Lab Vocab + Lecture Labeling
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
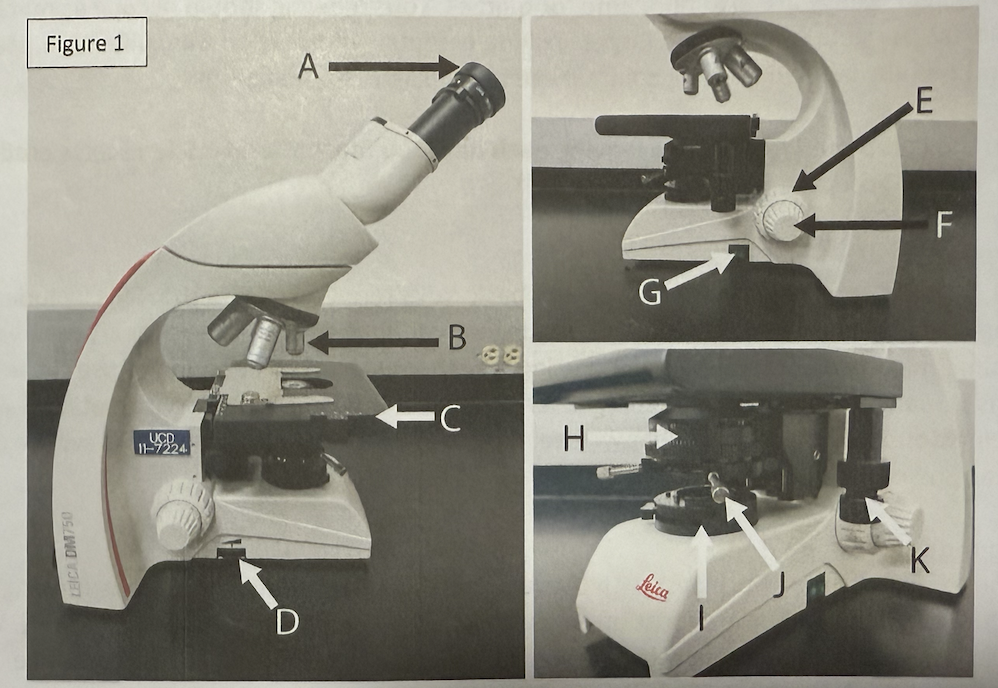
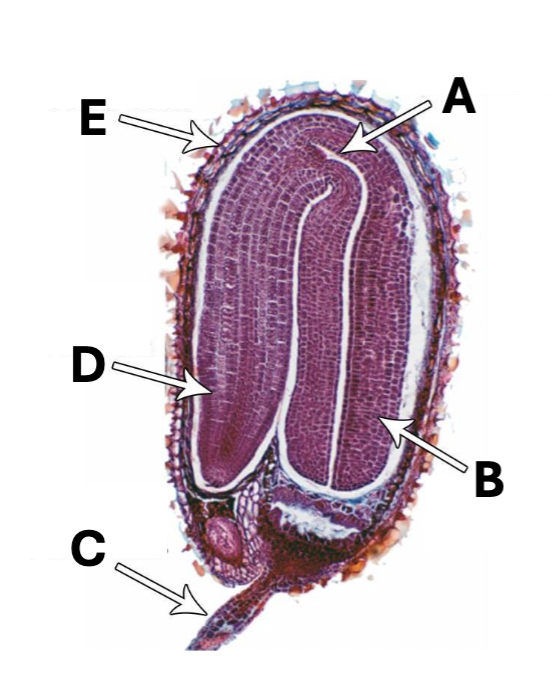
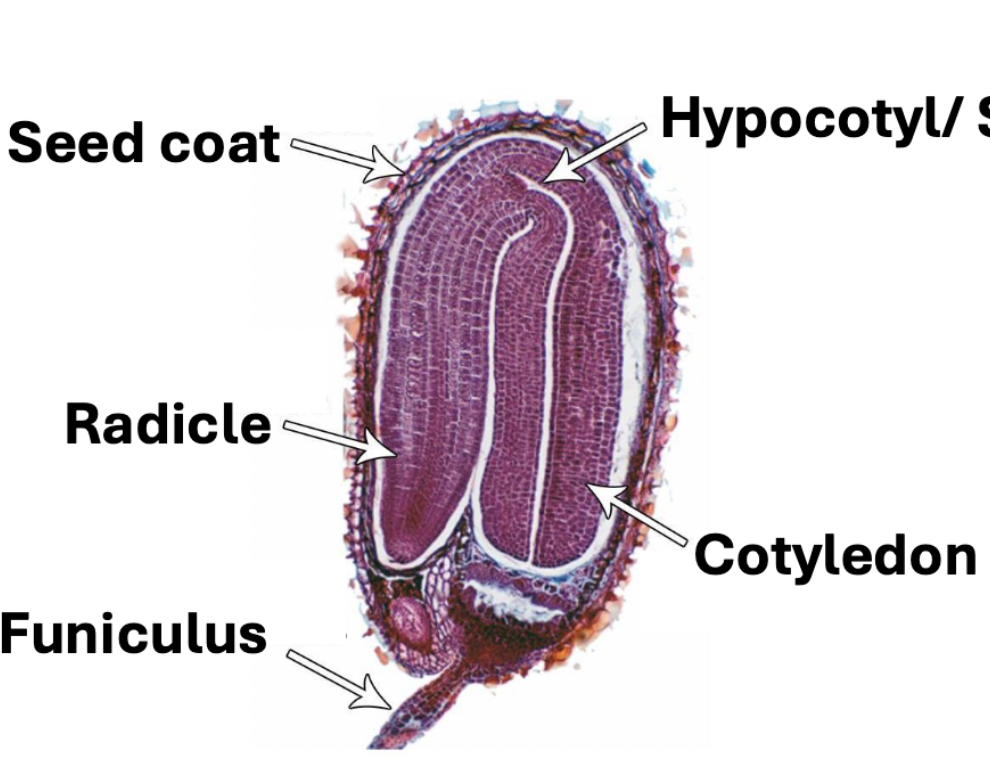
Label and say what is what
See Lab Manual
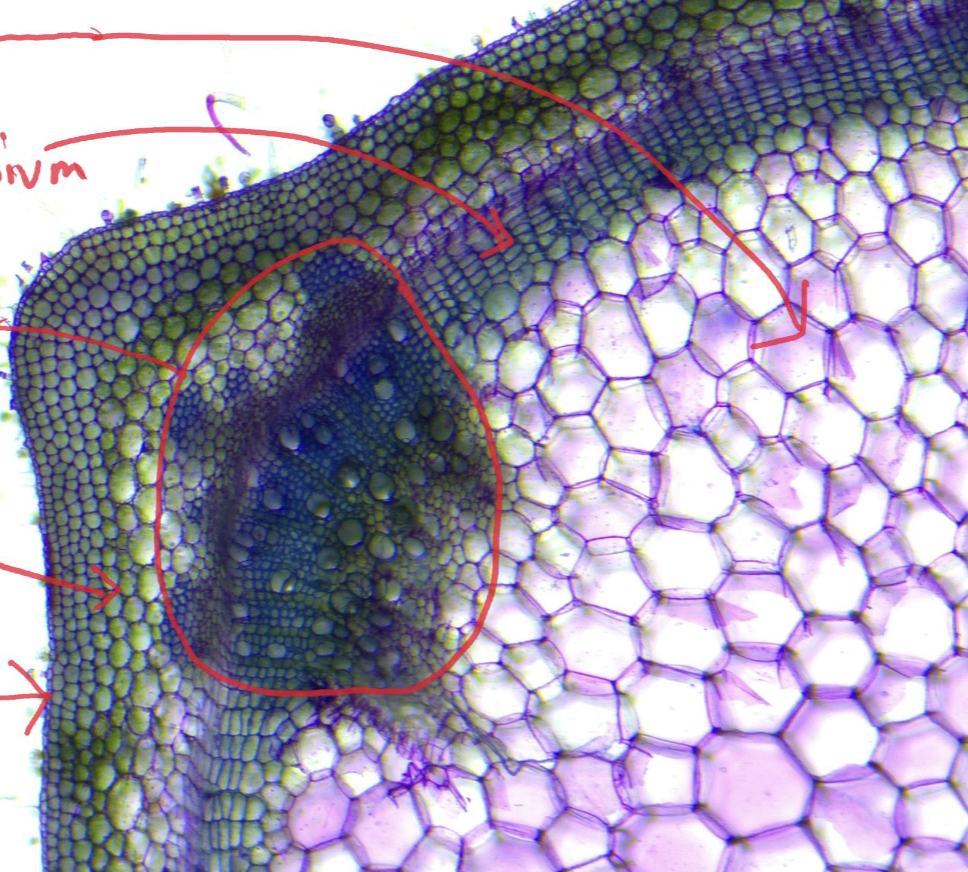
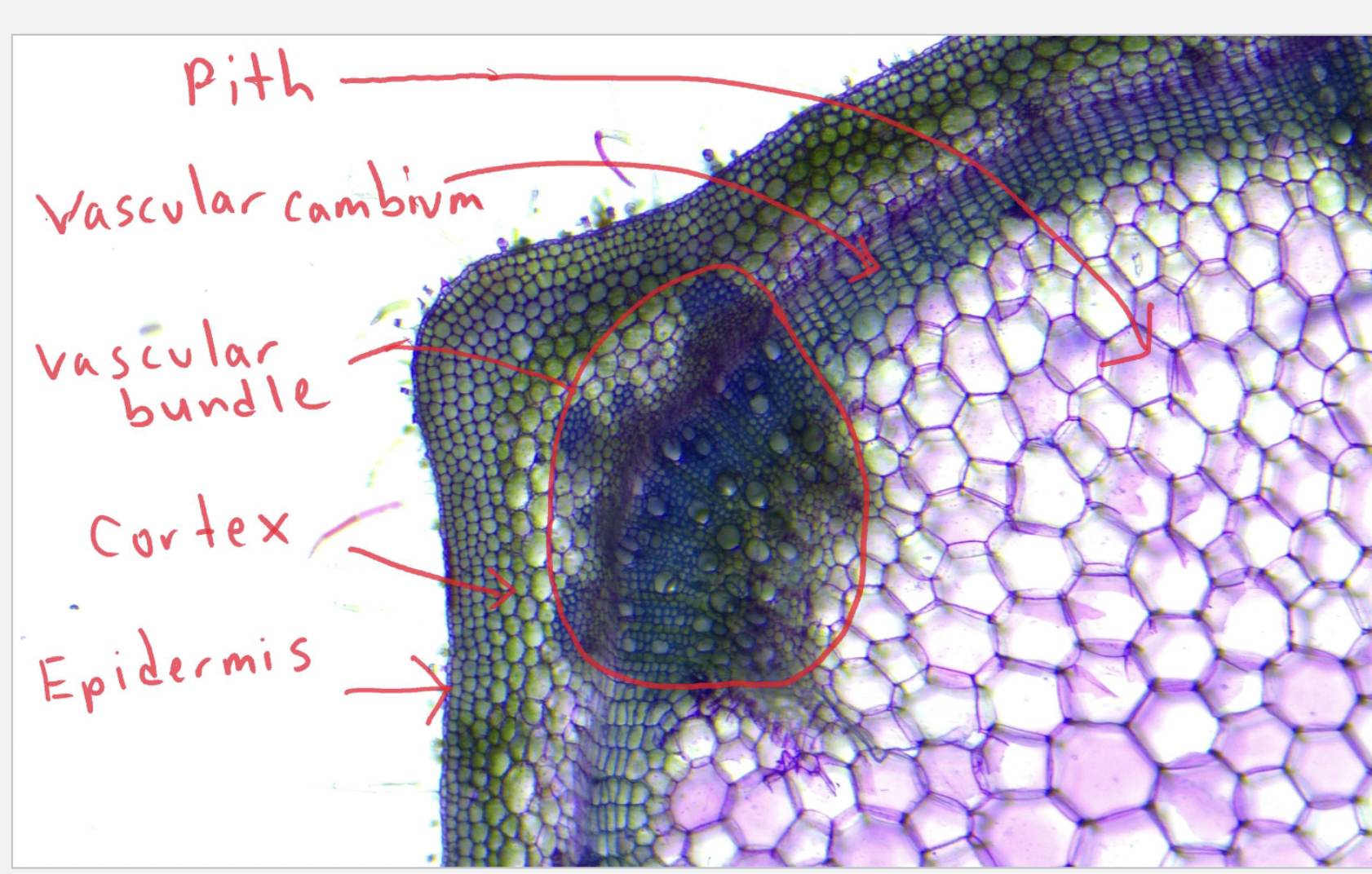
Label
TOP TO BOTTOM
Pith - The word "pith" has several meanings, but most commonly refers to the soft, spongy, central part of a plant stem or root made of parenchyma cells, which functions in storing nutrients and water
Label
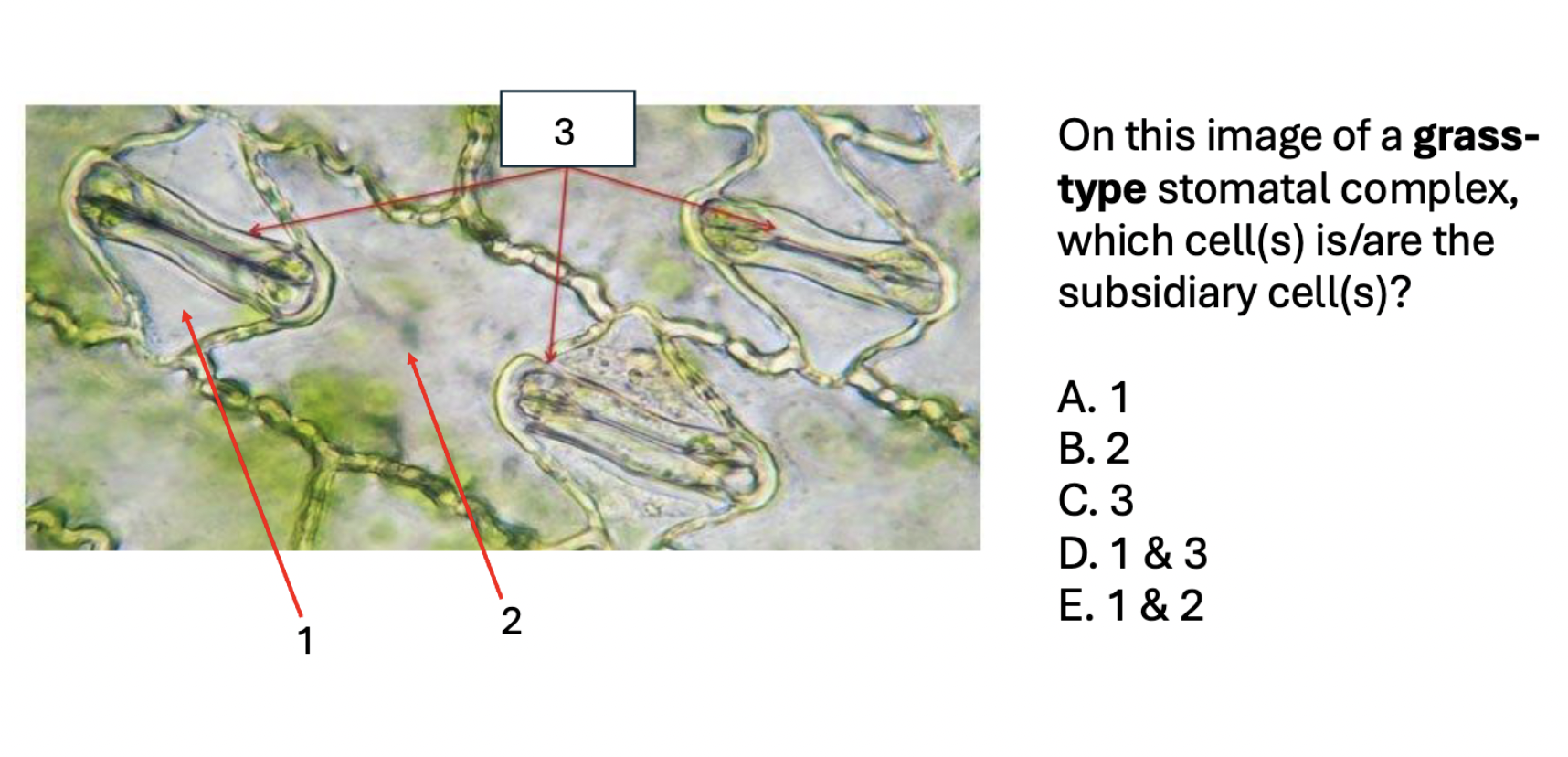
1 subsidiary
2 pavement
3 Guard
XS / TS section
Cross or Transverse
Cut lateral (imagine a cucumber slice)
LS section
Longitudinal
Vertically (imagine a got dog slice)
RLS section
Radial Longitudal Section (same as LS)
TLS
Tangential Longitudal Section
Similar to TS, but off center
CRT sectioning
prepared slide with cross, radial longitudal, and tangential
