Lumbar Orthopedics
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Minor sign
Assessment for:
- SI lesions
- Lumbosacral strain/sprain
- IVD
- Lumbopelvic fracture
- Musscular dystrophy/dystonia

Antalgia sign
Assessment for:
- Posterolateral disc protrusion
- Posteromedial disc protrusion
- Posterocentral disc protrusion
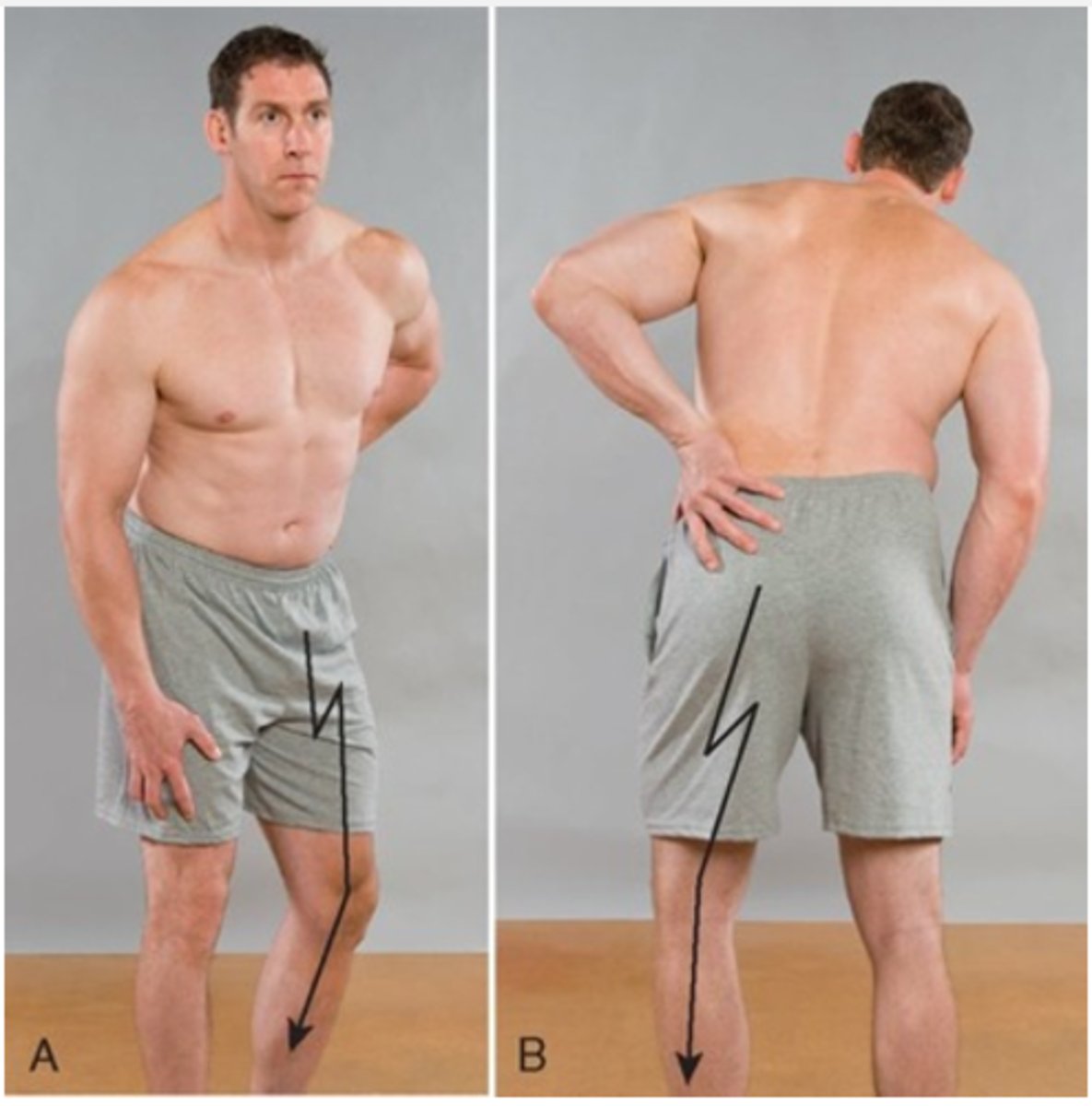
Posterolateral disc protrusion
When the disc protrudes lateral to the nerve root, the patient assumes an antalgic lean away from the side of the disc lesion or pain
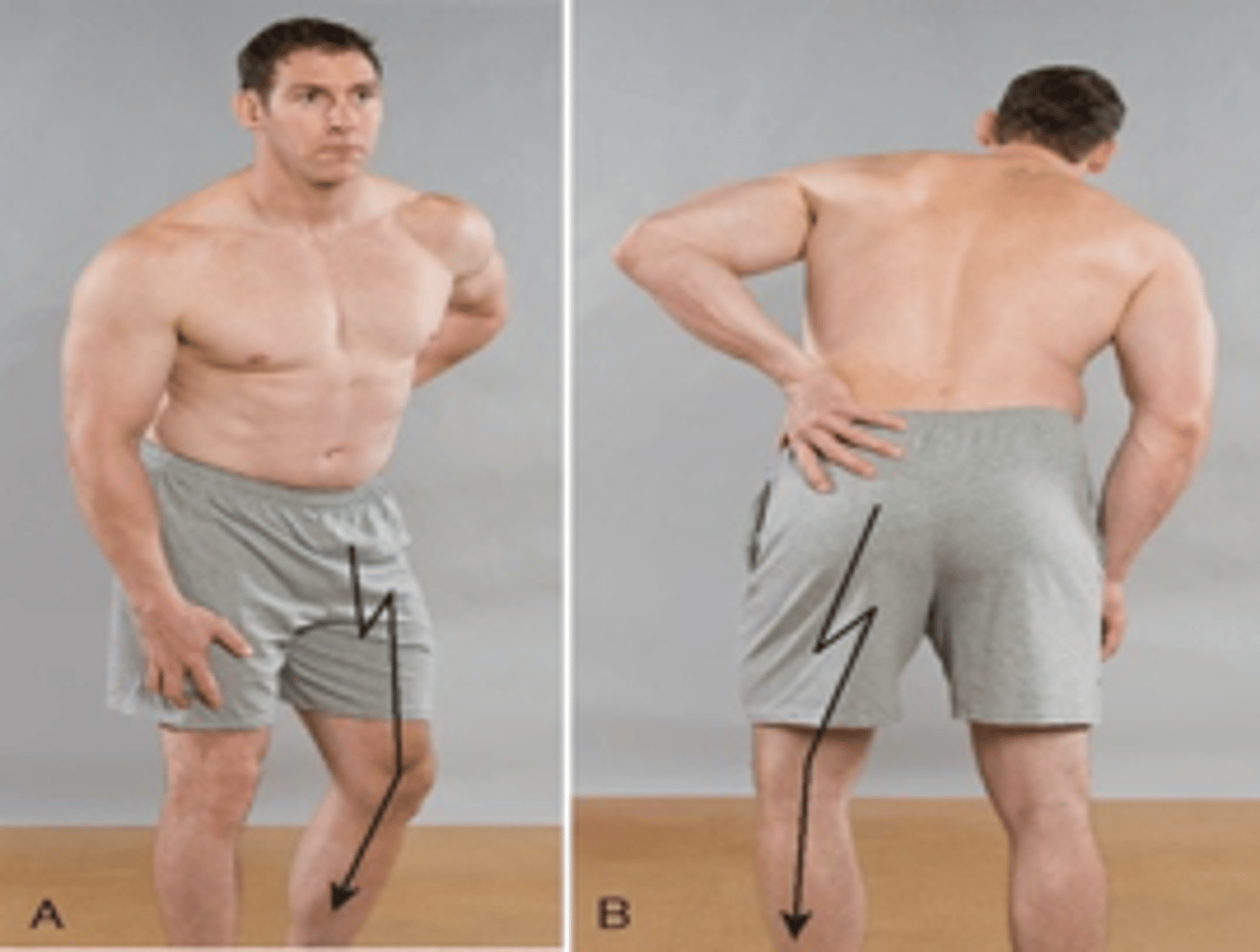
Posteromedial disc protrusion
When the disc protrudes medial to the nerve root, the patient assumes an antalgic lean into the side of the disc lesion or pain
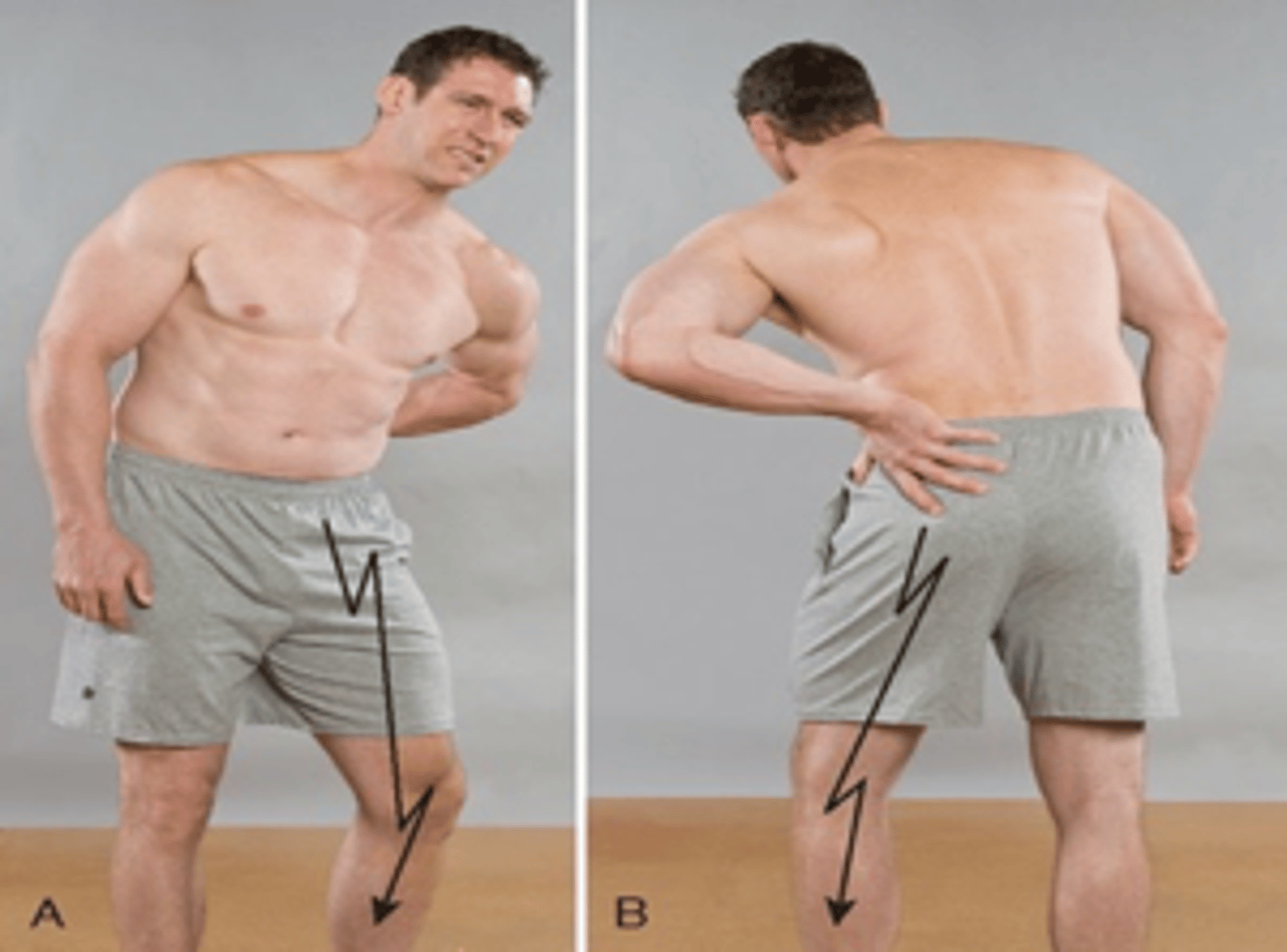
Posterocentral disc protrusion
With a central disc lesion, the patient assumes a flexed posture of the lumbar spine, with or without leaning to either side

Cox sign
Assessment for:
- Prolapse of IVD nucleus

Cox sign
_____ is present if during SLR the pelvis rises from the table rather than the hip flexing
Fajersztajn Test/Well-Leg-Raising Test
Assessment for:
- Lumbar nerve root lesion caused by IVD or dural sleeve adhesion
- AKA: Prostrate Leg-Raising Test, sciatic phenomenon, and cross-over sign
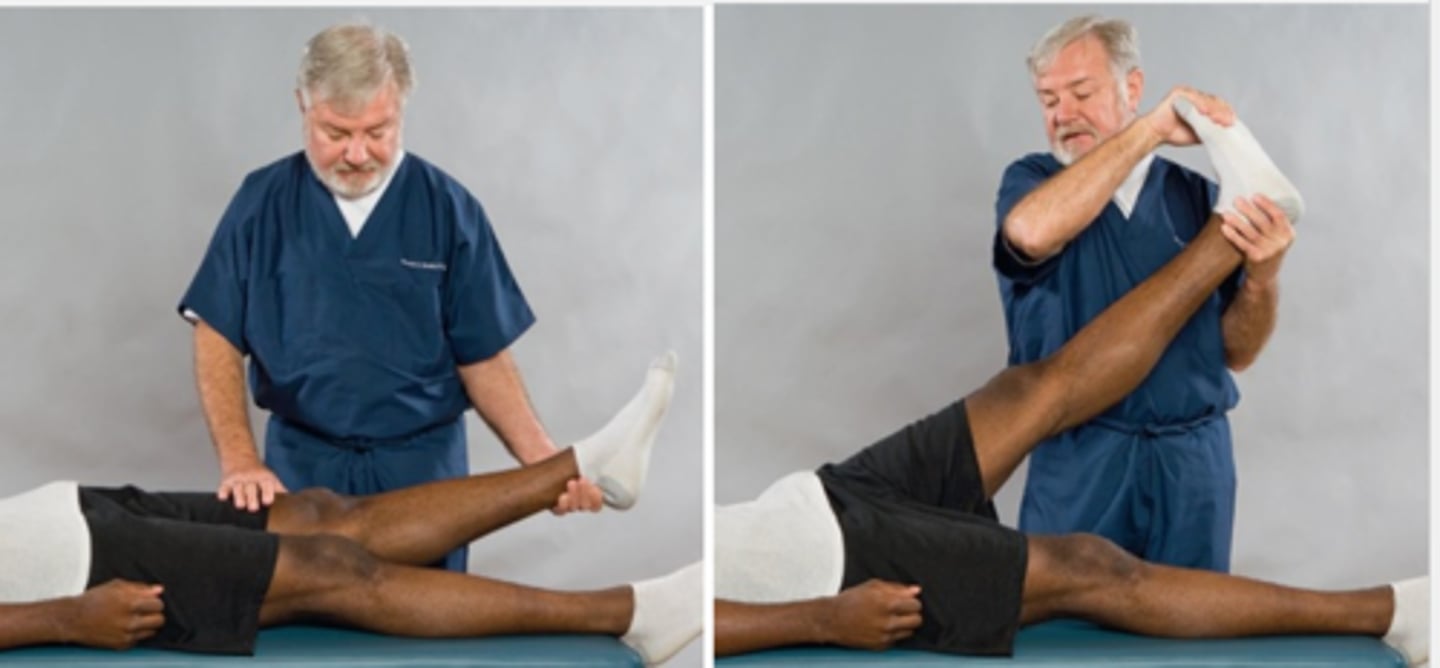
Asymptomatic
For the Fajersztajn Test/Well-Leg-Raising Test, the SLR and dorsiflexion of the foot are performed on the _____ side of the patient
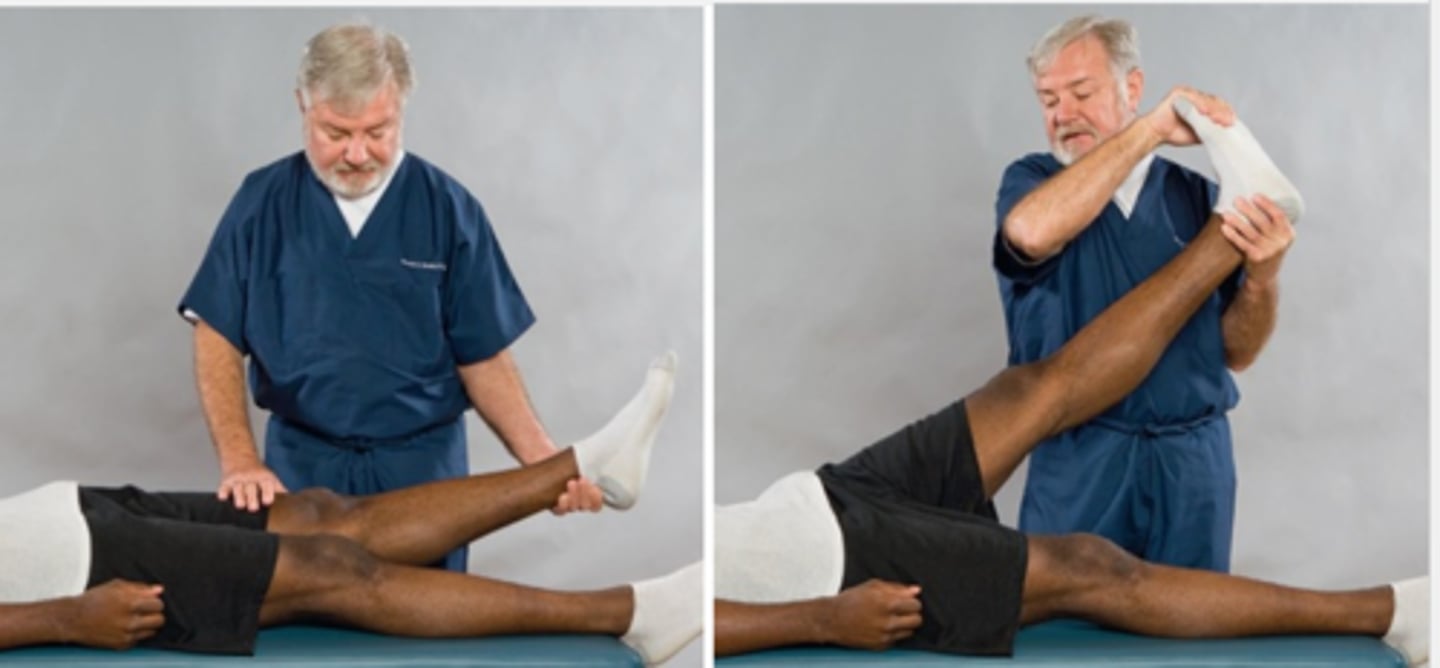
Pain produced on the symptomatic side
What would make the Fajersztajn Test/Well-Leg-Raising Test positive?
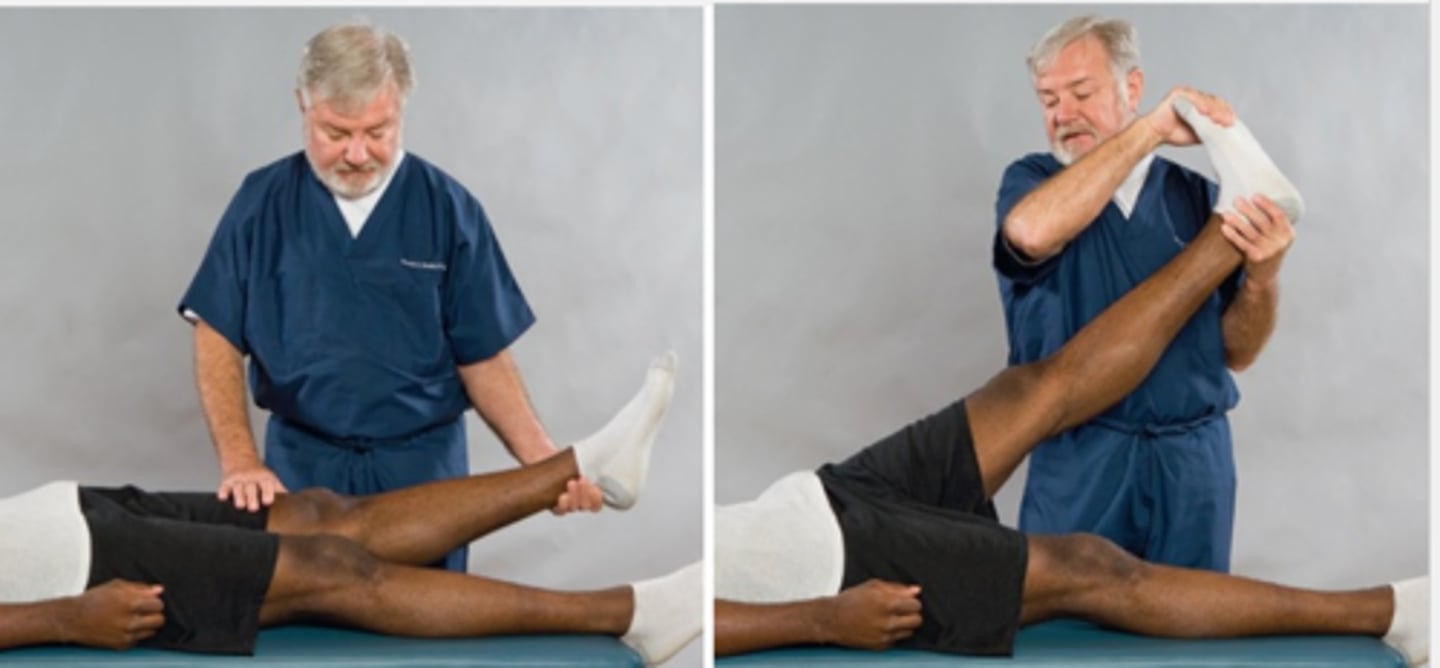
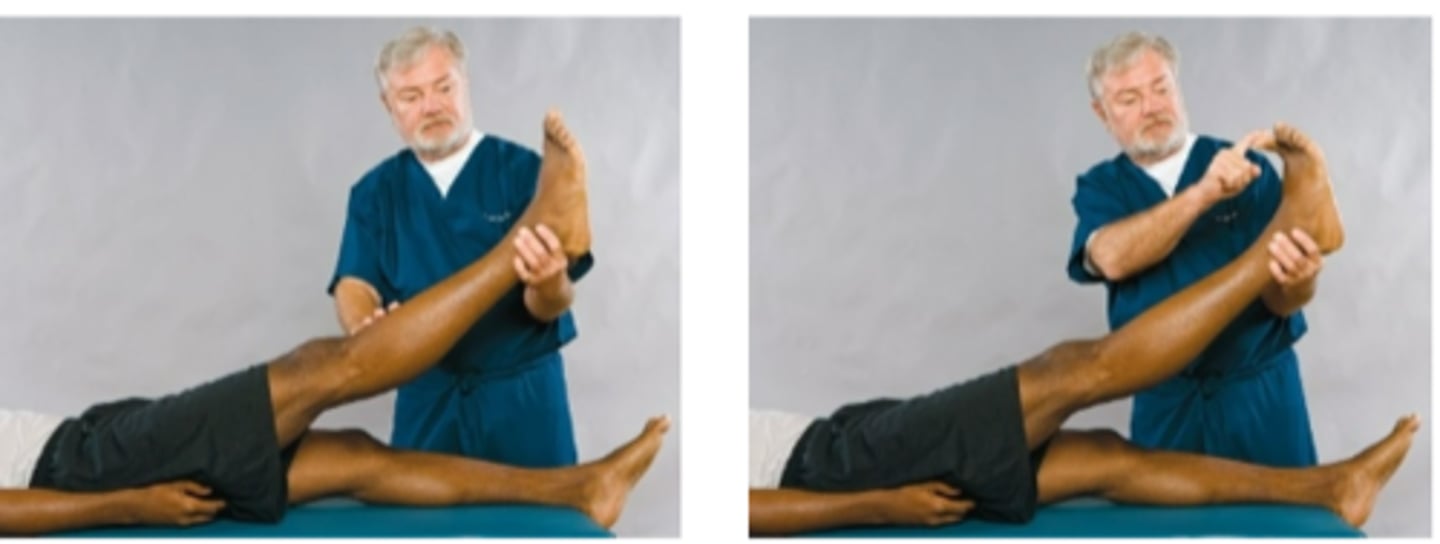
Straight-Leg-Raising Test
Assessment for:
- Space-occupying mass of the nerve root
- SI inflammation
- Lumbosacral involvement
