PDA Receptor theory I
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
pharmacology
study of body’s reaction to drugs
Alters the existing system
What does a drug do?
5 drug action targets
receptors, ion channels, enzyme, carrier molecules, microtubules,
morphine
cell surface receptor on neuro cells that block transmission of pain signa
GABAa receptor
Cl channel that when stimulated, causes chloride influx and results in hyperpolarization to suppress neuronal activity
Aspirin
targets cyclooxygenase, an enzyme through reducing pro-inflammatory factors.
GABA
the major inhibitory neurotransmitter is …
Cocaine
increase dopamine levels through blocking the carrier molecule uptake, to prevent dopamine from entering the presynaptic nerve terminal.
Taxol
targets microtubule to block mitotic spindles, leading to mitotic arrest and cell death.
receptor
a protein molecule that receives and respond to a neurotransmitter, hormone, drug, or other substances
cell surface receptors
large molecule (peptides), charged, hydrophilic
nuclear receptors
small, non-polar, lipophilic (readily diffuse through the plasma membrane)
agonist
A molecule that binds to a receptor and elicits a biological response
Antagonists
block binding of endogenous ligands to their receptors, resulting in reduced biological responses of their target cells. This property is useful in treating diseases/medical conditions.
Agonists
albuterol, terbutaline, isoproterenol, dobutamine are examples of?
Antagonists
propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol, nadolol are examples of what?
Antagonists
prazosin, phenoxybenzamine, yohimbine are examples of what?
Inverse agonists
an agent that binds to the same receptor-site as an agonist but exerts the opposite pharmacological effect; cause conversion, agitation, irritation
insomnia, agitation, inability to sleep
A drug induces sleep. What would be the effect of an inverse agonist of the receptor?
Affinity
a measure of how tightly a drug binds to its receptor
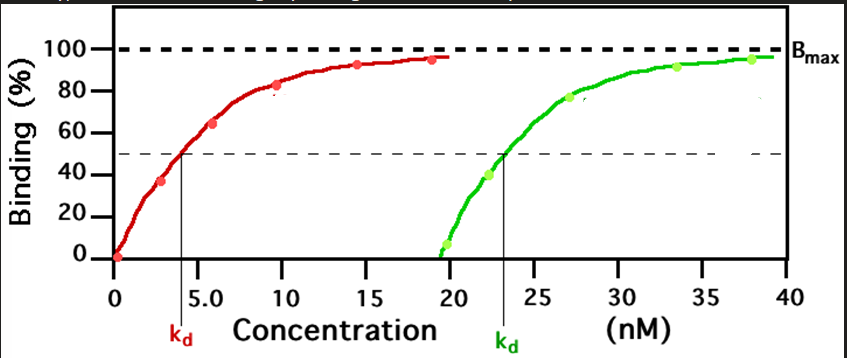
lower affinity ligand
The GRN line graph represents what?
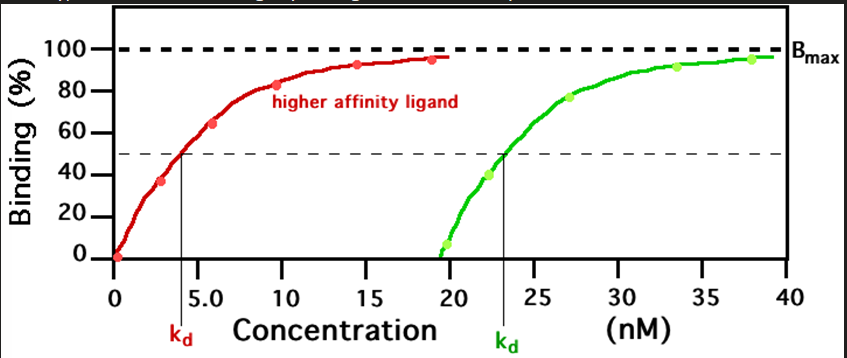
higher affinity ligand
The red line graph represents what?
