Psych unit 7
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:45 AM on 3/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
1
New cards
personality
a persons unique set of consistent behavioral traits
2
New cards
personality traits
durable disposition to behave in a particular way in variety of situations
3
New cards
factor analysis
using statistical techniques to identify clusters of related info
4
New cards
the 5 factor model (big 5) by costa and mcCrae - openess
a person high in this trait is relatively:
* receptive to new ideas
* creative
* broad in intrests
\
low:
* conventional
* practical
* narrow in intrests
\
* receptive to new ideas
* creative
* broad in intrests
\
low:
* conventional
* practical
* narrow in intrests
\
5
New cards
the 5 factor model (big 5) by costa and mcCrae - conscientiousness
high:
* responsible
* organzied
* disciplined
* acheivement-oriented
\
low:
* careless
* disorganized
* impulsive
* lazy
* responsible
* organzied
* disciplined
* acheivement-oriented
\
low:
* careless
* disorganized
* impulsive
* lazy
6
New cards
the 5 factor model (big 5) by costa and mcCrae - extraversion
high:
* out going
* fun loving
* assertive
* talkative
\
low:
* shy
* serious
* passive
* quiet
* out going
* fun loving
* assertive
* talkative
\
low:
* shy
* serious
* passive
* quiet
7
New cards
the 5 factor model (big 5) by costa and mcCrae - agreeableness
high:
* warm
* trusting
* helpful
* easy-going
\
low:
* cold
* suspicious
* uncooperative
* argumentative
* \
* warm
* trusting
* helpful
* easy-going
\
low:
* cold
* suspicious
* uncooperative
* argumentative
* \
8
New cards
the 5 factor model (big 5) by costa and mcCrae - neuroticism
high:
* emotionally unstable
* insecure
* anxious
* moody
\
low:
* emotionally stable
* confident
* calm
* even tempered
* emotionally unstable
* insecure
* anxious
* moody
\
low:
* emotionally stable
* confident
* calm
* even tempered
9
New cards
Allports trait theory - central traits / secondary traits
central: approx 7. main personality traits that are apparent to others and consistent accrosss diverse situations
\
secondary traits: unlimited number of traits that only show up in specific situations
\
secondary traits: unlimited number of traits that only show up in specific situations
10
New cards
cattellls trait theory (16 factor ) source vs surface traits
source traits: 16 underlying personality traits that influence surface behavior
\
surface traits: the combination of source traits that make up our personality. these are behaviors that others see and are unlimited
\
surface traits: the combination of source traits that make up our personality. these are behaviors that others see and are unlimited
11
New cards
Eysenck’s biological trait theory - introversion / extraversion
introverted:
* quiet
* reflective
* reserved
\
extraverted:
* outgoing
* active
* sociable
* quiet
* reflective
* reserved
\
extraverted:
* outgoing
* active
* sociable
12
New cards
evaluating trait theories advantage /disadvantage
advantages: gives us terminology to describe behavior
\
disadvantage:
* doesnt explain behavior
* does not creat a unique description for everyone ( like a horoscope) (barnum effect)
\
disadvantage:
* doesnt explain behavior
* does not creat a unique description for everyone ( like a horoscope) (barnum effect)
13
New cards
Physchodynamic perspective
Focus is on the __unconscious & early childhood__
14
New cards
Freud’s psychoanalytic theory / psycho analysis s: structure of personality / mind : ID
* Primitive, instinctual component of our personality
* operates on the pleasure principle (instant gratification)
* Includes: Eros (Life instinct) Thanatos (Death instict ) and Libido (Sexual energy)
* operates on the pleasure principle (instant gratification)
* Includes: Eros (Life instinct) Thanatos (Death instict ) and Libido (Sexual energy)
15
New cards
Freud’s psychoanalytic theory / psycho analysis s: structure of personality / mind : EGO
* operates on the reality principle (Delay gratification until Id’s urges can be satisfied in a socially acceptable way)
16
New cards
Freud’s psychoanalytic theory / psycho analysis s: structure of personality / mind : superego
* Moral component of personality (values, conscience, right v.s wrong)
* learned by parents and society
* learned by parents and society
17
New cards
Defense mechanism
unconscious reactions that protect a person from unpleasant emotions such as anxiety and guilt resulting from unconscious conflict
18
New cards
Defense mechanisms: Denial
\-refusal to recongnize or acknowledge a threatening situation
19
New cards
Defense mechanisms: repression
“pushing” threatining or conflicting events or situations out of conscious memory
20
New cards
Defense mechanisms: rationalization
making up accepted excuses for unacceptable behavior
21
New cards
Defense mechanisms: protection
placing on’es own unacceptable thoughts belonged to them and not to oneself
22
New cards
Defense mechanisms: reaction formation
forming an emotional reaction or attitude that is the oppisite of one’s threatening or unacceptable actual thoughts
23
New cards
Defense mechanisms: reaction formation
