Database Management System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:44 PM on 9/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
1
New cards
Data
It is a collection of a **distinct small unit of information**. It can be used in a variety of forms like text, numbers, media, bytes, etc. It can be stored in pieces of paper or electronic memory, etc.
2
New cards
Database
It is a **collection of related data** organized in a way that data can be easily accessed, managed and updated. It can be software-based or hardware-based.
3
New cards
Database Management System
It is a software that allows **creation, definition and manipulation of database**, allowing users to store, process and analyze data easily.
\
It provides protection and security to the databases. It also maintains data consistency in case of multiple users.
\
It provides protection and security to the databases. It also maintains data consistency in case of multiple users.
4
New cards
MySQL
Oracle
Microsoft SQL Server
IBM DB2
PostgreSQL
Oracle
Microsoft SQL Server
IBM DB2
PostgreSQL
Examples of popular DBMS used these days
5
New cards
Data stored into Tables
Reduced Redundancy
Data Consistency
Support Multiple user and Concurrent Access
Query Language
Security
DBMS supports transactions,
Reduced Redundancy
Data Consistency
Support Multiple user and Concurrent Access
Query Language
Security
DBMS supports transactions,
7 Characteristics of DBMS
6
New cards
normalization
DBMS follows *_______* which divides the data in such a way that repetition is minimum.
7
New cards
Live data
data that is being continuously updated and added,
8
New cards
Controls database redundancy
Data sharing
Easily Maintenance
Reduce time
Backup
Multiple user interface
Data sharing
Easily Maintenance
Reduce time
Backup
Multiple user interface
6 Advantages of DBMS
9
New cards
Cost of Hardware and Software
Size
Complexity
Higher impact of failure
Size
Complexity
Higher impact of failure
4 Disadvantages of DBMS
10
New cards
File-Based database
In 1968, _________ were introduced. Data was maintained in a flat file.
11
New cards
1968
In what year was the file-based database introduced?
12
New cards
1968-1980
Year range for the era of the Hierarchical Database.
13
New cards
Information Management System (IMS)
IBM's first DBMS that was a prominent hierarchical database model.
14
New cards
Charles Bachman
Who developed the first DBMS at Honeywell?
15
New cards
early 1960s
When did Bachman developed the first DBMS at Honeywell?
16
New cards
Integrated Data Store (IDS)
Charles Bachman developed the first DBMS at Honeywell called _______.
17
New cards
1971
When did the Integrated Data Store (IDS) get standardized by the CODASYL group.
18
New cards
Conference on Data Systems Languages
Meaning of CODASYL
19
New cards
1970 - Present
It is the era of Relational Database and Database Management.
20
New cards
Database Administrators
Application Programmer or Software Developer
End User
Application Programmer or Software Developer
End User
Database Users
21
New cards
Database Administrators
They are the one who manages the complete database management system. They take care of the security of the DBMS, it's availability, managing the license keys, managing user accounts and access etc.
22
New cards
Application Programmer or Software Developer
This user group is involved in developing and designing the parts of DBMS.
23
New cards
End User
They are the one who store, retrieve, update and delete data.
24
New cards
Hierarchical Model
Network Model
Entity-relationship Model
Relational Model
Object-oriented Model
NoSQL Model
Graph Model
Network Model
Entity-relationship Model
Relational Model
Object-oriented Model
NoSQL Model
Graph Model
7 Type of Database models
25
New cards
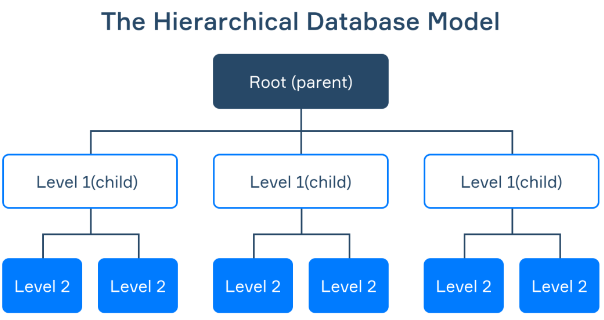
Hierarchical Model
This database model organizes data into a **tree-like structure**, with a **single root**, to which all the other data is linked.
