Chapter 11 - AP Environmental Science
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Undernutrition
The condition in which not enough calories are ingested to maintain health.
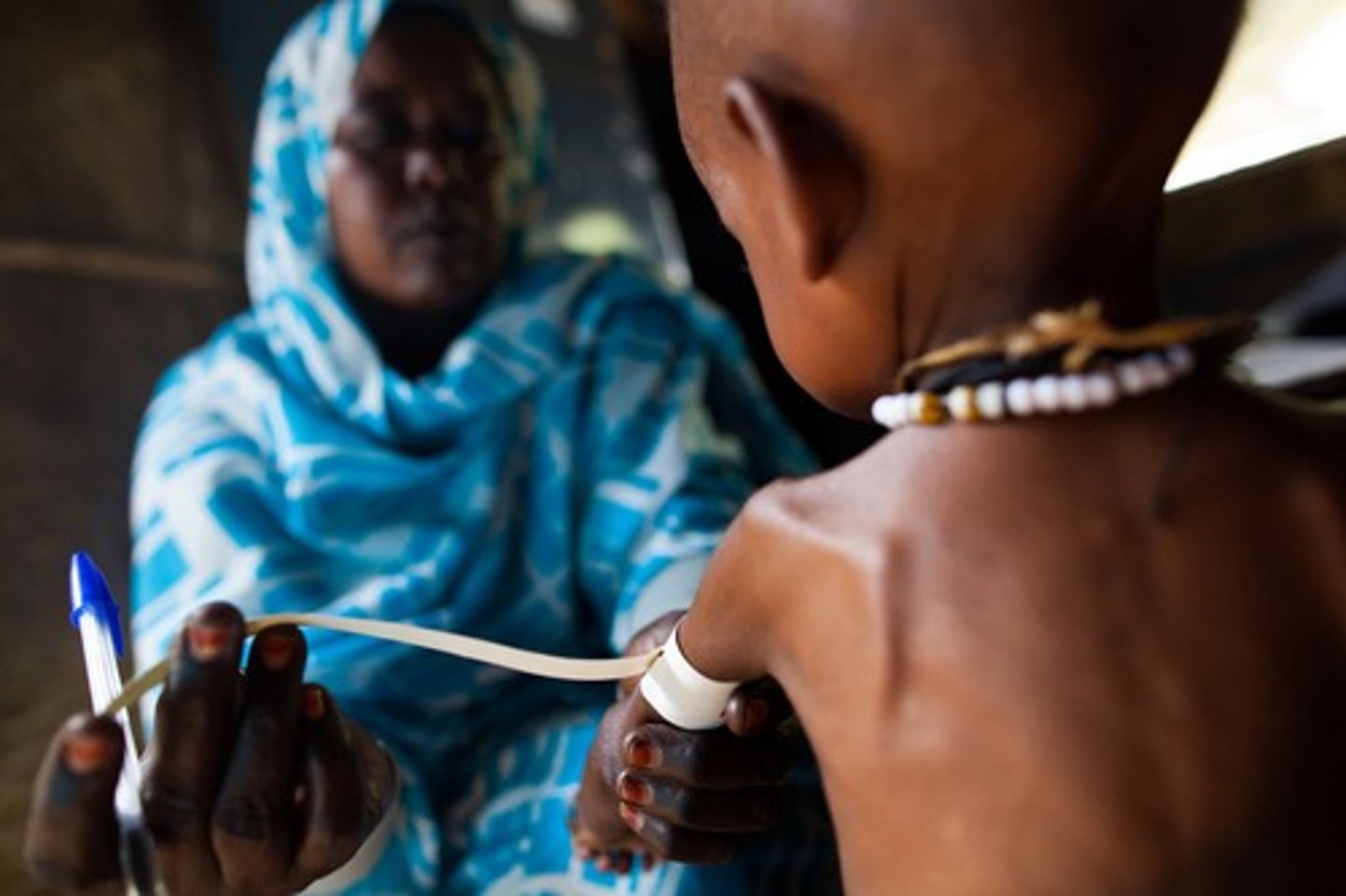
Malnourished
Having a diet that lacks the correct balance of proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.

Food security
A condition in which people have access to sufficient, safe. and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs for an active and healthy life.

Food insecurity
A condition in which people do not have adequate access to food.
Famine
The condition in which food insecurity is so extreme that large numbers of deaths occur in a given area over a relatively short period.

Anemia
A deficiency of iron.
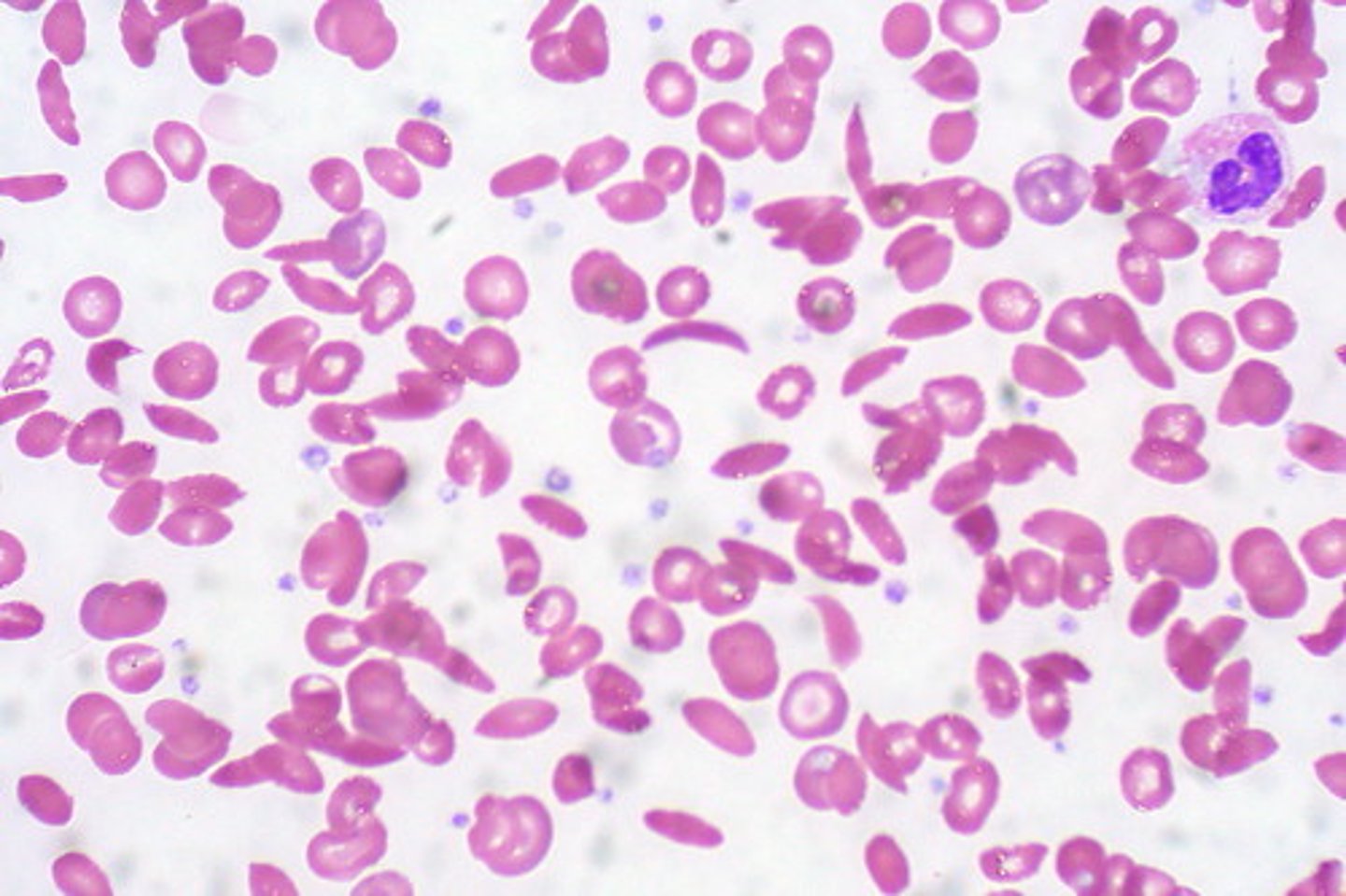
Overnutrition
Ingestion of too many calories and a lack of balance of foods and nutrients.

Meat
Livestock or poultry consumed as food.

Industrial agriculture
Agriculture that applies the techniques of mechanization and standardization. Also known as agribusiness.

Energy subsidy
The fossil fuel energy and human energy input per calorie of food produced.

Green Revolution
A shift in agricultural practices in the twentieth century that included new management techniques, mechanization, fertilization, irrigation, and improved crop varieties. Resulted in increased food output.

