Psych 104 Final Exam - Scully UAlberta 2023
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
Sigmund Freud
Founder of psychoanalysis and focused on the unconscious mind
Psychodynamic Theory
Freudian theory that unconscious forces determine behavior
- Impulses want to be expressed
- Defenses want to hold impulses back
Abraham Maslow
Originator of the hierarchy of needs and focused on personal growth
Humanistic Theory
Prioritizing personal growth with the hierarchy of needs
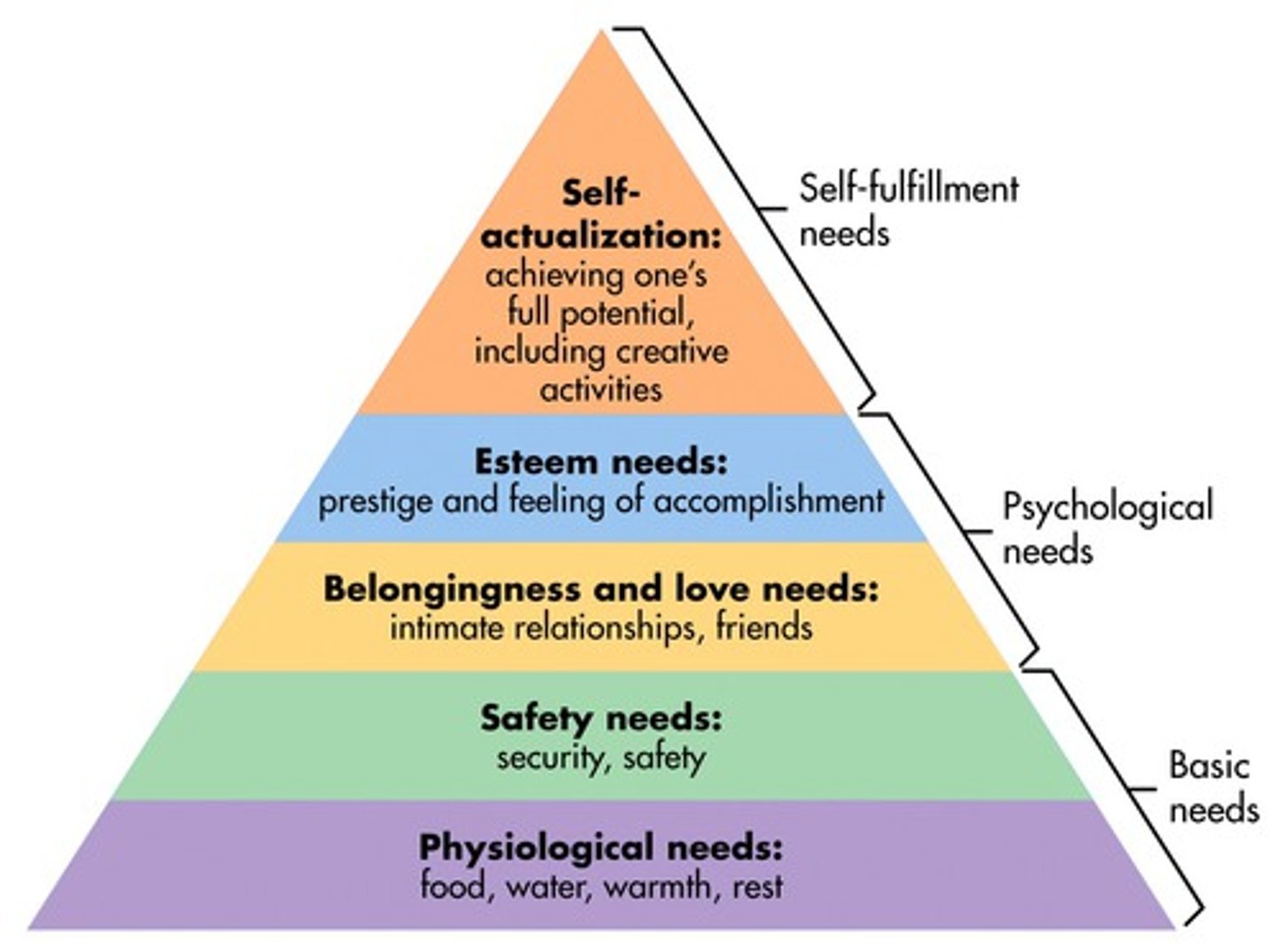
Hierarchy of Needs
Pyramid of needs growing toward "Self-Actualization" (reaching your "full potential")
B. F. Skinner
Radical Behaviourism - nature sand nurture effect who you are. Behaviour modification.
