Excretion + Circulation
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/113
Last updated 9:44 PM on 4/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
1
New cards
Two main needs of organisms -- excretory system and
1. Osmoregulation -- maintain H2O balance
2. Removal of toxic substances -- dilute these with H2O
2
New cards
Catabolic reactions
Breaks down; hydrolytic reaction
3
New cards
Anabolic reaction
To build, so synthesize; dehydration synthesis
4
New cards
Egestion
Undigested waste, feces
5
New cards
Excretion
Removal of metabolic waste, cell waste
6
New cards
Metabolic wastes
Waste created through metabolism of cells
7
New cards
Main metabolic waste
* CO2: cell respiration -- catabolic, breaking down of glucose
* H2O: cell respiration or any dehydration synthesis reaction
* Salt: neutralization reactions, acid + base
* Nitrogenous wastes: protein metabolis
* H2O: cell respiration or any dehydration synthesis reaction
* Salt: neutralization reactions, acid + base
* Nitrogenous wastes: protein metabolis
8
New cards
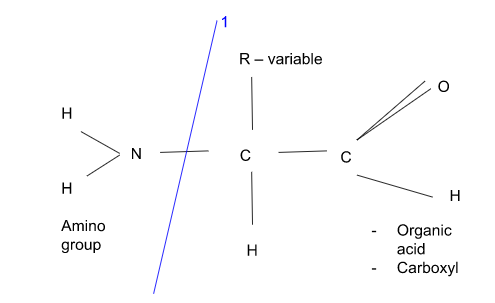
Protein metabolism
Break down protein/amino acids and produces nitrogenous wastes
9
New cards
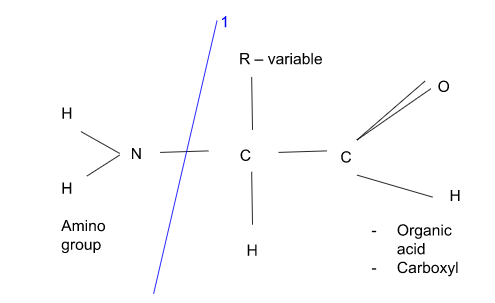
Deamination (liver)
Breaks apart amino acids → ammonia
10
New cards
NH3: ammonia
* Very toxic
* Must be diluted
* To dilute -- 1NH3: 1,000,000 H20
* then need to excrete out of the organism
* Marine organisms
* Must be diluted
* To dilute -- 1NH3: 1,000,000 H20
* then need to excrete out of the organism
* Marine organisms
11
New cards
Urea
* Land organisms
* Ammonia → (convert) → urea
* Uses a lot of ATP
* to dilute - 1 Urea: 100,000 H2O
* Ammonia → (convert) → urea
* Uses a lot of ATP
* to dilute - 1 Urea: 100,000 H2O
12
New cards
Uric acid
* Not soluble in H2O
* No/minimal H2O lost
* Large ATP cost
* Reptile, birds, insects, desert creatures (not camels)
* Comes out as a white paste
* No/minimal H2O lost
* Large ATP cost
* Reptile, birds, insects, desert creatures (not camels)
* Comes out as a white paste
13
New cards
Four main excretory organs
* Kidney
* urine → urea, water, salt
* Liver
* salt \[bile\]
* Skin
* sweat (water/salt), urea
* Lungs
* CO2, water
* urine → urea, water, salt
* Liver
* salt \[bile\]
* Skin
* sweat (water/salt), urea
* Lungs
* CO2, water
14
New cards
What does the skin do?
\
* Protects our body
* Physical
* Pathogens (disease-causing organisms)
* Chemical protection
* Radiation (melanin absorption/ UV)
* Thermoregulation – maintains body temperature
* Waterproof
* Sensations
* Vitamin D production
* Stores energy
* Protects our body
* Physical
* Pathogens (disease-causing organisms)
* Chemical protection
* Radiation (melanin absorption/ UV)
* Thermoregulation – maintains body temperature
* Waterproof
* Sensations
* Vitamin D production
* Stores energy
15
New cards
Liver performs many functions, including the production of urea:
1. Deamination → secretion of NH3
NH3 → Urea
2. Creates bile
16
New cards
How many kidneys do you need?