\
The hierarchy starts from the **Root** data, and expands like a tree, adding **child** nodes to the **parent** nodes.
\
The hierarchy starts from the **Root** data, and expands like a tree, adding **child** nodes to the **parent** nodes.
26
New cards
It has one-to-many relationships; it is easier and faster to fetch the data.
Advantages of the Hierarchical Model
27
New cards
It is less flexible, it doesn't support many-to-many relationships.
Disadvantages of the Hierarchical Model
28
New cards
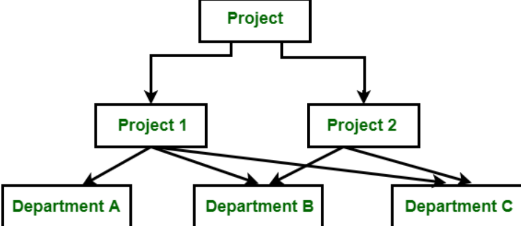
Network Model
This database model is an extension of the Hierarchical model. Data is organized more like a **graph**, and allowed to have more than one parent node.
\
Data is **more related** as more relationships are established in this database model.
\
This was the most widely used database model before Relational Model was introduced.
\
Data is **more related** as more relationships are established in this database model.
\
This was the most widely used database model before Relational Model was introduced.
29
New cards
As the data is more related, accessing the data is also easier and fast.
It supports complex relationships
It allows more flexibility
It supports complex relationships
It allows more flexibility
Advantages of the Network Model
30
New cards
Network
Integrated Data Store (IDS) is based on _______ model.
31
New cards
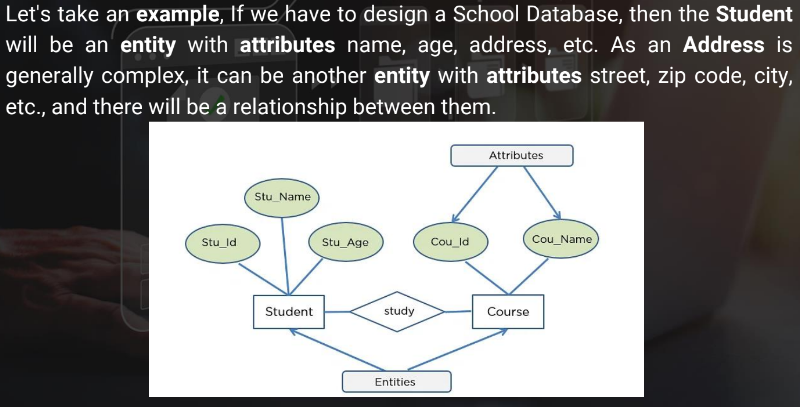
Entity-relationship Model
In this database model, relationships are created by dividing objects of interest into **entities** and their characteristics into attributes.
\
It represents the relationships **in pictorial form** to make it easier for different stakeholders to understand. It is good to design a database, which can then be turned into tables in a relational model
\
It represents the relationships **in pictorial form** to make it easier for different stakeholders to understand. It is good to design a database, which can then be turned into tables in a relational model
32
New cards
It is easy to understand and design
We can represent data structures easily.
We can represent data structures easily.
Advantages of the ER Database Model
33
New cards
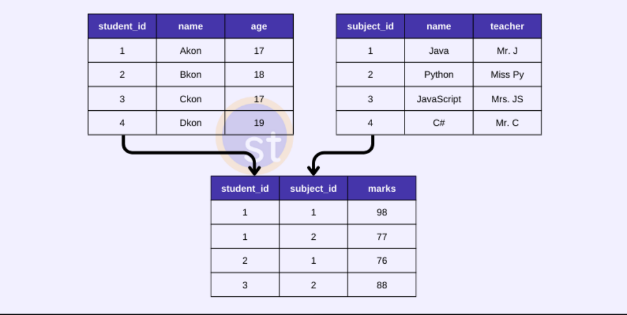
Relational Model
In this model, data is organized in **two-dimensional tables** and the **relationship** is maintained by **storing a common field.**
34
New cards
E.F Codd
Who introduced the relational database model?