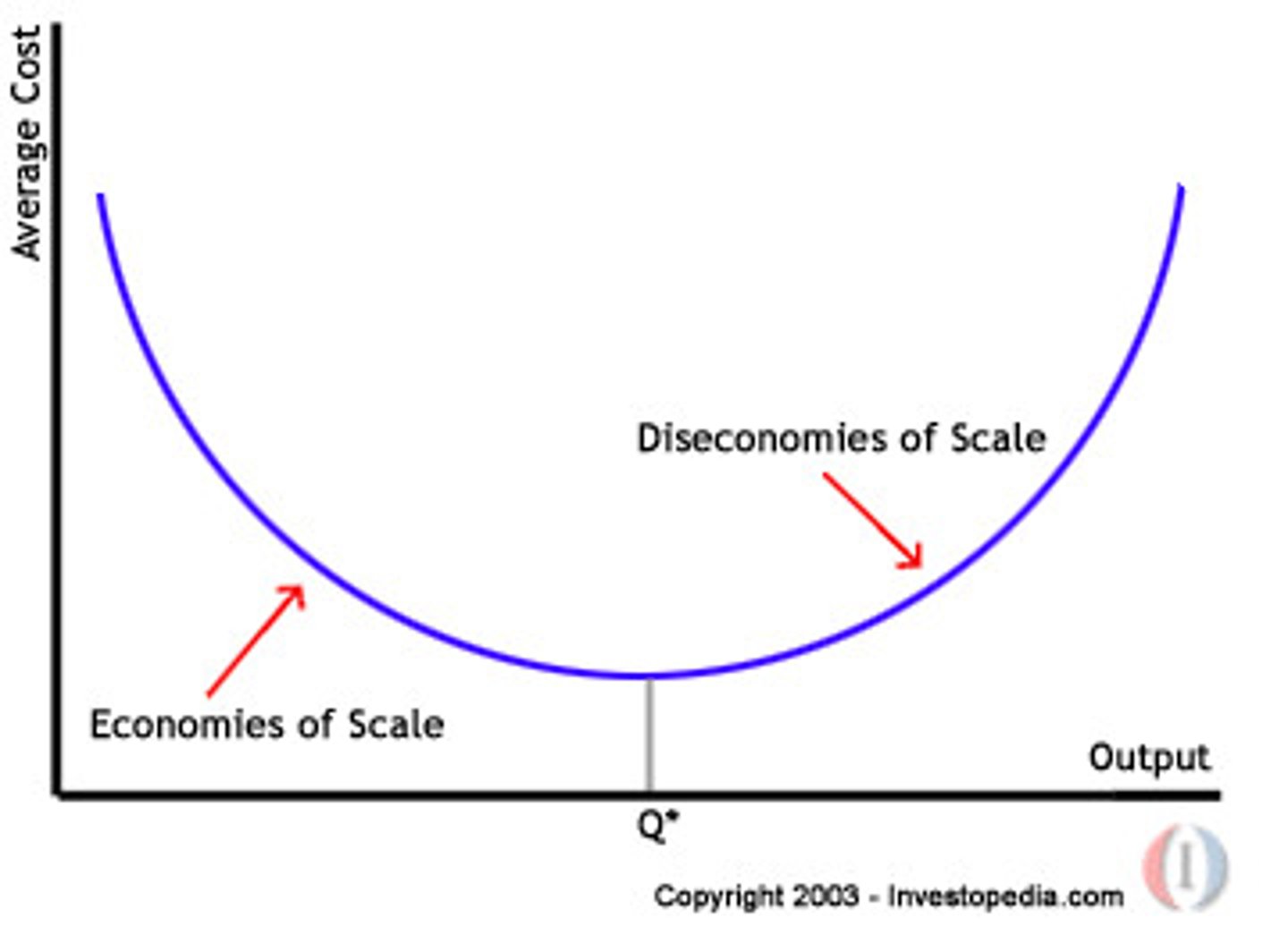
Economies of scale
The observation that average costs of production fall as output increases.
Waterlogging
A form of soil degradation that occurs when soil remains under water for prolonged periods.
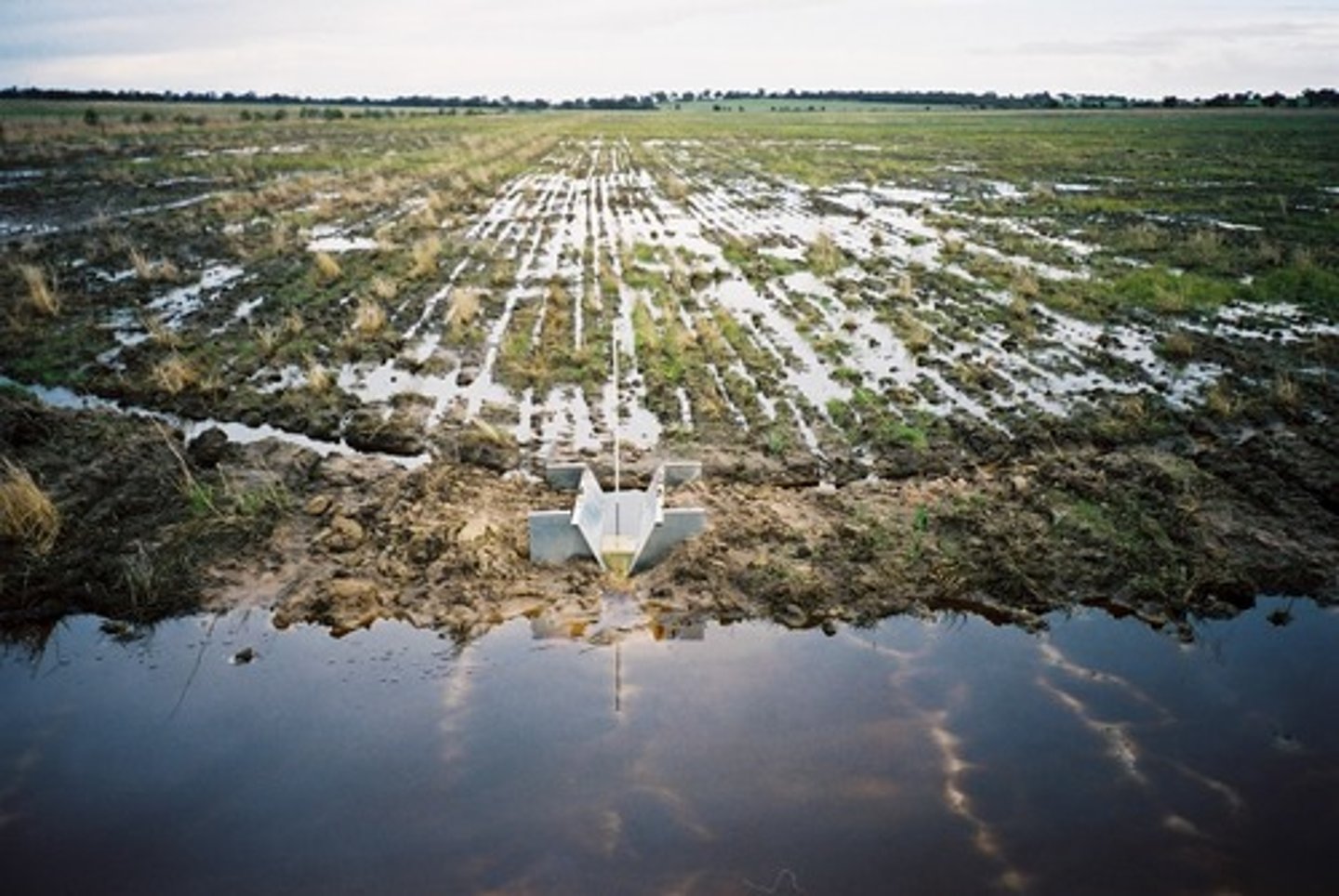

