BIO 101: Lab 8 - Diffusion and Osmosis
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
diffusion
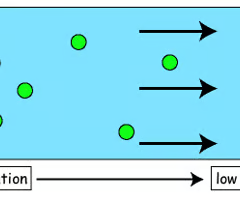
Movement of solute molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
dialysis tubing
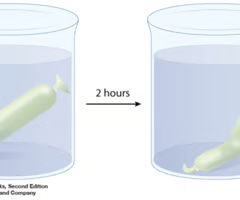
Plastic-like cellulose tubing with tiny holes to allow small molecules to pass through (semi-permeable).
concentration gradient
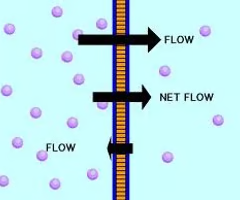
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another
selectively permeable
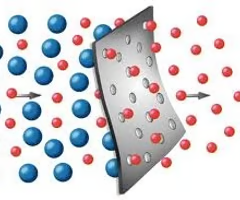
a property of cell membranes that allows some substances to pass through, while others cannot
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
osmosis
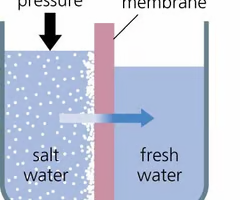
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
isotonic

when the concentration of two solutions is the same
hypertonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration of solutes
hypotonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the lesser concentration of solutes
turgor pressure (turgid)
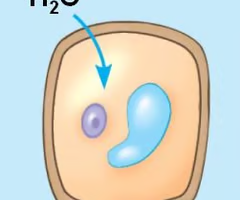
The pressure placed onto the cell wall as a result of water in the cell
plasmolysis
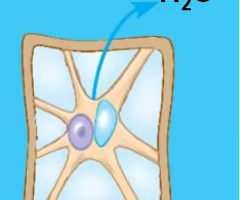
This happens when a cell shrinks inside its cell wall while the cell wall remains intact.
cytolysis
This happens when a cell (other than a red blood cell) swells until pressure bursts it, resulting in cell death.
hemolysis
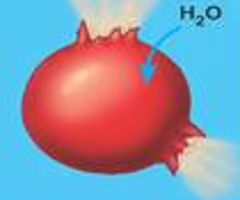
the rupture or destruction of red blood cells.
crenation
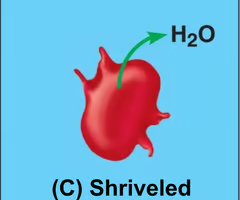
This happens when a cell shrinks and shrivels; can result in cell death if severe.
flaccid
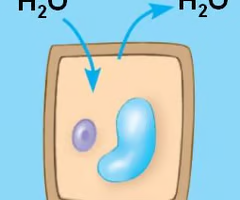
plant cells in isotonic solutions (not full of water but not really shriveled up either)