35
New cards
tables; rows
The basic structure of data in the relational model is ______. All the information related to a particular type is stored in ______ of that table.
36
New cards
relations
Tables are also known as _________ in the relational model.
37
New cards
MySQL, Oracle
Example of Relational Model
38
New cards
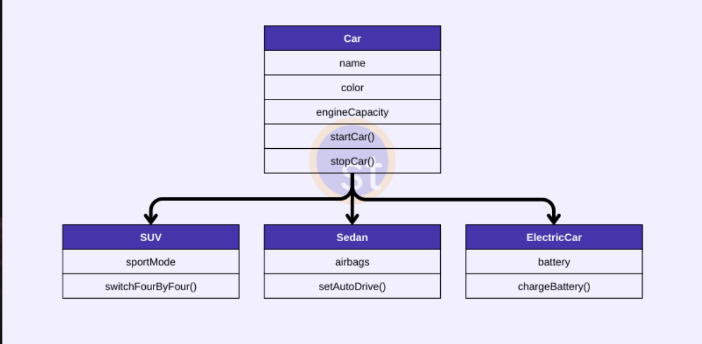
Object-oriented Model
In this database model, data is stored in the form of **objects**. This database model is not mature enough as compared to the relational database model.
39
New cards
MongoDB
A very popular example of an Object Database management system or ODBMS is _______ which is also a NoSQL database.
40
New cards
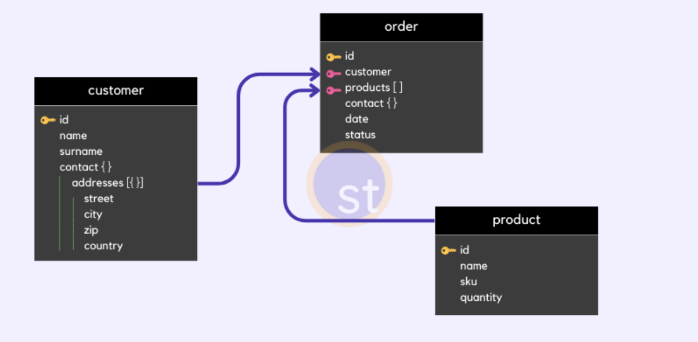
NoSQL Model
This database model supports an **unstructured** **style** of storing data. Data is stored as **documents**. The documents look more like **JSON strings** or Key-value based object representations.
\
This database model is well-suited for Big data applications, real-time analytics, CMS (Content Management systems), etc.
\
This database model is well-suited for Big data applications, real-time analytics, CMS (Content Management systems), etc.
41
New cards
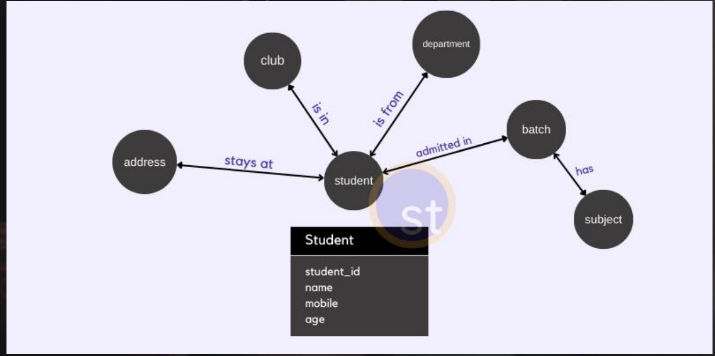
Graph Model
This database model is based on more **real-world like relationships.** Data is represented using **Nodes** or entities. The nodes are related using **edges**.
\
In modern applications like social networks, recommendation systems, etc. this model is well-suited.
\
In modern applications like social networks, recommendation systems, etc. this model is well-suited.
