CELL BIO UNIT 2 NOTES
1/201
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
202 Terms
Oxidative phosphorylation
ADP+PI → ATP INNER MEMBRANE
Electron transport equation-
NADH + ½ O2+H+->NAD+ +H2O NET OF INNER TRANSPORT
Biological oxidation is important
so humans don’t combust spontaneously and the energy in the bonds are in small dosages
_____is important for biological oxidation so there is a place for
O2
What cycle feeds into complex one in the mitochondria
Citric Acid Cycle
Write the mitocondria energy diagram on the board
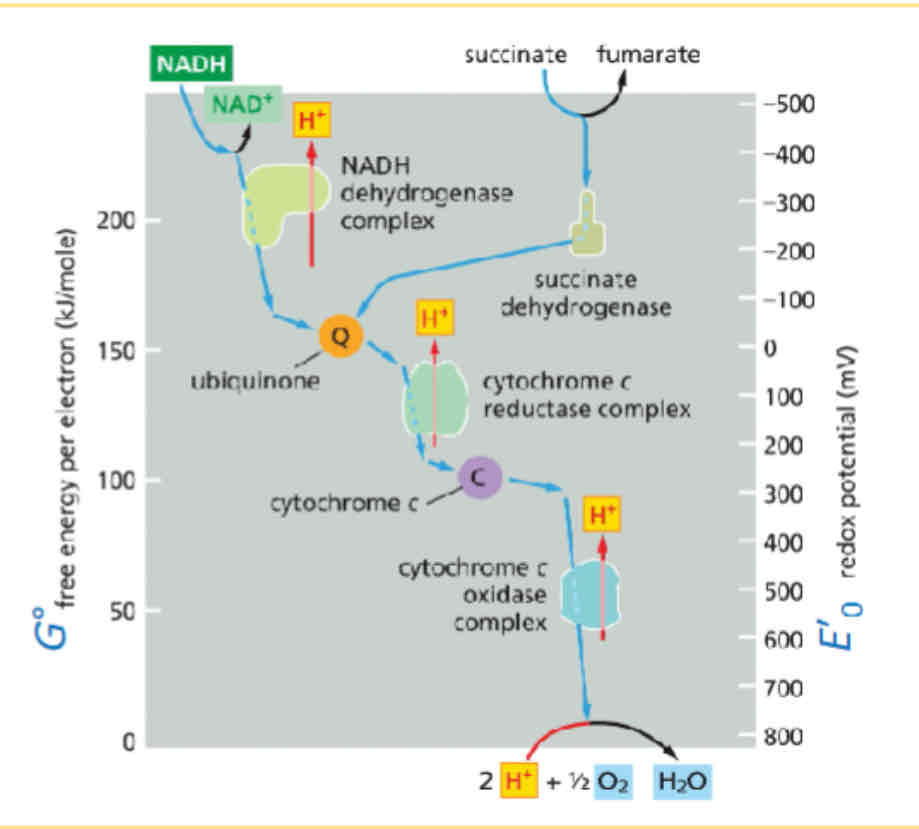
A molecule must first be_________ in order to be _______.
Reduced, oxidized
Redox is measured in - and free energy in -
mV, KJ/mole
Redox potential can be influences by
Redox concentration
The heme group is attached to what complex
Cytochrome C
The copper complex is attach to what complex
Complex 4, cytochrome C oxidase
The iron sulfur complex is found where
Cyctocrome C oxidase/reductase and Q
The matrix arm of the NADH dehydrogenase
Electron transport
The membrane arm is associated with
Proton pumping
Pros and cons of proton highways
40x faster but it’s non selective hypothesized to be unidirectional
Draw when 2H+ joins Q
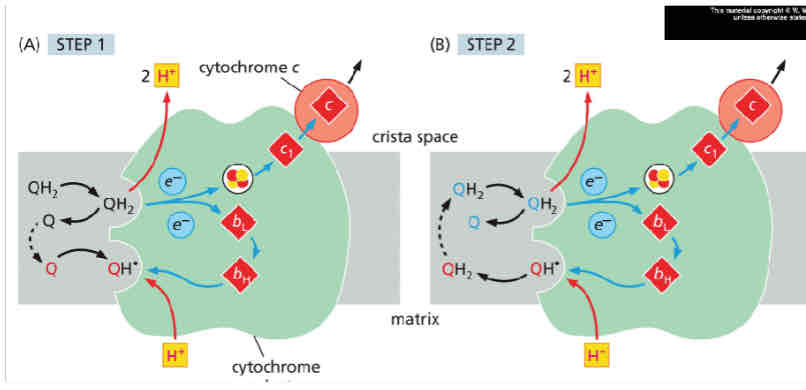
Cytocrome C can indicate
Cell death
Describe the glycolysis equation
1 glucose > 2 pyruvate+2NADH(1.5ATP)+2ATP
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
2pyruvate>2acetyl coA+2NADH(2.5 ATP per)
CAC equation
2acetyl CoA>6NADH+2FADH2+2GTP
Net mirocondria equation
2pyruvate > 8NADH+2FADH2 (1.5 ATP)+2GTP
Net fatty acid oxidation
1 palmitoyl CoA-> 8Acetyl CoA +7NADH +7 FADH2
Net Acetyl CAC equation
8 Acetyl CoA.>24 NADH + 8 FADH2 +8 GTP
Net result mitocondria equation palymitoyl
1 palmitoyl CoA >31 NADH +15FADH2 +8 GTP
Why does NADH have 2 values because the
Location changes
What is the free energy value of ATP hydrolysis
-30.5 kJ/mole
What is the free energy value of 1 ATP
-54 kJ/mole
What kind of reaction is NADH to O2
A spontaneous one
How many protons run through the ETC
14
What percentage of energy reaches the next complex
61.4%
Delta G is coupled with positive , what examples
NADH oxidation and creation of the proton gradient
Diffusion of the proton gradient and generation of atp synthase
Rotor stalk is used for what
To anchor the F1 subunit to drive atp synthase
Describe the protons being moved through the atp synthase
