Paper Science Exam 2
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Chemical Pulping
Liberate fibers by removing lignin in middle lamellae, remove lignin from cell wall
Chemical Pulping Objectives
Object is to remove residual lignin, and have a final brightening step to brighten what chromophores remain
Mechanical Pulping Objectives
Object is to brighten (subject to brightness reversion)
Chemical Pulping Benefits
high strength, more flexible, denser
Pulping Methods
Alkaline (Soda & Kraft), Acid (Sulfite), and Neutral Sulfite Semichemical
Delignification
Breaking down the chemical structure of lignin, making it soluble in water
Delignification Selectivity
Removing lignin without degrading hemicelluloses
Dissolving Pulp
Low yield (30-35%) bleached chemical pulp with high cellulose content (95%), cellulose is degraded and only alpha cellulose remains (which is insoluble in NaOH)
Kappa Number (K)
Measure of lignin content in pulp to monitor the amount of delignification, K = lignin % * 5
Pulp Viscosity
Measure of average chain length of cellulose in pulp (degree of polymerization DP, which is the # of glucose units in the chain)
Soda Process
Developed by Burgess & Watts in 1861, the approach used NaOH which degrades cellulose too much, but cold soda pulping is good for straw, grasses, and other non-woods because it dissolves the middle lamella
Kraft Process
NaOH + Na2S + H2O → 2NaOH + NaHS, hydrosulfide protects cellulose from hydrolysis (NaOH) by enhancing selectivity while slowing condensation (reformation) of lignin
Delignification of Kraft Process
Reduces lignin to about 3-5%
White Liquor
NaOH + Na2S (the reagents)
Black Liquor
waste liquor that contains reactants, extractives, lignin, and some hemicellulose
Green Liquor
Partially recovered liquor, mostly Na2CO3 and Na2S (react with Ca(OH)2 to recausticize)
Bleaching
Reduces lignin to less than 1%
Chemical Recovery
Evaporation (of spent liquor to increase consistency), Combustion (heat is recovered for use in processes), Recaustisizing (react green liquor with Ca(OH)2)
Kraft Process Variables
Wood Species (HW, SW, Eucalyptus), Cooking Liquor Chemistry (liquor to wood ratio, sulfidity), Cooking Conditions (temperature at 170 degrees C for 1.5 - 3 hours), H-factor
H-factor
Area under curve (reaction rate vs. time) indicates extent of reaction
Lignin in Digester
Lignin is replaced by water in the digester
Draw Kraft Process Diagram
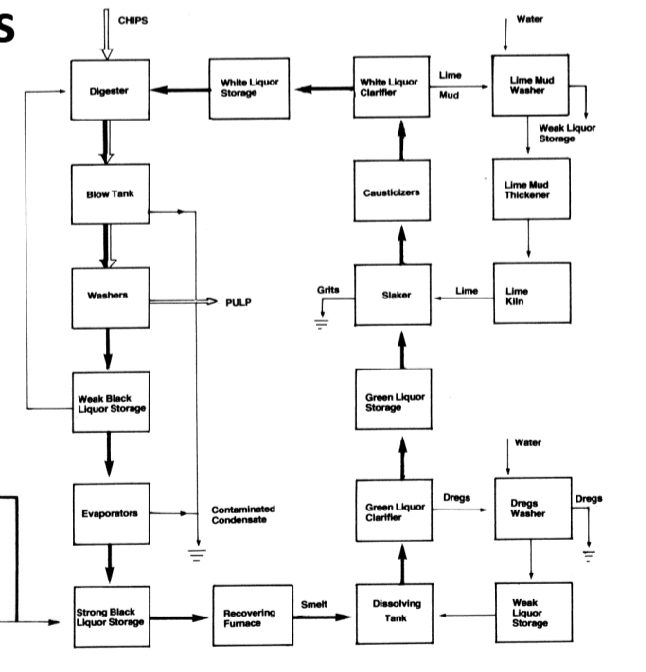
Kamyr Continuous Digester
Impregnation (115 degrees C), Heating (157 → 170 degrees C), Cooking (170 → 172 degrees C), Washing (160 → 130 degrees C), Cooling (85 degrees C) —— identify zones and draw digester
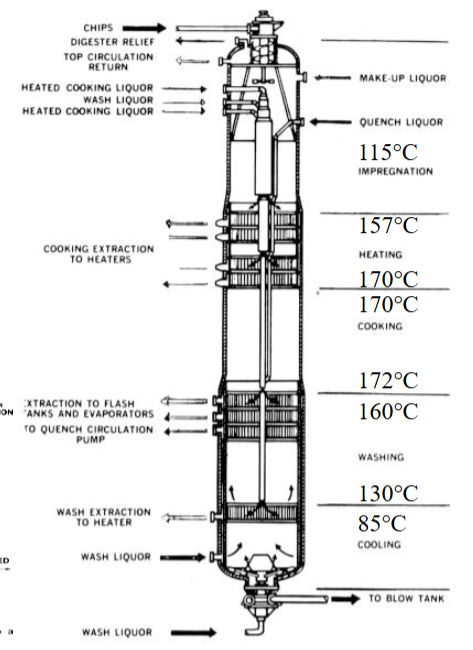