forming an emotional reaction or attitude that is the opposite of one’s threatening or unacceptable actual thoughts
24
New cards
Defense mechanisms: displacement
expressing feelings that woke be threatining at the real target onto a less threatening substitute target
25
New cards
Defense mechanisms: regression
falling back on childlike patterns as a way of coping with stressful b situations
26
New cards
Defense mechanisms: identification
trying to become like someone else to deal with one’s anxiety
27
New cards
defense mechanisms: compensation (substitution)
trying to make up for areas in which a lack is perceived by becoming superior in some other area
28
New cards
defense mechanisms: sublimination
turning socially unacceptable urges into socially acceptable behavior
29
New cards
defense mechanisms: intellectualization
removing emotions from a situation; very logical thinking
30
New cards
Eysencks biological trait theory - neuroticism (emotionality)
high: moody
anxious
restlessness
excitable
\
low:
\
calm
even tempered
anxious
restlessness
excitable
\
low:
\
calm
even tempered
31
New cards
Eysencks biological trait theory - psychoticism
high
* cruel
* hostile
* aggressive
* impulsive
* self s entered
\
low:
* warm
* caring
* concerned for others
* cruel
* hostile
* aggressive
* impulsive
* self s entered
\
low:
* warm
* caring
* concerned for others
32
New cards
psycho sexual stages of development
* Fixation
* Fixation
IF a state is not resolved successfully, a fixation may result. A fixation is a preoccupation with a particular source of pleasure
33
New cards
Oral Stage of psychosexual stage (0-1 yr)
* mouth is sourse of pleasure
* focus is on breastfeeding / weaning to determine if successful resolution
fixation: biting chewing sarcasm , smoking, etc
* focus is on breastfeeding / weaning to determine if successful resolution
fixation: biting chewing sarcasm , smoking, etc
34
New cards
anal stage (1-3 yrs) psychosexual stage / anal retentive / anal expuslive
focus is on potty training to determine if successful resolution
anal retentive: (Too early or too harsh)
* organized
* clean
* likes control
\
anal expulsisve (too late or too lax)
* messy
* disorganized
* impulsive
anal retentive: (Too early or too harsh)
* organized
* clean
* likes control
\
anal expulsisve (too late or too lax)
* messy
* disorganized
* impulsive
35
New cards
Phallic stage Of psycho sexual stage (3-5) / Oedipus complex & electra complex
sourse of pleasure : genitals
\
Oedipus complex (boys) and electra complex (girls)
oedipus : little boys desire mommy and want to kill daddy
( as a result, children use reaction formation and identification and cling to the same-sex parent. this is where the morals of the super ego are learned)
* girls develop penis envy
* fixation: mommy/daddy issues; trouble finding a mate
\
Oedipus complex (boys) and electra complex (girls)
oedipus : little boys desire mommy and want to kill daddy
( as a result, children use reaction formation and identification and cling to the same-sex parent. this is where the morals of the super ego are learned)
* girls develop penis envy
* fixation: mommy/daddy issues; trouble finding a mate
36
New cards
latency stage (5 years - adolescence)
sexual impulses are dormant; nothing really happens. most interaction occurs with same - sex children
37
New cards
genital stage (adolescence +)
sexual desires reappear ; earlier fixations reappear; sexual energies are channeled towards peers of other sex, rather than towards oneself
38
New cards
Carl Jung analytical psychology - personal uncons
houses material that isnt within one’s conscious awareness bc it has been repressed ot forgotten (our traditional view of unconscious)
39
New cards
Carl Jung analytical psychology - collective unconscious
shared unconscious
* a store house of latent memory traces ineherited from peoples ancestral past; shared by entire human race
* a store house of latent memory traces ineherited from peoples ancestral past; shared by entire human race
40
New cards
Carl Jung analytical psychology - archetypes
symbols of collective unconscious
* ancestral memories ; emotionally charged images and thought forms that have universal meaning (used in dream analysis)
* ancestral memories ; emotionally charged images and thought forms that have universal meaning (used in dream analysis)
41
New cards
Carl Jung analytical psychology - persona
mask to hide true self (Being fake)
* how we present ourselves to the world. the persona represents all of the different social masks that we wear among various groups and situations. it acs to shield the ego from negative images
* how we present ourselves to the world. the persona represents all of the different social masks that we wear among various groups and situations. it acs to shield the ego from negative images
42
New cards
alfred individual psychology
striving for superiority (overcoming feelings of inferiority )
striving for superiority (overcoming feelings of inferiority )
inferiority: a feeling , often unconscious, that one is “lesser” to others in some way (pshycial social economical intellectual etc)