As the protons move they loose their negative and is pushed into the matrix
Each hairpin is depicted as a bump, how many protons do you need for 20 hairpins
20 protons
What drives the rotor around
The charge differential and sink
What is the function of dimers
They stabilize the atp synthase
How many revolutions per minute and per turn
8000 , 3
The inner membranes space is the more
Positive side
What makes bacteria different in terms of ETC
They use a pump nutrients into the cell and in anaerobic bacteria atp pumps and na but no gradient is established
What is the equivalent of the mitocondria matrix in chloroplast
Stroma
What is the equivalent of cristae in chloroplasts
Thylakoids
Where is ATP produced in chloroplasts? And consumed?
Stroma
High level electrons are excited by what and what molecule replaces those electrons
Light, water is split by p680
Carboxylation equation
5C +1C=6C/2=3C
What does Rubisco do
Fixes the carbon
What is reduction
is gain of electrons and remodeling of bonds 6 3 Carbon molecules NADPH is in the bond energy , 5 continue because we keep one to break down
Regeneration equation
5 * 3C +ATP from light
carbon cycle net equation
CO2+ribulose 1,biphosphate>w/rubisco intermediate +H2O2 molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate
Make sure you know how to draw this diagram
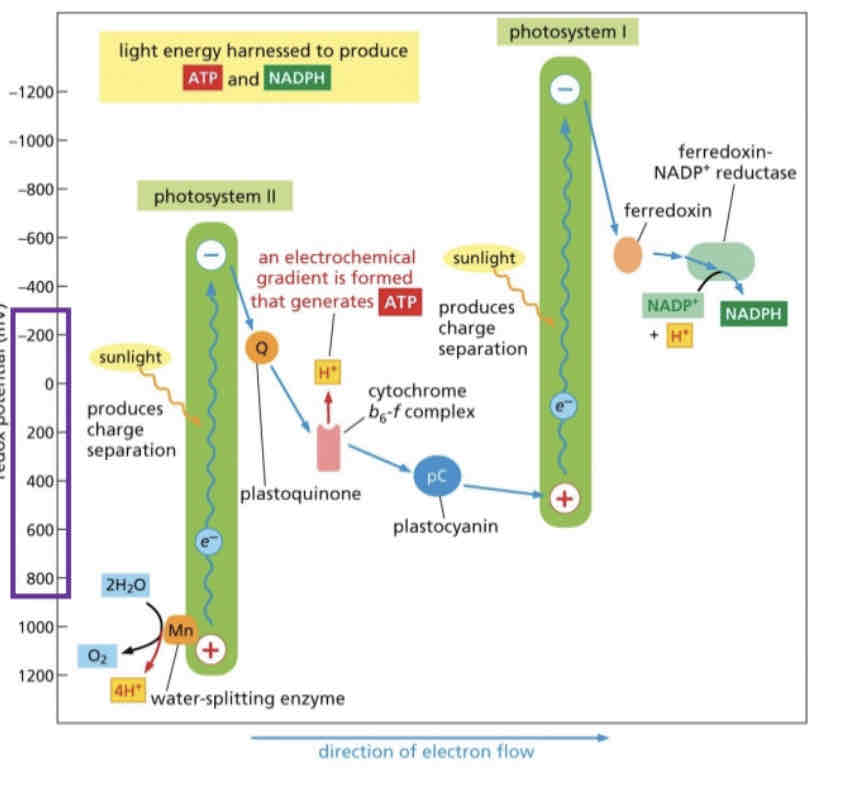
What does Mn cluster do
Water for electrons to be excited into the z scheme
Photosystem 2 has
One rapid pathway photosystem 1 has multiple
What is the alpha rotor made of
has 12 subunits=12 - charged residues
What happens every time a proton enters the alpha rotor
Every time a proton enters the hairpin is moved one over
How many protons are needed for 3 ATP
12
What is ancient orgin ATP synthase function
(used originally for protons not ATP) first then ETC and then they’d are combined
What did atp synthase start from
ancestral fermenting minimal atp and H2S synthesis’s
Describe the purpose of purple non sulfur bacteria
Purple non sulfur bacteria used something like cytochrome c but it wasn’t
The cytoskeleton is akin to
Freeway system made out of ants
What is the purpose of the cytoskeleton
maintains org,cell structure , cell shape changes,cell movement, and intracellular trafficking of vesicles/organelles, cell division
Cytoskeleton react in response to a lot of signals and as a result can