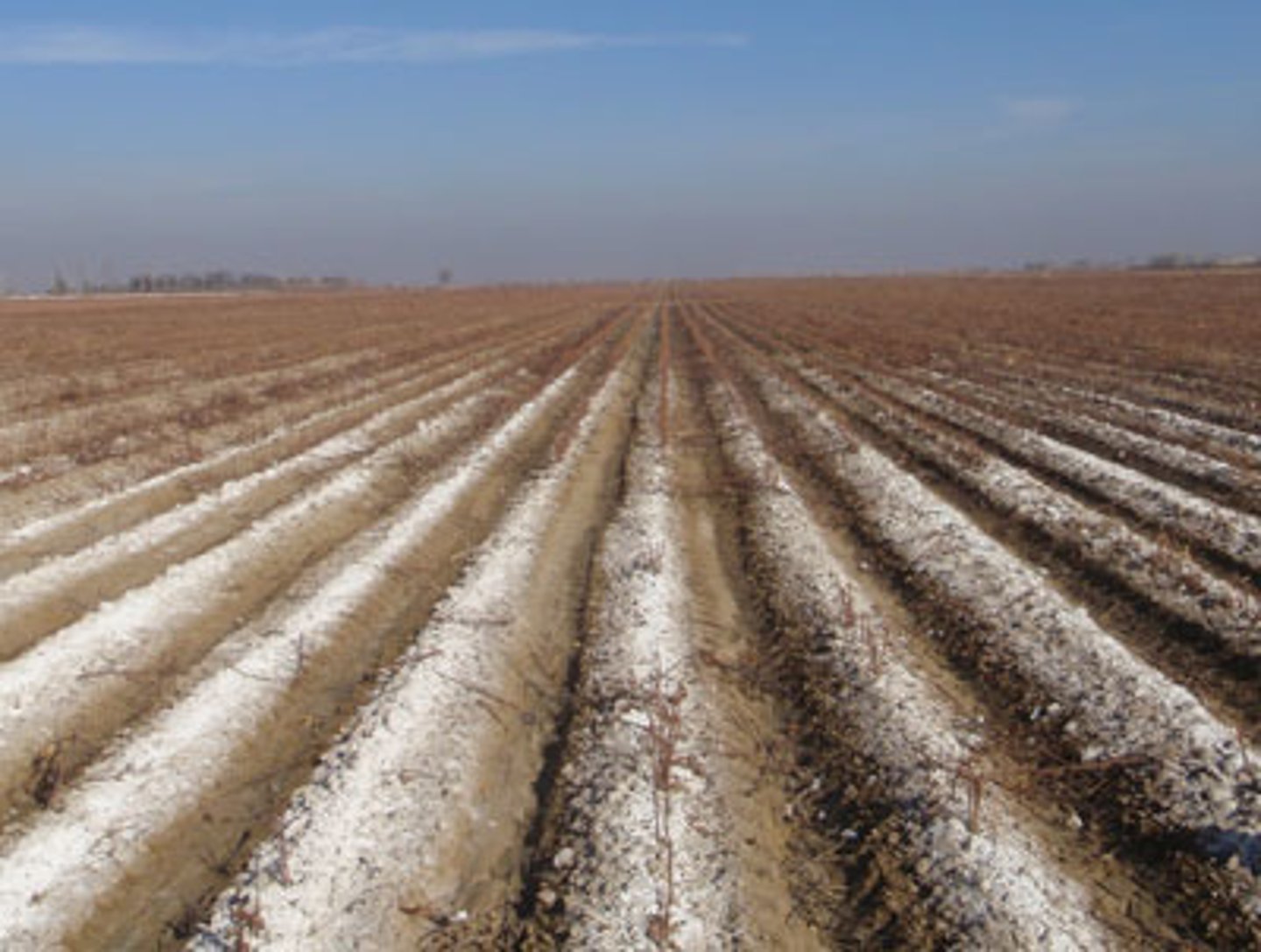
Salinization
A form of soil degradation that occurs when the small amount of salts in irrigation water becomes highly concentrated on the soil surface through evaporation.

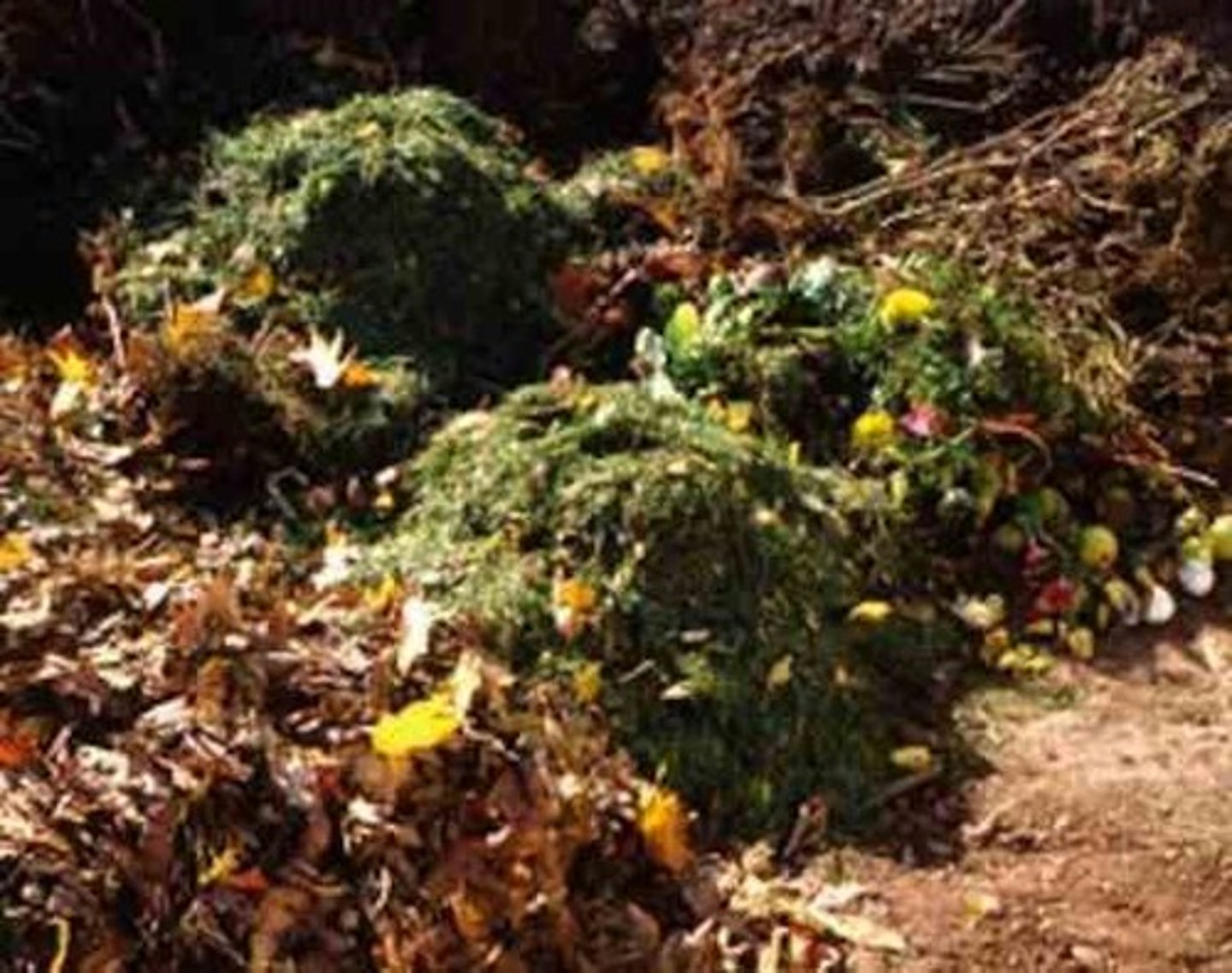
Organic fertilizer
Fertilizer composed of organic matter from plants and animals.

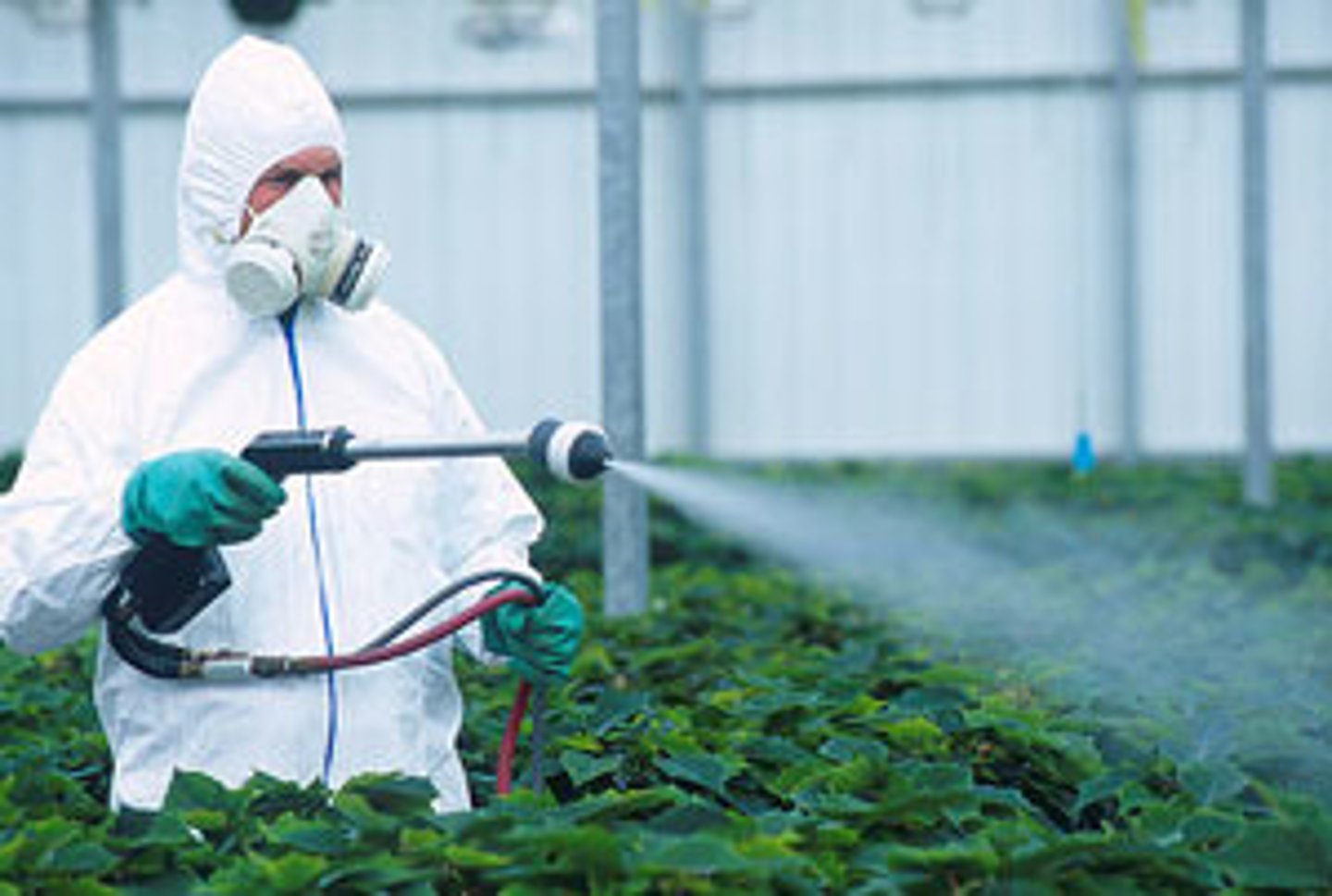
Synthetic fertilizer
Produced commercially, normally with the use of fossil fuels. Also known as inorganic fertilizers.