42
New cards
Neo4j
Example Database of Graph Model
43
New cards
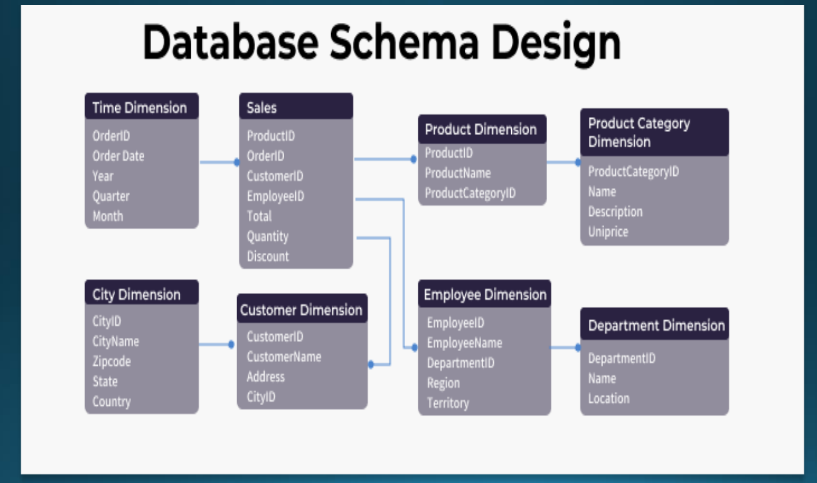
Database Schema
The **overall design** of a database is called _____. It is the **skeleton structure** of the database and it represents the **logical view** of the entire database. It is represented by using the visual diagram which shows the database objects and their relationships with each other.
44
New cards
Data Modeling
The process of database creation is ________.
45
New cards
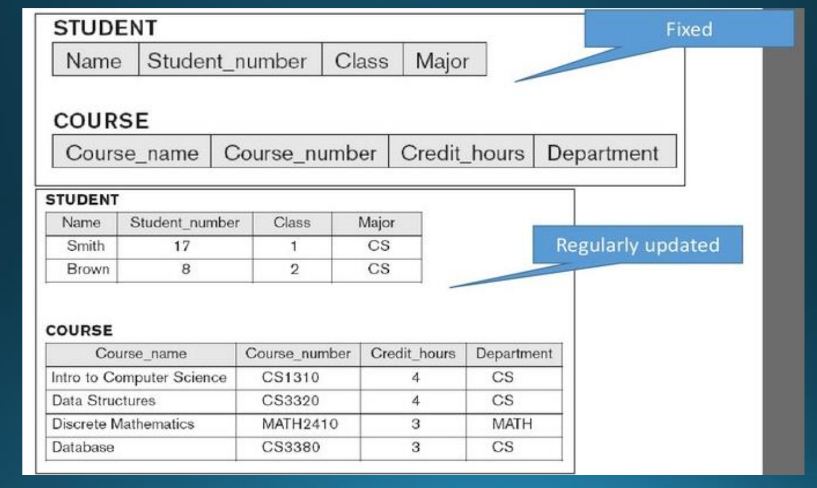
Database State or Instance
The data in the database at a particular moment of time is called ____. It changes every time the database is updated.
46
New cards
ANSCI/SPARC Architecture (American National Standards Institute, Standards Plainning and Requirements Committee)
The Three Schema Architecture is also called ________.
47
New cards
Three Schema Architecture
It is used to describe the structure of a specific database system. It is used to **separate the user applications and physical database** to **three-levels** and **breaks database down into three categories.**
48
New cards
It enables multiple users to access the same data with a personalized view, separating the user’s view from the physical structure of the database.
Objectives of Three Schema Architecture
49
New cards
Internal Level
Conceptual Level
External Level
Conceptual Level
External Level
Levels of Three Schema Architecture
50
New cards
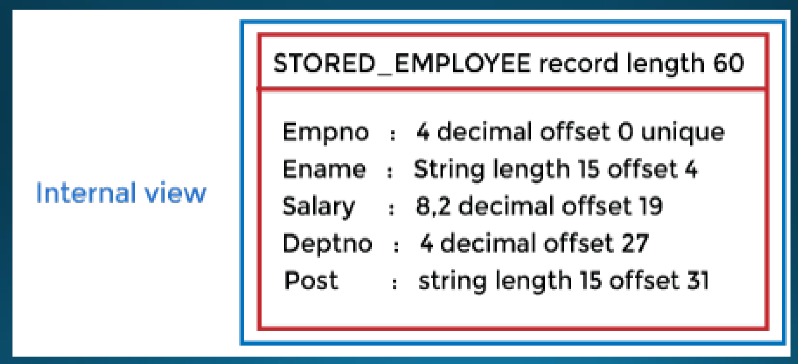
Internal Level
It has an internal schema which describes the **physical storage structure of the database.**
\
It uses the **physical data model**. It is used to define how the data will be stored in a block. It is used to describe complex low-level data structures in detail.