You can survive with one but it is better to have two
17
New cards
Functions of the kidney
\
* Filter Blood – MAIN FUNCTION
* Once the unclean blood enters, the kidneys filter it, and out comes urine and clean blood
* Regulates blood pressure
* Through water retention (holds onto water)
* Red blood cell production (control of rbc production – don’t actually make them)
* Monitors blood cell count
* Erythropoietin (EPO) – a hormone that the kidney sends to the blood marrow to tell it to make more RBC
* High altitude results in less oxygen in the air so your body needs to make more which makes more EPO and makes more RBC
* Regulates pH
* Filter Blood – MAIN FUNCTION
* Once the unclean blood enters, the kidneys filter it, and out comes urine and clean blood
* Regulates blood pressure
* Through water retention (holds onto water)
* Red blood cell production (control of rbc production – don’t actually make them)
* Monitors blood cell count
* Erythropoietin (EPO) – a hormone that the kidney sends to the blood marrow to tell it to make more RBC
* High altitude results in less oxygen in the air so your body needs to make more which makes more EPO and makes more RBC
* Regulates pH
18
New cards
What could kidney stones be due to?
Diet or genetics
19
New cards
Dialisis
external kidney, a machine does the filtering of blood for you and the clean blood goes back in
20
New cards
How much urine does your kidney produce a day and what does the color of your urine say about your drinking habits?
It makes about 1L of urine per day. If your urine isn’t clear, your a probably dehydrated.
21
New cards
Bladder
\
* Fills up
* Has stress receptors on it telling you that you have to go to the bathroom
* Not good to keep stretching out your bladder and letting it get full because it will lose its elasticity
* Sphincter at the bottom prevents bladder from bursting
* Fills up
* Has stress receptors on it telling you that you have to go to the bathroom
* Not good to keep stretching out your bladder and letting it get full because it will lose its elasticity
* Sphincter at the bottom prevents bladder from bursting
22
New cards
Bacterial infections (bladder)
\
* Bacterial goes up the urethra
* UTI: bacterial infection of the urinary tract
* If left untreated it could cause kidney failure
* Bacterial goes up the urethra
* UTI: bacterial infection of the urinary tract
* If left untreated it could cause kidney failure
23
New cards
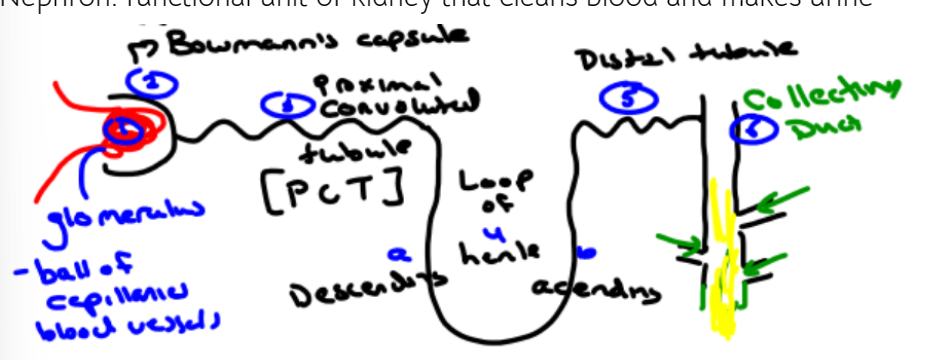
Nephron
Functional unit of kidney that cleans blood and makes urine
24
New cards
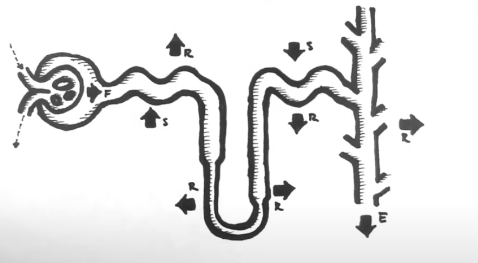
Three processes nephron uses to clean blood and create urine/filtrate
* Filtration
* Reabsorption
* Secretion
* Reabsorption
* Secretion
25
New cards
Filtration
\
* Happens between blood ball of capillaries (called glomerulus) and bowman's capsule
* Works because of blood pressure
* Passive transport – no energy used here
* Non-selective – don’t differentiate good vs bad
* Sort by size
* All the small stuff goes in the Bowman’s capsule (Urea, H2O K+, Amino acids, creatine, salt, glucose)
* Glucose, amino acids, and H2O shouldn’t be thrown out and the body will have to take them back
* Big chunky stuff like RBC and WBC remains in the blood vessels/capillaries
* Happens between blood ball of capillaries (called glomerulus) and bowman's capsule
* Works because of blood pressure
* Passive transport – no energy used here
* Non-selective – don’t differentiate good vs bad
* Sort by size
* All the small stuff goes in the Bowman’s capsule (Urea, H2O K+, Amino acids, creatine, salt, glucose)
* Glucose, amino acids, and H2O shouldn’t be thrown out and the body will have to take them back