Monocropping
An agricultural method that utilizes large plantings of a single species or variety.

Pesticide
A substance, either natural or synthetic that kills or controls organisms that people consider pests.

Insecticide
A pesticide that targets species of insects and other invertebrates that consume crops.

Herbicide
A pesticide that targets plant species that compete with crops.

Broad spectrum pesticide
A pesticide that kills many different types of pest.

Selective pesticide
A pesticide that targets a narrow range of organisms.

Persistent pesticide
A pesticide that remains in the environment for a long time.
Nonpersistent pesticide
A pesticide that breaks down rapidly, usually in weeks or months.
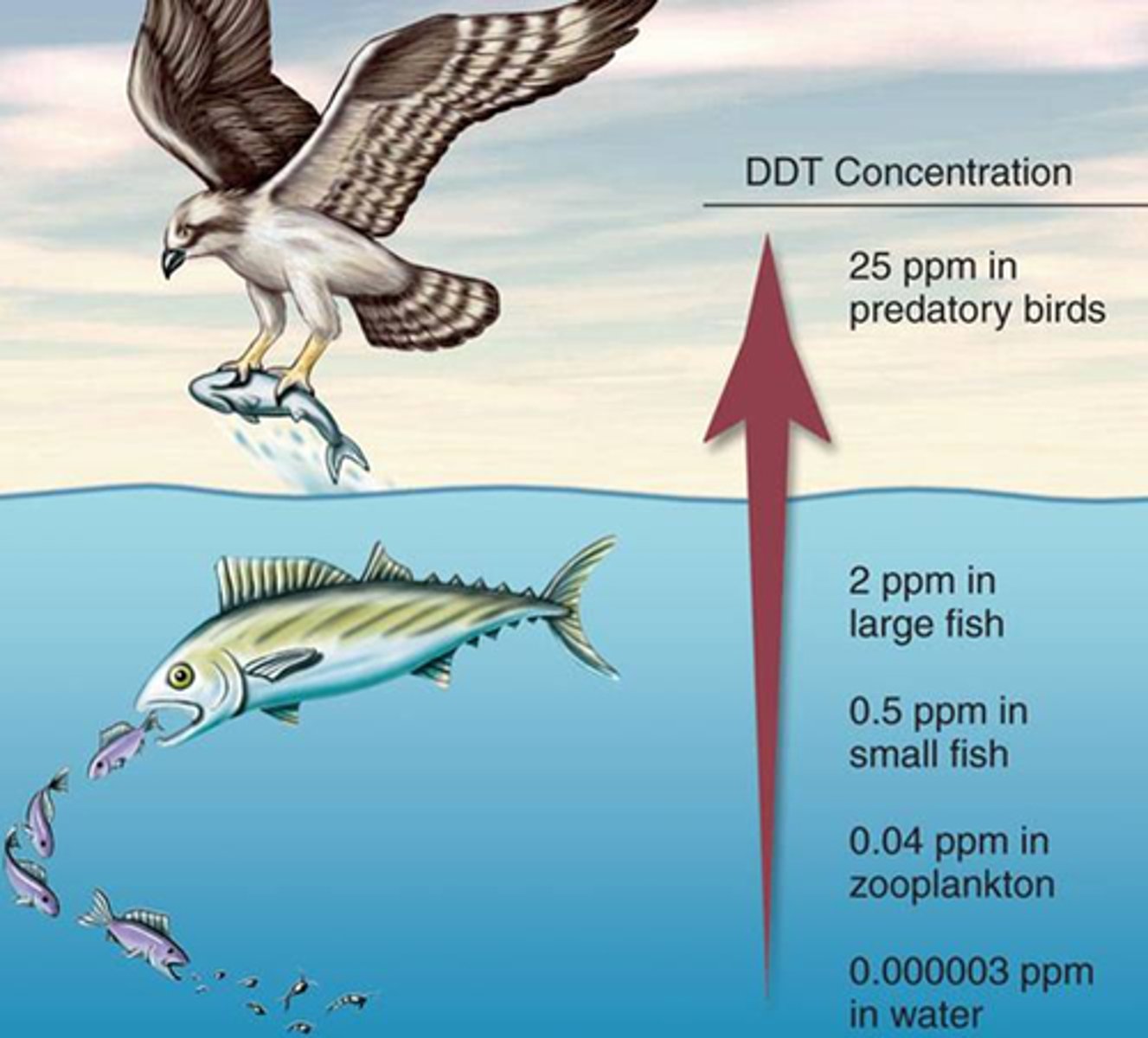
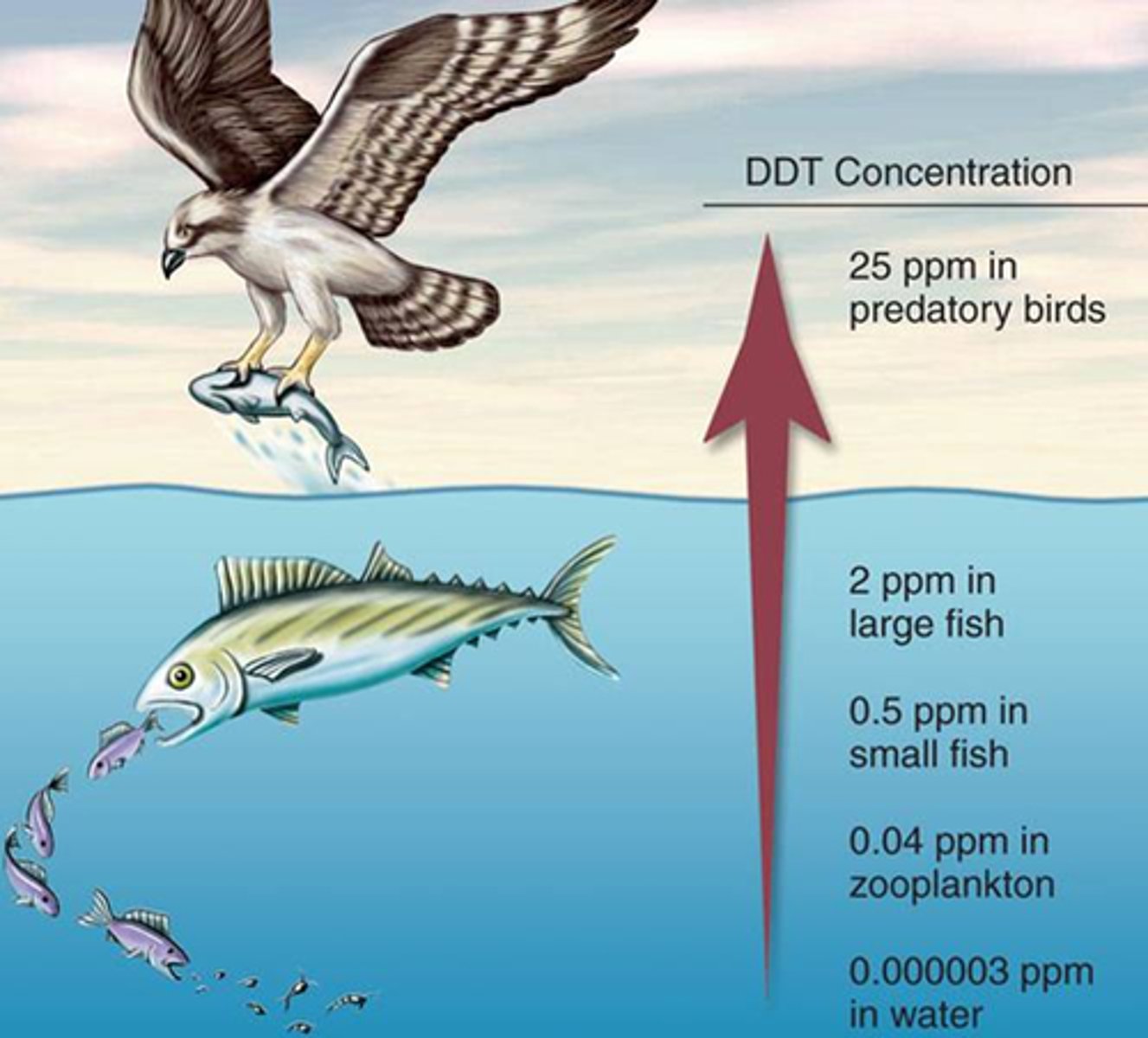
Bioaccumulation