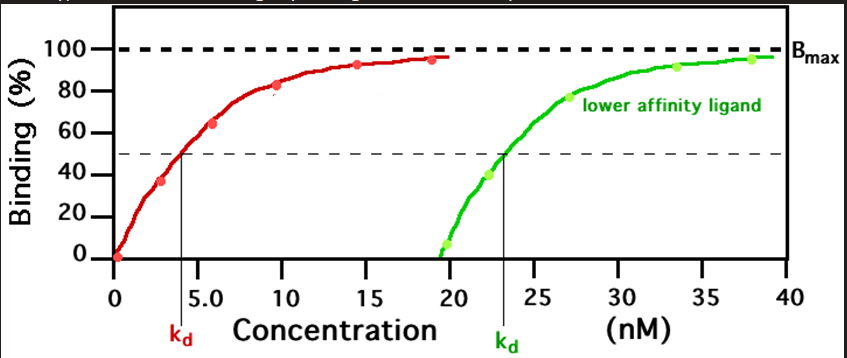
Smaller kd equals higher affinity
What does the graph imply
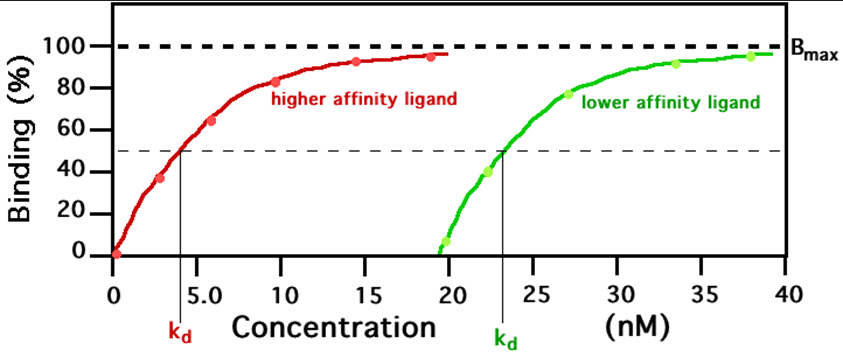
Kd
the concentration of ligand at which half of the receptor binding sites are occupied
efficacy
intrinsic activity or the ability to produce a therapeutic effect; how well it activities receptor
Full agonists
produce a maximal response (ex. morphine)
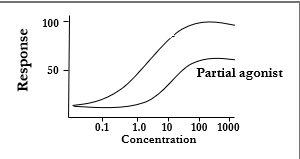
Partial agonists
produce submaximal response (ex. buprenorphine)
partial agonists
The bottom graph line describes what?
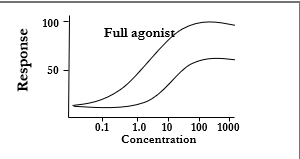
Full agonists
The top graph line represents what?
potency
measure the drug activity
The smaller the EC50, the better the potency
What does the arrow imply?
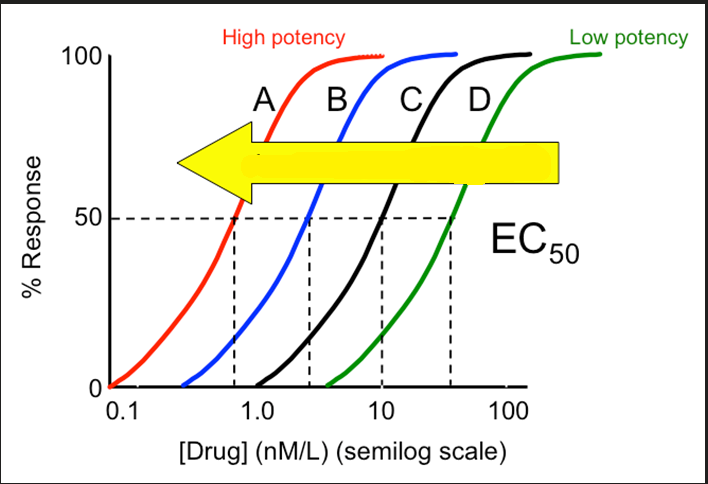
EC50
represents the concentration of a compound
where 50% of its effect is observed
IC50
represents the concentration of an inhibitor
that is required for 50% inhibition
spare receptors
a maximal response is elicited without all receptors being
occupied
ED50 < kd
There are spare receptors when …
competitive reversible antagonism
The following graph implies what?
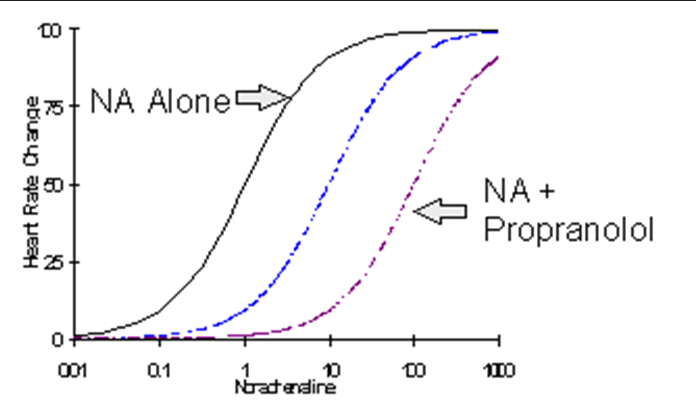
More concentration for NA
Increasing propranolol mean what for the maximal heart rate?
