Group 2
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What ion do they form and how?
Lose 2 electrons to form 2+ ions to achieve a full outer shell.
Atomic radius down the group
Increases due to increasing electron shells
Reactivity down the group
Increases due to increased shielding
1st IE down the group
Decreases due to increased size/ shielding
What is shielding?
More shells between the outer electrons and the nucleus decreases nuclear attraction making outer electrons easier to remove
Ionisation energy down the group
Decreases due to greater atomic radius and more shielding
Melting point down the group
Decreases as the metal ions get larger down the group so the attractive forces have to act over a greater distance
General reaction with water
Redox reaction to produce a metal hydroxide and hydrogen. The metal hydroxide forms as an alkaline solution
Describe the reaction of magnesium in water
Reacts very slowly
What does magnesium + water produce
Magnesium hydroxide
Describe the reaction with magnesium in steam
Provides more energy than water so it burns with a bright white flame
What does magnesium + steam produce?
Hydrogen and magnesium oxide
What colour is magnesium oxide?
White powder
How do the group 2 elements (except magnesium) react with water including observations and precipitates fomed
Can react with cold water increasingly vigorously down the group
Observations include: fizzing, metal dissolving, solution heating up
Calcium produces a white ppt, less and less forms as you go down the group
What is calcium hydroxide used for and why?
Used in agriculture to neutralise acidic soils
What can aqueous calcium hydroxide be used for?
Limewater - tests for carbon dioxide as it turns cloudy because calcium carbonate is produced
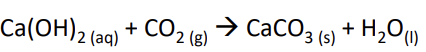
Solubility of group 2 hydroxides down the group
Increases
What is magnesium hydroxide used as and why?
An antacid because it is alkaline and can neutralise acids. It is also the least soluble group 2 hydroxide.
Solubility of group 2 sulfates down the group
Decreases
What is barium sulfate used for and why?
Barium meals/ X-ray. It is toxic if it enters the bloodstream however this does not happen because it is insoluble.
Barium sulfate colour
White precipitate
What is barium chloride used for?
To test for sulfate ions as it reacts to form barium sulfate (white ppt)
What is magnesium used for and why?
The extraction of titanium from titanium chloride via a displacement reaction
Equation between titanium chloride and magnesium

What is calcium oxide used for and why?
Reacts with sulfur dioxide to remove it from factory pollutants and prevent it being released into the atmosphere
Calcium oxide + sulfur dioxide equation