Build up of substances, such as pesticides, or other chemicals in an organism. Occurs when an organism absorbs a substance at a rate faster than that at which the substance is lost by catabolism and excretion.
Pesticide resistance
Decreased susceptibility of a pest population to a pesticide that was previously effective at controlling the pest.
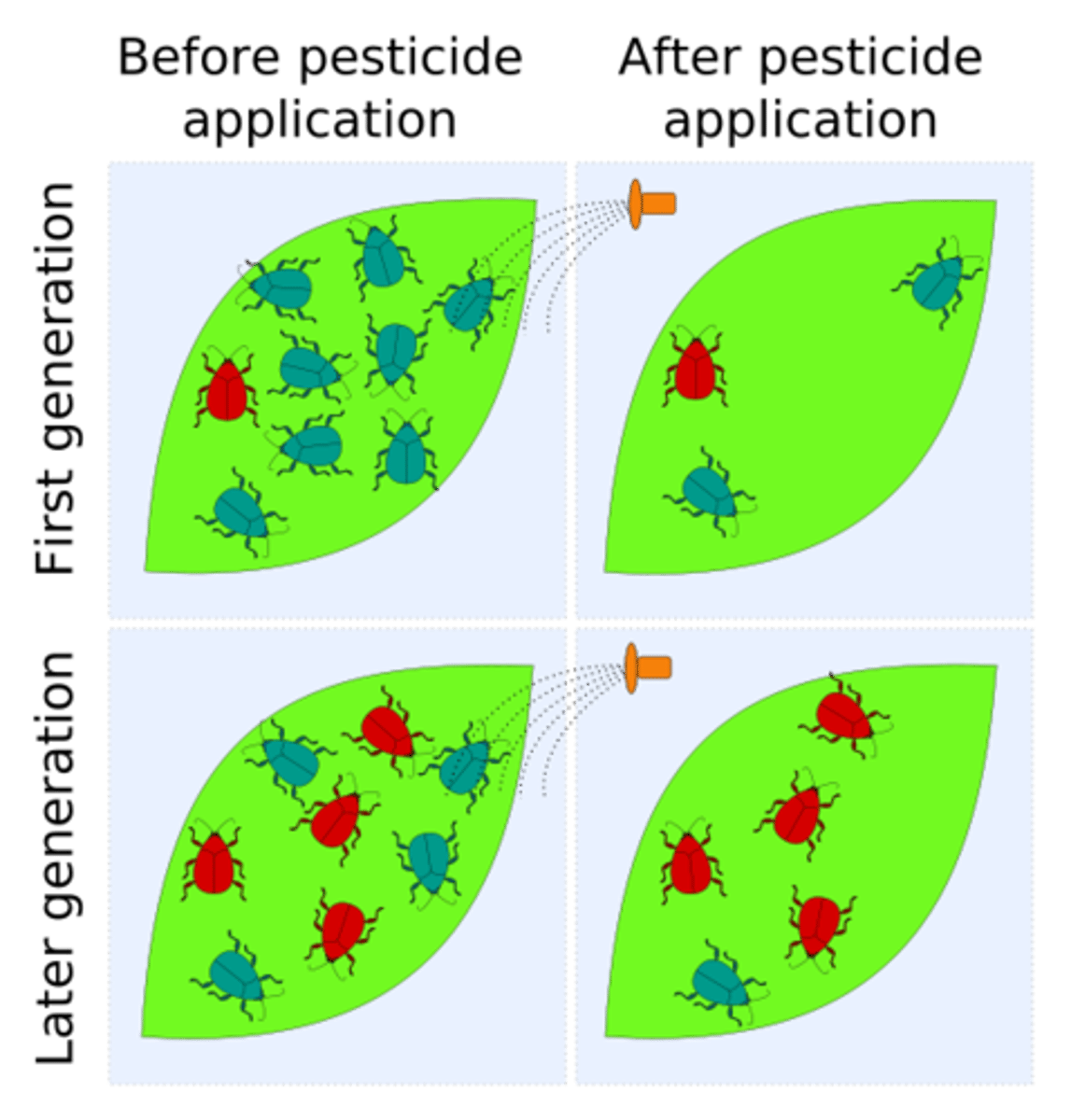
Pesticide treadmill
A cycle of pesticide development, followed by pest resistance, followed by new pesticide development.
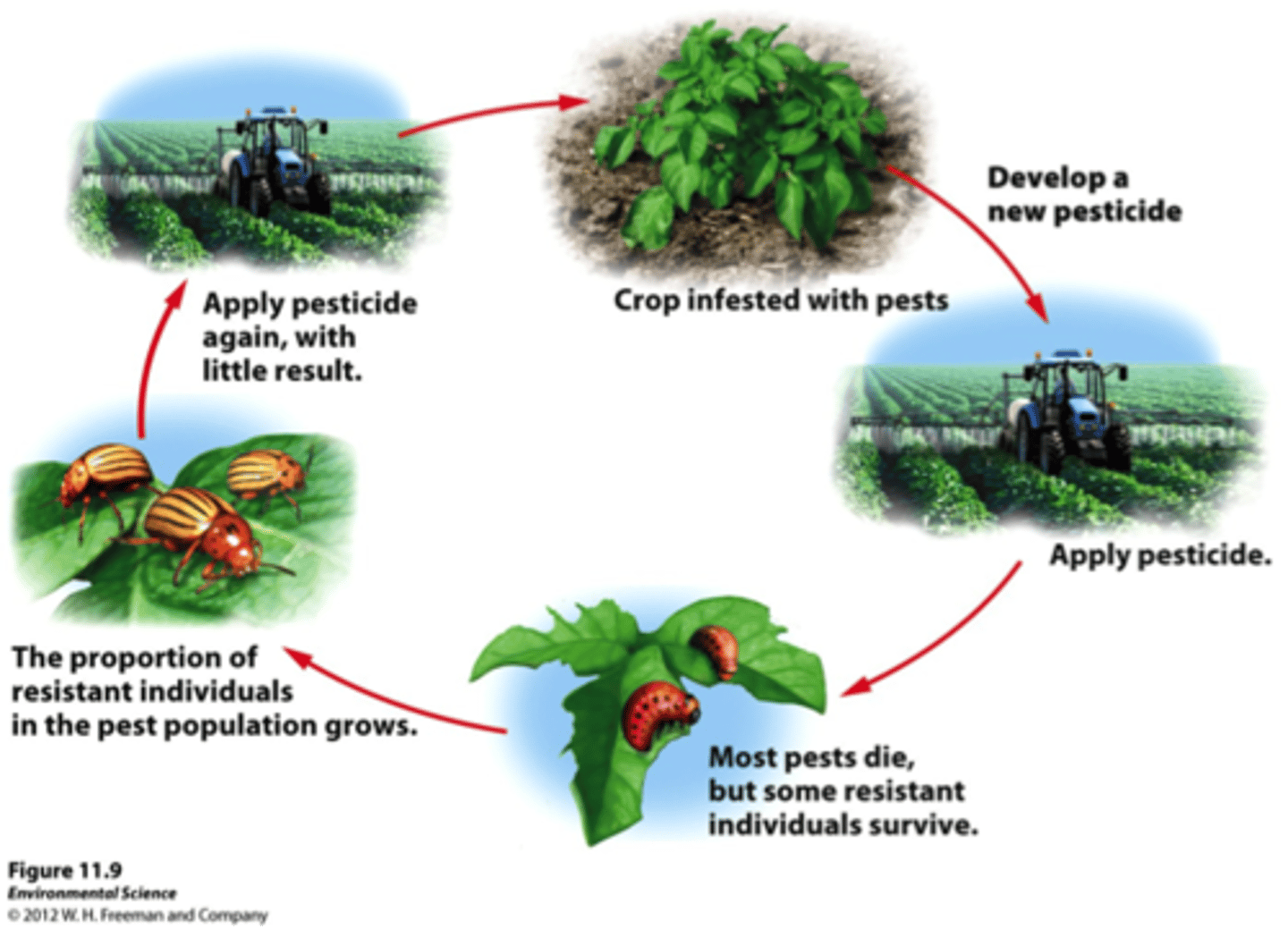
Conventional agriculture
The farming systems that include the use of synthetic chemical fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, other continual inputs, mechanization, and genetically modified organisms.
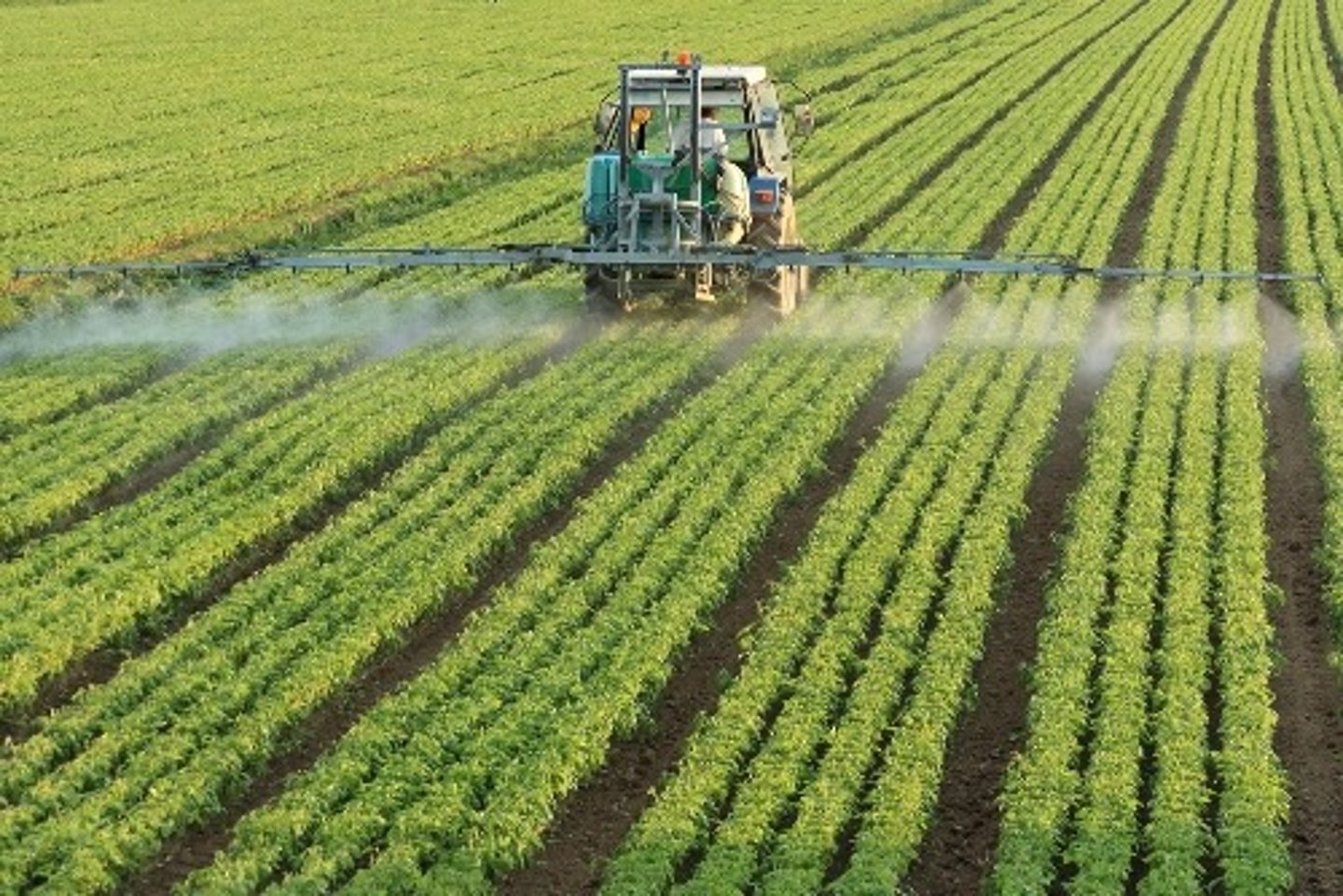