Continuous Digester
Presteaming, chip chute, high pressure feeder, heaters (heat exchangers), condenser for extractives, recirculation of liquor, heating zones
Breaking bonds in cellulose to break off lignin
1) Alkaline hydrolysis: drops strength (decreases chain length & viscosity); 2) Peeling reaction: stops bond breaking with NaS, drops yield (loses some money); both should limit temperature to prevent cellulose degradation
Sulfite Pulping (<5% of market)
Acid hydrolysis via NaHSO3: acid tears apart lignin and Na makes lignin negative and therefore soluble (to be washed out)
Condensation of Lignin
Lignin reforms back into an insoluble polymer that is impossible to remove, and is called a burned cook because the pulp becomes black
Sulfite Pulping Cooking Liquor
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3, forms bisulfite (pH 3 - 5)
Calcium Salts in Cooking Liquor (abandoned due to insoluble salts)
CaCO3 + 2H2SO3 → Ca(HSO3)2 + CO2 + H2O
Ca(HSO3)2 → H2SO3 (FREE) + CaSO3 (COMBINED)
Sodium Salts in Cooking Liquor
Na2CO3 (SODA ASH) + H2SO3 → 2NaHSO3 + CO2 + H2O
Ammonium Salts in Cooking Liquor
NH4OH (AMMONIA)+ H2SO3 → NH4HSO3 + H2O
Magnesium Salts in Cooking Liquor
Mg(OH)2 + 2H2SO3 → Mg(HSO3)2 + H2O
Mg(HSO3)2 → H2SO3 (FREE) + MgSO3 (COMBINED)
Neutral Sulfite Semi-Chemical Pulping (NSSC, 7% of market)
Na2SO3 + Na2CO3, high yield (80%) similar to CTMP, only removes middle lamella, usually made from hardwood, has good compressibility for liner medium due to stiffer fibers
Strength Comparison of Pulping Methods
CTMP > TMP > RMP > PGW > SGW
Solid % Before Multiple-Effect Evaporators
15%
Solid % in Concentrated Black Liquor Storage
70%
Clarifier
Takes out solids
Dregs Washer
Non-dissolving solids removed, washes out Na2S so it doesn’t combust in the atmosphere
Smelt out of recovery boiler
Na2CO3, Na2S, dregs
Steam from recovery boiler
Runs through multiple-effect evaporators
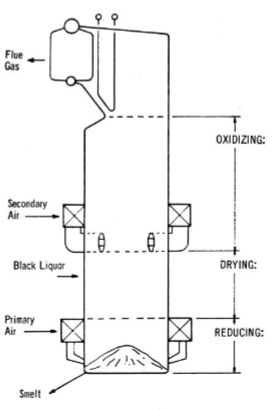
Recovery Boiler
100m tall, biggest building on site, bottleneck of the process
Recovery Boiler Zones
Drying, oxidizing, reducing. Black liquor goes into the drying section, some organics rise into the oxidizing section before dropping down to the reducing section
Draw Recovery Boiler
Slaking
CaO is introduced into green liquor, CaO (lime) + H2O → Ca(OH)2 (slaked lime/milk of lime)
Recaustisizing
Ca(OH)2 + Na2CO3 → CaCO3 + 2NaOH
Lime Kiln
Rotating kiln going from 200 to 1200 degrees Celsius to turn CaCO3 into CaO
Brownstock Washer
Separates black liquor from wood pulp fibers after cooking
1980s
Mechanical Pulping → Chemical Pulping
Acid process → Alkaline process
Bleaching in Europe
Total Chlorine Free (Peroxides → Oxygen)
Bleaching in U.S.
