Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
At a conference, the speaker's grand finale was sautéing mealworms (insect larvae) in butter and serving them to the audience. They were crunchy (like popcorn hulls) because their exoskeletons contain the polysaccharide __________.
chitin
In living organisms, DNA exists as a __________ with the strand(s) __________.
double helix; running antiparallel
The type of bond that forms to join monomers (such as sugars and amino acids) into polymers (such as starch and proteins) is a(n) __________ bond.
covalent
The secondary structure of a peptide backbone is stabilized by __________ forming either a(n) __________ or a(n) __________.
hydrogen bonds; α helix; β pleated sheet
The sequence of amino acids in a protein is called the __________ structure of the protein.
primary
Sugars have a(n) __________ group that interacts with a _________ group that forms ring structures when the dry molecule is placed in water.
carbonyl (-C=O); hydroxyl (-OH)
A polysaccharide that is used for storing energy in human muscle and liver cells is __________.
glycogen
A shortage of phosphorus in the soil would make it especially difficult for a plant to manufacture __________.
DNA
The lipids that form the main structural component of cell membranes are __________.
phospholipids
The tertiary structure of a protein includes all of the following interactions except _________ bonds.
peptide
Generally, animals cannot digest (hydrolyze) the glycosidic linkages between the glucose molecules in cellulose. How then do cows get enough nutrients from eating grass?
Microorganisms in their digestive tracts hydrolyze the cellulose to individual glucose units.
The proper three-dimensional shape and folding of a protein is assisted by _________.
molecules called chaperonins
Which type of protein shields a newly forming protein from cytoplasmic influences while it is folding into its functional form?
Chaperonins
Sugars are molecules that have __________ C:H:O and are called __________.
a 1:2:1 ratio of; carbohydrates
The subunits (monomers) in cellulose are linked together by __________.
glycosidic linkages
Which is the term for compounds that do not mix with water?
Hydrophobic
Nitrogenous bases are classified as either purines or pyrimidines. Examples of purines are __________.
adenine and guanine
Macromolecules, the molecules of life, include all of the following except __________.
trace elements
In a dehydration synthesis reaction, __________ is always formed as a by-product of the reaction.
water
Protein molecules are polymers (chains) of __________.
amino acid molecules
The components of nucleic acids are __________.
a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate
Carbohydrates are used in our bodies mainly for __________.
energy storage and release
One characteristic shared by sucrose, lactose, and maltose is that __________.
they are all disaccharides
When comparing saturated and naturally occurring unsaturated fats, the unsaturated fats have __________ and are __________ at room temperature.
cis double bonds; liquids
Which of the following is a polymer?
Cellulose, a plant cell wall component
The sex hormones estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone belong to which class of molecules?
Lipids
__________ is always involved in hydrolysis reactions.
Water
The molecule with four fused rings that is found in animal membranes and is the precursor of vertebrate sex hormones is __________.
cholesterol
Sickle-cell anemia is a disease that is caused by __________ in the __________ of the protein.
a single amino acid change; primary structure
The peptide bond is __________.
a covalent bond joining amino acids together to form a polypeptide
Large polymers are known as __________
macromolecules
A _______ is a long molecule consisting of many similar blocks
Polymer
The repeating units that serve as building block are called
monomers
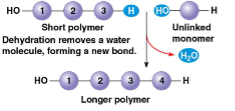
Dehydration reaction
synthesizing a polymer
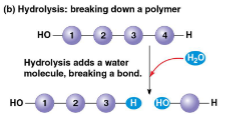
Hydrolysis
breaking down a polymer
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrate macromolecules are polysaccharides, polymers composed of many sugar budling blocks
Monosaccharides _____________________
have molecular formulas that are usually multiples of CH2O
The most common monosaccharide
Glucose (C6H12O6)
How are monosaccharides classified?