Shifting agriculture
An agricultural method in which land is cleared and used for a few years until the soil is depleted of nutrients.
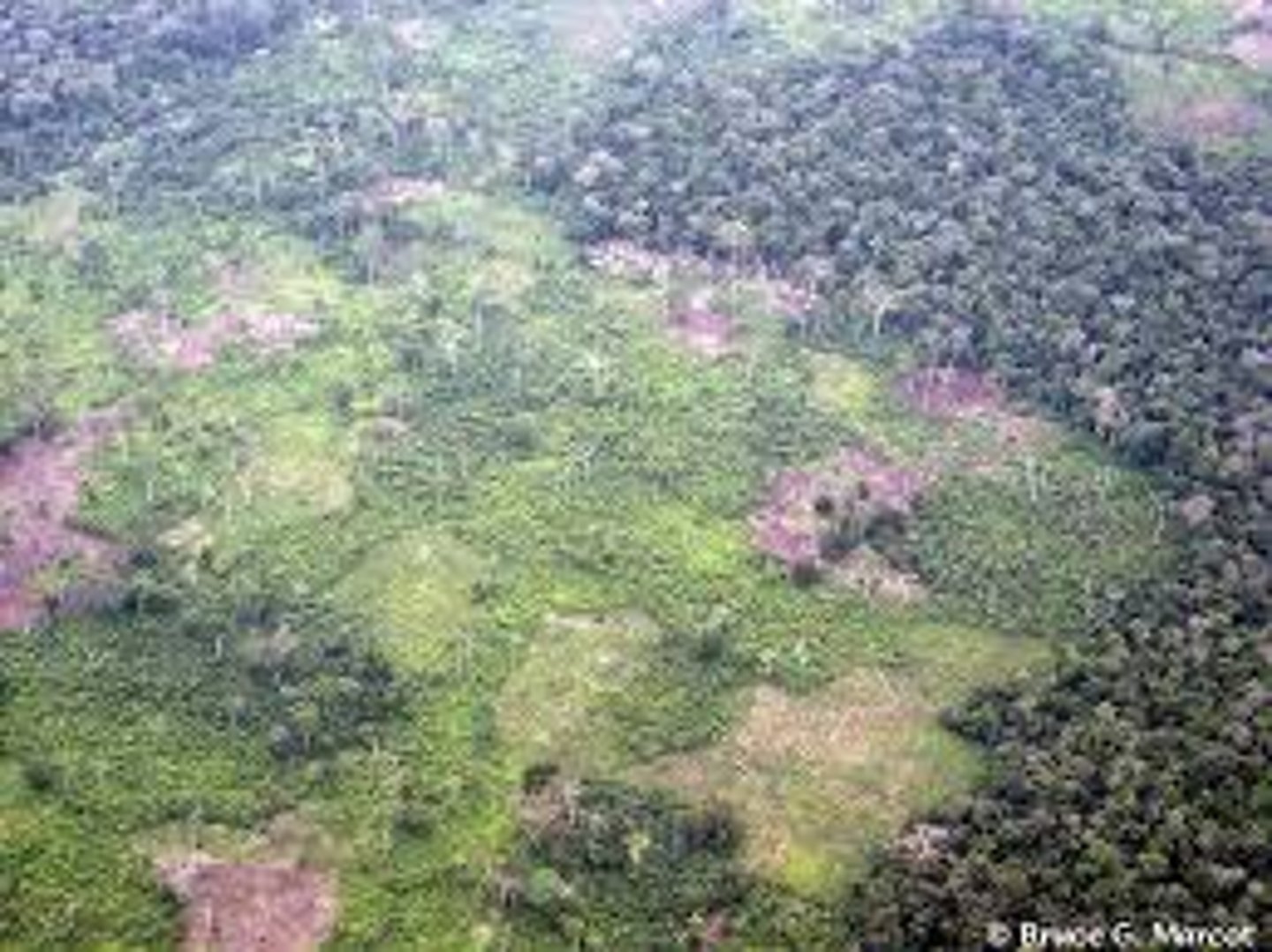

Desertification
The transformation of arable, productive land to desert or unproductive land due to climate change or destructive land use.

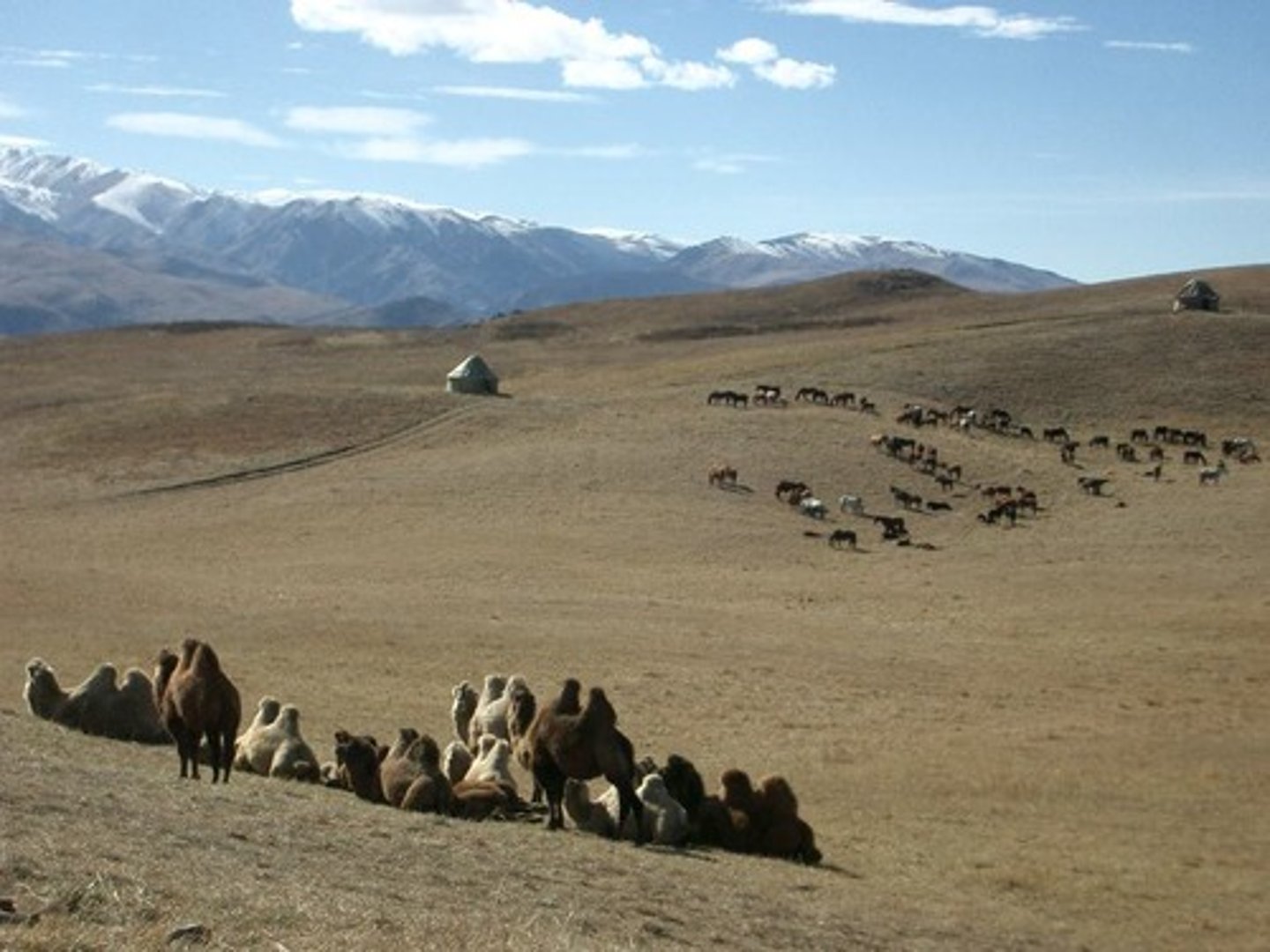
Nomadic grazing
The feeding of herds of animals by moving them to seasonally productive feeding grounds, often over long distances.