* as a result we use compensation (Efforts to overcome imagined or real inferiorities ) which drives us to excel (strive for superiority ) in other areas in our lives
* as a result we use compensation (Efforts to overcome imagined or real inferiorities ) which drives us to excel (strive for superiority ) in other areas in our lives
43
New cards
karen Horney
\*Womb envy, ( men compensate in other ways)
* while freud argued personality differences in gender were biological, Horney argued that they were societal / cultural. she also focused on how different personalities were a representation of different ways of attaining love / affection
* while freud argued personality differences in gender were biological, Horney argued that they were societal / cultural. she also focused on how different personalities were a representation of different ways of attaining love / affection
44
New cards
object relations
early relationships between infants and significant objects (Esp people) shape personality
45
New cards
evaluating psychodynamic perspectives

46
New cards
Cognitive - behavioral perspectives on personality
emphasizes cognitive processes, such as thinking and judging, in the development of personality. these cognitive processes contribute to learned behaviors that are central to one’s personality
47
New cards
B F skinner and behaviorism
personality ( response tendencies) is developed through rewards and punishments
48
New cards
Albert Bandura’s social cognitive theory : reciprocal determinism
thoughts / cognition, behaviors and environmental factors all interact and influence each other
49
New cards
Albert Bandura’s social cognitive theory - self efficacy
one’s beliefs about thier ability to succeed (produce expected outcomes ) in a new situation. Can be high or low. Can be general or situation specific
50
New cards
walter mischel’s theories - the person-situation controversiy
mischels theories focused on the importance of the situation in determining behavior. identified certain “person variables” and “situational variables” in guiding behavior
51
New cards
Julian rotters expectancy theory - locus of control
behavior is determined by the extent to which u believe ur actions impact ur env.
* people are described as having either an internal LOC (yes, my behavior impacts my environment ) or an external LOC (no, my behavior foes not impact my env)
* people are described as having either an internal LOC (yes, my behavior impacts my environment ) or an external LOC (no, my behavior foes not impact my env)
52
New cards

Evaulating cognitive behavioral perspectives
53
New cards
Humanistic perspectives AKA phenomenological
Emphasizes the unique qualities in humans, especially their freedom to choose thier destiny and potential fro personal growth; be the best they can be
54
New cards
Carl rogers person centered theory - self concept
“self schema”
* collection of beliefs about one’s own nature, human qualities and typical behavior
* (people are subjective in thier self concept)
* collection of beliefs about one’s own nature, human qualities and typical behavior
* (people are subjective in thier self concept)
55
New cards
Carl rogers person centered theory - self discrepancy theory (incongruence)
actual self: who we are
ideal self: who we wish we were
ought self: who “they” say we should be
ideal self: who we wish we were
ought self: who “they” say we should be
56
New cards
Carl rogers person centered theory - conditions of worth
the development of the self is determined by the extent to which parents make thier love conditional (positive self concept is based on unconditional love)
\
* conditions of worth are created when the person is evaluated rather than the behavior
\
* conditions of worth are created when the person is evaluated rather than the behavior
57
New cards
Mallows Hierachy / theories: self actualization
the need to fulfil one’s potential ; be the best u can be
58
New cards
Mallows Hierachy / theories: growth orientation vs deficiency orientation
growth orientation: focusing on waht you have
\
deficiency orientation: focusing on what’s missing
\
those with a growth orientation are healthier and more likely to reach self - actualization
\
deficiency orientation: focusing on what’s missing
\
those with a growth orientation are healthier and more likely to reach self - actualization
59
New cards
Mallows Hierachy / theories: self tracscendence needs
need to find meaning and indentity beyond the self
60
New cards
Mallows Hierachy / theories: esteem needs
need for self esteem, achievement, competence and independence; neede for recognition and respect from others
61
New cards
Mallows Hierachy / theories: safety needs
need to feel that the world is organized and predictable ; need to feel safe , secure, stable
62
New cards
Mallows Hierachy / theories: psychological needs
need to satisfy hunger and thirst
63
New cards
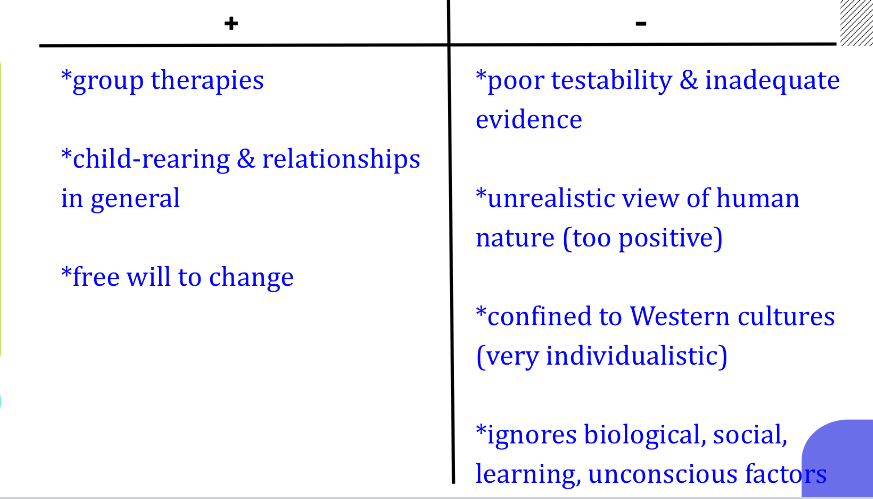
evaluating humanistic perspectives
64
New cards
Individualisms versus collectivism impact on personality
Individualism: putting personal goals ahead of group goals & defining one's identity in terms of personal attributes rather than group membership.