IKI stain
Iodine Potassium Iodine
Stains Starch a DARK BLUE to BROWN to ORANGE depending on starch present
Nuclei may stain pale gold and cell walls may become yellow
Toluidine blue
Lignified walls and tannin stuctures become deep blue
Cell walls of non-lignified tissue will stain pinkish-purple to red
Phloroglucinol-HCl
stains lignified tissue red
Sudan IV
Cutin, suberin, and waxy/oily sunstances turn red
Aniline blue
tests for presence of callose in the phloem or bark
turns phloem and sieve plates/ares with callose blue
MICROSCOPE PARTS! NAME THEM! WHAT ARE THEY? DO YOU KNOW THEM? LETS FIND OUT
add them here, but also in the other labeling set
Need to get a better image to label
Stomatal complex (what do they consist of + fxn)
Comprized of stomata, guard cells, and subsidiary cells
Stomata = hole
guard cells = open and close hole
subsidiary = surround guard
Stomata
Pores the plant that assists in gas exchange and assist in photosynthesis and water movement
stomata is the HOLE
Stellate
Star shaped arrangement
ex: stellate aerenchyma
Subsidiary cell
surround the guard cells in various arrangements
Anomocytic type
Diacytic type
Paracytic type
Anisocytic type
grass/parallel type
Guard cell
Surround the sides of the stomata and allow it to open and close when needed
Peltate
meaning “shield shaped”
Pavement Cells
Pavement cells are shaped like puzzle pieces and provide protection. These
cells also secrete a non-cellular waxy cuticle that helps prevent desiccation
Stomatal pore
the tiny openings within a stomata (?)
Anomocytic type stomata arrangement
Random arrangement of subsidiary cells around guard cells
Paracytic type stomata arrangement
Subsidiary cells are PARALLEL to guard cells (1 for each)
Diacytic type stomata arrangement
subsidiary cells are perpendicular to guard cells (one on top one on bottom)
Anisocytic type stomata arrangement