Sustainable agriculture
Agriculture that fulfills the need for food and fiber while enhancing the quality of the soil, minimizing the use of nonrenewable resources, and allowing economic viability for the farmer.
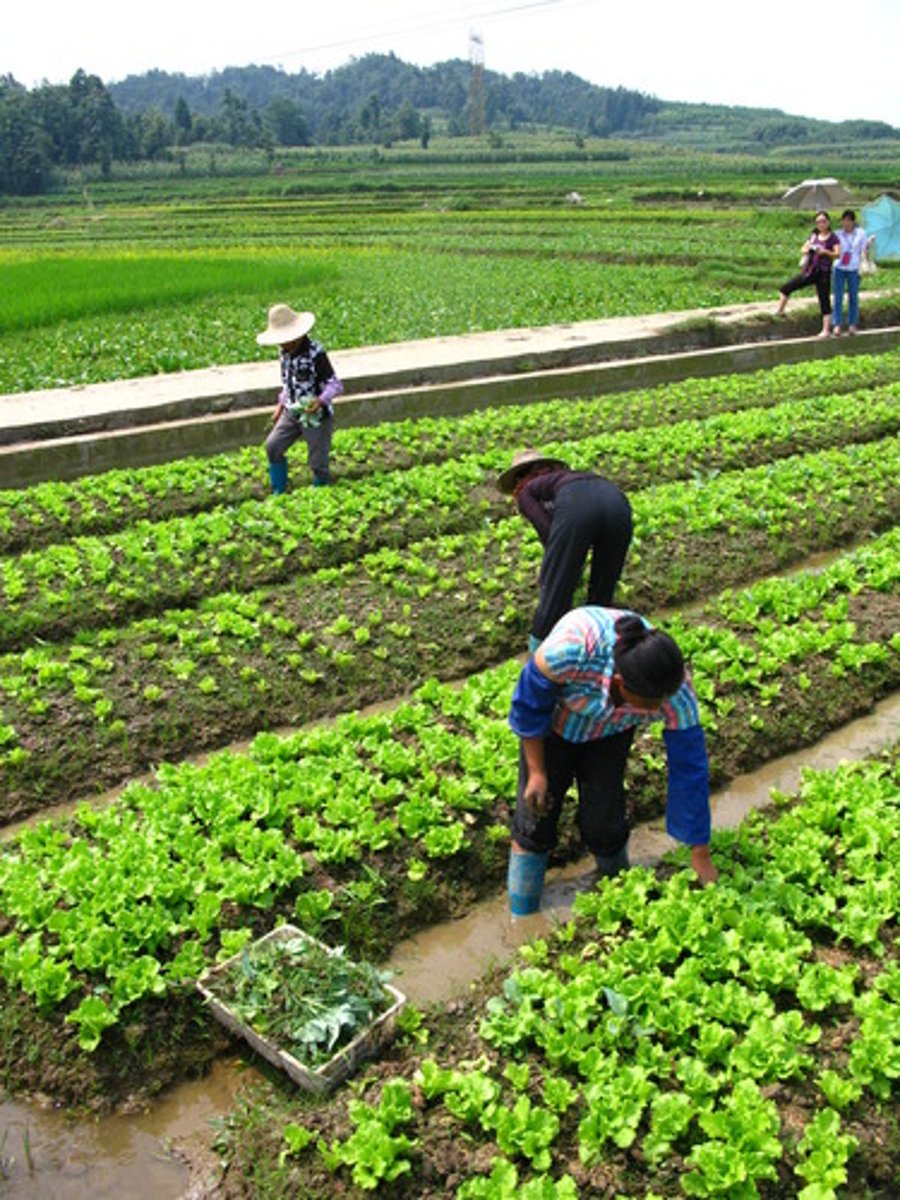

Intercropping
An agricultural method in which two or more crop species are planted in the same field at the same time to promote a synergistic interaction.
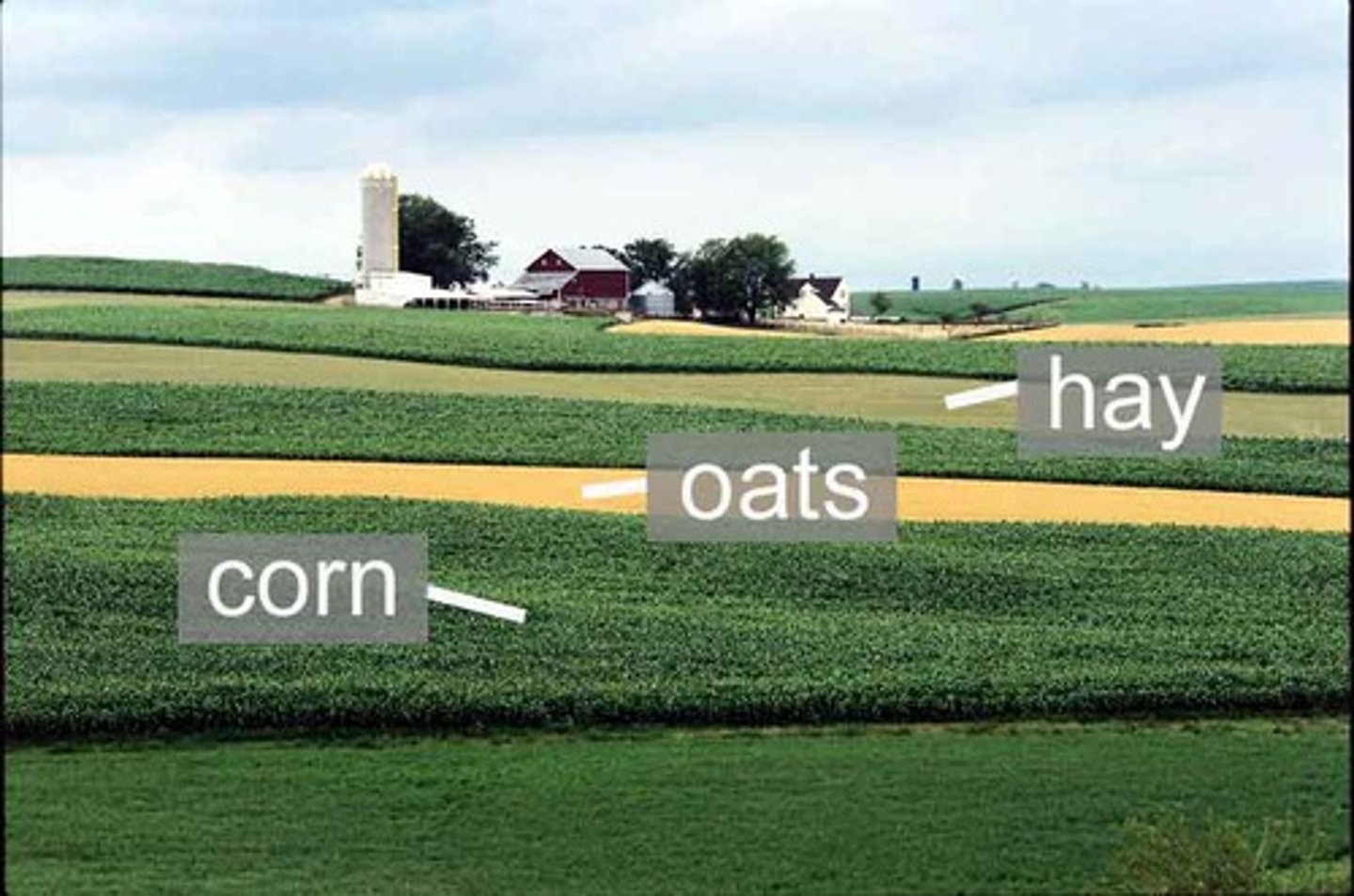