Correlation
look for relationship between variables. Correlation is NOT Causation
Positive Correlation
Increase in one variable relates to an increase in the other
Negative Correlation
Increase in one variable relates to a decrease in the other
Experiment
Only way to infer causality
Correlation vs Experiment
Correlation looks for a mutual relationship between variables. Experiment looks for the causal relationship between variables
Classical Conditioning
Ivan Pavlov - a neutral stimulus comes to signal the occurrence of another stimulus
Unconditioned Stimulus
Biologically significant stimulus that already has a response associated with it
Conditioned Stimulus
Previously Neutral Stimulus that comes to elicit a conditioned response
Unconditioned Response
Response associated with Unconditioned Stimulus
Conditioned Response
With enough pairings of the conditioned response with an unconditioned stimulus, the conditioned stimulus will come to elicit the same response as the paired unconditioned response
Operant Conditioning
Learning that is controlled by the consequences of the organism's behaviour
Classical vs Operant Conditioning
Classical - Automatic, stim that precede behaviour, Autonomic NS
Operant - Voluntary, consequences that follow behaviour, skeletal muscles
Reinforcement
Any outcome that strengthens the probability of a response
Positive Reinforcement
Consequences consist of presenting something pleasant
Negative Reinforcement
Consequences consist of removing something unpleasant
Discriminative Stimulus
Any stimulus that signals the availability of reinforcement
Continuous Reinforcement
Every "correct" response is reinforced
Partial Reinforcement
Only some "correct" responses are reinforced
"Fixed" Partial Reinforcement
Reinforcement occurs after a fixed number of responses or fixed time interval
"Variable" Partial Reinforcement
Reinforcement occurs after an average number of responses of passage of time
"Ratio" Partial Reinforcement
Certain percentage of responses are reinforced
"Interval" Partial Reinforcement
Certain amount of time must elapse between reinforcements
"Fixed Ratio Schedule" Partial Reinforcement
Reinforcement given after a "FIXED" number of responses
"Variable Ratio Schedule" Partial Reinforcement
Reinforcement given after a "VARIABLE" number of responses, centered around an average
"Fixed Interval Schedule" Partial Reinforcement
First correct response after a fixed time interval is reinforced
"Variable Interval Schedule" Partial Schedule
Reinforcement given for first correct response after a variable time interval, centered around an average
H.M. Case Study
- Bilateral temporal lobectomy (Remove hippocampus, amygdala, and other stuff).
- Working memory does NO require medial temporal structures
- Declarative memory and Procedural memory are different systems
Ghrelin
INCREASE appetite
Leptin
DECREASES appetite
Hunger as a Motivator
Expectation that eating will be pleasurable and will reduce hunger
Hypothalamus (Motivation)
Plays a roll in regulating hunger, thirst, sexual arousal, and body temperature
Random Sampling
- Similarity of pop doesn't matter
- Multiple experiments can be conducted on different samples, if results are similar, more generalizability
- Similarity of sample and pop is sometimes reasonable
Hearing
- Sound as a Stimulus
- Sound waves are vibrations of molecules that travel through a medium (eg. air)
Frequency (Hearing)
Measured in cycles per second or hertz
Wavelength (Hearing)
Measured in distance (e.g., mm, cm, m)
Amplitude (Hearing)
Measured in decibels
Purity (Hearing)
Sound envelope
Place Theory (Hearing)
Perception of pitch corresponds to the vibration of different PORTIONS along basilar membrane
Frequency Theory (Hearing)
Perception of pitch corresponds to the rate at which the ENTIRE basilar membrane vibrates
Vision
- Light as a Stimulus
- A form of electromagnetic radiation that travels as a wave
Amplitude (Light)
Affects perception of brightness
Wavelength (Light)
Affects perception of colour
Action Potential
Cell is stimulated and electrical charges flow across cell membrane
Sympathetic Nervous System
Fight or Flight response
Autonomic Nervous System
Rest and Digest system
Stages of Sleep
1. Light Sleep (1-10 mins)
2. Deeper Sleep (10-25 mins)
3 & 4. Deeper Sleep after (10-30 mins)
5. Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep
Stage 1 Sleep
Light Sleep - alpha/beta waves transition to theta waves
Stage 2 Sleep
Deeper Sleep - brain waves decelerate, heat rate slows, body temp. decreases, muscles relax, eye movement ceased
Stage 3 & 4 Sleep
Deeper Sleep - Appearance of delta waves
Stage 5 Sleep
Rapid Eye Movement (REM) - 20-25% of night's sleep. Cycles last 20-60min.