\n
Collectivism: putting group goals ahead of personal goals & defining one's identity in terms of the groups one belongs to.
\n
\n
Collectivism: putting group goals ahead of personal goals & defining one's identity in terms of the groups one belongs to.
\n
65
New cards
object tests (self report inventories)
T/F , Y/N, MC Questions/statements that can be scored
66
New cards
MMPI
Minnesota Multiphasic personality inventory
Most widely used; used in diagnosis
(566 T/F Questions ; 10 clinical scales and 4 validity scales)
Most widely used; used in diagnosis
(566 T/F Questions ; 10 clinical scales and 4 validity scales)
67
New cards
16PF (Cattell) & NEO - PI - R (Costa & McCrae) (Big 5)
NEO-PI : Compares results from private and public versions
68
New cards
MBTI (Myers- briggs type indicator )
another objective test (Gives 4 letters = personality type)
69
New cards
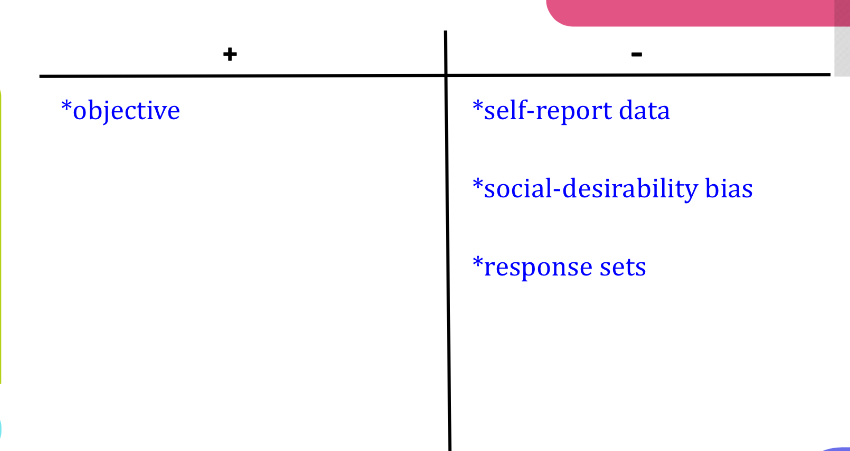
Evaluating objective tests
70
New cards
projective tests
participants respond to vague, ambiguous
stimuli in ways that may reveal the subject’s __unconscious__ needs, feelings, & personality traits & can be analyzed in many different ways
\n
stimuli in ways that may reveal the subject’s __unconscious__ needs, feelings, & personality traits & can be analyzed in many different ways
\n
71
New cards
Thematic apperception test (TAT)
Tell the story of a picture
72
New cards
Rorschach ink blot test
shown a series of inkblots ; respond to what u see
73
New cards
evaluating projective tests

74
New cards
Motivation
the factors that influence the initiation, direction , intensity and persistence of behavior
75
New cards
sources of motivation : biological factors:
food water sleep sex temperature phsiological factors (drugs or hormones) “internal”
76
New cards
sourse of motivations: social factors
for what? approval of others, acceptance, fitting in/ standing out. by whom: parents / sibilants, friends, teammates, teachers , media , culture / race / religions etc “external “
77
New cards
sourse of motivations - cognitive factors
ex: beliefs , thoughts, expectations & views of yourself and of the world curiousity, intellectual growth, etc “internal”
78
New cards
sourse of motivations : emotional factors
love, happiness, anger , fear , jealousy “internal”
79
New cards
primary vs secondary drives /motives
primary: biological need; directly related to survival (Ex: food , water , oxygen, sleep etc)
\
secondary : acquired drives that are culturally determined/learned ( ex: obtaining money, intimacy, social approval , etc)
\
secondary : acquired drives that are culturally determined/learned ( ex: obtaining money, intimacy, social approval , etc)
80
New cards
Drive theory
we are motivated to maintain homeostasis (balance) thie theory best explains biological needs
81
New cards
homeostasis
state of physiological equalibrium or stability
82
New cards
drive
internal state of tension that motivates an organism to behave in a certain way in order to restore homeostasis
83
New cards
incentive theory
incentive = an external goal
we are motivated to obtain desirable stimuli or avoid negative stimuli ex: $, promotion, food, aprooval, a good grade etc.