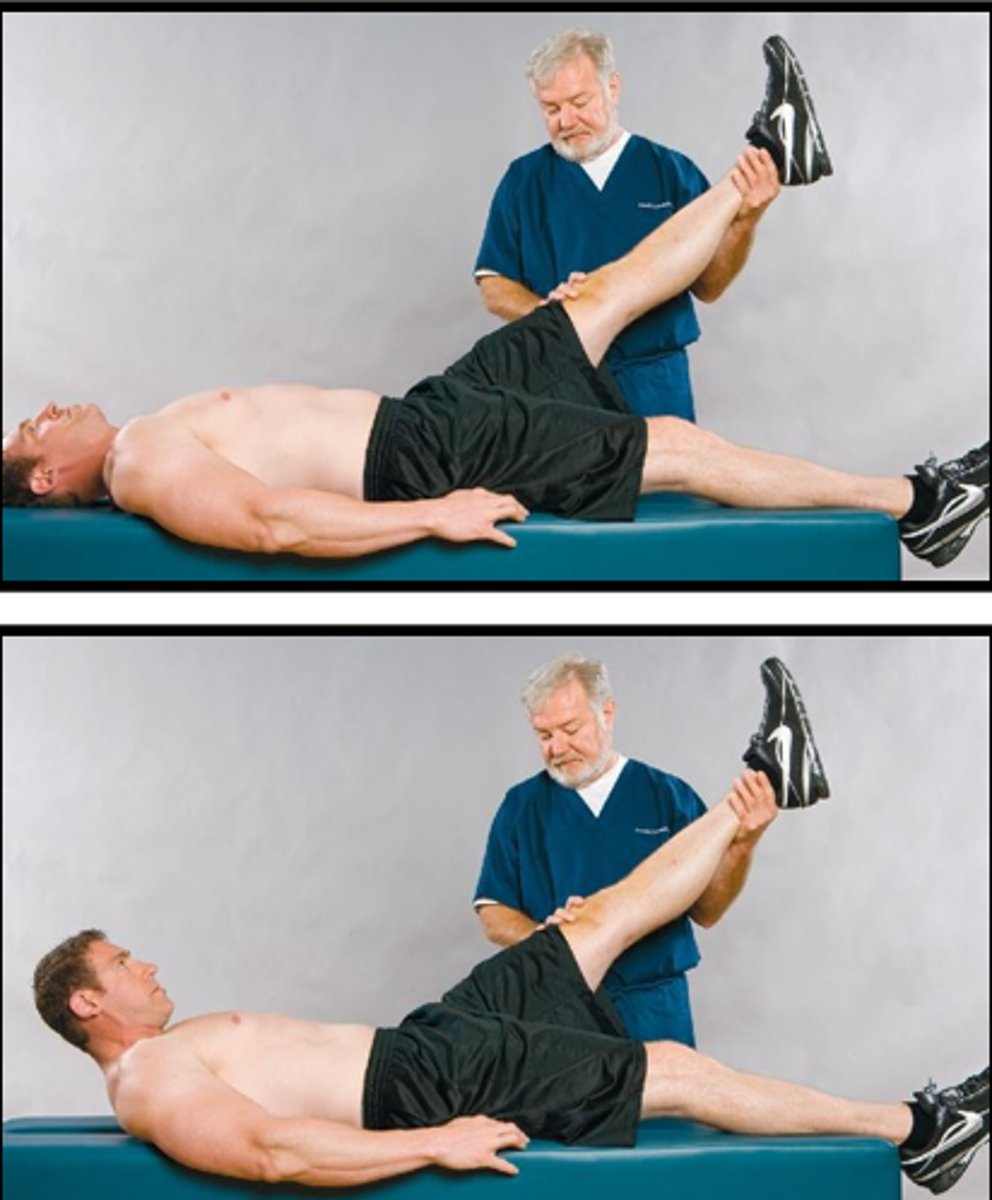
Bragard Sign
Assessment for:
- Sciatic neuritis
- Spinal cord tumor
- IVD lesions
- Spinal nerve irritation
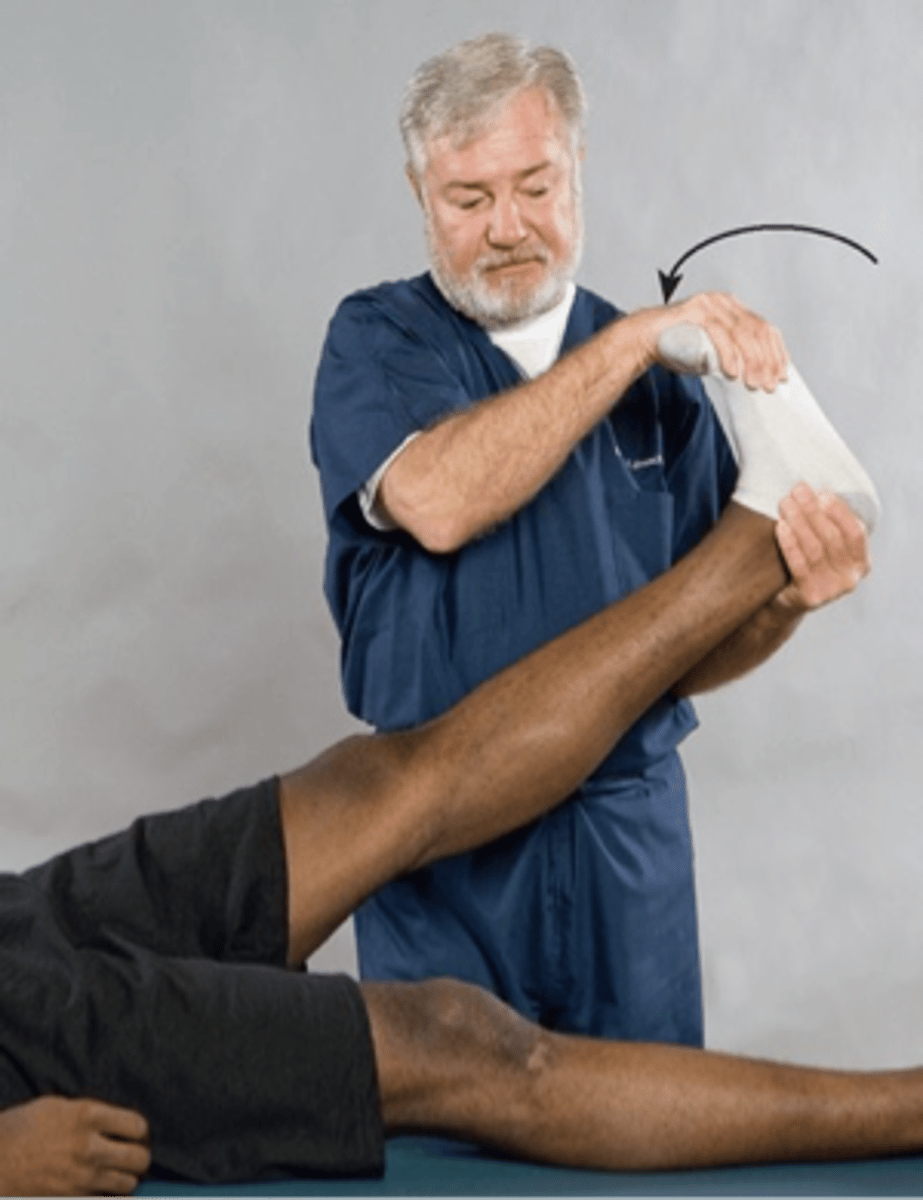
Sicard Sign
Assessment for:
- Sciatic radiculopathy

Turyn Sign
Assessment for:
- Sciatic radiculopathy
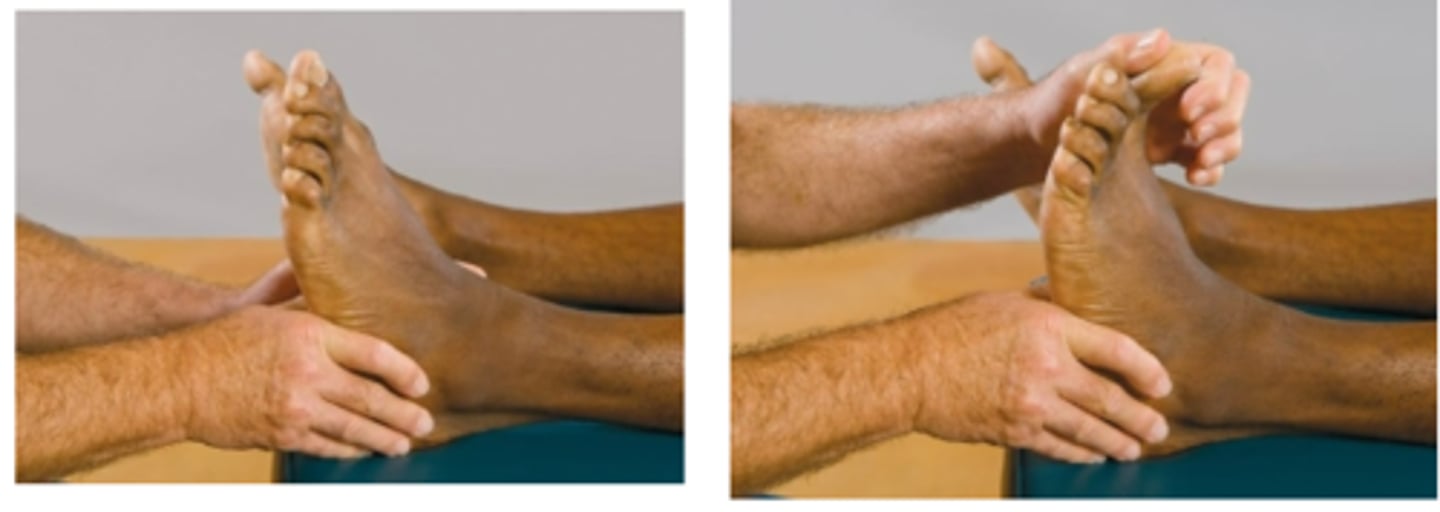
Demianoff Sign
Assessment for:
- Spasm of the sacrolumbalis (iliocostalis lumborum) musculature
Lumbar
The Demianoff sign is present when the action produces a pain in the _____ region
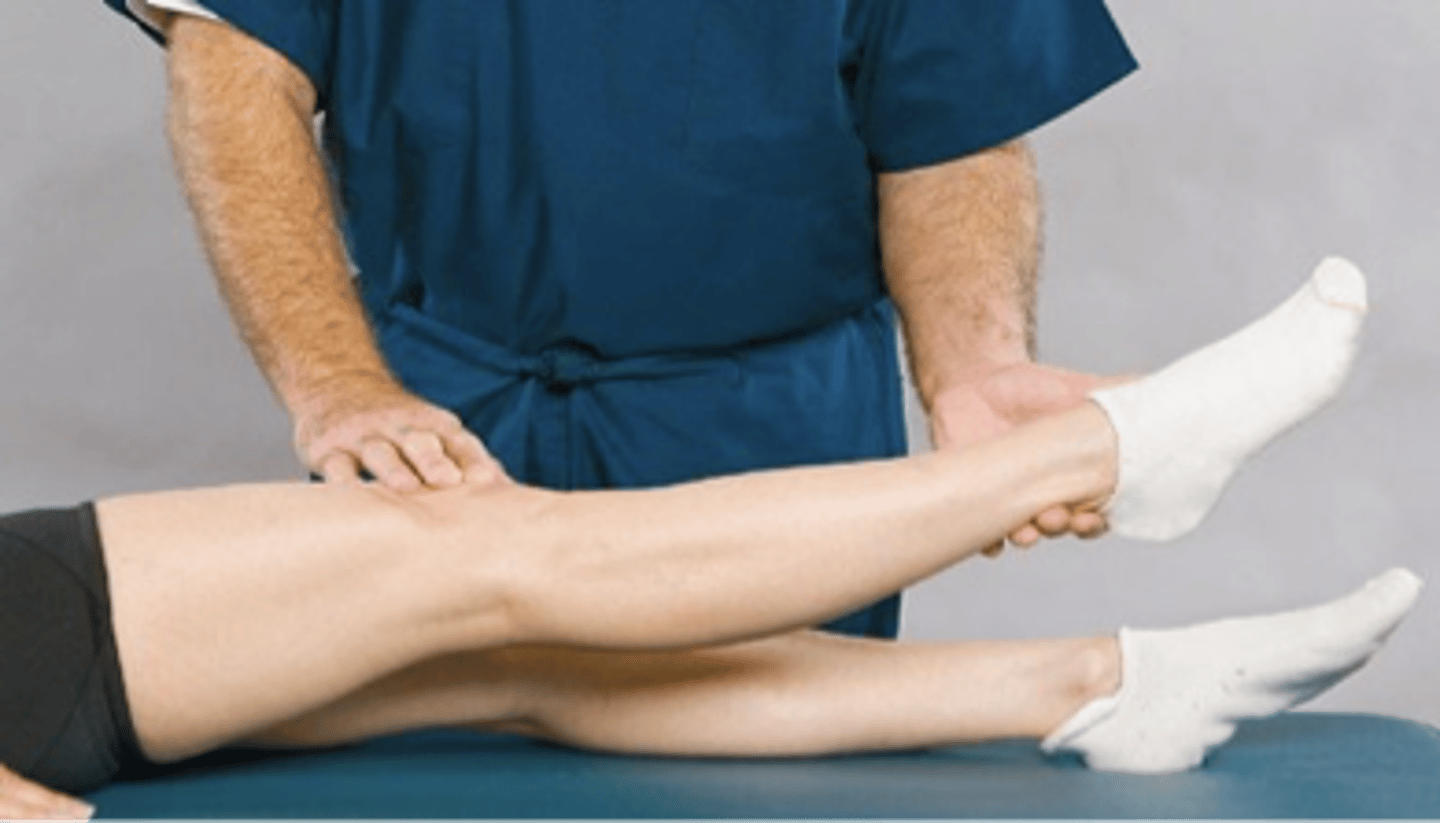
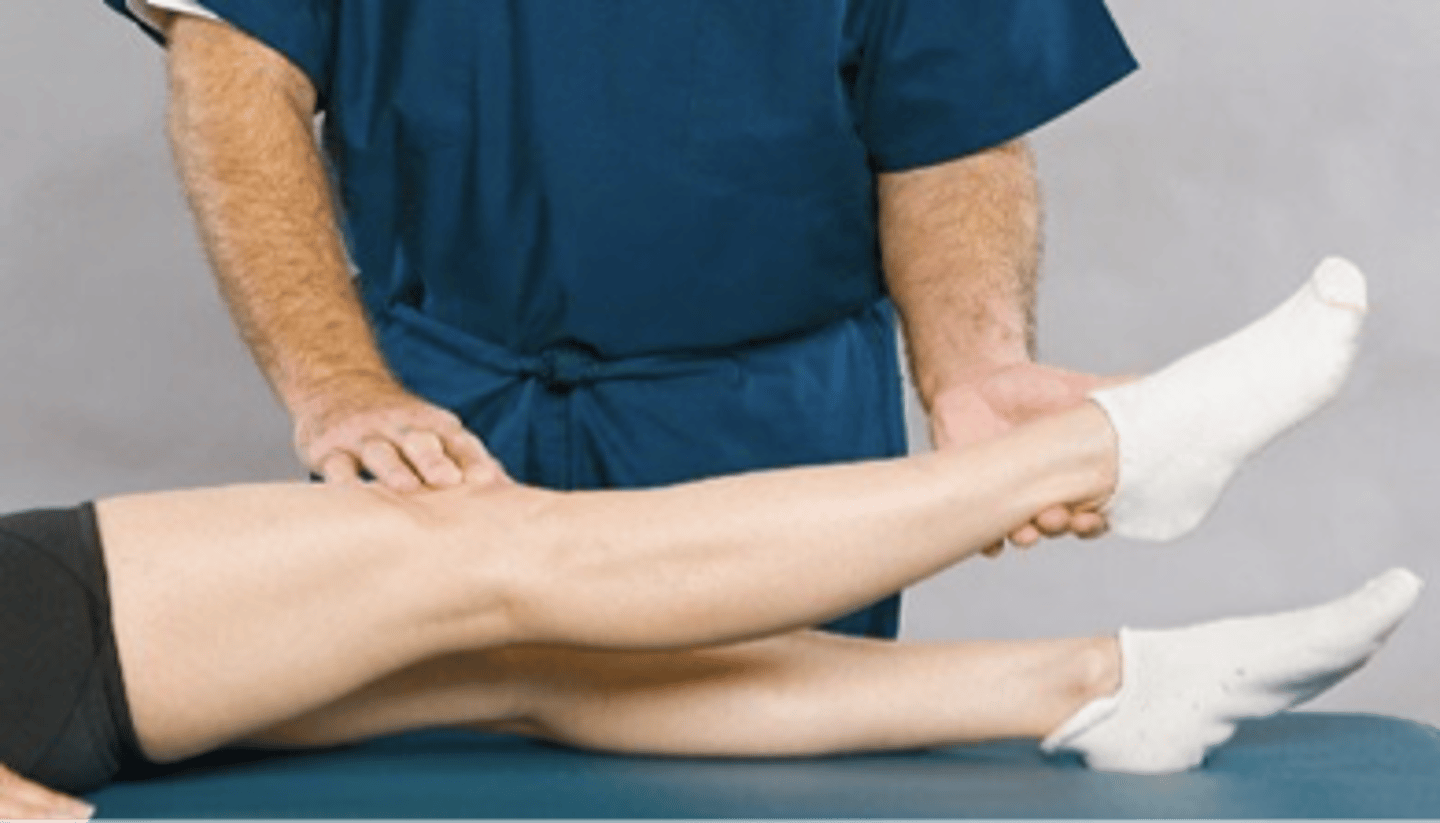
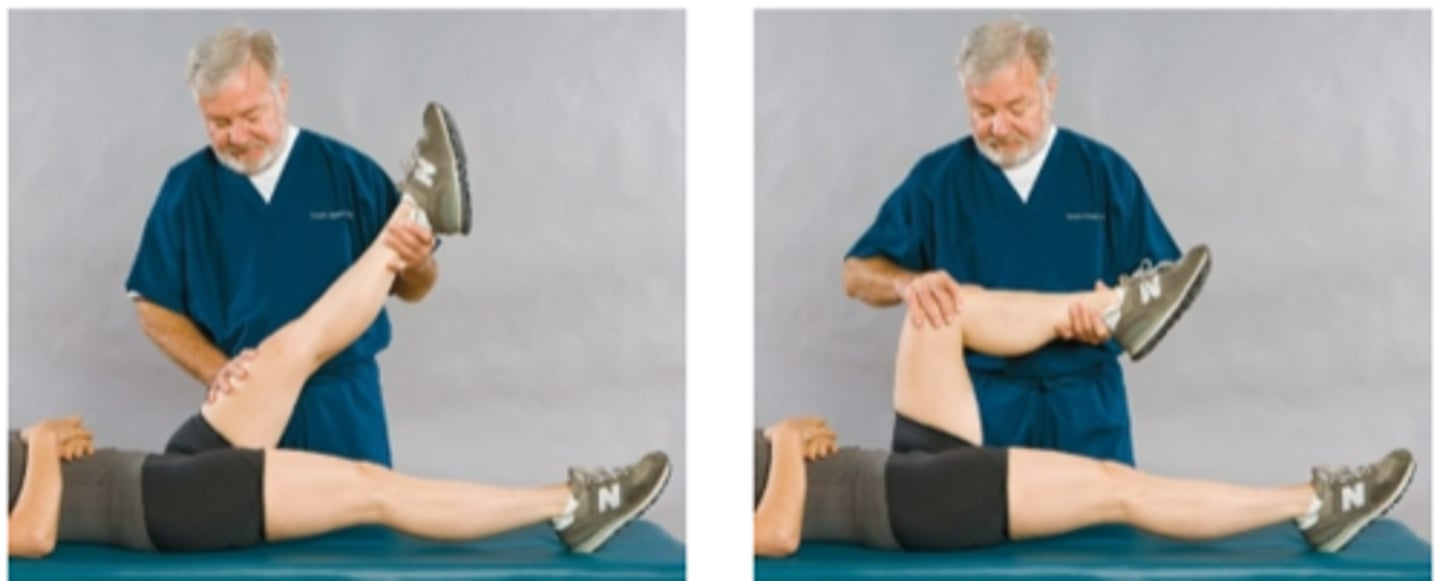
Lasegue Differential Sign
Assessment for:
- Intervertebral radiculopathy vs. hip joint disease
Lasegue Rebound Test
Assessment for:
- IVD
- Intervertebral nerve root
- Piriformis spasm
- Ischiotrochanteric groove adhesion
Disc
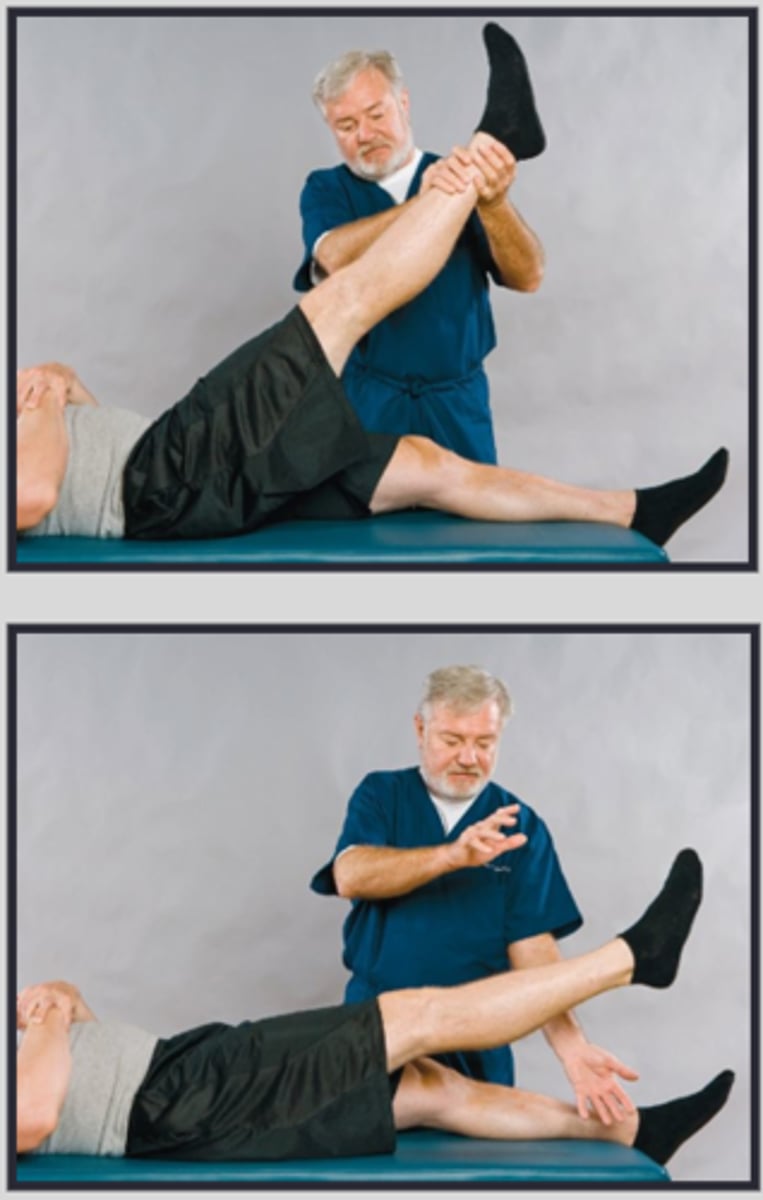
Lasegue Rebound Test
- Without warning, the examiner removes support from the elevated leg, allowing it to drop to the examination table. A positive test indicates _____ involvement
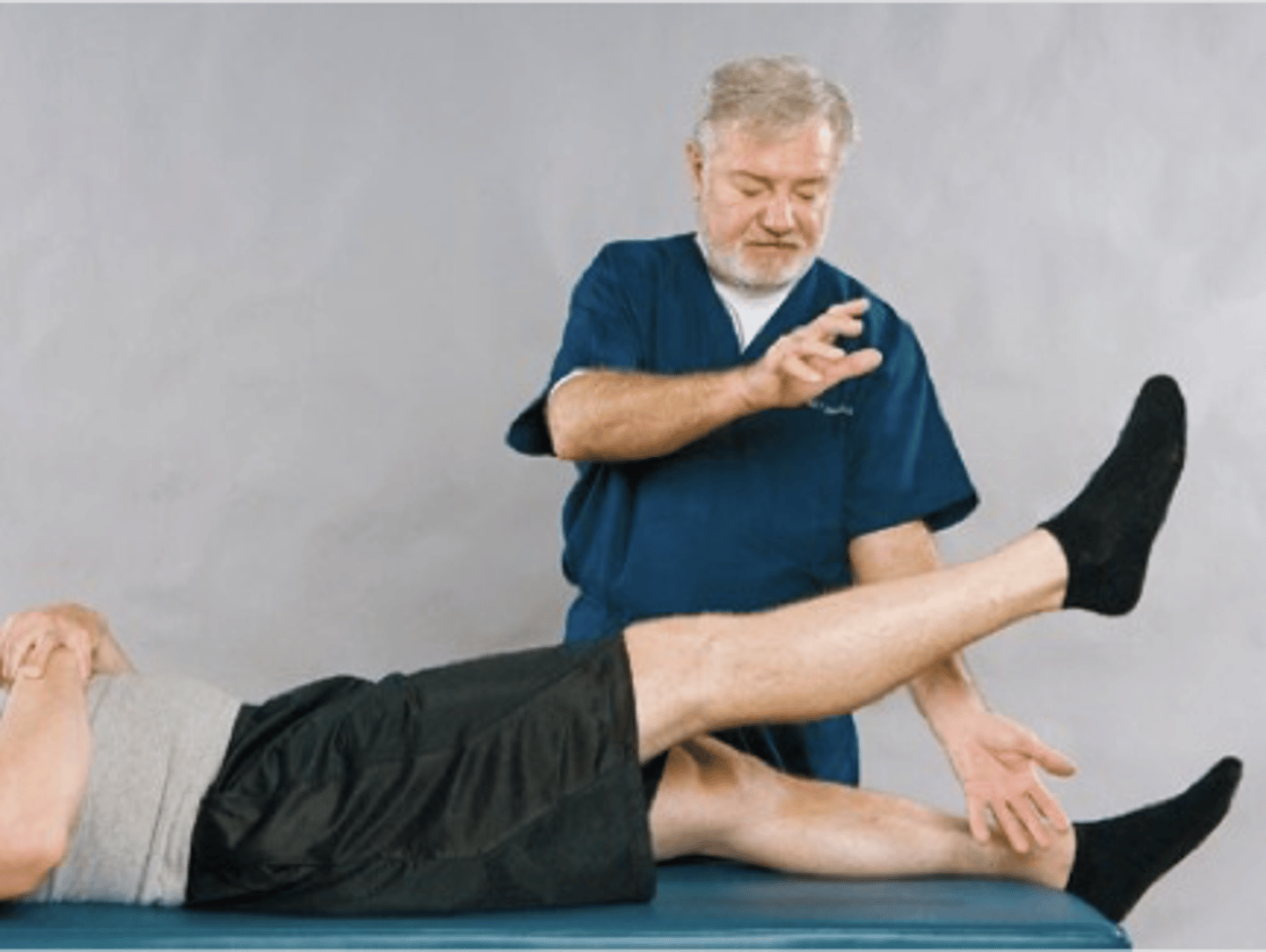
Lasegue Sitting Test
Assessment for:
- Sciatic nerve
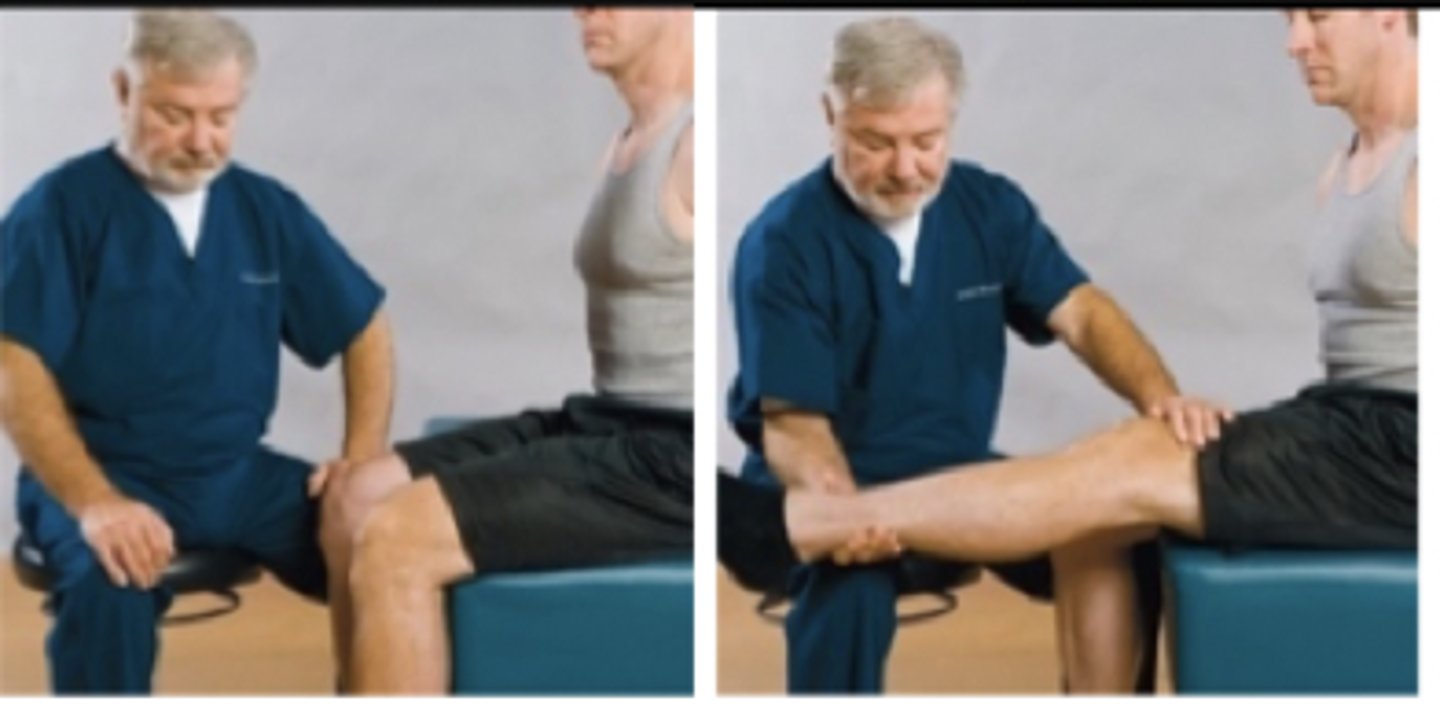
Lasegue Test or Sign
Assessment for:
- Sciatica from lumbosacral or SI Lesions
- IVD
- Spondylolisthesis
- Dural sleeve adhesions
- IVF encroachment
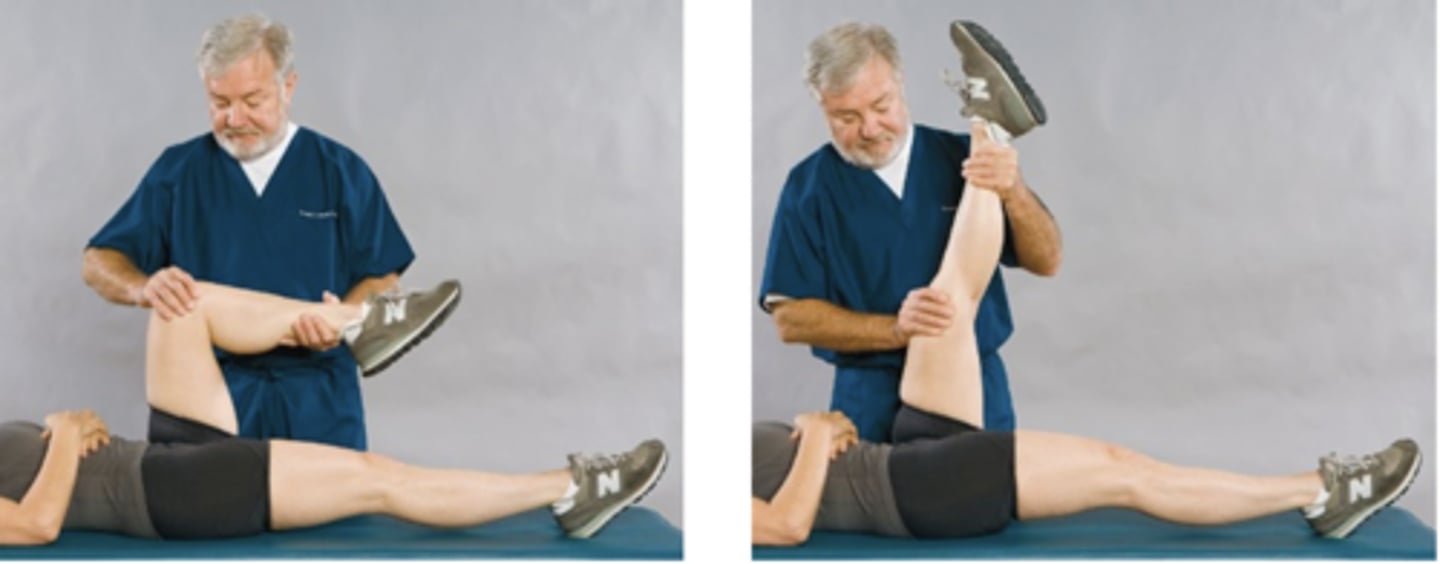
Bechterew Sitting Test
Assessment for:
- Sciatica
- IVD lesion
- Vertebral exostoses
- Dural sleeve adhesions
- Muscular spasm
- Vertebral subluxation
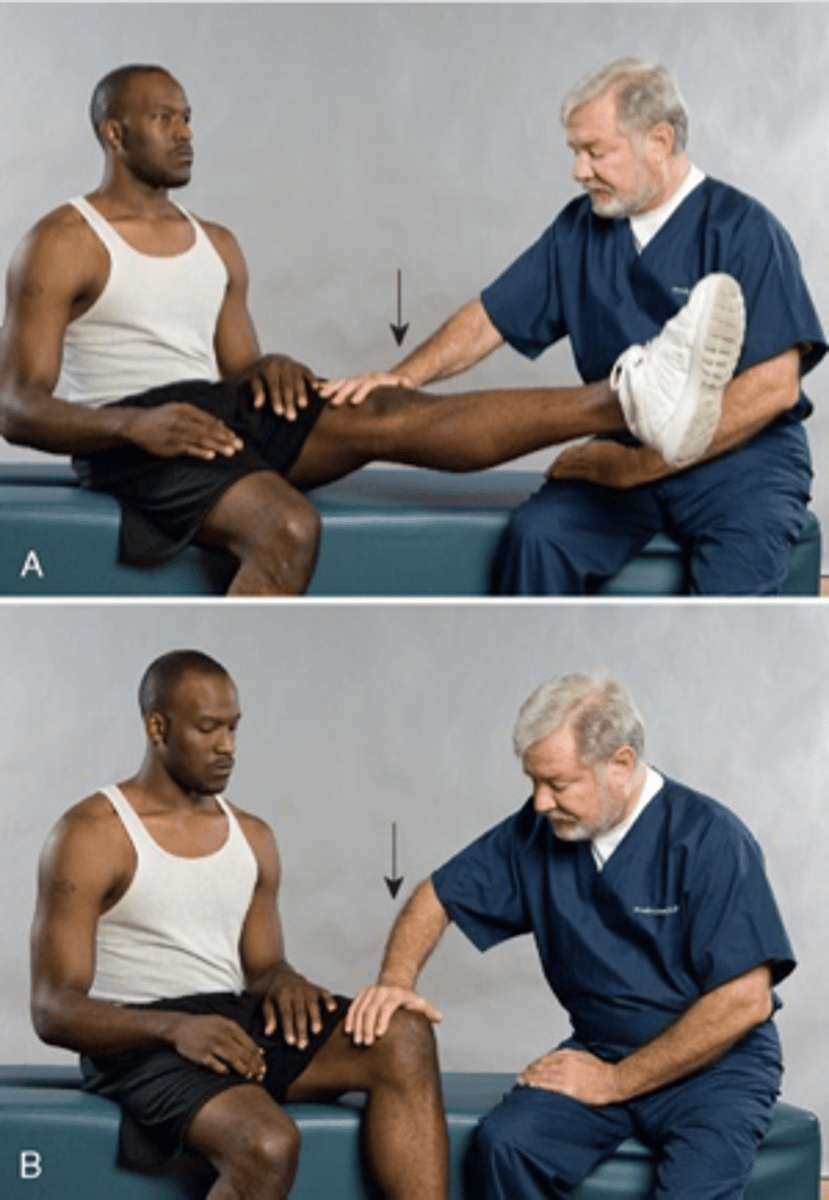
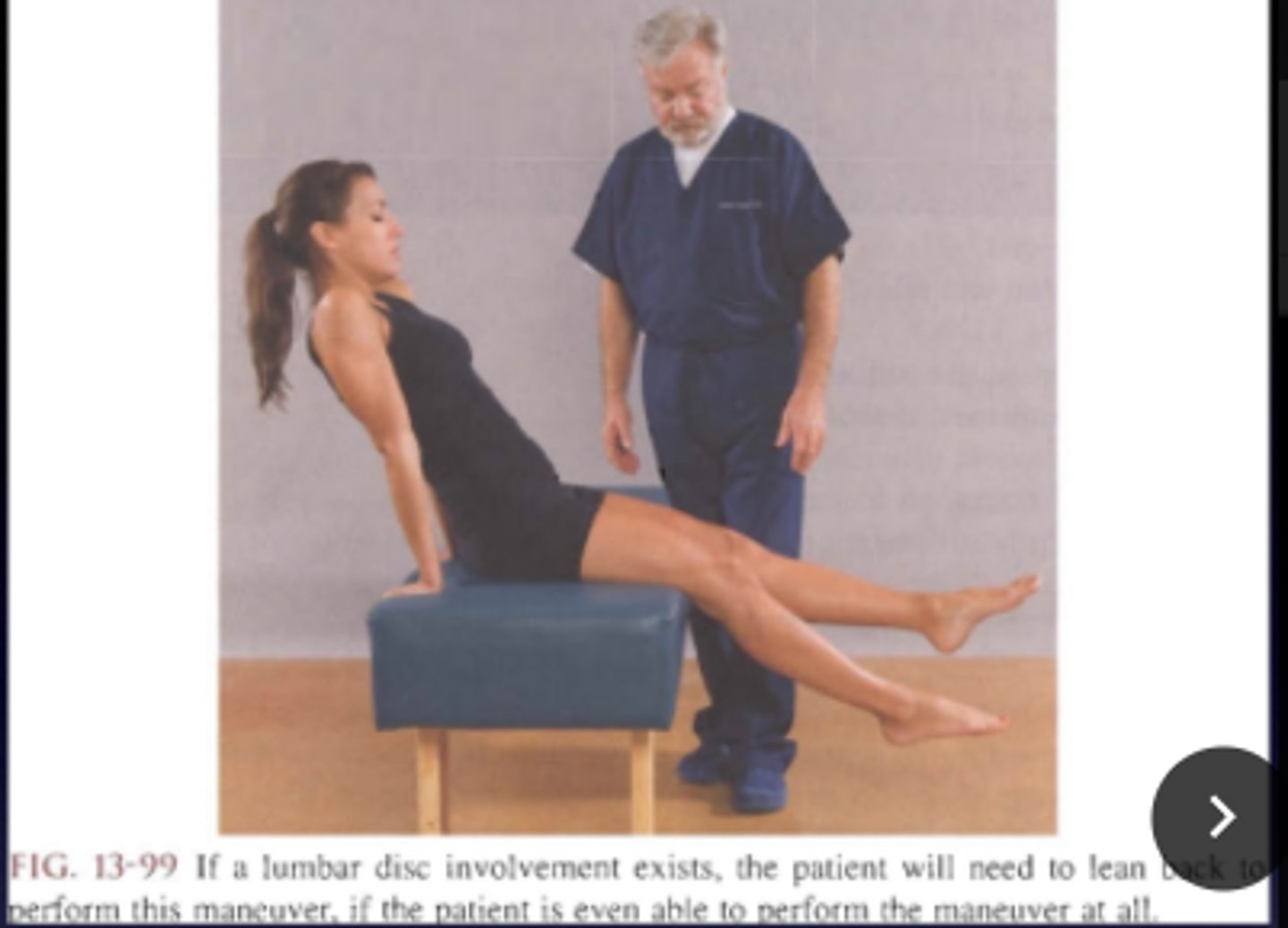
Tripod Sign
- Patient is seated then have the patient extend both legs
- Patient will be unable to stay in the position or will have reproductions of low or leg symptoms.