\
It uses the **physical data model**. It is used to define how the data will be stored in a block. It is used to describe complex low-level data structures in detail.
51
New cards
Physical Schema
The internal schema is also known as a ______.
52
New cards
Storage Space Allocations (e.g., B-Trees, Hashing, etc.)
Access Paths (Primary and Secondary Key, Index, Pointer, etc)
Data compression and encryption techniques
Optimization of internal structures
Representation of stored fields
Access Paths (Primary and Secondary Key, Index, Pointer, etc)
Data compression and encryption techniques
Optimization of internal structures
Representation of stored fields
The internal level is concerned with the following:
53
New cards
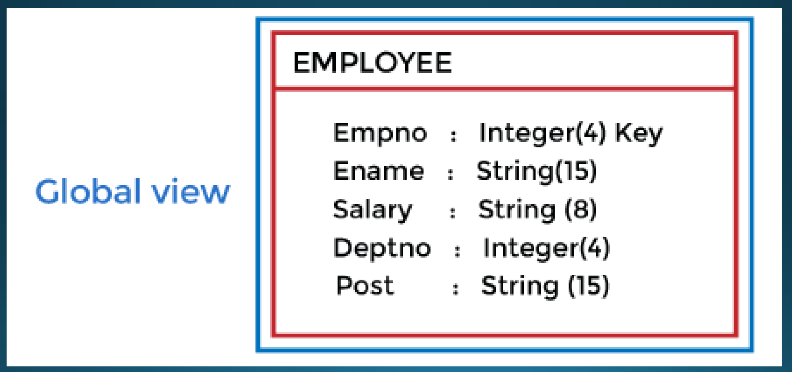
Conceptual Level
It describes the **structure of the whole database.** It describes what data are to be stored in the database and their relationship with each other.
\
Internal details such as implementation of the data structure are hidden.
\
Internal details such as implementation of the data structure are hidden.
54
New cards
Logical Level
Conceptual level is also known as _________.
55
New cards
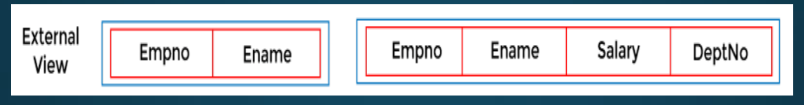
\
\
External Level
\
External Level
It is also known as ***view schema***. It describes the database part that a particular user group is interested and hides the remaining database from that user group.
\
It describes the end user interaction with the database systems.
\
It describes the end user interaction with the database systems.
56
New cards
Subschema
The database contains several schemas that sometimes called as ______. It is used to describe the different view of the database.
57
New cards
Mapping
DBMS is responsible for the correspondence between the three types of schema. The correspondence is called ________.
58
New cards
Conceptual/Internal Mapping
External/Conceptual Mapping
External/Conceptual Mapping
Two Types of Mapping in the Database Architecture
59
New cards
Data Definition Language (DDL)
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Data Control Language (DCL)
Transaction Control Language (TCL)
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Data Control Language (DCL)
Transaction Control Language (TCL)
Five DBMS Languages
60
New cards
Database Definition Language (DDL)
__**DBMS Language**__. It is used to **define database structure or pattern.** It is used to create schema, tables, indexes, constraints etc in the database. It can create the **skeleton of the database**. It is used to store the information of the metadata.
61
New cards
Create (create obj)
Alter (alter db structure)
Drop (delete obj)
Truncate (remove all records)
Rename (rename obj)
Comment
Alter (alter db structure)
Drop (delete obj)
Truncate (remove all records)
Rename (rename obj)
Comment
Tasks under DDL
62
New cards
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
__**DBMS Language**__. It is used for **accessing and manipulating data** in the database. It handles user requests.
63
New cards
Select (retrieve data)
Insert (insert data)
Update (update data)
Delete (delete records)
Merge (performs UPSERT)
Call (call SQL or Java subprog)
Explain Plan
Lock Table
Insert (insert data)
Update (update data)
Delete (delete records)
Merge (performs UPSERT)
Call (call SQL or Java subprog)
Explain Plan
Lock Table
Tasks under DML
64
New cards
Data Control Language (DCL)
__**DBMS Language**__. It is used to retrieved the stored or saved data. Its execution is transaction. It also has rollback parameters.
