NUMBER SENSE
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Percentages
A way to represent part-to-whole relationships, where the percent is the part out of 100.
Example.
One half: 50%=12=0.5050%=21=0.50
Numerator
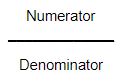
the top term of a fraction
Example.
In 110101 the numerator is 1
Factors
Values that are multiplied to get another number.
Example.
Some factors of 12 are 3 and 4 because 3×4=123×4=12
Double Number Line Diagram
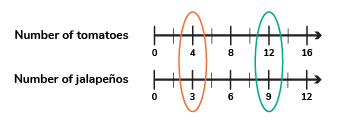
Consists of two parallel number lines, each representing a different unit
Used to visualize and compare ratios
Example.
Reducing Fractions
dividing the numerator and denominator by any common factors to put the fraction in lowest terms
Example.
Fraction Composition
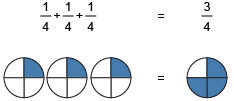
Adding fractions to come up with a larger one
Example.
¼ + ¼ + ¼ = ¾
Denominator

the bottom term of a fraction
EXAMPLE:
Fraction Decomposition
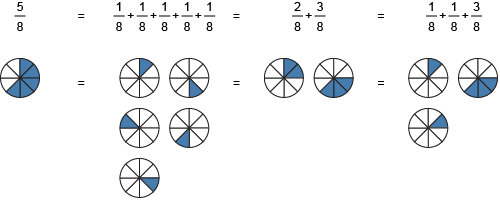
Breaking down a fraction into smaller fractions that total to the original
Example.
2/3 = 1/3 + 1/3
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more numbers; the smallest number two or more numbers will divide into evenly
Example.
For 12 and 15, LCM = 60
Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60
Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60
Fractions
usually represent partial numbers
Example.
One half: 50%= 1/2 =0.50
Factor Tree
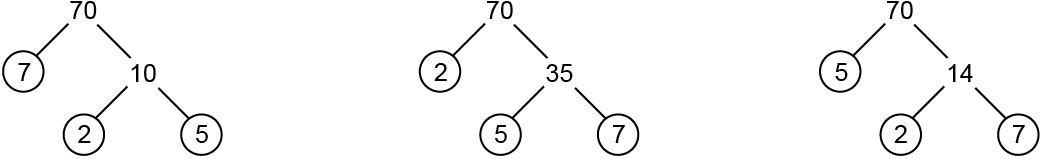
A visual process to find the factors of a number
Composite Numbers
natural numbers that are divisible by numbers other than one and themselves
Example.
6 is divisible by 2 and 3
Decimal Fractions
fractions with a denominator of 10
Example.
Greatest Common Factor (GCF) / Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
the greatest factor that is common to two or more numbers; the largest number that will divide evenly into two or more numbers
Example.
For 12 and 15, GCF = 3
Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
Factors of 15: 1, 3, 5, 15
Order of Operations

PEMDAS: the set order in which multi-step equations must be solved: Parenthesis, Exponents, Multiplication and Division (left to right), Addition and Subtraction (left to right)
Relatively Prime
two numbers are relatively prime if they share no common factors
Example.
34 and 15
Prime Factorization
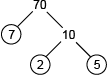
the process of writing a number in terms of its prime factors
Example.
12=2×2×312=2×2×3
Decimal
Numbers less than 1 displayed using place values and the powers of ten
Example.
0.024
Ratio
A comparison that shows the relative size of two or more values.
Example.
The ratio of boys to girls is: 4 to 5; 4:5; 4/5; 0.8.
Prime Numbers
natural numbers greater than 1 that have no numbers that will divide into them without a remainder
Example.
2, 3, 5, 7....
Real Numbers
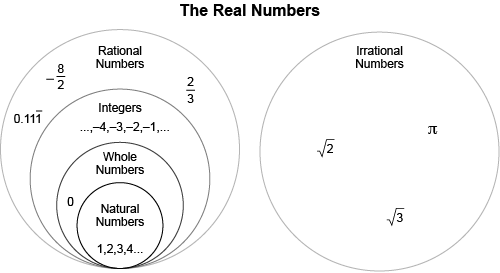
numbers that have a specific value
Example.
-2, 3, 1/2, 3.2, √2
Prime Factor
a prime number or term that can be multiplied by another to get a number.
Example.
2×6=122×6=12, 2 is a prime factor