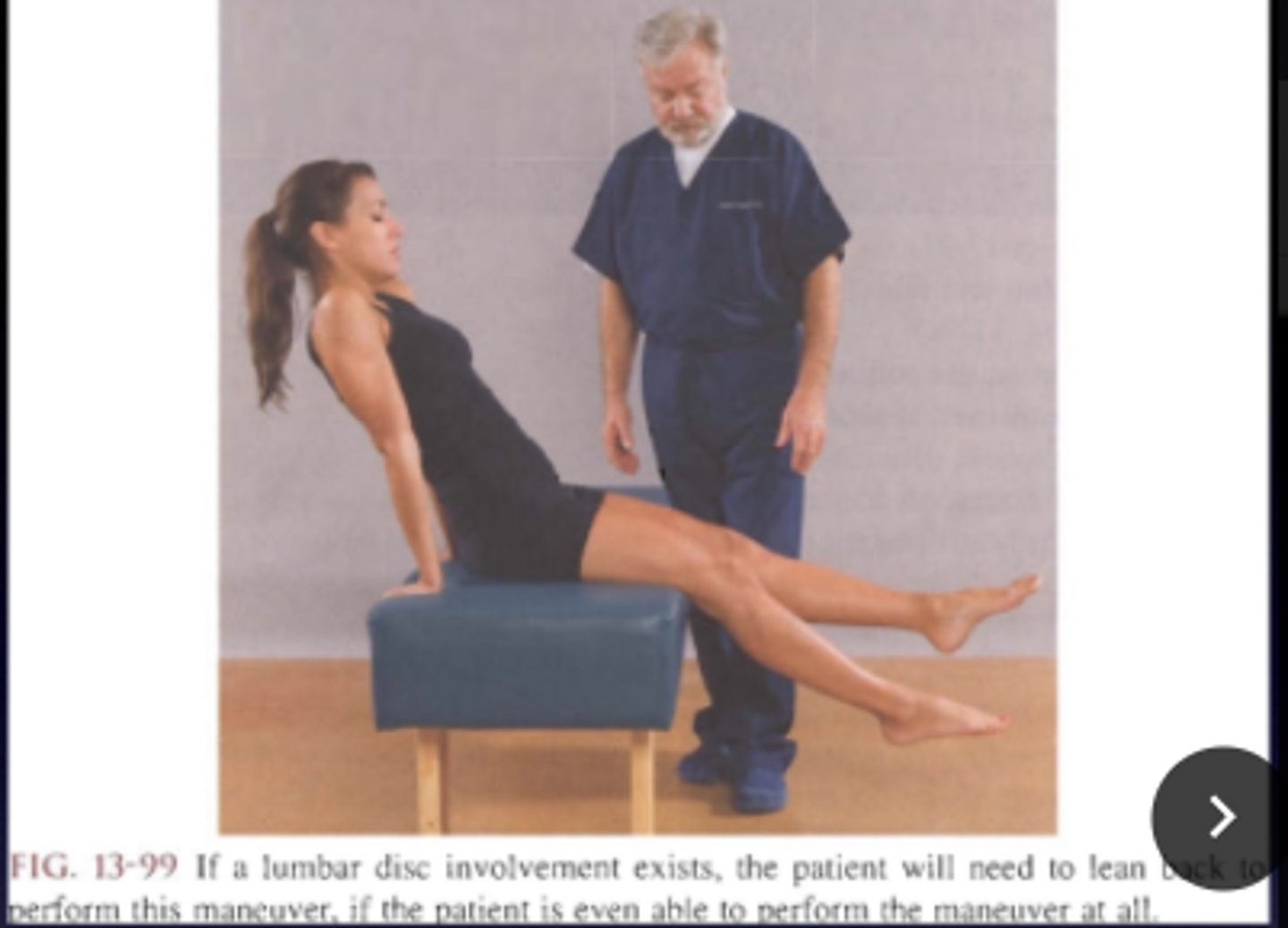
Bechterew Sitting Test
Indications of the Tripod Sign are the same as the _____
- Sciatica
- IVD lesion
- Vertebral exostoses
- Dural sleeve adhesions
- Muscular spasm
- Vertebral subluxation
Bowstring Sign
Assessment for:
- Lumbar nerve root compression
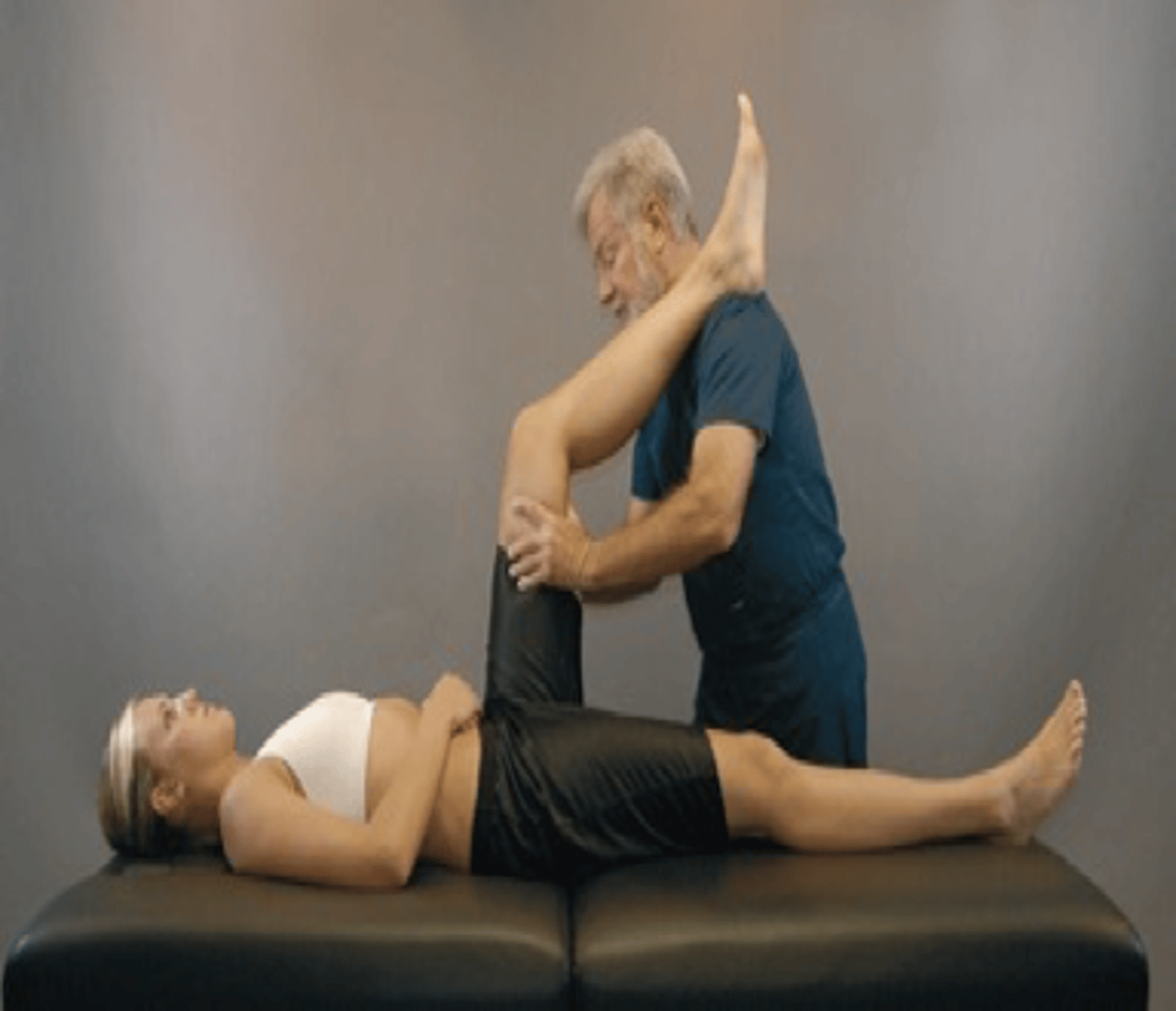

- With the patient in the supine position, the examiner moves the patient's leg until it is above the examiner's shoulder
- At this point, firm pressure should be exerted on the hamstring muscles
- If pain is not elicited, pressure is applied to the popliteal fossa
Explain the procedure for the Bowstring Sign

Nerve root compression
With the Bowstring Sign, pain in the lumbar region or radiculopathy is a positive sign for _____

Deyerle Sign
Assessment for:
- Sciatic nerve irritation
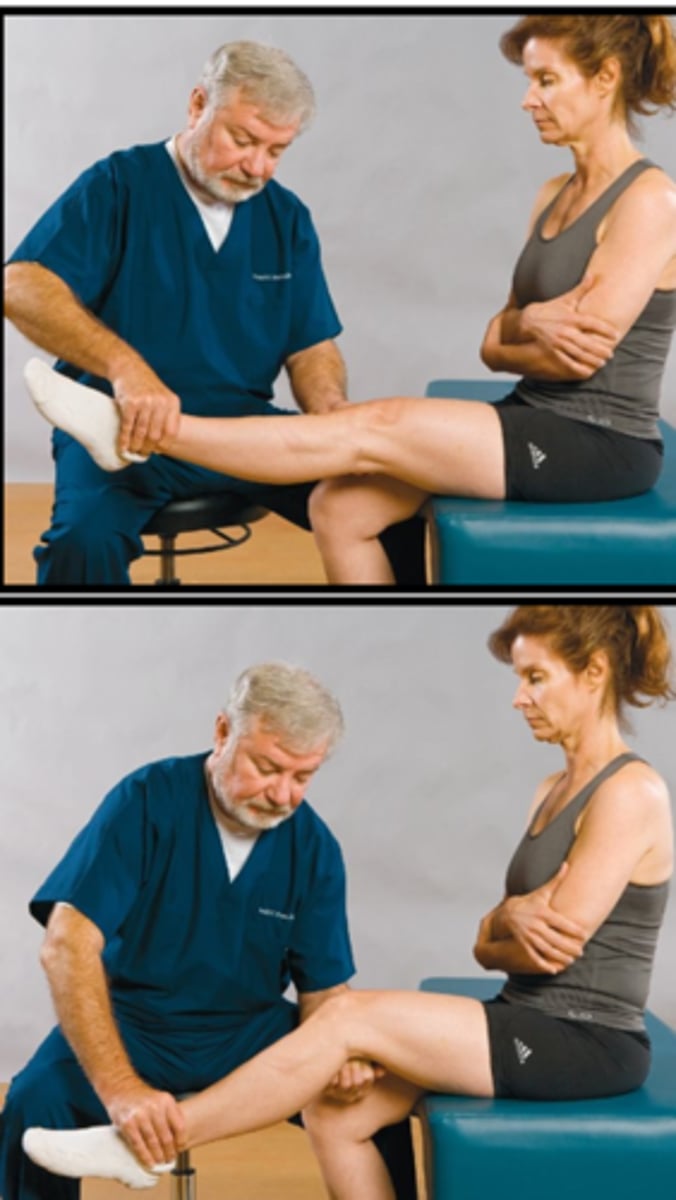
Radicular
The Deyerle Sign is present if _____ symptoms are present
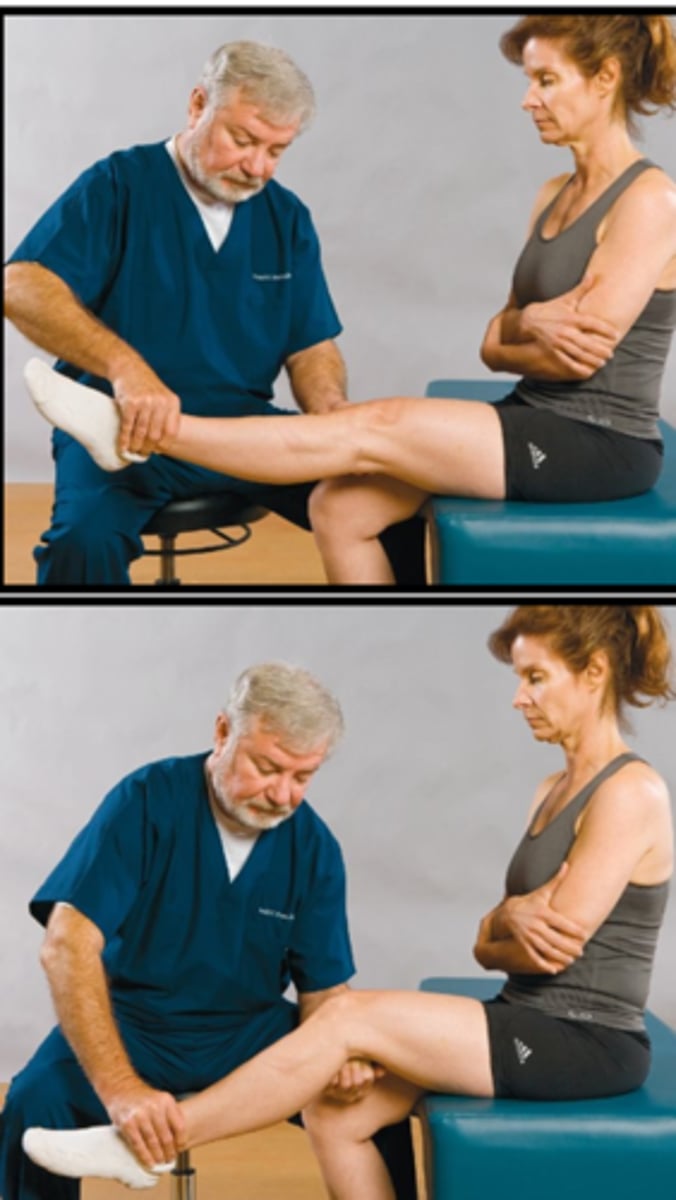
Popliteal fossa
With the Deyerle Sign, extend the affected leg until pain is produced then apply pressure to the _____ when the knee is flexed
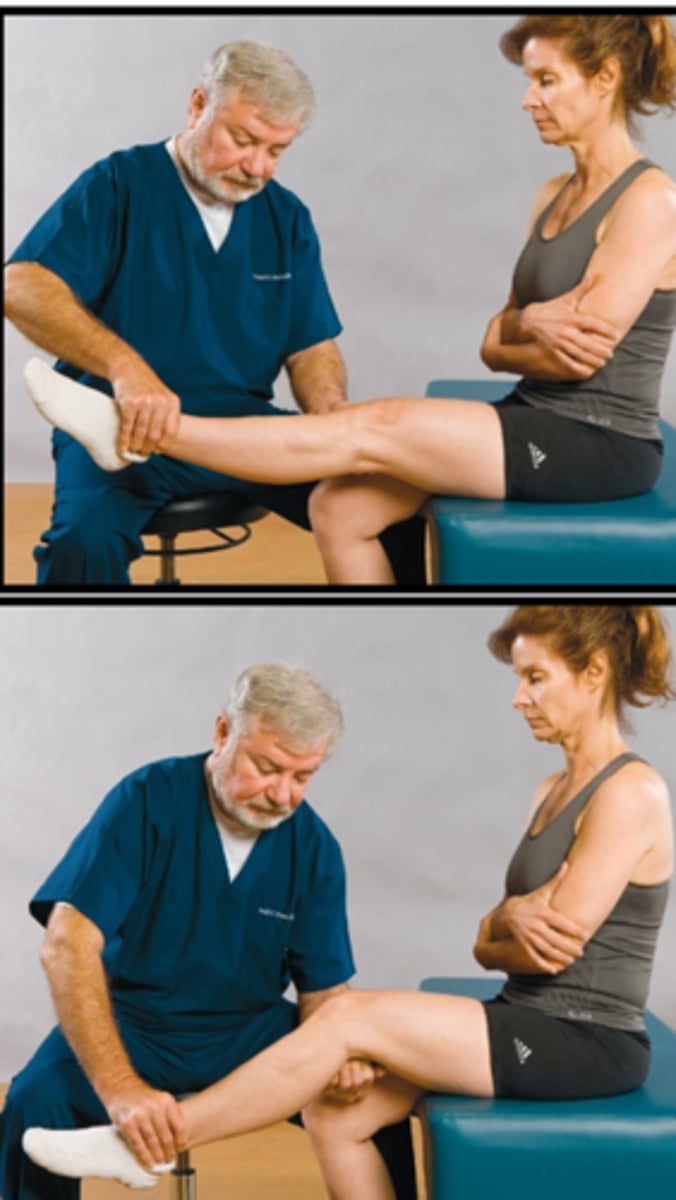
Kemp Test
Assessment for:
- Intervertebral nerve root encroachment
- Muscular strain
- Ligament sprain
- Pericapsular inflammation
True
T/F The Kemp Test can be performed seated or standing
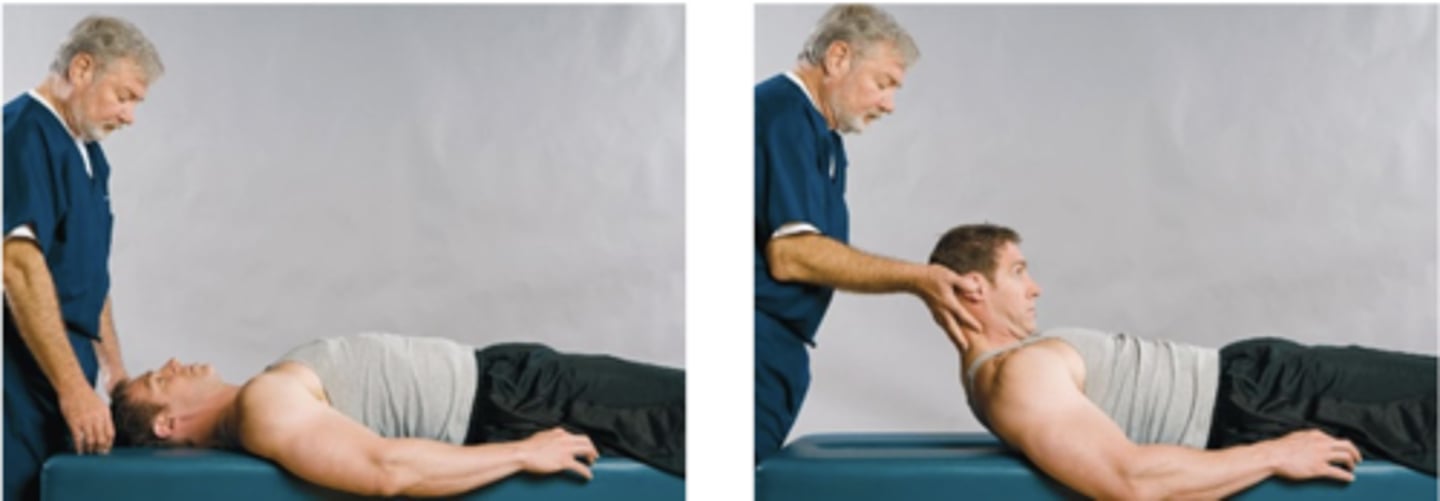
Lindner Sign
Assessment for:
- Lumbar nerve root
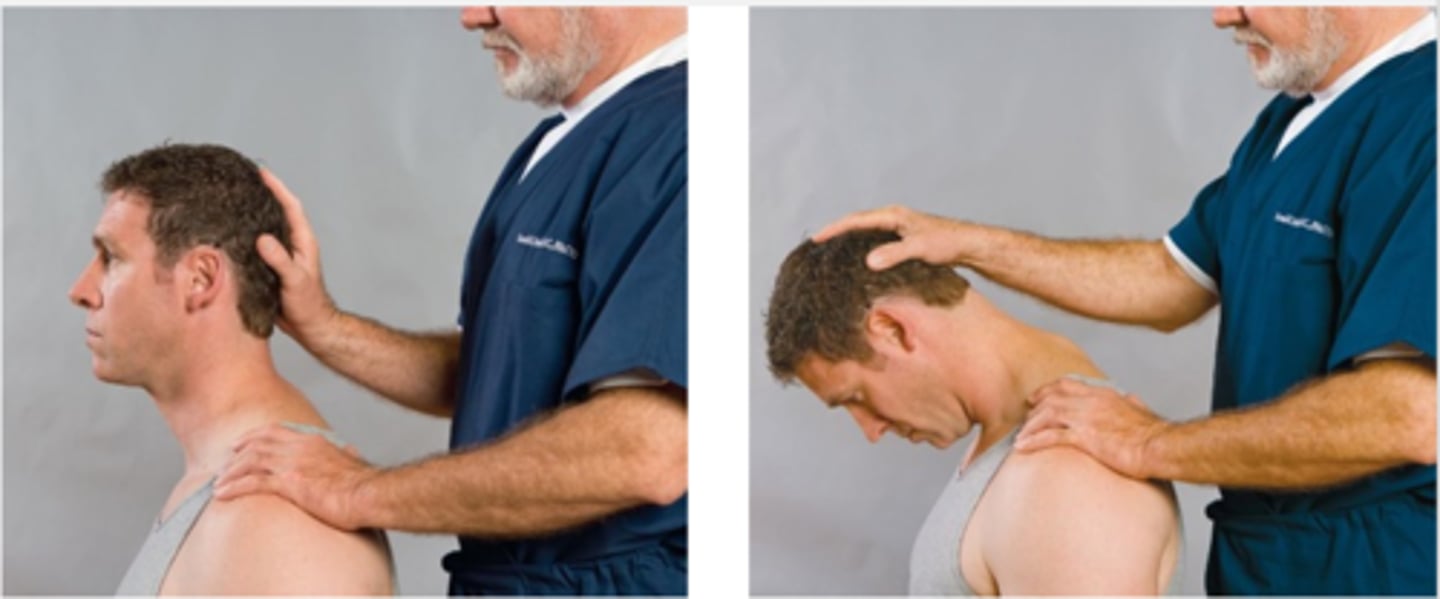
Supine
What is another position the Lindner Sign can be done in?