Elemental Chlorine Free (Chlorine dioxide, ClO2)
Reductive Bleaching
Brightens remaining materials (Mechanical Pulping)
Oxidative Bleaching
Removes remaining lignin (alkali is used to remove oxidized lignin) (Chemical Pulping)
Chlorine (C)
ECF (primarily used, chlorine and hypochlorite are eliminated) and TCF; Not used because of dioxin
Chlorine dioxide (D)
Used in all bleached paper, unstable/explosive when 12-15% is in gas phase so use upflow towers to prevent gas accumulation, good selectivity towards lignin
Alkaline Extraction (E)
NaOH deprotonates lignin fragments so they are negatively charged which dissolves lignin from previous stage
Hypochlorite (H)
NaOCl
Oxygen delignification (O)
O2
Peroxide (P)
H2O2
PO
Oxygen-peroxide
Peracetic acid (Pa)
CH3CO3H
N
Neutralization
Enzymes (X)
Xylanase attacks xylans, which are hemicellulose attached to lignin
Ozone (Z)
O3
Bleaching Sequence
OD(EOP)D - O reduces lignin, D0 oxidizes to remove lignin, D1 reduces remaining chromophores
Jordan Conical Refiner
An old refiner meant for secondary (tickler) refining
HC Refining
For mechanical pulping
LC Refining
For almost every pulp
Disk Refining
Not designed to shorten fibers; rids S1 layer to liberate microfibrils (some fines are created in the process)
Acids and Bases
Used to control pH; high pH (alkaline) deprotonates fibers while low pH us bad because it can react with CaCO3 to make salt and gas which causes foam
Alum
pH and retention: attracted to negative fibers and attaches filler to fibers
Retention aids
Keep fines and fillers in paper (long positively charged polymers)
Drainage aids
Water removal on the wire
Pitch control chemicals
Prevents deposits/accumulation of pitch (which comes from extractives in mechanical pulp)
Stickies control chemicals
Prevents accumulation of adhesives/stickies from recycled pulp
Biocides
Microorganism control
Process Chemicals
Added to improve process
Functional Chemicals
Added to change paper properties
Sizing agents
Control penetration of liquids, control the rate of wetting in paper
Dry strength agents
Make dry paper stronger (cationic starch)
Wet strength agents
Make wet paper stronger
Optical Brightening Agents (Colorants)
Dumps UV back into 457 nm to increase brightness
Clay (filler)
Flat platy structure, used to create glossy surfaces, inert, has a slight cream color (lowers brightness)
Calcium Carbonate (filler)
PCC shape versus ground
Titanium Dioxide (filler)
expensive but scatters light very well
Talc (filler)
similar to clay, flat platy structure, hydrophobic, used in Asia
Stock prep
Blend chest (everything is blended) which goes to the machine chest (feeds paper machine)
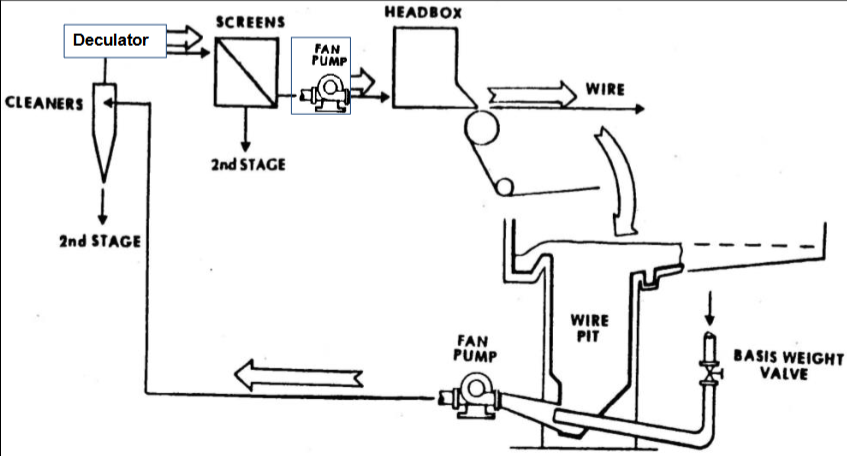
Stock approach system
Basis weight control/valve, fan pump 1, hydrocyclones, deculator, fan pump 2, pressure screens, headbox (in this order)
Draw Stock Approach System Diagram
*2nd fan pump should come before the pressure screens
Solid % coming out of pulp mill
10%
Solid % coming out of machine chest
3%
Solid % coming onto paper machine from headbox
0.5%
Stuff Box
On top of building connected to basis weight control valve creating an almost constant pressure; has a Weir which is a dam inside to maintain pulp level to keep constant pressure
Hydrocyclones/Centricleaner
spins to separate light and heavy particles (removes sand/dirt/grit from pulp)
Deculator
Removes air after hydrocyclones
Pressure Screens
Doesn’t plug, has hydrofoils, has many designs