* Big chunky stuff like RBC and WBC remains in the blood vessels/capillaries
26
New cards
Reabsorption
\
* Specific – use specific protein channel (passive)/pumps (active)
* Passive and active depending on what you are going to use
* Tubule → blood
* Take back the good stuff that got filtered and pull it out of the filtrate
* Substances reabsorbed
* H2O – osmosis – passive
* Glucose – active (w/ pumps)
* Salt – X factor (can do anything) – passive/active
* Body moves it around in order to move the water, changes tonicity
* Amino acids – active
* Specific – use specific protein channel (passive)/pumps (active)
* Passive and active depending on what you are going to use
* Tubule → blood
* Take back the good stuff that got filtered and pull it out of the filtrate
* Substances reabsorbed
* H2O – osmosis – passive
* Glucose – active (w/ pumps)
* Salt – X factor (can do anything) – passive/active
* Body moves it around in order to move the water, changes tonicity
* Amino acids – active
27
New cards
Secretion
\
* Throw out more bad stuff (toxins/drugs)
* Blood → tubule
* Selective and active
* Throw out more bad stuff (toxins/drugs)
* Blood → tubule
* Selective and active
28
New cards
Filtrate
Stuff in the nephron tubule, stuff that is supposed to be garbage
29
New cards
Nephron tonicity
Blood is hyper and Bowman’s capsule is hypo so that water flows into the blood vessels
30
New cards
Cortex (region of kidney)
\
* Top part
* Less salty
* Distal tubule
* Everything that’s left that’s good comes out, only waste should remain
* Top part
* Less salty
* Distal tubule
* Everything that’s left that’s good comes out, only waste should remain
31
New cards
Medulla (region of the kidney)
\
* Bottom part
* Salty
* Loop of Henle
* Collecting duct
* Bottom part
* Salty
* Loop of Henle
* Collecting duct
32
New cards
Loop of Henle
\
\
* Descending
* Only permeable to water, eventually reaches equilibrium
* Ascending
* Salt removal (active) to make the inside hypo
* Not permeable to water
\
* Descending
* Only permeable to water, eventually reaches equilibrium
* Ascending
* Salt removal (active) to make the inside hypo
* Not permeable to water
33
New cards
Collecting duct
\
* Has extra channels in it that only open when ADH (antidiuretic – stops you from peeing) opens them so that water can come out
* When ADH goes down, you pee more
* When it goes up, you retain the water
* Caffeine and alcohol blocks ADH causing you to pee more
* Has extra channels in it that only open when ADH (antidiuretic – stops you from peeing) opens them so that water can come out
* When ADH goes down, you pee more
* When it goes up, you retain the water
* Caffeine and alcohol blocks ADH causing you to pee more
34
New cards
ADH hormone (antiduretic)
* controls the rate of water excretion
* released for posterior pituitary gland
* acts when the body is in a state of under-hydration and needs to retain water
* causes more water to be reabsorbed by collecting ducts
* released for posterior pituitary gland
* acts when the body is in a state of under-hydration and needs to retain water
* causes more water to be reabsorbed by collecting ducts
35
New cards
Vena Cava
Veins that bring blood to the right atria/heart
36
New cards
Atria
Receive blood from the body
37
New cards
Left atrium
Pumps blood to the whole body
38
New cards
Right Atrium
Pumps blood to the lungs
39
New cards
Pulmonary artery
Brings blood to the lungs, only deoxygenated artery
40
New cards
Pulmonary vein
Only oxygenated vein in the body
41
New cards
Aorta
Largest blood vessel, under the most pressure
42
New cards
Which side of the heart is deoxygenated and which is oxygenated?