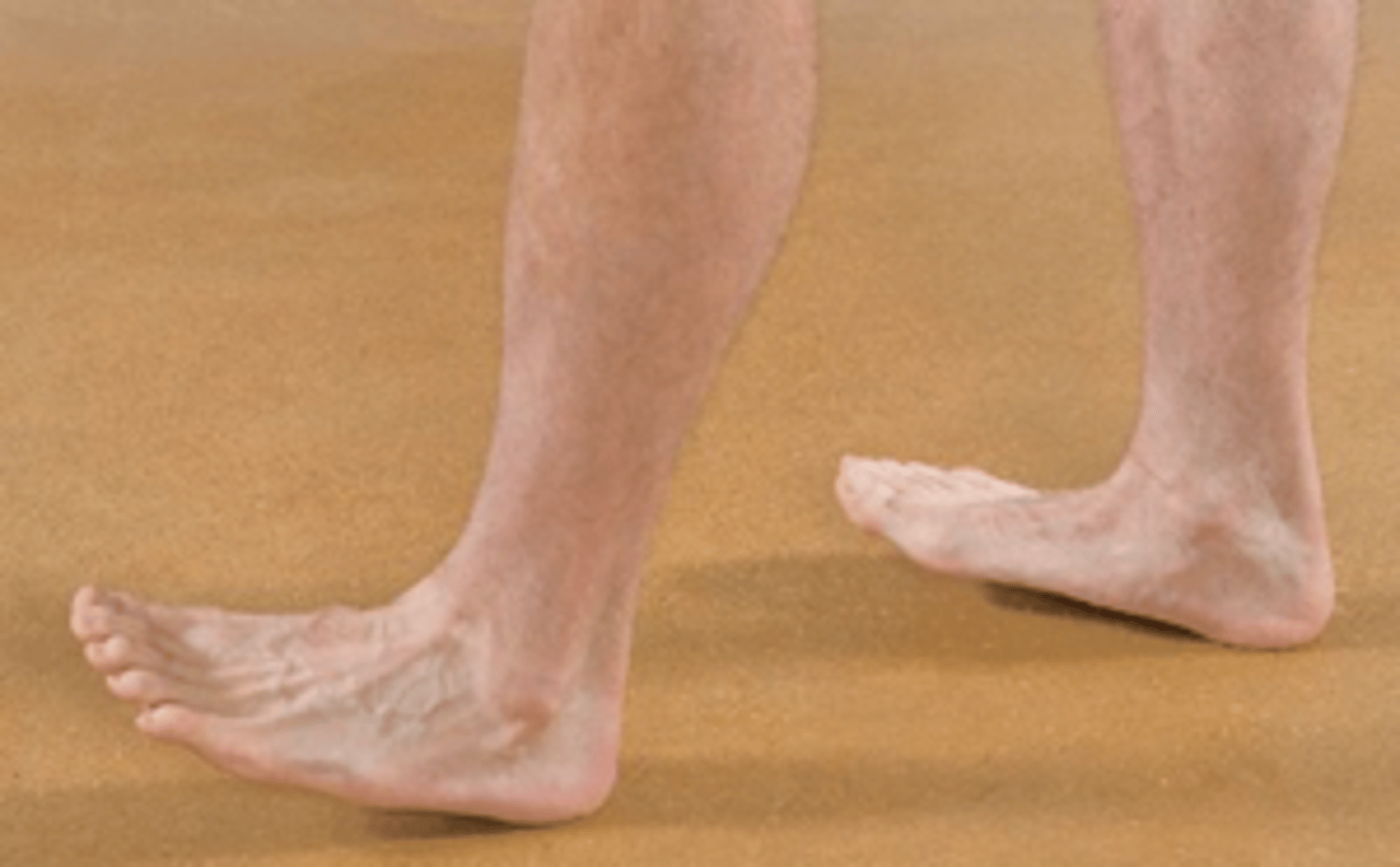
Heel/Toe Walk Test
Assessment for:
- L5 or S1 nerve root motor deficiency
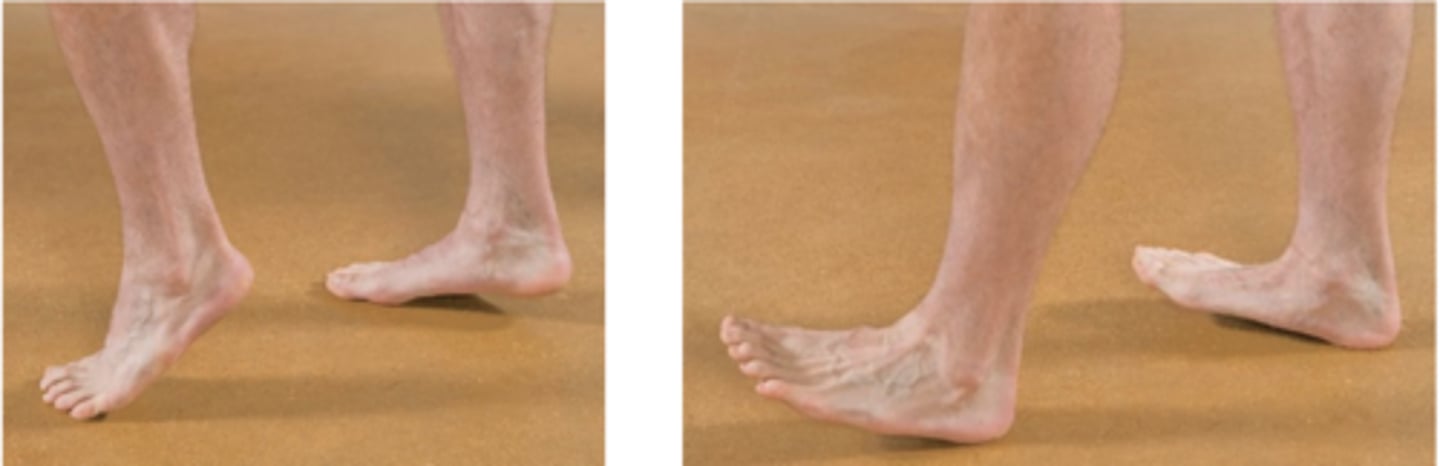
- S1
- Tibial
Toe walk is indicative of _____ weakness with _____ nerve involvement
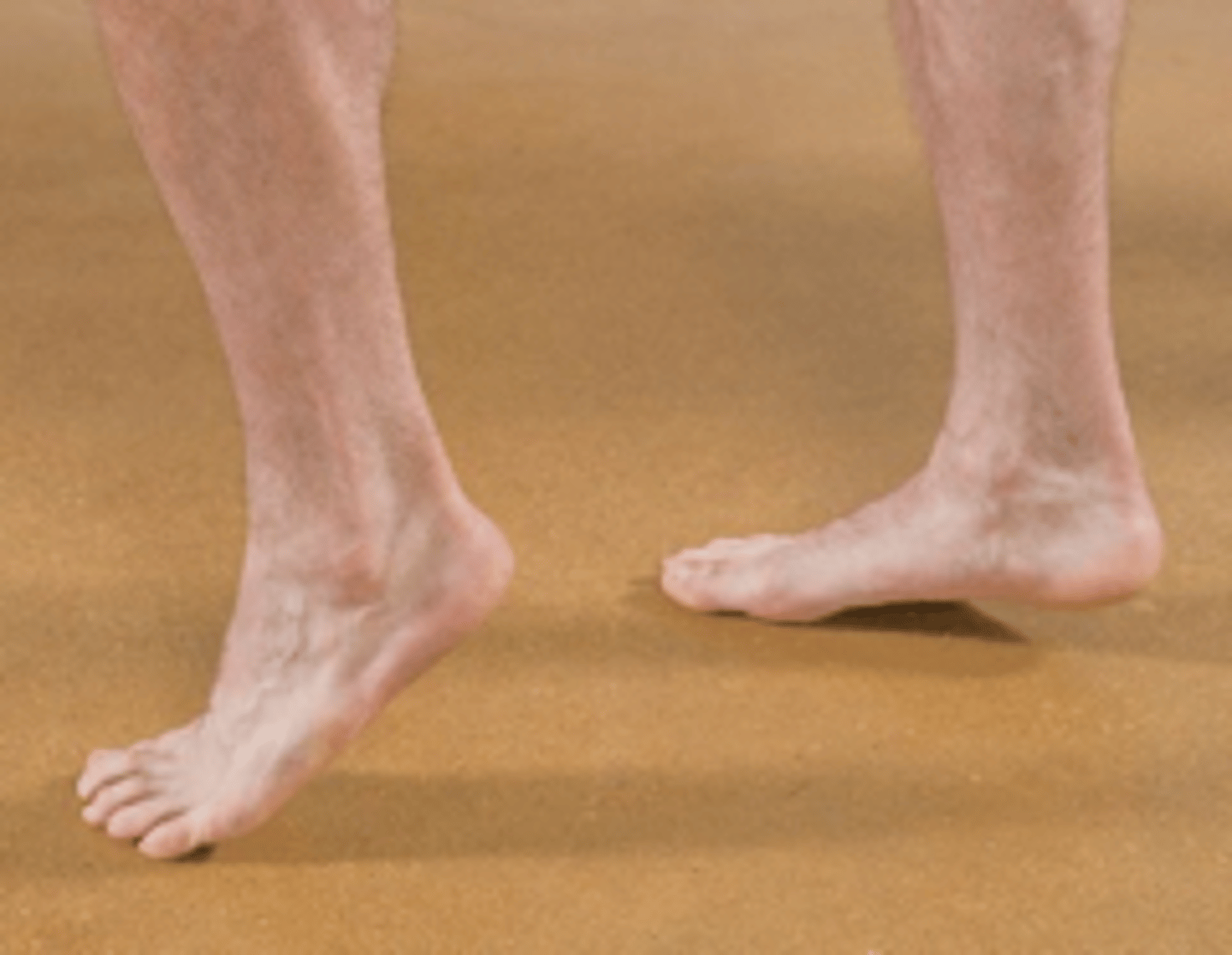
- L5
- Common peroneal
Heel walk is indicative of _____ weakness with _____ nerve involvement

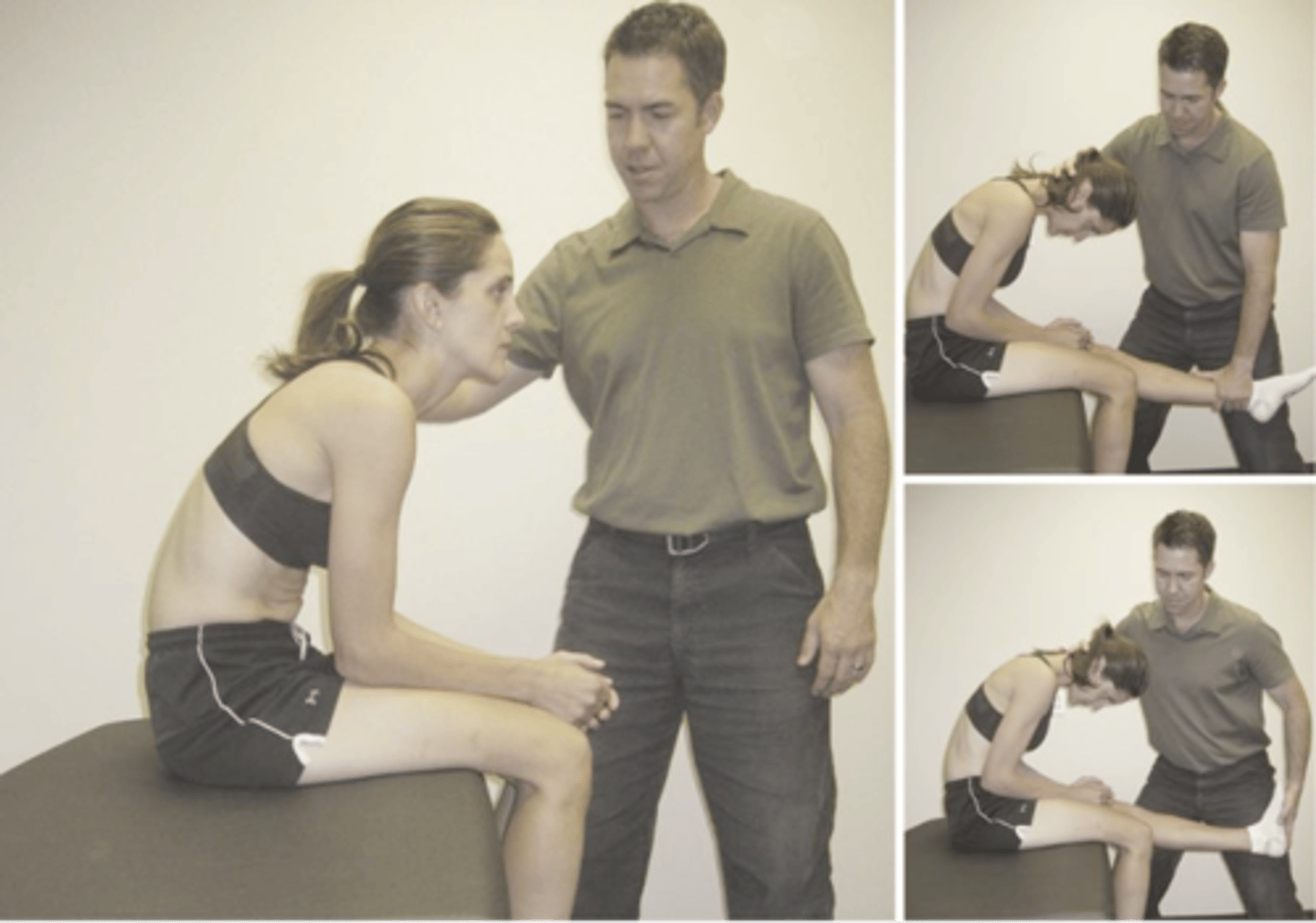
Slump Test
- Patient flexion of T/L
- Head full flexion
- Straighten affected leg
- Dorsiflexion foot
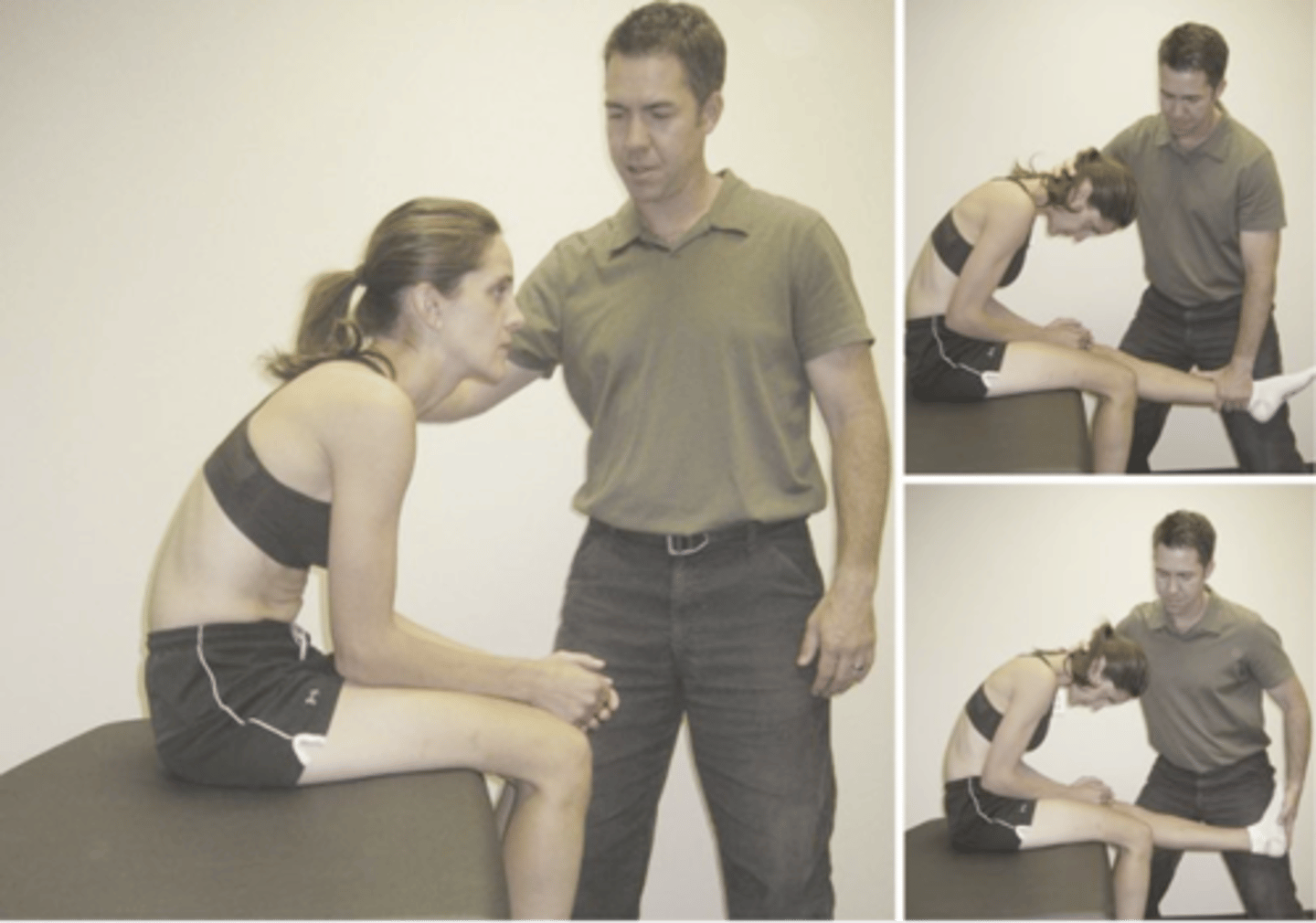

Radicular pain
What is a positive sign in the Slump Test?

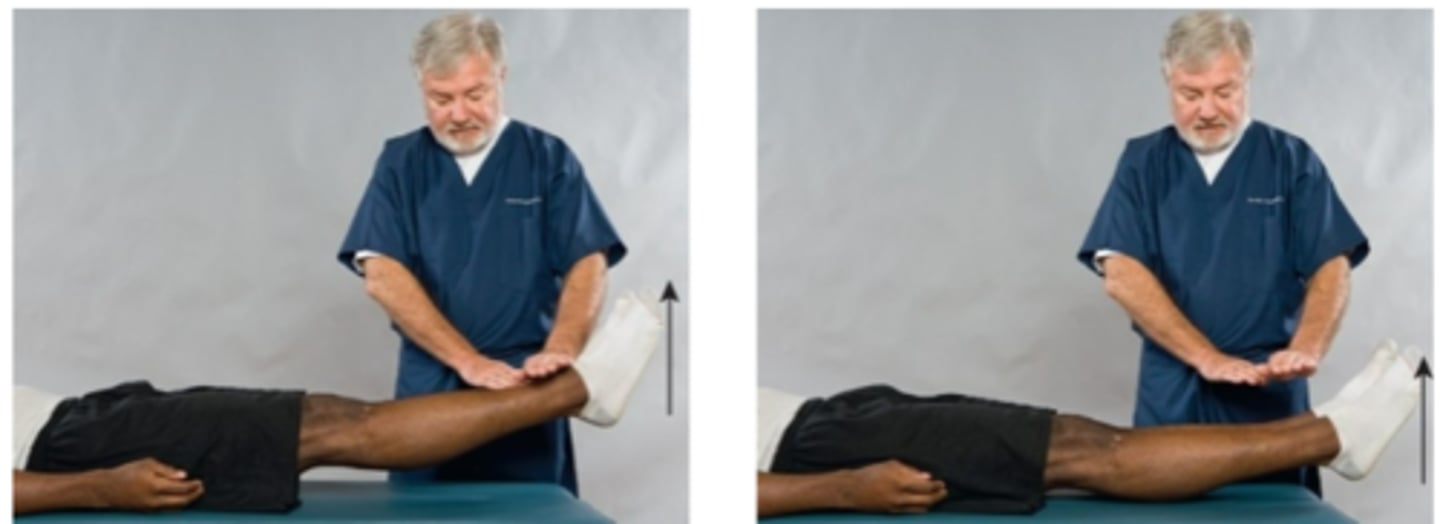
Milgram Test
Assessment for:
- IVD
- Space-occupying lesion
Lewin Punch Test
Assessment for:
- Spinal lesion
- IVD
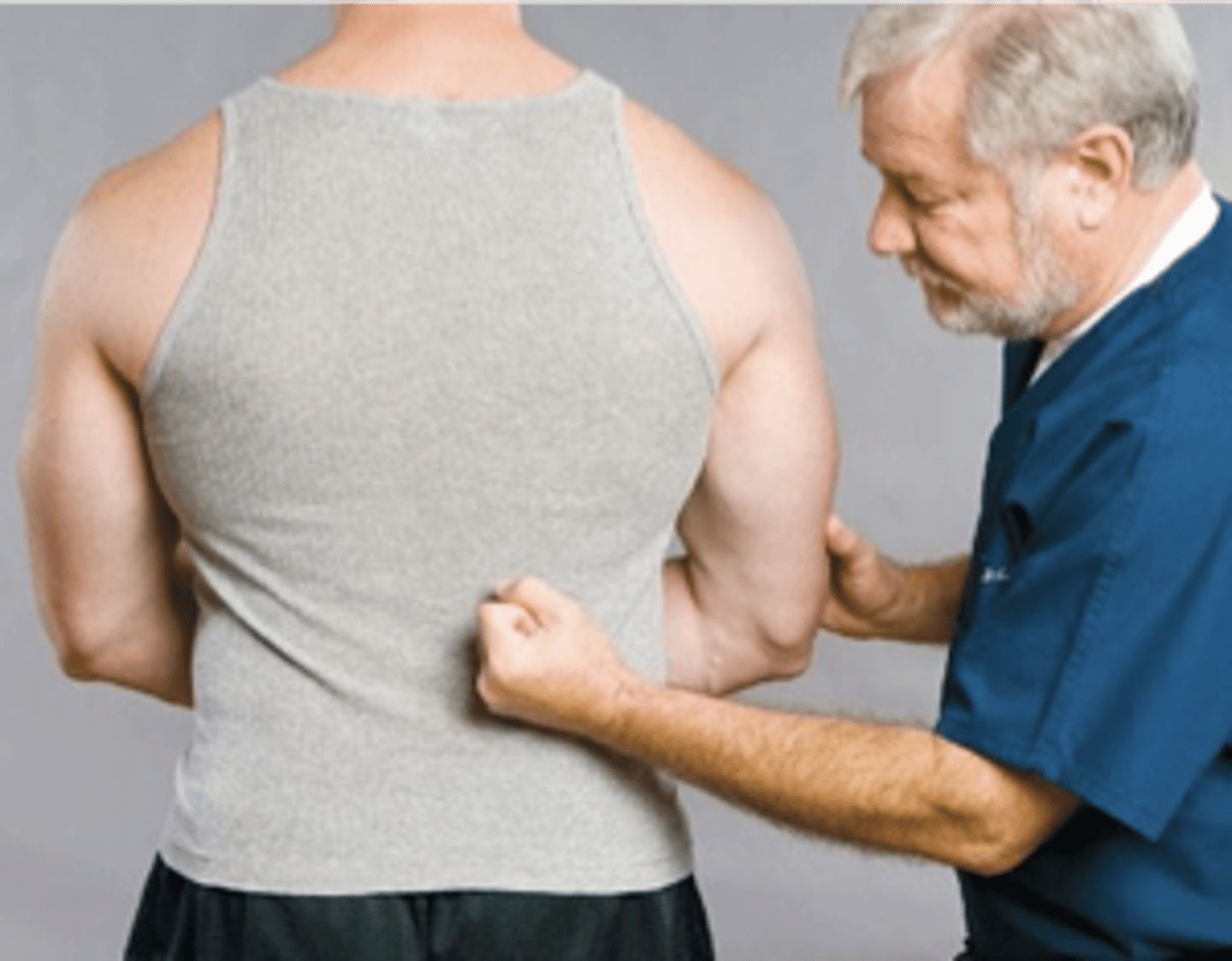
Lewin Snuff Test
Assessment for:
- IVD rupture
- Space-occupying mass
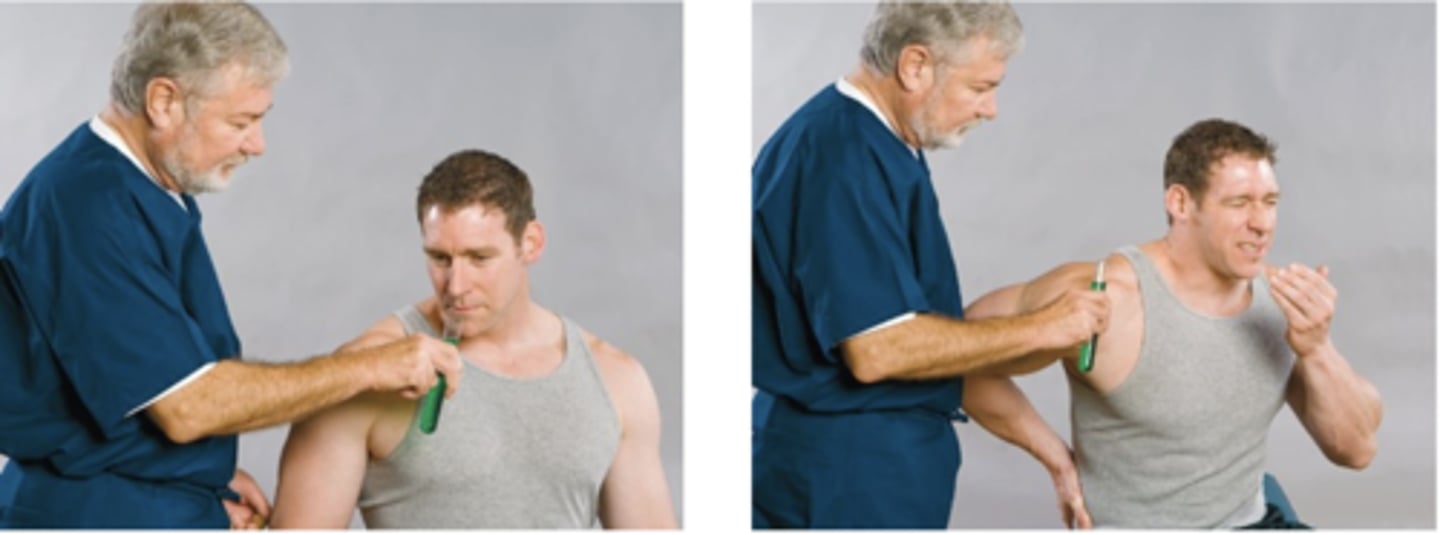
Neri Sign
Assessment for:
- IVD/lumbosacral and SI sprain
- Lumbopelvic subluxation
Neri Sign
The _____ is present if the patient flexes the knee on the affected side and if trunk flexion causes pain in the leg
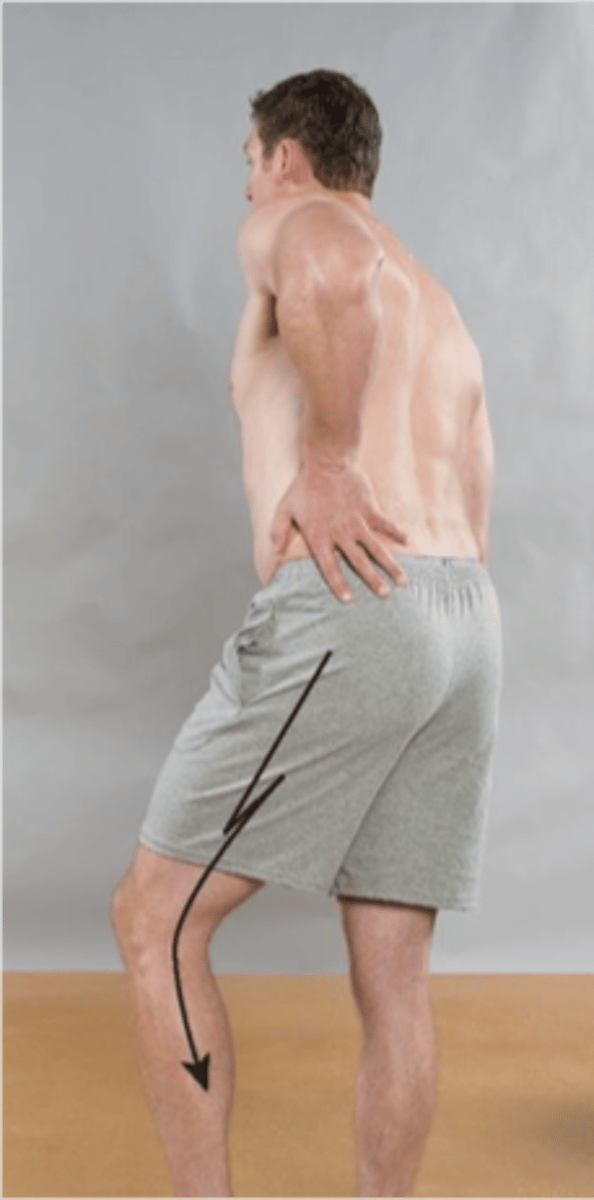

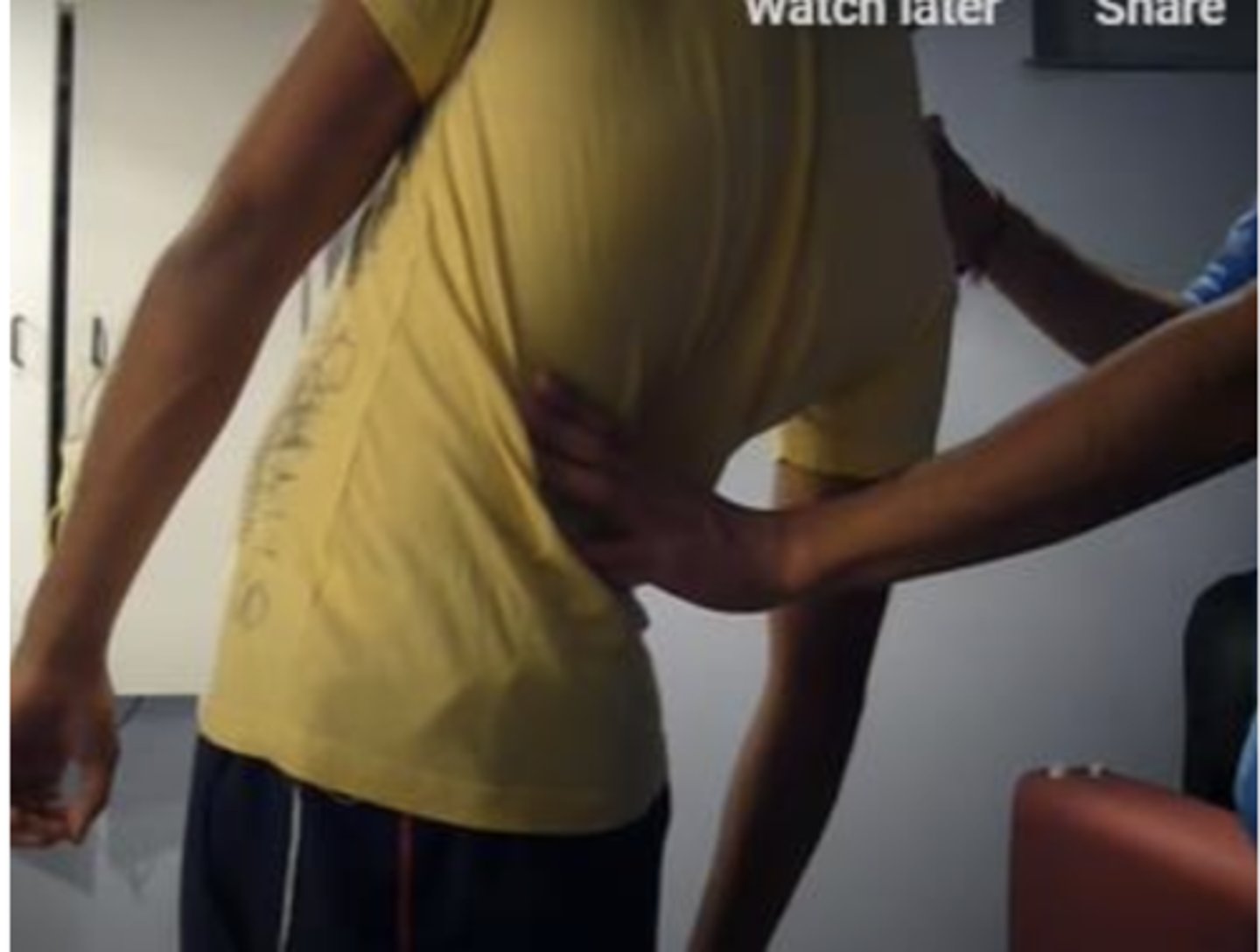
Extension-Rotation Test
Like Kemp's, but performed standing
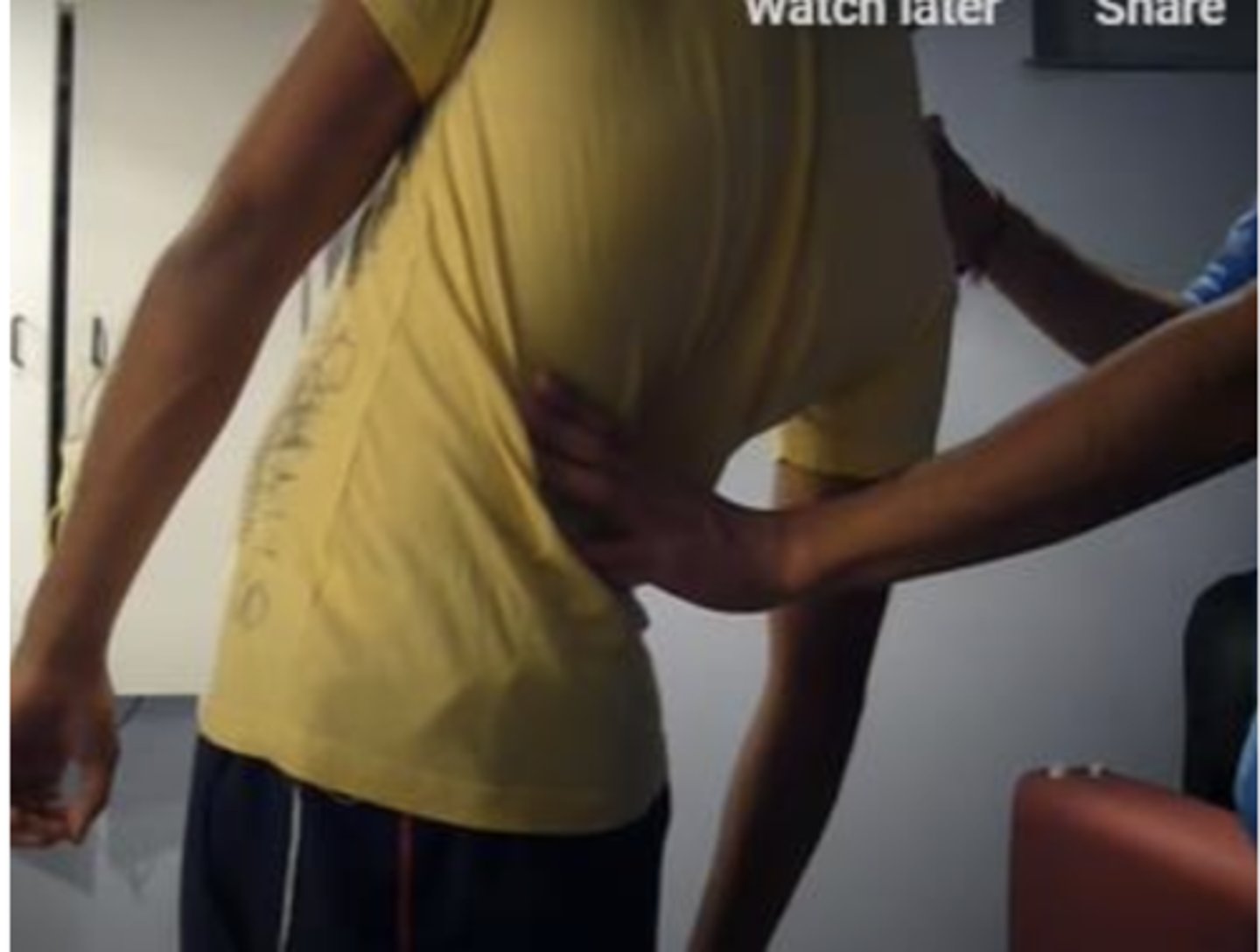