65
New cards
Grant (grant access)
Revoke (revoke access)
Revoke (revoke access)
Tasks under DCL
66
New cards
Transaction Control Language (TCL)
__**DBMS Language**__. It is used to run changes made by the DML statement. It can be grouped into a logical transaction.
67
New cards
Commit (save transaction)
Rollback (restore db to orig)
Rollback (restore db to orig)
Tasks under TCL
68
New cards
Database System
The DBMS software together with the database is called ______.
\
It can be defined as an organization of components that define and regulate the collection, storage, management and use of data in a database. Its overall purpose is to record and maintain information.
\
It can be defined as an organization of components that define and regulate the collection, storage, management and use of data in a database. Its overall purpose is to record and maintain information.
69
New cards
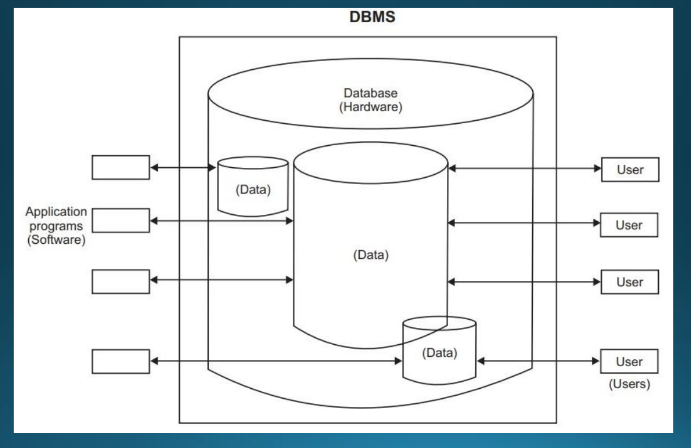
Data
User
Database (Hardware)
Application Programs (Software)
User
Database (Hardware)
Application Programs (Software)
Figure of the Database System
70
New cards
Data
__**Figure of the Database System**__. They are stored in a single database. They are both shared and integrated. Multiple users can access the same piece of data but may be for different purposes.
71
New cards
Hardware
__**Figure of the Database System.**__ It consists of the secondary storage devices like disks, where the database resides together with other devices.
72
New cards
Software
__**Figure of the Database System**__. This layer is called the ***DBMS***. It is a layer or interface that exists between the physical database and the users. It shields the database users from the hardware details.
73
New cards
Users
__**Figure of the Database System.**__ They are the people interacting with the database system in anyway.
74
New cards
Application Programmers
Online Users
End Users or Naive Users
Database Administrators (DBA)
Online Users
End Users or Naive Users
Database Administrators (DBA)
__**Figure of the Database System**__. Four types of users
75
New cards
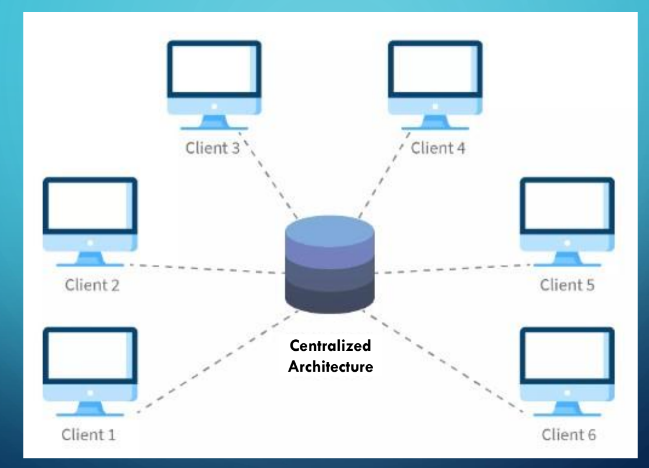
Centralized Architecture
All data is stored on a **single server**, and all clients connect to the server to access and manipulate the data.