three subsidiary cells of differing sizes
Grass / parallel type stomata arrangement
in the middle of the long subsidiary cells
special paracitic
SEE LECTURE PHOTO // CLICKER
Protoderm
A type of primary meristem that is associated with DERMAL tissue
procambium
a type of primary meristem that forms vascular tissue
ground meristem
A type of primary meristem that becomes ground tissue
Periclinal Division
Division that adds parallel to the cell surface
ADDS THICKNESS
Anticlinal Division
Division type that adds perpendicular to the surface
ADDS WIDTH // Surface Area
Bulliform cells
One method of reducing water loss from stomata
Causes the plant / leaf to roll and reduce surface area
Trichome
Trichomes can be unicellular or multicellular, glandular (or not), and serve a
variety of functions including defense, reflection, dispersal, and digestion
Hypostomatic
Stomata are only on the bottom
Common in dry areas
Amphistomatic
Stomata are on both sides
Epistomatic
Stomata are only on TOP
aquatic plants like water lilies
papillate
Found on petals (ex Viola); small bumps that are NOT trichomes
seen during an XS cut
Parenchyma
“workhorse” cells in the plant body. They have diverse functions (storage, photosynthesis, repair, secretion, aeration), have thin primary walls, intercellular spaces, and are alive at maturity
Found throughout all organs of plants
Collenchyma
Provides flexible support in growing parts of the plant; think “bendy” parts like young stems and leaf petioles. These cells are not lignified but do have thickened primary (cellulosic) walls
Located a few cell layers below epidermis, in leaves, petioles, young stems.
Sclerenchyma
These are the strongest and most rigid plant cells, with thick, lignified secondary walls.
They provide mechanical support and protection, especially in woody stems, vascular bundles, and seed coats.
