Gibbs and Enzymes
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Gibbs Free Energy G
The amount of energy capable of doing work during a reaction at constant temperature and pressure
Free energy ΔG
The amount of free energy released negative ΔG or absorbed positive ΔG during a reaction at constant temperature and pressure
Standard free energy change (ΔG°)
298 K reactants 1 M, products 1 M,
Biochemical standard free energy (ΔG°’)
298 K reactants 1 M, products 1 M, pH 7 H2O 55.5 M
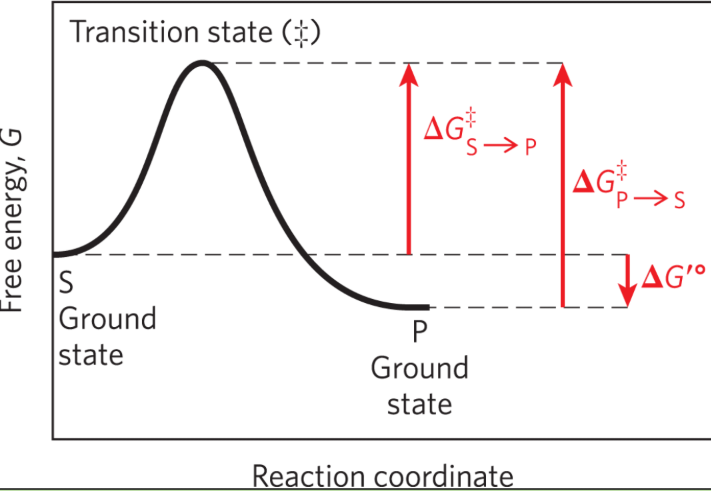
Ground state
The free energy of an average molecule of S or P
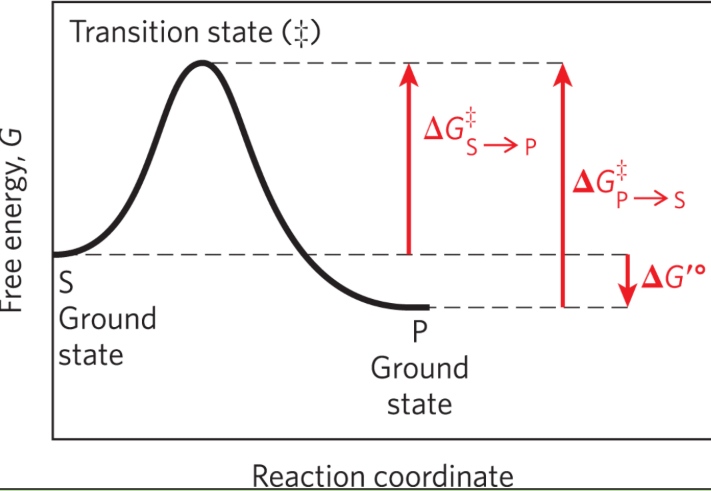
Transition state
The point of highest free energy
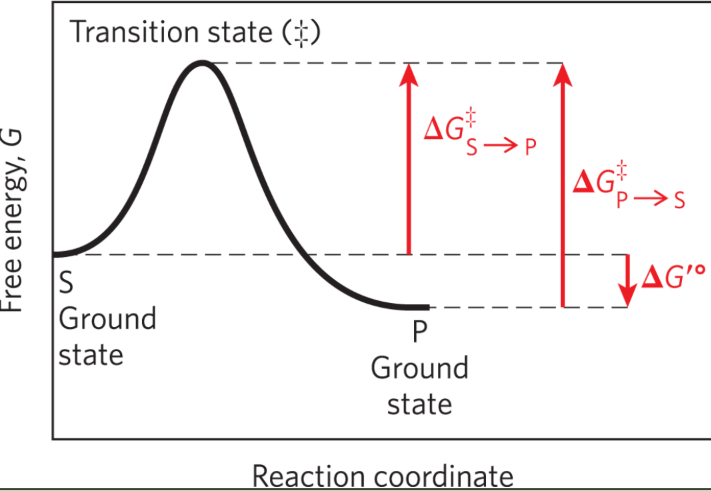
Activation energy ΔG‡
The difference in free energy between the ground state and transition state
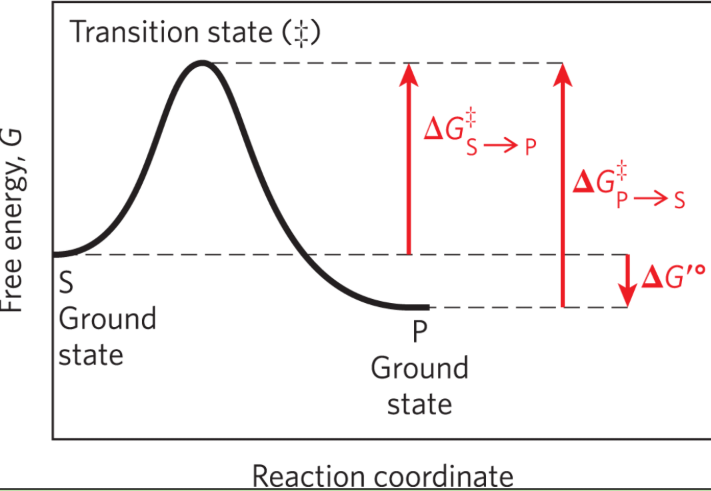
Reaction rate