Facet
In the Extension-Rotation Test, localized pain indicates _____ involvement
Spinal Percussion Test
Assessment for:
- Osseous or soft-tissue injury
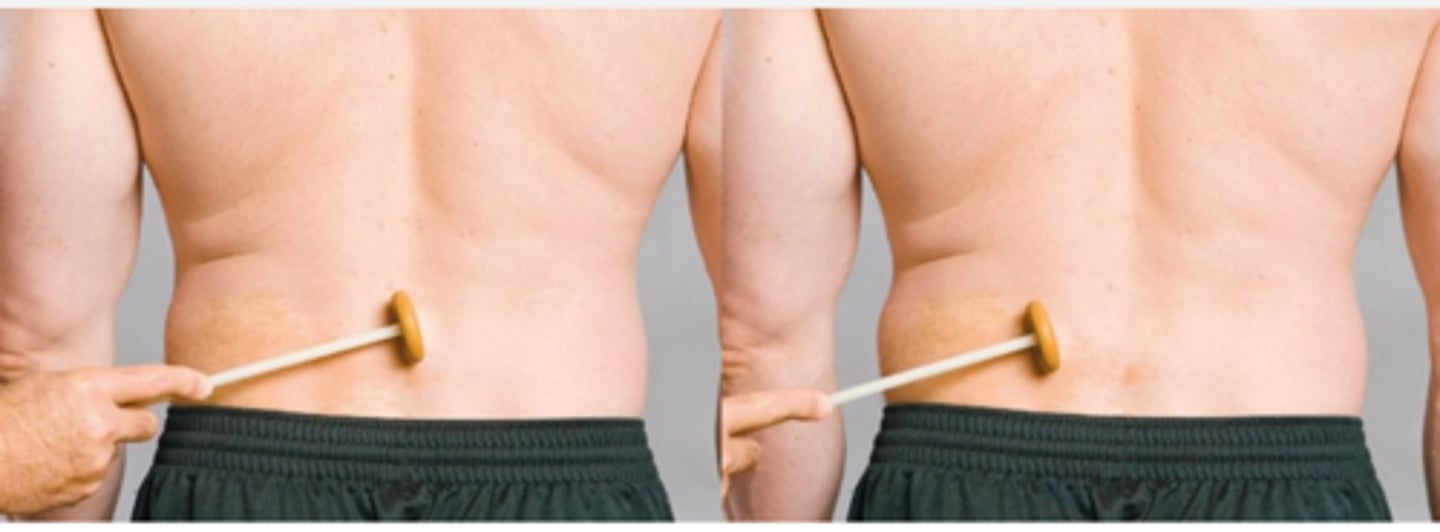
- Fracture
- Sprain
With the Spinal Percussion Test, pain over the SP indicates _____ or _____
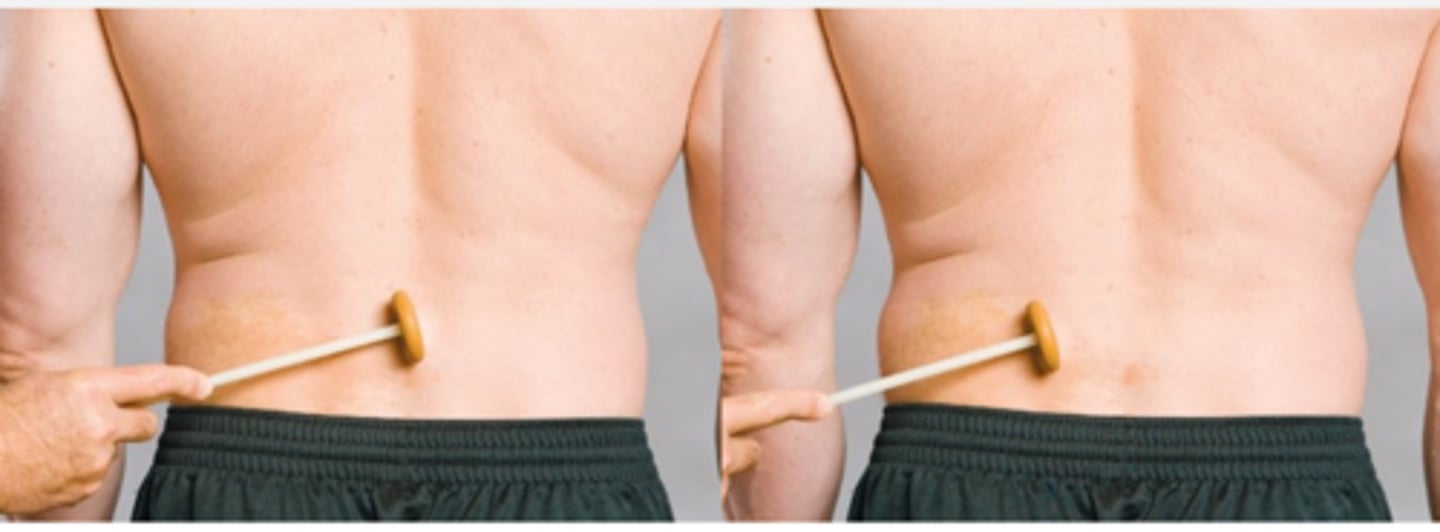
- Strain
- Myalgia
With the Spinal Percussion Test, pain over the paraspinals indicates _____ or _____
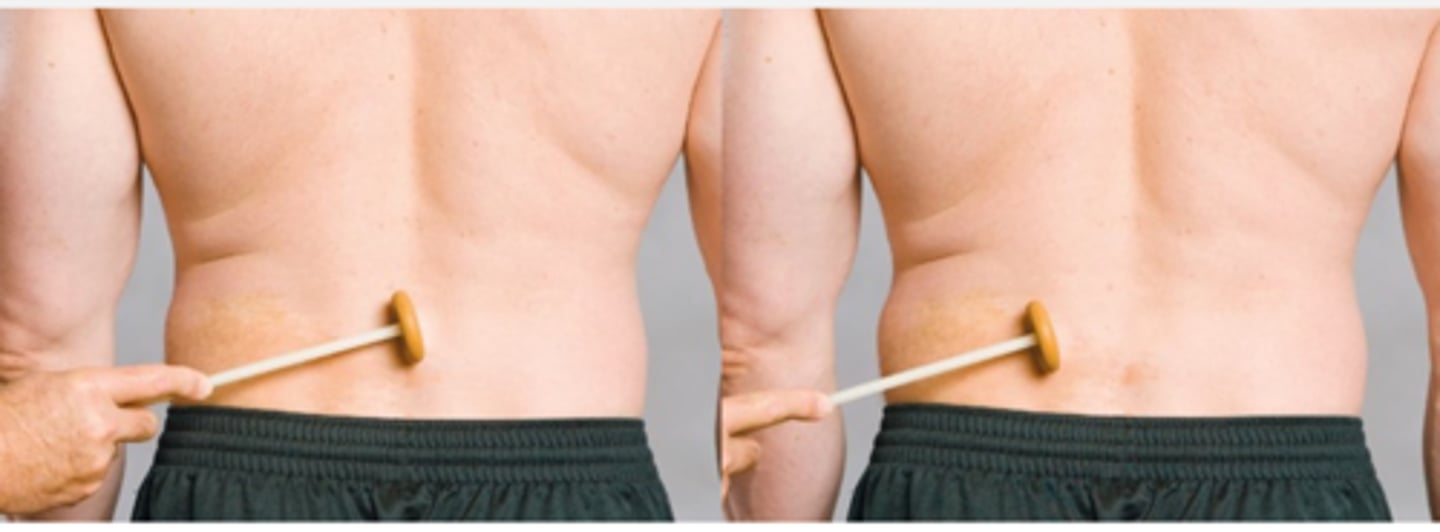
Nachlas Test
Assessment for:
- SI or lumbosacral disorders
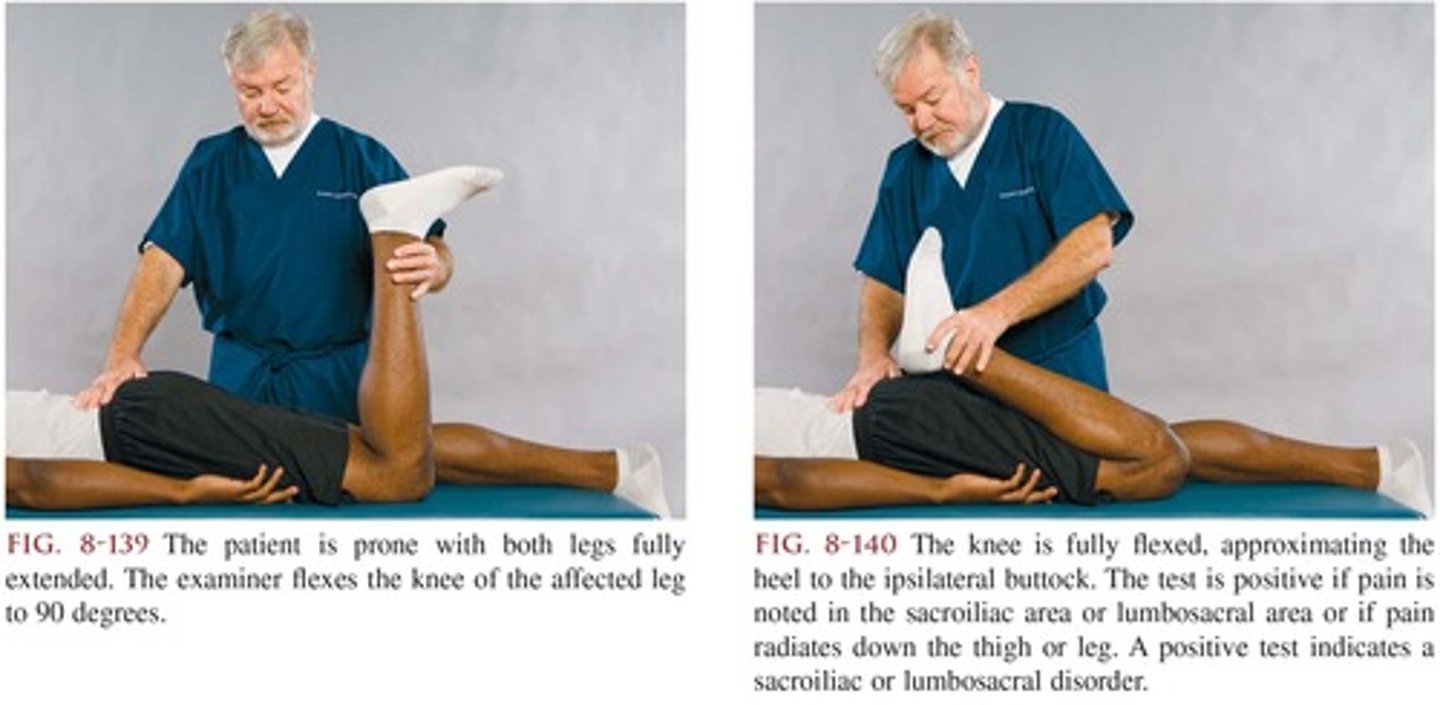
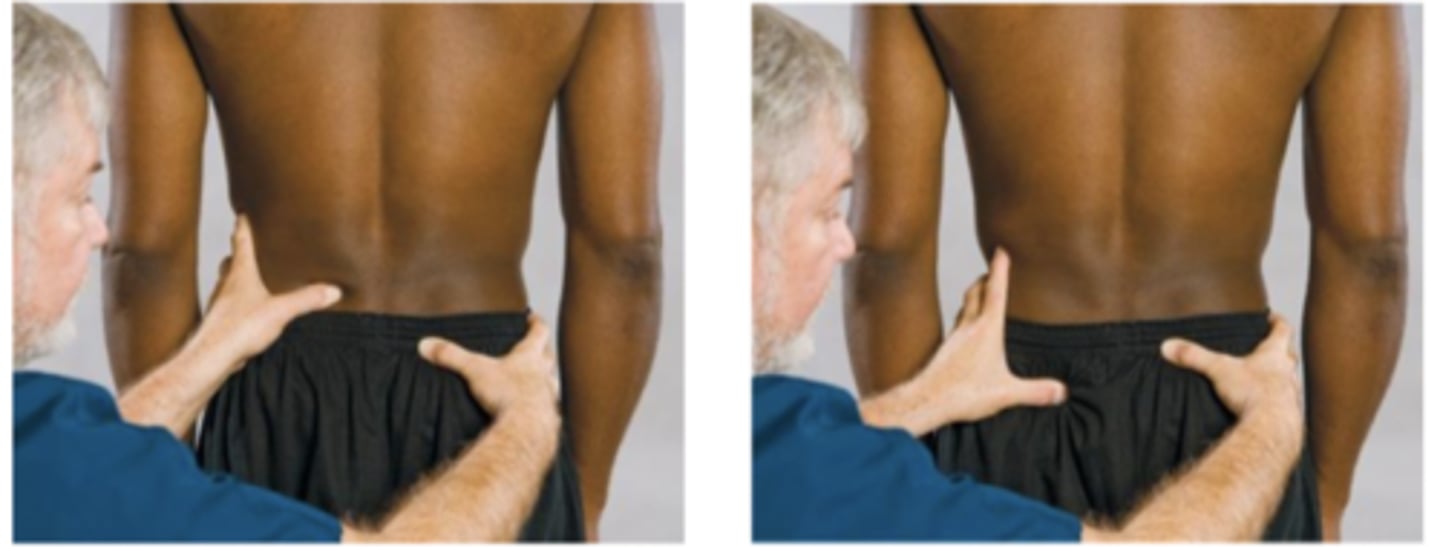
Mennell Sign
Assessment for:
- SI joints
Bilateral Leg-Lowering Test
Assessment for:
- Mechanical lumbosacral lesion
- IVD lesion
- Vertebral exostoses
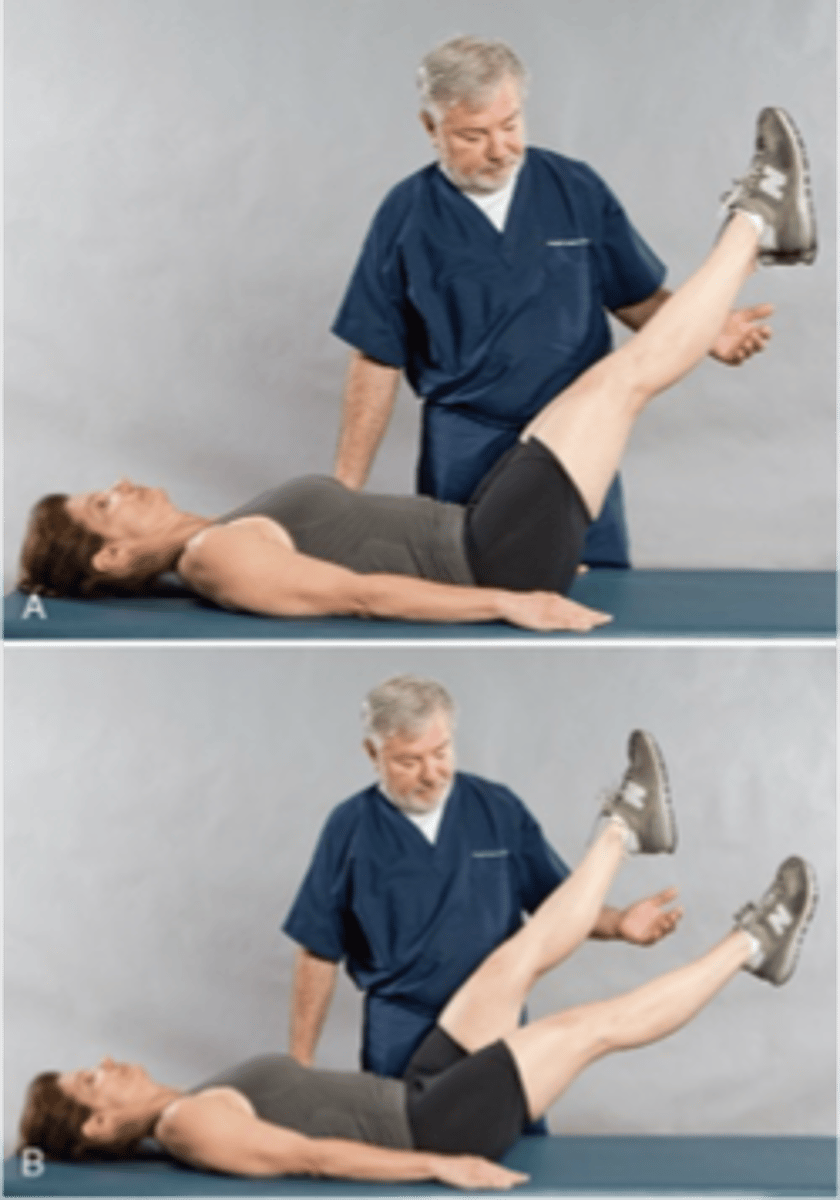
Legs drop or lower back pain is produced
The Bilateral Leg-Lowering Test is positive if _____
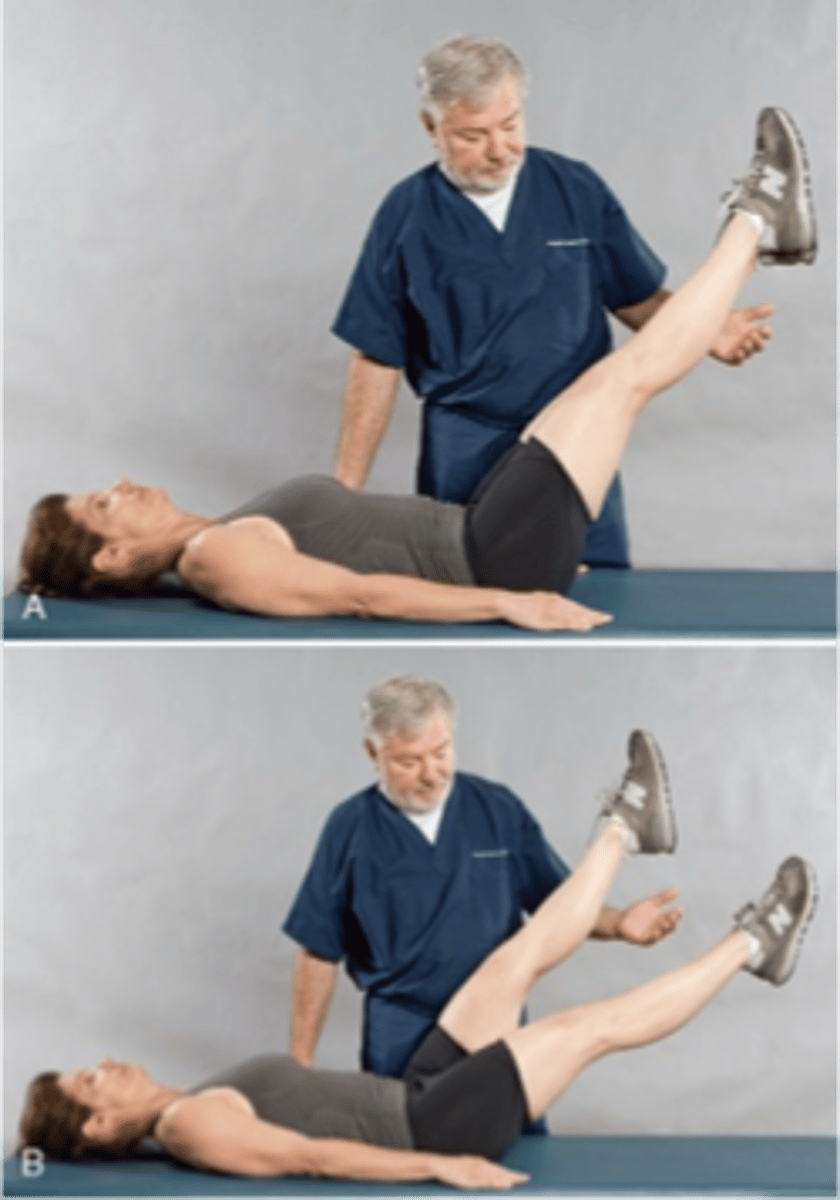
Double-Leg-Raise Test
Assessment for:
- Lumbosacral joint involvement
- AKA: Bilateral Straight-Leg-Raising Test
If both legs raised together produce a pain at an earlier angle than a single leg raise
Explain how a Double-Leg-Raise Test would be positive
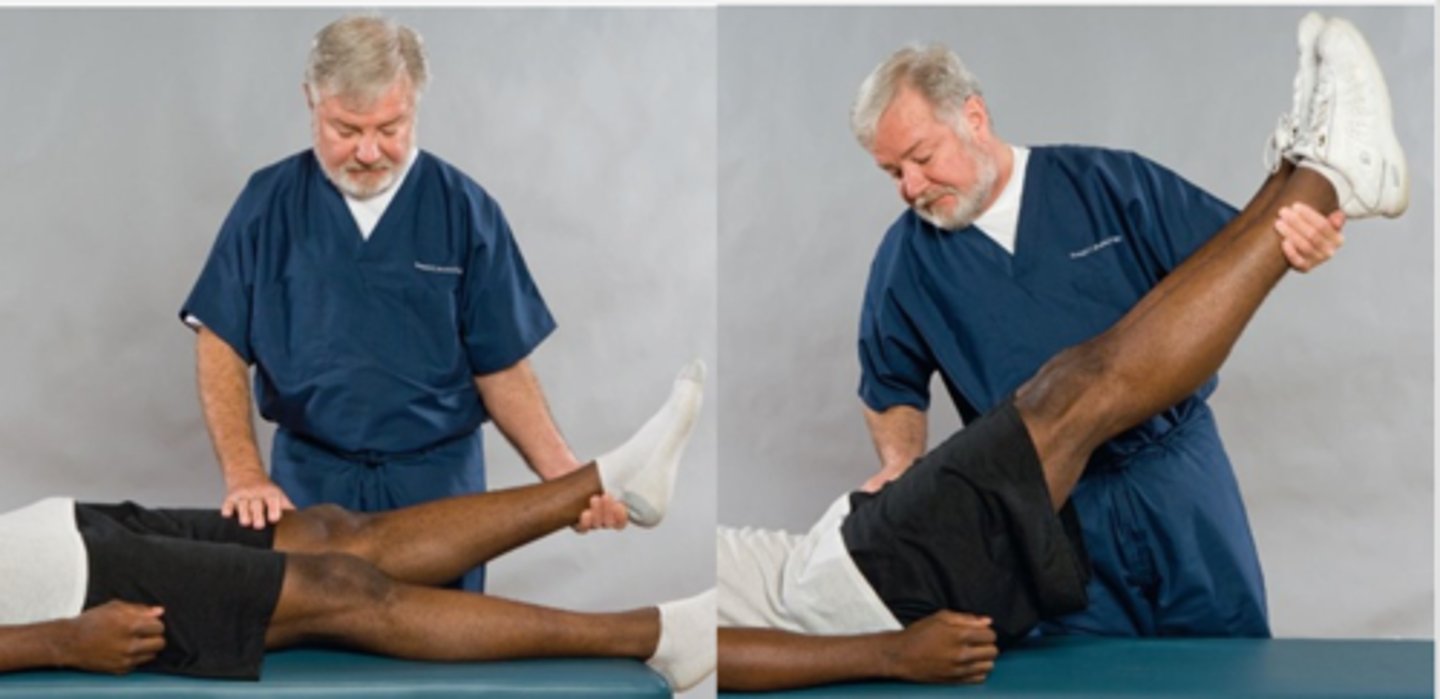
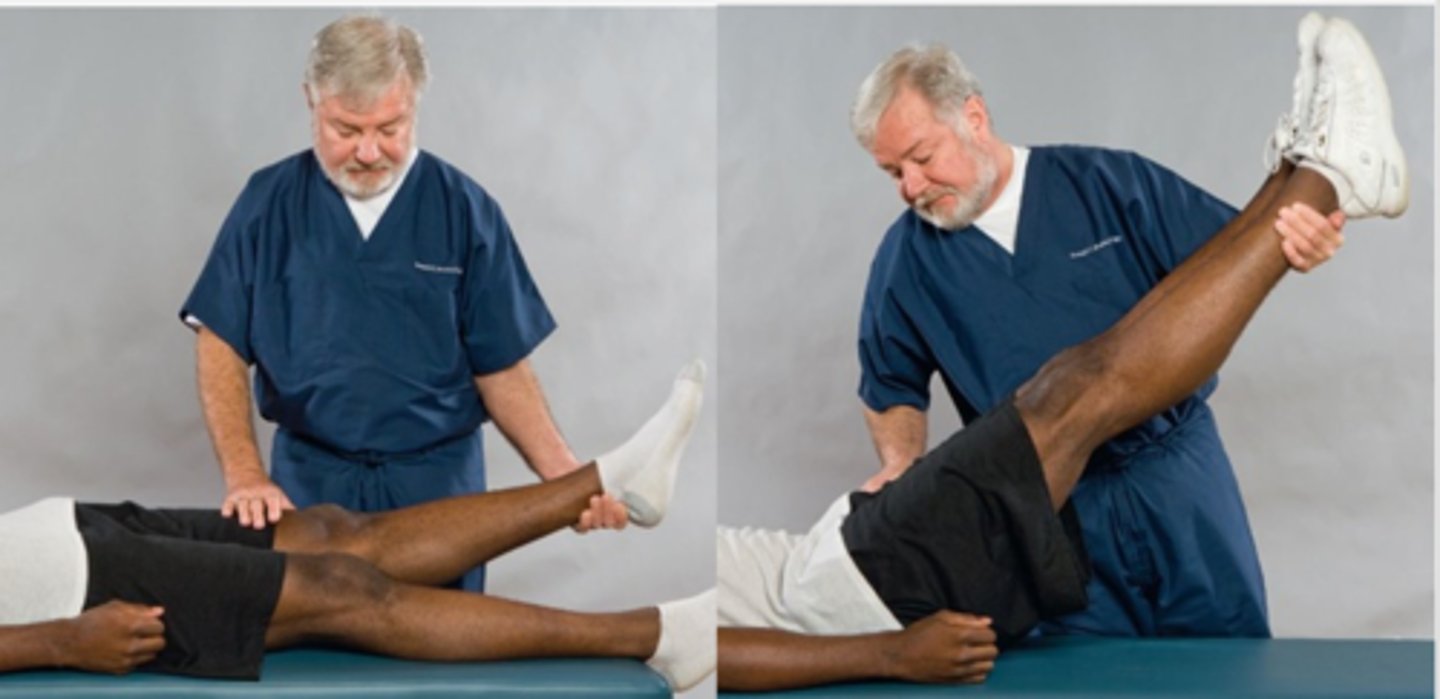
Lewin Supine Test
Assessment for:
- Lumbar arthritis