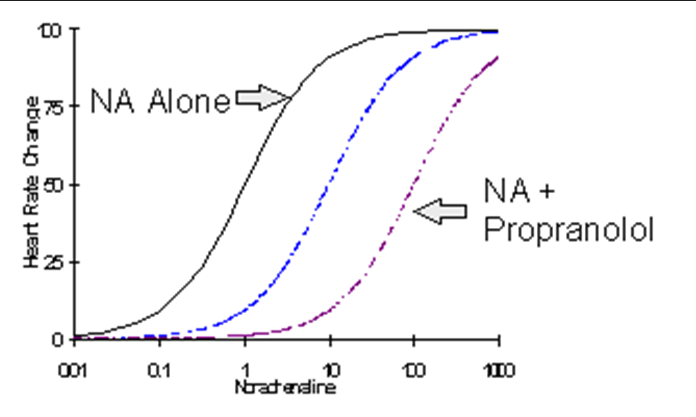
competitive irreversible antagonism
The following graph represents what?
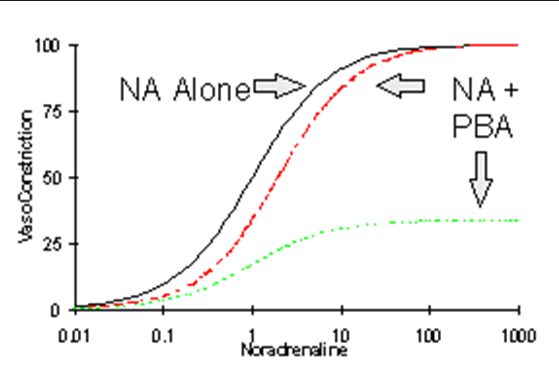
The GRN line cannot reverse due to blood vessel constriction
Increasing PBA implies what?
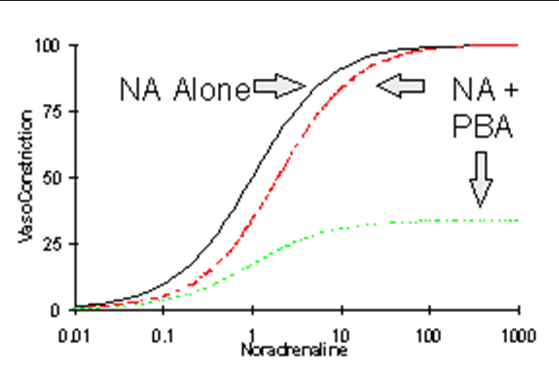
non-competitive/functional antagonism
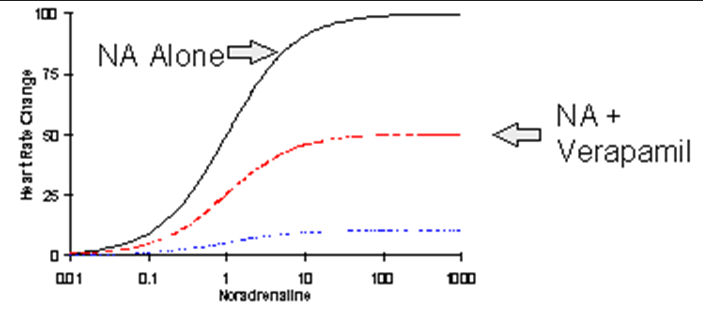
The following graph represents what?
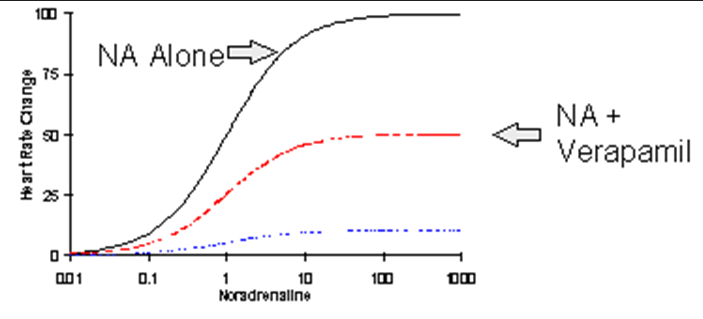
lowers the maximal response
Increasing verapamil means what
physiological antagonism
body function regulation
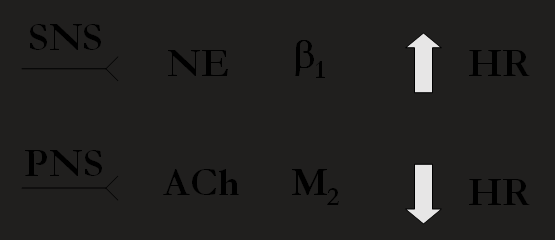
chemical antagonism
drug-drug interactions followed by suppression
chemical antagonism
heparin prevent clog formation (anticoagulant)
chemical antagonism
In the case of digoxin overdosage, an antidote digoxin immune Fab (Digibind) is used. Digibind binds and inactivates digoxin. What type of antagonism is this?
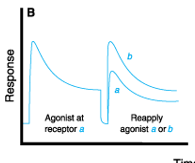
Desensitization
body’s protective mechanism against high concentration and prolonged exposure to hormones, neurotransmitter, and drugs
Desensitization
The loss of responsiveness to the continuing or
increasing dose of a drug
Homologous desensitization
The following graph represents what?