Right side -- deoxygenated
Left side -- oxygenated
Left side -- oxygenated
43
New cards
Autorhythmic
Can generate its own electrical impulse and can contract on its own. The heart is autorhythmic.
44
New cards
Needs of organisms/cells
* Get O2, H2O, glucose, nutrients
* Removed CO2, nitrogenous (waste)
* Removed CO2, nitrogenous (waste)
45
New cards
How do single celled organisms get nutrients and get rid of wastes?
Through diffusion and active transport. It can do this stuff since it is in contact with the environment.
46
New cards
Multicellular organisms use ___________ to get nutrients and remove wastes.
circulatory system
47
New cards
Parts of the circulatory system
* Pump -- “heart”
* Tubes -- “blood vessels“
* road ways
* Liquid - holds “stuff“ -- “blood“
* Tubes -- “blood vessels“
* road ways
* Liquid - holds “stuff“ -- “blood“
48
New cards
Arteries and Arterioles
* carry blood away from the heart
* Oxygenated
* high pressure
* Oxygenated
* high pressure
49
New cards
Veins and venules
* carry blood to the heart
* Deoxygenated blood
* Low pressure
* Deoxygenated blood
* Low pressure
50
New cards
Capillaries
* next to every cell
* One cell thick
* Exchange of substances between the blood and the interstitial fluid occurs in several ways
* Non-polar molecules (O2 and CO2) diffuse through the epithelial cells of the capillary wall
* Larger molecules may be carried across an epithelial cell in vesicles formed by endocytosis on one side of the cell and release their contents by exocytosis on the other side
* Water and small solutes (sugars and salts) can move freely through the pores in the wall and narrow clefts between the epithelial cells making up the wall -- the capillary wall is leaky
* One cell thick
* Exchange of substances between the blood and the interstitial fluid occurs in several ways
* Non-polar molecules (O2 and CO2) diffuse through the epithelial cells of the capillary wall
* Larger molecules may be carried across an epithelial cell in vesicles formed by endocytosis on one side of the cell and release their contents by exocytosis on the other side
* Water and small solutes (sugars and salts) can move freely through the pores in the wall and narrow clefts between the epithelial cells making up the wall -- the capillary wall is leaky
51
New cards
Blood pressure
how much force the blood is exerting on the walls of the arteries
\
Normal: 20/80
Systolic 20 means the heart is contracting/expanding
Diastolic 80 means the heart is relaxing
\
Normal: 20/80
Systolic 20 means the heart is contracting/expanding
Diastolic 80 means the heart is relaxing
52
New cards
Why do veins and arteries dilate?
Because they have smooth muscles
53
New cards
What can smooth muscle do?
Moves around blood and has the ability to dilate as well as constrict
54
New cards
What do blood vessels on the skin’s surface do?
They dilate to remove heat from body into the environment
\
Drinking alcohol increases this.
\
Drinking alcohol increases this.
55
New cards
What do your veins do when it’s cold out?
They constrict to maintain body temperature
56
New cards
What is the only blood vessel where exchange with cells occur?
Capillary
57
New cards
Which blood vessel is on the surface and which is deeper? Why?
Veins are on the surface and arteries are deeper so that they are better protected.
58
New cards
Which has less smooth muscle, the veins or the arteries?
The veins
59
New cards
What does the valve do?
It prevents backflow
60
New cards
What is the result of the extremely low pressure in the veins?
It makes it hard to move blood valves however the wideness of the veins helps with that.
61
New cards
Why is the capillary under pressure? And why do you want this?
It is under pressure because it is narrow and you want it narrow so things move slower allowing diffusion to occur.
62
New cards
What does interstitial fluid do?
It acts as a buffer for the cells and allows us to maintain homeostasis
63
New cards
What does the constant movement of the blood vessels allow?
It allows for the maintaining of the concentration gradient by allowing diffusion to occur.
64
New cards
What are varicose veins?
When the valve malfunctions so the vein twists on itself and goes to the surface of the skin.
65
New cards
What is always placed next to a vein?