- Fibrosis
- Spondylosis
- Sacroiliac arthrosis
- Sciatica
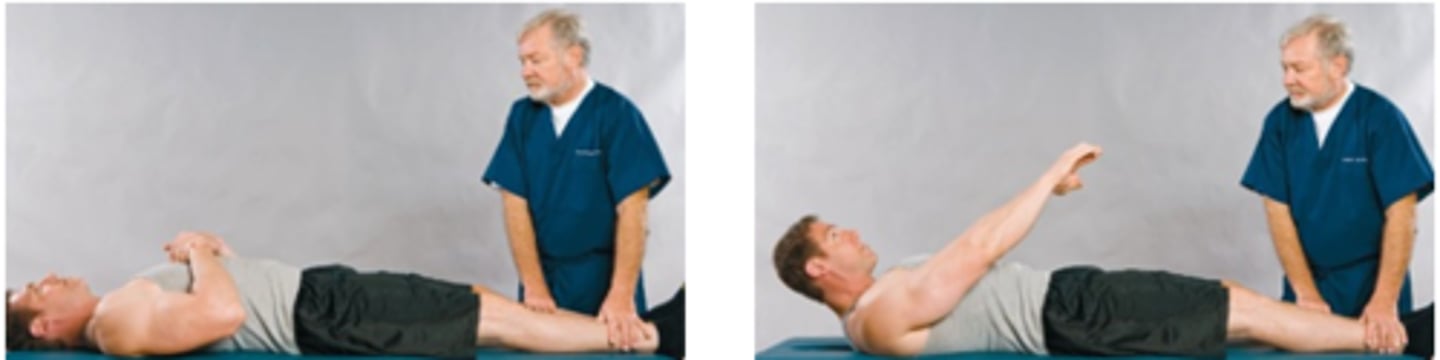
Quick Test
Assessment for:
- Low back or LE pain
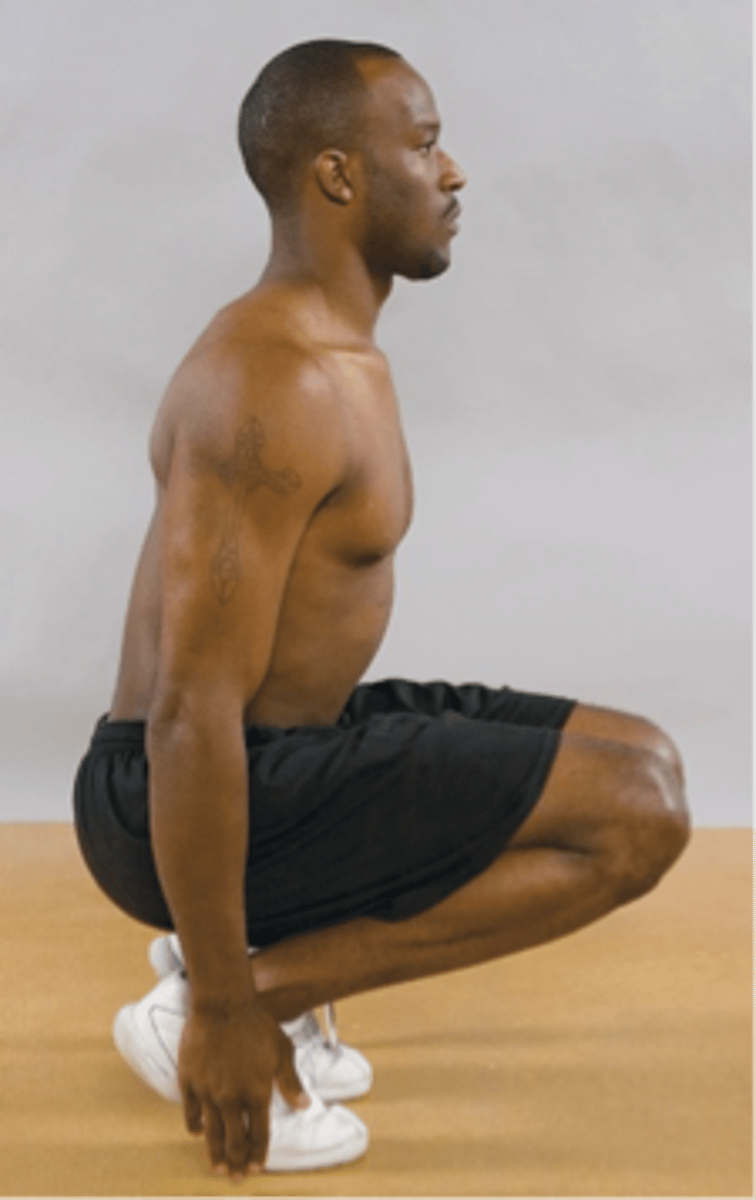

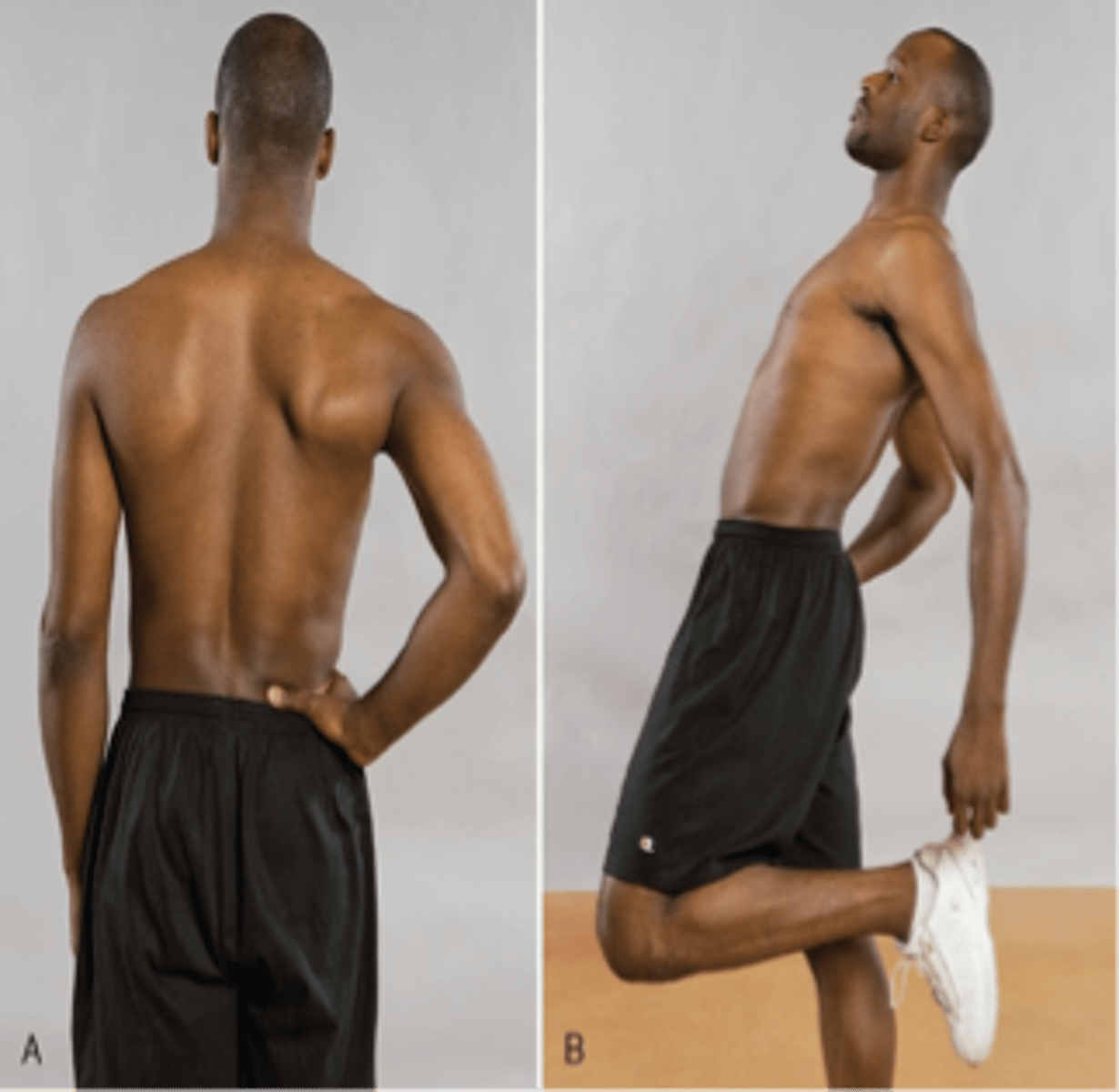
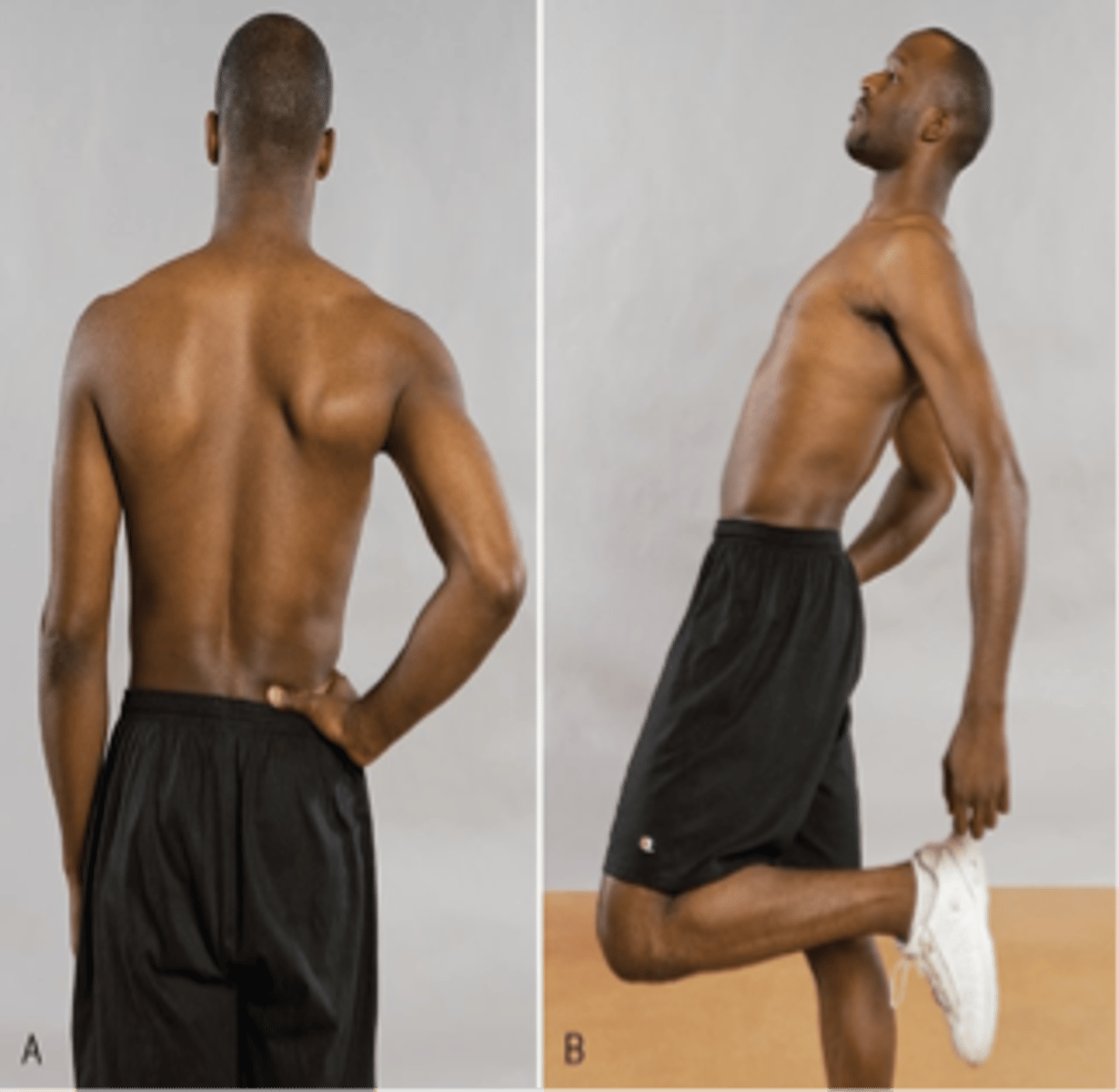
Jackson One-Legged Hyperextension Test
Patient stands on one leg and hyperextends back
Pars fracture
With the Jackson One-Legged Hyperextension Test, back pain will be reproduced on the symptomatic side if an impending _____ exists
Ely Sign/Ely Heel-to-Buttock Test
Assessment for:
- Lumbar radicular pain
- Femoral nerve inflammation
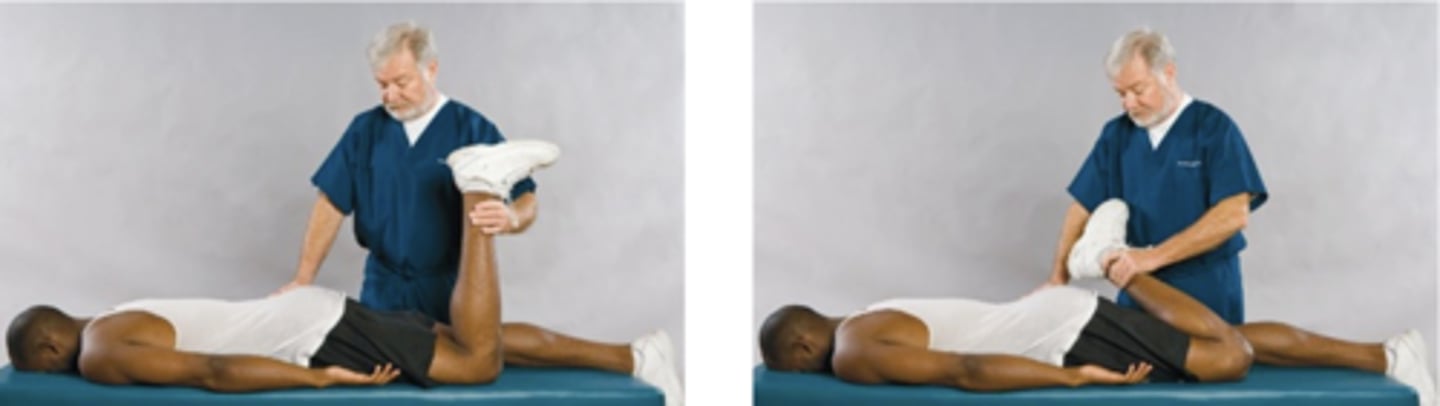
Anterior thigh
With the Ely Heel-to-Buttock Test, pain in the _____ is a positive finding and indicates inflammation of the lumbar nerve root
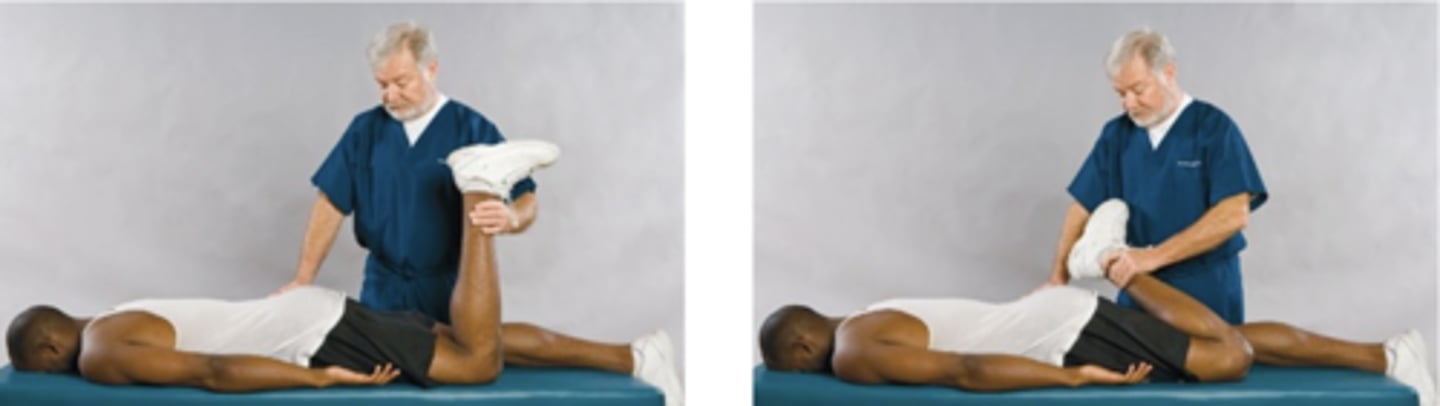
Iliopsoas
With the Ely Heel-to-Buttock Test, inability to extend the thigh may be indicative of an _____ muscle spasm
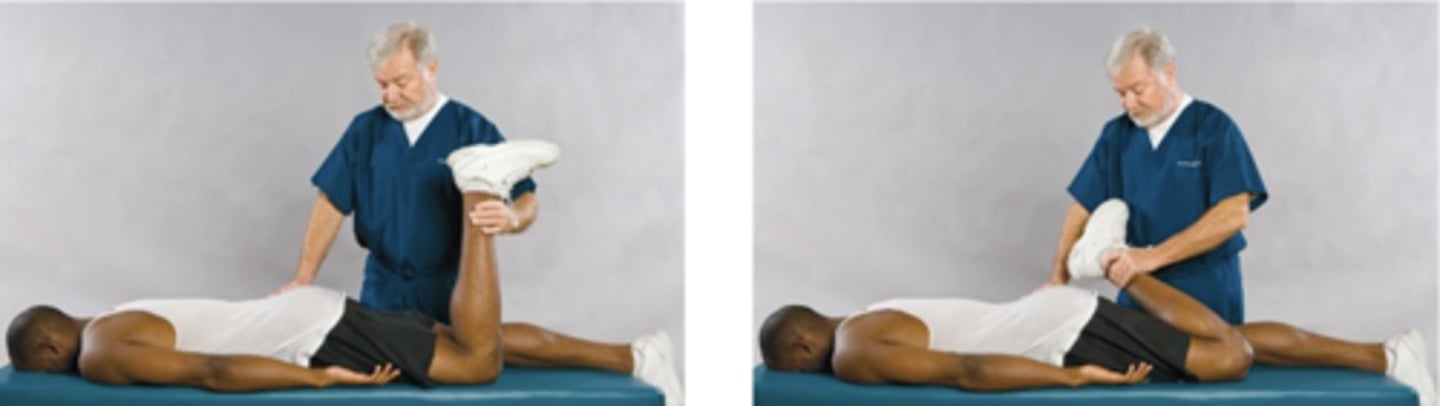
Femoral Nerve Traction Test
Assessment for:
- Mid-lumbar nerve root involvement (L2, L3, L4)
L2-L4
The Femoral Nerve Traction Test is positive if anterior thigh pain is produced and indicates radiculopathy that involves _____
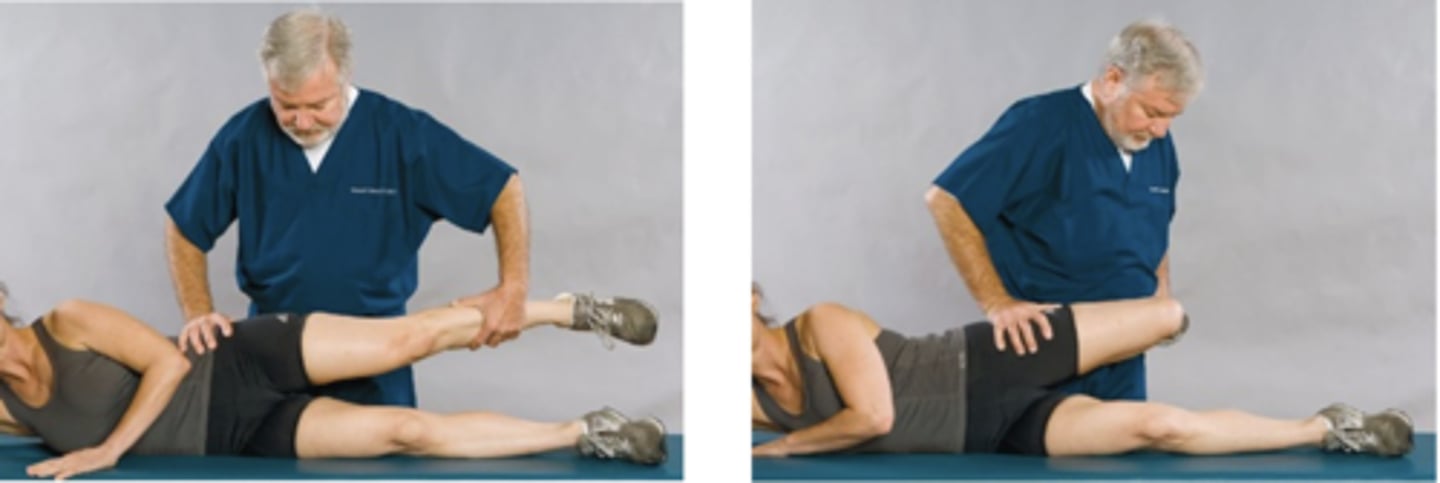
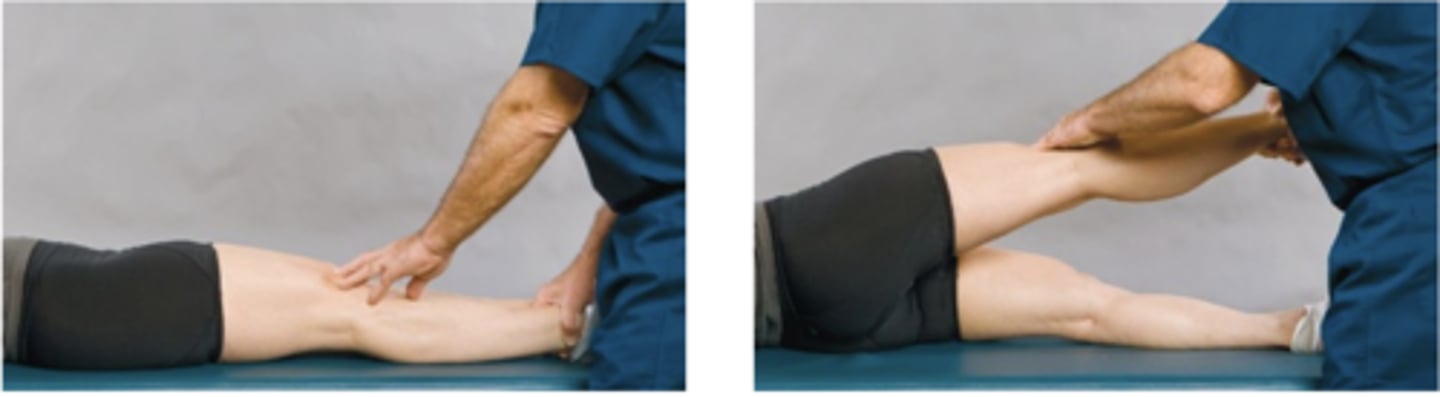
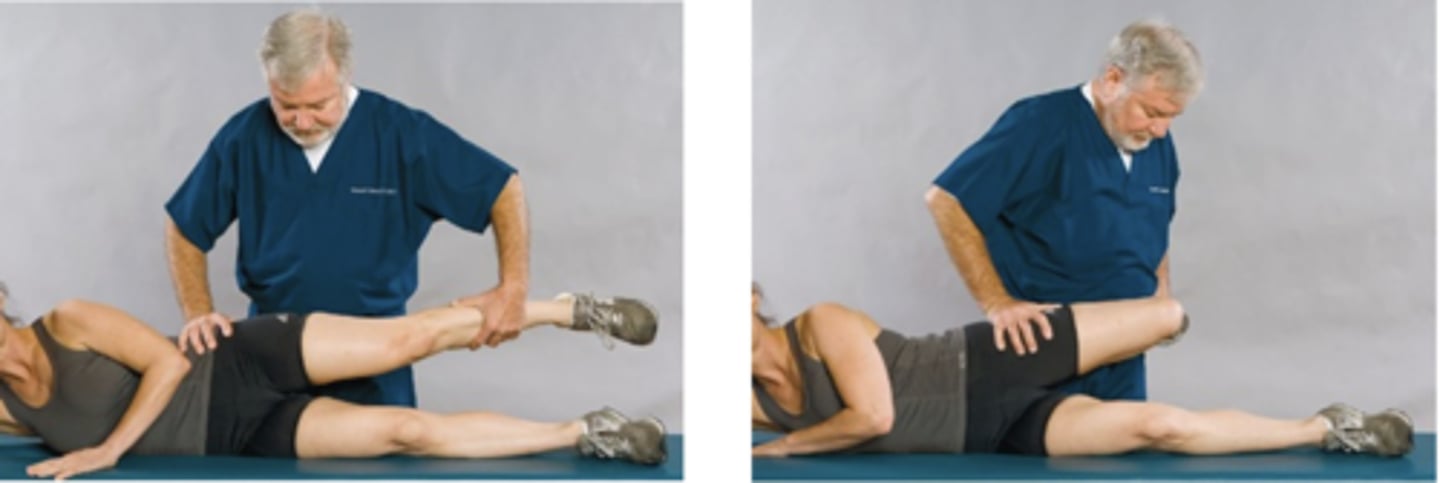