DEAD AT MATURITY
Chlorenchyma
a general term referring to parenchyma tissue rich in chloroplasts and actively carrying out photosynthesis
mesophyll is leaf exclusive
Aerenchyma
has intercellular air spaces.
develop by cells separating during growth or cell lysis leaving behind cavities. T
facilitate gas exchange between submerged and aerial organs and buoyancy
Plasmodesmata
JXNS between cells that exist where there is a primary cell wall
Allows for communication and resource exchange
Brachysclereids
Variety of Sclerencyma, very clustered with lignin
Astrosclereids
Star shaped sclerenchyma
see photo
Macrosclereids
Long, fiber like sclerenchyma beneath the cell wall (?)
see photo
Trichosclereids
long, needle-like, branched plant cells made of sclerenchyma tissue that grow in some plants, particularly in aquatic species like water lilies and Monstera
(?)
Fibers
Variety of sclerenchyma
Sclereids
variety of sclerenchyma with subcatagories
Mesophyll
LEAF parenchyma that are high in chloroplast content and deal with photosynthesis and gas exchange
Septate fibers
???
living, elongated cells that are divided into compartments by internal cross-walls called septa
Xylary fibers
?????
structural, non-living cells within the xylem tissue of plants, providing mechanical support and strength to the plant body
Extraxylary fibers
????
plant fibers located outside the xylem, in tissues like the cortex (cortical fibers), phloem (phloem or bast fibers), or around the periphery of the vascular bundle (perivascular fibers)
Angular Collenchyma
Angular collenchyma is a type of plant tissue characterized by thickened cell walls at the corners or angles where cells meet, providing mechanical support to the plant
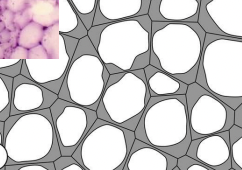
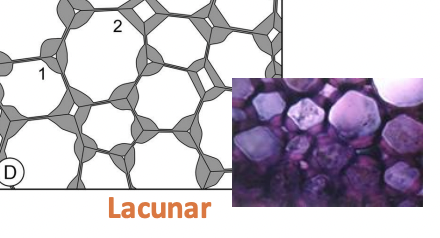
Lancunar Collenchyma
Lacunar collenchyma is a type of plant tissue where cells have unevenly thickened primary cell walls
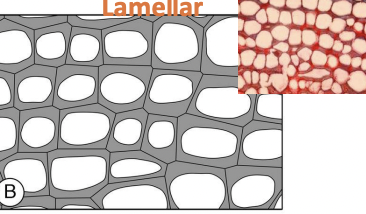
Lamellar Collenchyma
Lamellar collenchyma is a plant tissue where cells have continuous layers of thickening, specifically along their tangential walls, which are parallel to the surface of the organ
Annular Collenchyma
EVENLU CELL WALL TISSUE
Collenchyma types
Angular
Lamellar
Annular
Lancunar
Simple tissue
Only has one cell type, named after it
Complex Tissue
Made of multiple Cell types,
gets a unique name
Totipotent
Ability to de-differentiate and become a new cell type essentially
Lignin
Offers RIGID support
makes secondary cell wall
Cell walls with lignin are dead at maturity
Vascular Tissue
Xylem // Phloem
Xylem
vascular tissue that carries water
Protoxylem VS Metaxylem
META is BIGGER
Protoxylem is the first-formed xylem that develops during organ elongation and is smaller, less efficient, and has simple, incomplete walls
metaxylem is the later-formed xylem that matures after elongation, with larger, more complete, pitted walls, and greater water conduction efficiency
Vascular bundles
a strand of conducting vessels in the stem or leaves of a plant, typically with phloem on the outside and xylem on the insid
Secondary wall thickenings
Annular
Helical
Scalariform
reticulate
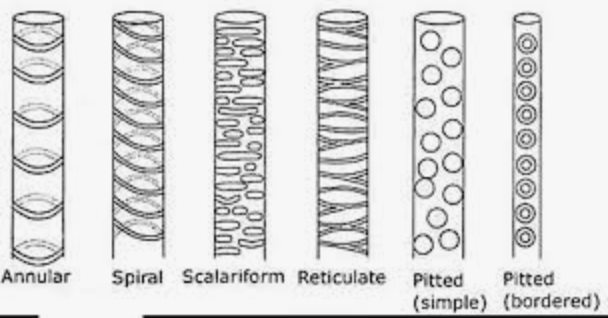
Annular Wall thicknings
ring-like bands of secondary cell wall material deposited inside the primary wall of early xylem cells (protoxylem) and other tracheary elements
Helical Wall thicknings
spiral, reinforced sections of a plant cell's secondary cell wall that prevent it from collapsing under tension. Found in xylem tissues like protoxylem and tracheids
Scalariform Wall thicknings
plant cell wall patterns where secondary wall material is deposited in parallel, ladder-like bands, resembling the rungs of a ladder.