The location of the carbonyl group ( as aldose or ketose )
The number of carbons in the carbon skeleton
Trioses
Three carbon sugars ( C3H6O3)
Pentoses
five carbon sugars ( C5H10O5 )
Hexoses
Six-carbon sugars ( C6H12O6 )
Though often drawn as linear skeletons, _____________
in aqueous solutions many sugars form rings
What does Monosaccharides serve as _____________
major fuel for cells and as raw material for building molecules
A disaccharide is formed when_________
a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides
This covalent bond between two monosaccharides is called_________
a glycosidic linkage
Polysaccharides have___________
storage and structural roles
How do we determine the function and architecture of a polysaccharide?
-By its sugar monomers
-The positions of its glycosidic linkages
Simplest form of starch
Amylose
What is starch and what does it consist of ?
A storage polysaccharide of plants and consists of glucose monomers
___________ is a storage polysaccharide in animals
Glycogen
Where is glycogen mainly stored?
In the liver and muscle cells
When the demand for sugar increases_______________
Hydrolysis of glycogen in these cells releases glucose
What is a major component of the tough wall of plant cells?
The polysaccharide cellulose
________________ is a polymer of glucose
Cellulose
The two rings for glucose
Alpha ( α )
Beta ( β )
Enzymes that digest starch by hydrolyzing α linkages___________________
cant hydrolyze β linkages in cellulose
Where can chitin be found?
In exoskeleton of arthropods
What does Chitin provide?
structural support for the cell walls of many fungi
What does not include true polymers?
Lipids
What does lipids consist mostly of?
hydrocarbon regions
The most biologically important lipids are?
Fats, phospholipids, and steroids
A fatty acid consists of ?
A carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton
Why does fats separate from water?
Water molecules hydrogen-bond to each other and exclude the fats
How are triacylglycerol created?
Three fatty acids are joined to glycerol by an ester linkage
Which fatty acid have the maximum number hydrogen atoms?
Saturated fatty acids
Does saturated fatty acids have double bonds?
NO
which one has one or more double bonds?
Unsaturated fatty acids
What is the major function of fats?
Energy storage
Where do humans and other mammals store their long-term food reserves?
In Adipose cells
what do adipose tissue also do?
Cushions vital organs and insulates the body
In a phospholipid___________________
Two fatty acids and a phosphate group are attached to glycerol
Are the two fatty acids tails on a phospholipid hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
hydrophobic
The phosphate group that is attached to glycerol is hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
hydrophilic
Steroids are lipids characterized by ________
A carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings
________ accounts for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells
Proteins
What acts like a catalysts that speeds up chemical reactions?
Enzymes
What is the function of Enzymatic proteins?
Selective acceleration of chemical reactions
What is the function of Defensive proteins?
Protection against disease
What is the function of storage proteins?
Storage of amino acids
What is the function of transport proteins?
Transport of substances
What is the Function of Hormonal Proteins
Coordination of an organism’s activities
What is the Function of receptor proteins
Response of cell to chemical stimuli
What is the function of contractile and motor proteins?
Movement
What is the function of structural proteins?
Support
Proteins are all constructed from the _____________________
same set of 20 amino acids
________ are unbraced polymers build from these amino acids
Polypeptides
For proteins, what does it consist of?
One or more polypeptides
Amino acids are organic molecules________
with amino and carboxyl groups
Amino acids differ in their properties due to differing side chains called_____
R groups
Amino acids are linked by covalent bonds called____________
peptide bonds
What determines a protein’s three dimensional structure?
The sequence of amino acids
In what level of protein structure does it have coils and folds in the polypeptide chain?
Secondary structure
How are tertiary structure determined?
By interactions among various side chains ( R groups )
Quaternary structure results when_______
two or more polypeptide chains form one macromolecule
Protein consist of how many polypeptides?
Four
The loss of protein’s native structure is called?
Denaturation
A denatured protein is biologically _______
inactive
The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide is programmed by a unit of inheritance called_______?
gene
What are the two types of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA