Biochemistry Chapters 1-3
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Atmosphere
gases and UV light = simple organic compounds
Thermal vents
heart and small organic compounds = small organic compound
Compartimentation
protection from environment
high lock concentrations of vital
what makes a cell a cell
barrier
inside chemically different from outside
Noncovalent bonds
weaker than covalent
this is wanted bc its easier to break and reform
electrostatic
polar molecules
have dipole moments
charge-induced dipole interactions
induced by charged molecules
dipole induced dipole interactions
induced by polar moles with permanent dipole moment
membranes
amphipathic
powered by hydrophobic effect
buffering range
pKa plus or minus 1
1st law of thermodynamics
energy is neither created or destroyed
work is done to a system when
heat is added
work
force applied over distance
a change in pressure or volume
Reversible process
near equilibrium
processes at equilbrium
lowest energy state of system
forward and reverse are equal
Irreversible process
set up far from equilibrium state and moves towards it
example - burning paper
2nd law of thermodynamics
entropy(S) is always increasing
increasing randomness and disorder
3rd law of thermodynamics
entropy of a pure, perfect crystalline substance is zero at absolute zero
PEP vs ATP
pep had a high phosphoryl group transfer than ATP
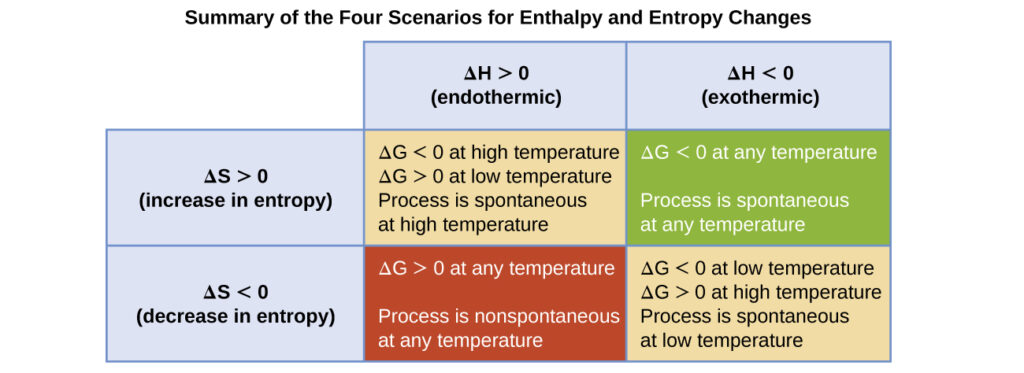
summary of the four scenarios for enthalpy and entropy changes