Contractile-type things like muscles are next to veins so the moving muscles can squeeze the veins to allow blood to move.
66
New cards
What does aspirin do?
It dilates and thins blood
67
New cards
Angioplasty
Inflate balloon to press plaque up against edge of blood vessel to create space
68
New cards
What is a heart murmur? What does it mean? How could you cure it?
It is a faulty valve in the heart.
It means that there is sometimes backflow.
Up until a human reaches a certain age, it can fix itself. After that, you will need a valve replacement.
It means that there is sometimes backflow.
Up until a human reaches a certain age, it can fix itself. After that, you will need a valve replacement.
69
New cards
Thoracic Cavity
Area of the heart, lungs, ribcage, diaphragm
70
New cards
Pericardium
Membrane surrounding the heart
* fluid that lubricates heart results in less friction during heat beats
* fluid that lubricates heart results in less friction during heat beats
71
New cards
SA (sinoatrial) node
* Group of cells that act as the “pacemaker“
* Can be influenced by the brain
\
* the pacemaker which sets the rate at which all the muscle cells of your heart contract
* Located on the upper wall of your right atrium
* It generates electrical impulses
* Sequence of electrical events in the heart
* Signals from the SA node spread through both atrium so they contract in unison
* Impulses pass to a relay point called the AV node (located between the RA and RV) which delay the signal about 0.1 second before the ventricles contract
* Specialized muscle fibers relay the signals to the apex of the heart and up through the walls of the ventricles triggering the strong contractions that drive blood out of the heart
* Can be influenced by the brain
\
* the pacemaker which sets the rate at which all the muscle cells of your heart contract
* Located on the upper wall of your right atrium
* It generates electrical impulses
* Sequence of electrical events in the heart
* Signals from the SA node spread through both atrium so they contract in unison
* Impulses pass to a relay point called the AV node (located between the RA and RV) which delay the signal about 0.1 second before the ventricles contract
* Specialized muscle fibers relay the signals to the apex of the heart and up through the walls of the ventricles triggering the strong contractions that drive blood out of the heart
72
New cards
What’s a normal bpm?
40-60 bpm
73
New cards
Heart attack
Cells die in heart due to a lack of O2 -- a blockage prevents the cells from getting O2 which kills them
\
* damage or death of cardiac muscle tissue usually as a result of blockage of blood vessels
* Electrical shocks applied to the chest by a defibrillator may reset the SA node and restore proper cardiac function
* AED (automatic external defibrillators): designed to be used by laypeople and are placed in public places where they are easily accessible
\
* damage or death of cardiac muscle tissue usually as a result of blockage of blood vessels
* Electrical shocks applied to the chest by a defibrillator may reset the SA node and restore proper cardiac function
* AED (automatic external defibrillators): designed to be used by laypeople and are placed in public places where they are easily accessible
74
New cards
Bypass surgery
Take blood vessel (vein) from another part of the body to replace the one in the area of the heart attack to increase blood flow in that area.
75
New cards
AV (atrioventricular) node
Tells ventricles to contract
76
New cards
ECG (electrocardiogram)
Shows the electrical impulse in the heart
\
* Provides data about heart health such as the existence of arrhythmias
* Arrhythmias: abnormal heart rhythms including heart rates that are too slow or fast and fibrillations (flutterings) of the atria or ventricles
* Fibrillations may occur in a healthy heart when drugs such as caffeine cause a group of cells to generate heart beats outside the SA node
\
* Provides data about heart health such as the existence of arrhythmias
* Arrhythmias: abnormal heart rhythms including heart rates that are too slow or fast and fibrillations (flutterings) of the atria or ventricles
* Fibrillations may occur in a healthy heart when drugs such as caffeine cause a group of cells to generate heart beats outside the SA node
77
New cards
Tacchycardia
Heart beat is too fast (180 bpm)
78
New cards
Bradycardia
Heart beat is too low
79
New cards
What does an artificial pacemaker do?
It helps take over for a non-functional SA node
80
New cards
How much blood is there in human?
About 5L
81
New cards
What is the purpose of blood?