Depolarize and rebuild the cell skeleton to move better
What filaments are dynamic to reformation
Actin and microtubules
All filaments need ___________
1000 monomeric subunits and even though they are simple prokaryotes have different derivatives for this
Wht filament has + and - ends
Microtubules
In what circumstances would microtubules not be polar
Intermediate filaments are made of a-helical region its coiled together until dimer becomes a Teramer and it is no longer polar
Microtubules are normally made out of
32 IFs and it is used for mesenchymal cell muscle and keratin
What does nuclear lamins do
give tremendous structural support unless it’s phosphorylated and it falls apart
What are epidermal ifs used for
keratin filaments connect through desmosomes or hemidesmosomes
What is EBS
rapid blistering and lack of pressure resistance a problem with the epediermal IF
What are actin filaments
most abundant proteins in animals, all cells need it, 7nm , used as a reference control in everything and thin mesh work, relatively short lived and creates striated muscles
How do you make a cell move really quickly
Dynamic bursts of polymerazation
What is G-Actin
is a mono subunit, it is a spherical protien with a + and - end and had ATP embedded inside the g-actin so it can polymerize and fix in place in f-actin
F-actin
there is a + and - end,Suitable pool of charged g-actin ATP,Add more readily to the + end You cannot depolymerize from the middle Polymerization happens in one configuration
Myosin’s effect on f-actin
creates a barb and the plus end is more barbed
Describe the process of polymerizing
1.lag phase2.growth phase3.equilibrium phase lots of gactin to factin ,Lag phase - nucleation it’s rryl long,The growth phase occurs as a monomer add to the exposed ends of the growing filaments, causing filament elongation,If a gactin needs to be added then it needs to be removed, balanced, We run out of free subunits and it hits an equilibrium, Disassembly is more favorable at the - end ,Once they are in the polymer there is no difference in the - and + surface
Why is the plus end more stable
because they ATP binds initially (glue) that does not happen to the negative end
Critical concentration
is higher for the ATP bound + side then the ADP bound - side, Hydrolysis is not necessary
What is treadmilling
when the actin filaments results when assembly at the plus end is concomitant with depolymerization at the minus end