76
New cards
Monolithic Architecture
Centralized architecture is also called as _____.
77
New cards
It’s simple, easy to manage. Clients use the same data.
Advantage/s of Centralized Architecture
78
New cards
Bottleneck (clients and/or data increase)
Server goes down, everyone lose the access
Server goes down, everyone lose the access
Disadvantage/s of Centralized Architecture
79
New cards
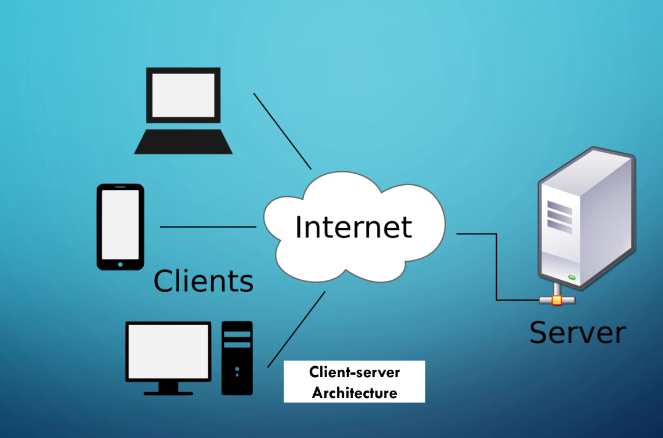
Client-server architecture
It is a network application that breaks down tasks and workloads between **clients and servers** that reside on the same system or are **linked by a computer network.** *(basta may Internet)*
\
It is more complex than a centralized architecture.
\
It is more complex than a centralized architecture.
80
New cards
It is more scalable and more fault-tolerant.
Clients and/or data increase? Then add/upgrade servers
Clients and/or data increase? Then add/upgrade servers
Advantage/s of Client-Server Architecture
81
New cards
Traffic Congestion
Cost
Maintenance
Resources
Cost
Maintenance
Resources
Disadvantage/s of Client-Server Architecture
82
New cards
Architecture of DBMS
It is the **representation of DBMS design.** It helps to design, develop, implement, and maintain the DBMS. It allows dividing the database system to individual components that can be modified, replaced, and altered.
83
New cards
One Tier Architecture
Two Tier Architecture
Three Tier Architecture
Two Tier Architecture
Three Tier Architecture
3 Types of DBMS Architecture
84
New cards
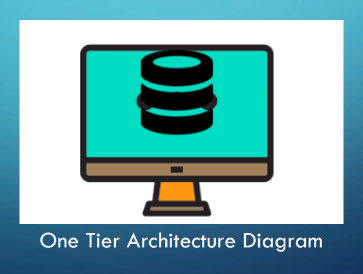
One Tier Architecture
The **simplest architecture of Database** in which the client, server, and the Database all reside on the **same machine.** It provides functionality to access Database directly.
\
It is used when **data is constant**. Its updates or modifications directly affect the Database.
\
It is used when **data is constant**. Its updates or modifications directly affect the Database.
85
New cards
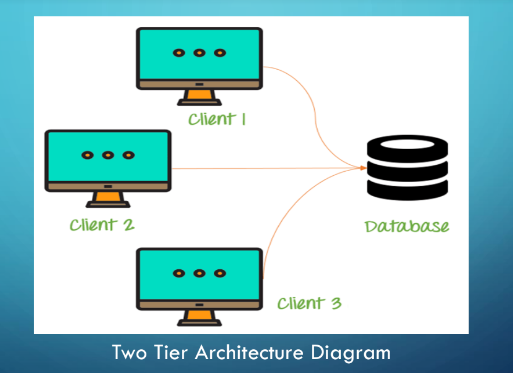
Two Tier Architecture
The **presentation layer** runs on a client (PC, Mobile, Tablet) and data is stored on a server. It provides additional security to the DBMS as it is not exposed to the end-user directly.
\
It is faster to access, and simpler to maintain. It has the capacity for several concurrent users. It is comparable to **client-server setup.** It is used when we want to use **applications and APIs** to access DBMS.