This form of thickening is found in tracheary elements of the xylem, particularly in metaxylem, where it provides mechanical support
reticulate wall thickning
a pattern in plant xylem cells where the secondary cell wall is laid down in a network or net-like pattern, with unthickened areas forming a mesh.
This pattern is found in tissues that have completed their elongation, such as metaxylem
Tracheids
a type of water-conducting cell in the xylem which lacks perforations in the cell wall
Pits
thin areas or openings in the secondary cell walls of xylem cells (tracheids and vessel elements) that allow water and dissolved ions to move laterally between adjacent cells
facilitating the efficient upward transport of water throughout the plant
Boardered Pits
bordered pits are a specific type of pit with an overarching secondary cell wall, forming a protective border that creates a smaller opening called the pit chamber and aperture
Vessel Element
Vessel elements form continuous, wide tubes for rapid water transport in angiosperms, while narrower, tapered tracheids are found in all vascular plants and conduct water more slowly through pit pairs between individual cells
Perforation Plate
the end wall of a plant xylem vessel element with one or more openings that allow water and dissolved minerals to flow between adjacent cells
Xylary Fibers
elongated, lignified sclerenchyma cells found within the plant's xylem tissue, providing structural support and strength to the water-conducting tissue
Procambium
a plant tissue, specifically a primary meristem, responsible for producing the primary vascular tissues, xylem and phloem
Vascular cambium
Connected Cambium that leads to secondary (vascular?) growth
a layer of meristematic cells in dicotyledonous plants and gymnosperms that produces secondary xylem (wood) internally and secondary phloem (inner bark) externally, forming a continuous ring that increases the plant's stem and root diameter
Primary Xylem
Primary xylem is the initial xylem tissue produced by a plant during primary growth from apical meristems, responsible for transporting water and minerals upwards from the roots.
It consists of protoxylem, the first and typically narrowest elements formed, and metaxylem
Vascular cambium
includes connecting cambium and the vascular bundle’s cambium
Primary xylem
the initial xylem tissue produced by a plant during primary growth from apical meristems, responsible for transporting water and minerals upwards from the roots
Secondary Xylem
a vascular tissue in woody plants that increases stem and root diameter and provides structural support
Vascular tissue system
a network of specialized cells in plants that transports water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant body
xylem and phloem
Pith
Inner portion of ground tissue
Residual procambium
leftover procambium after it splits into primary xylem and primary phloem
Phloem
transports sugars
Sieve tube members
specialized, living cells in the phloem of flowering plants that, along with companion cells, form sieve tubes for long-distance transport of sugars
Sieve cells
a sieve element of a primitive type present in ferns and gymnosperms, with narrow pores and no sieve plate
Sieve plate
an area of relatively large pores present in the common end walls of sieve tube elements.
Callose
Callose functions in plants by forming specialized cell wall components and acting as a defense barrier to protect against pathogens and environmental stress
Companion cell
living, specialized plant cells in the phloem tissue that provide metabolic and physical support to sieve tube elements
Bicollateral bundle
a type of vascular bundle in plants where the xylem is located between two distinct phloem strands—one on the outer and one on the inner side
P protein
a structural protein found in the sieve elements of the phloem tissue in plants that forms protein bodies or filaments to prevent the loss of photosynthate when the sieve element is damaged
Lateral sieve areas
perforated regions in the side walls of sieve elements (sieve-tube members and sieve cells) that allow for cytoplasmic connections to companion cells and other phloem cells, facilitating the movement of nutrients and metabolites throughout the plant
Phloem fibers
long, thick-walled, dead sclerenchyma cells found in the phloem (inner bark) of dicotyledonous plants, providing structural support and mechanical strength to the stem
Secondary phloem
a vascular tissue in plants produced by the vascular cambium during secondary growth, which increases a plant's girth, or thickness
Phloem rays
Phloem rays are radial strips of living parenchyma cells within the secondary phloem, serving as storage for carbohydrates and other compounds like tannins, and facilitating horizontal transport of water and nutrients from the vascular cambium to the inner phloem tissues