Memorize this drug table
Image
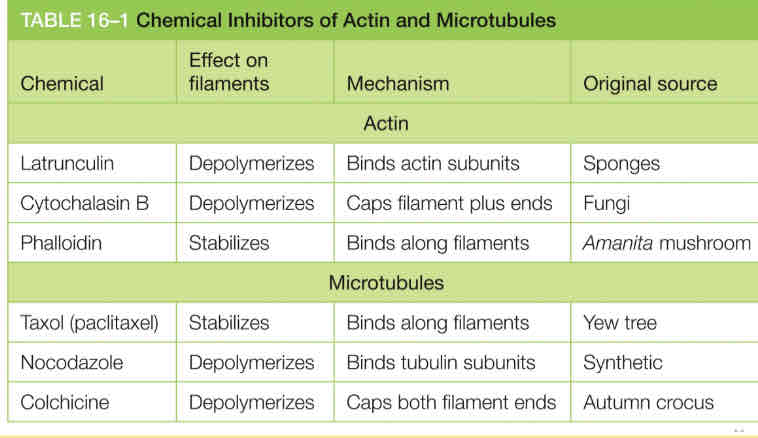
Arp2 and Arp3 filaments are related heavily to what
Actin
Arp 3/2 binds to what
NPF and clicks both into a active state so it can bind to a uncleared actin filament (ON MINUS END
ARPS Actin
ARPS kind of glue onto the edge (70° angle) these make branched formations
What is profilin opposed by
Thyomisin
Profilin
Forms clamp the actin and myosin to the membrane (associated with the plus end)
What are the mechanisms of muscle fibers
Uniform Z disks lead to striating ,Tropomodilin and CapZ prevent polymerization and depolarizing
What does cofilin do
to break off actin filament ends(induces severe twisting) and creates new ends to deassemble more rapidly
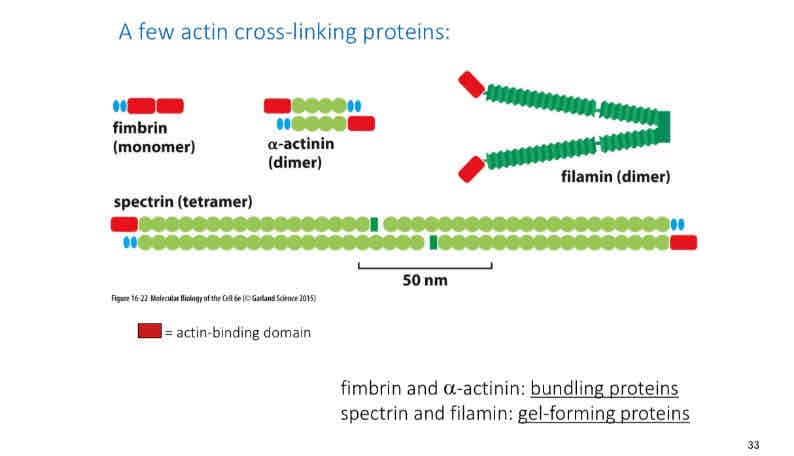
Filamin
Is a gel forming protien that the brain relies on
Make sure to memorize these protiens
Image
What does cadaherins respond to
protiens respond to adherin junctions
What conditions are best for cadaherins
High calcium is needed for cadaherims to link and then anchor to the cytoskeleton
Under tension what happens to protiens
are extended to reduce stress on the molecule
Adherin junction properties
cell connections, important and weak, useless without junction can generate force and bend and pull tubes out
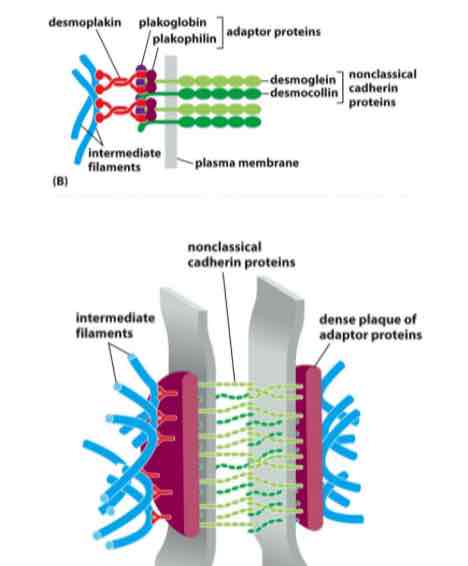
What are desmosomes
Cell to cell anchoring junctions they are embedded within the plasma membrane microtubules are strewn within
Make sure you understand embedment of cadeherims in desmosomes
Image
What are integrins
is like cadaherins but it binds to the extracellular material
What are tight junctions
elaborate array of protien, function is to seperate spaces that are created by a layer of cells, separates interstitial and blood stream(Tupperware lid) creates a seal
Clodins and aculin
Series of protiens stitched together with lateral attachments across
What are the limitations of gap junctions
connects cytosol , chemical synapses, only 1000 daltons can pass small ions and molecules can pass
Gap junctions that are small
Stack together
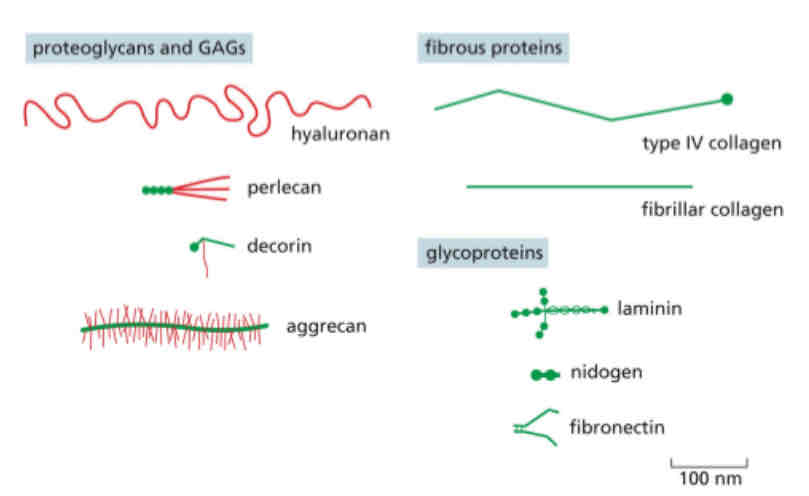
What is the ECM like
is diverse and complicated mixture, its secreted and it can be structural or space filling,
Make sure to memorize this
These make you durable and promotes compression resistance, fibrous protiens provide tensile resistance