Crop rotation
An agricultural technique in which crop species in a field are rotated from season to season.
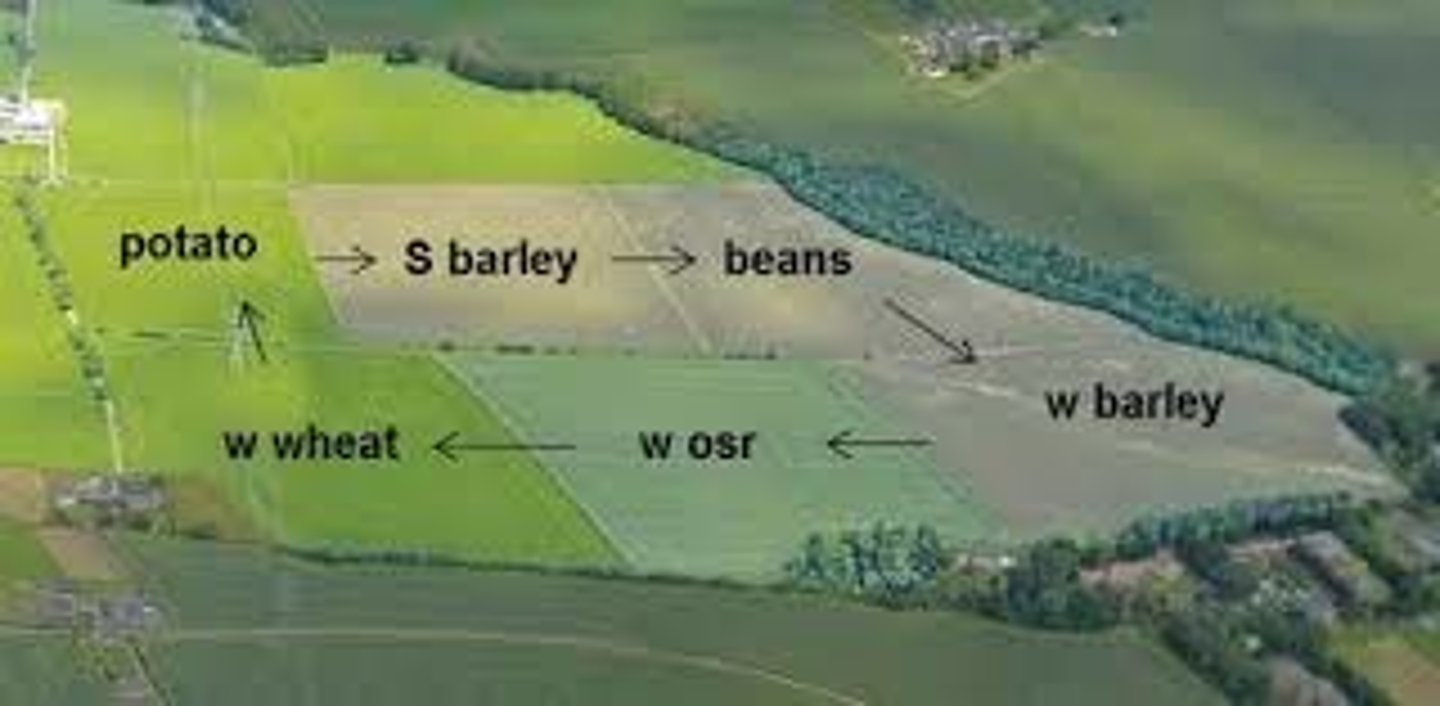
Agroforestry
An agricultural technique in which trees and vegetables are grown next to each other in rows or other patterns.
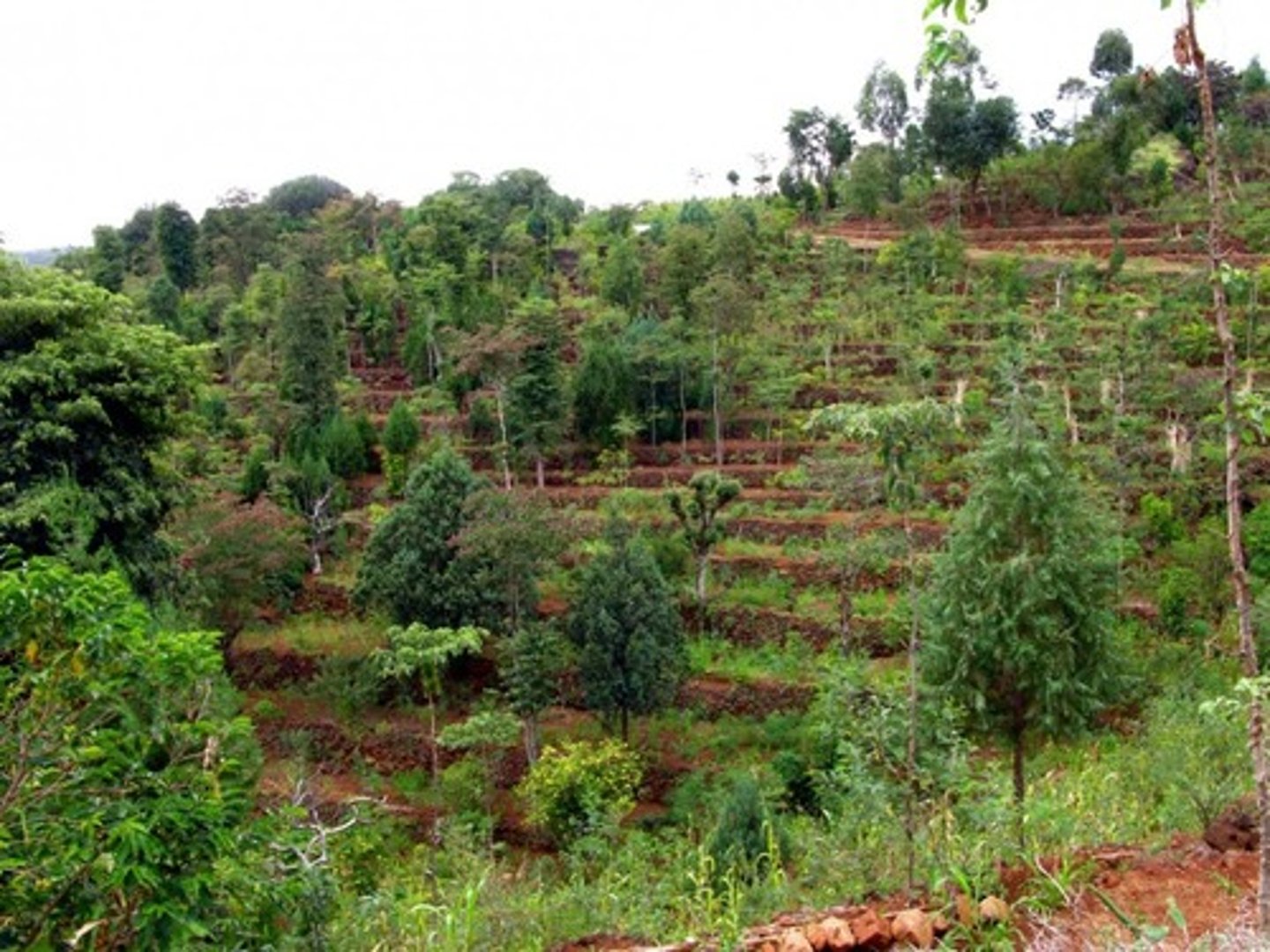

Contour plowing
An agricultural technique in which plowing and harvesting are done parallel to the topographic contours of the land.

No-till agriculture
An agricultural method in which farmers do not turn the soil between seasons as a means of reducing topsoil erosion.

Integrated pest management (IPM)
An agricultural practice that uses a variety of techniques designed to minimize pesticide inputs.

Organic agriculture
Production of crops without the use of synthetic pesticides or fertilizers

Concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs)
An animal feeding operation (AFO)—a farm in which animals are raised in confinement—that has over 1000 "animal units" confined for over 45 days a year.

Fishery
A commercially harvestable population of fish within a particular ecological region.

Fishery collapse
The decline of a fish population by 90% or more.

Bycatch
The unintentional catch of nontarget species while fishing.

Individual transferable quotas (ITQs)
A fishery management program in which individual fishers are given a total allowable catch of fish in a season that they can either catch or sell.

Aquaculture
Farming aquatic organisms such as fish, shellfish and seaweeds.

Annual plant
A plant that lives for only one season.

Perennial plant
A plant that lives for multiple years.

fungicide
A pesticide that targets species of fungus that can damage crops.

biomagnification
The concentration of toxins in an organism as a result of its ingesting other plants or animals in which the toxins are more widely disbursed.
Agrobiodiversity
Includes not only a wide variety of species, but also the many ways in which farmers can exploit biological diversity to produce and manage crops, land, water, insects, and biota.
carbon sequestration
The process through which agricultural and forestry practices remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere.
Community Supported Agriculture
A group of individuals who pledge support to a farm operation so that the farmland becomes, either legally or spiritually, the community's farm, with the growers and consumers providing mutual support and sharing the risks and benefits of food production.
Conservation Tillage
A broad range of soil tillage systems that leave a residual cover on the soil surface, substantially reducing the effects of soil erosion from wind and water. These practices minimize nutrient loss, decreased water storage capacity, crop damage, and decreased farmability.