Understanding Risk and Risk-Taking Behaviour
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
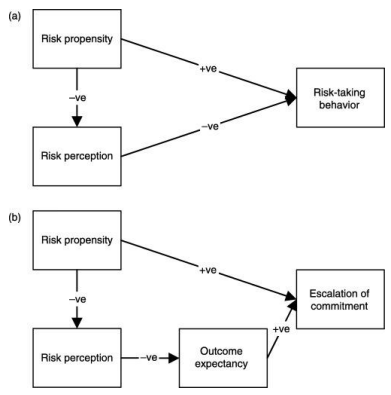
Sitkin & Pablo (1992) Conceptual Framework of Risk-Taking Behaviour
risk perceptions influence taking/avoiding risks. perceptions shaped by context.
risk propensity = tendency for risk-taking vs avoiding. stable but changeable over time.
risk perception = assessment of situation risk. reflects extent individual perceives situations as threat/out of control.
outcome expectancy = judgements of controllability of outcome, regardless of ability to influence.
Modern View of Risk (Mishra, 2014)
risk = uncertainty + possible gains/losses. not just danger, also opportunity.
Risk Propensity
Kogan & Wallach (1964) - general tendency to take/avoid risks. important for understanding who takes risks + why.
Josef et al. (2016) - varies between individuals; can change with experience/age.
Risky Behaviour (Trimpop, 1994)
behaviour where:-
outcomes uncertain
potentially sig. costs/benefits
affects physical, economic or psychosocial wellbeing
take risks due to expectations based on past experience. mediated by speed of learning from outcomes, degree of hating losses/loving gains + tolerance for uncertainty.
Typical Traits of Risk-Takers (Zuckerman, 2007)
impulsive, sensation-seeking
higher boredom proneness
difficulty regulating emotions
risky financial behaviours
risky health/safety behaviours
risky social/ethical behaviours
alcohol and drugs intensify risk-taking + peer pressure and social norms.
Risk Domains
risk-taking varies across domains e.g. finance, gambling, social, health (Mirsha, 2014).
risk unavoidable → decisions involve uncertainty + meaningful consequences. risk propensity differs due to traits/experiences.
risk perceptions drive behaviour - influenced by context/how situation is presented (framing).
Nicholson et al. (2006)
risk propensity links with age, sex + objective measures of career-related risk taking.
risk propensity high in extraversion and openness, low in neuroticism, agreeableness, and conscientiousness.
Rolison, Hanoch & Woods (2012)
age differences may depend on methodology of measuring risk-taking.
BART - behaviour depends on initial risk perception of first balloon+adjustment of behaviour in response to gains/losses.
young adults INITIALLY more willing to take greater risks - changes with experience.
older adults use simpler decision strats, make more errors (Mata et al., 2010).
Ps attend more to losses than gains.