Prone Knee-Bending Test
Assessment for:
- L2/L3 nerve root lesion
- Femoral nerve inflammation
- Quadriceps strain
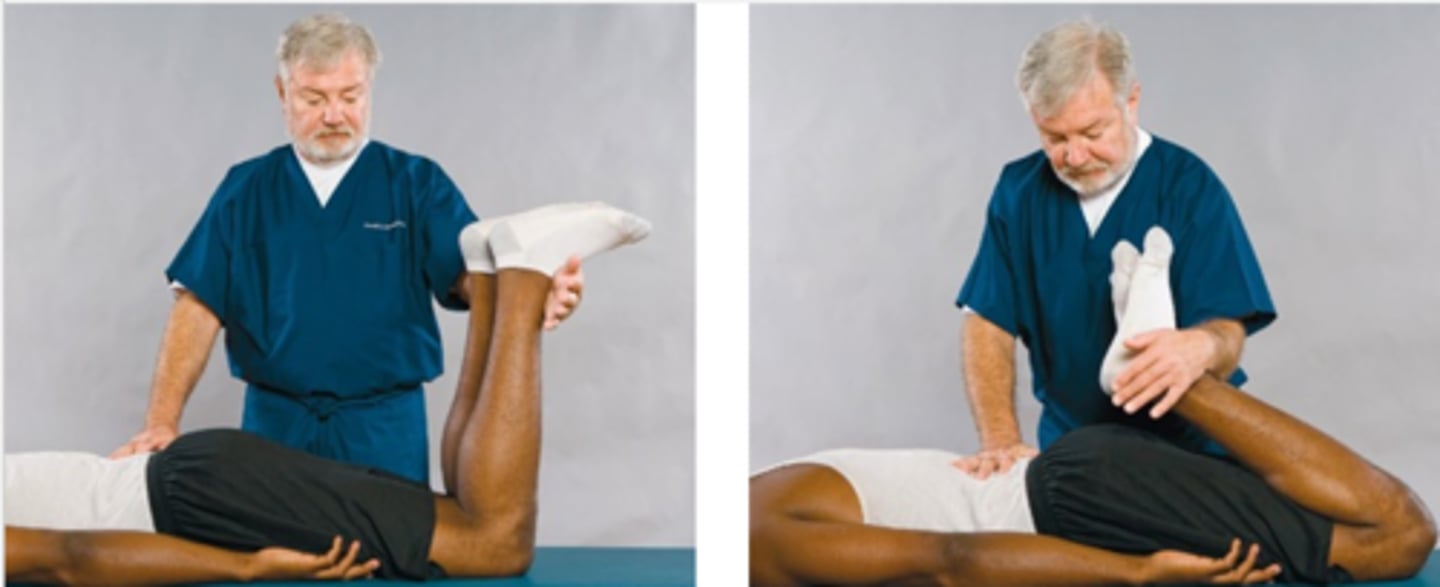
Hyperextension Test
Assessment for:
- L3/L4 nerve root inflammation
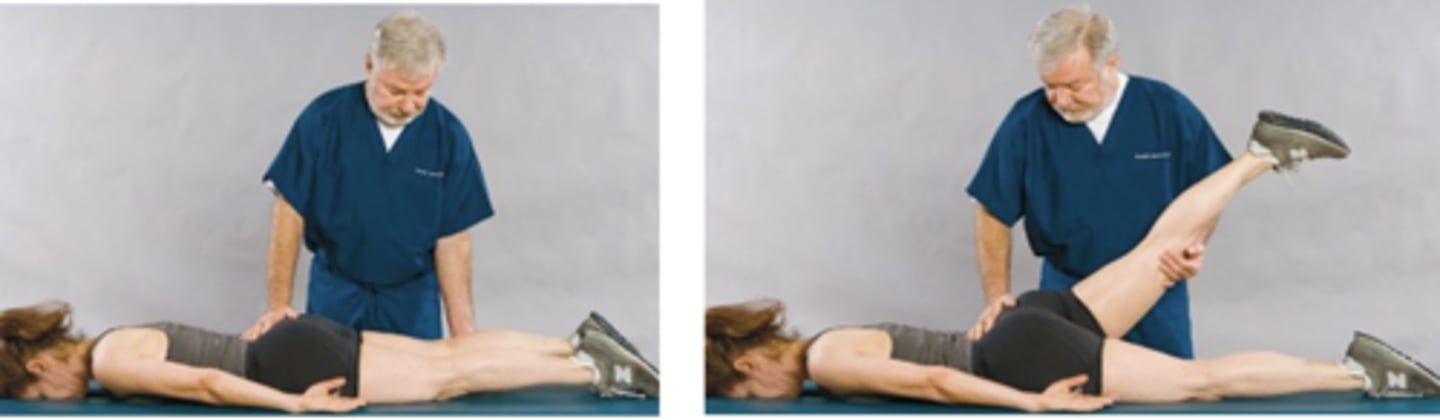
Kernig Sign
Assessment for:
- Meningeal irritation
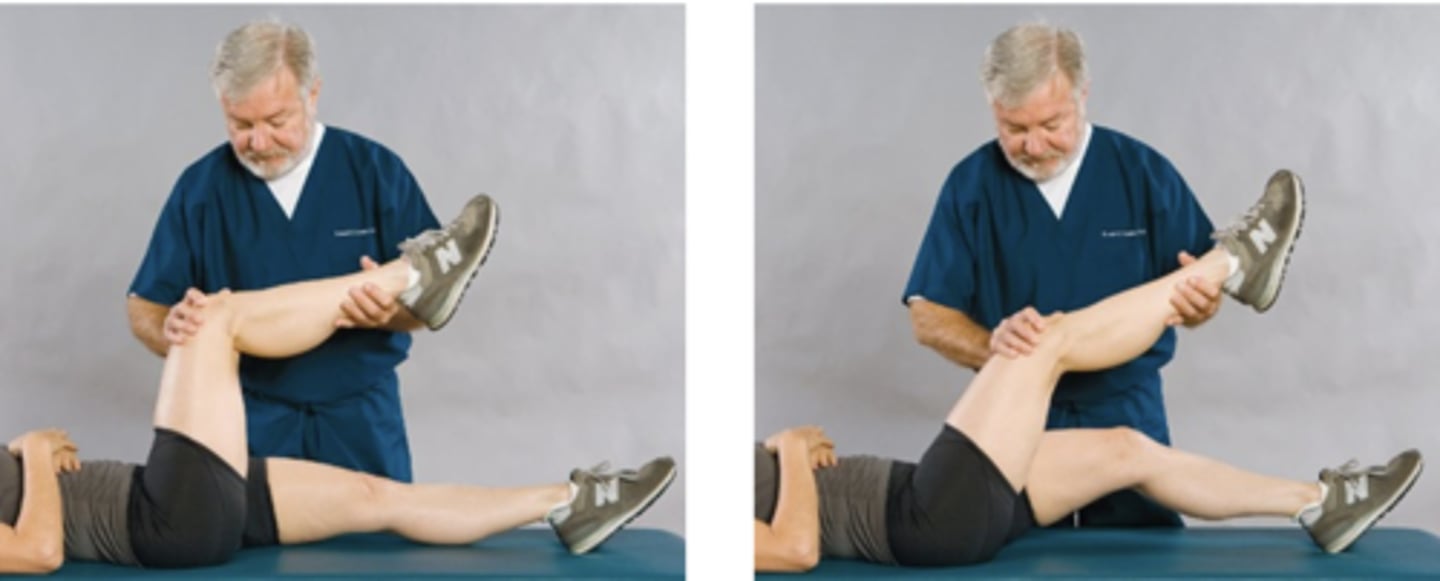
Brudzinski Sign
Assessment for:
- Meningeal irritation
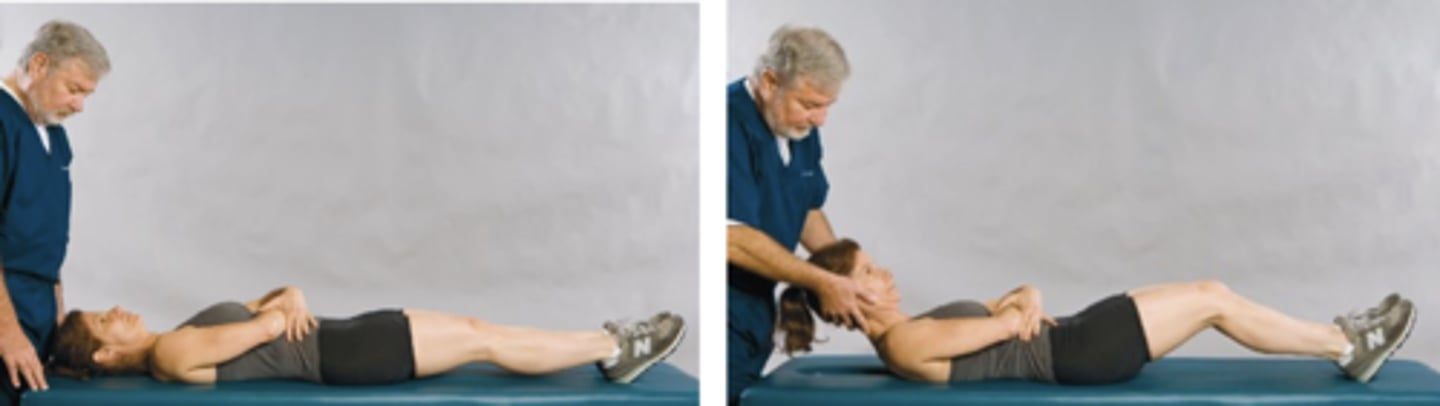
Lewin Standing Test
Assessment for:
- Hamstring tightness
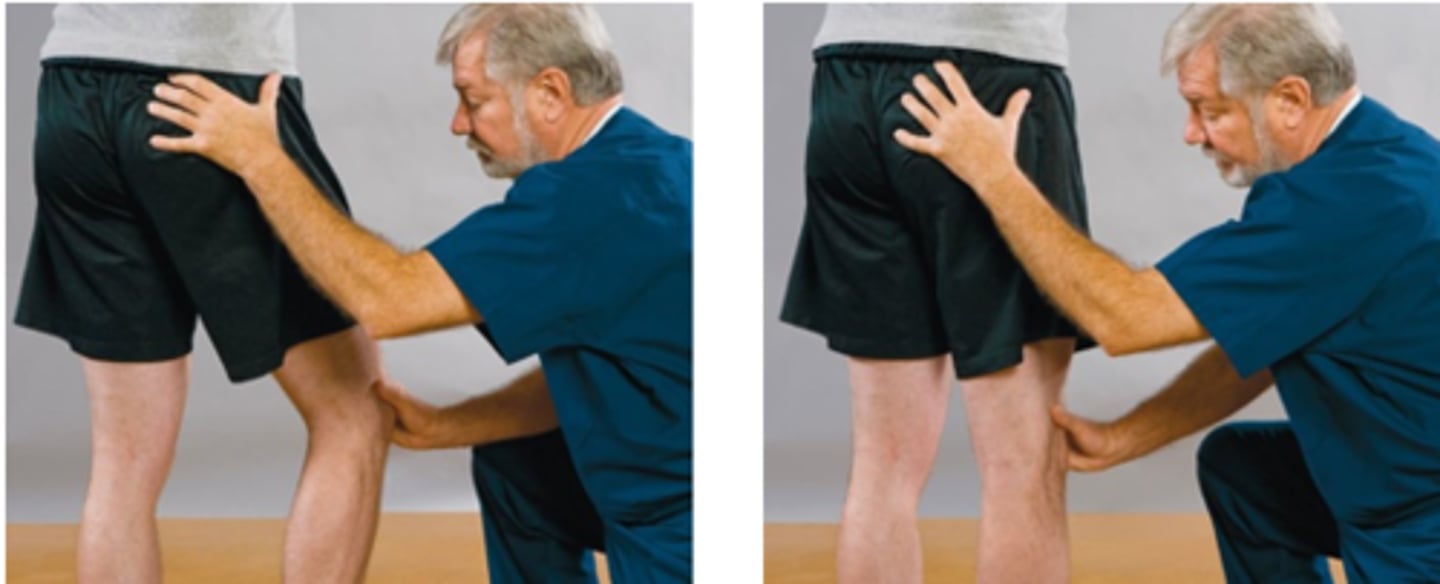
Matchstick Test
Assessment for:
- Denervation hypersensitivity
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
For the Matchstick Test, use the end of a cotton-tip applicator and apply pressure over the lower back and hamstrings looking for indentations which persist for several minutes. If this is positive it may be indicative of _____
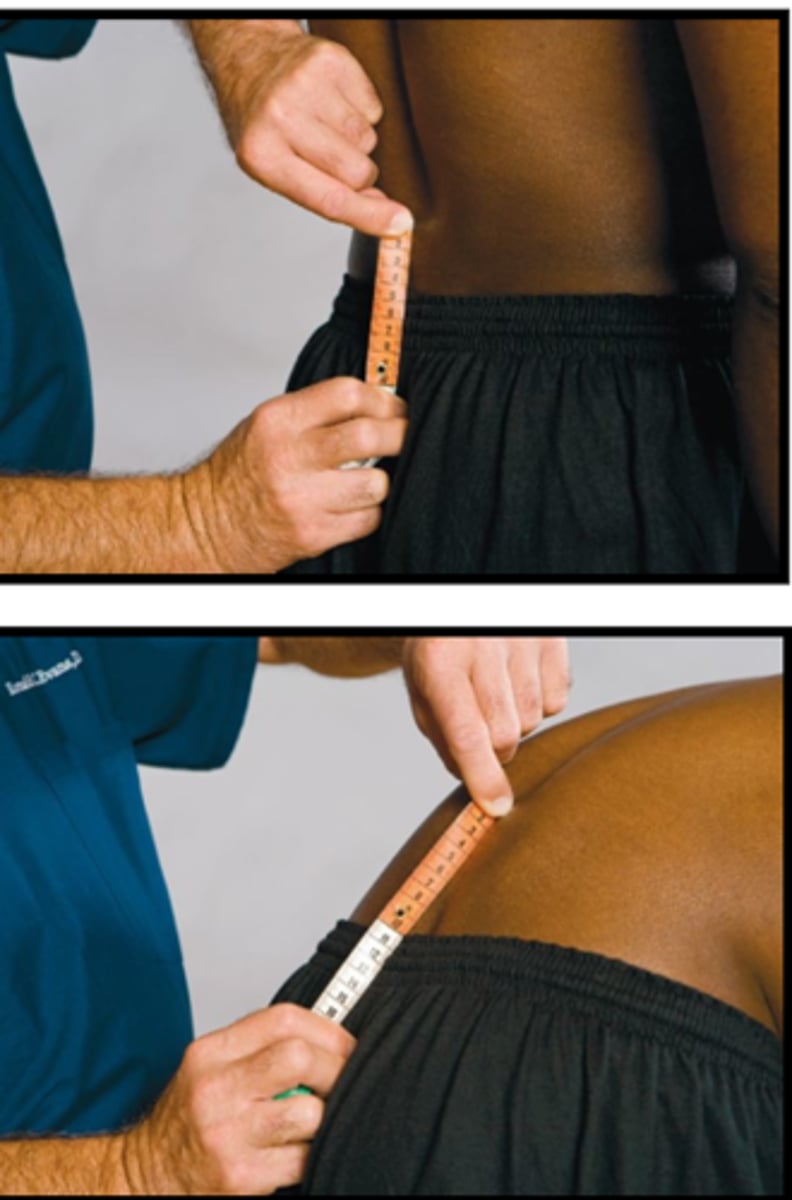
Schober Test
Assessment for:
- Lumbar spine motion
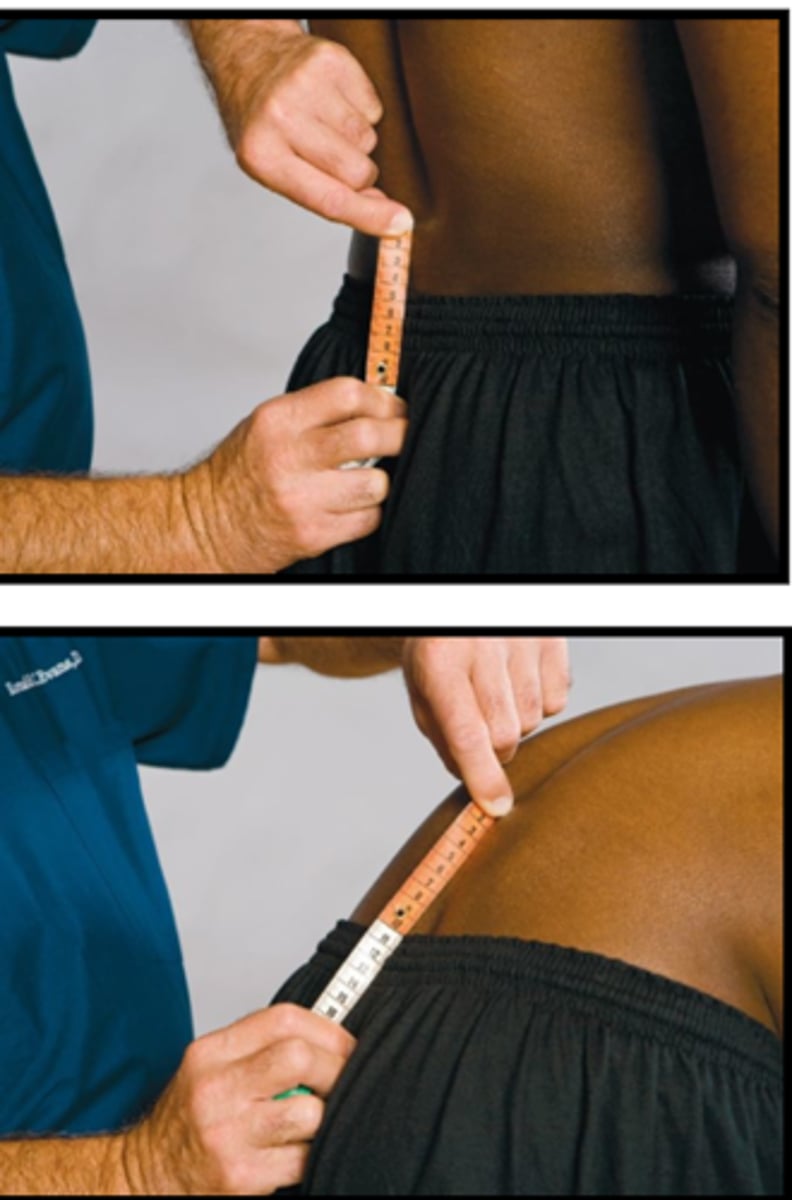
S2
Schober Test landmark
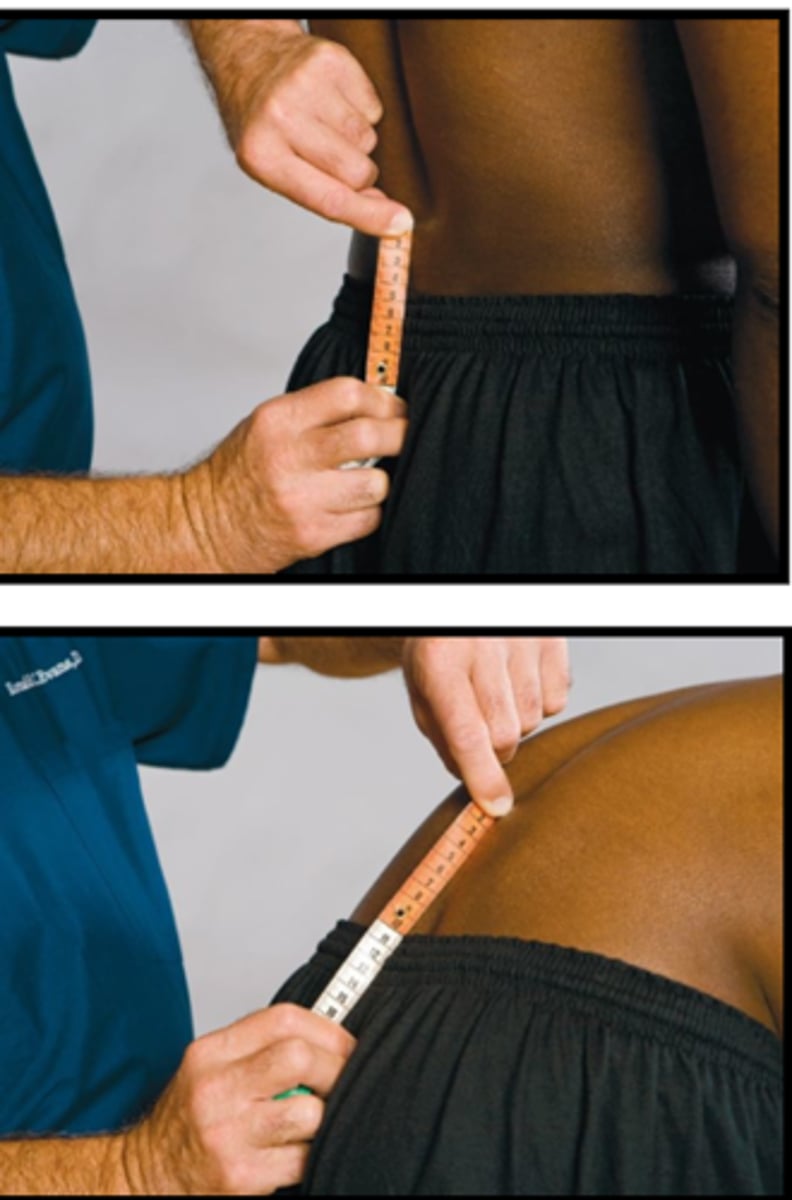
- 0.5 cm
- 10 cm
Schober Test S2 measurements:
- _____ below
- _____ above
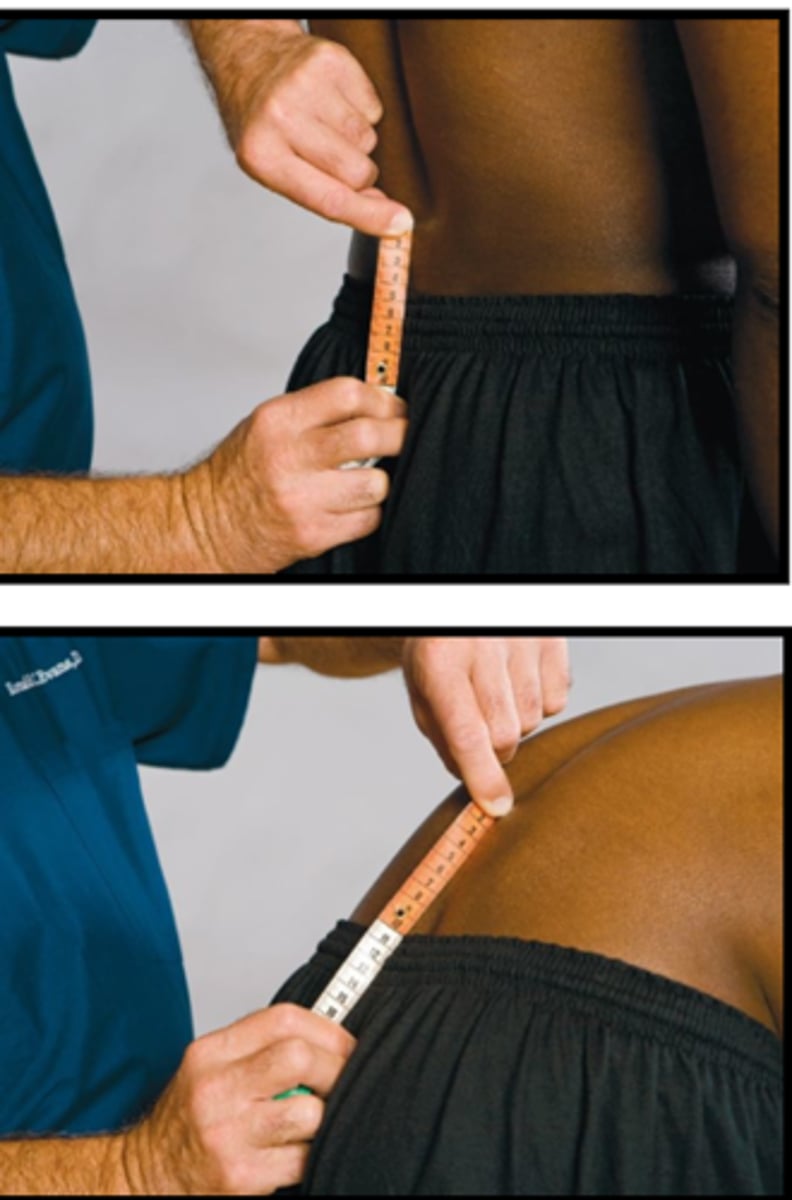
- Measure distance between S2 landmarks
- Have patient flex forward and remeasure
Explain the Schober Test