Structuralism
- breaks down mind into individual parts
- breaks consciousness into STRUCTURAL components
- Introspection - "look within"
Functionalism
- study the FUNCTION of consciousness
- gave way to other psychological ideologies
Humanism
- Self-Actualization
- Abraham Maslow
Depressant (Drug)
Depress the effects of the central nervous system. Sedative - calming. Hypnotic - sleep inducing.
Stimulant (Drug)
"Rev" (excite) central nervous system
Opiate/Narcotics (Drug)
Relieve pain and induce sleep
Insomnia
Chronic difficulty in falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restful sleep
Narcolepsy
Experience episodes of sudden sleep
Sleep Apnea
Blockage of airway interrupts sleep
Night Terrors
Sudden waking episodes characterized by screaming, perspiring, and confusion, followed by a return to deep sleep
Sleepwalking
Episodes where a person walks while asleep
Sensory Memory
Briefly holds sensory information
Sensory Registers
Subsystems of sensory memory; initial information processors
Types of Sensory Registers
- Iconic Store - Holds VISUAL information
- Echoic Store - Holds AUDITORY information
Short-Term Memory
Temporarily stores and processes a limited amount if information in consciousness
Information Storage in Short-Term Memory
Visually (Images), Phonologically (Sound), Semantically (Meaning), Action (Motor Patterns)
Chunking (Memory)
Group units into larger "bits"
Maintenance vs Elaborative Rehearsal
Maintenance - Repetition
Elaborative - Meaning
Working Memory
Limited-capacity system for storage and manipulation of information for complex tasks
Long-Term Memory
Durable storage of past events and learned knowledge
Declarative Memory
- CAN be verbalized
- Episodic (personal experiences) and Semantic (general factual knowledge)
Procedural Memory
- CANNOT be verbalized
- Skills and actions
Anterograde Amnesia
Loss of ability to retain NEW knowledge
Retrograde Amnesia
Loss of ability to remember PAST knowledge
Serial Position Effect (Memory)
Describes relationship between a word's position in a list and its probability of recall
Primacy Effect (Memory)
Remember things at the BEGINNING of the list
Recency Effect (Memory)
Remember things at encountered MOST RECENTLY (end of list)
Effortful Processing (Memory)
Intentional, effortful conscious process
Automatic Processing
Unintentional process requiring minimal attention
Levels of Processing (Memory)
Structural, Phonemic, Semantic
Mnemonic Devices (Memory)
Mental strategies that aid in remembering information
Simple Mnemonic Devices
Hierarchies - Organize items based on how related they are
Chunking - Combine items into larger units of meaning
Visual-Based Mnemonics
Weird pictures. Interacting images
Semantic Mnemonics
First-Letter Technique - ROY G BIV
Narrative Technique - Tell a story
Complex Mnemonics
Method of Loci - Link what you need to remember with a place that you know well (real or not)
Associative Networks (Memory)
Theory that memory can be represented as a network of associated concepts. Each concept represented by a node and connected with lines representing association
Priming (Memory)
The activation of a concept by another. Exposure to one stimulus influences a response to a subsequent stimulus without guidance or intention
Neutral Networks (Memory)
Unlinked nodes. Pattern/Set of nodes activated together
Retrieval (Memory)
Process of transferring information from LTM back into working memory (consciousness)
Distinctiveness (Memory)
Things that stand out are more easily recalled
Flashbulb Memories
Memory for the circumstances in which you first learned about a very surprising and emotionally arousing event (e.g., 9/11)
Cued Recall (Memory)
Cues: Stimuli that lead to activation of information stored in LTM.
Multiple cues = better retrieval
Matching Conditions (Memory)
Retrieval may be increased by matching conditions of retrieval to conditions that existed at encoding
Encoding Specificity (Memory)
Learn information together with its context (e.g., learn how to drive in a car, not reading "how to drive" on paper while sitting in a stationary chair)