we are motivated to obtain desirable stimuli or avoid negative stimuli ex: $, promotion, food, aprooval, a good grade etc.
84
New cards
instinct (evolutionary) thoery
based on survival, natural selection, reproductive capacity, automatic, involuntary, and unlearned behaviors
ex: birds fly south for the winter
ex: birds fly south for the winter
85
New cards
arousal theory
people are motivated to maintain thier optimal level of arousal (which is different for everyone)
* if over aroused ( above your optimial level) = motivated to reduce ur level of arousal
VIce verca
* if over aroused ( above your optimial level) = motivated to reduce ur level of arousal
VIce verca
86
New cards
lateral hypothalamus
feeding center; “ON” Switch
87
New cards
Ventromedical hypothalamus/nucleus
satiety center; “OFF” switch/ satiety = feeling full
88
New cards
paraventricular nucleus (PVN)
Controls the selection of specific foods and blood sugar levels
89
New cards
hormonal regulation: insulin
secreted by pancreas; reduces appetite
90
New cards
hormonal regulation: ghrelin
released by an empty stomach = stimulates appetite ; causes stomach contractions
91
New cards
hormonal regulation: CCK
Delivers satiety (Full) signals to the brain
92
New cards
hormonal regulation: Leptin
Long term regulation of hunger, high leptin = high fat storage ; less hunger
93
New cards
enviornmental factors of hunger and eating
palatability ( tastes good = eat more) quantity available (more food = eat more) variety available (increased variety = eat more) cultural factors, learned preferences
94
New cards
set point theory
internal thermostat that fights to maintain body weight within a certain stage (maintained by food intake and metabolism) \*unique to each individual ; this is the body’s “normal” weight
95
New cards
fixed mindset vs growth mindset
Fixed: belief that your basic qualities, like ur intelligence or talent are simply fixed traits
\
growth : belief that ur most basic abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work. - brains and talent are just the starting point ( love of learning and resilience are essential )
\
growth : belief that ur most basic abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work. - brains and talent are just the starting point ( love of learning and resilience are essential )
96
New cards
need for acheivement
need for a personal accomplishment
\
characteristics of a HIGH need for acheivemnt:
1. Enjoy the process of struggling for achievement
2. Feel intense satisfaction when achievement is reached
3. Set challenging- but realistic- goals
4. Take risks & not upset by failure
5. Seek out constructive criticism from competent sources
6. Preoccupied with performance & level of ability
7. Select tasks with clear outcomes
\
LOW:
1. Success produces feelings of relief at having avoided failure
2. Prefer tasks that ensure success
3. Quit in response to failure
4. Do not seek out criticism
\
characteristics of a HIGH need for acheivemnt:
1. Enjoy the process of struggling for achievement
2. Feel intense satisfaction when achievement is reached
3. Set challenging- but realistic- goals
4. Take risks & not upset by failure
5. Seek out constructive criticism from competent sources
6. Preoccupied with performance & level of ability
7. Select tasks with clear outcomes
\
LOW:
1. Success produces feelings of relief at having avoided failure
2. Prefer tasks that ensure success
3. Quit in response to failure
4. Do not seek out criticism
97
New cards
need for affliction
need to belong to and identify with a group
\n
\n
98
New cards
need for aprooval
need to have other people think highly of you
\n \n
\n \n
99
New cards
intrinsic vs extrinsic motivation
Intrinsic: desire to attain internal satisfaction
Extrinsic: desire to attain external rewards
Extrinsic: desire to attain external rewards
100
New cards
overjustification effect
giving a reward for an already desired behavior willl reduce ones aspiration to engage tin that behavior (When introducing extrinsic rewards diminishes intristic motivation) ex- reading month, preffesonal athletes