensory, temp regulation, metabolic
functions of the skin
22
New cards
epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous layer
layers of the skin (outside to inside)
23
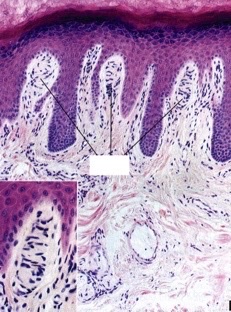
New cards
stratified squamous keratinized
what type of epithelium in the epidermis?
24
New cards
face, lips, scalp
where is the kertinized epidermis thinnest?
25
New cards
soles of feet, elbows
where is the kertinized epidermis thickest?
26
New cards
wavy
what is the appearance of a stratified squamous keratinized epithelium basement membrane?
27
New cards
keratin
tough, strong, resilient protein fiber that forms intermediate filaments inside the epithelial cells in the epidermis
28
New cards
the entire cytoplasm becomes filled with keratin fibers and nuclei die
why do cells in the upper levels of skin become keratinized?
29
New cards
keratinocytes
name for cells of the epidermis
30
New cards
stratum basale
epidermis cells that are attached to the basement membrane; includes mitotically active stem cells whose division continuously replenishes the epithelium
31
New cards
stratums basale, spinosum, granulosum, ludicum, corneum
epidermis layers from youngest up
32
New cards
stratum spinosum
Metabolically active epidermis cells
33
New cards
stratum granulosum
\-cells undergoing keratinization and producing lipid secretions to prevent water loss
\-visibly darker stained epidermis layer
\-visibly darker stained epidermis layer
34
New cards
stratum lucidum
thin layer of epidermis cells completing keratinization
35
New cards
stratum corneum
dead, fully keratinized, protective apical cells
36
New cards
desmosomes to hold cells together
what are the “spines” in the stratum spinosum and their function?
37
New cards
keratohyaline granules
what are the basophilic protein masses in the stratum. granulosum called?
38
New cards
secretion of lipids
how does stratum granulosum prevent dehydration?
39
New cards
corneum, lucidum, granulosum, spinosum, basale
name the epidermis layers
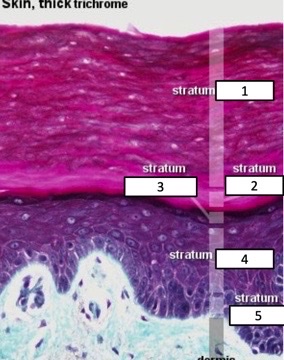
40
New cards
basal epidermis layer
where are melanocytes found?
41
New cards
melanocytes
\-cells that produce black or brown pigments for the skin that protects from UV light
\-recognizable by pale cytoplasm
\-recognizable by pale cytoplasm
42
New cards
langerhans cells
\-population of skin-resident macrophages
\-function as immune cells in phagocytosis and antigen presentation
\-function as immune cells in phagocytosis and antigen presentation
43
New cards
stratum spinosum, clear cytoplasm and irregular cell shape/size
where are langerhans cells mostly found, how are they identified?
44
New cards
merkel cells
Epidermis sensory cells that can respond to light touch
45
New cards
corneum, granulosum, lucidum, spinosum, basale, keratinocytes, melanocyte, langerhans cell
numbers then letters
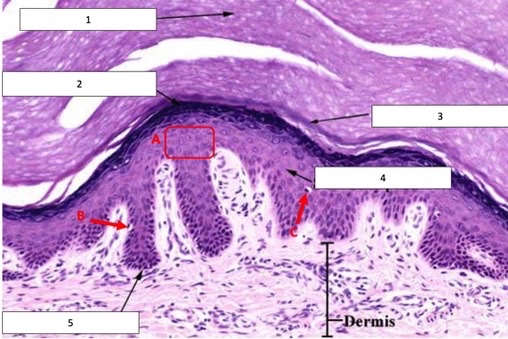
46
New cards
highly proliferative and high carcinogen exposure (UV)
why is the epidermis prone to cancer?
47
New cards
dermis
underlying supportive connective tissue directly under epidermis
48
New cards
papillary dermis
interface with epidermis; loose CT and blood vessels (must supply blood to epidermis!)
49
New cards
reticular dermis
dense irregular CT that surrounds hair follicles and glands; contains nerves and vasculature
50
New cards
elastic fibers
found in dermis for flexibility
51
New cards
increases adhesion and resistance to mechanical stress
why is the interface between the dermis and epidermis wavy?
52
New cards
blisters
what occurs when the epidermis and papillary dermis become detatched
53
New cards
stratum corneum, spinosum, basale, lucidum, granulosum
name the epidermis layers
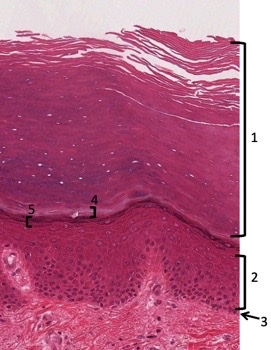
54
New cards
corneum and ludidum
in which layers are the cells dead (fully keratinized)?
55
New cards
stratum granulosum
Which layer produces lipids for water retention?
56
New cards
stratum basale
Which layer contains stem cells?
57
New cards
stratum spinosum
Which layer contains specialized desmosomes to maintain epithelial integrity and confer resistance to mechanical stress and abrasion?