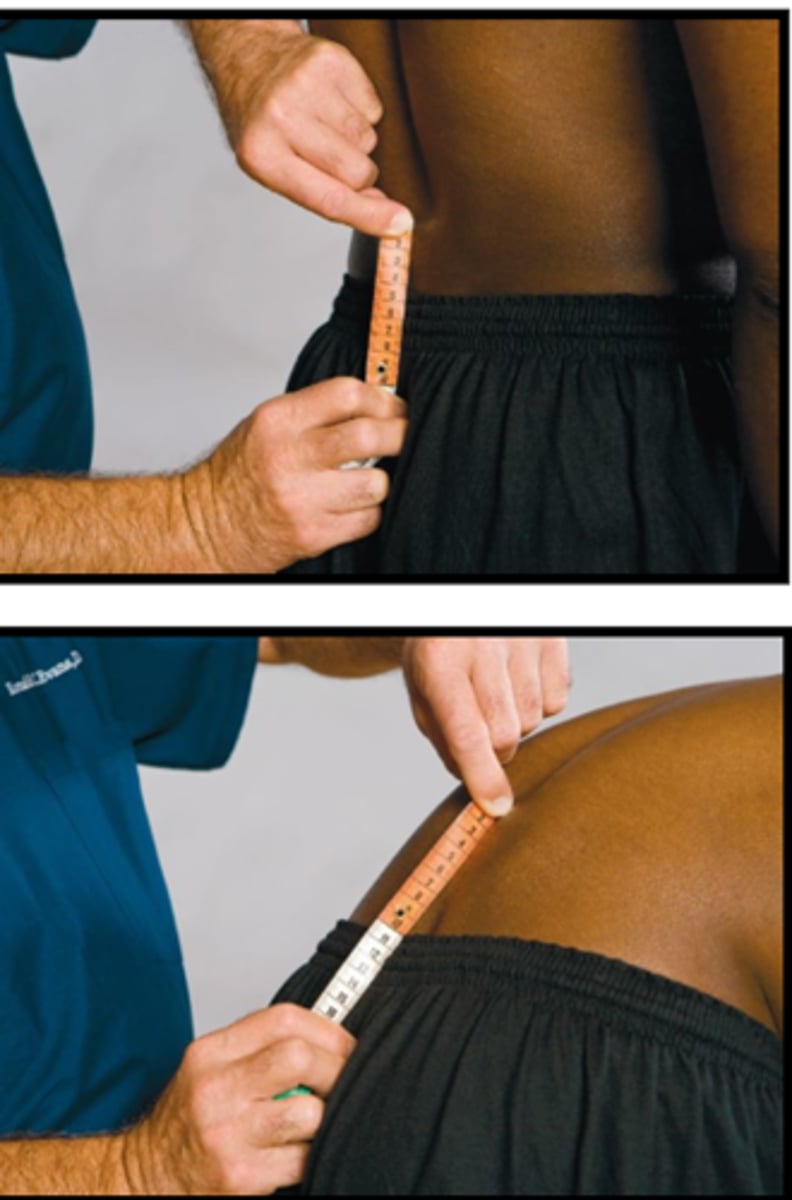
5-8 cm
A normal Schober Test measurement is _____ separation
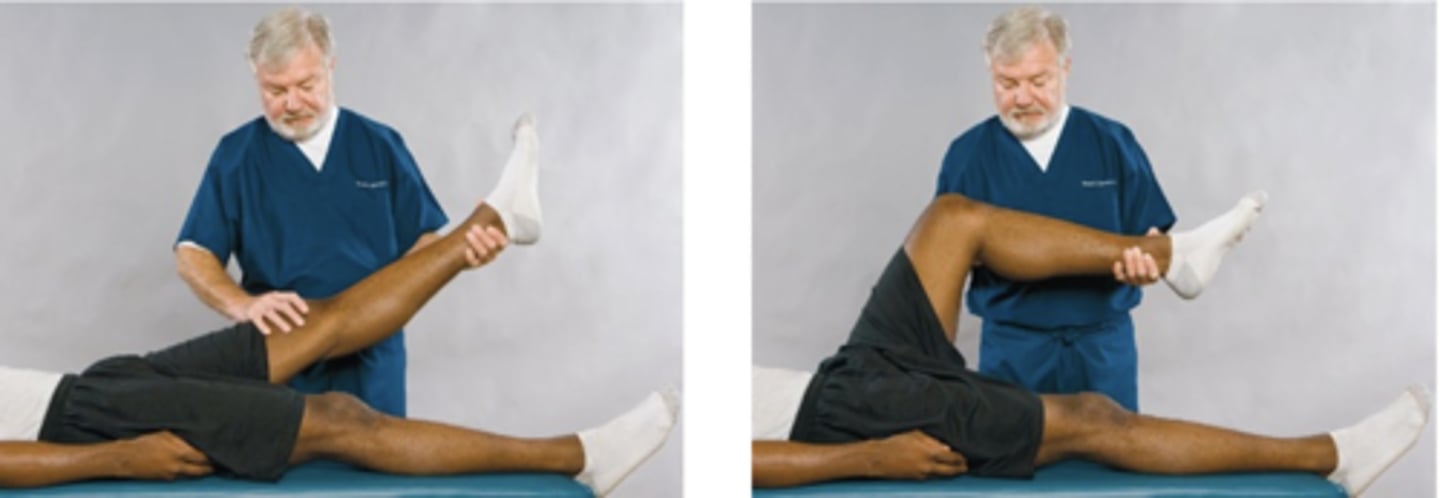
Sign of the Buttock
Assessment for:
- Gluteal bursitis
- Tumor
- Abscess
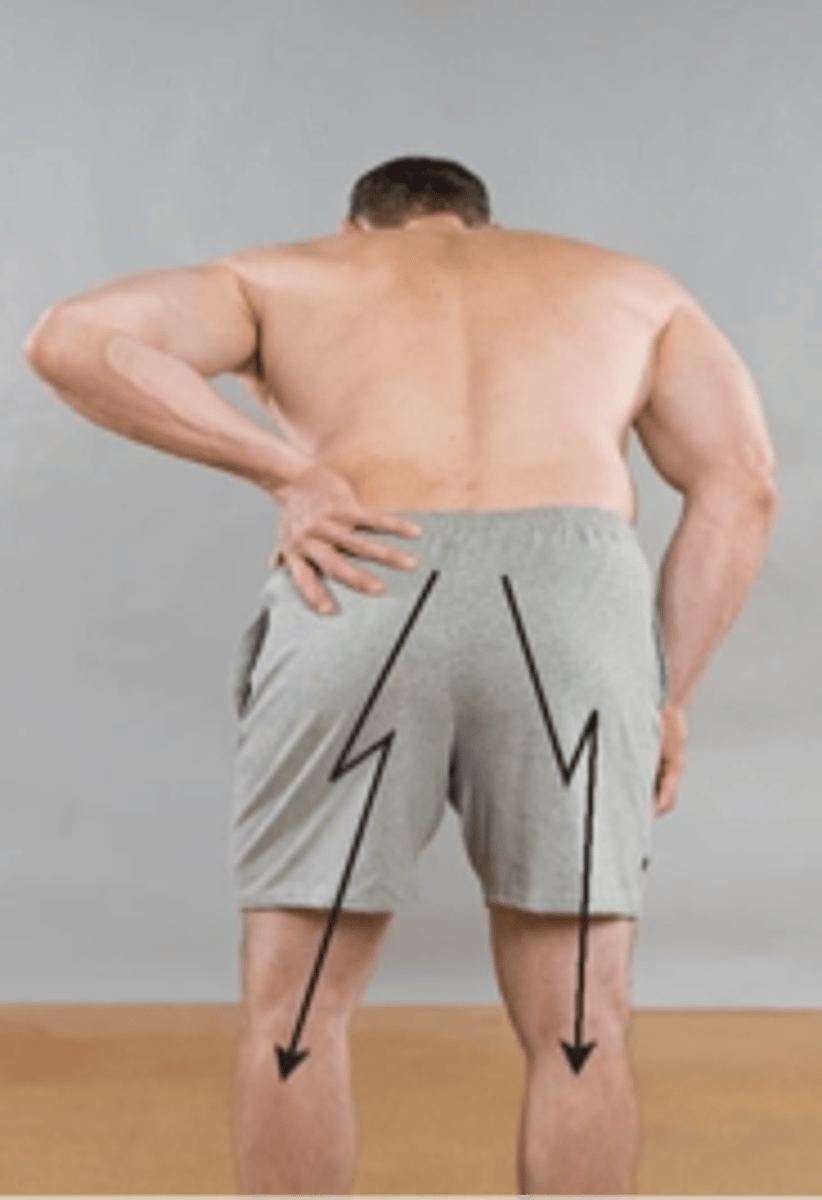
Vanzetti Sign
Assessment for:
- Sciatic scoliosis
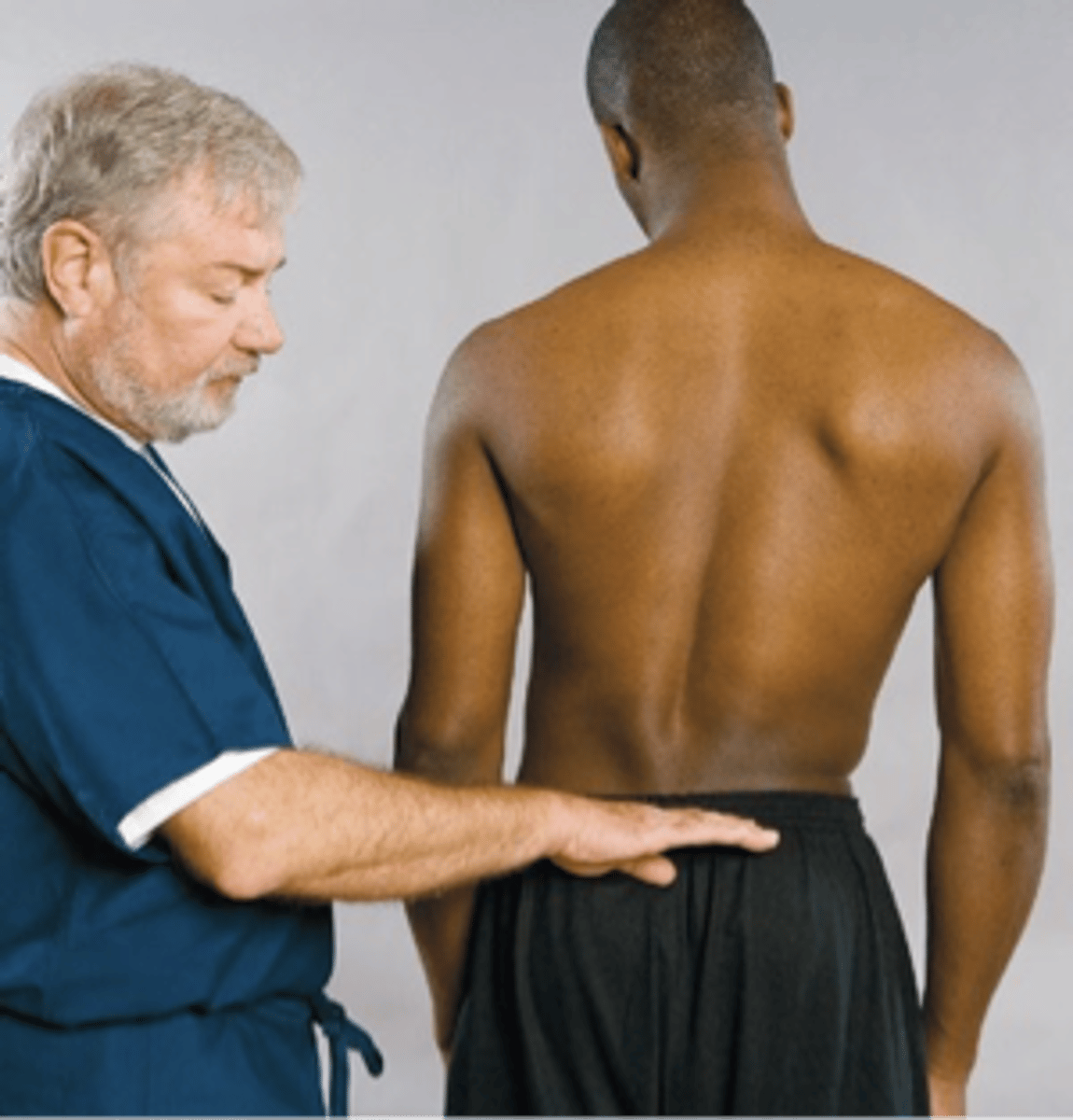
Nerve root compression
Vanzetti Sign indication:
- Iliac crest even with antalgia = sciatic due to _____
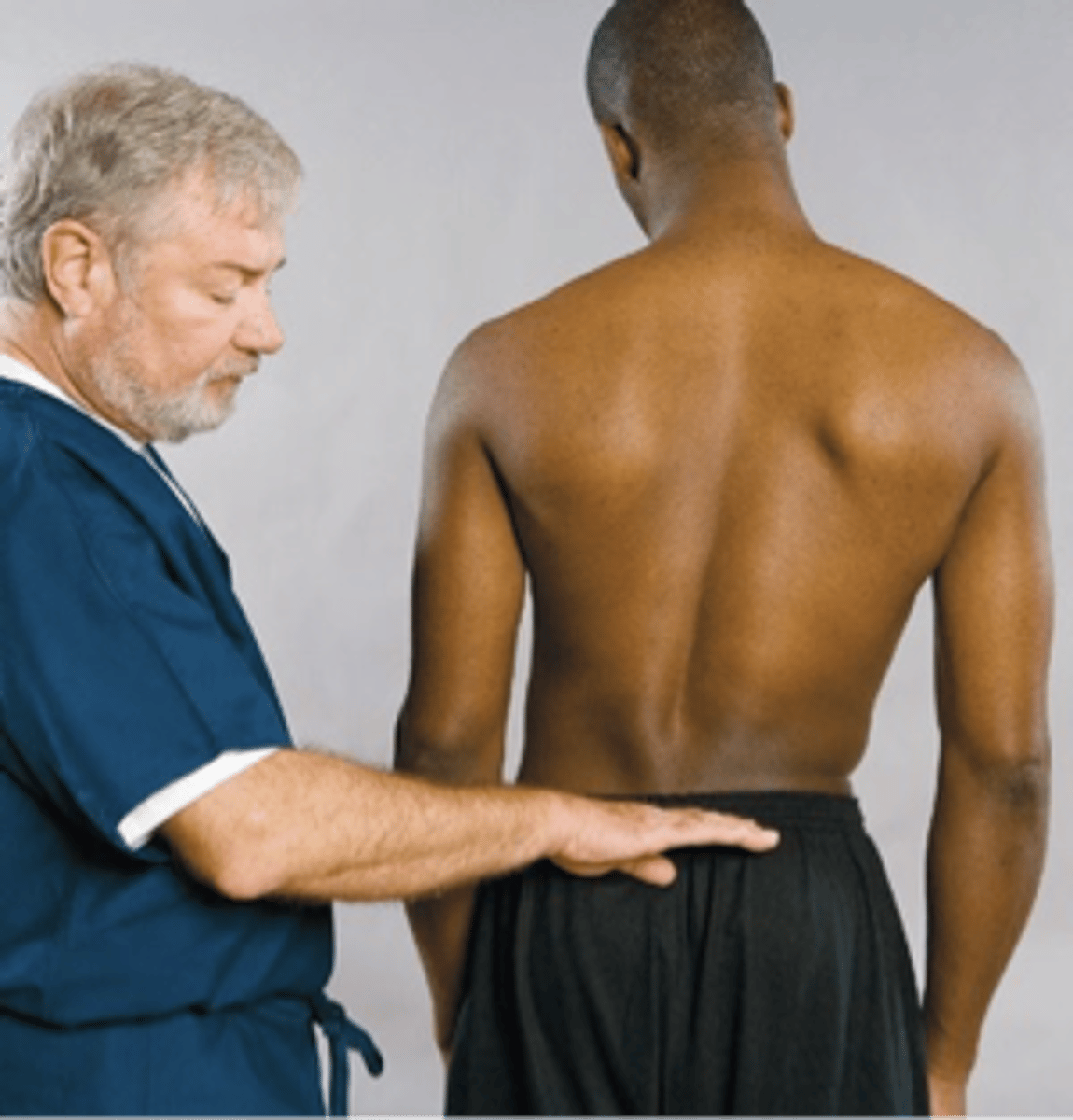
Scoliosis
Vanzetti Sign indication:
- Iliac crest uneven with antalgia = sciatic due to _____
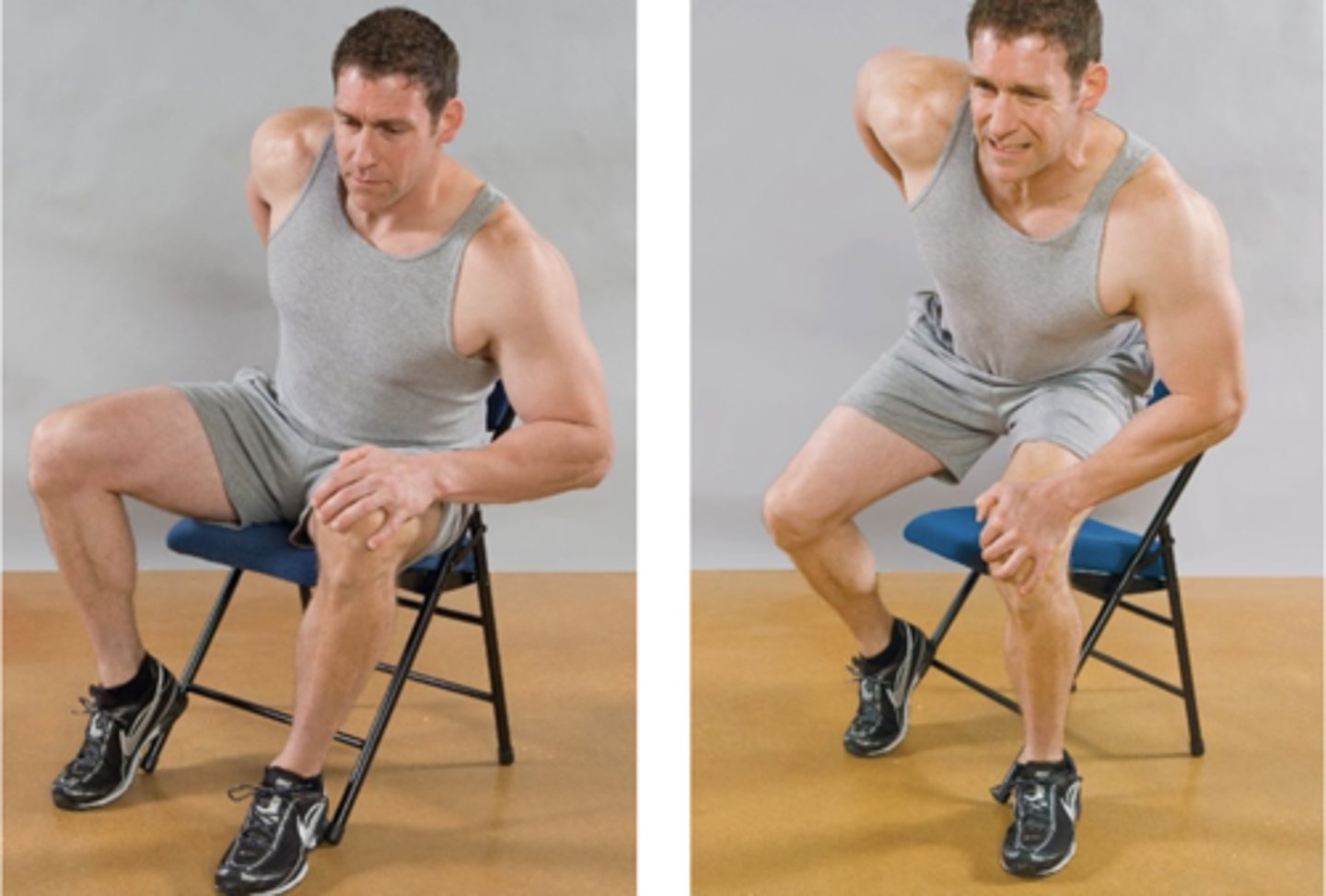
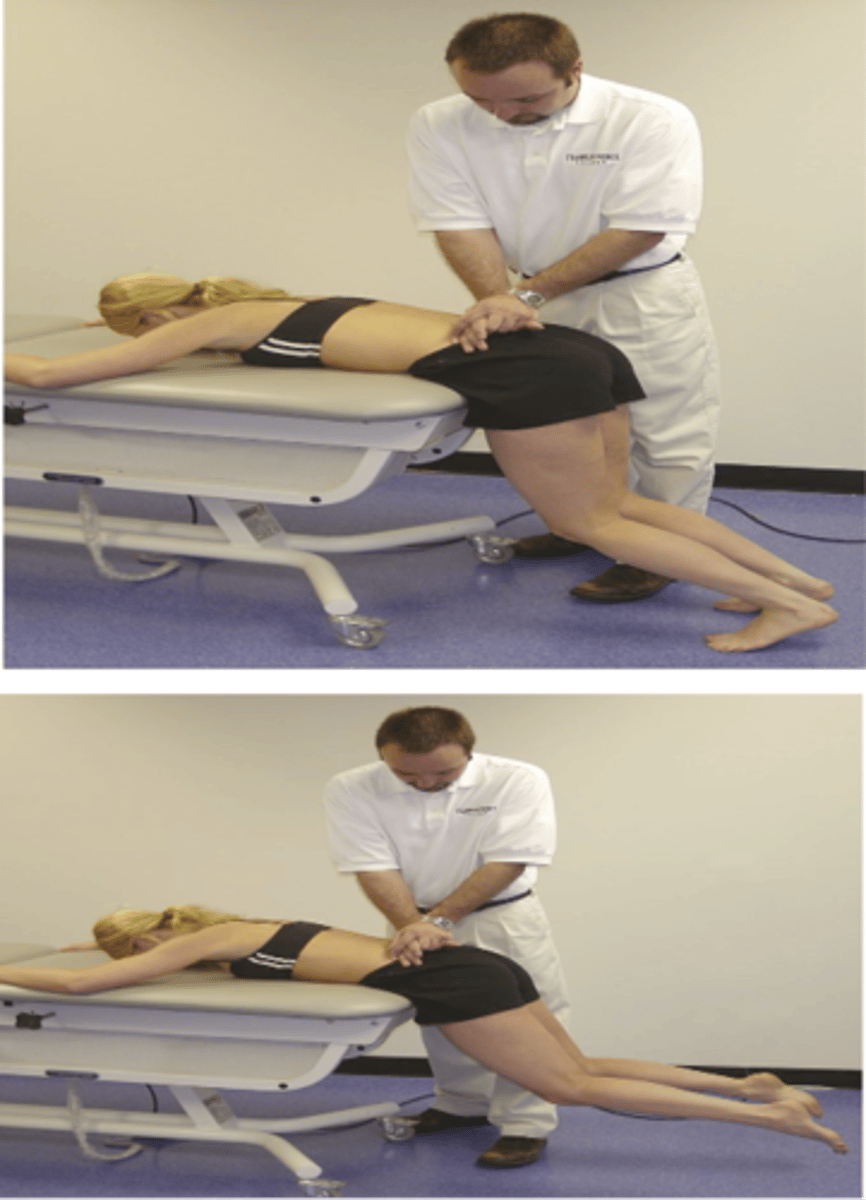
Prone Instability Test
- P-A compression over spinous processes L5-L1 with legs on floor
- Have patient lift feet off floor then apply P-A compression over L5-L1
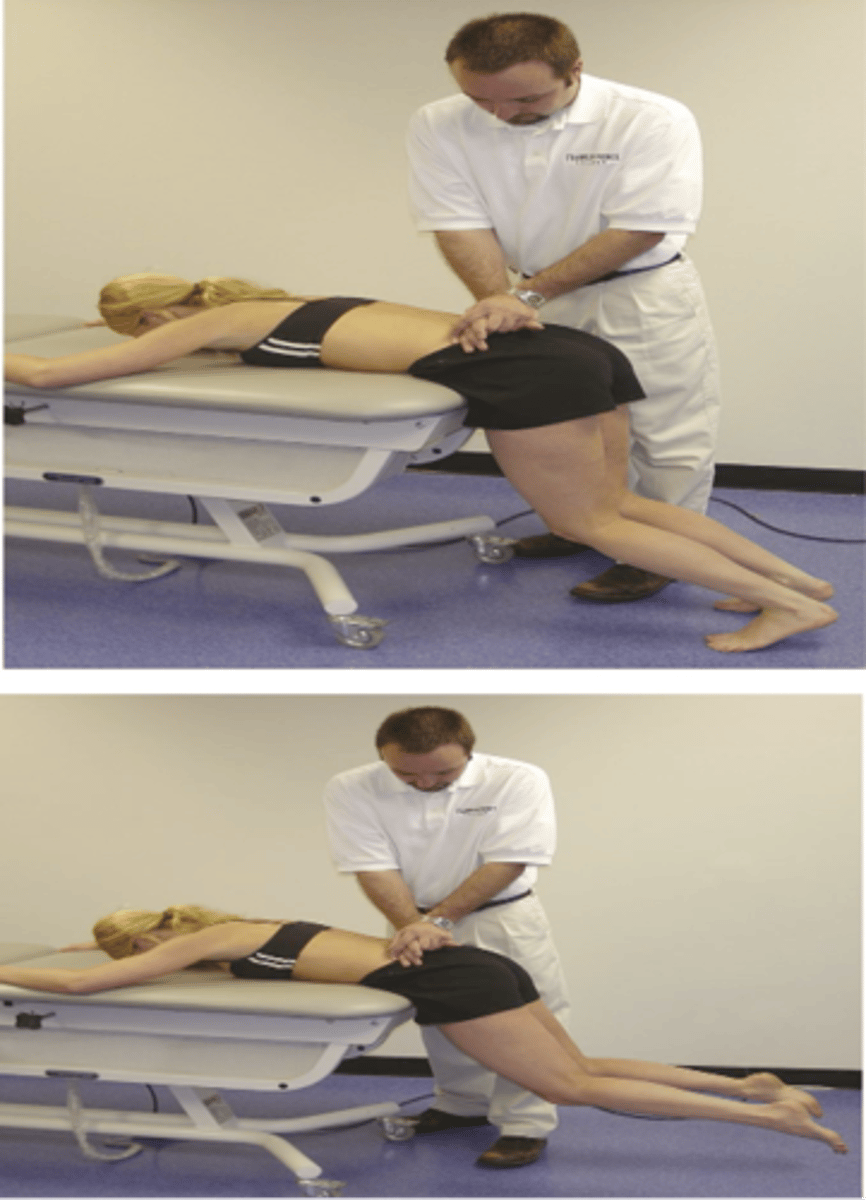
Instability
With the Prone Instability Test, if pain decreases, then suspect _____
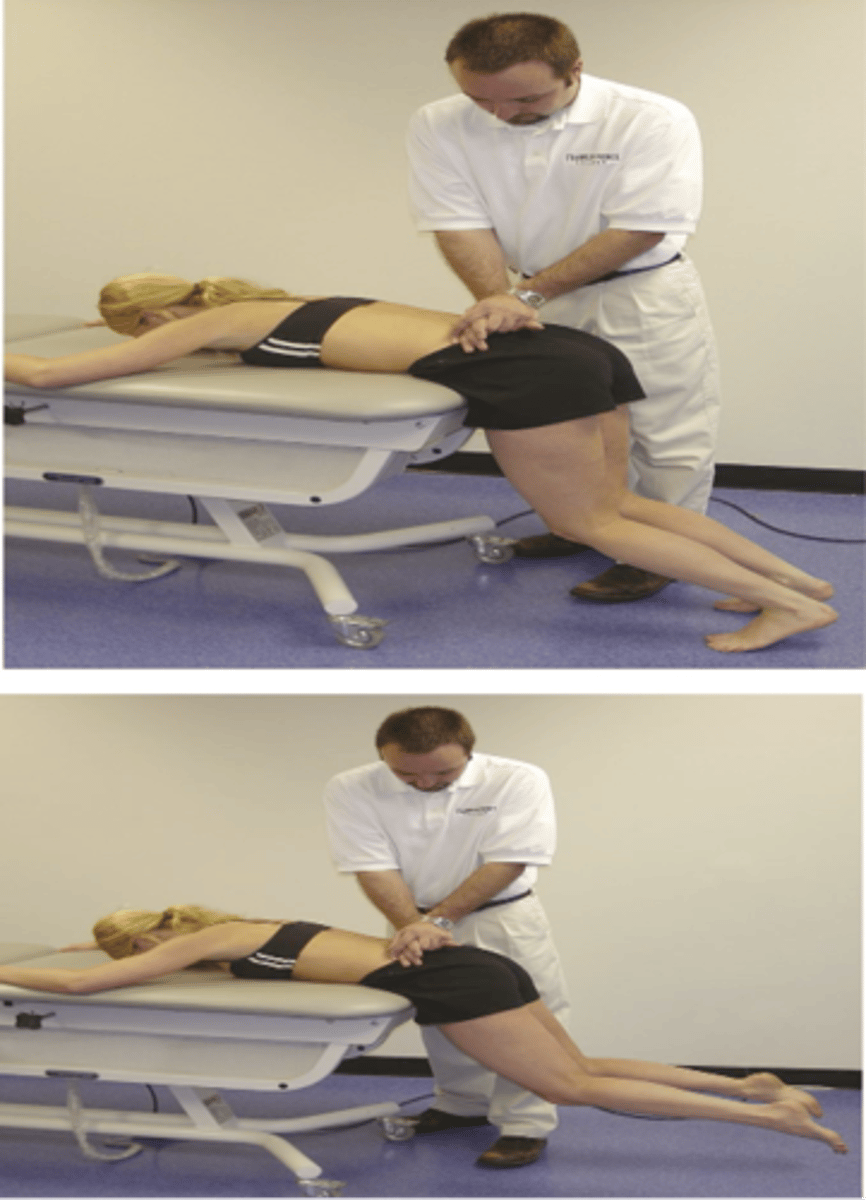
Extensor muscle
With the Prone Instability Test, pain decreases due to _____ contraction ("bracing") instability
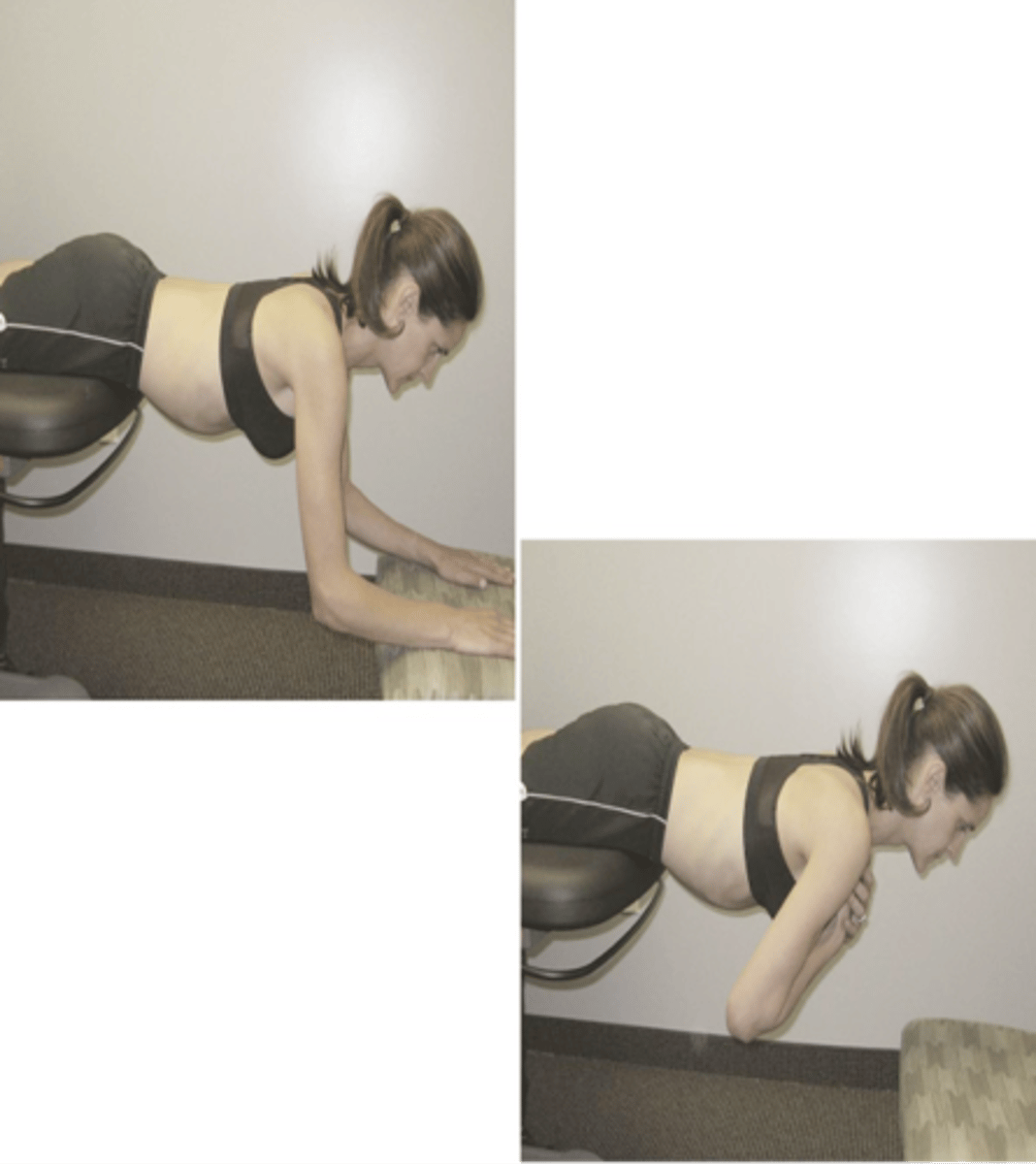
Modified Biering Sorensen Test
- Patient begins in supported position, then extends trunk and holds for as long as possible
- Assessment for:
• Endurance
• Strength