The rate of the reaction is defined by the energy barrier that must be overcome to convert S to P
Reaction equilibrium ΔG°’ less than zero
Free energy of the product is less than free energy of the substrate. Under standard conditions the reaction is spontaneous. At equilibrium the concentration of product is greater than substrate
Relationship between ΔG°’ and Keq
ΔG°’ = RT ln (K*eq) (with T in Kelvin and R = gas constant)
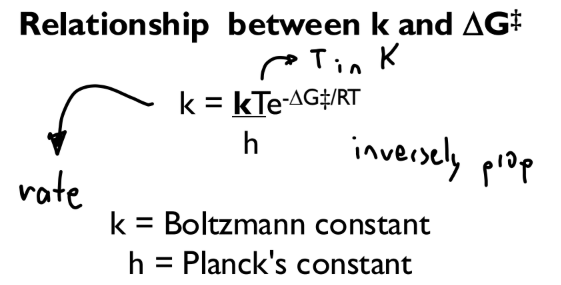
Relationship between k and ΔG‡
Effect of enzymes on reaction rate
Enzymes increase rate by decreasing ΔG‡
Enzyme reaction scheme
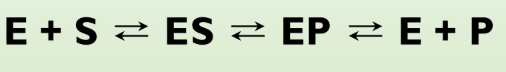
Definitions in enzyme reaction scheme
E equals enzyme. S equals substrate. P equals product. ES and EP equal intermediates of E plus S and E plus P
Effect of enzymes on activation energy
ΔG‡ required to form ES and EP is much lower than the uncatalyzed reaction
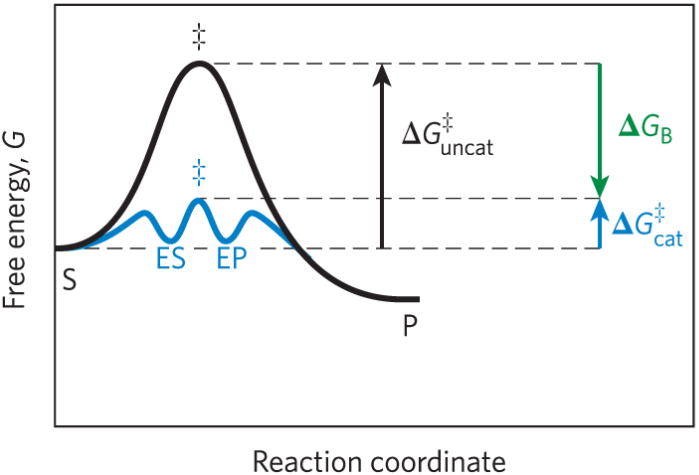