* Transports O2
* Immunity/ protection
* Temperature
* Thermoregulation
* Immunity/ protection
* Temperature
* Thermoregulation
82
New cards
Red blood cells (erythrocytes)
* Carry O2
* Disc shape
* Contain hemoglobin which combines O2 and is iron derivative
* Anemia → low RBC/hemoglobin count
* hectorite
* Fatigue, internal bleeding
* 2-3 million RBC/sec
* 1 uL - 4 million RBC
* lives 120 days
* no nucleus or organelles
* made in the bone marrow
* Liver and spleen process out old ones
* Disc shape
* Contain hemoglobin which combines O2 and is iron derivative
* Anemia → low RBC/hemoglobin count
* hectorite
* Fatigue, internal bleeding
* 2-3 million RBC/sec
* 1 uL - 4 million RBC
* lives 120 days
* no nucleus or organelles
* made in the bone marrow
* Liver and spleen process out old ones
83
New cards
Polycethemia
* too many RBC
* caused by a tumor
* caused by a tumor
84
New cards
Sickle-cell
* turn moon shaped and become rigid
* blocks blood vessels
* resistant to malaria
* blocks blood vessels
* resistant to malaria
85
New cards
White blood cells (Leukocytes)
* 80-90 years
* Have all organelles, can leave circulatory system
* Different types of WBC
* Basophil
* Eosinophil
* Neutrophil
* Lymphocyte
* Monocyte
* Defense and immpunity
* Have all organelles, can leave circulatory system
* Different types of WBC
* Basophil
* Eosinophil
* Neutrophil
* Lymphocyte
* Monocyte
* Defense and immpunity
86
New cards
Platelets
* cell fragments
* responsible for blood clotting
* responsible for blood clotting
87
New cards
Why is the shape of the red blood cells important?
It increases the surface area thereby increasing the amount of diffusion that can occur
88
New cards
Systemic circulation
Heart→whole body→heart
89
New cards
Pulmonary circulation
heart→lungs→heart
90
New cards
Renal circulation
Heart→kidney→heart
91
New cards
Coronary circulation
Heart→heart→heart
92
New cards
hepatic circulation
Heart→liver→heart
93
New cards
Order of circulatory system
Arteries→arterioles→capillaries→venules→veins→vena cava→heart
94
New cards
Open circulatory system
called “open” because fluid is pumped through open-ended vessels and flows out among the tissues; there is no distinction between the circulatory fluid and the interstitial fluid
95
New cards
Closed circulatory system
* the vessels keeping blood distinct from the interstitial fluid
* Three kinds of vessels:
* Arteries
* Carry blood away from the heart to body organs and tissues
* Capillaries
* Convey blood between arteries and veins within each tissue
* Veins
* return blood to the heart
* Often called the cardiovascular system
* Three kinds of vessels:
* Arteries
* Carry blood away from the heart to body organs and tissues
* Capillaries
* Convey blood between arteries and veins within each tissue
* Veins
* return blood to the heart
* Often called the cardiovascular system
96
New cards
Human cardiovascular system
* Blood leaves the heart through the **pulmonary arteries** that carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs and the **aorta,** which begins the oxygenated blood’s journey to the body tissues
* Blood flows into the heart through **pulmonary veins** which bring oxygenated blood from the lungs and two large veins that carry blood from the body tissues
* The **superior vena** cava returns deoxygenated blood to the heart from the upper body and the **inferior vena cava** brings it from the lower body
* Blood flows into the heart through **pulmonary veins** which bring oxygenated blood from the lungs and two large veins that carry blood from the body tissues
* The **superior vena** cava returns deoxygenated blood to the heart from the upper body and the **inferior vena cava** brings it from the lower body
97
New cards
Atrioventricular (AV) valve
valves between the atria and ventricles
98
New cards
Semilunar valve
Located at the exit from each ventricle
99
New cards
Cardiac Cycle
* the rhythmic sequence in which the heart contracts and relaxes
* When the heart contracts: it pumps blood
* when the heart relaxes: blood fills it’s chambers
* When the heart contracts: it pumps blood
* when the heart relaxes: blood fills it’s chambers
100
New cards
Diastole (cardiac cycle phase) -- relaxed
blood flows into all four chambers; blood enters the RA and from the vena cava and the LA from the pulmonary artery, the AV valves are open and the semilunar valves are closed; lasts about 0.4 second and the ventricles nearly fill with blood