58
New cards
epidermis, papillary dermis, reticular dermis, epidermal ridges, dermal papillae
name these skin layers then blue and red arrows
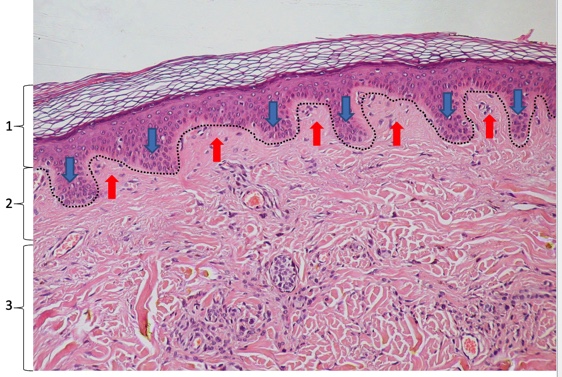
59
New cards
when it is hot so the body can lose heat
when does blood travel through papillary loops?
60
New cards
shunts to block bloodflow to papillary loops
what is used when its cold to maintain internal body temperature?
61
New cards
sensory receptors
• Nerve endings in skin – either encapsulated \n and/or formed into semi-organized structures, \n or existing as free nerve endings with no \n myelin or capsule
62
New cards
response to sensation and touch
what is the function of sensory receptors?
63
New cards
meissner corpuscles
\-located in dermal papillae directly under epidermis
\-sensitive to light touch
\-sensitive to light touch
64
New cards
meissner corpuscle
what structure?
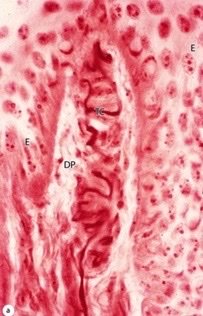
65
New cards
lamellated corpuscles
\-Located in dermis or subcutaneous layer of skin
\-less sensitive, sense vibrations or pressure
\-Concentric circular layers of axons and Schwann cells, encapsulated by CT
\-less sensitive, sense vibrations or pressure
\-Concentric circular layers of axons and Schwann cells, encapsulated by CT
66
New cards
lamellated corpuscle
what structure?
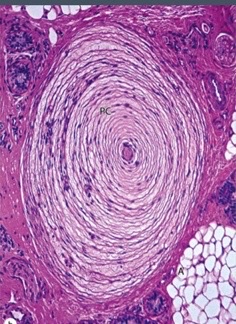
67
New cards
meissner corpuscles, light sensation
Which sensory structure and what is its function?
68
New cards
lamellated corpuscles, pressure or course touch
Which sensory structure and what is its function?
69
New cards
epidermal invaginations
from where do hair follicles form?
70
New cards
fully keratinized cells
what makes up the hair
71
New cards
hair bulb
\-At base of hair follicle \n • Includes hair (dermal) papilla \n • Also includes bulb matrix
72
New cards
bulb matrix
includes melanocytes and epidermal stem cells that are \\n actively dividing and undergoing keratinization to produce the hair
73
New cards
hair root sheath
\- Encompasses the hair as it extends towards the skin surface
• Includes inner epithelial root sheath and outer connective \n tissue root sheath
• Includes inner epithelial root sheath and outer connective \n tissue root sheath
74
New cards
medulla
innermost cells of the hair
75
New cards
cortex
surround the medulla in the hair, most densely packed with keratin
76
New cards
cuticle
thin outer layer of squamous cells on hair
77
New cards
glassy membrane
discreet basement membrane secreted by hair follicle root epithelial cells
78
New cards
arrector pili muscle
smooth muscle attached to hair
79
New cards
sebaceous glands
glands always associated with hair follicles that produce lipids to protect hair and epidermis
80
New cards
acinar glands with holocrine secretion
what type of glands are sebaceous glands
81
New cards
cells rupture and die to distribute their product
what is holocrine secretion?
82
New cards
dermal papilla, hair bulb, CT root sheath, epithelial root sheath, transition to hair
name the structure of the hair follicle
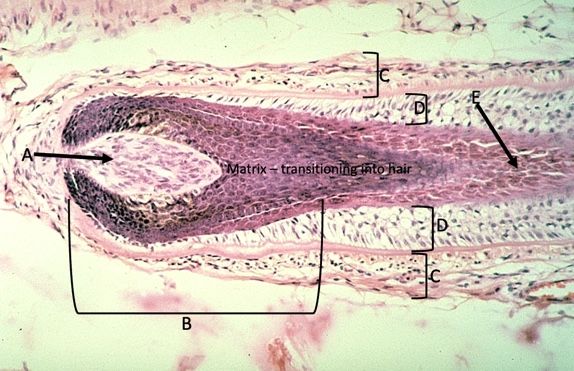
83
New cards
temp regulatuion, antibacterial, waste disposal, pheromone production
functions of sweat
84
New cards
eccrine
widely distributed sweat glands– temperature regulation and waste disposal
85
New cards
apocrine
armpits, genitalia, eyelid – pheromone production (vestigial in humans)
86
New cards
dermis and subcutaneous layers
where are sweat glands located?
87
New cards
meandering tubular glands in dermis
structure of eccrine sweat glands
88
New cards
ducts are acidophilic from mitochondria, glands have mostly clear cells and a few dark staining
hoe do eccrine ducts vs glands stain
89
New cards
stratified cuboidal
what epithelium is found in sweat ducts?
90
New cards
large lumens
major difference in apocrine sweat gland appearance
91
New cards
eccrine, apocrine
identify the sweat glands