How enzymes reduce ΔG‡
Enzymes reduce Delta G double dagger by stabilizing the transition state
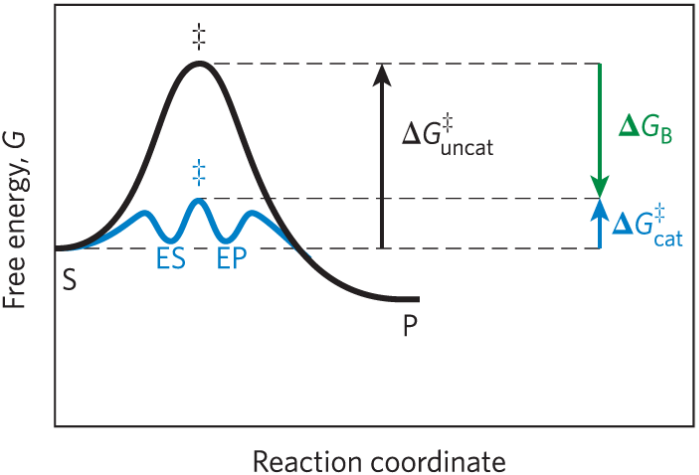

Binding energy (ΔGB)
Derived from the enzyme substrate interaction
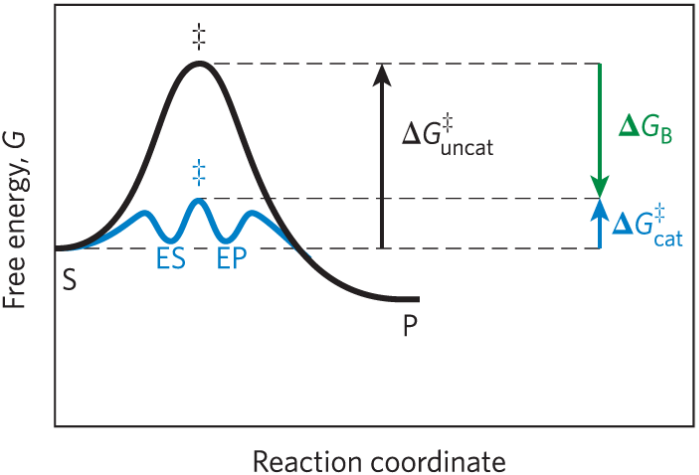
Role of binding energy
Multiple weak interactions between the active site and substrate stabilize the transition state and reduce ΔG‡
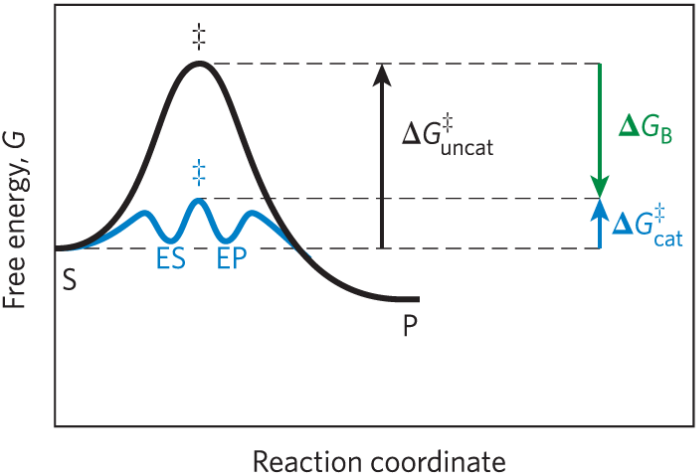
Enzyme catalytic mechanisms
Acid base catalysis. Covalent catalysis. Metal ion catalysis
Acid base catalysis
Transferring a proton to the substrate stabilizes charged intermediates formed during reactions
Covalent catalysis
A transient covalent bond forms between enzyme and substrate creating a new reaction path with lower free energy
Metal ion catalysis
Ionic interactions with a metal ion contribute binding energy or mediate oxidation reduction reactions