\
It is faster to access, and simpler to maintain. It has the capacity for several concurrent users. It is comparable to **client-server setup.** It is used when we want to use **applications and APIs** to access DBMS.
86
New cards
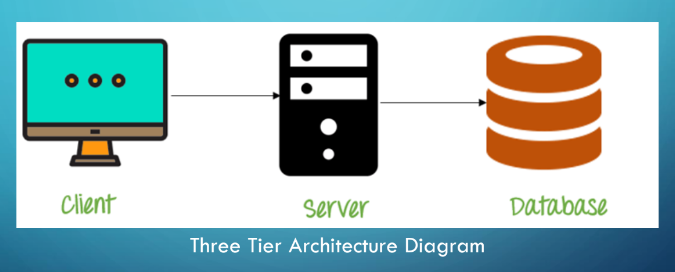
Three Tier Architecture
It is the most popular client-server architecture in DBMS.
\
The development and maintenance of functional processes, logic, data access, data storage, and user interface is done independently as separate modules.
\
It contains a **presentation layer, application layer, and database server.**
\
The development and maintenance of functional processes, logic, data access, data storage, and user interface is done independently as separate modules.
\
It contains a **presentation layer, application layer, and database server.**
87
New cards
Based on Data Model
Based on Number of Users
Based on Database Distribution
Based on Cost of Database
Based on Usage
Based on Number of Users
Based on Database Distribution
Based on Cost of Database
Based on Usage
5 Classifications of DBMS (Based on …)
88
New cards
Relational Data Model
Entity-Relationship Model
Object-Based Data Model
Semi-structured Data Model
Entity-Relationship Model
Object-Based Data Model
Semi-structured Data Model
Classifications of DBMS Based on Data Model
89
New cards
Relational Data Model
__**Data Model Classification**____.__ **Table** is used to represent data and the relationship among that data. It is the most currently used data model.
90
New cards
Entity-Relationship Model
__**Data Model Classification**____.__ It represents data using **objects** and the relationship among these objects. Each **entity** in the this model is distinguishable from other entities in the model.
91
New cards
Object-Based Data Model
__**Data Model Classification.**__ An **extension of the E-R model** which also include notion for encapsulation, methods.
\
There is also an ***object-relational data model*** which is a combination of the object-oriented data model and relational data model.
\
There is also an ***object-relational data model*** which is a combination of the object-oriented data model and relational data model.
92
New cards
Semi-structured Data Model
The data items or objects of the **same kind** might have a **different set of attributes.**
93
New cards
Extensible Markup Language
It represents the semi-structured data.
94
New cards
Single user
Multiple users
Multiple users
Classifications of DBMS Based on Number of Users
95
New cards
Centralized DBMS
Distributed DBMS (DDBMS)
Distributed DBMS (DDBMS)
Classifications of DBMS Based on Database Distribution
96
New cards
Homogeneous DDBMS (same DBMS, all sites)
Heterogeneous DDBMS (diff DBMS, diff sites)
Heterogeneous DDBMS (diff DBMS, diff sites)
Two Types/Classifications of DDBMS
97
New cards
Low Cost DBMS ($100 to $3k)
Medium Cost DBMS ($10k to $100k)
High Cost DBMS ($100k+)
Medium Cost DBMS ($10k to $100k)
High Cost DBMS ($100k+)
Classifications of DBMS Based on Cost of Database
98
New cards
Online transaction processing(OLTP) DBMS
Online analytical processing(OLAP) DBMS
Big data and analytics DBMS
Online analytical processing(OLAP) DBMS
Big data and analytics DBMS
Classifications of DBMS Based on Usage
99
New cards
Online transaction processing(OLTP) DBMS
__**Usage Classification.**__ It **manages** **the** **operational data**. It is initiated in real time, in simultaneous by lots of user and applications hence it must have ***high volume of short, simple queries.***
100
New cards
Online analytical processing(OLAP) DBMS
__**Usage Classification.**__ It uses the operational data for **tactical and strategical decision making**.
\
Limited users deal with ***huge amount of data, complex queries.***
\
Limited users deal with ***huge amount of data, complex queries.***